DNA replication, translation, transcript- IB Bio HL
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
DNA replication is required for 2 processes:
Reproduction— need copies of base sequences of their parents
Growth and tissue replacement in multicellular organisms
Why is DNA called semi-conservative replication?
When DNA is replicated, two strands of helix are separated, used as templates to progressively add nucleotides. When complete, each DNA molecule has 1 original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
What type of bonds are broken by helicase when separating the double helix?
Hydrogen bonds (between complementary bases)
What is complementary base pairing and why is it important?
Adenine can only pair with thymine, and guanine can only pair with cytosine. It ensures that the two resulting DNA molecules are identical in their base sequences and easier to check/proofread
Replisome
Functional subunits (ex, helicase and DNA polymerase)
Helicase is
a ring shaped protein that separates the two strands of DNA by breaking the hydrogen bonds between bases, allowing one strand to be pulled through its hole and one to pass alongside it — uncoiling it
DNA polymerase’s role is…
adding free nucleotides one at a time to template strands in order to reform hydrogen bonds, then making a covalent bond between phosphate group of free nucleotide and the sugar at the end of the new strand
What type of bond is formed between the newly attached nucleotide and new strand?
Covalent bonds
What is a PCR machine?
Automated method of DNA replication that allows selected sequences to be amplified. Taq DNA polymerase produces large numbers of selected base pairs
DNA has a ____ charge due to the phosphates in the sugar-phosphate chain
negative
Nucleotides are linked to form strands of DNA or RNa with ___ bonds between sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of the next one
covalent bonds
Terminal nucleotides either have a ____ or a ______ group that has not been used to form a covalent bond with another nucleotide
sugar or phosphate
The ___ group bonds with another nucleotide
OH
What is the only direction DNA polymerase can continuously assemble new strands?
5’ to 3’
DNA strands are anti-parallel because…..
their 5’ to 3’ directions are opposite
Leading strand
Strand in which DNA polymerase adds nucleotides continuously towards replication fork
Lagging strand
Where DNA polymerase adds nucleotides moving away from the replication fork, in segements called Okazaki fragments
DNA primase
a type of RNA polymerase, assembles a chain of about 10 RNA nucleotides on the template strand, to provide a site where DNA polymerase III can bind and start adding nucleotides to the 3′ end of a DNA strand.
DNA polymerase III
Binds to template strand on 3’ side of an RNA primer and assembles chain of complementary base pairs to those on the template strand. Also proofreads
DNA polymerase I
An exonuclease (breaks bonds between nucleotides) and a polymerase (links nucleotides).
Binds to 3’ end of okazaki fragment and 5’ start of primer
Replaces RNA nucleotides and replaces them with DNA nucleotides
DNA ligase
Connects gap left by DNA polymerase I by making sugar-phosphate bond between adjacent nucleotides
Prokaryotic proofreading is done by
DNA polymerase III by inserting nucleotide with the correcy base
Transcription is…
The synthesis of RNA using DNA as a template
Why does transcription only occur on one of the two starnds of DNA?
RNA is single stranded
RNA polymerase does:
binding DNA at the start of the gene that is being transcribed
unwinding the DNA double helix and separating it into two single strands (template and coding strands)
moving along the template strand
positioning RNA nucleotides on the template strand with bases complementary to those of the template
linking the RNA nucleotides by covalent sugar–phosphate bonds to form a continuous strand of RNA
detaching the assembled RNA from the template strand and allowing the DNA double helix to reform
There is no ____ in RNA, it is replaced with ____.
thymine, uracil
What makes bases complementary?
They can form hydrogen bonds with each other but not with other bases
Sense strand/coding strand
DNA sequence whos base is being copied
Antisense strand/template strand
Has complementary base sequence to sense strand
Transcription of sense strand results in
RNA strand with same base sequence as the sense strand of DNA (with uracil instead of thymine)
After transcription the 2 DNA strand pair up with each other again linked by ____, making them briefly chemically vulnerable to mutations
hydrogen bonds
Two processes are needed to produce a specific polypeptide using the base sequence of a gene
Transcription and translation
Transcriptome
full range of messenger RNA, or mRNA, molecules expressed by an organism
Polypeptide
short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds
Amino acids
organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups that combine to form proteins
Where is the information needed to make a polypeptide located?
Base sequence of RNA molecule (copied from a gene by transcription)
What is the process of making an amino acid seeuence from an RNA’s base code, from mRNA, aka polypeptide synthesis?
Translation
Where does translation occur?
Cytoplasm
mRNA
Type of RNA with info for making polpeptide that travels from one part of the cell to the other — thus messenger RNA
3 components of polpeptide synthesis
mRNA allows ribosomones to bind to it, and has a sequence of codons that specifies polpeptide amino acid sequence, with stop and start codon
transfer RNA (tRNA) translates base sequence of mRNA into amino acid sequence
uses anticodon w 3 bases at one end and attachment point for amino acid at the other
each tRNA molecule has specific shape recognizerd by the activating enzyme, which allows it to attach the correct amino acid
ribosomes- contain small and large subunit.
small subunit: had binding site for mRNA
large subunit: 3 binding sites for tRNA + catalytic site that maks peptide bonds between amino acids to assemble polypeptide
Why does the ability to translate depend on complementary base pairs?
The three bases of an anticodon on a tRNA must be complementary to the three bases of the next codon on mRNA for the tRNA to be able to bind to the ribosome and deliver its amino acid
Why is DNA suited for data storage?
holds long sequences of bases
can be arranged in any order
can be accurately copied
Living organisms use a ____ code, with groups of x bases coding for an amino acid
triplet
codon
sequence of 3 bases on the mRNA, which causes a specific amino acid to be added to the polypeptide
Which codons correspond to an amino acid?
Three letters are used to indicate each amino acid in the table of the genetic code. Each of the 20 amino acids has between one and six codons. Read the three letters of each codon for the amino acid. For example, the amino acid tryptophan has one codon which is UGG.
What amino acid sequence would be translated from a sequence of codons in a strand of mRNA?
The first three bases in the mRNA sequence are the codon for the first amino acid, the next three bases are the codon for the second amino acid and so on. Look down the left hand side of the table to find the first base of a codon, across the top of the table to find the second base and down the right-hand side to find the third base. For example, GCA codes for the amino acid alanine
What base sequence in DNA would be transcribed to give the base sequence of a strand of mRNA?
A strand of mRNA is produced by transcribing the template or antisense strand of the DNA. This therefore has a base sequence complementary to the mRNA. For example, the codon AUG in mRNA is transcribed from the base sequence TAC on the template or antisense strand of the DNA. A longer example is that the base sequence GUACGUACG in mRNA is transcribed from CATGCATGC on the template strand of DNA. Note that adenine pairs with thymine in DNA but with uracil in RNA
Each cycle of translation of an mRNA molecule results in…
one additional amino acid added to polpeptide chain
Process of translation
An activating enzyme with an active site that fits the tRNA binds to it and attaches the specific amino acid corresponding to the anticodon of the tRNA.
The tRNA carrying a single, attached amino acid binds to the A (aminoacyl) site on the ribosome, with its anticodon linked by complementary base pairing to the next codon on mRNA.
The single amino acid on the tRNA is linked to the end of the growing polypeptide by the formation of a peptide bond. The tRNA now holds the whole of the growing polypeptide.
The tRNA moves from the A to the P (peptidyl) site as the ribosome moves along the mRNA by one codon. The anticodon of the tRNA is still paired with the codon on the mRNA.
The polypeptide held by the tRNA is transferred to another tRNA that has arrived at the A site.
The tRNA moves from the P to the E (exit) site as the ribosome moves along the mRNA by one more codon. This causes the anticodon of the tRNA to separate from the codon on the mRNA and the tRNA to separate from the ribosome.
The cycle starts again with an amino acid being linked to a tRNA
Gene mutation
Change to base sequence of a gene
Sickle cell disease
Caused by mutated gene that codes for beta-globin polypeptide in haemoglobin, causing typical HbA allele to change to HbS, which when transcribed, causes mRNA to produce incorrect codon, leading to incorrect amino acid to be produced
What is transcription?
The process of synthesizing messenger RNA (mRNA) from a DNA template.
What is a promoter region?
A specific DNA sequence where RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription
What modifications occur to mRNA after transcription?
Capping of the 5' end, polyadenylation at the 3' end, and splicing to remove introns.
What is translation?
The process of synthesizing a protein from an mRNA template using ribosomes and tRNA.
What is the role of tRNA in translation?
tRNA carries amino acids to the ribosome and pairs its anticodon with the codon on the mRNA.
What are the two subunits of a ribosome, and what do they do in translation?
The large subunit catalyzes peptide bond formation, and the small subunit binds to the mRNA and tRNA.
What are the roles of start and stop codons?
The start codon (AUG) initiates translation, and stop codons (UAA, UAG, UGA) terminate translation.
How are peptide bonds formed during translation?
Peptide bonds are formed between the amino acids of adjacent tRNAs in the ribosome during elongation.
What are polyribosomes?
Multiple ribosomes translating the same mRNA strand simultaneously to increase efficiency.
What are the three stages of translation?
Initiation (assembly of the ribosome and start of translation)
elongation (addition of amino acids to the growing chain)
termination (release of the completed polypeptide).
Key differences between transcription and translation
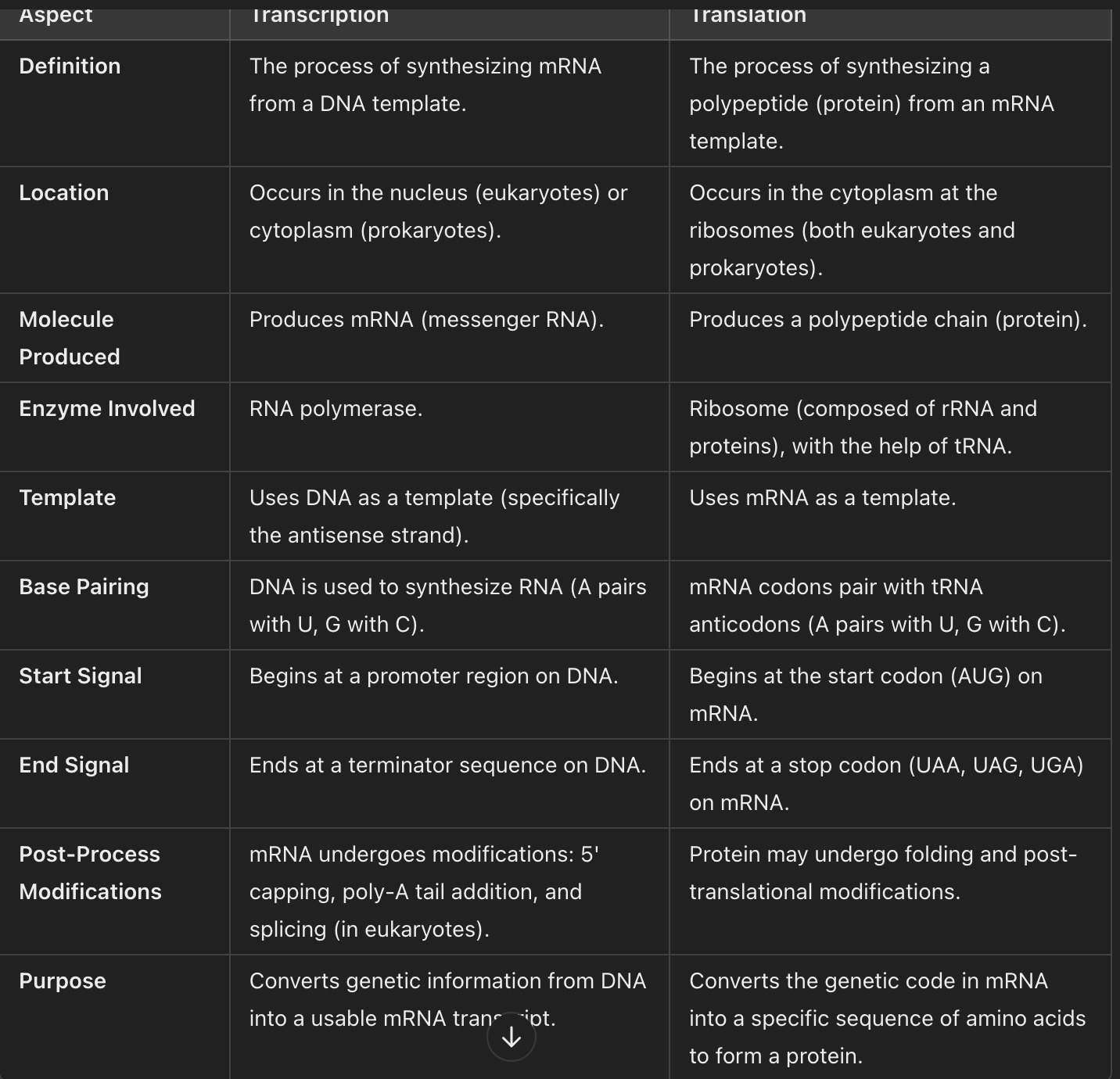
Central dogma of biology
DNA stores genetic information in the nucleus (eukaryotes) or cytoplasm (prokaryotes) as a blueprint.
Transcription (of DNA to mRNA), as if it’s copying the blueprint, where a temporary copy of a specific gene (mRNA (messenger RNA)) is made
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
Translation (mRNA to protein), occurs in the ribosomes of the cytoplasm
How is RNA modified to give mRNA a special structure?
Five-prime caps, with a 3 phosphate nucleotide instead of 1 phosophate
Poly A tails
What are the steps to initiate translation?
An activating enzyme attaches the amino acid methionine to an initiator tRNA that has the anticodon UAC.
The initiator tRNA binds to the small subunit of the ribosome. This produces a ternary complex—a structure composed of three parts which in this case are he small subunit of the ribosome, the initiator tRNA and the amino acid.
The ternary complex binds to the 5′ end of the mRNA and slides along it, using the UAC anticodon to scan for the start codon AUG.
The small subunit stops moving along the mRNA, with the UAC anticodon linked to the AUG codon by hydrogen bonds