Progestins
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Recall the 6 facts of progestin
Progestins are group names and not single molecules
can be used alone for BC & hormone replacement therapy or in conjunction with estrogen in combination oral contraceptive
Used to treat endometriosis & pain associated with it
Used to treat breast, uterus, and kidney cancer by changing the cell’s ability to use other hormones
secreted during the second half (luteal phase) in preparation for pregnancy
stimulate angiogenesis in the endometrium when egg is fertilized & implanted
What are the steps in the synthesis of endogenous progestin?
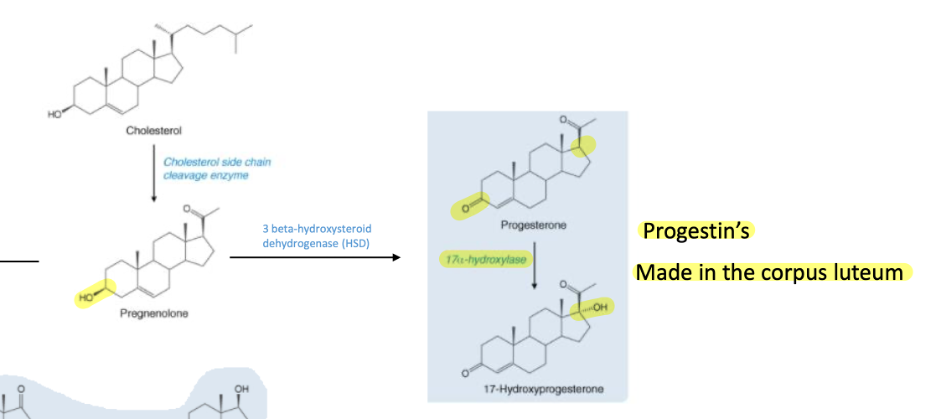
2 Types of Pregestins: Natural progesterone
important for maintaining pregnancy by suppressing menstruation & uterine contractility
switch proliferative to secretory state in preparation of the uterus for implantation of fertilized egg in the second half of menstrual cycle (day 15-28)
what are the 4 uses of synthetic progestins & their 2 types
contraceptions
menopause symptoms
endometriosis
dysfunctional uterine bleeding
Progesterone derivatives
19-NORTESTOSTERONE DERIVATIVES
What are the 2 types of 19-nortestosterone derivatives & what do they do?
estranes
gonanes
decrease androgenic synthesis
What type of receptors is progestin receptor, PR-A,PR-B?
progestin receptor: type I nuclear hormone receptors
PR-A & PR-B: type II
What does PR-A receptor do?
inhibits PR-B mediated transcription when both are present in the same cell as well as repress estogen, androgen, glucorticoid, and mineralocorticoid receptor activities
describe the signaling steps of progestin with its receptors
1.Hormone binds to NR and HSP dissociates
2. Dimerization between two NR-Ligand
3. Translocation to nucleus
4. NR dimer binds to HRE of DNA
5. Recruitment of coactivators and proteins
for transcription to mRNA
6. New protein to modify cell function
Endogenous progesterone maintains what ?
pregnancy
What does contraceptives (progestin only-mini pill) do?
prevents the LH surge & inhibits ovulation
thickens cervical mucus
thins lining of uterus making implantation less likely
Explain how synthetic progestin treats endometriosis
stimulates atrophy or regression of endometrial lesions
How does hormone replacement therapy (HRT) work?
added to estrogen to reduce risk of uterine cancer in women who haven’t had a hysterectomy
inhibits estrogen induced proliferation of endometrium
Side Effects of Progestin only contraceptives (6)
irregular, unpredictable spotting and breakthrough bleeding
Acne
headache
mood changes
weight gain
decrease bone density
Progestin only contraceptives contraindications (10)
presence or hx of:
thromboembolic or cerebrovascular disease
MI or CAD
Congenital hyperlipidemia
carcinoma of the breast or female reproductive tract
impaired liver function
migraine headaches
hypertension
DM
Pregnancy
gallbladder disease
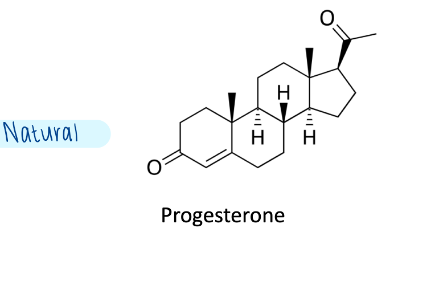
What is the structural difference between natural & synthetic progestin?
-CH3 at C6 on some synthetics
-ene at C6-7
Substitutions at C17 or C20
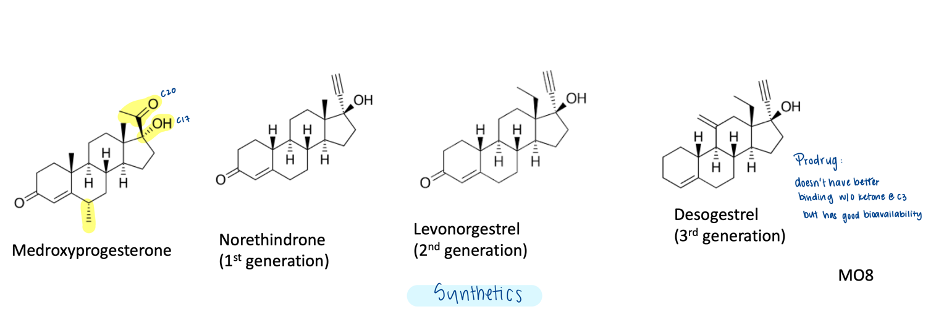
What are the 4 available forms of progesterone
Crinone Vaginal gel
Endometrin Vaginal Insert
Progesterone IM injection sol
Progesterone/PROMETRIUM oral capsule
Pharmacokinetics of PO progesterone
low oral bioavailability
extensively metabolized
highly protein bound
large Vd
PK values are highly variable
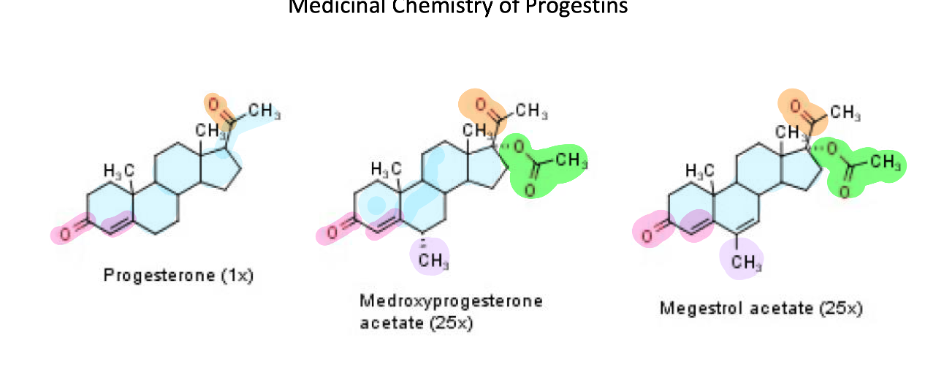
5 SARs for Progesterone derivatives
Pregnane nucleus (required)
3-keto & 4-5 double bond (required)
20-keto
17-hydroxyl ester (increases activity)
6-methyl (increases oral stability)
6 SARs for 19-norprogestins derivatives
estrane nucleus
3-keto & 4-5 double bond
17-beta OH
17-alpha-ethynyl group
18-ethyl (in place of methyl)
11-exocyclic double bond