Histo 17 | The Oral Cavity
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
https://voca.ro/1hfmSfcjZmxb
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
What type of epithelium is found in the lining of the mouth?
Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium, but it can become keratinized in areas that experience irritation.
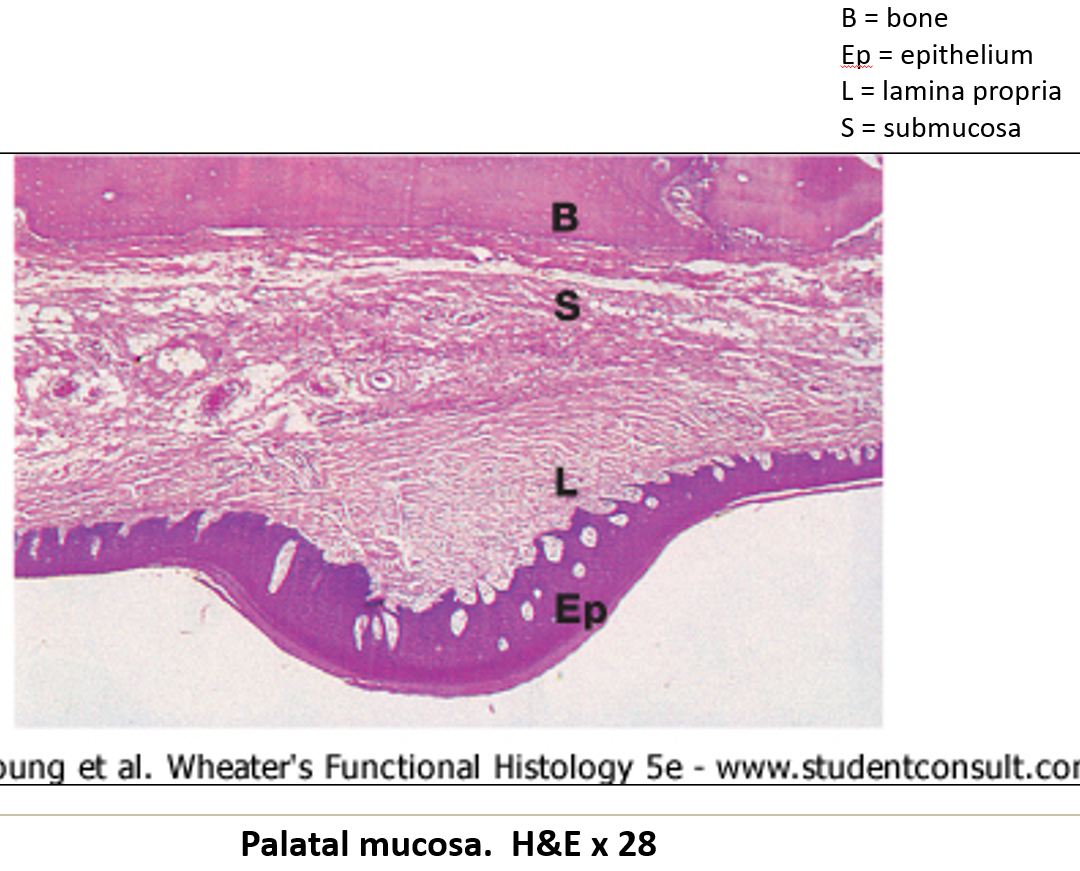
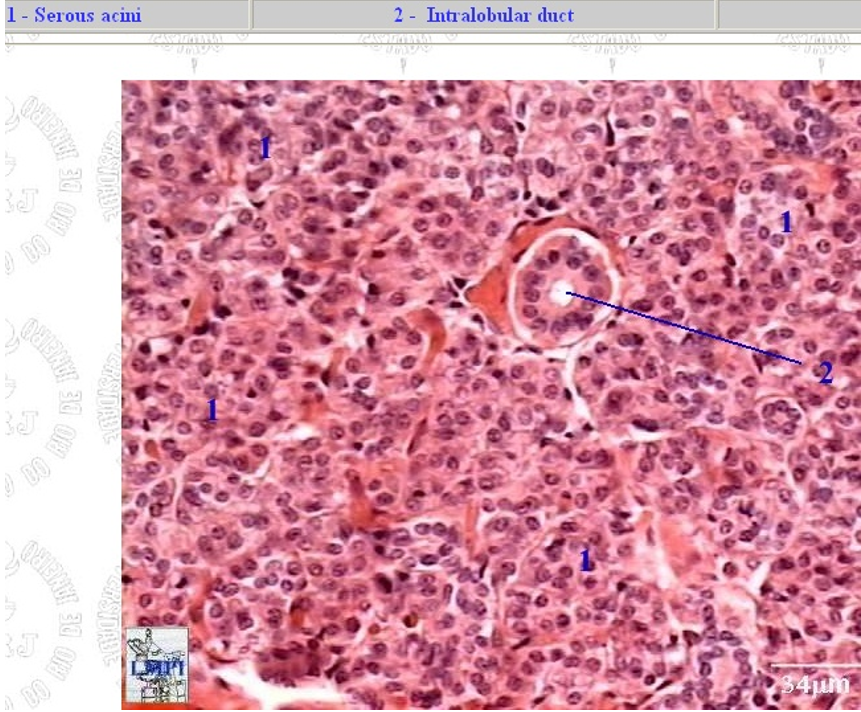
What is found in the submucosa of the mouth?
many small salivary glands, which can be serous, mucous, or seromucous.
What is the red margin of the lips?
The area where keratinized epithelium changes to nonkeratinized epithelium.
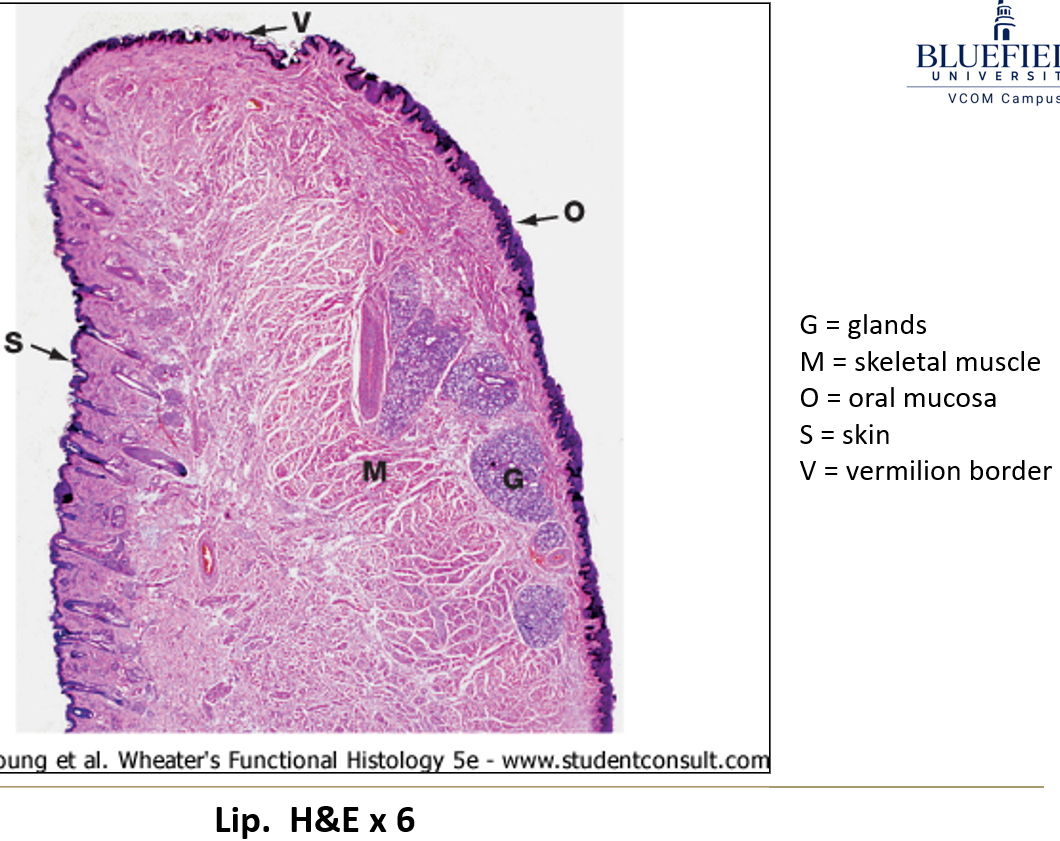
What is the vermilion?
The red part of the lips that has dry epithelium.
Why does the vermilion appear red?
Because of the high number and height of connective tissue papillae, which have lots of capillaries.
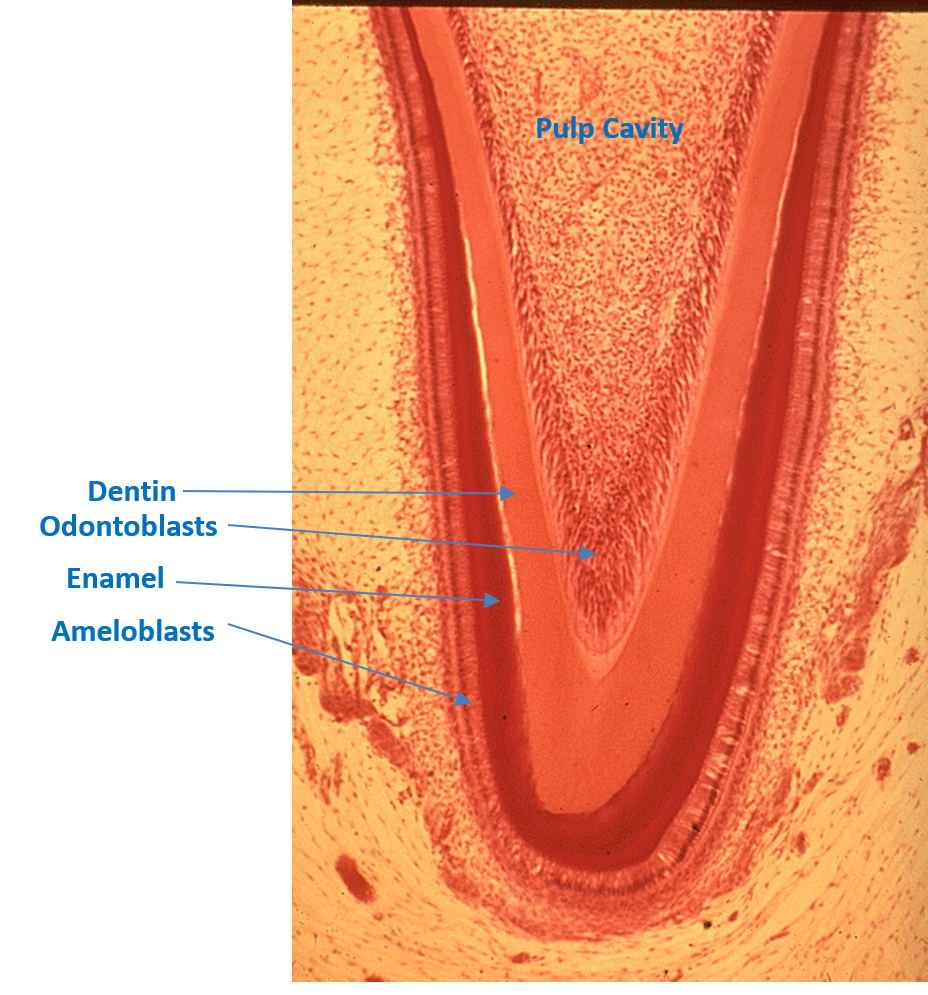
What are teeth mainly made of?
Mostly made of dentin, which is 80% calcium hydroxyapatite.
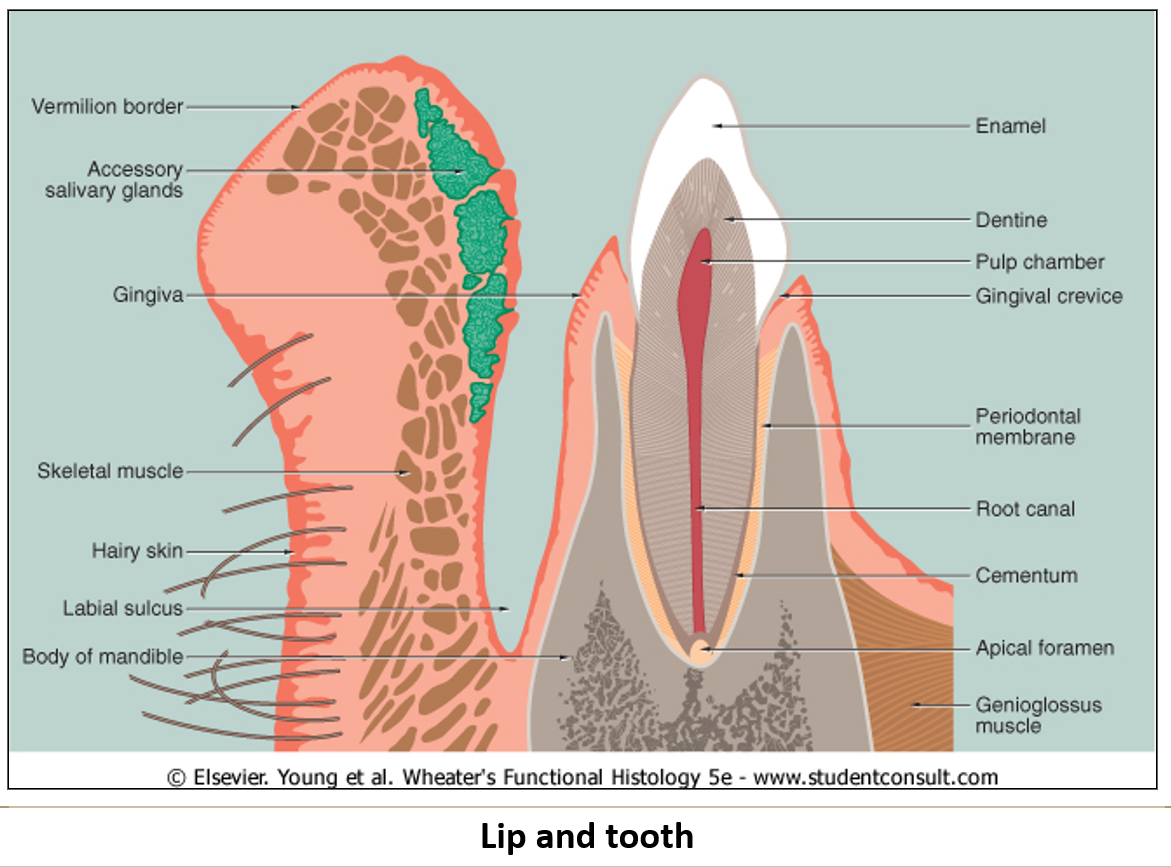
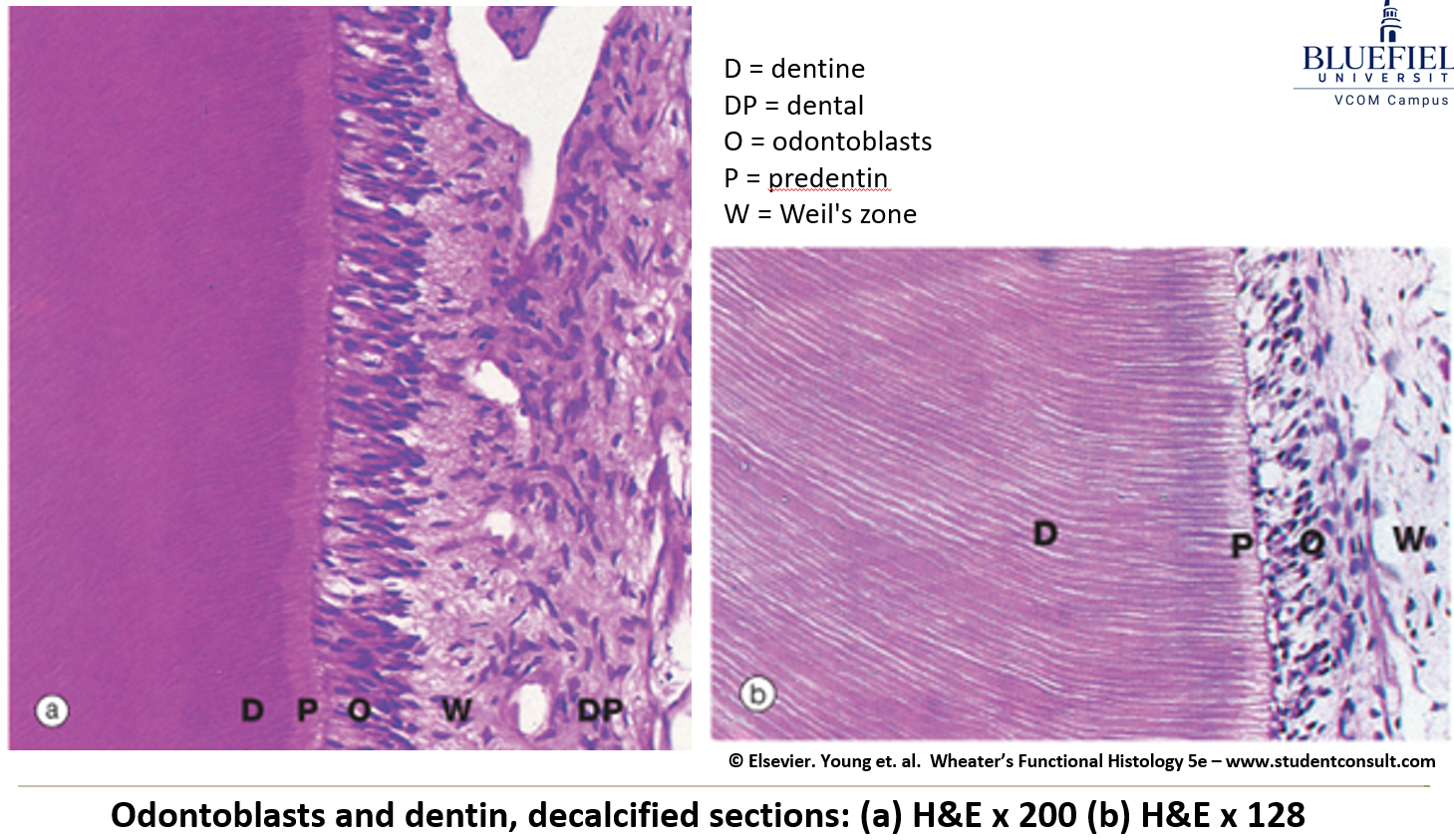
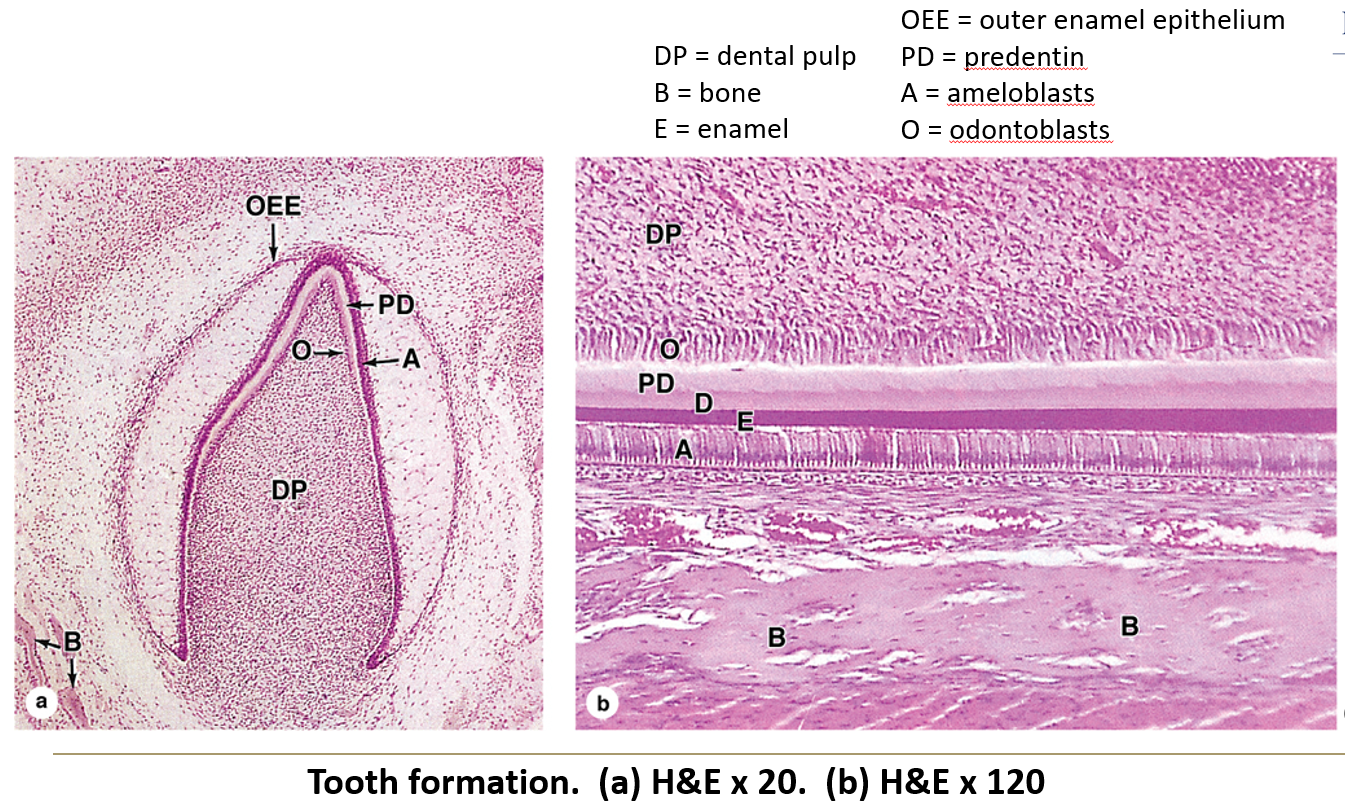
What do odontoblasts do?
They are cells that line the inside of dentin and help form and maintain it.
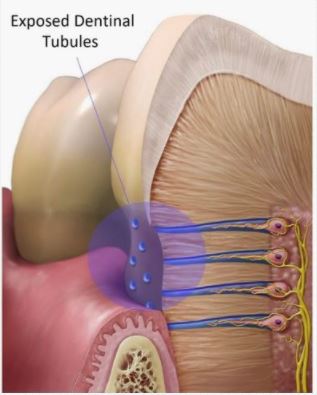
What are dentin tubules?
Long tubes inside the dentin. They carry odontoblast processes and act like pain sensors, especially when there are cavities.
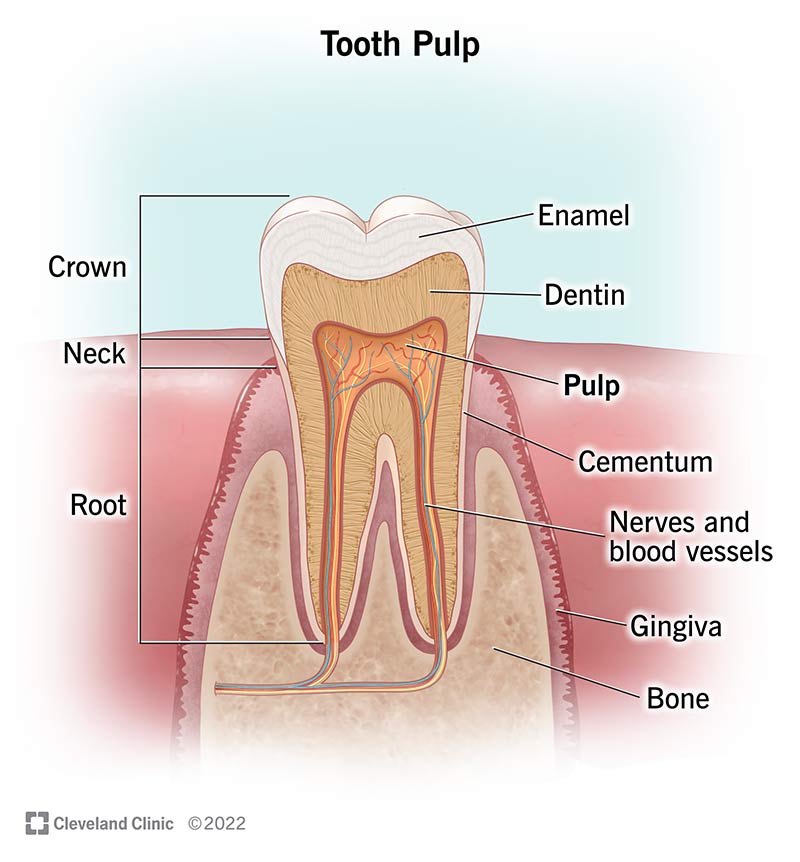
What is the pulp cavity?
The hollow center of the tooth, filled with connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves that come in through the root canal.
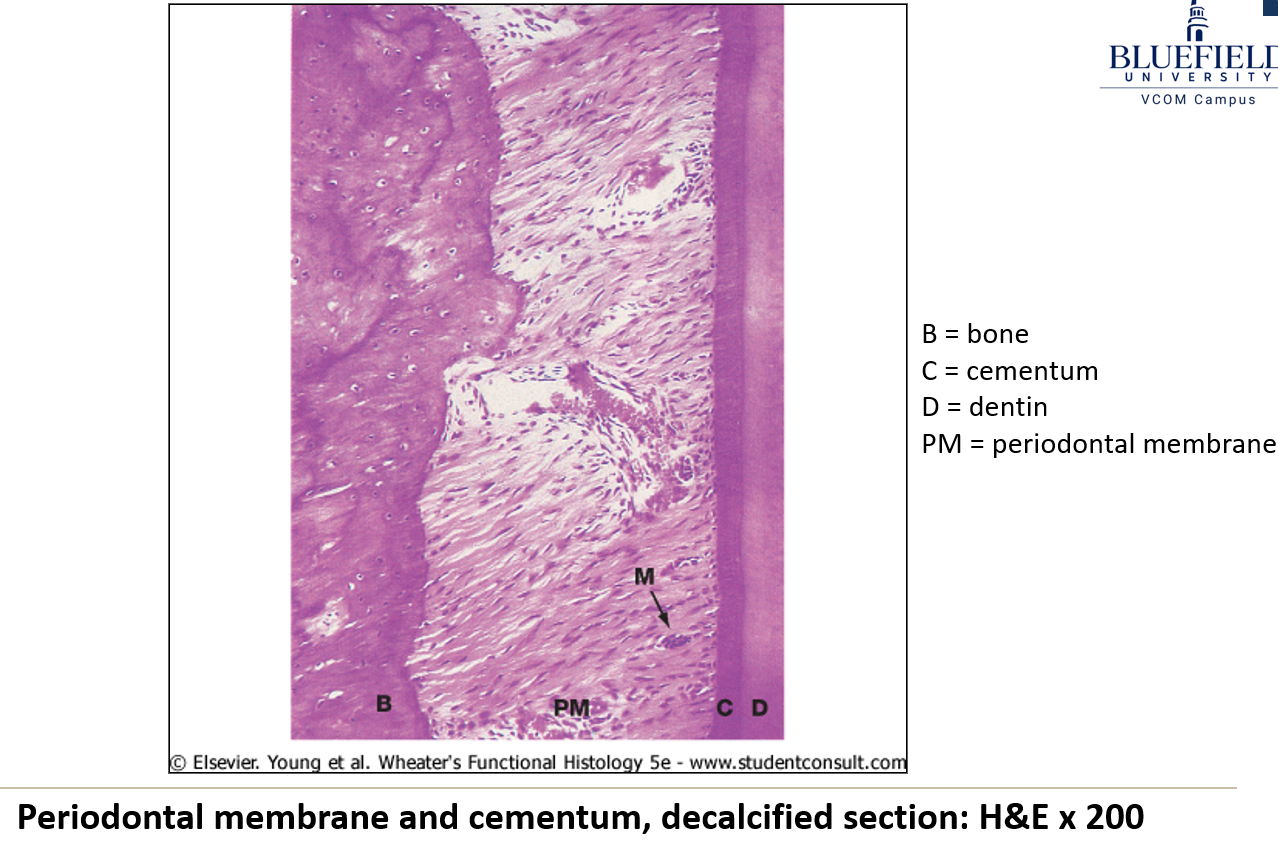
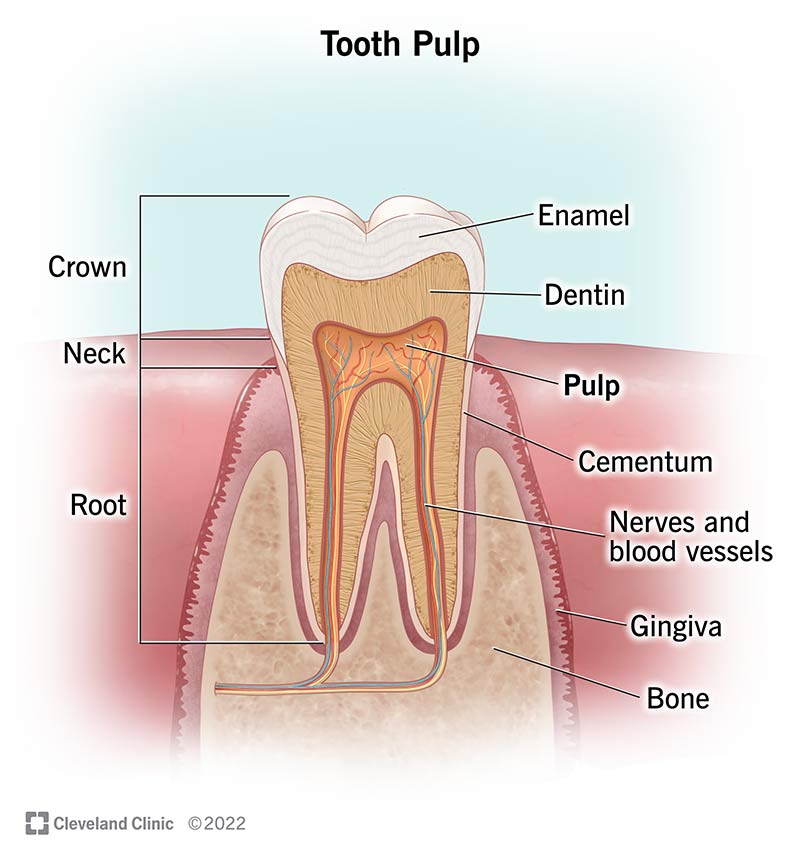
What is the crown of a tooth?
The part of the tooth you can see in the mouth. It’s covered with enamel.
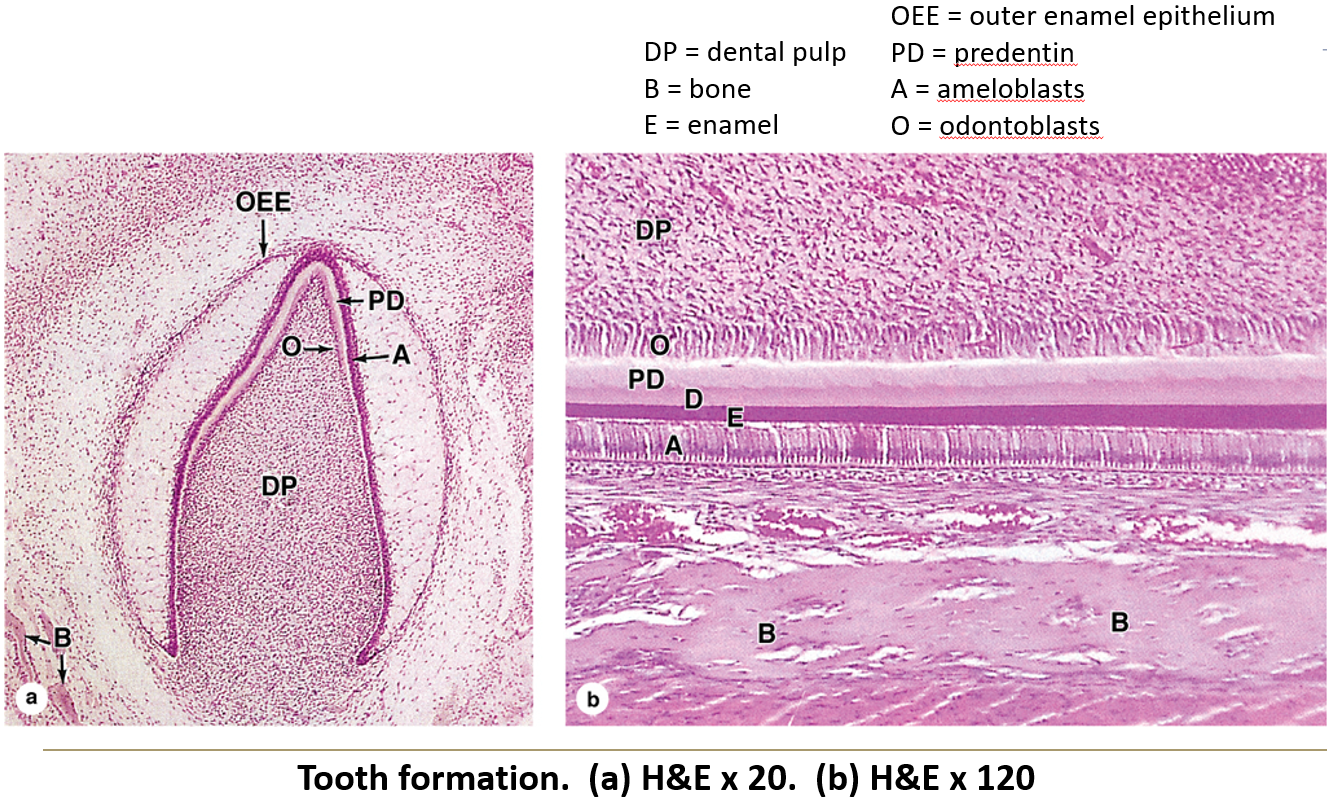
What are ameloblasts and what do they do?
Embryonic cells that form enamel but disappear after the tooth erupts.
What is the root of a tooth?
The part of tooth that extends through the gingiva and into the alveolus
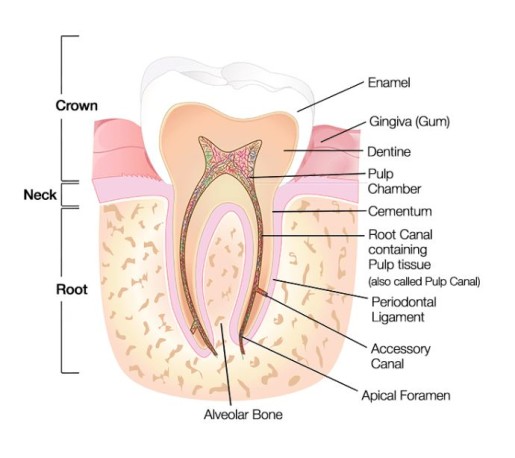
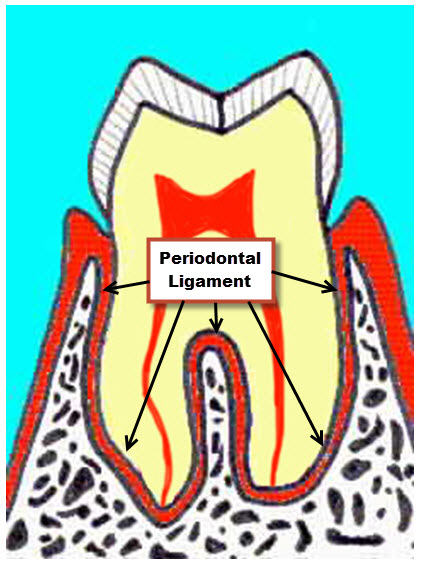
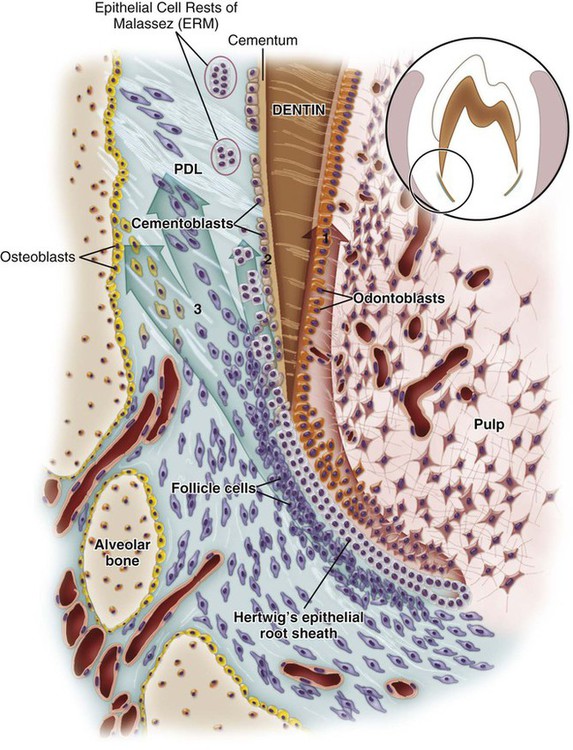
What is the periodontal ligament?
The connective tissue that anchors the tooth root into the alveolus, using a bone-like substance called cementum.
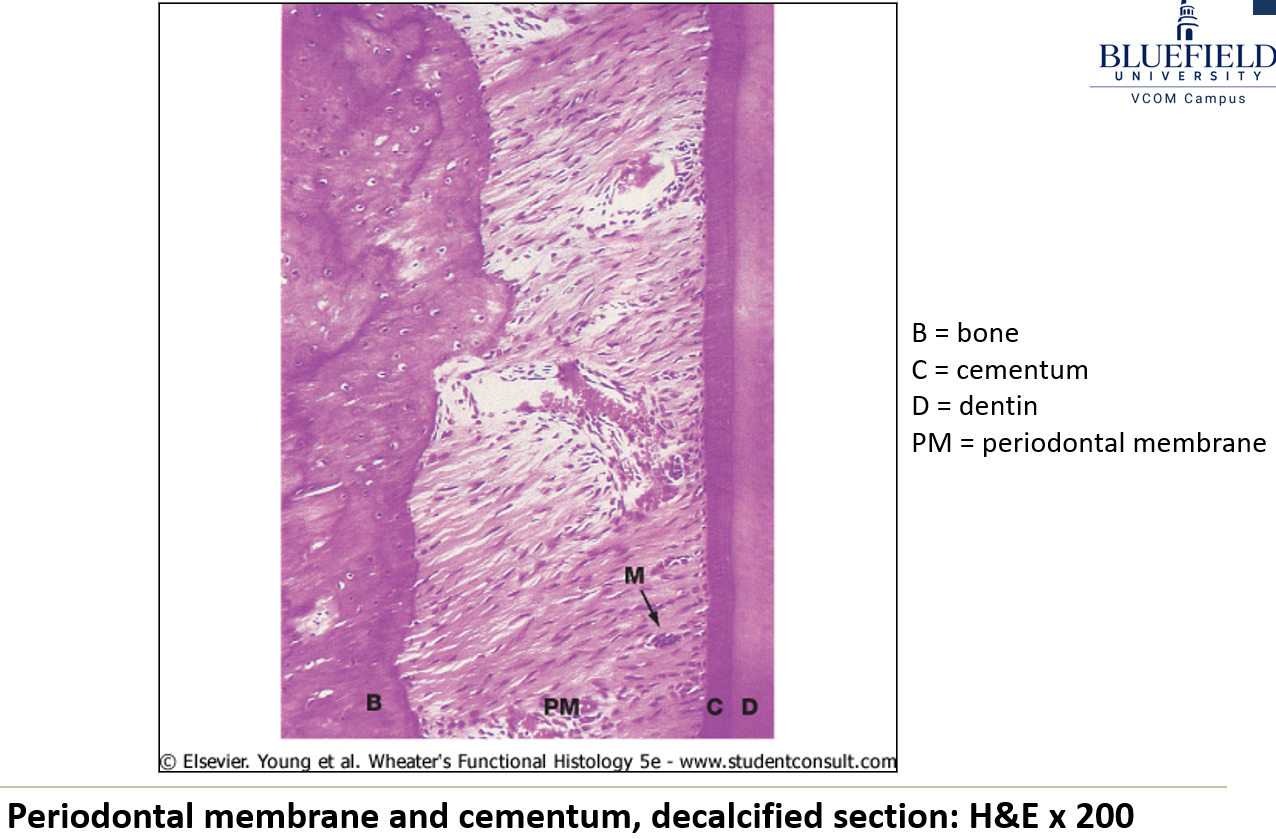
What are cementocytes?
Cells that look like osteocytes and are found deep inside the periodontal ligament.
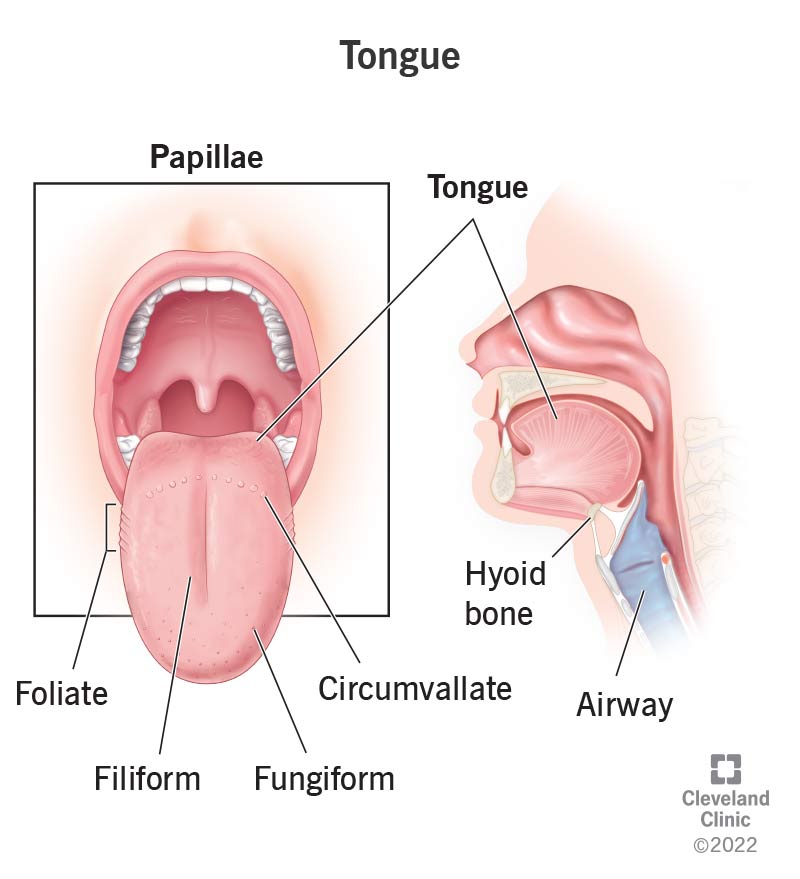
What are the main functions of the tongue?
Tasting, speaking, gripping, and moving food.
Where are taste buds located?
Mostly on the tongue, but also on the soft palate, pharyngeal walls, and epiglottis.
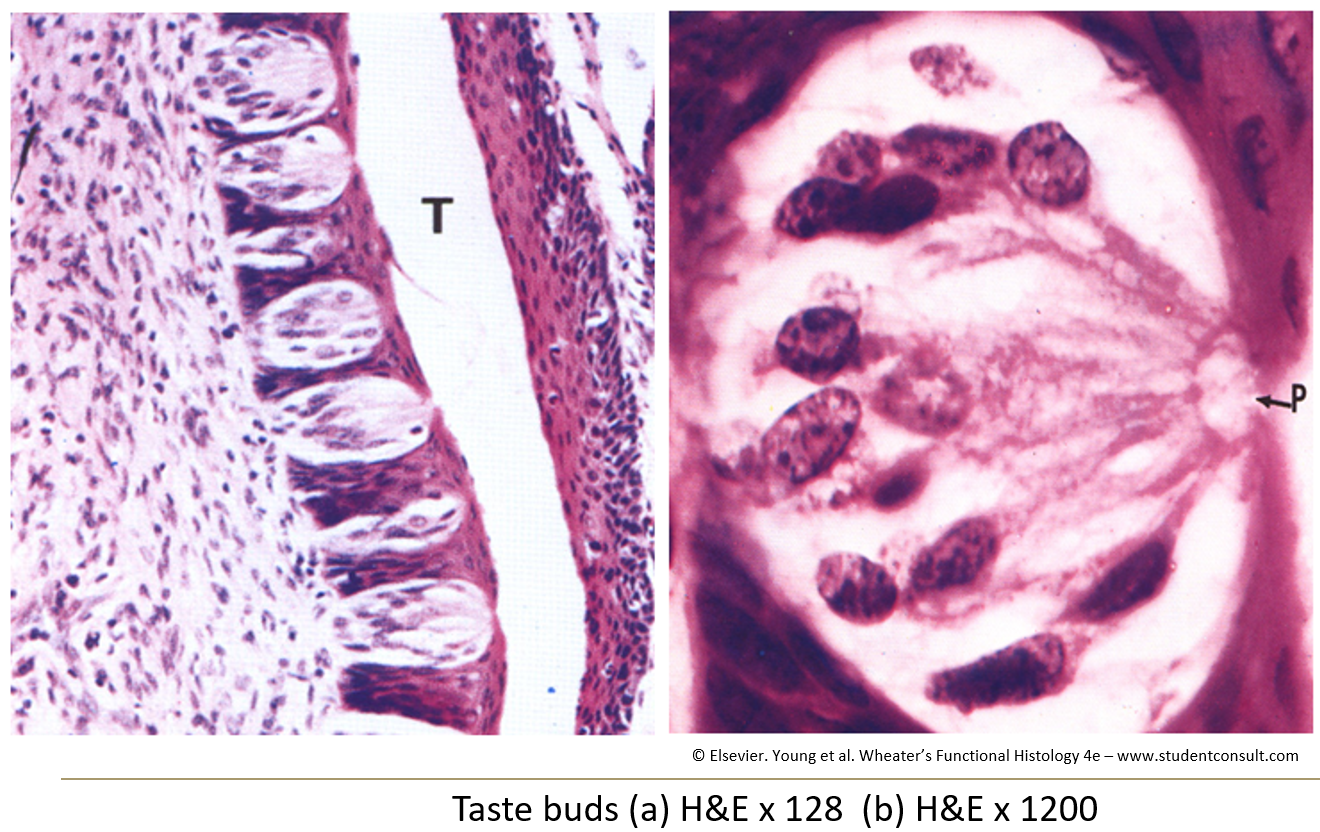
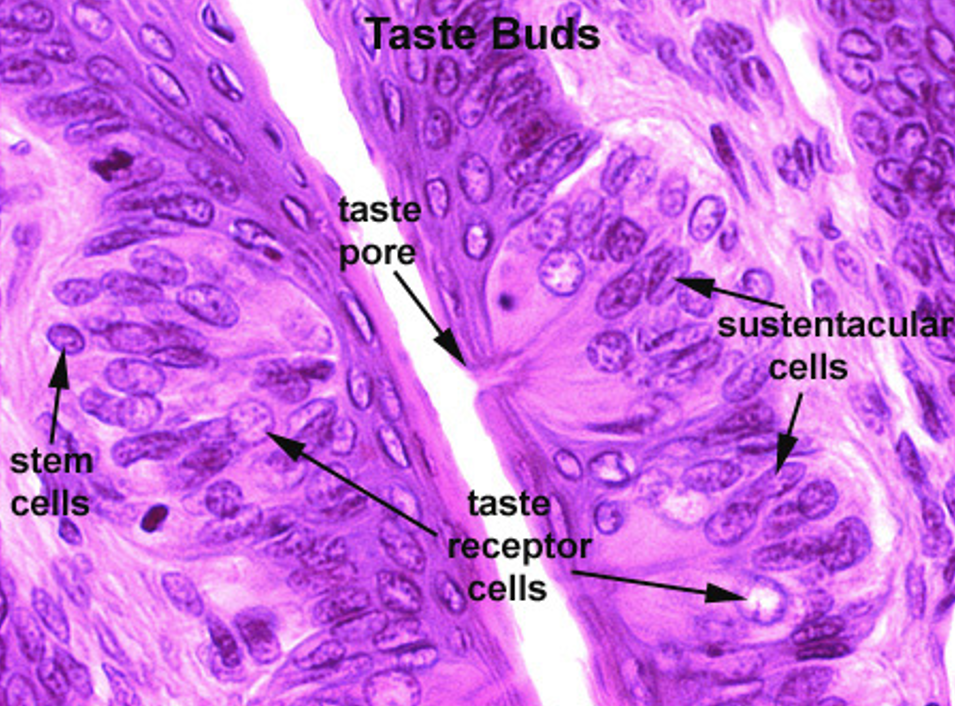
What do taste buds look like?
Barrel-shaped structures that go through the epithelium from the basal lamina.
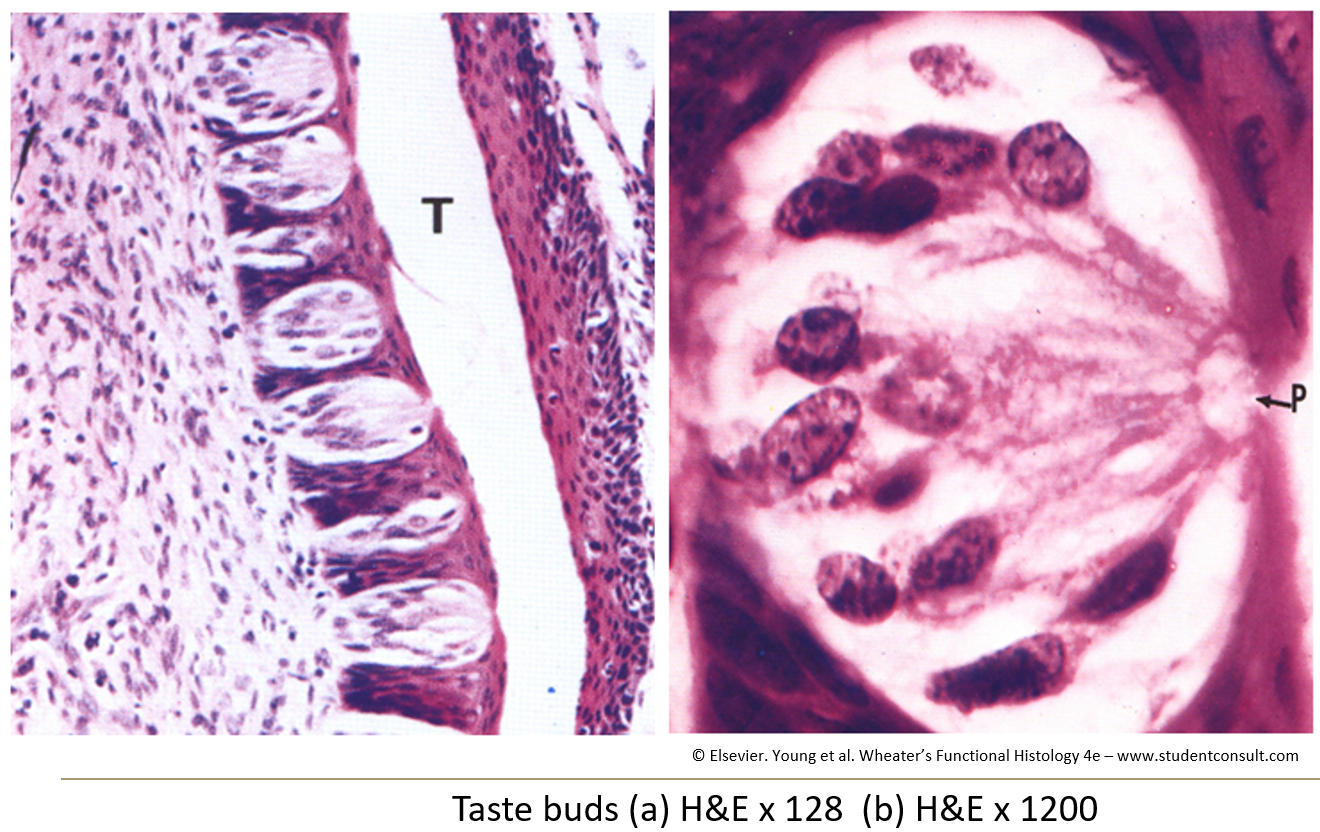
What is a taste pore?
An opening in the taste bud where microvilli from taste cells stick out. Nerve fibers are wrapped around the base.
How are the muscles in the tongue arranged?
They are arranged in different directions (planes and angles) to allow for flexible movement.
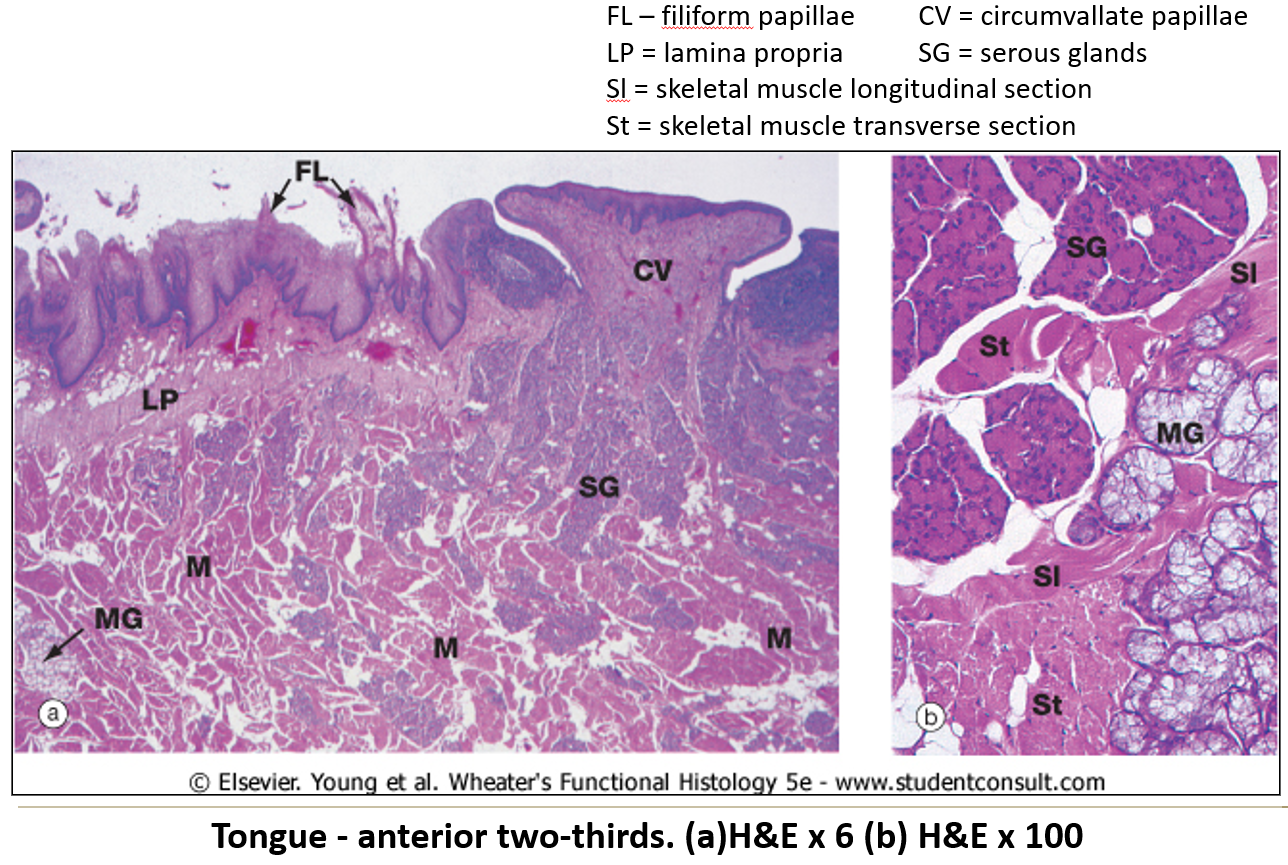
What kinds of glands are found in the tongue?
Both serous and mucous glands.
What are papillae and what is their function?
Projections on the tongue that help grip food.
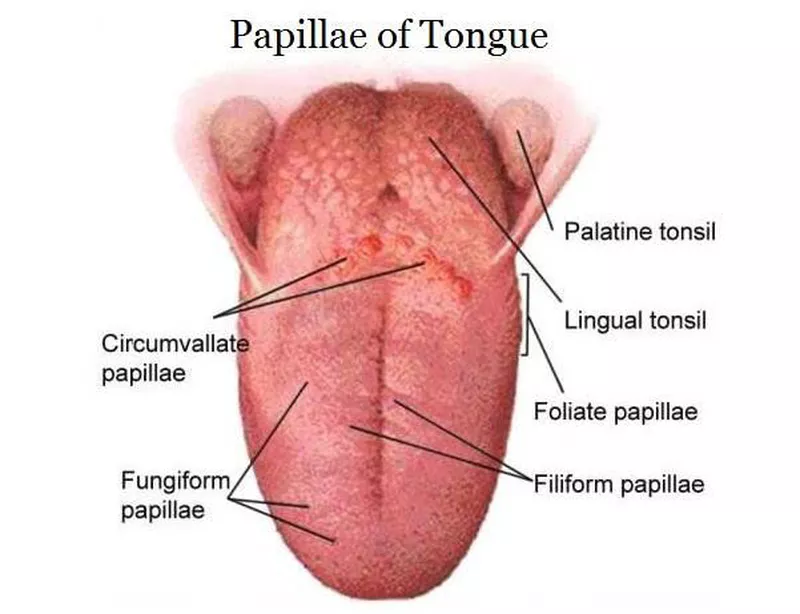
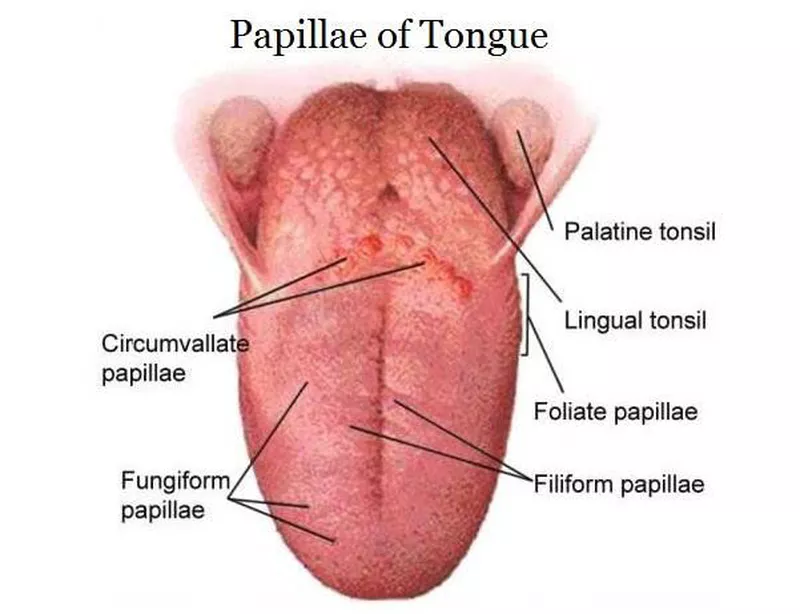
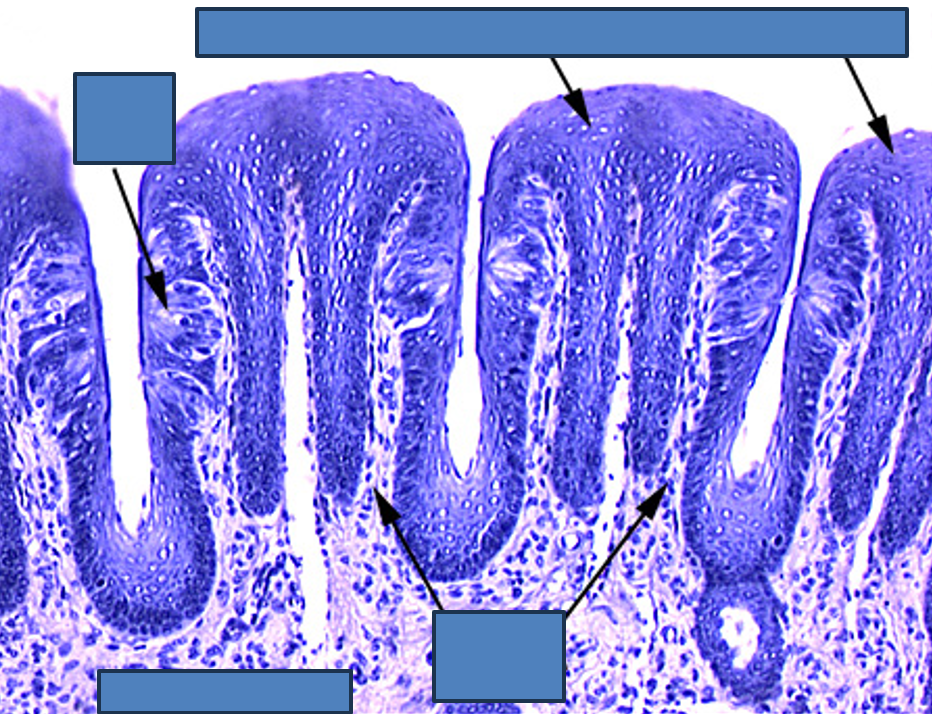
What are filiform papillae?
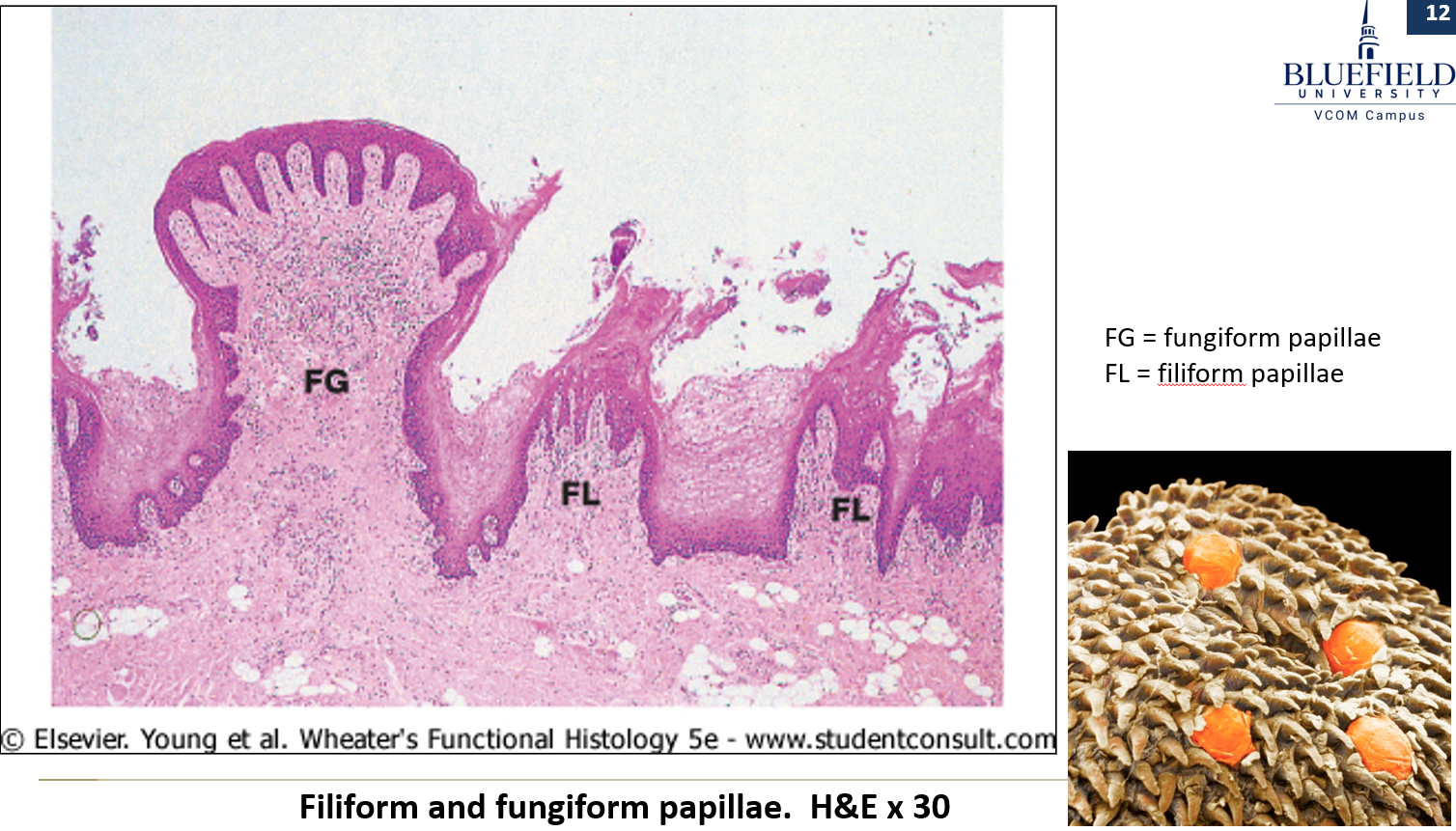
Long, pointed, and appear white due to keratin. They are the most numerous papillae.
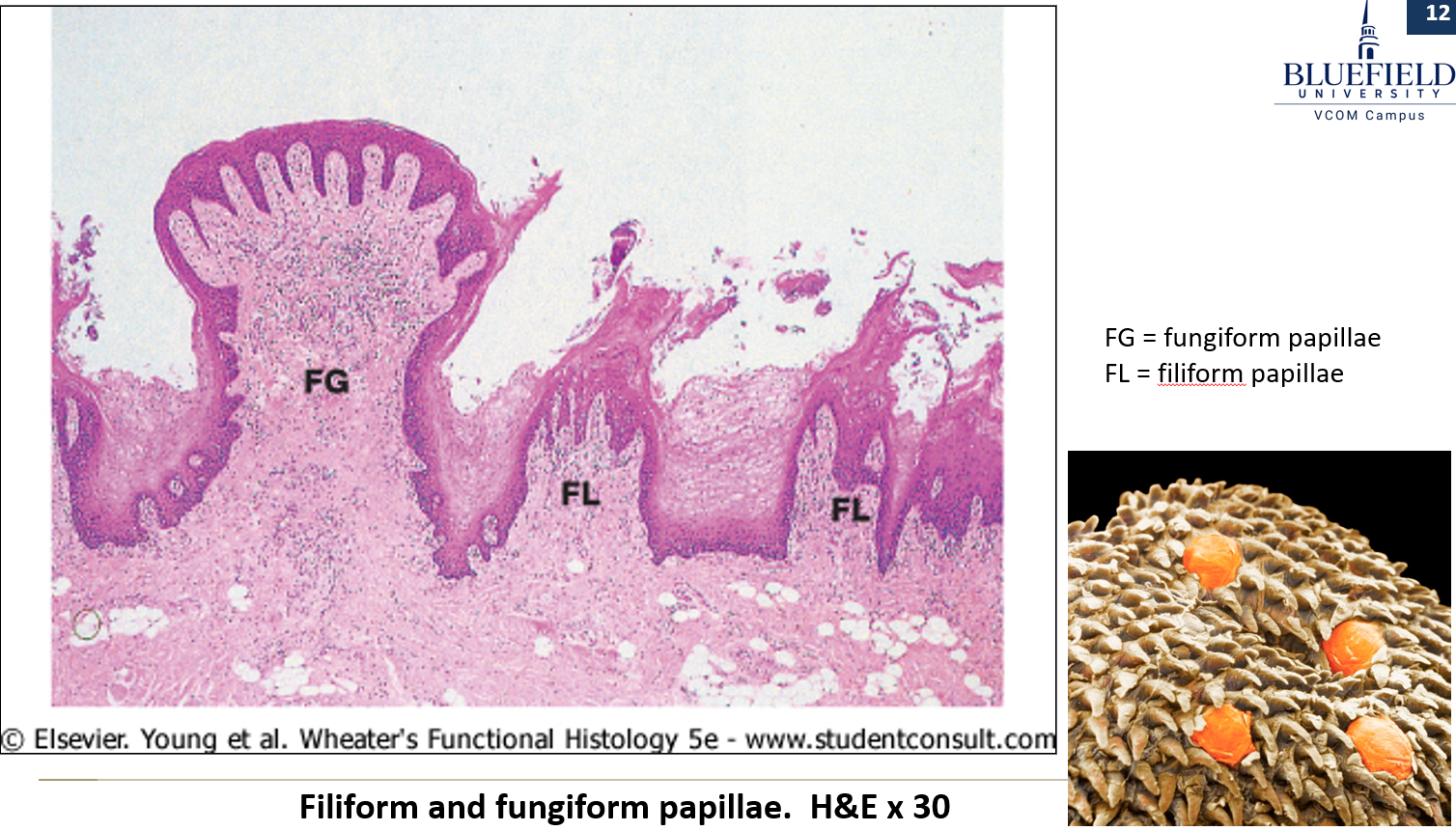
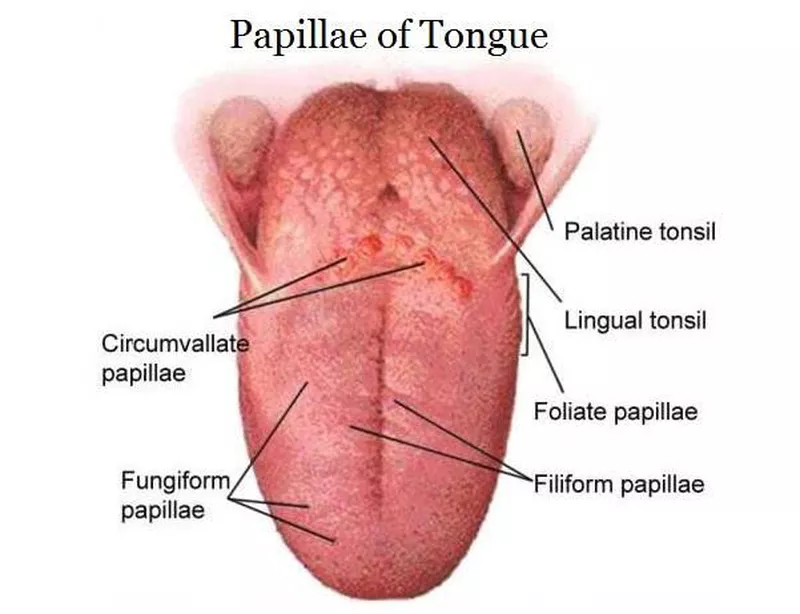
What are fungiform papillae?
Mushroom-shaped, have nonkeratinized epithelium, and look like small red spots. Some contain taste buds.
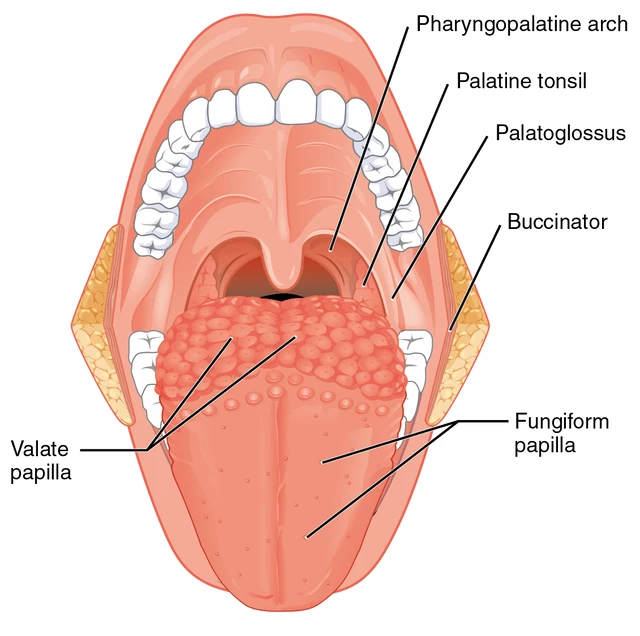
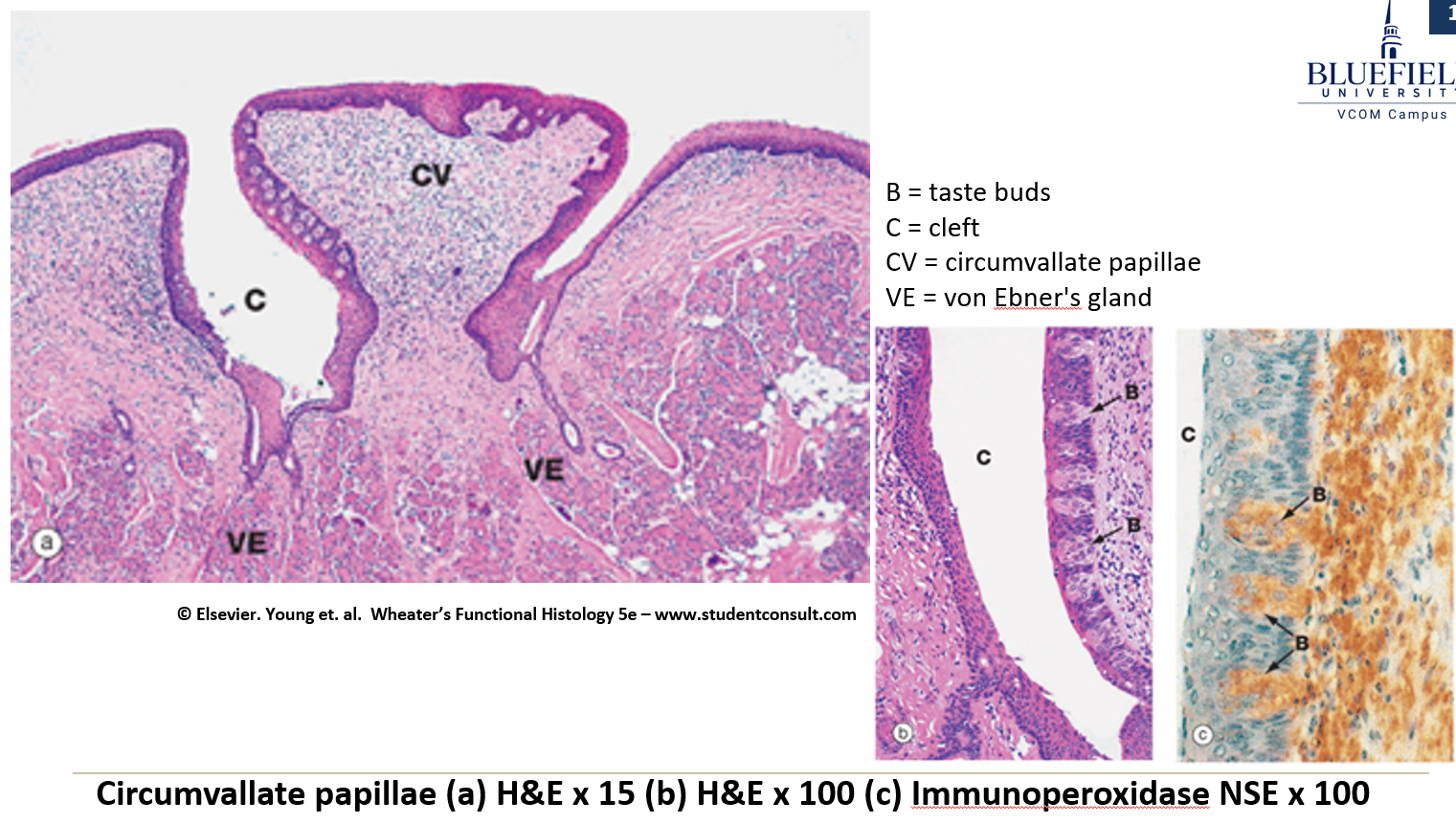
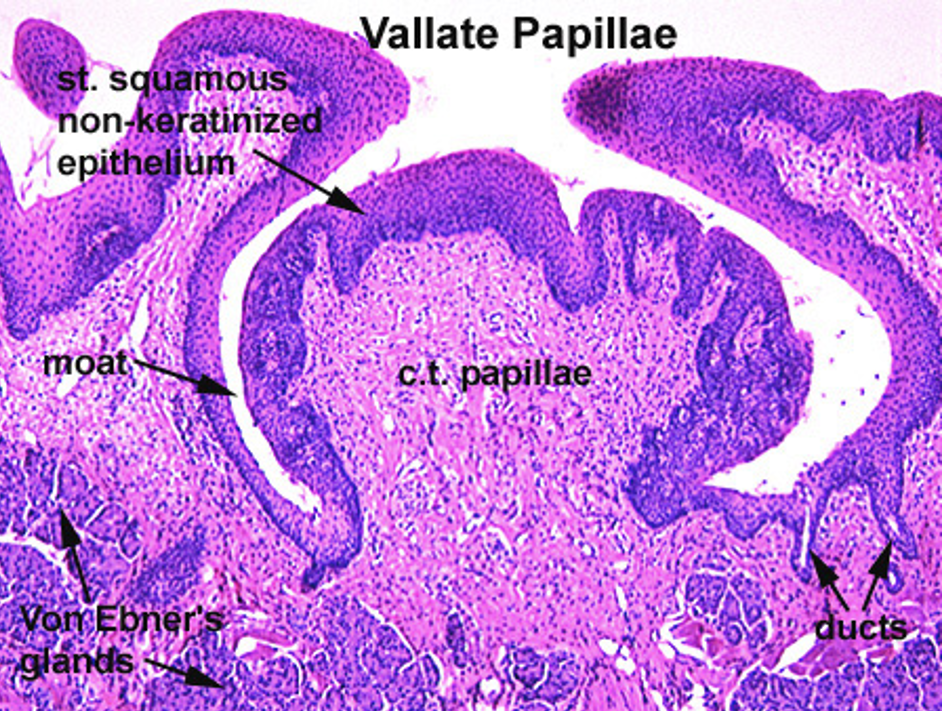
What are vallate papillae?
Large and round, surrounded by deep crypts. The walls of the crypts have many taste buds.
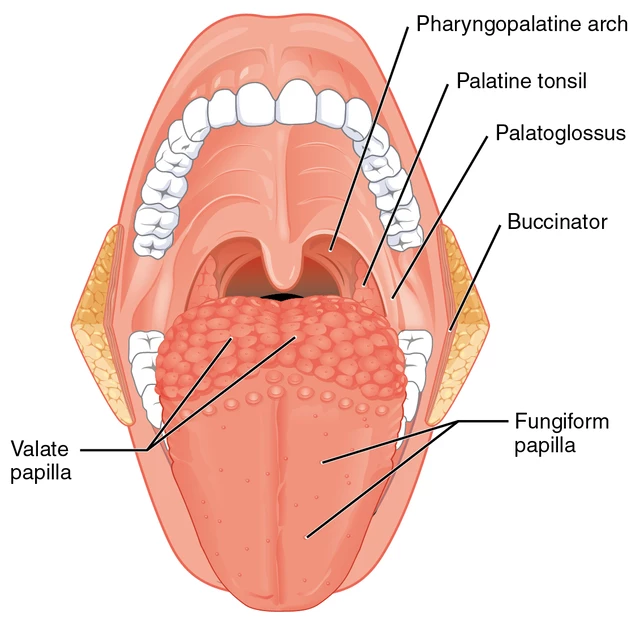
What are von Ebner glands and what do they do?
Serous glands that release secretions into the base of the moat around the vallate papillae.
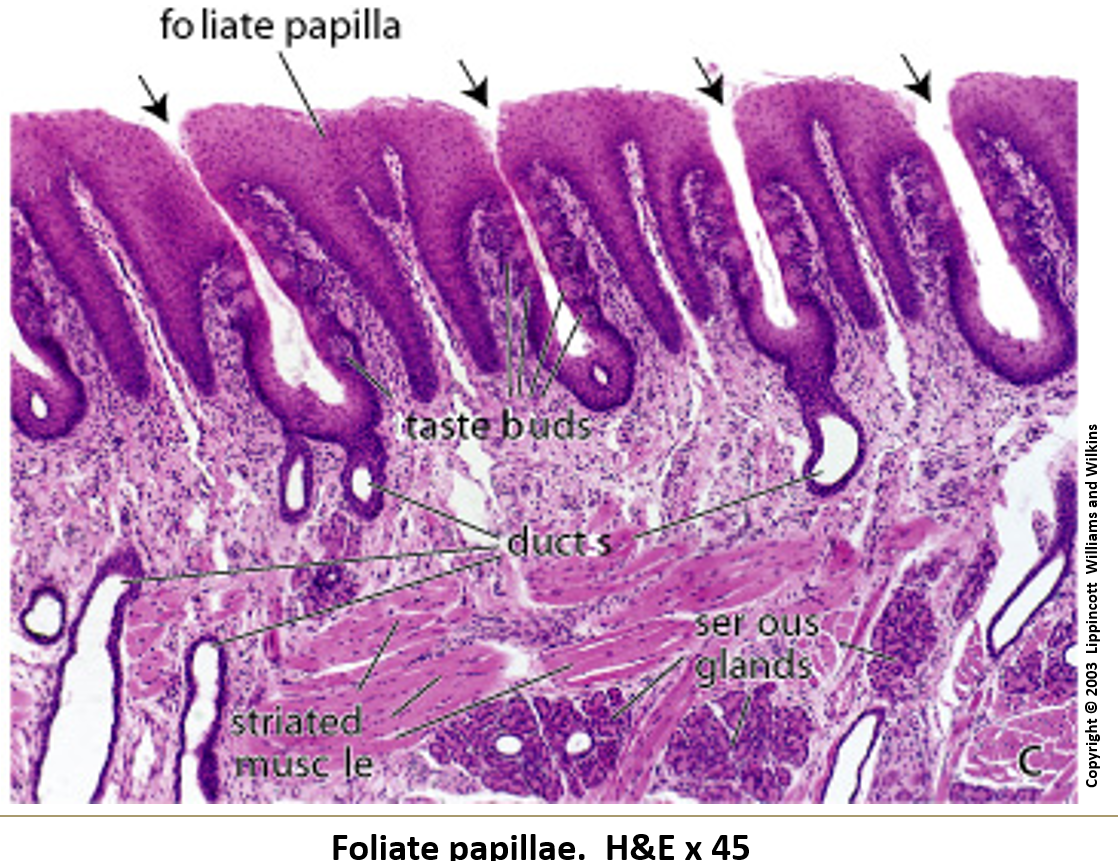
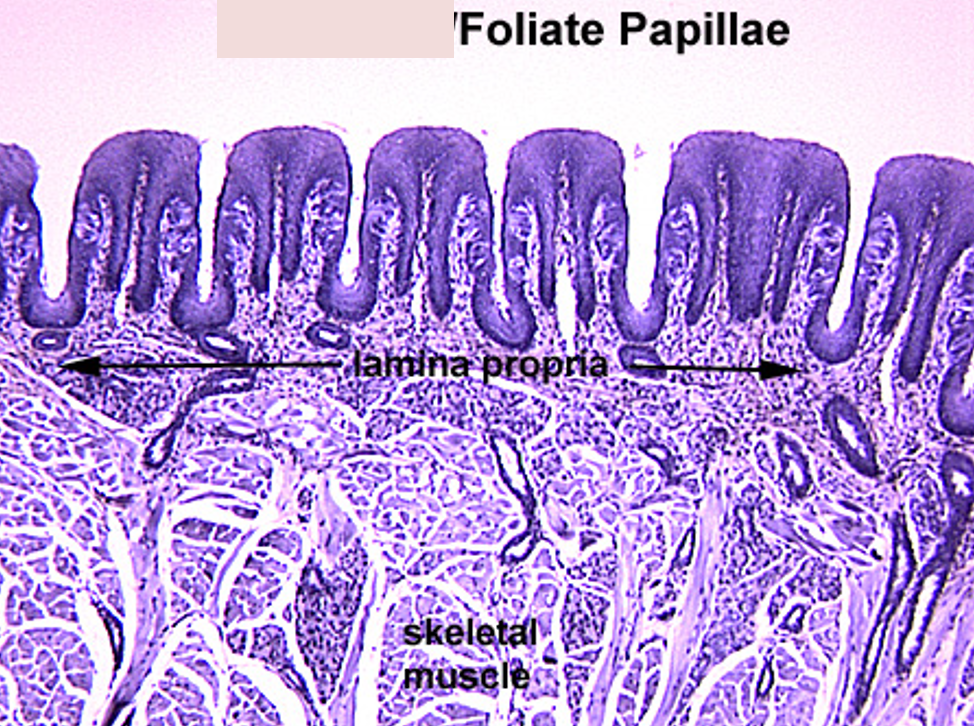
What are foliate papillae?
Leaf-shaped and found on the sides of the back of the tongue. They have taste buds, and serous gland ducts open between them.
How are salivary glands organized?
They have lobes separated by connective tissue, which are further divided into lobules.
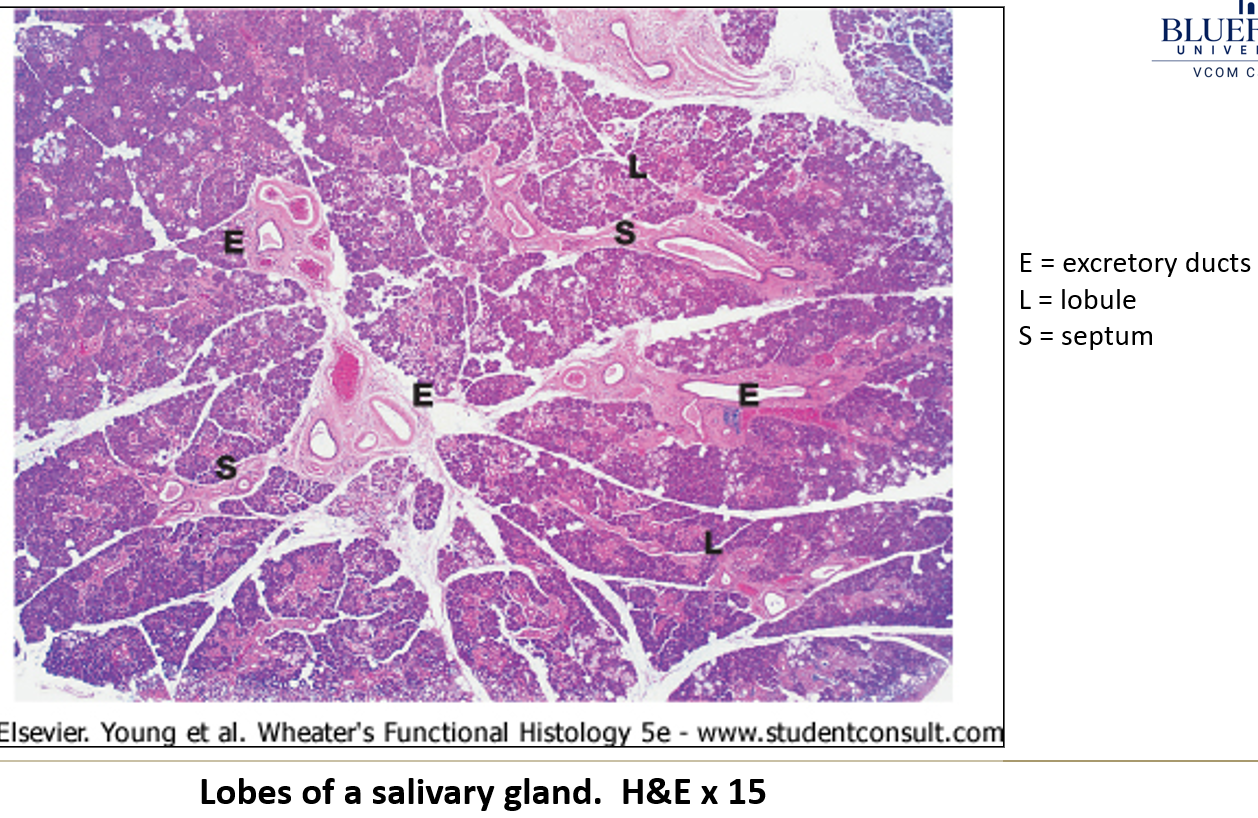
What type of gland structure do salivary glands have?
They are either compound acinar or compound tubuloacinar.
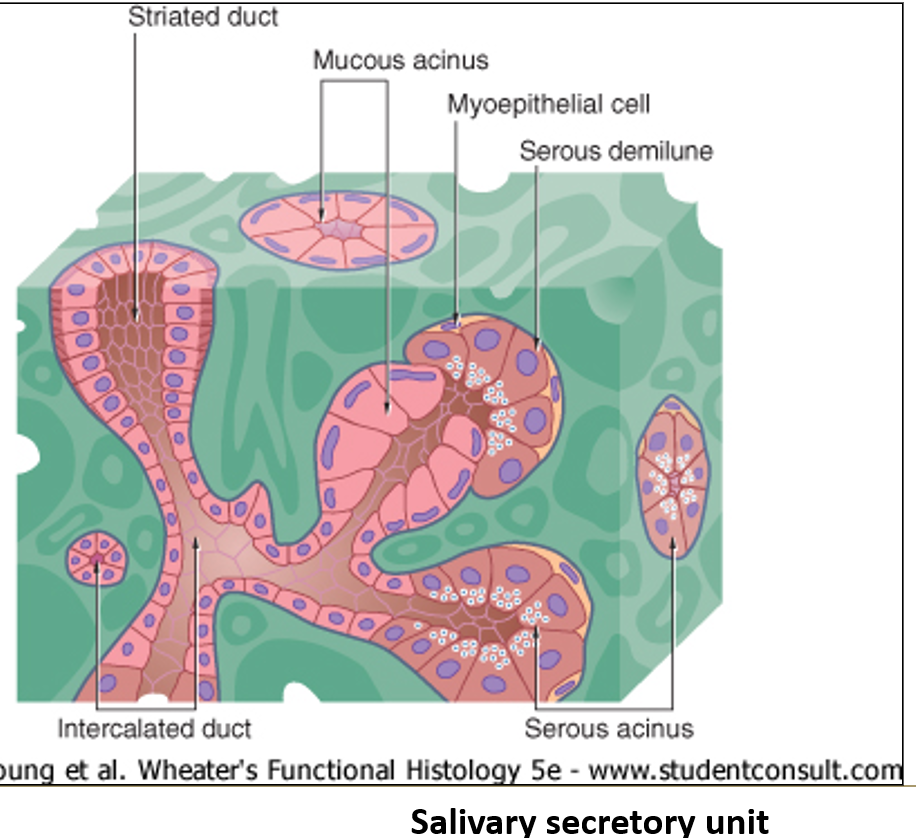
What do myoepithelial cells do?
They surround each acinus and contract to push out the secretions.
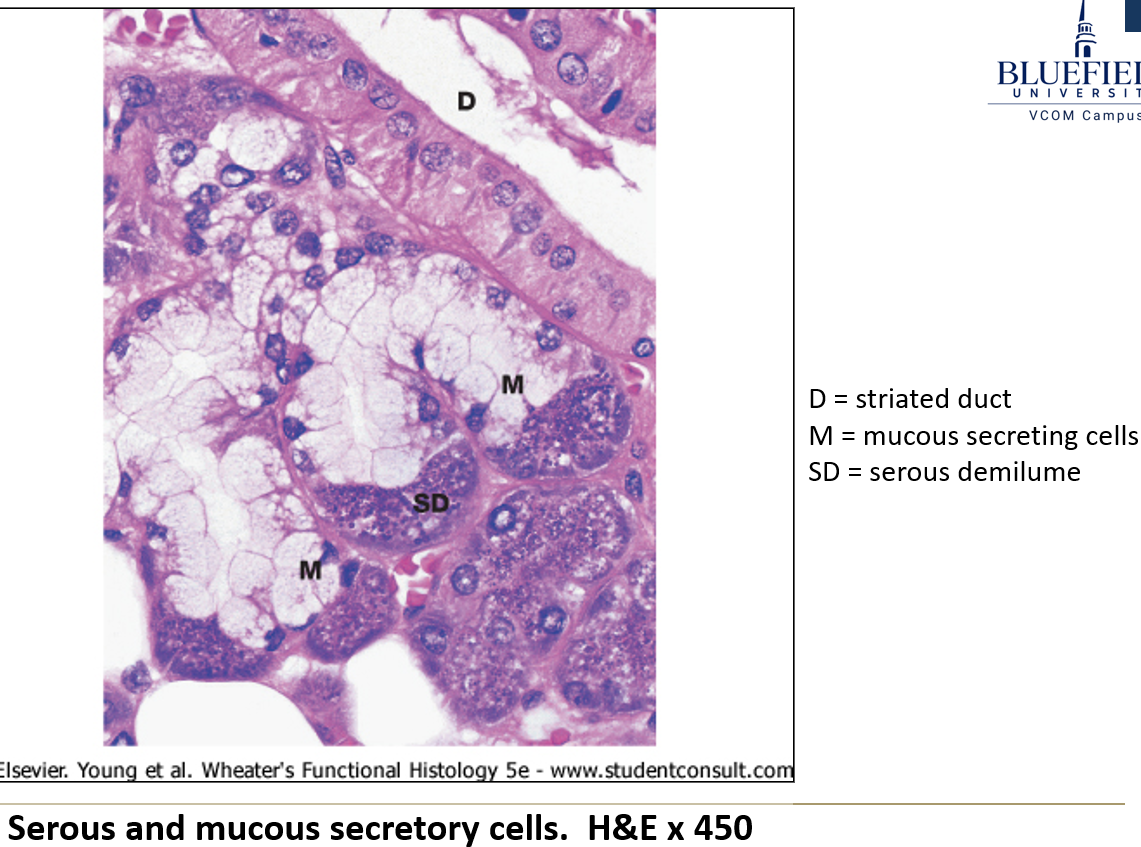
What are the two main types of secretory cells in salivary glands?
Serous cells: release water, salts, enzymes, and proteins
Mucous cells: have a foamy look and release mucus to help lubricate food
Do secretory cells get nerve input?
Yes, they receive direct innervation.
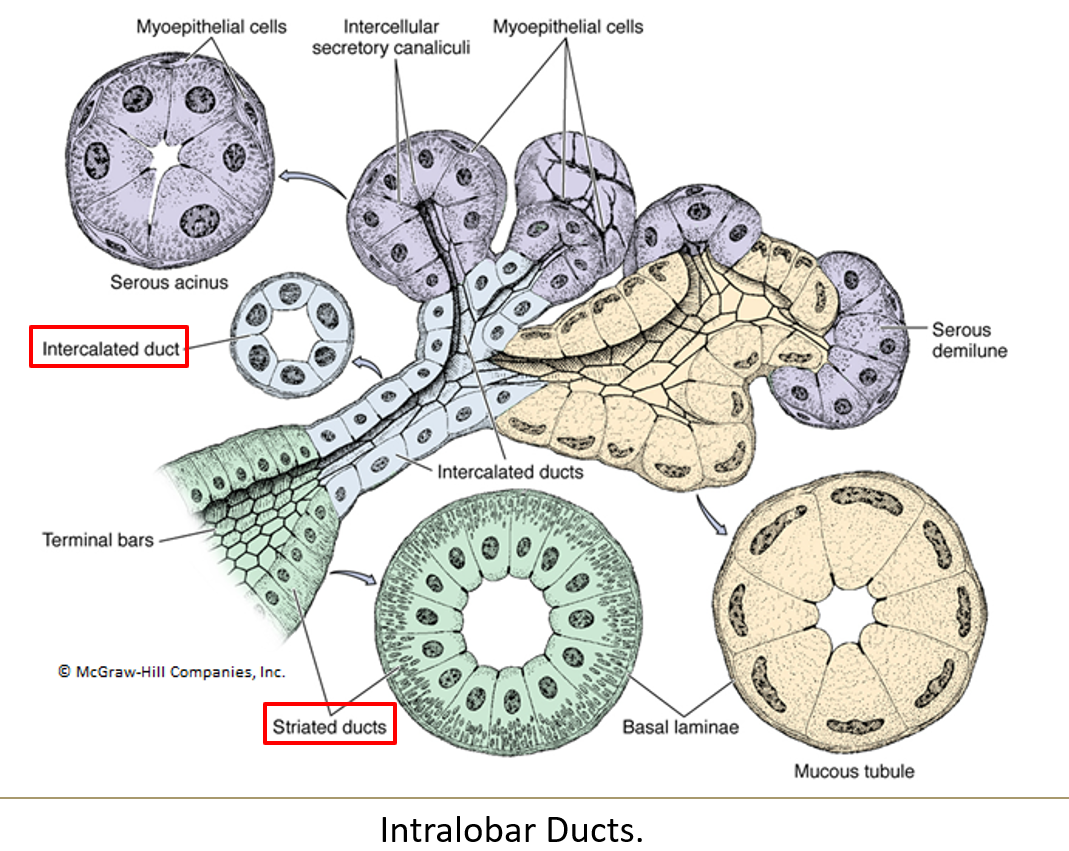
What is the order of ducts from the acinus to the exit?
Acini > intercalated ducts > striated ducts > interlobar ducts > secretory duct
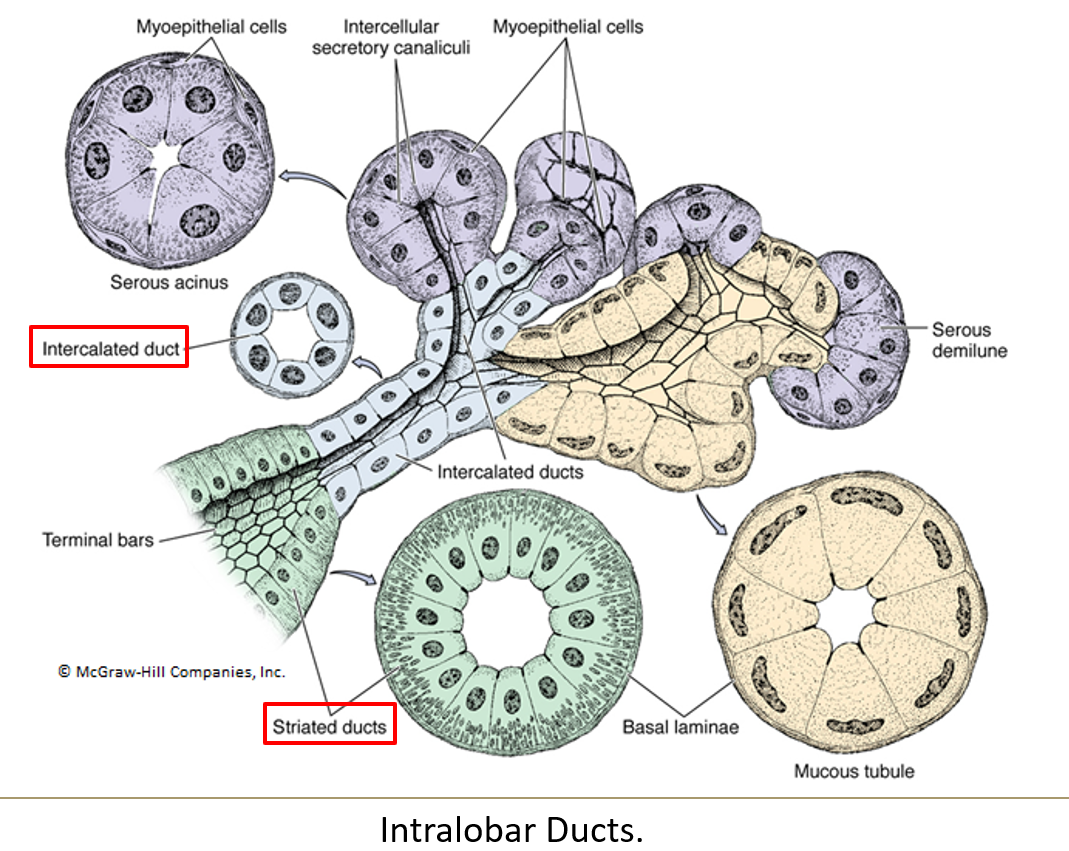
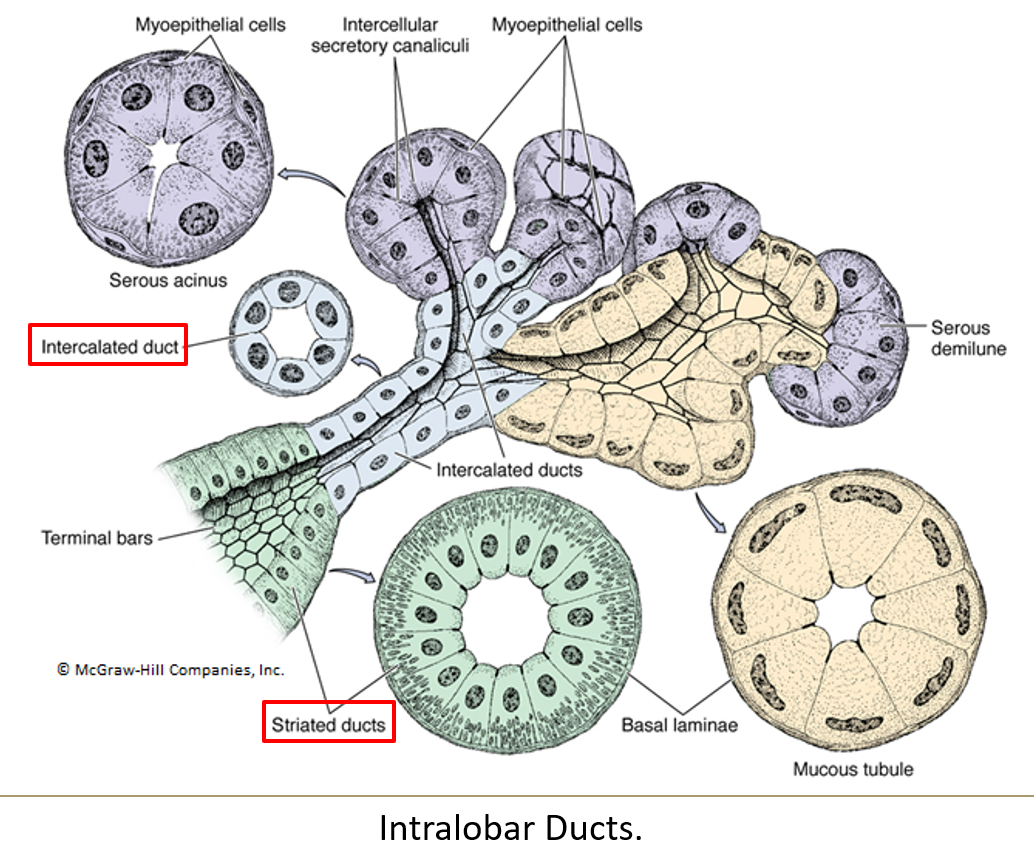
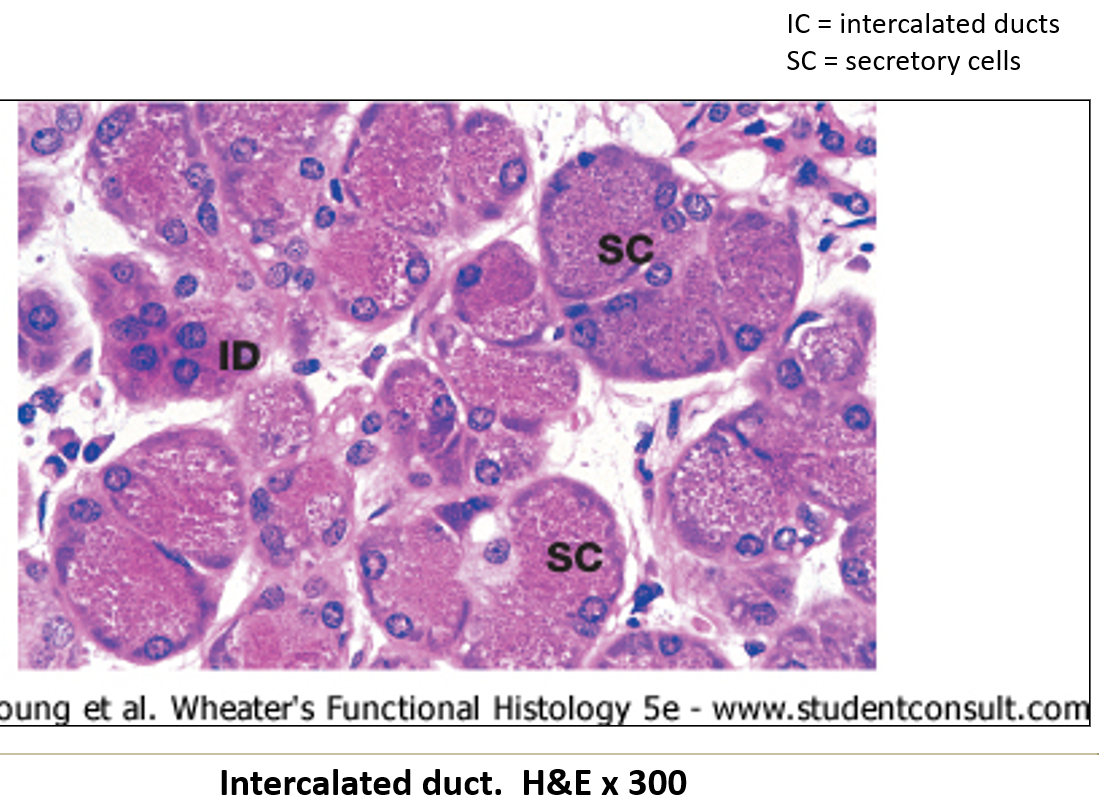
What epithelium lines intercalated ducts?
Simple squamous or low cuboidal epithelium.
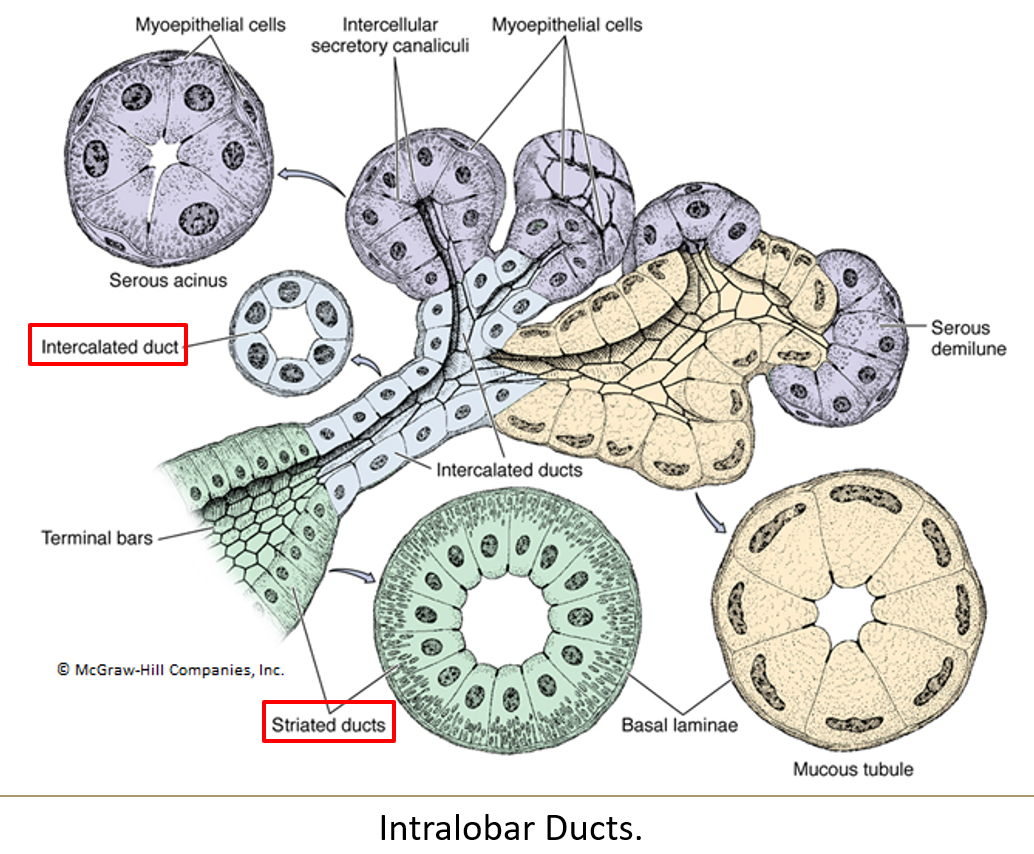
What lines the striated ducts and what is their function?
Simple columnar cells with striations at the base
They concentrate saliva using ion pumps
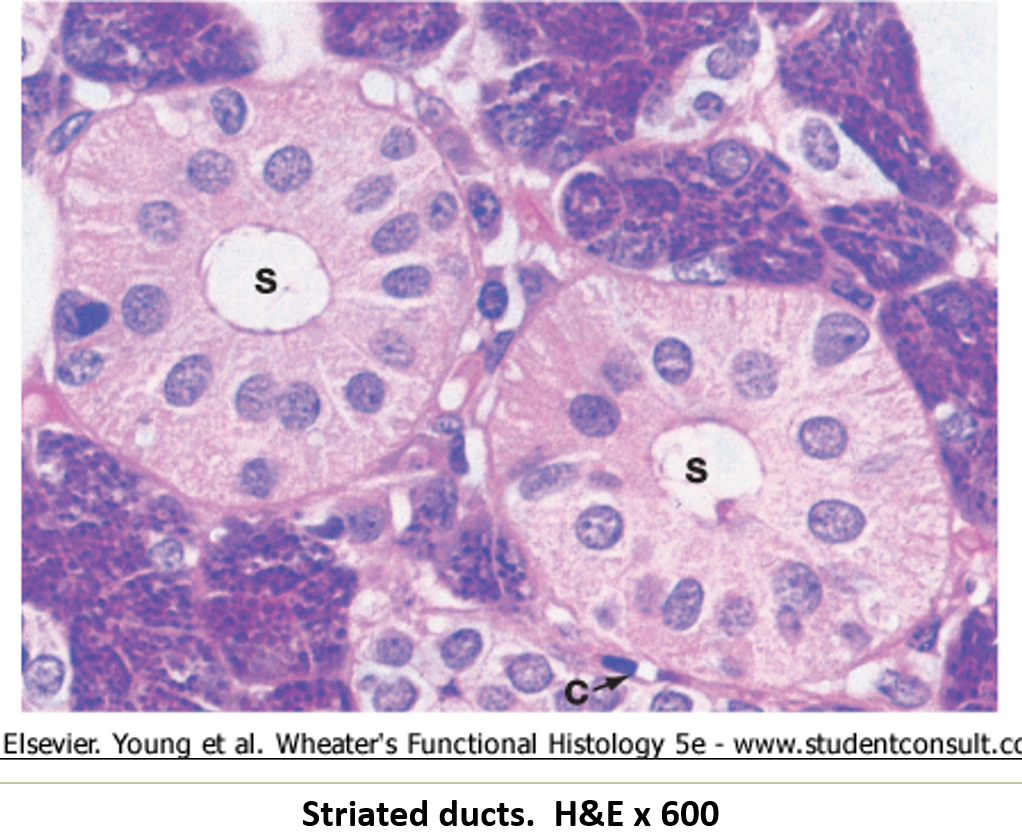
What features help striated ducts perform their function?
Highly folded basal membrane with mitochondria
Nucleus and cytoplasm pushed toward the center
What hormones can change the activity of striated ducts?
Aldosterone and ADH.
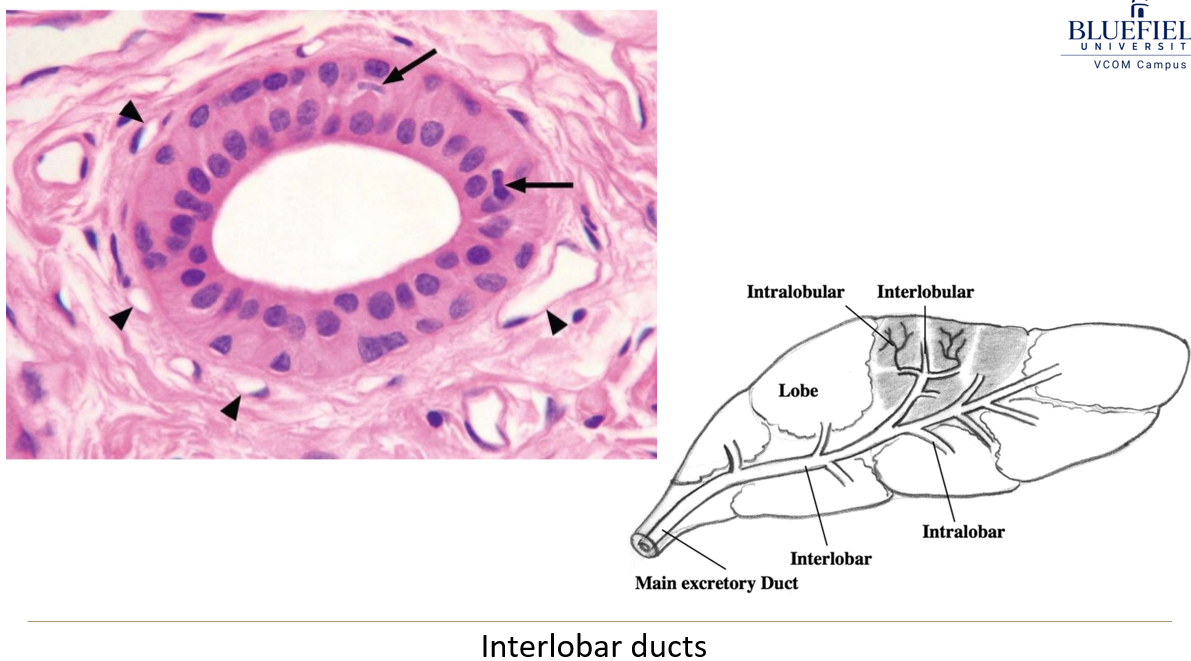
What are interlobar ducts, and how do they form?
Larger ducts found in exocrine glands that transport secretions between the lobes of the gland.
They form when several intralobar ducts (which include intercalated and striated ducts) merge together. Interlobar ducts eventually drain into the main excretory duct of the gland.
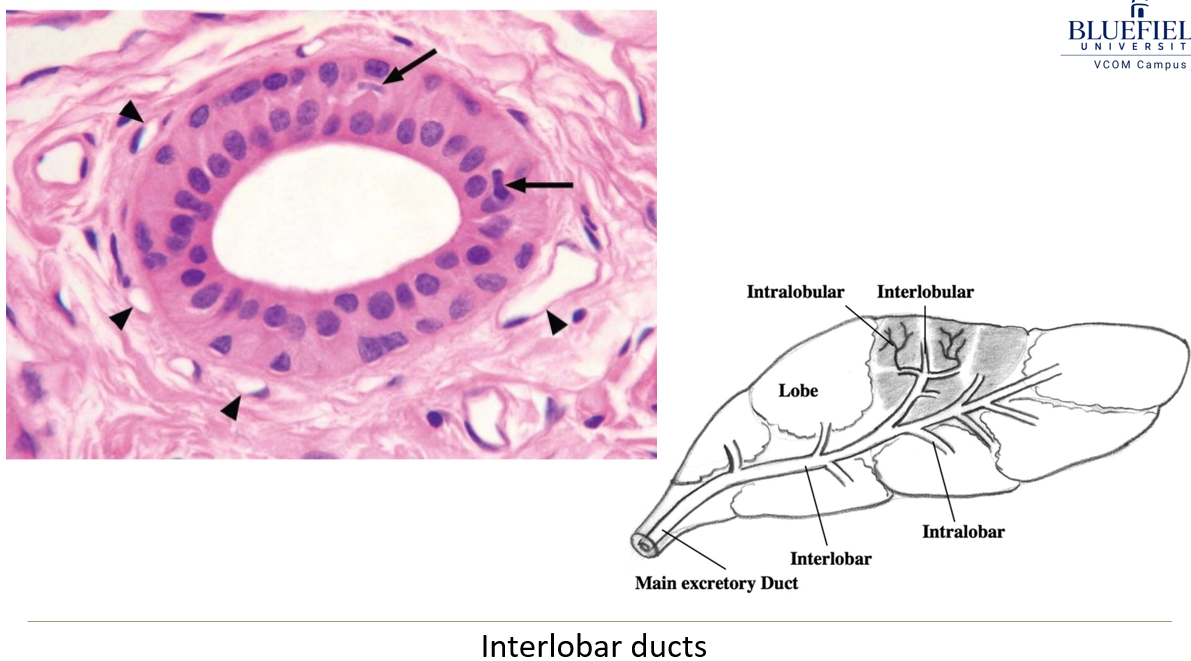
What kind of epithelium lines interlobar ducts?
They start with simple columnar epithelium and change to stratified cuboidal or columnar epithelium.
What are secretory ducts?
Final ducts that carry saliva to the oral cavity.
What epithelium lines the secretory ducts?
They are lined by stratified cuboidal/columnar or pseudostratified epithelium, which changes to stratified squamous before opening into the mouth.
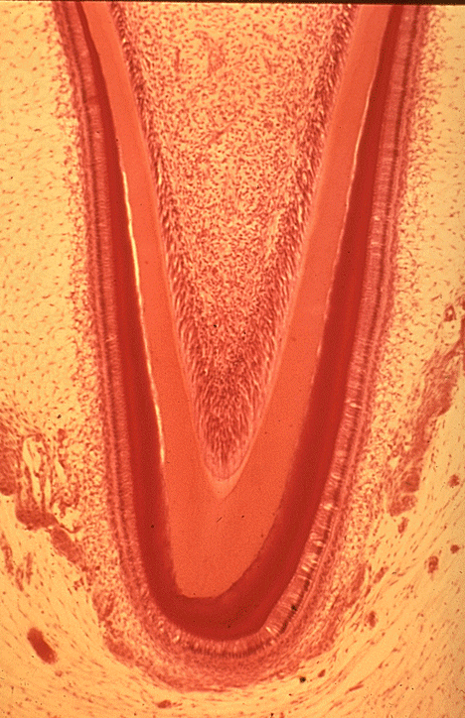
Identify this structure
Tooth
Odontoblasts, a row of tall nuclei between the dentin and pulp cavity, right next to the dentin can be observed
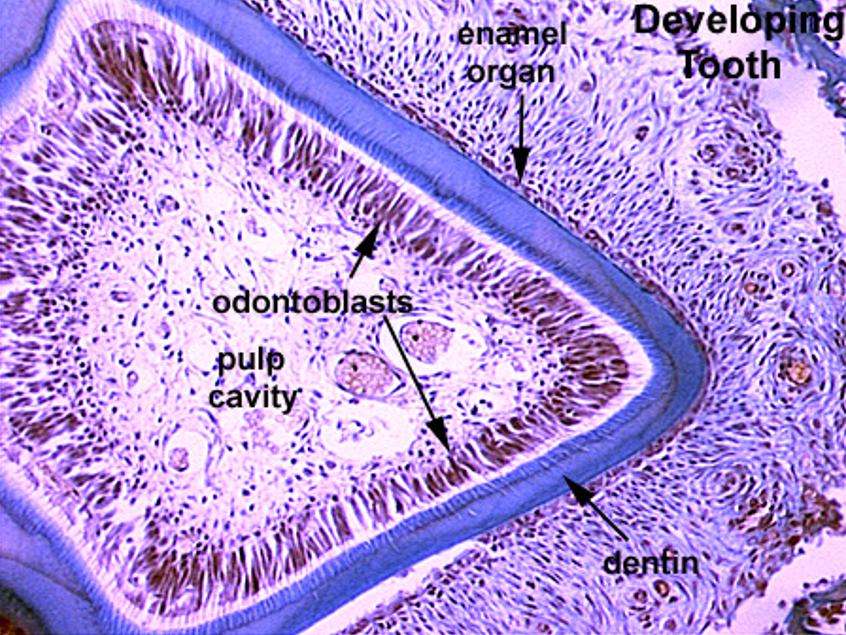
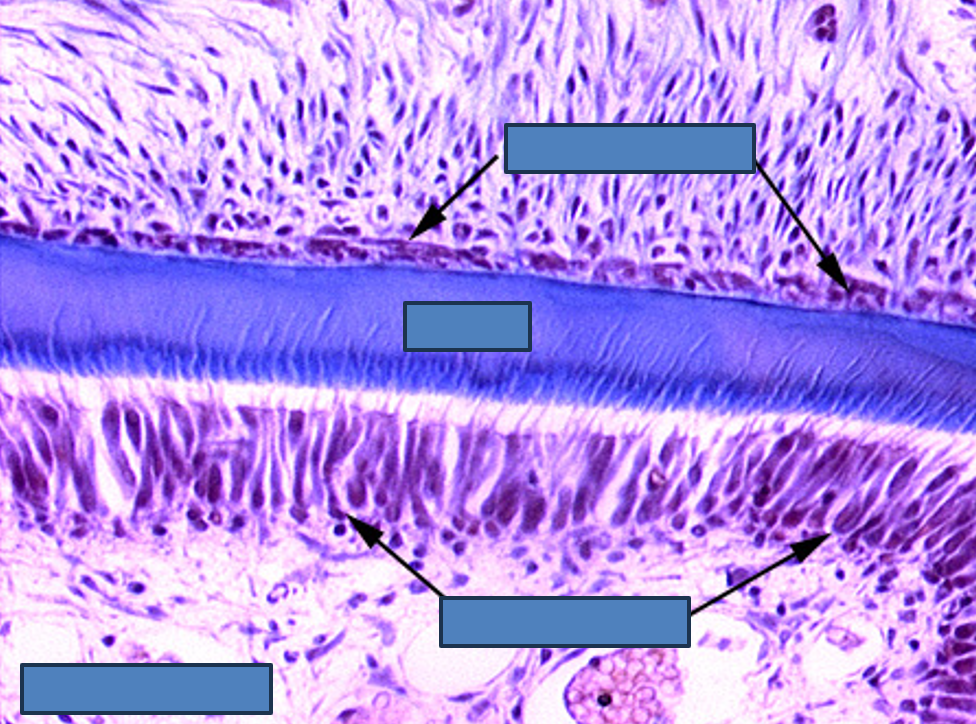
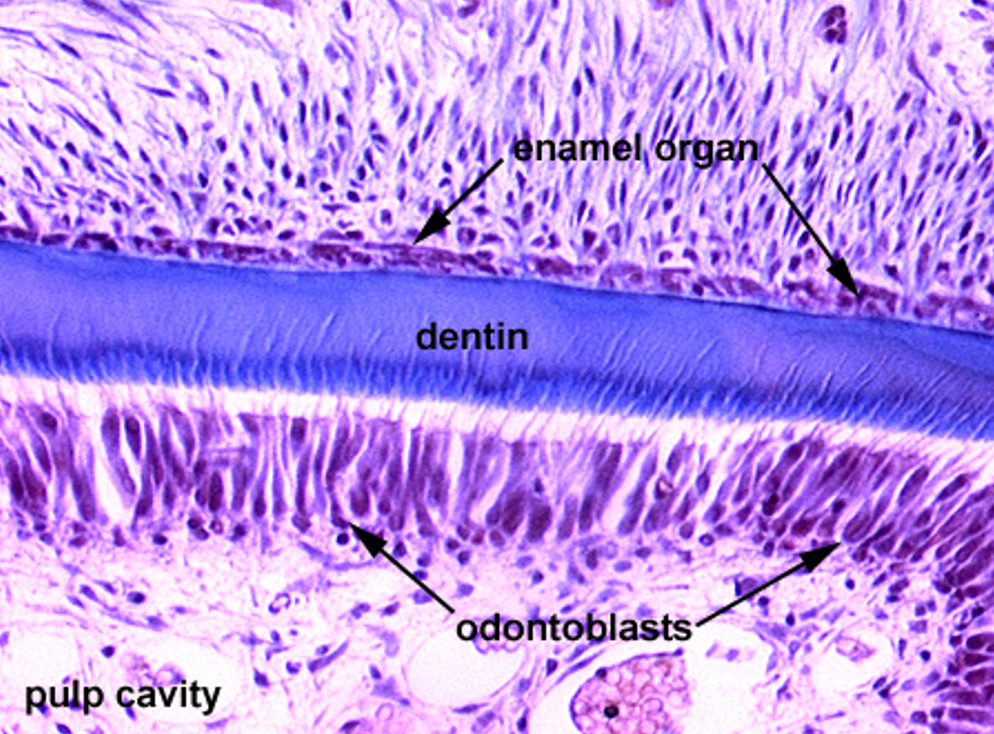
Identify this structure
Tooth
Dentin observed above tall row of nuclei (odontoblasts) with enamel above it
Identify this structure
Tooth
Dentin observed above tall row of nuclei (odontoblasts)
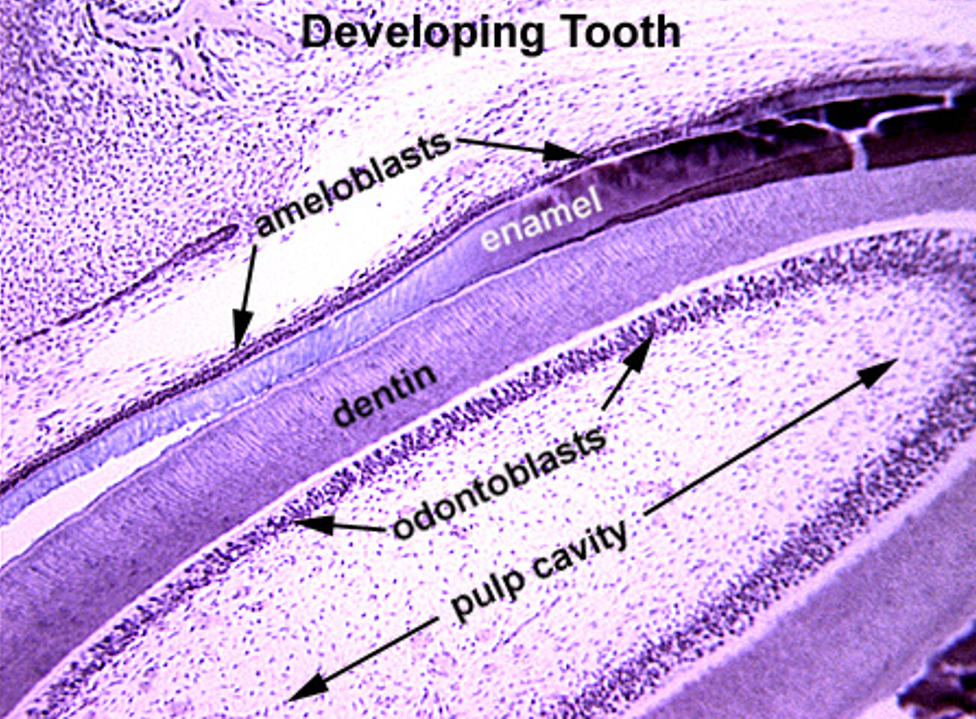
Identify this structure
Tooth
Dentin/dentin tubules observed above tall row of nuclei (odontoblasts)
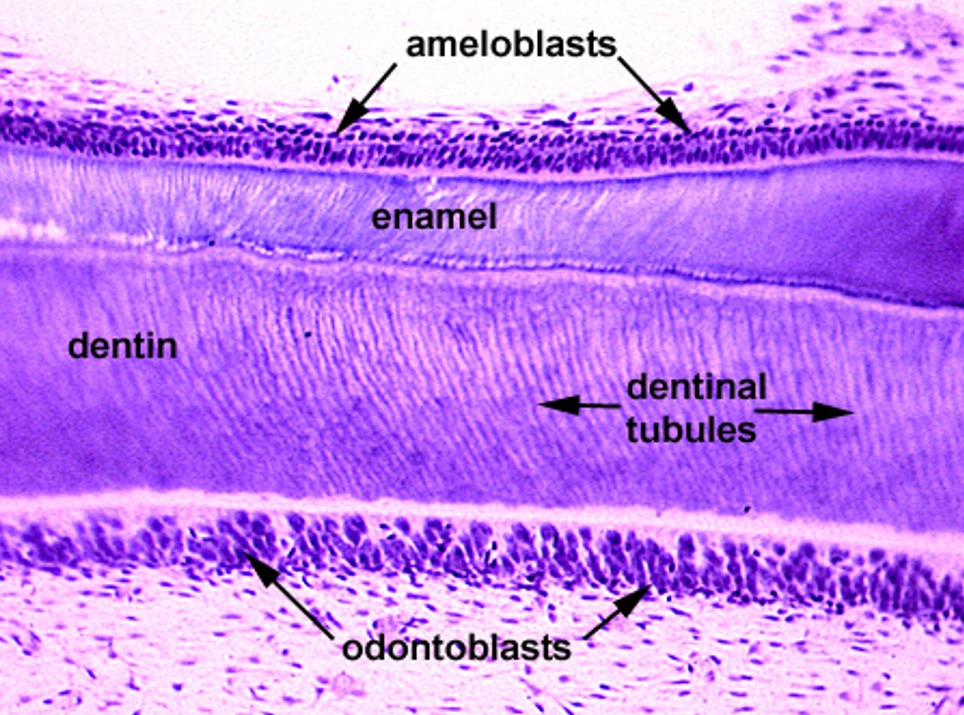
Identify the following: pulp cavity, dentin, pre-dentin, odontoblasts, enamel & ameloblasts.
Tooth
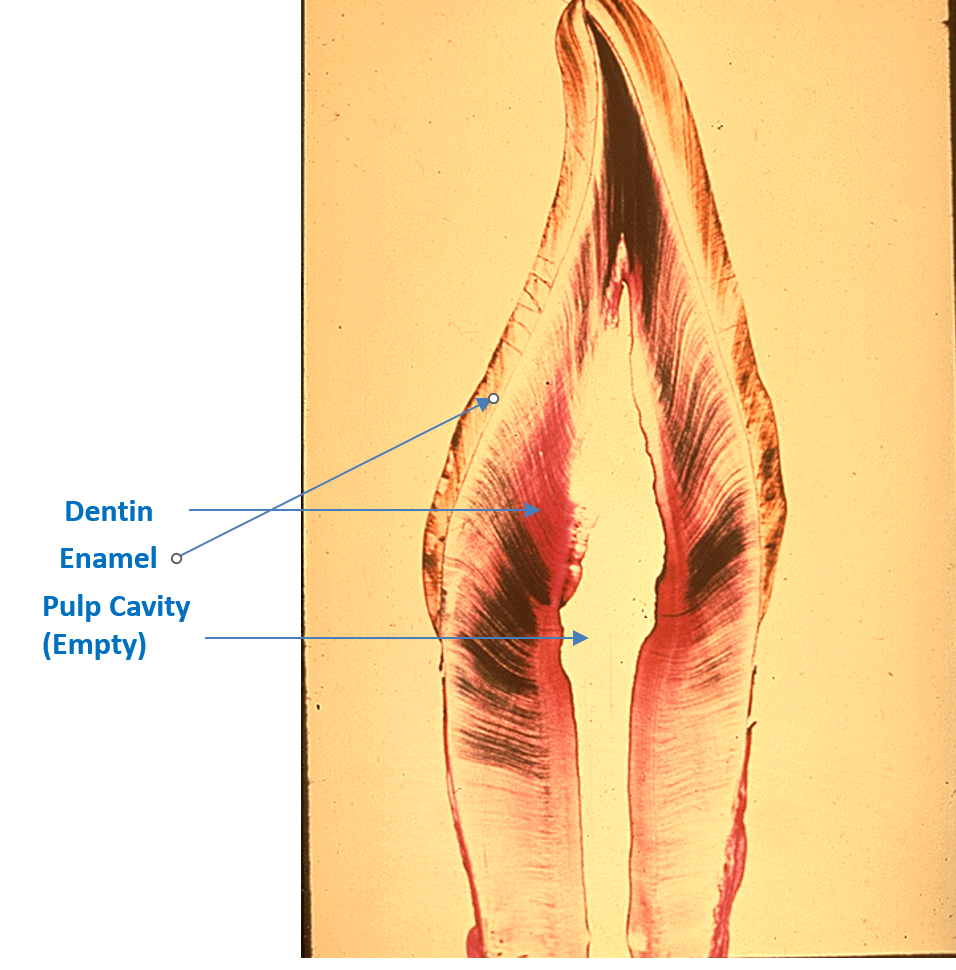
Identify the following: pulp cavity, dentin and enamel.
Tooth
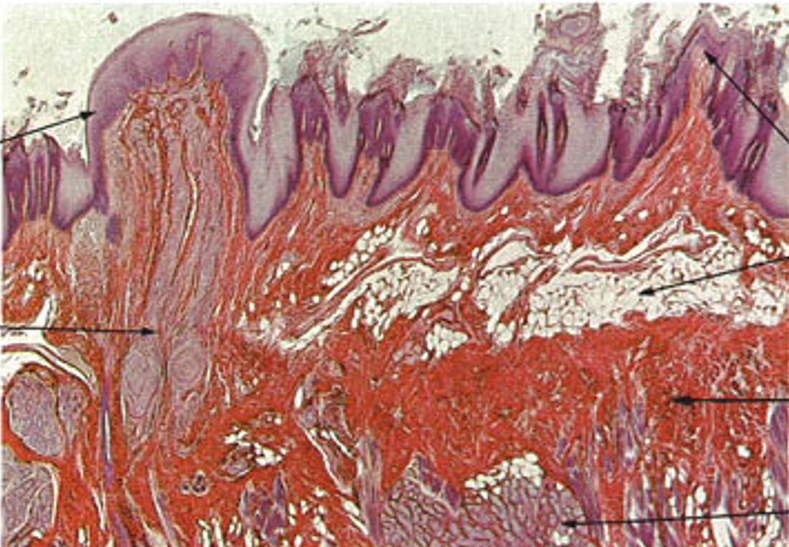
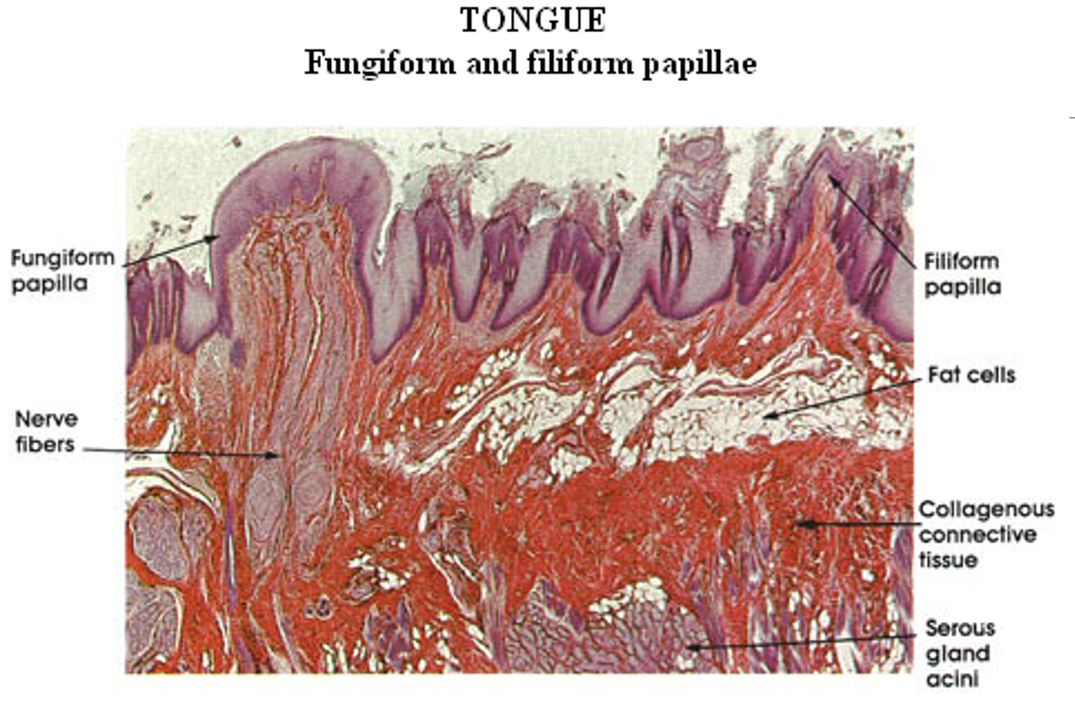
Identify this structure
Tongue
Jagged torn up surface (papillae)
Adipose can be observed
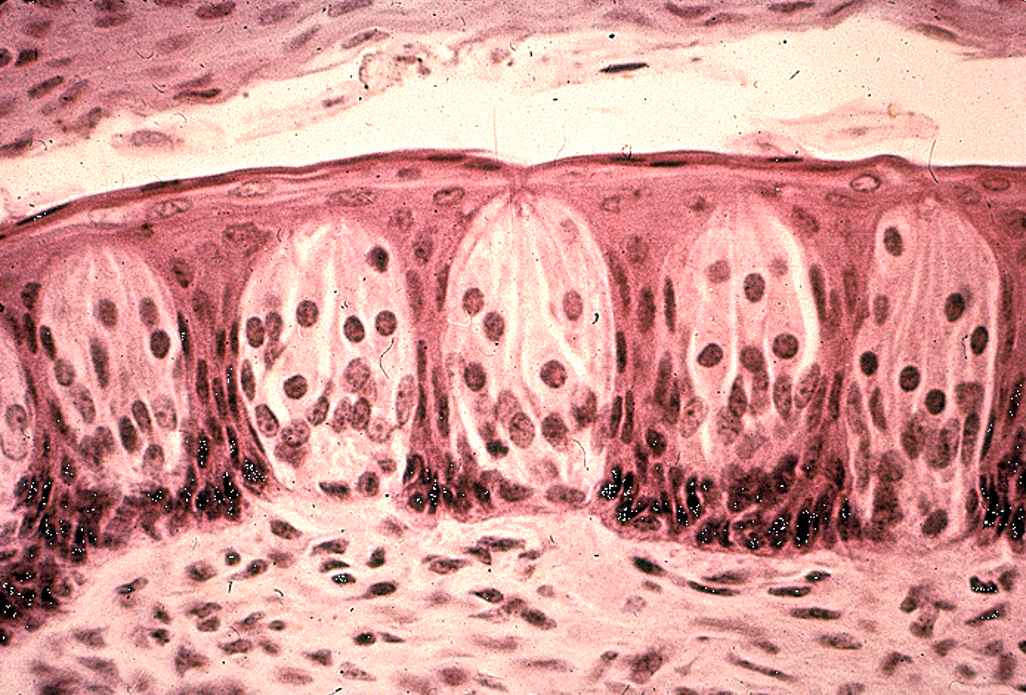
Fungiform papillae appear as round, mushroom-shaped structures
Filiform papillae are slender, sharp, pointed, conical, and heavily keratinized structures
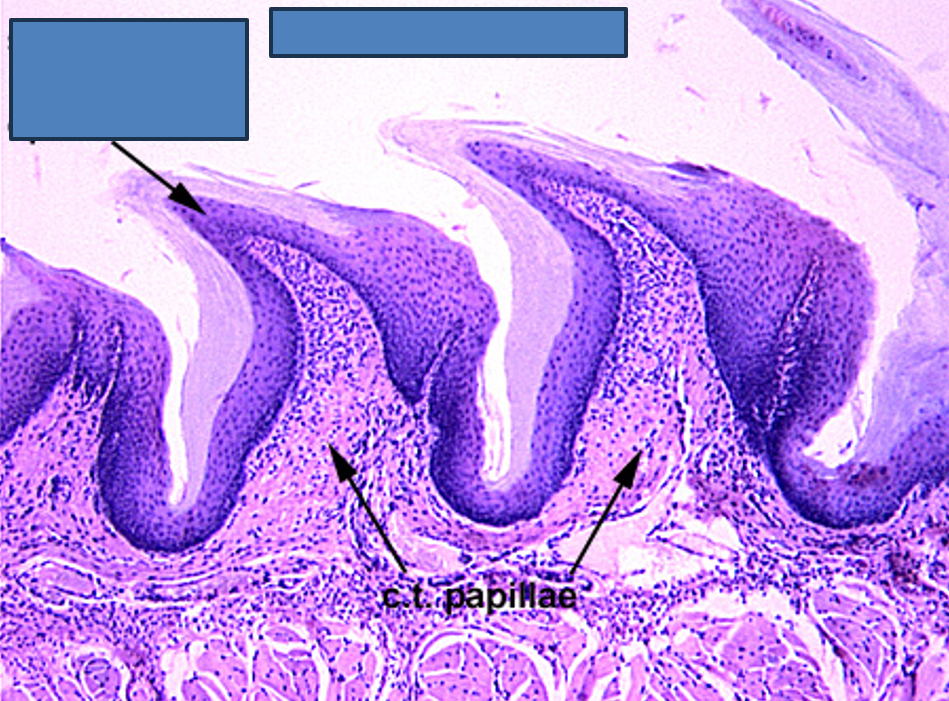
Identify this structure
Tongue (Filiform Papillae
Jagged torn up surface (papillae)
Filiform papillae have keratinized papillae (sharp-looking)— extra epithelium over it
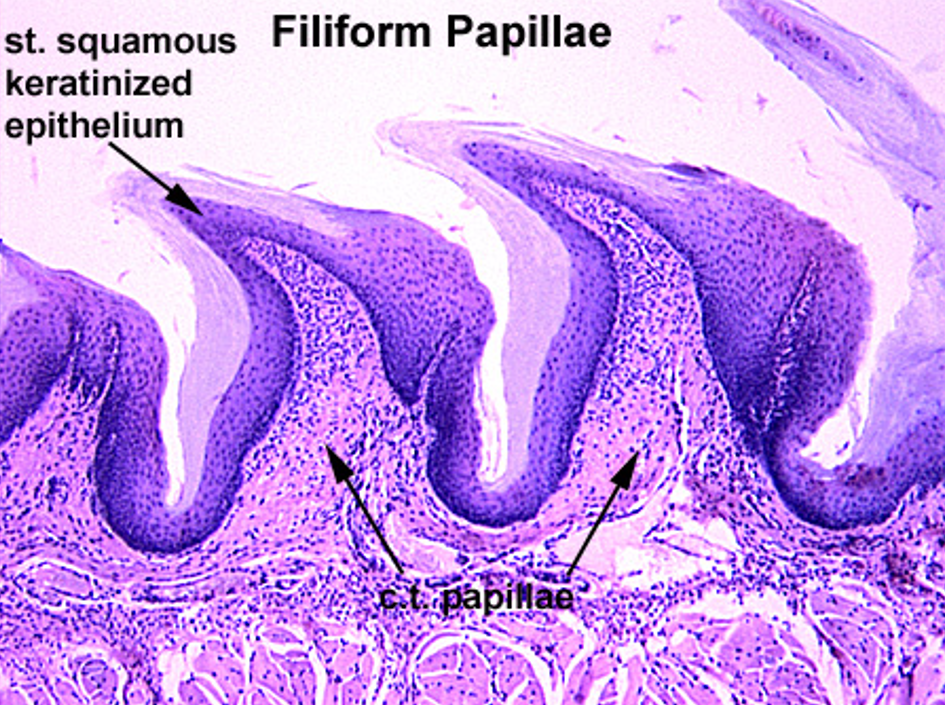
Identify this structure
Foliate Papillae
Square shaped papillae
Identify this structure
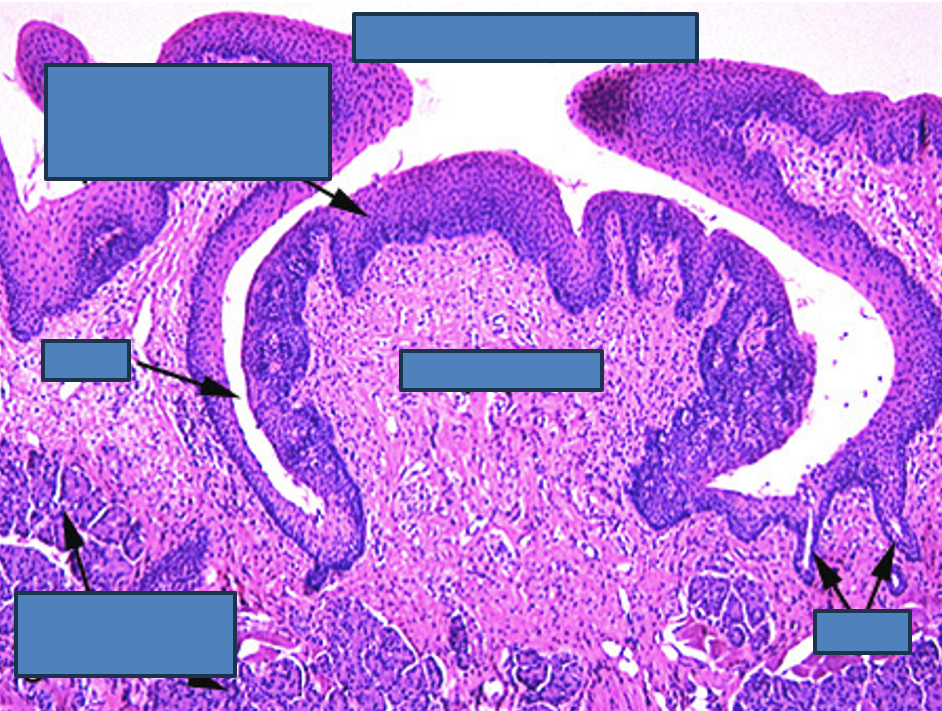
Vallate Papillae
papillae appears like a mushroom below the surface
has moat surrounding it
Identify this structure
Foliate Papillae
Square shaped papillae
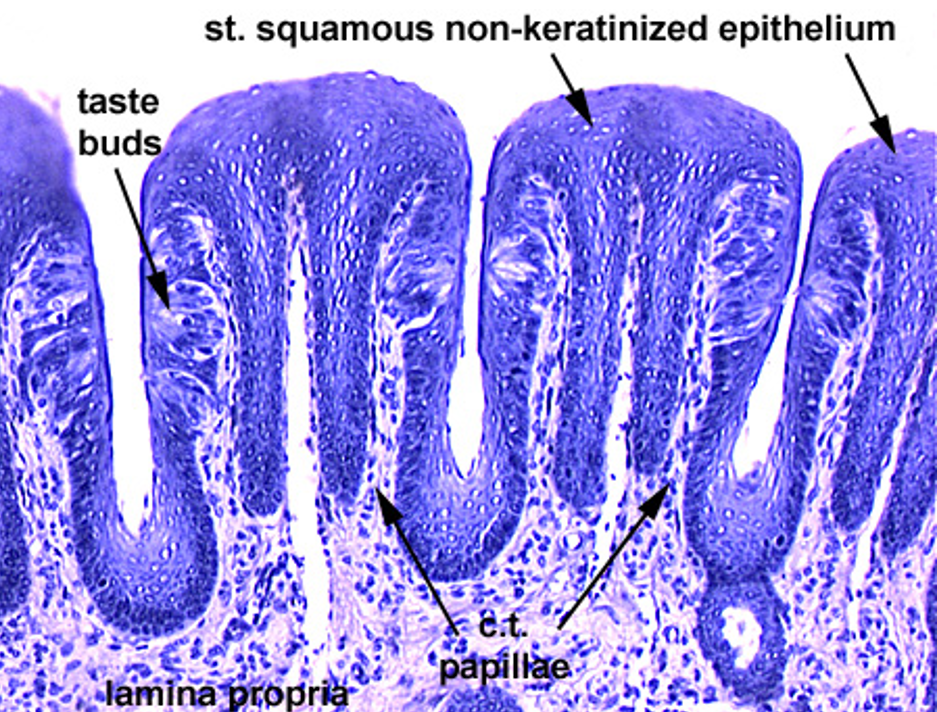
Identify this structure
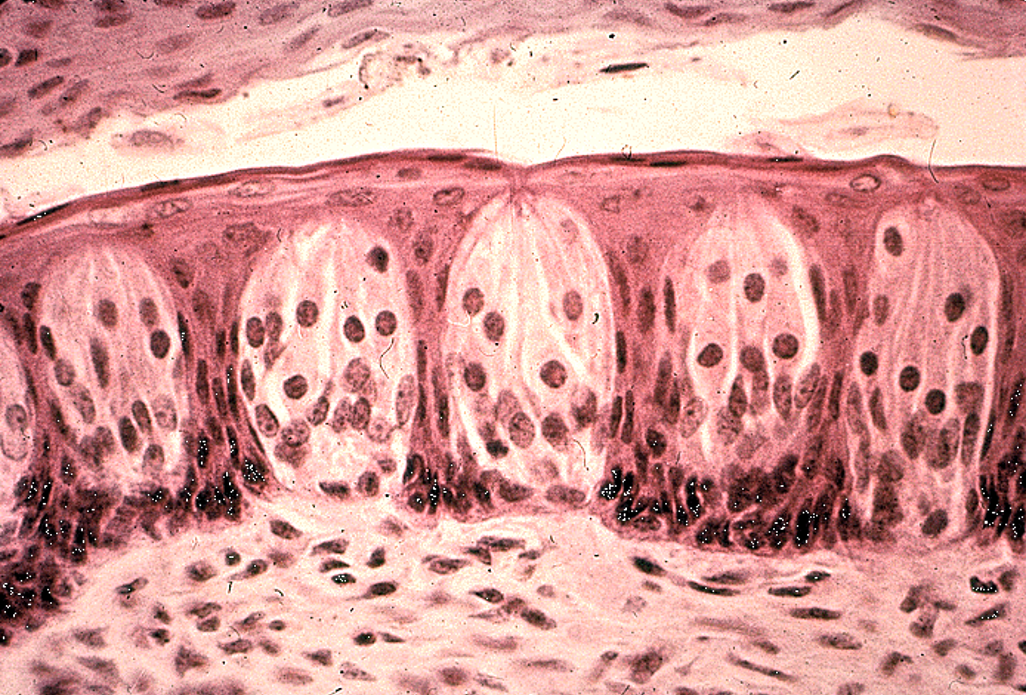
Taste buds
barrel-shaped structures
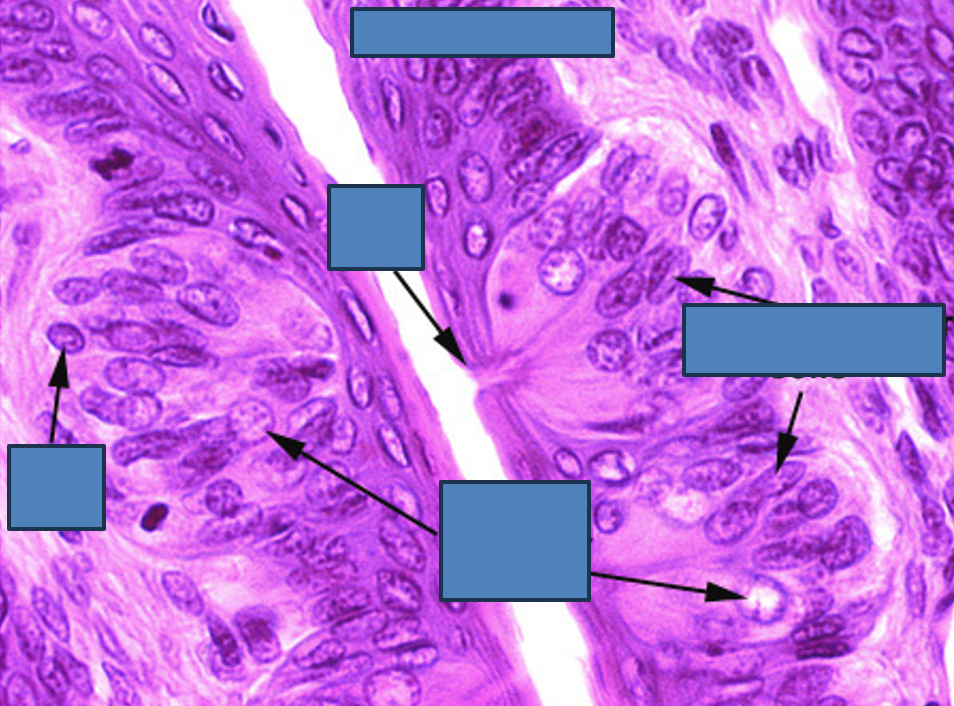
Identify this structure
Medium power view of taste buds.
barrel-shaped structures
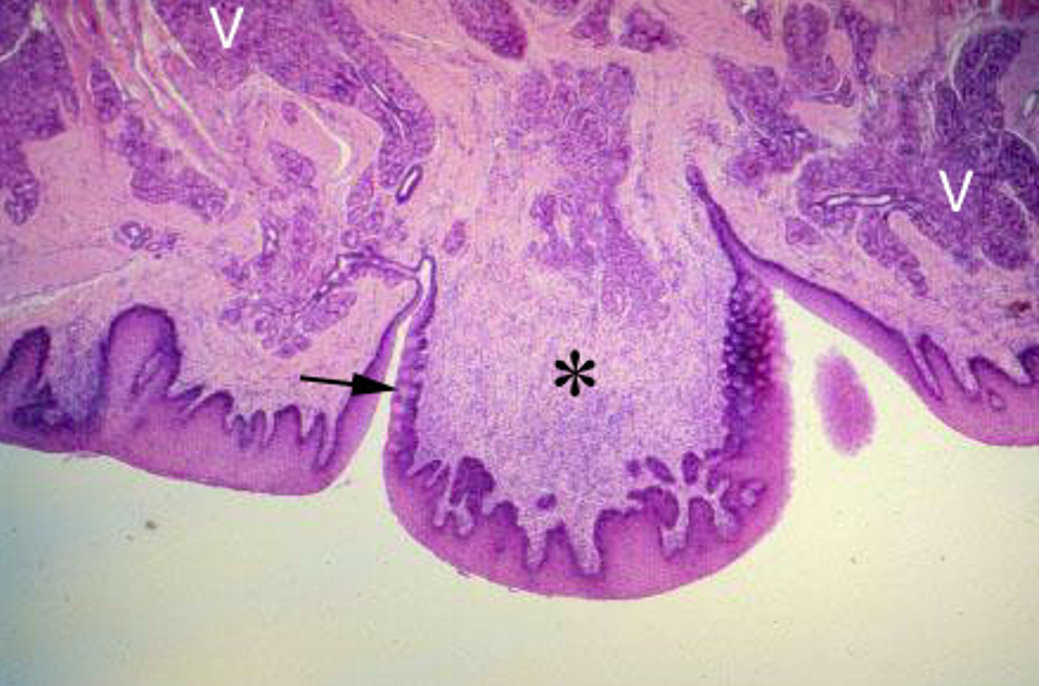
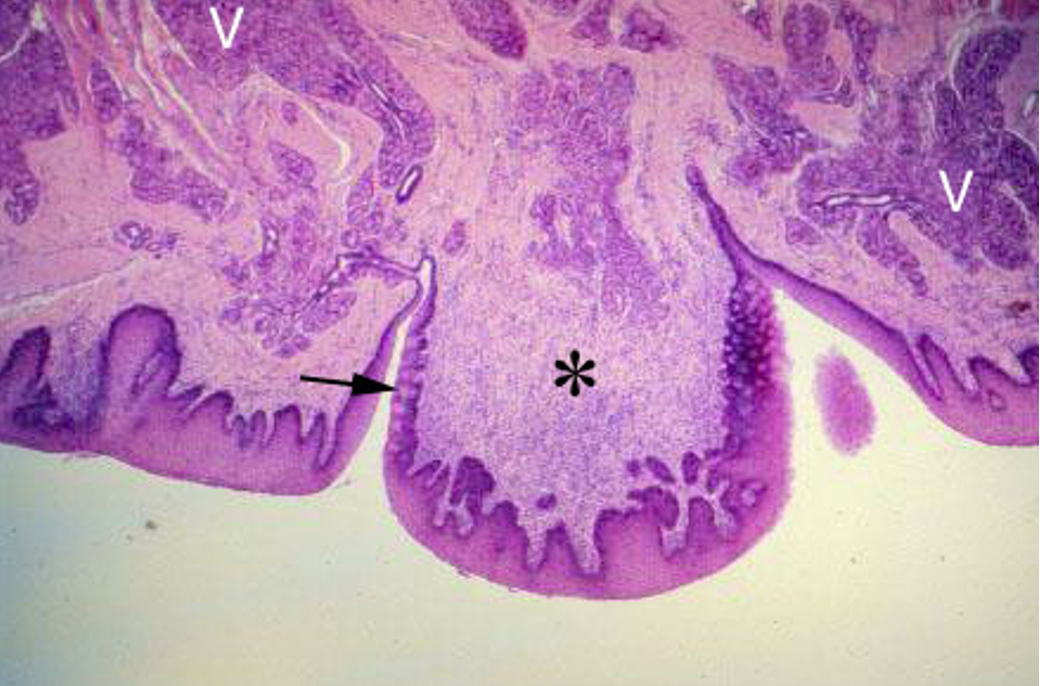
Identify this structure
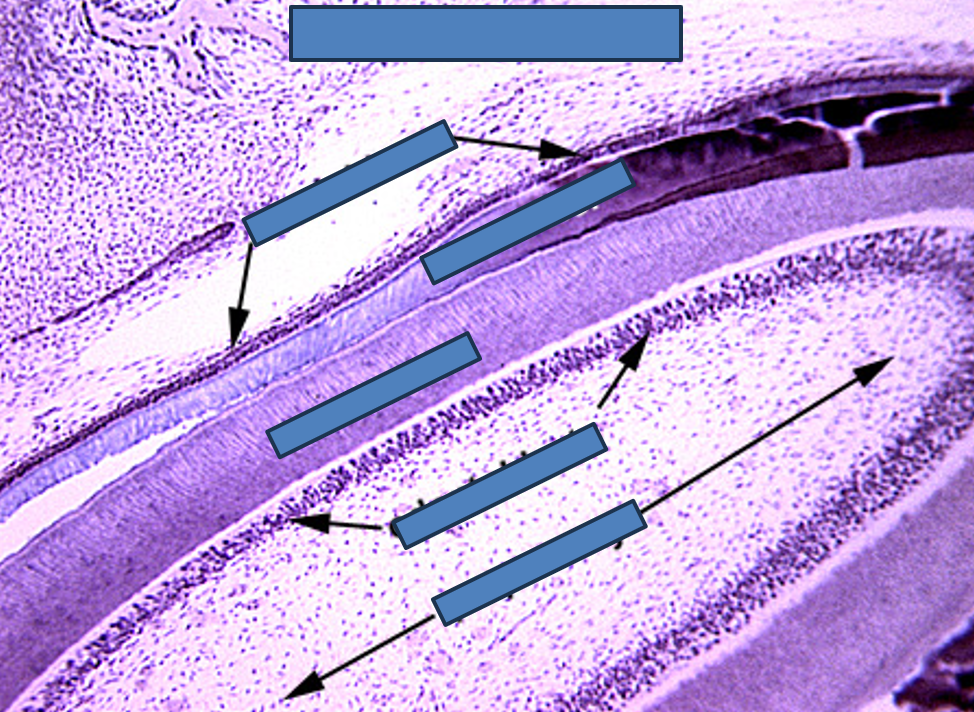
Circumvallate papilla
Tongue (H&E). Low power magnification of circumvallate papilla (*). Note the Serous glands (V) that empty in the moat surrounding the papilla. Taste buds are located on the lateral surface of the papilla (arrowhead).
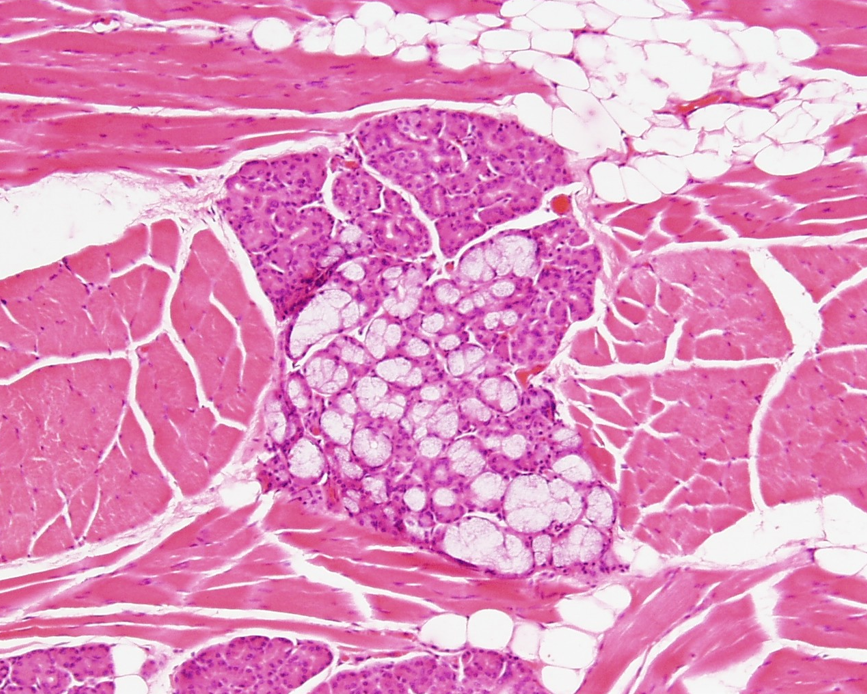
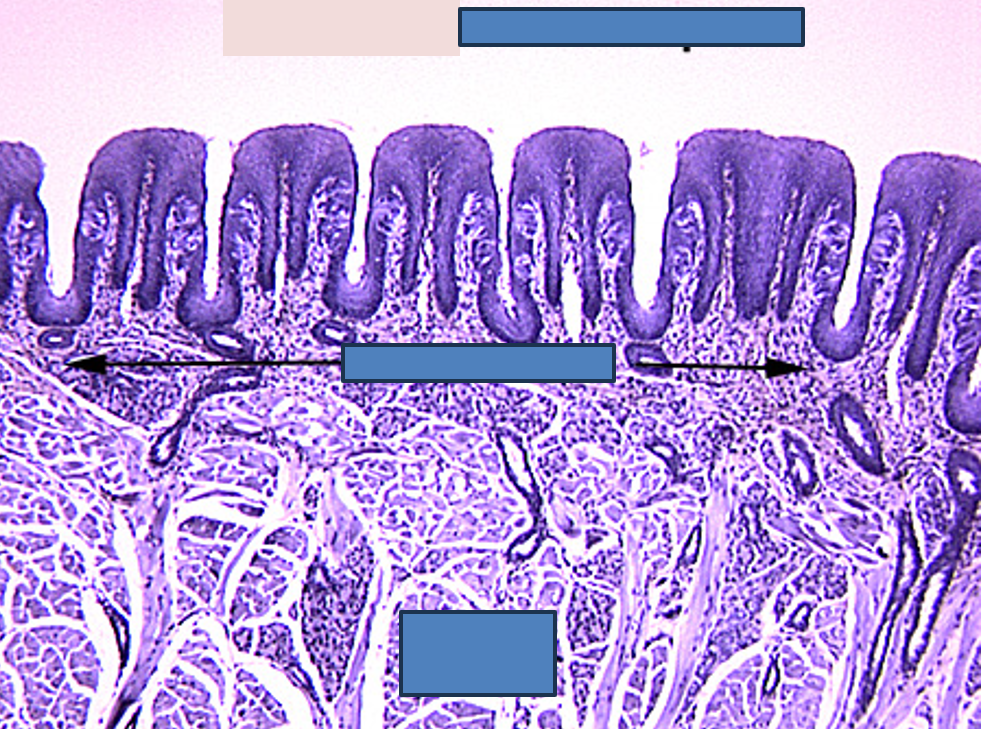
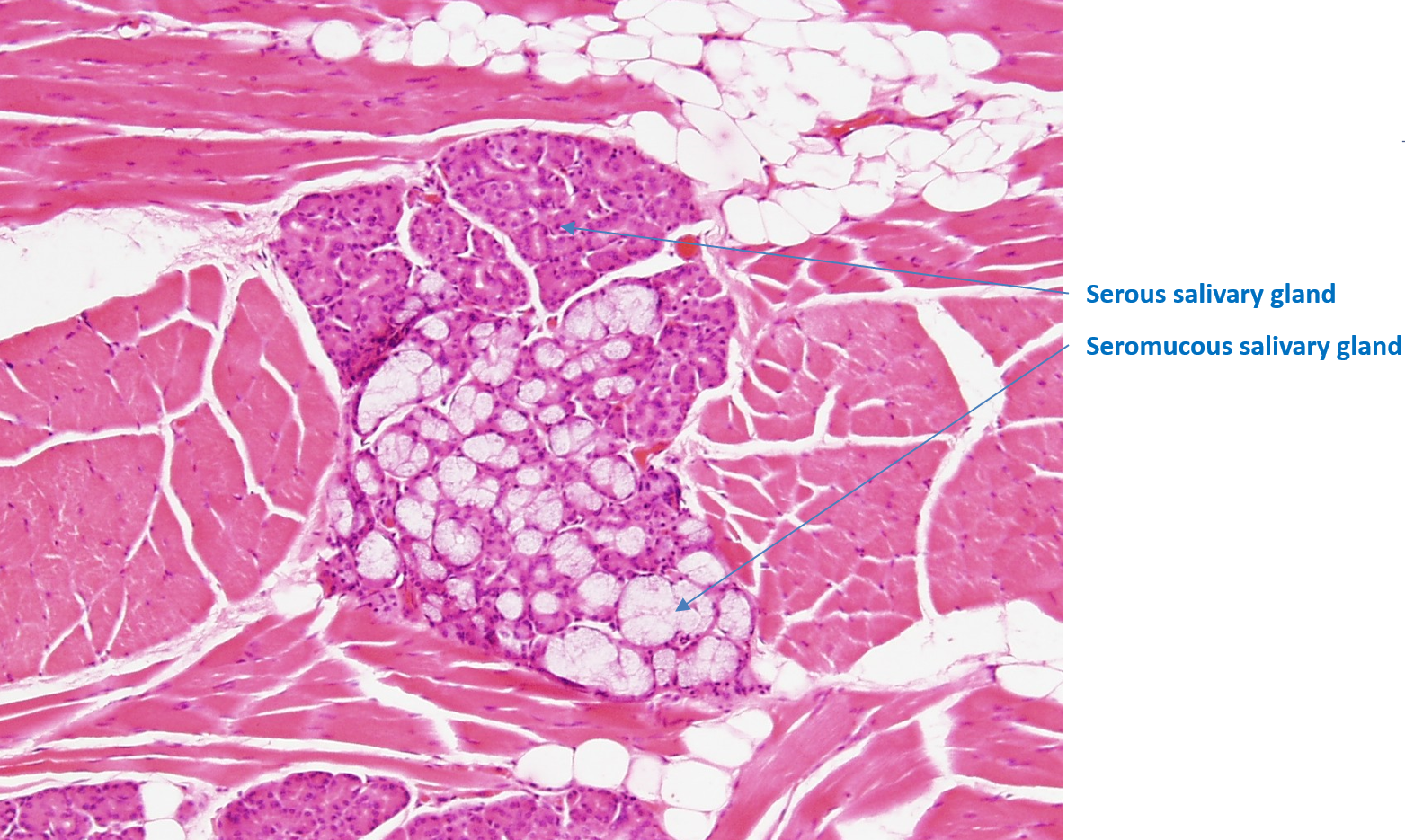
Identify the serous and seromucous salivary glands.
Tongue
Adipose tissue can be observed
Serous and seromucous glands observed
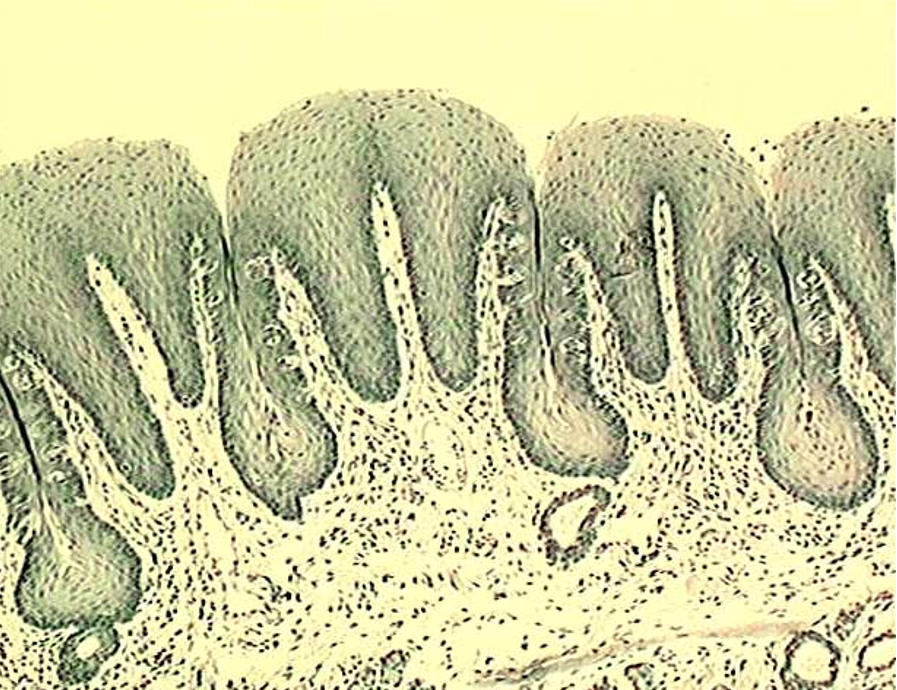
Identify the type of papillae
Foliate Papillae
Note the taste buds on the lateral surface.
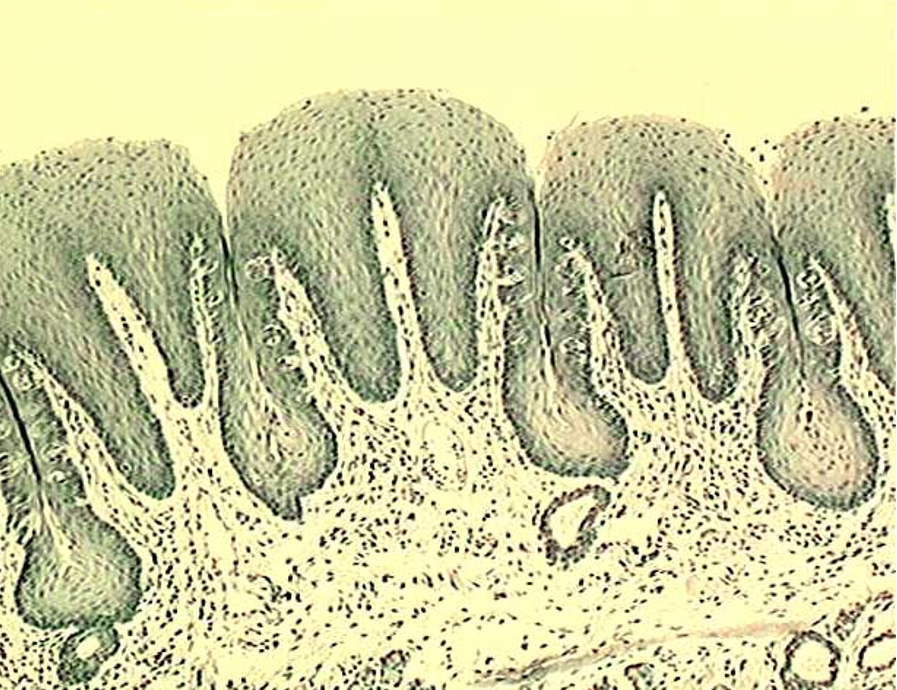
Identify the types of papillae.
Filiform Papillae
Filiform papillae have keratinized papillae (sharp-looking) — extra epithelium over it
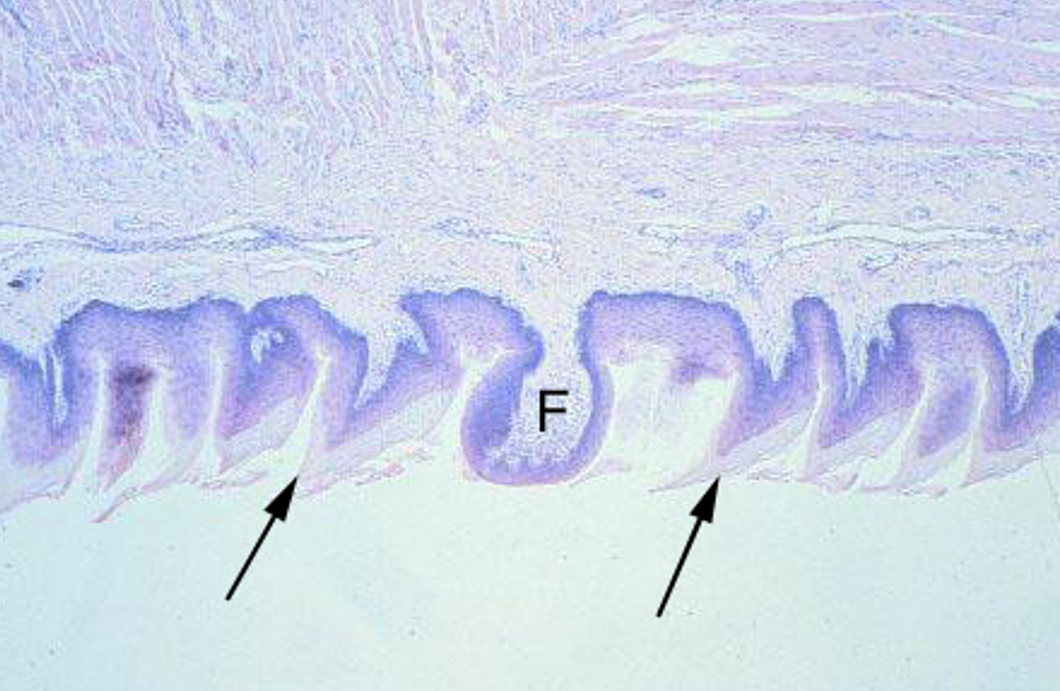
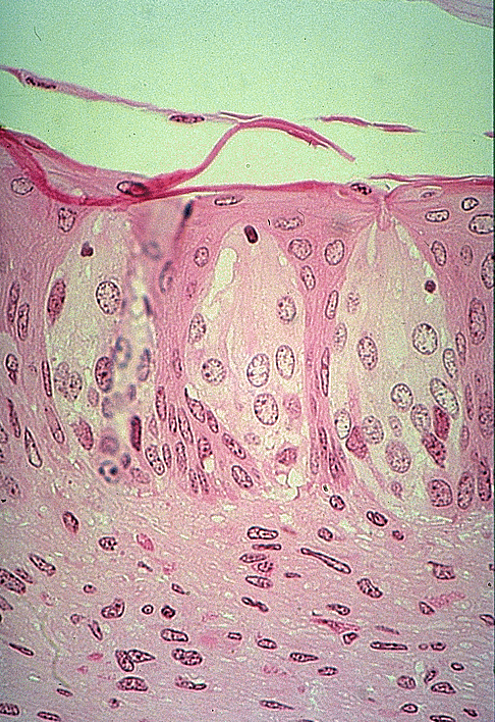
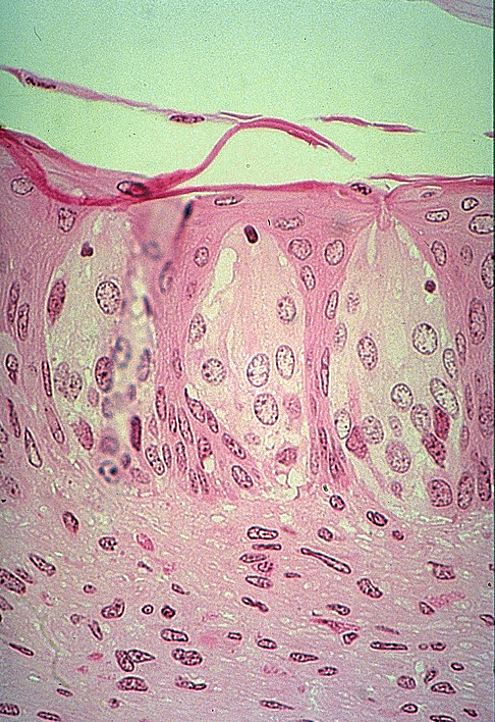
Identify the taste buds and taste pore.
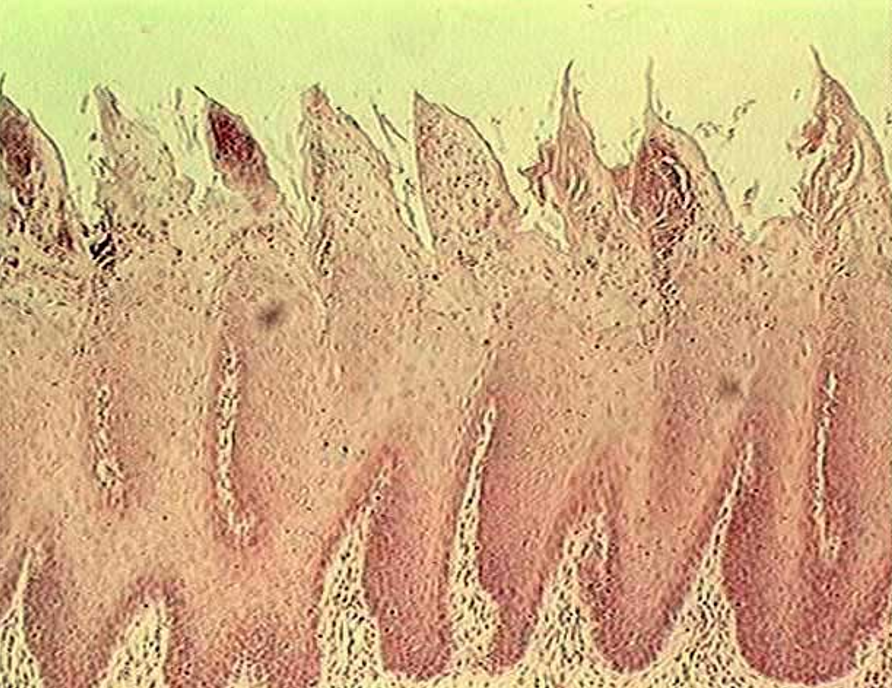
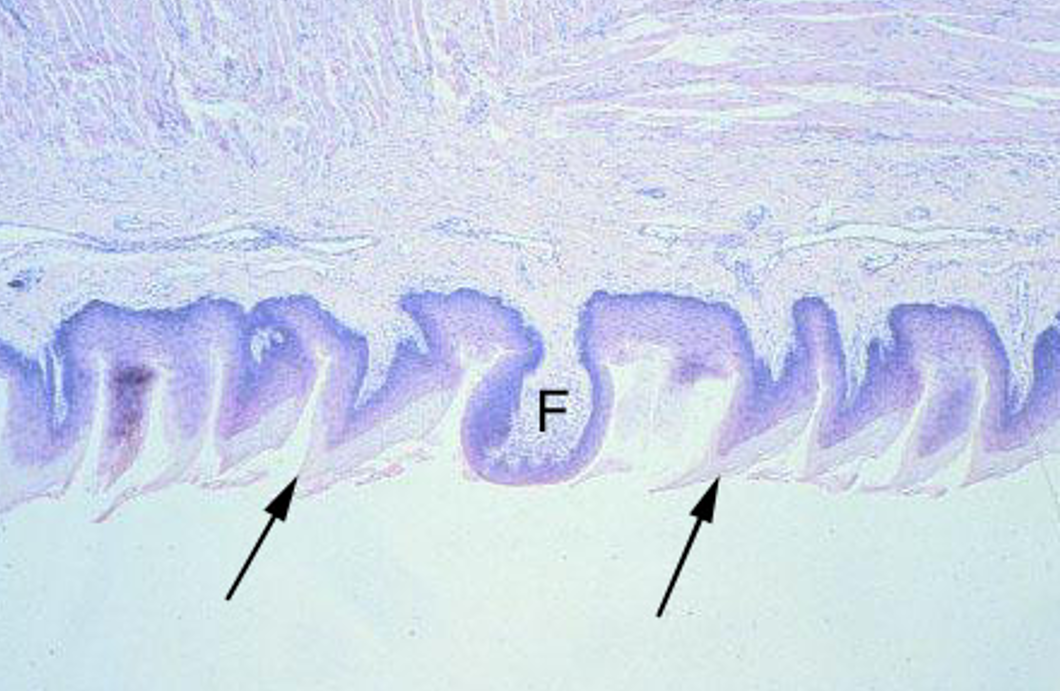
Identify the type of papillae.
Filiform Papillae
sharp-looking structures
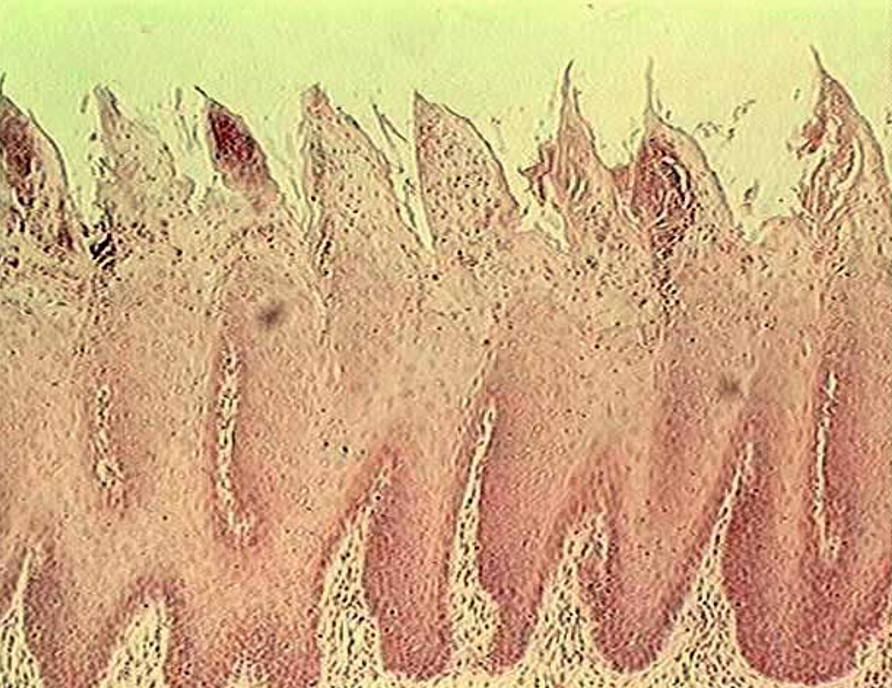
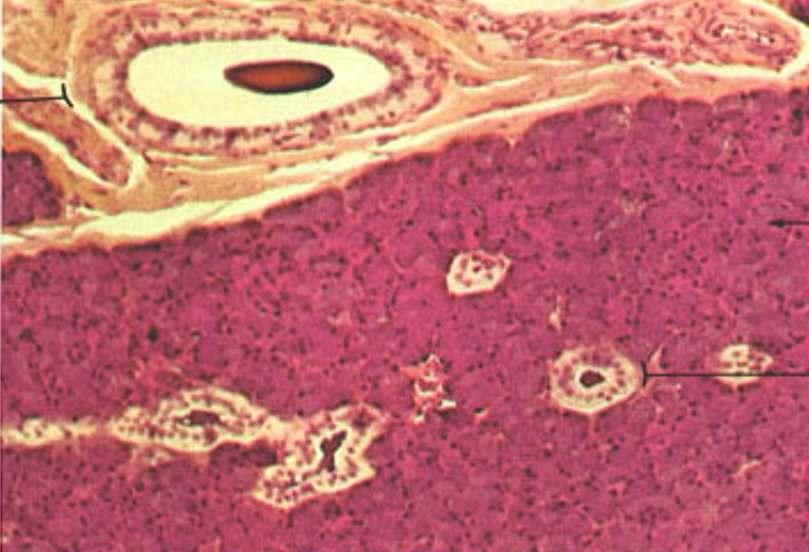
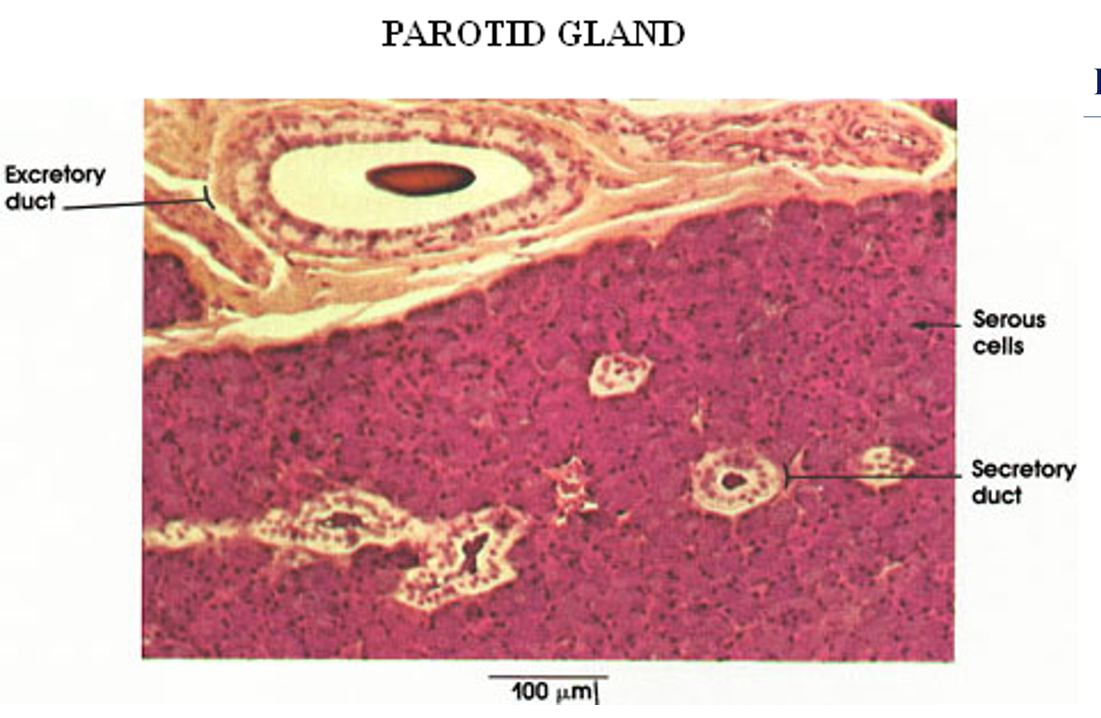
Identify this structure
Parotid gland
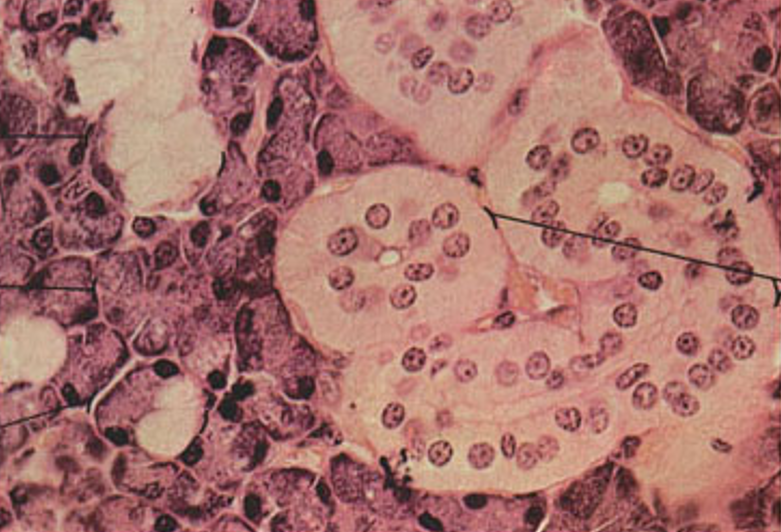
Identify this structure
Submandibular gland
mixed serous and mucous acini (with serous demilunes) and striated ducts
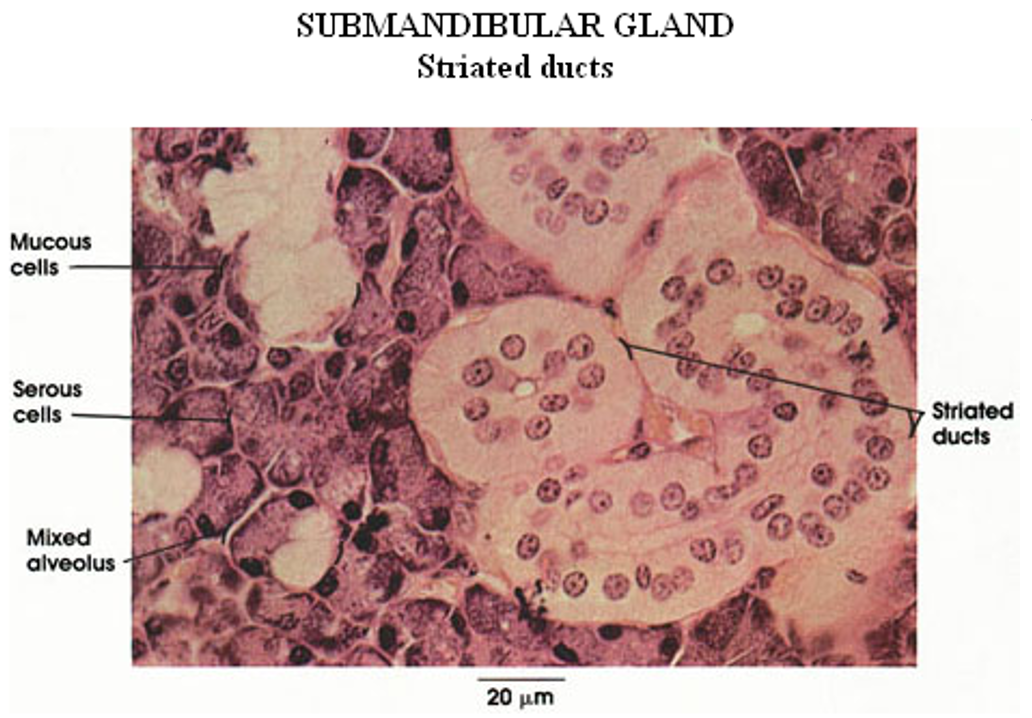
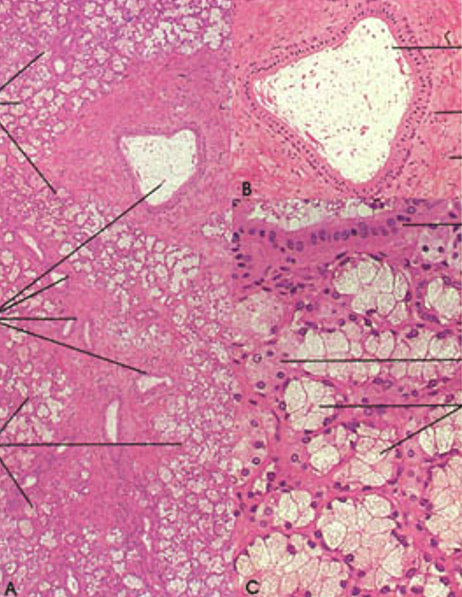
Identify this structure
Sublingual gland
Mostly mucous acini (pale-staining)
Few serous demilunes. Fewer striated ducts than in submandibular
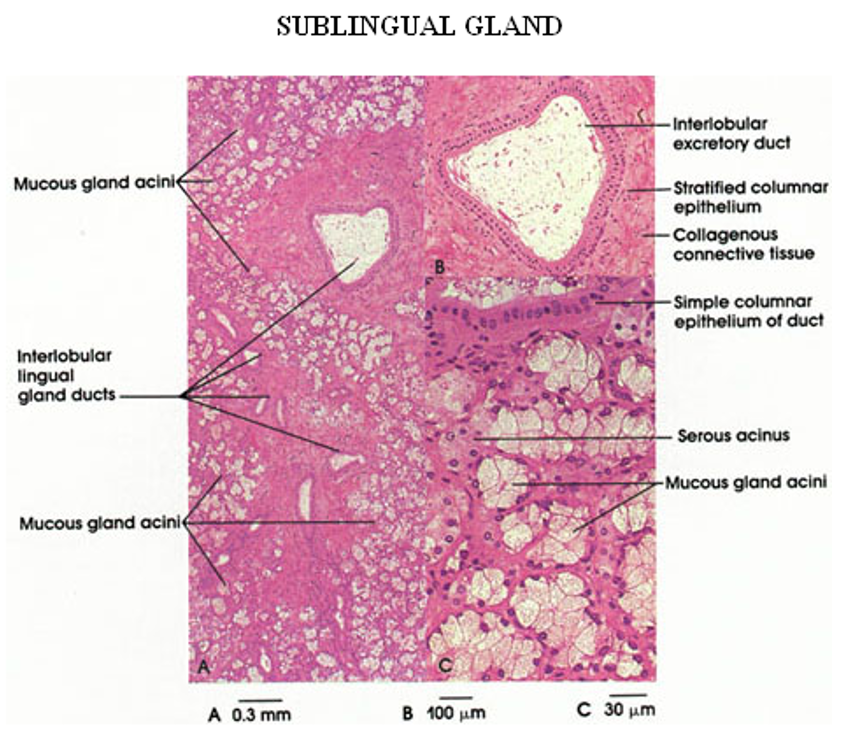
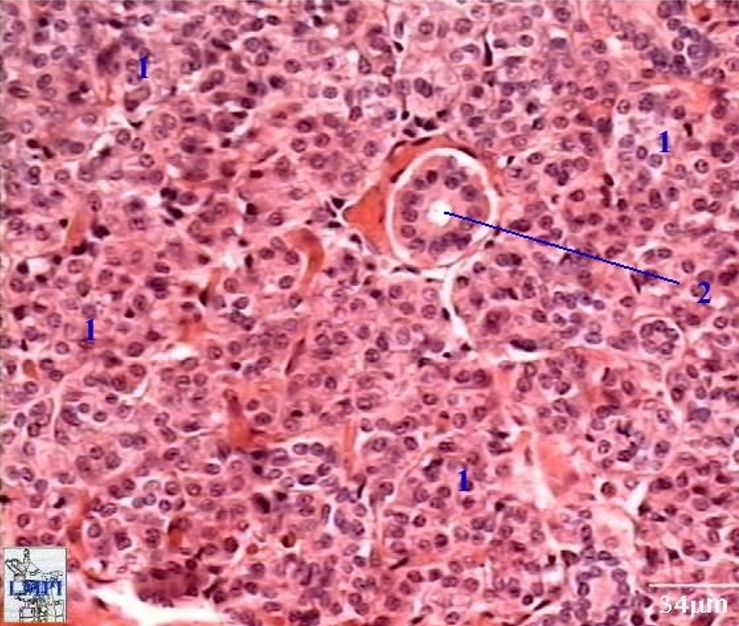
Identify the salivary gland and types of acini.
Submandibular gland
mixed serous (pink) and mucous acini (dirty white) and striated ducts
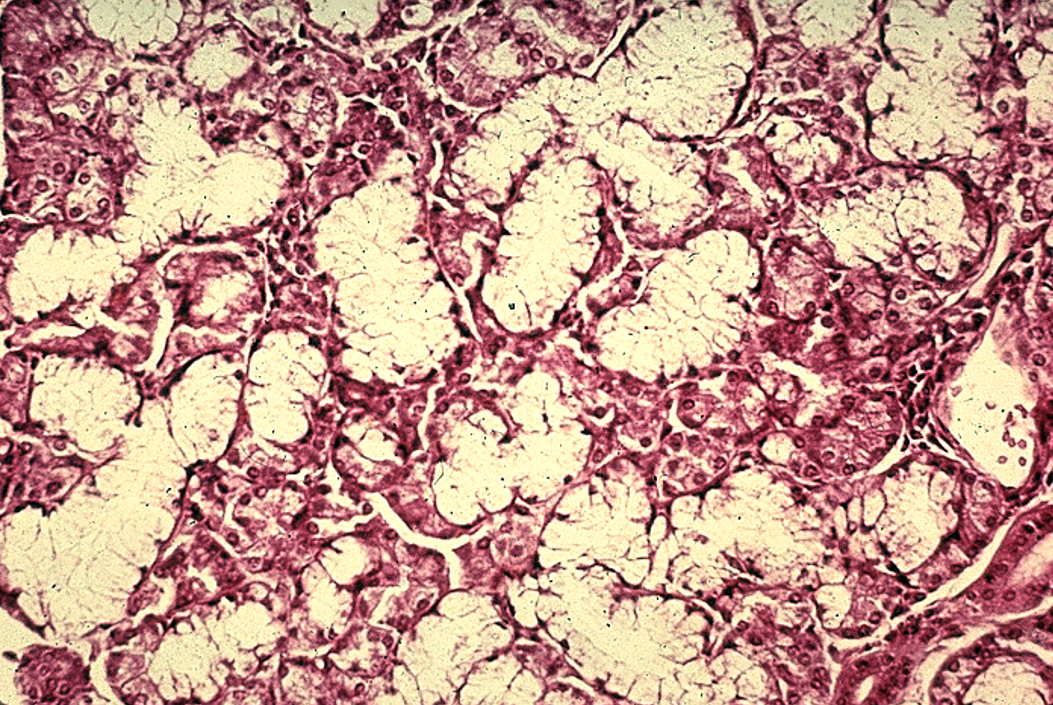
Identify the salivary gland and types of acini.
Submandibular gland
mixed serous (pink) and mucous acini (dirty pink—overstained in this slide) and striated ducts. Serous demi-lumes observable
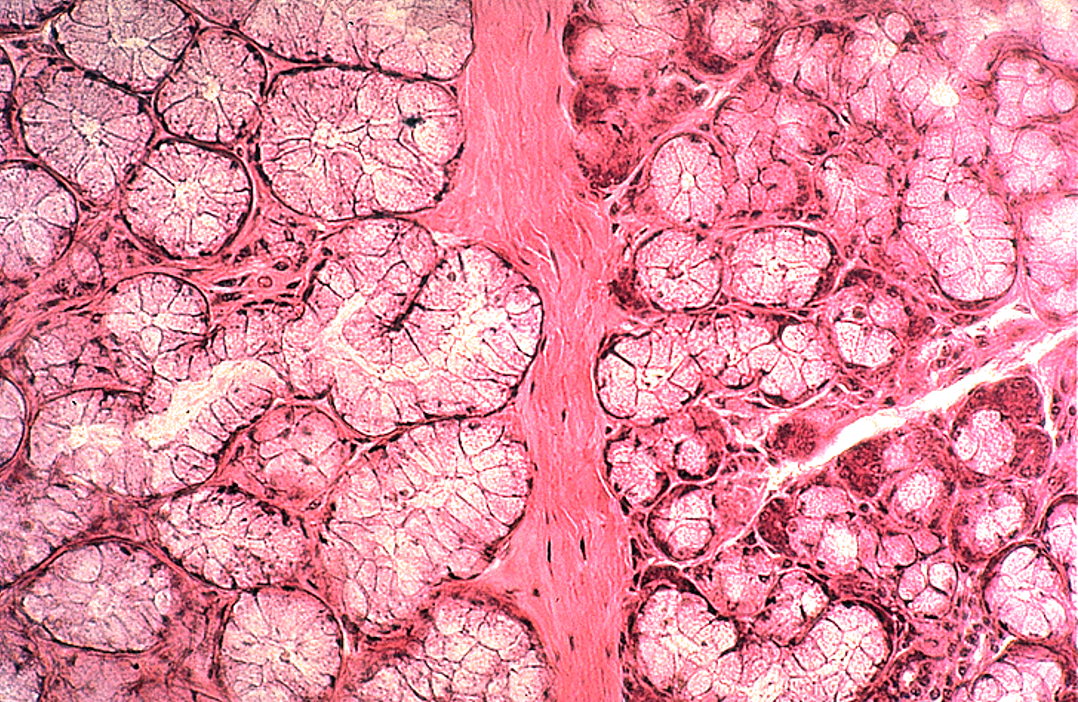
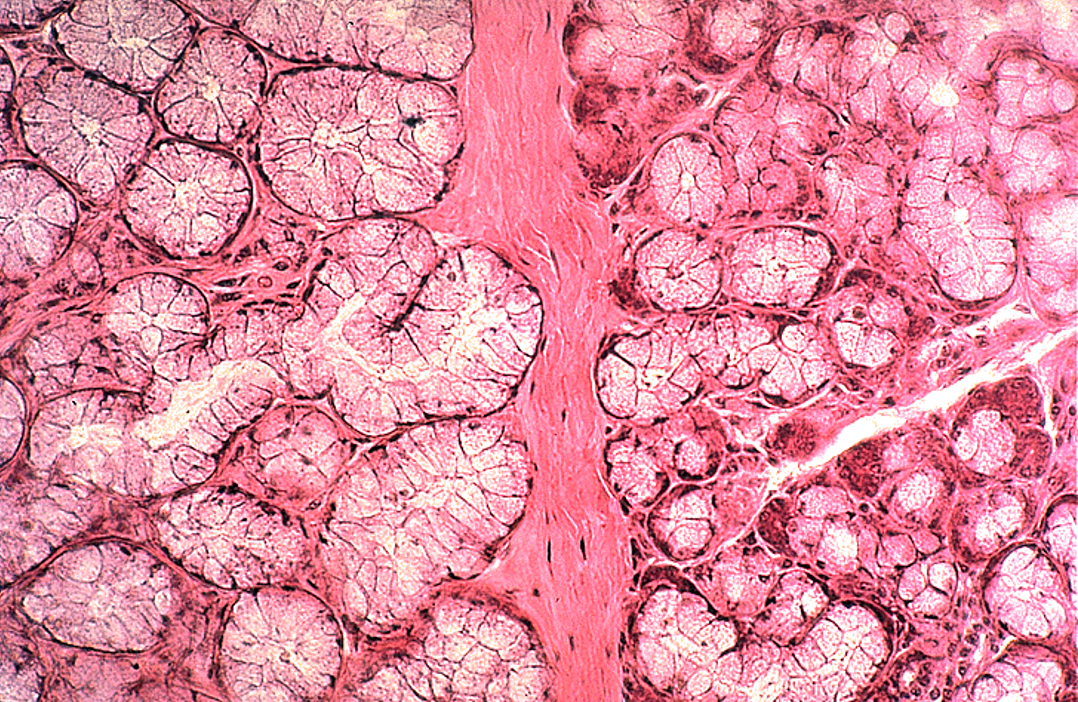
Identify the salivary gland and types of acini.
Submandibular gland
mixed serous and mucous acini (with serous demilunes) and striated ducts
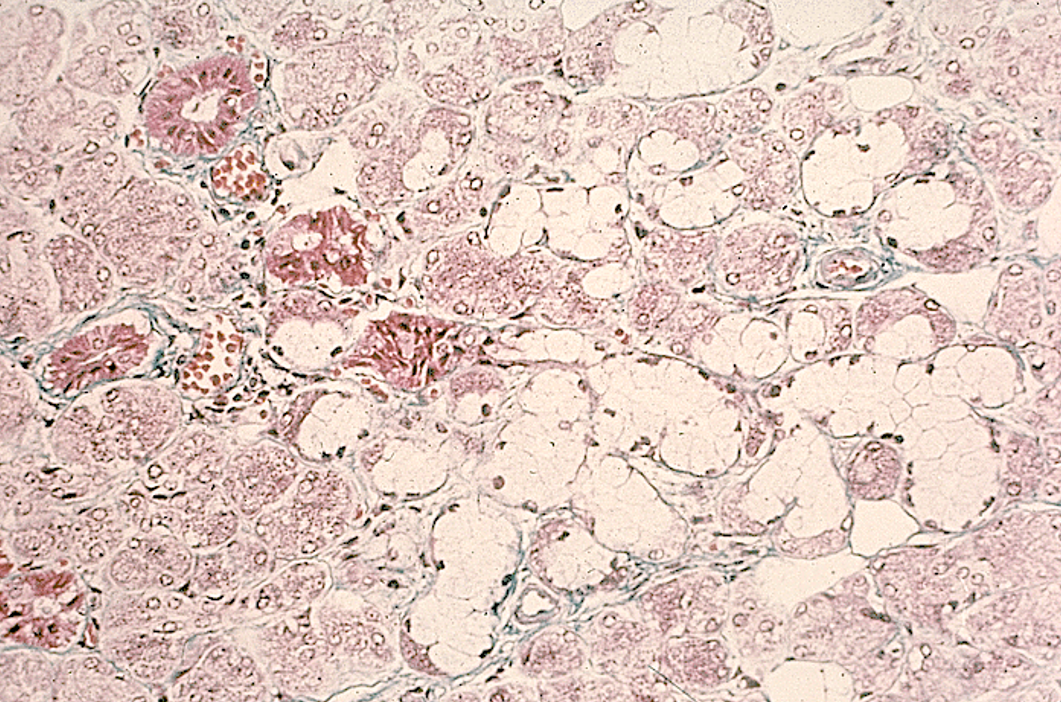
Identify the gland, the types of acini and the ducts.
Mostly serous and dirty white glands
Submandibular gland
mixed serous and mucous acini and striated ducts
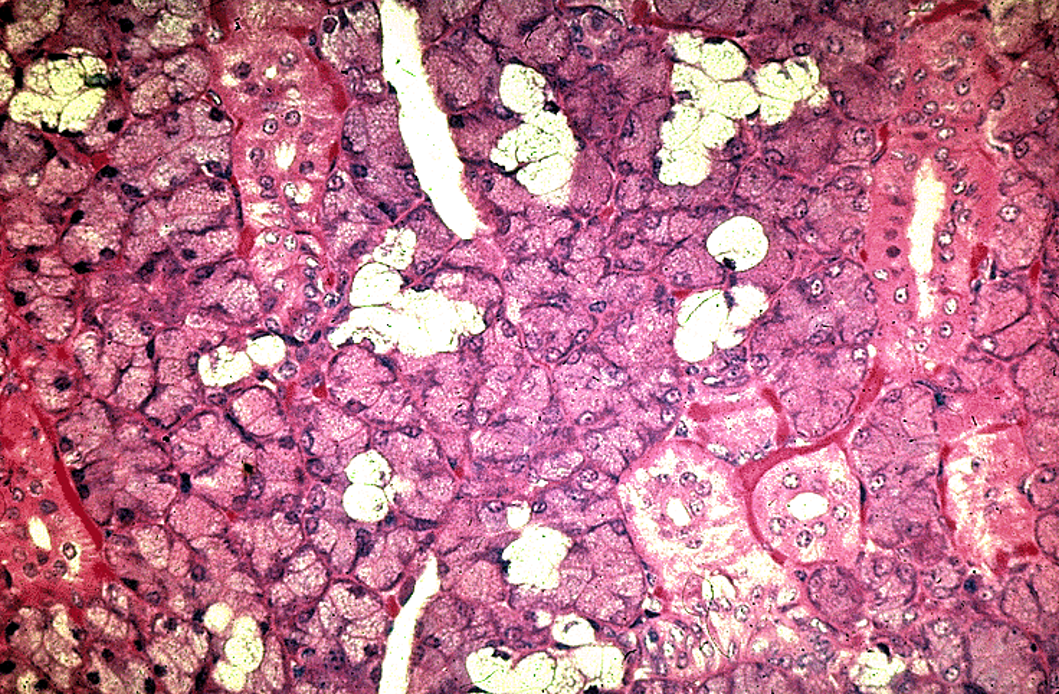
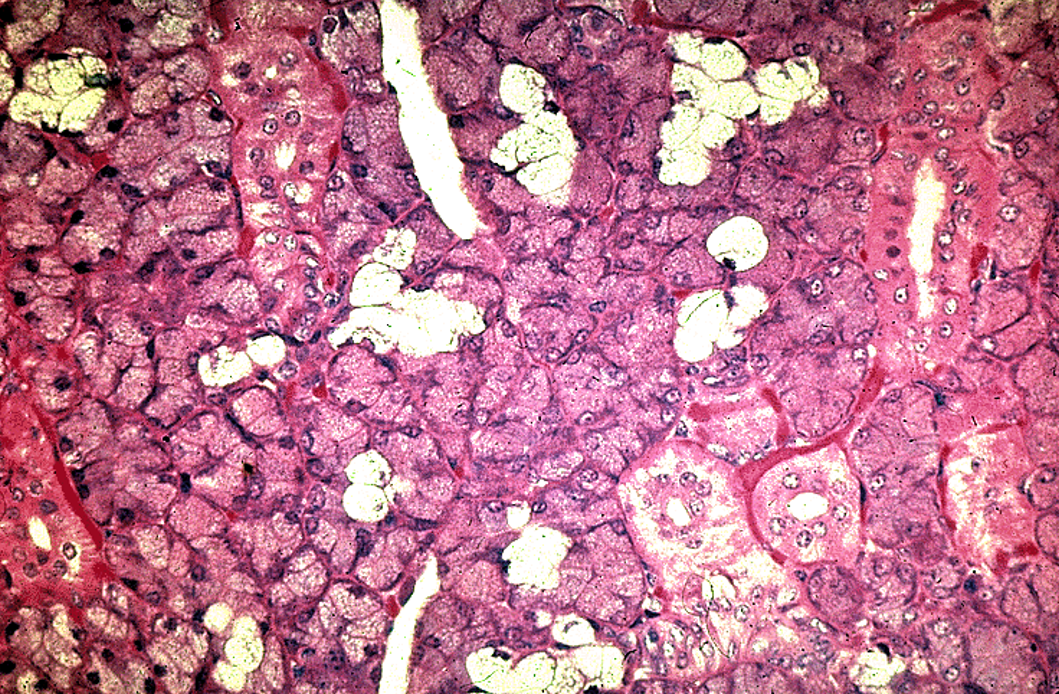
Identify the salivary gland and types of acini.
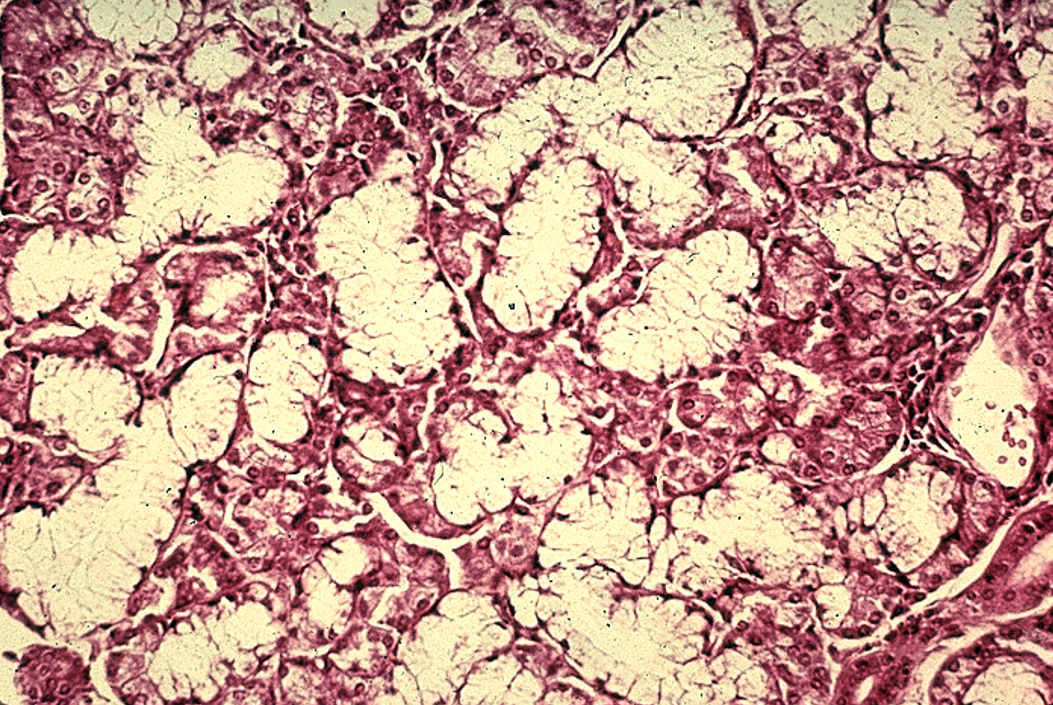
Parotid gland
only serous acini (dark-staining, no mucous cells) and lots of striated ducts.
Many adipose cells
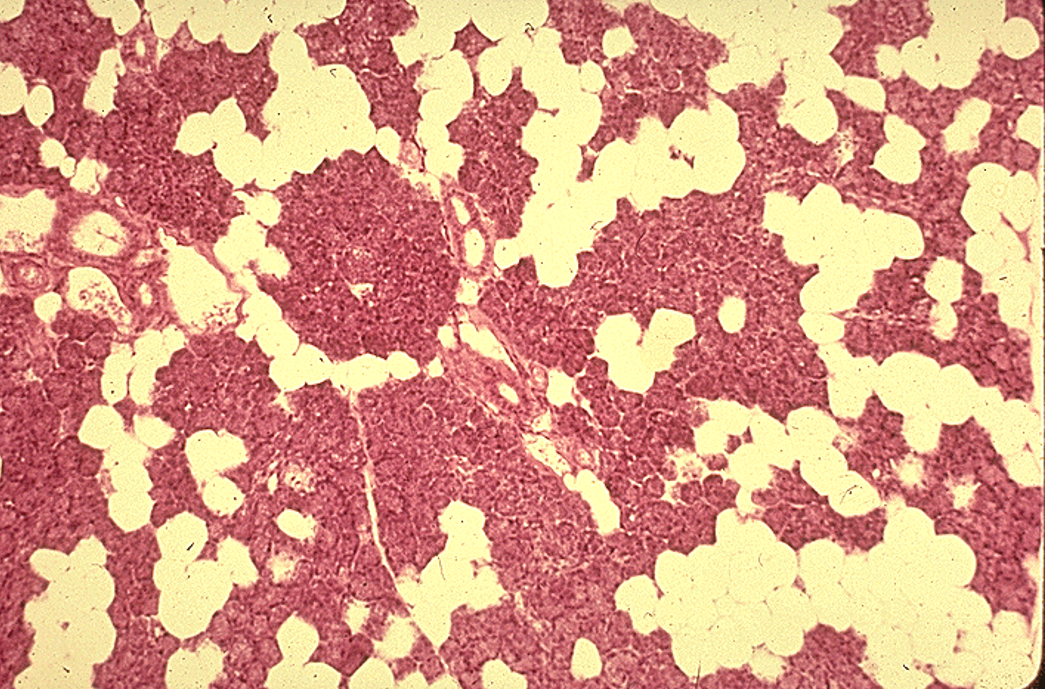
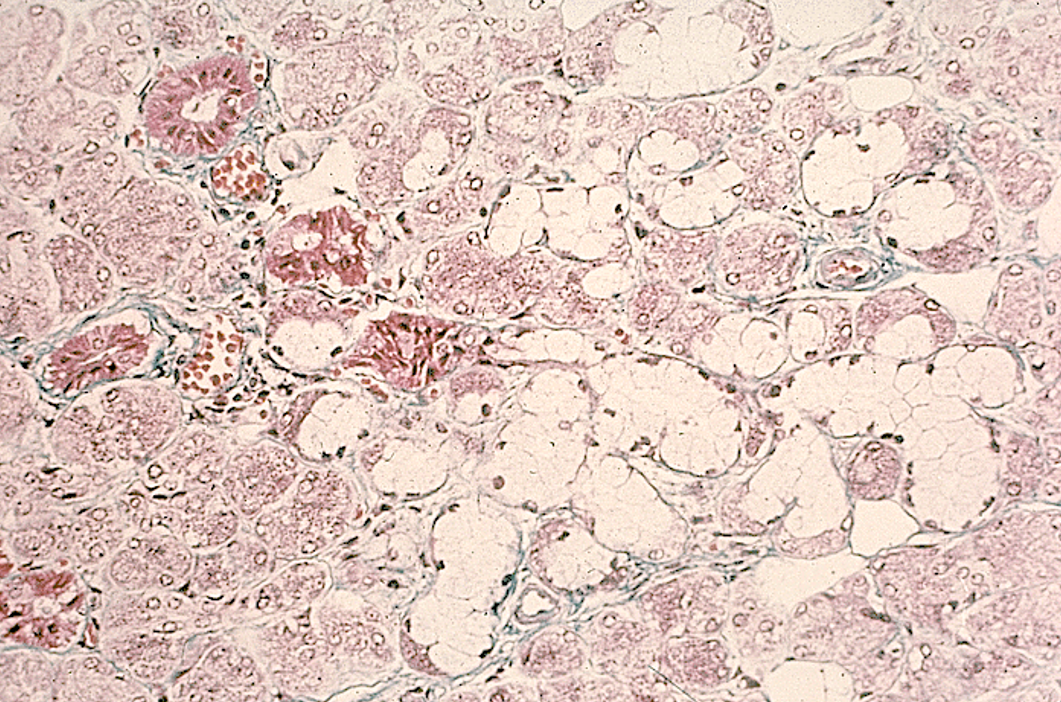
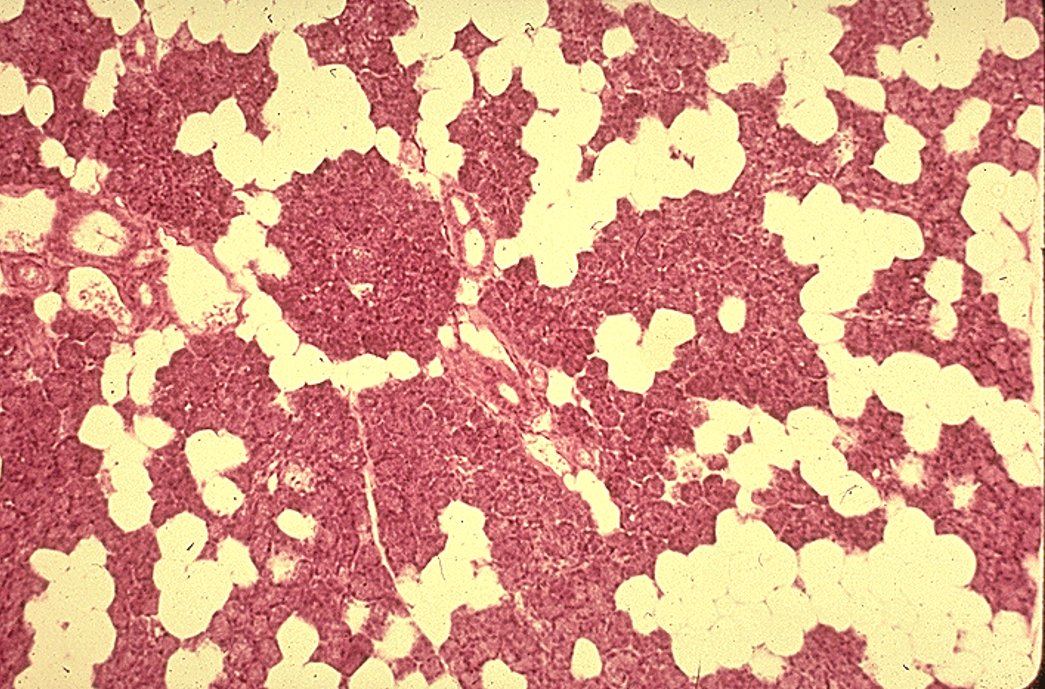
Identify the salivary gland and types of acini.
Sublingual gland
Mostly mucous acini (pale-staining)
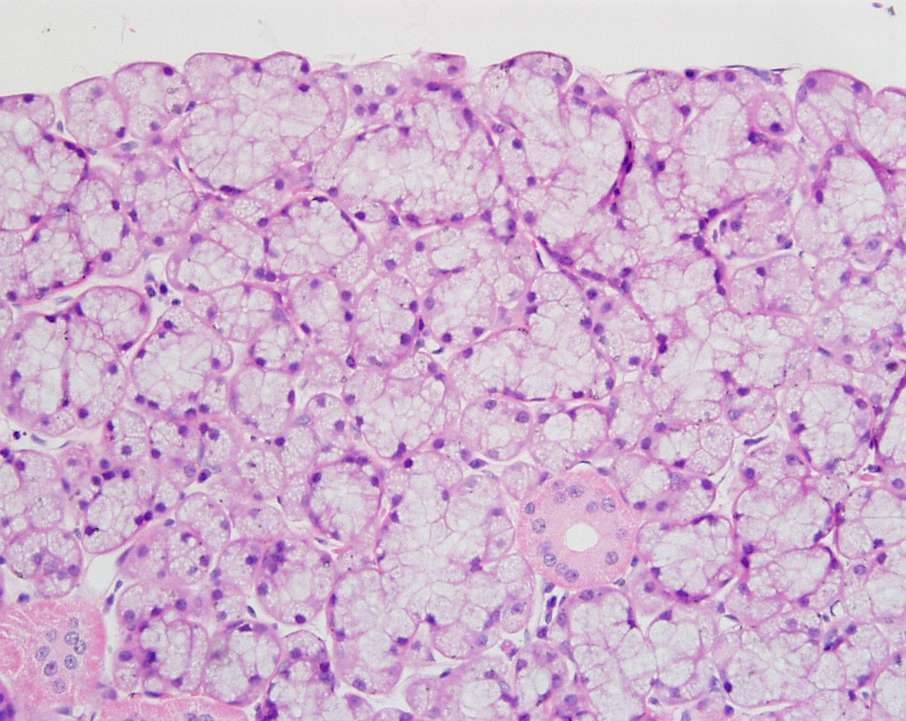
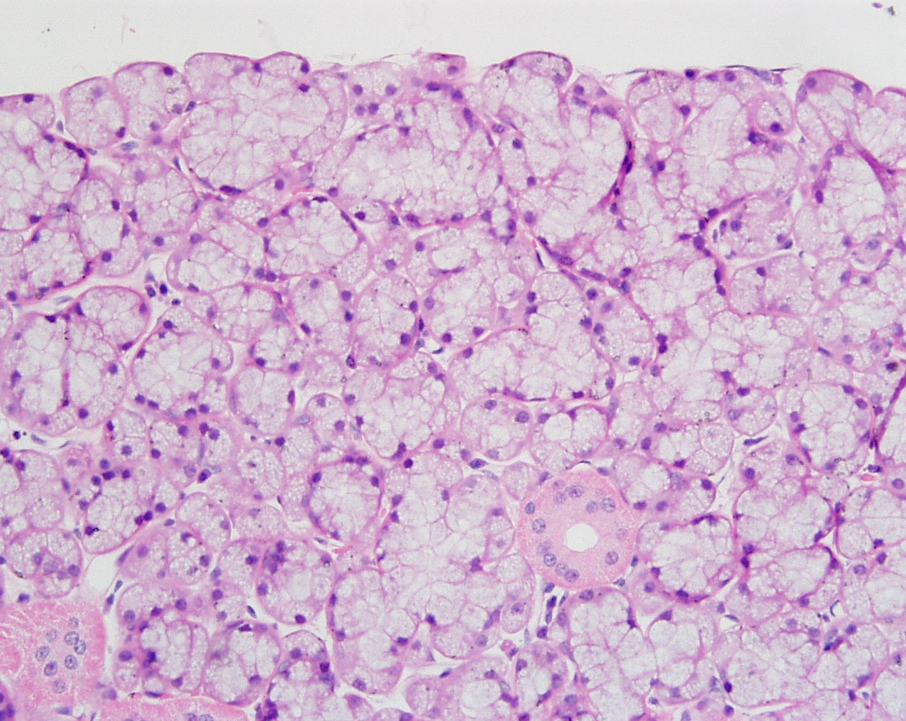
Identify the gland, the types of acini and the ducts.
Sublingual gland
Mostly mucous acini (pale-staining) observable
Serous demilume observable
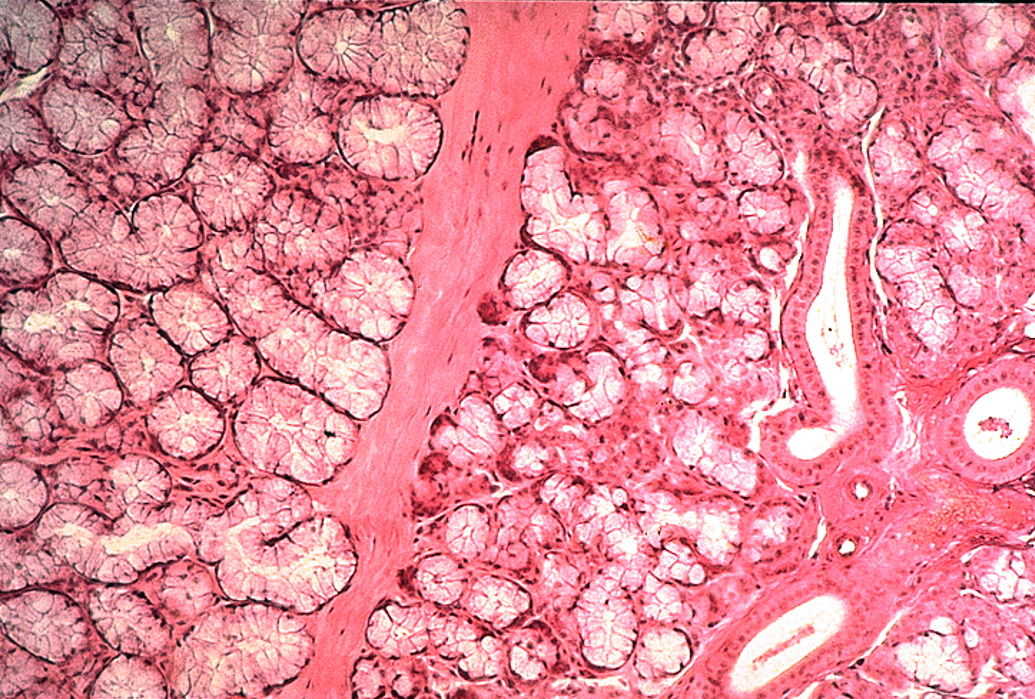
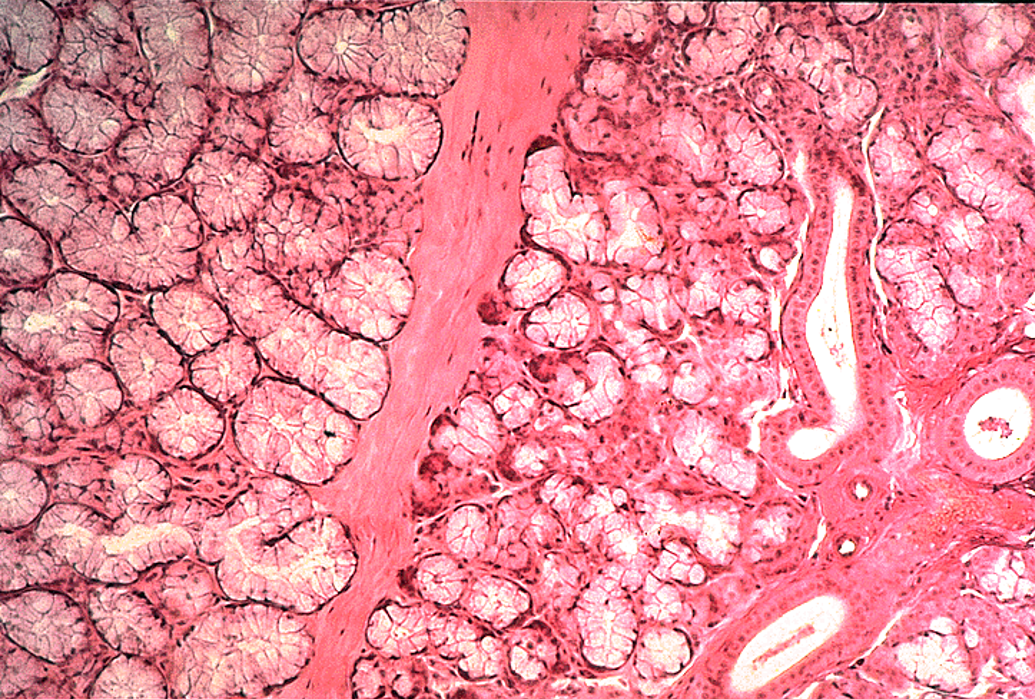
Identify the salivary gland and types of acini.
Parotid gland
Nuclei are close to the lumen; striated duct
Mostly serous
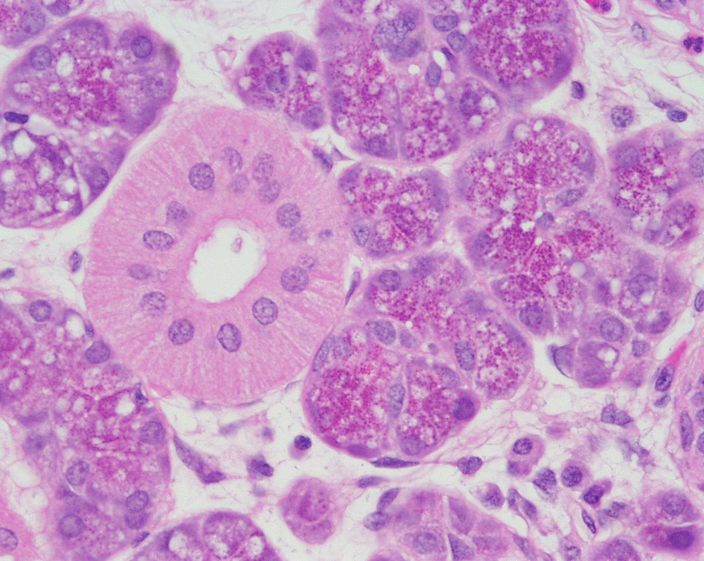
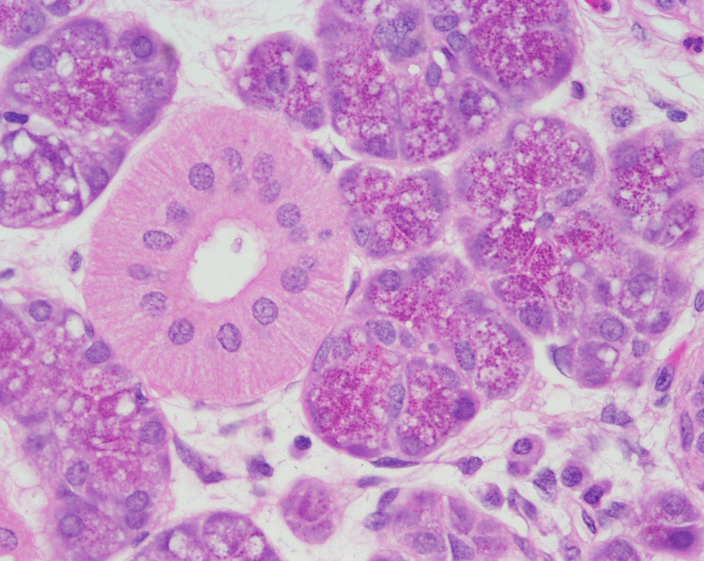
Identify the salivary gland and types of acini.
Sublingual gland
Mostly mucous acini (pale-staining)
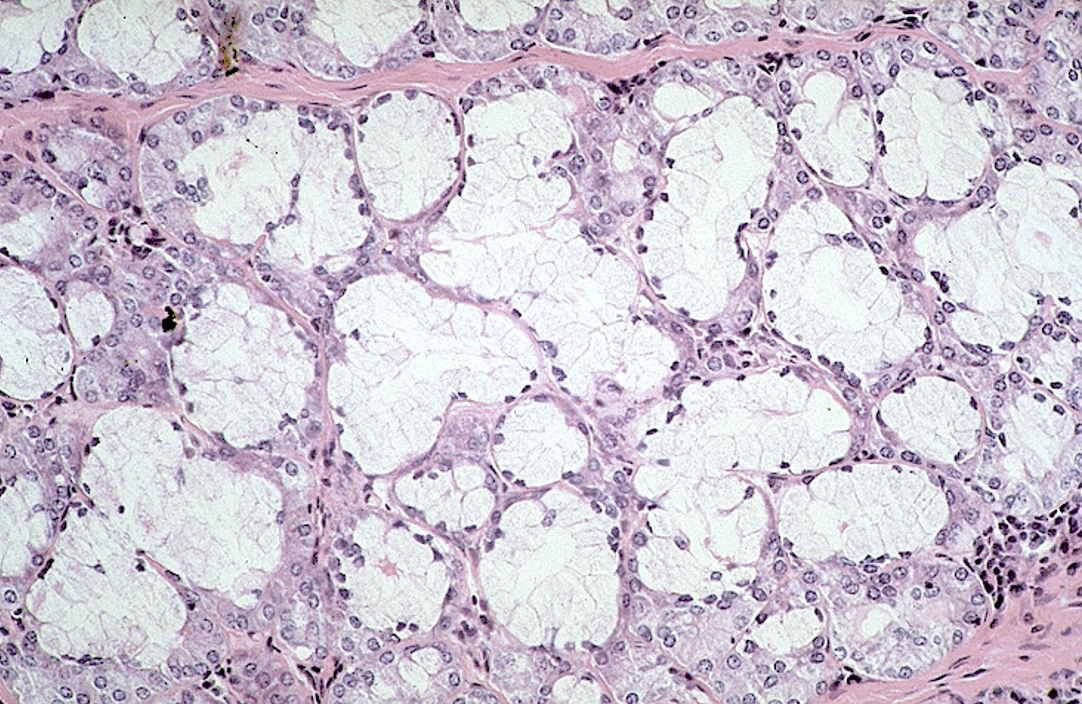
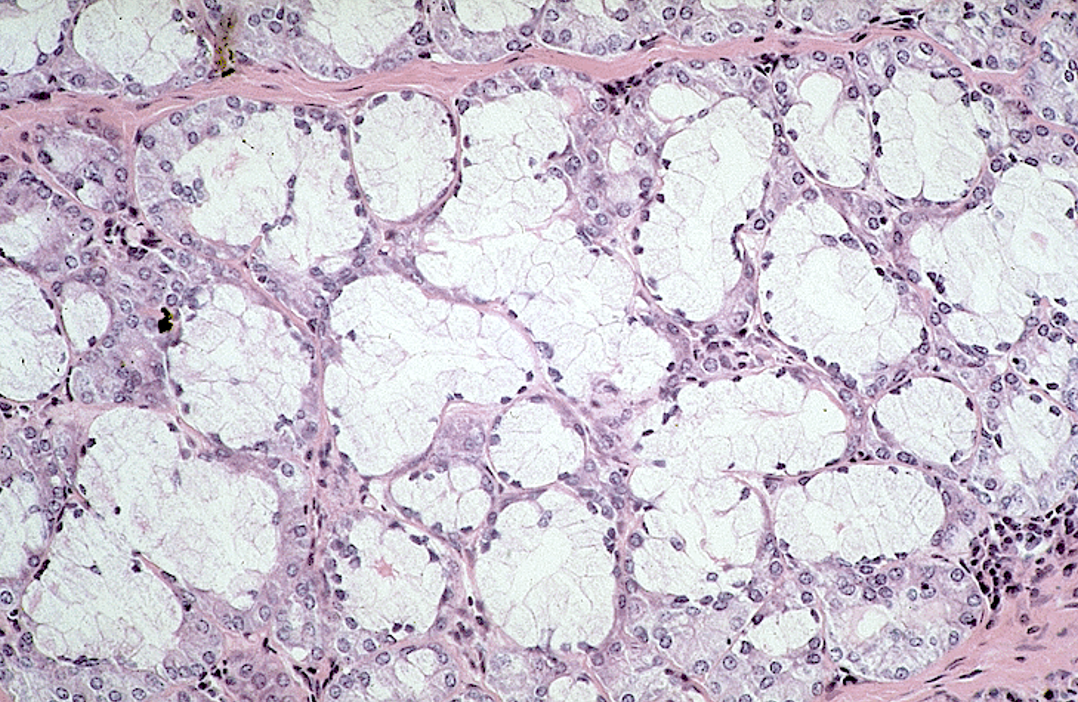
Identify the gland, the types of acini and the ducts.
Parotid gland
Many serous acini
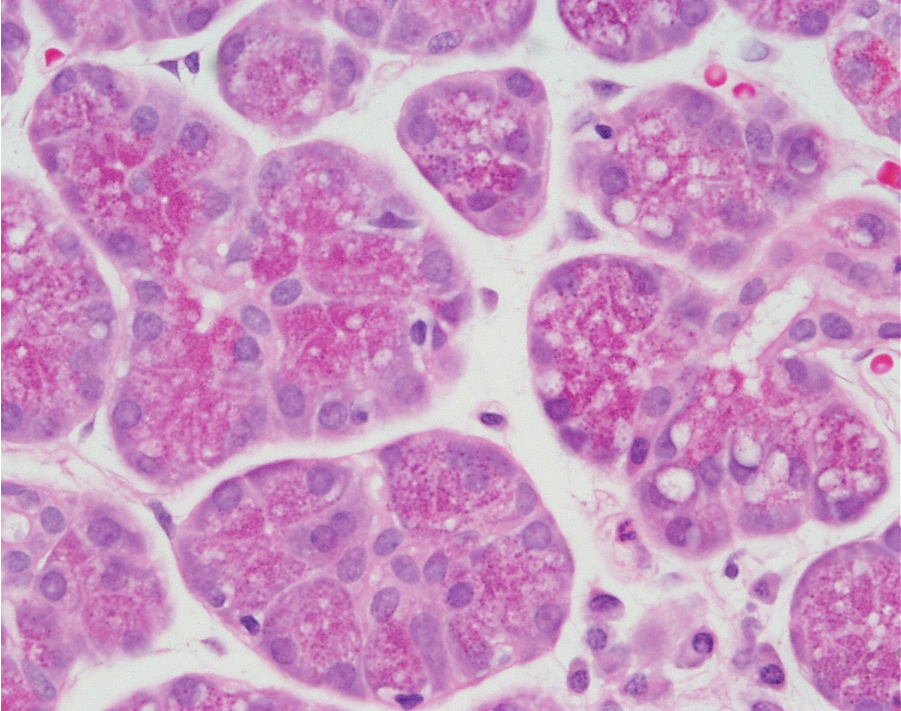
Identify the salivary gland and types of acini.
Parotid gland
Many serous acini