Honors Chemistry: Matter, Measurement, and Error Analysis Quiz
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Accuracy
The closeness of a measured value to a standard or known value.
Precision
The closeness of two or more measurements to each other.
Systematic Error
An error that consistently occurs in the same direction, affecting the accuracy of measurements.
Random Error
An error that occurs unpredictably and affects the precision of measurements.
Percent Error
The difference between the measured value and the accepted value, divided by the accepted value, multiplied by 100.
Percent Difference
The absolute difference between two measurements divided by the average of those measurements, multiplied by 100.
Mega
A metric prefix meaning 10^6.
Kilo
A metric prefix meaning 10^3.
Base Units
Units of measurement without any prefix, equivalent to 10^0.
Centi
A metric prefix meaning 10^-2.
Milli
A metric prefix meaning 10^-3.
Micro
A metric prefix represented by the symbol 𝜇, meaning 10^-6.
Nano
A metric prefix meaning 10^-9.
Pico
A metric prefix meaning 10^-12.
Physical Properties
Characteristics of a substance that can be observed or measured without changing its composition.
Chemical Properties
Characteristics that describe a substance's ability to change into different substances.
Physical Change
A change that affects one or more physical properties of a substance without altering its chemical composition.
Chemical Change
A change that results in the formation of new chemical substances.
Monatomic Elements
Elements that consist of single atoms.
Diatomic Elements
Elements that consist of two atoms, which may be of the same or different elements.
Pure Substance
A material with a constant composition that cannot be separated into simpler substances by physical means.
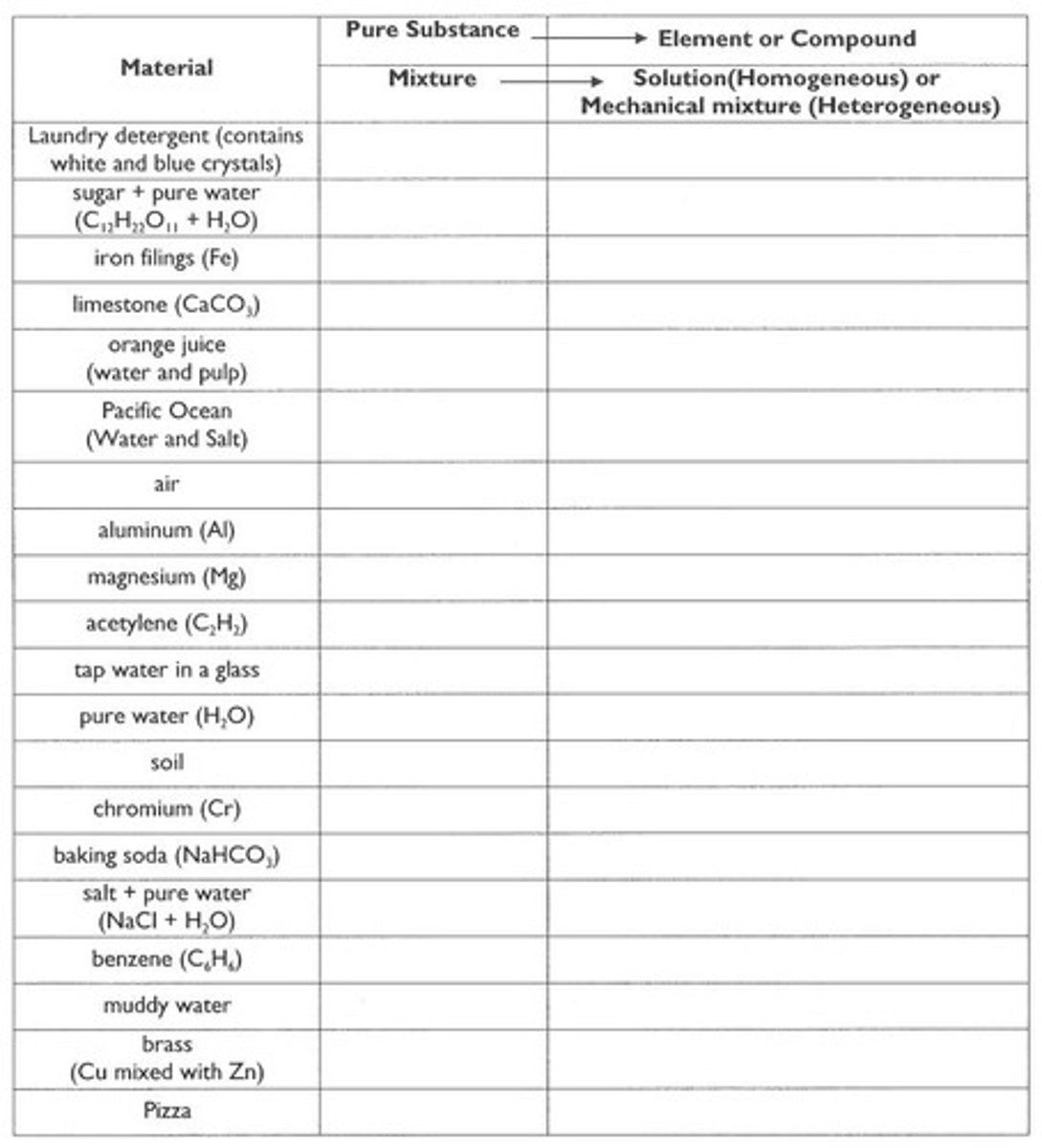
Mixture
A combination of two or more substances that retain their individual properties and can be separated by physical means.
Physical property
A characteristic of a substance that can be observed without changing its identity.
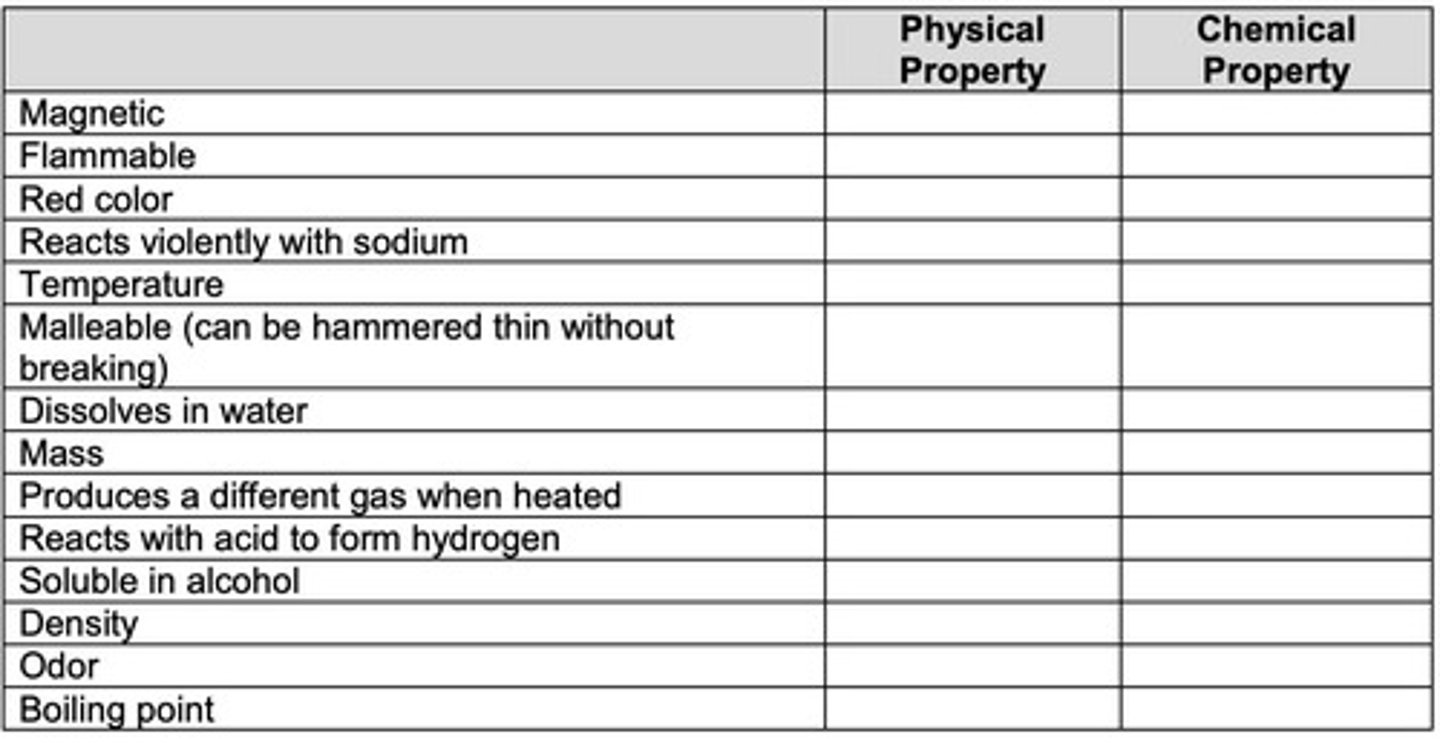
Chemical property
A characteristic of a substance that describes its ability to change into different substances.
Color change
Evidence that a chemical change may have occurred.
Fizzing or foaming
Evidence that a chemical change may have occurred.
Production of sound
Evidence that a chemical change may have occurred.
Production of heat or light
Evidence that a chemical change may have occurred.
Production of an odor
Evidence that a chemical change may have occurred.
Chemical changes
Cannot be reversed by physical changes.
Cutting hair
An example of a physical change.
Mixing sugar and water
An example of a physical change.
Baking soda reacts with vinegar
An example of a chemical change that forms a gas.
Baking cookies
An example of a chemical change.
Diamonds scratching glass
An example of a physical change.
Burning a tree
An example of a chemical change.
Water freezing
An example of a physical change.
Phase of matter with least spacing
Solid.
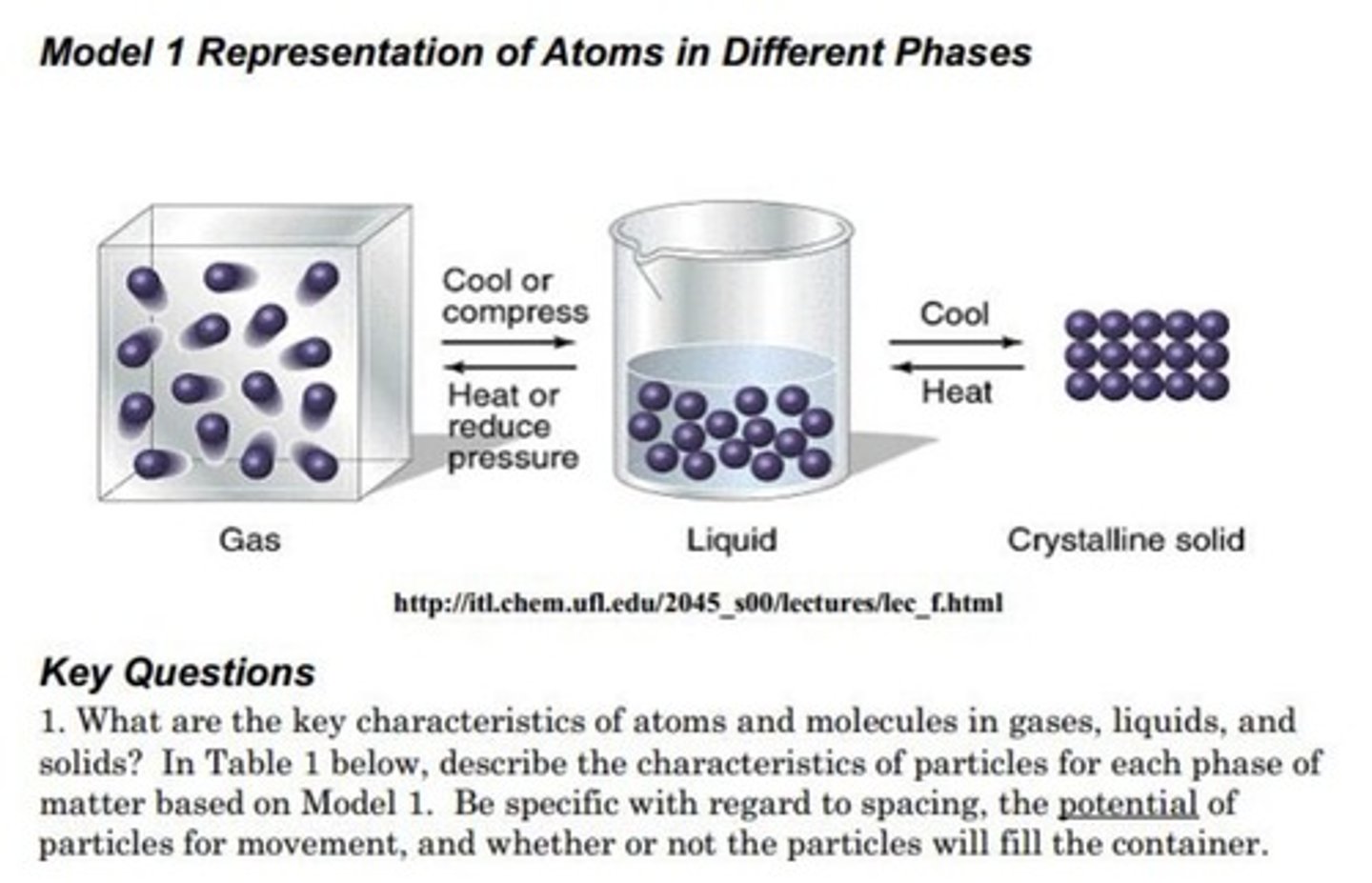
Phase of matter with greatest spacing
Gas.
Phase of matter without definite shape
Liquid.