DMS 242 Final Review- Study Guide
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
What are the endometrial effects of Tamoxifen?
Endometrial hyperplasia, cystic echotexture, polyps, and increased risk of endometrial carcinoma.
Rhizomelia
Shortening of proximal long bones such as the femur and humerus.
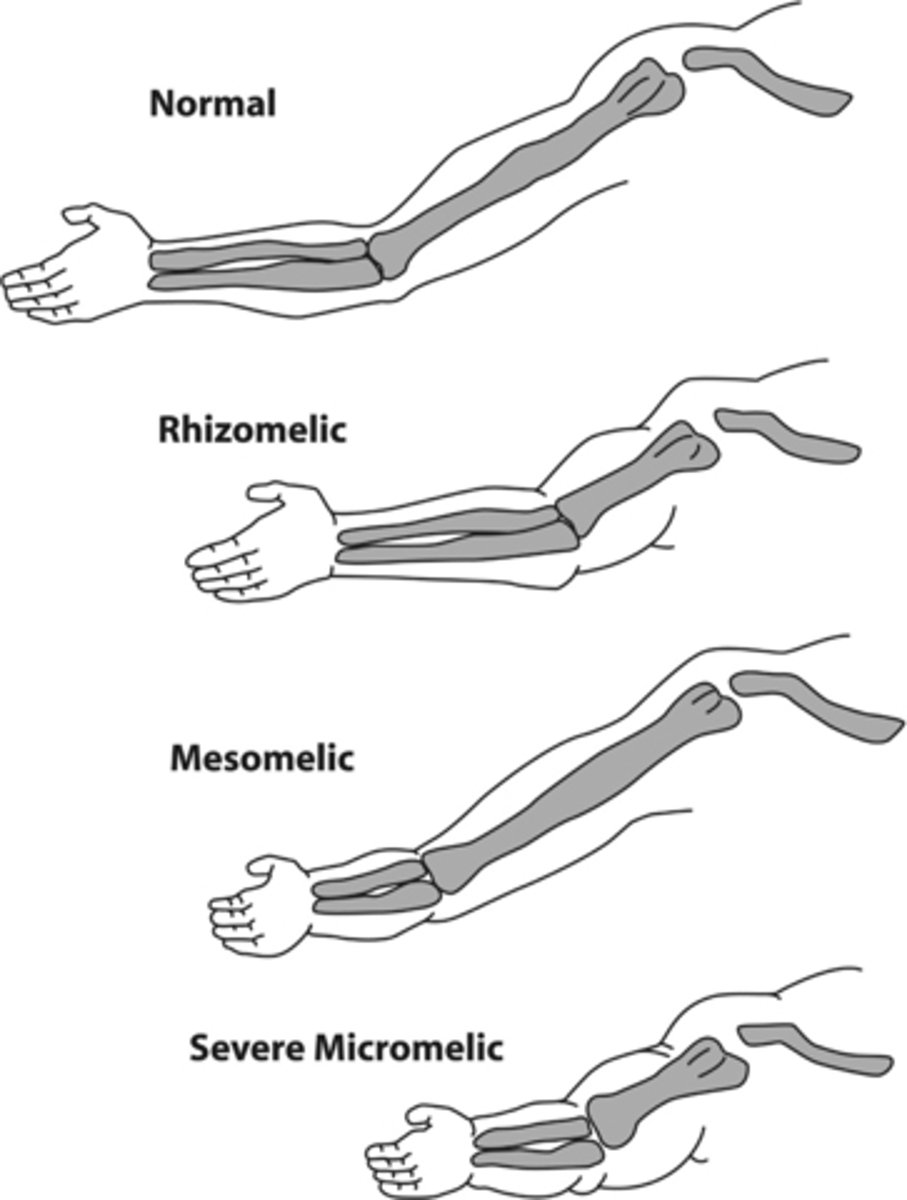
Micromelia
Shortening of the entire limb.
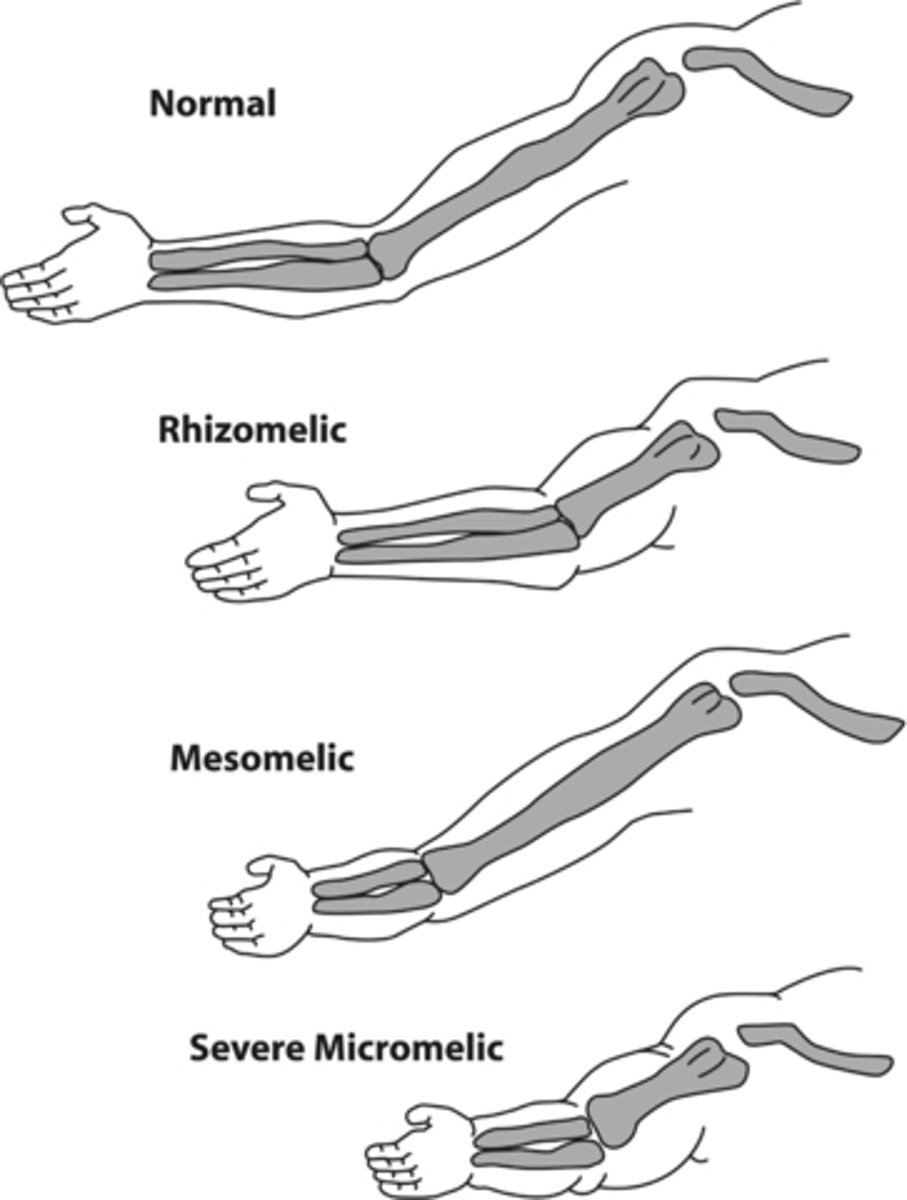
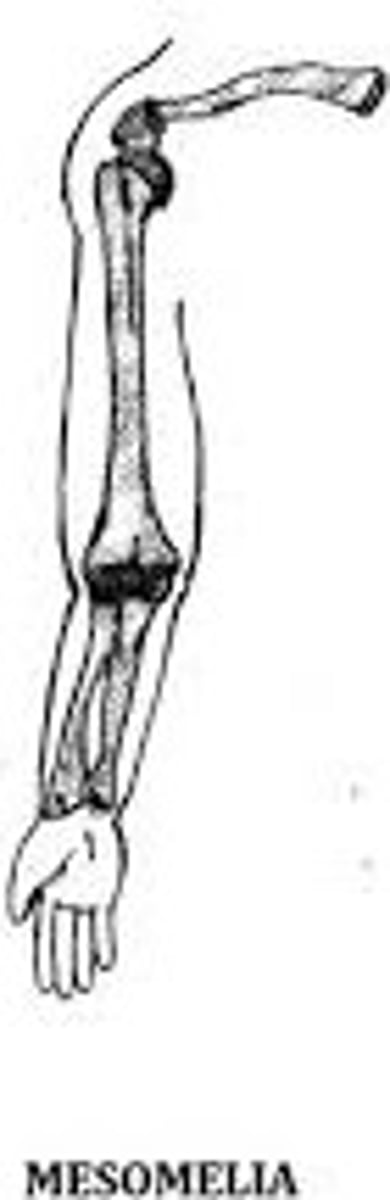
Mesomelia
Shortening of distal long bones like the tibia/fibula and radius/ulna.
What are the characteristics of Camptomelic Dysplasia?
Narrow chest, bowing of long bones, micrognathia, cleft palate, and it is fatal.
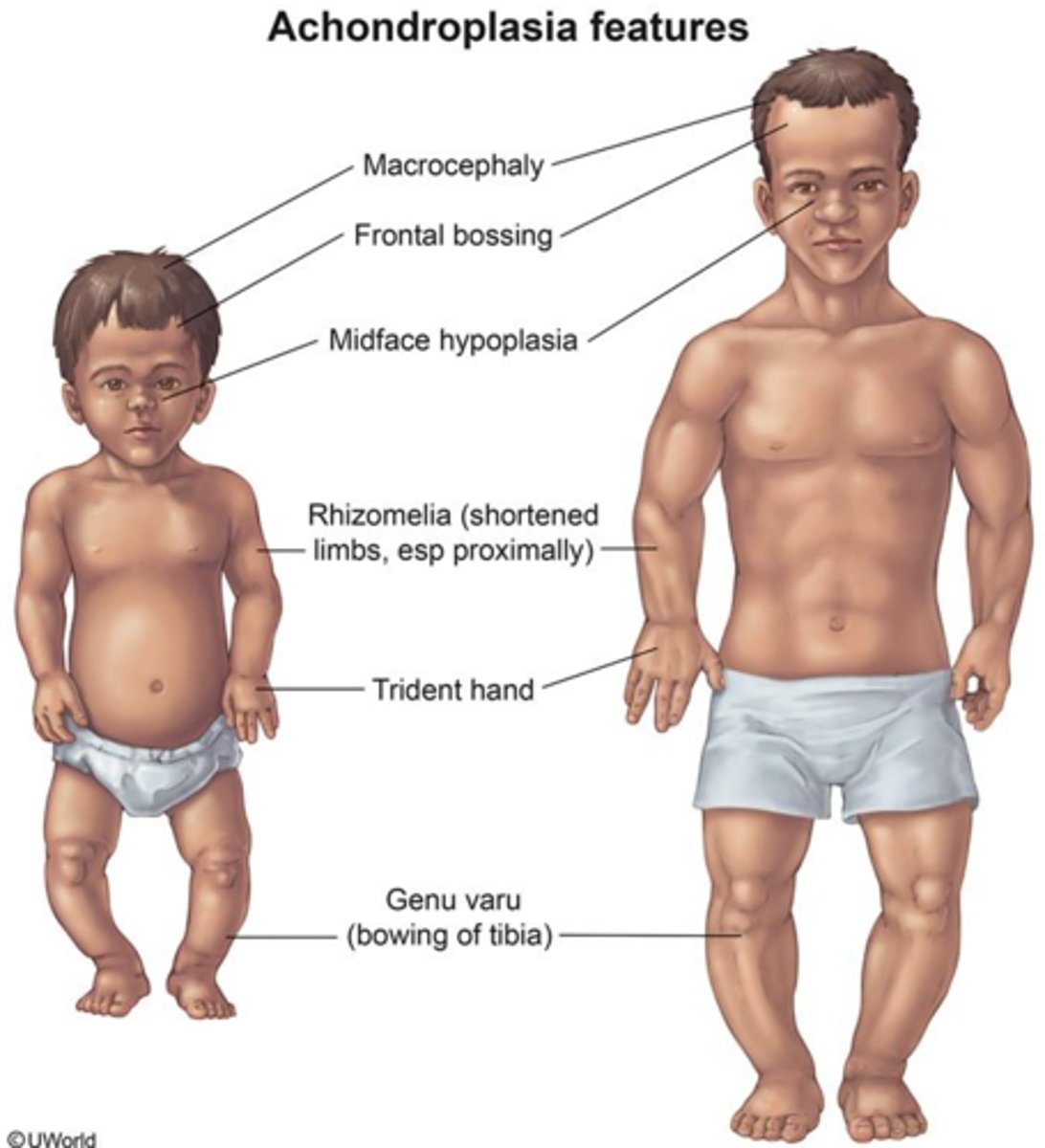
What is the most common non-lethal skeletal dysplasia?
Heterozygous Achondroplasia, characterized by mesomelia, trident hand, and large head with frontal bossing.
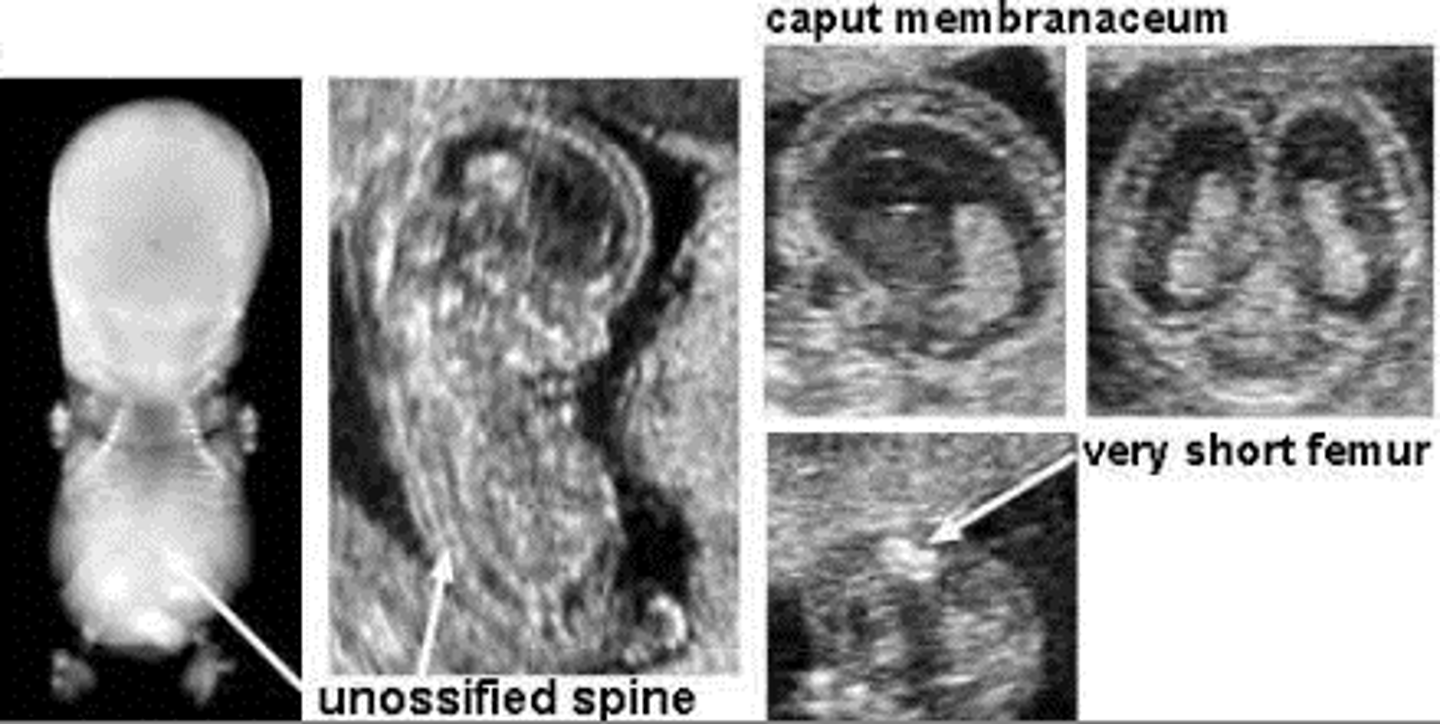
Achondrogenesis
A lethal condition due to failure to produce cartilage, resulting in short limbs and small chest, lethal due to pulmonary hypoplasia.
Short-rib Polydactyly Syndrome
A lethal condition characterized by short ribs, micromelia, and postaxial polydactyly.
Hypophosphatasia
A condition where bones are not mineralized, leading to soft, thin, bowed bones, and it can be fatal.
What are the types of Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI)?
Type I: Mildest form with fewer fractures and normal stature;
Type II: Most severe and lethal with pulmonary hypoplasia
Type III: Severe with bone deformities
Type IV: Moderately severe.
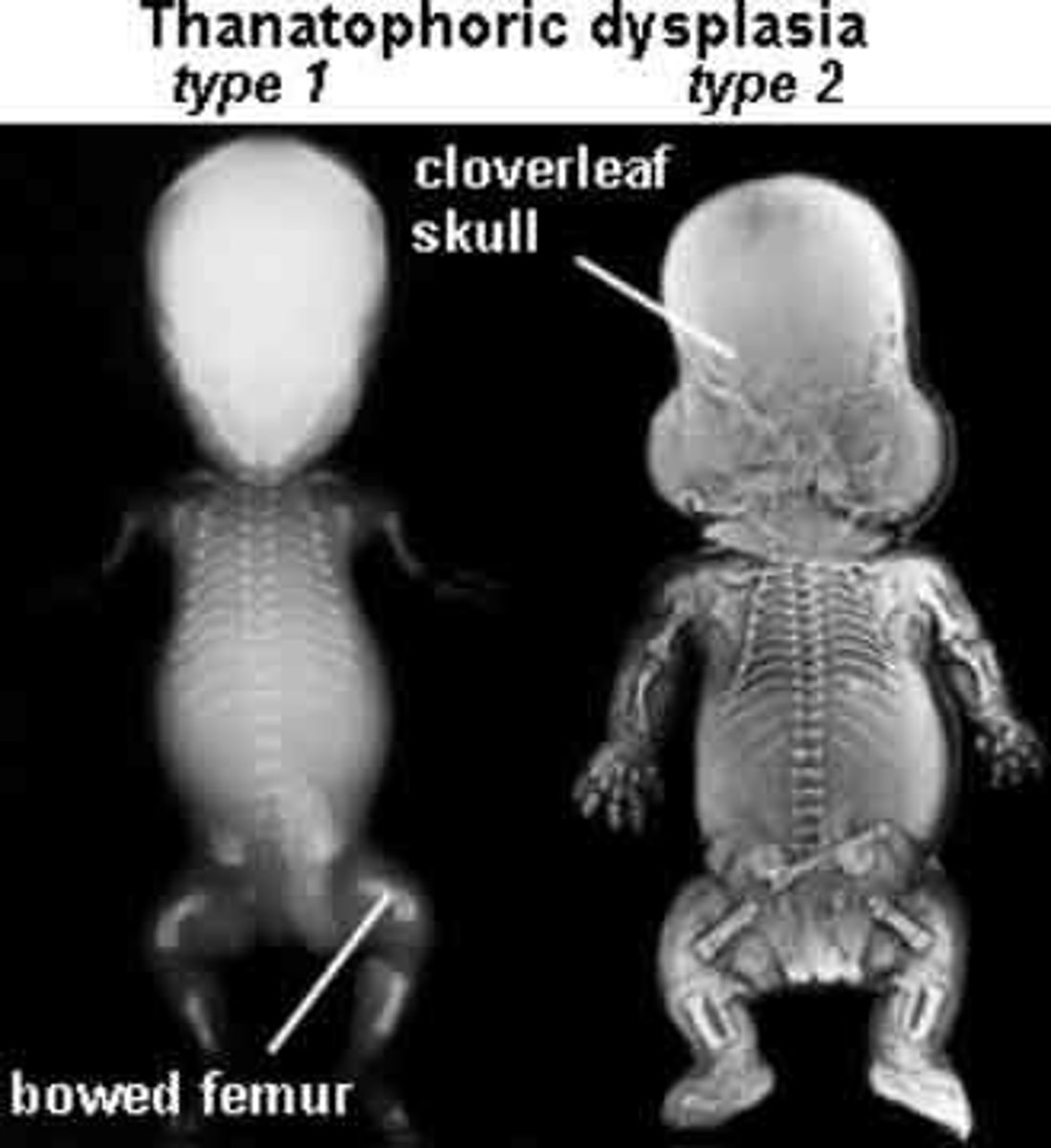
Thanatophoric Dysplasia
The most common lethal skeletal dysplasia, with Type I showing platyspondyly and curved femurs, and Type II showing straight femurs, and a cloverleaf skull.
Meckel-Gruber Syndrome
A fatal condition characterized by encephalocele, polydactyly, and cystic dysplastic kidneys.
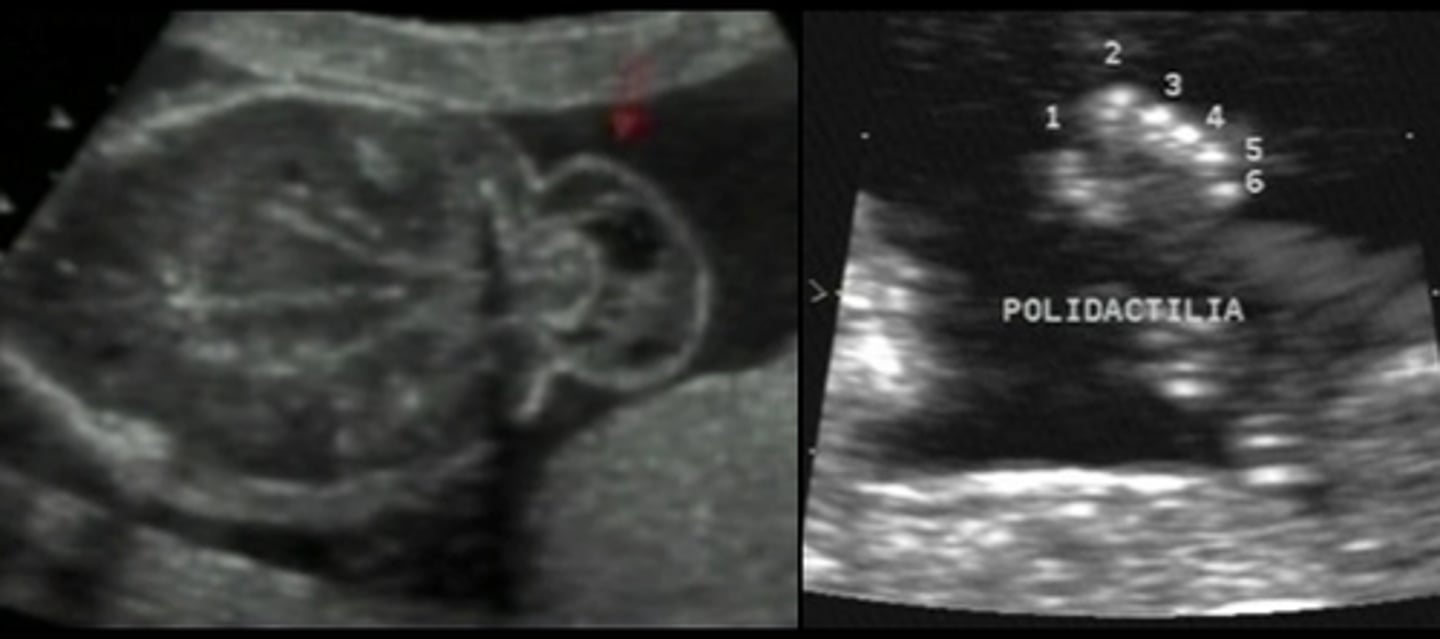
What are the features of Beckwith-Weidemann Syndrome?
Macrosomia, enlarged organs, macroglossia, and omphalocele, which is not lethal.
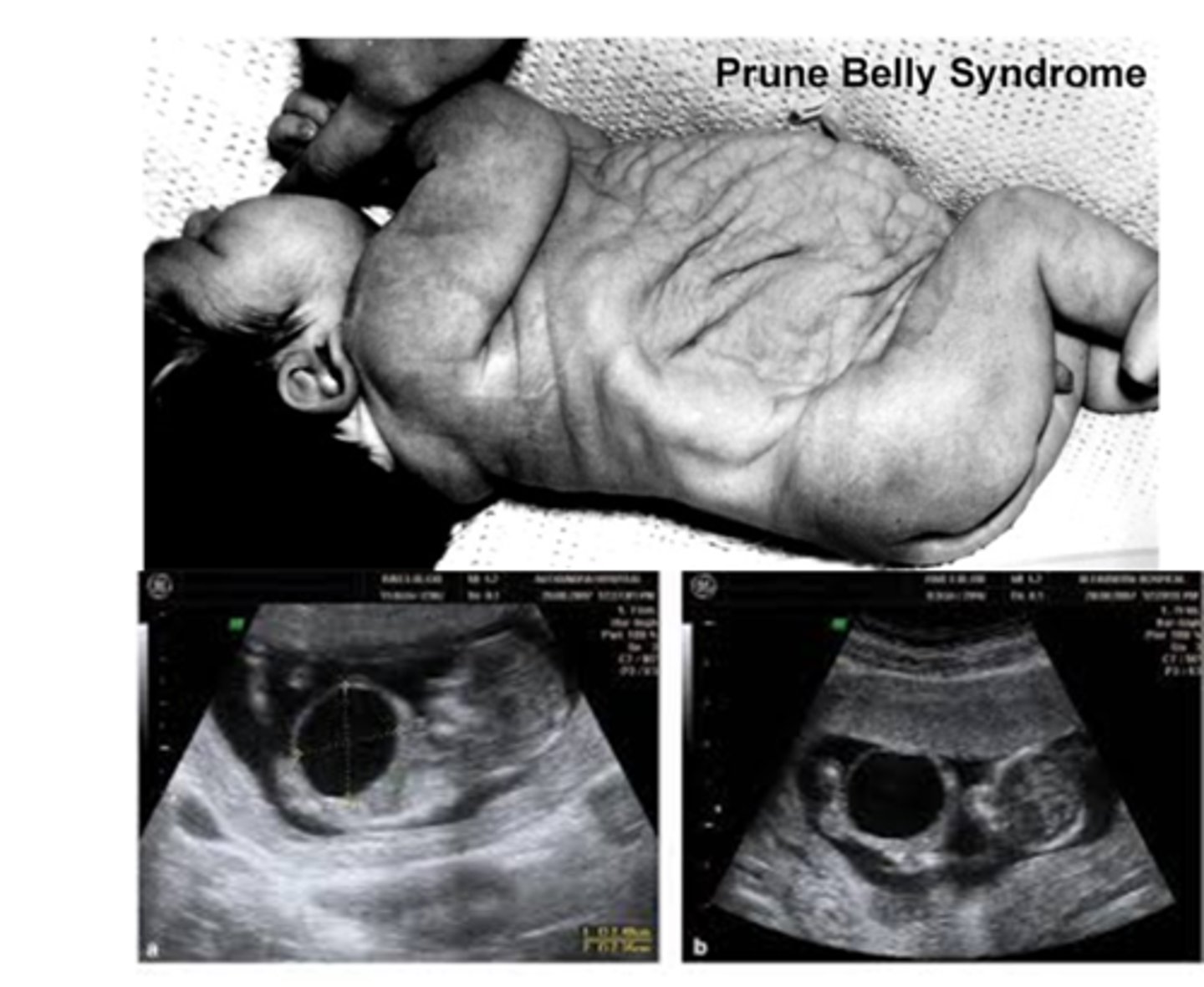
What is Prune Belly Syndrome?
Characterized by lack of abdominal muscles, megacystis/megaureter, and bilateral cryptorchidism; can be lethal or mild.
What is Spina Bifida?
A neural tube defect that can present as Occulta or Aperta.
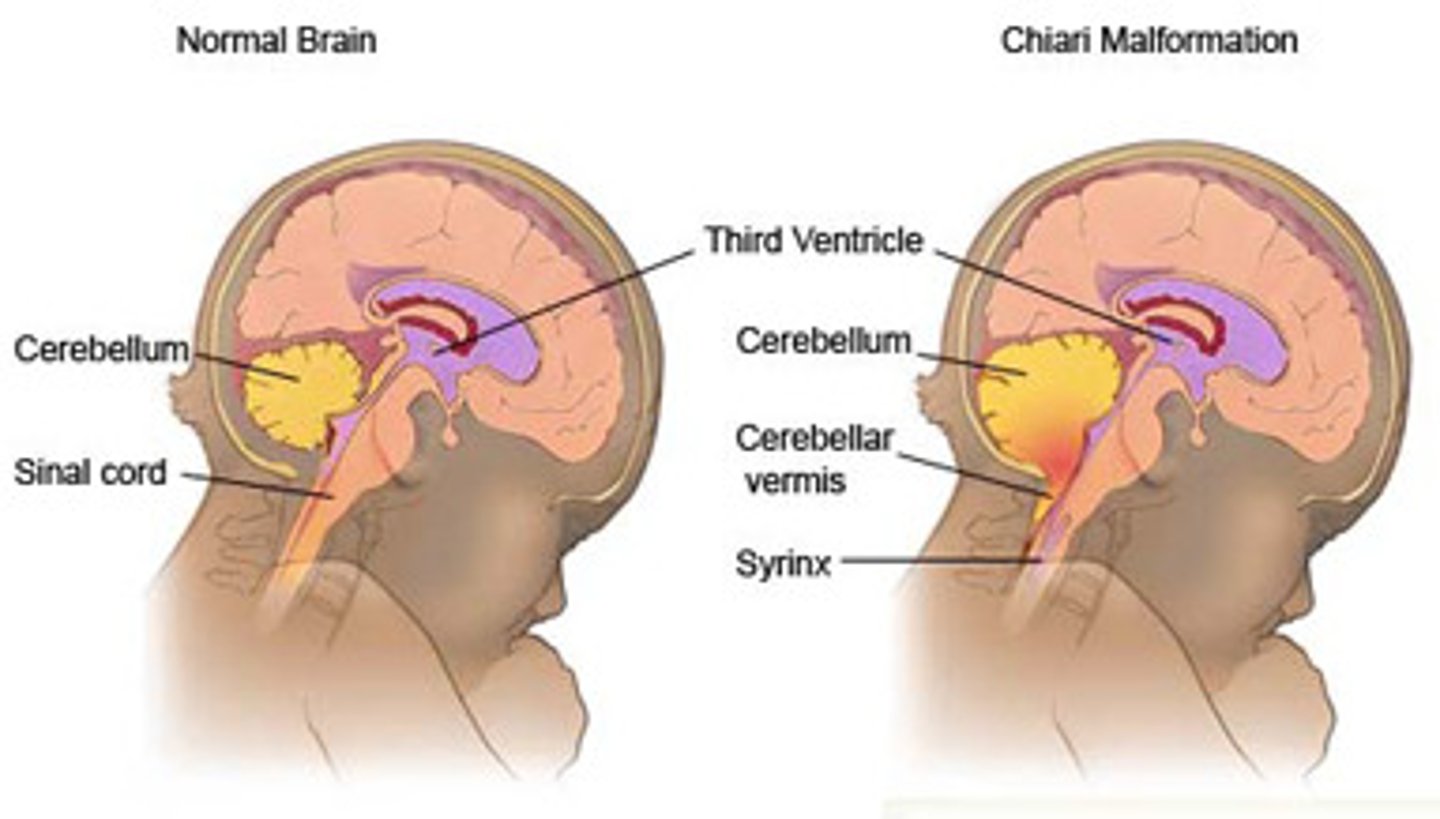
What are the signs of Arnold Chiari II malformation?
Lemon and banana signs, associated with spina bifida/ myelomeningocele.
What is Encephalocele?
A condition usually occurring in the occipital region, where brain tissue protrudes through a defect in the skull.
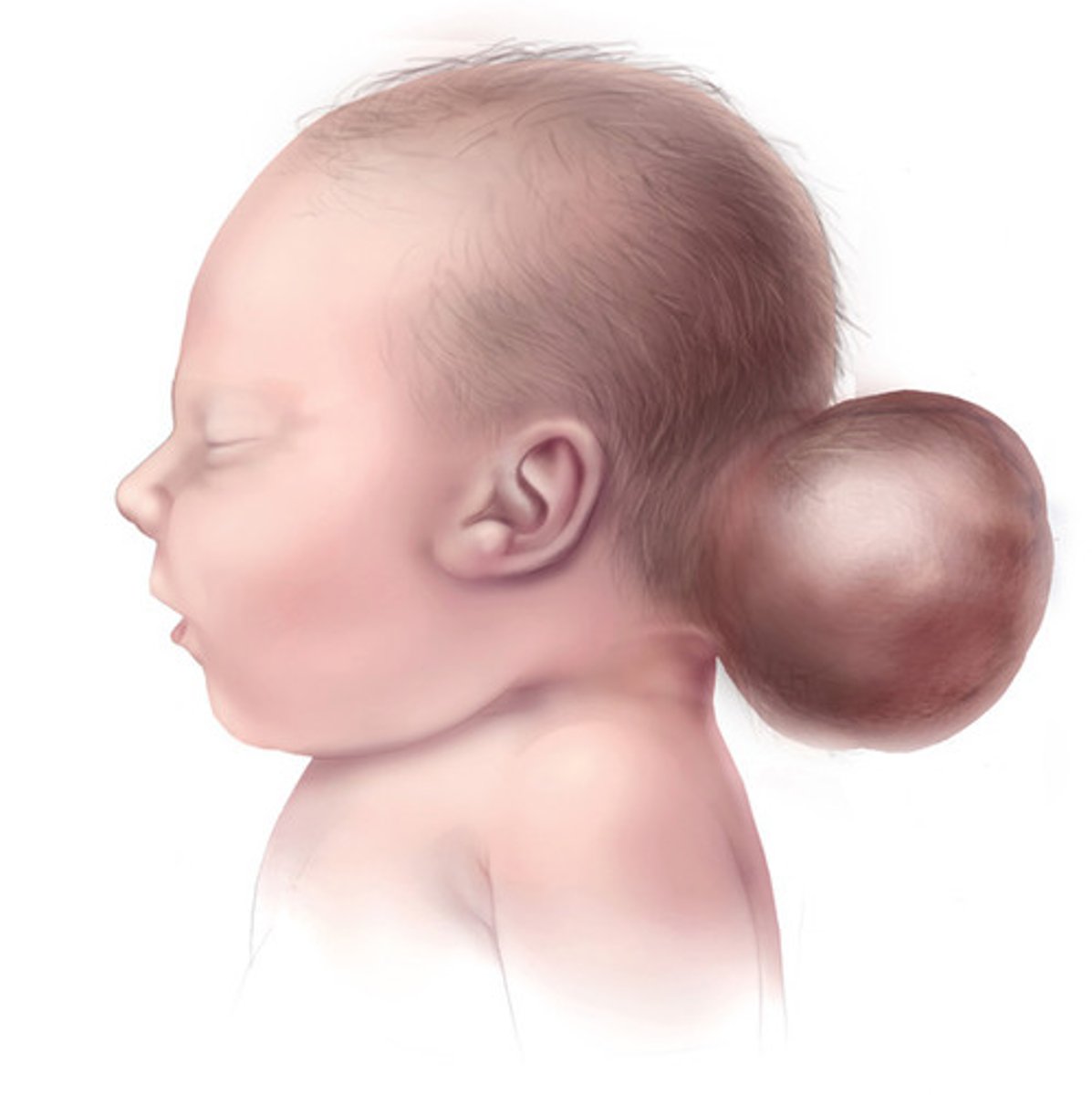
What is the Pentology of Cantrell?
midline defects characterized by omphalocele, ectopia cordis, diaphragmatic defect, pericardial defect, and sternal cleft.
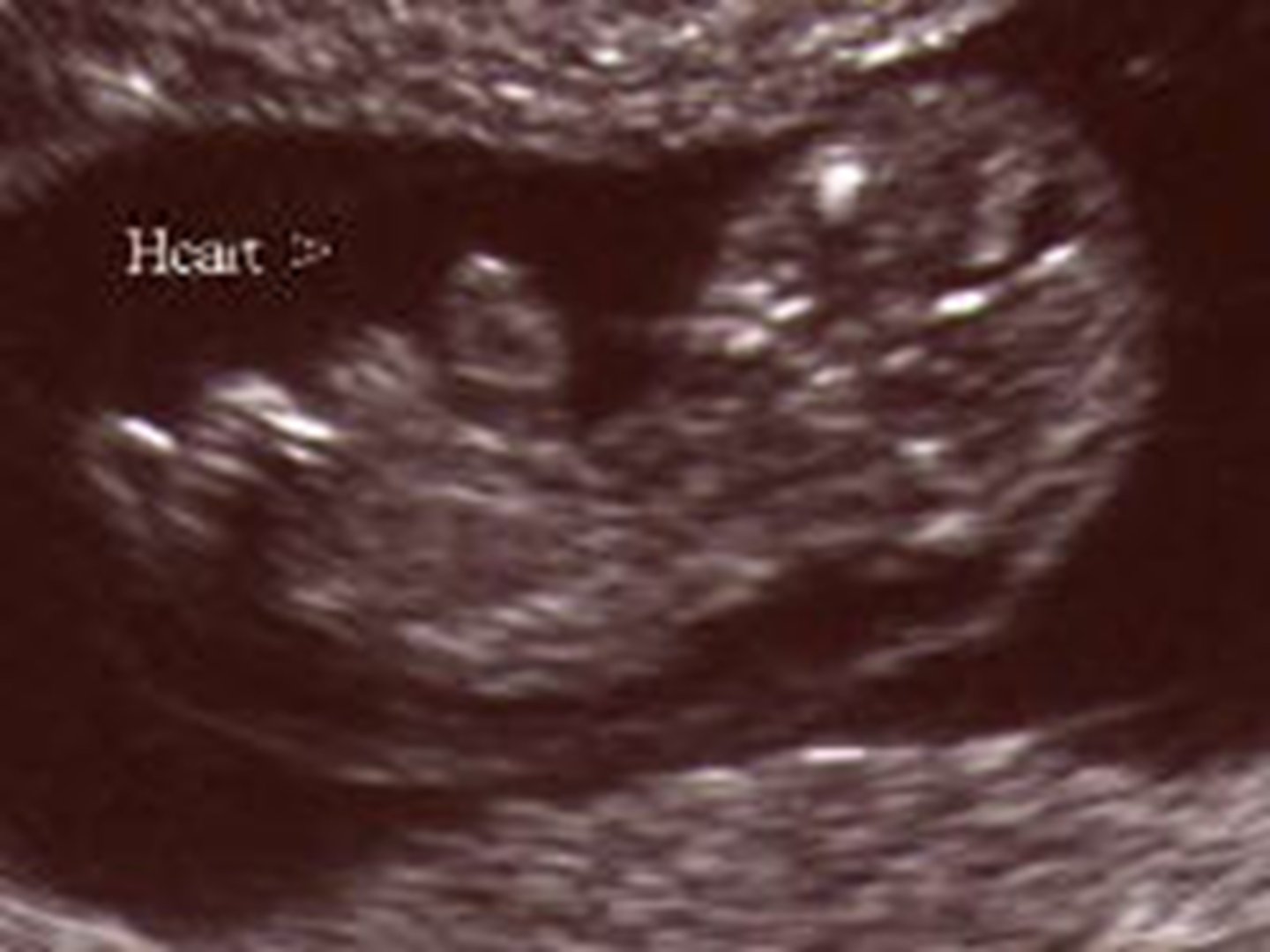
What is Anencephaly?
A condition where there is no cranium or brain tissue.
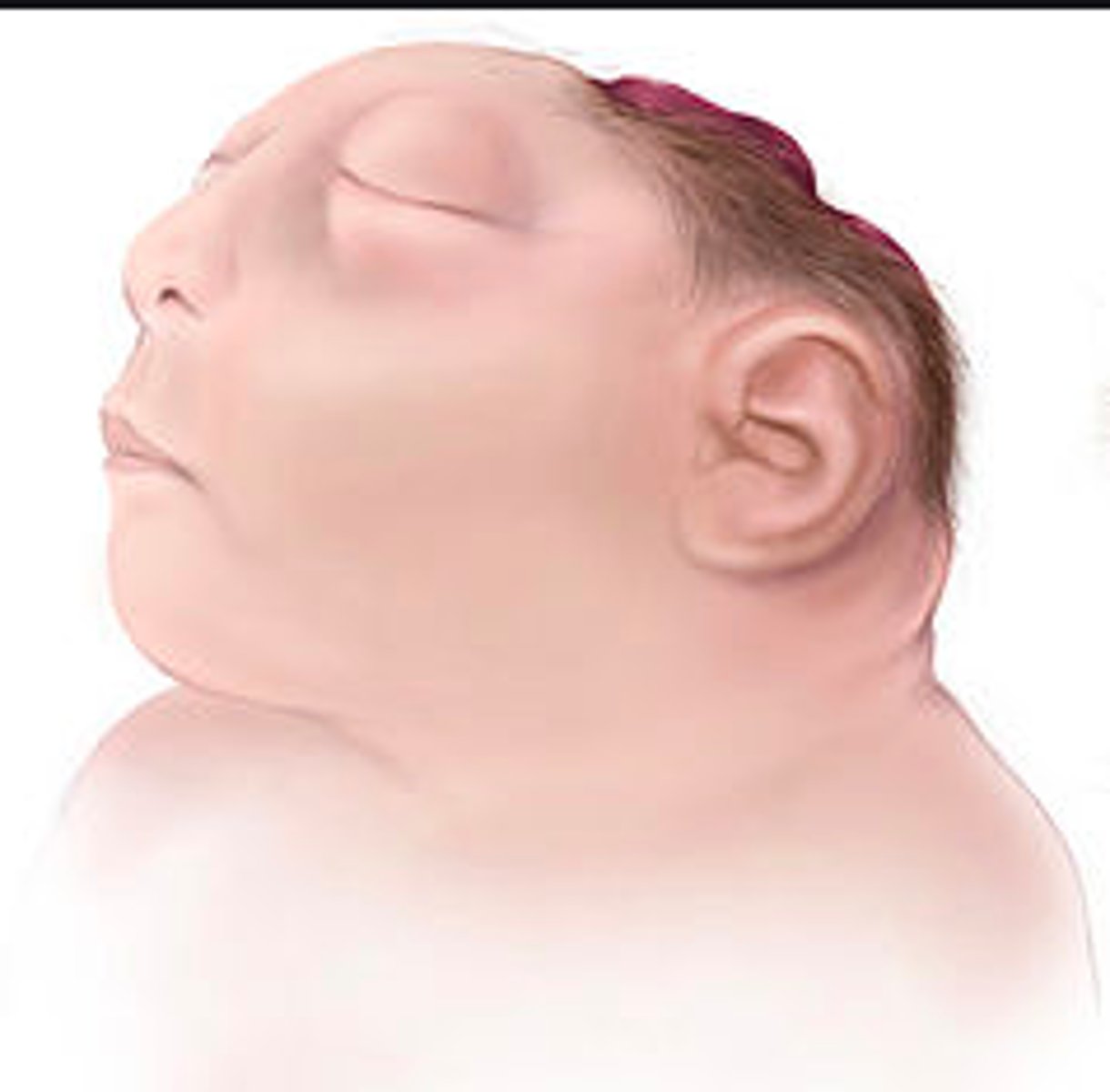
What is Hydranencephaly?
Destruction of cerebral hemispheres due to vascular insult, with basal ganglia, brain stem, and meninges preserved.
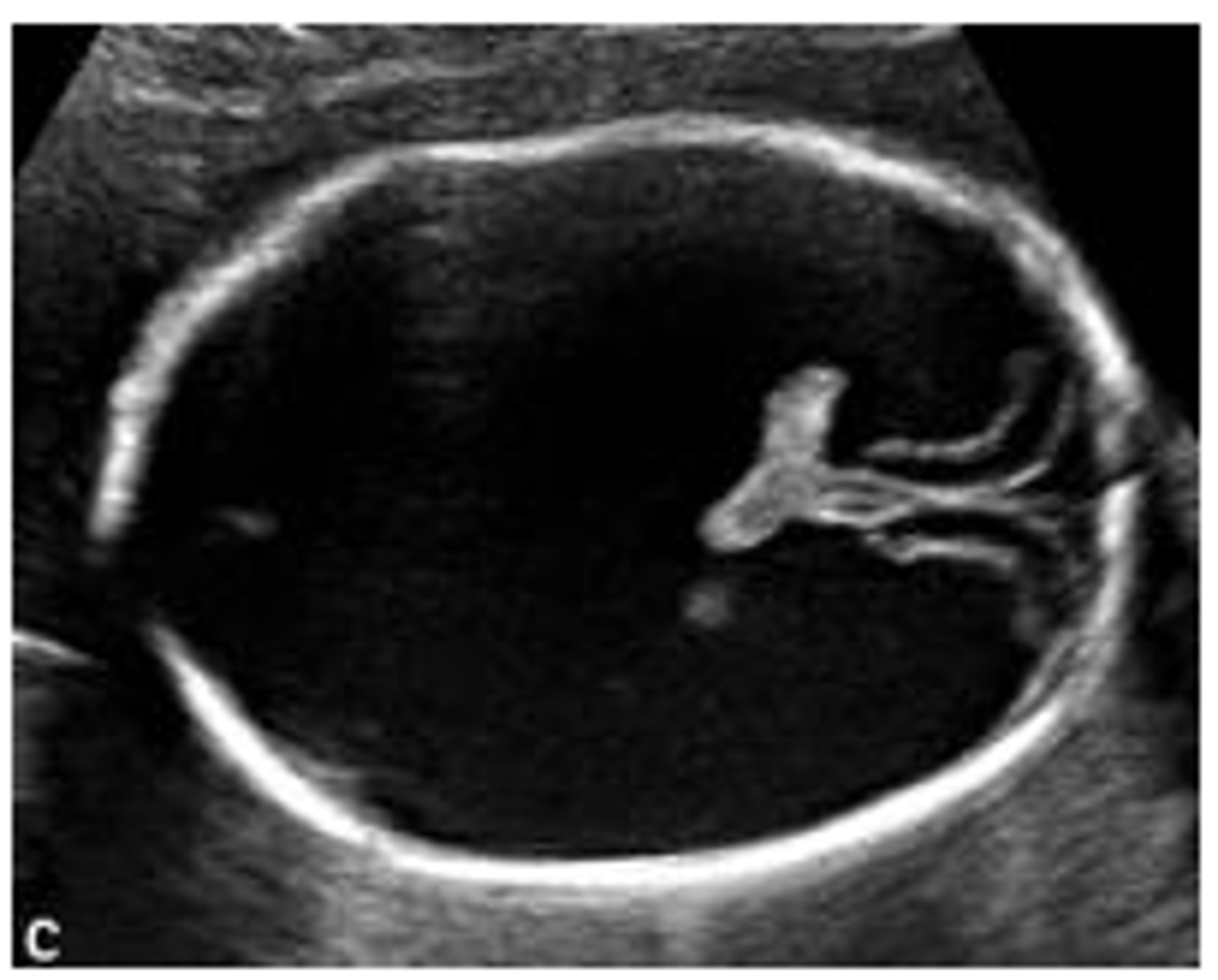
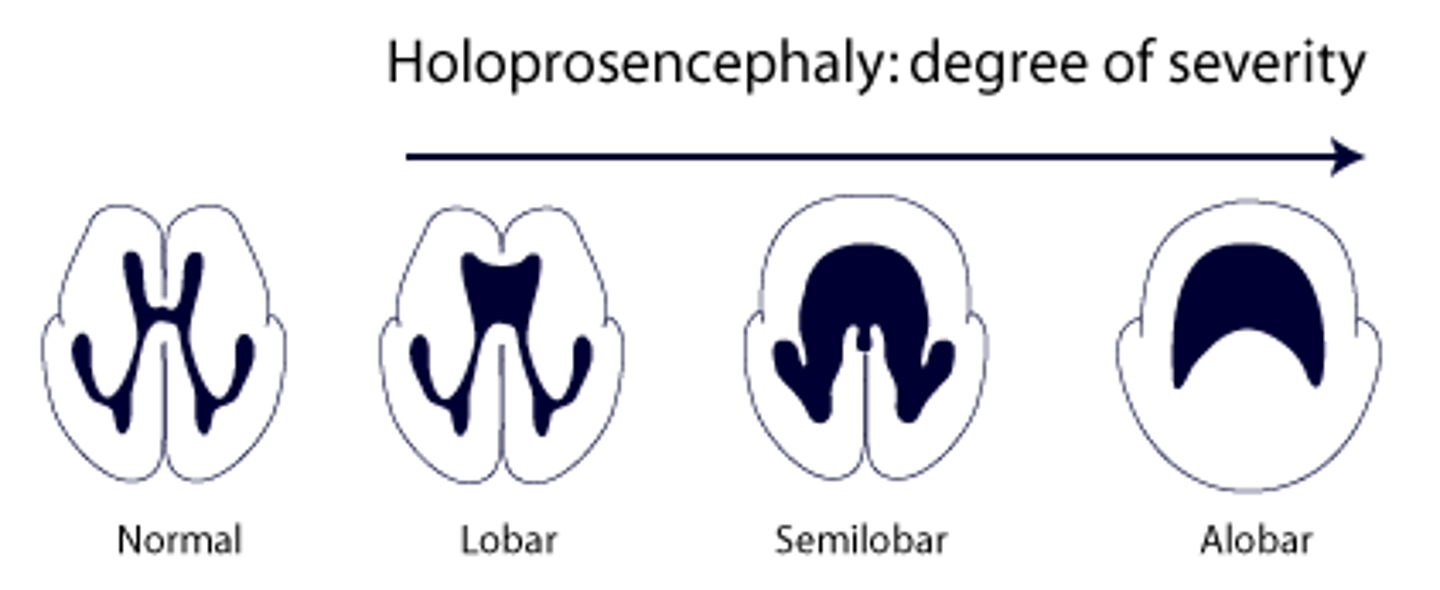
What are the types of Holoprosencephaly?
Lobar, Semilobar, and Alobar (most severe), associated with Trisomy 13/Patau.
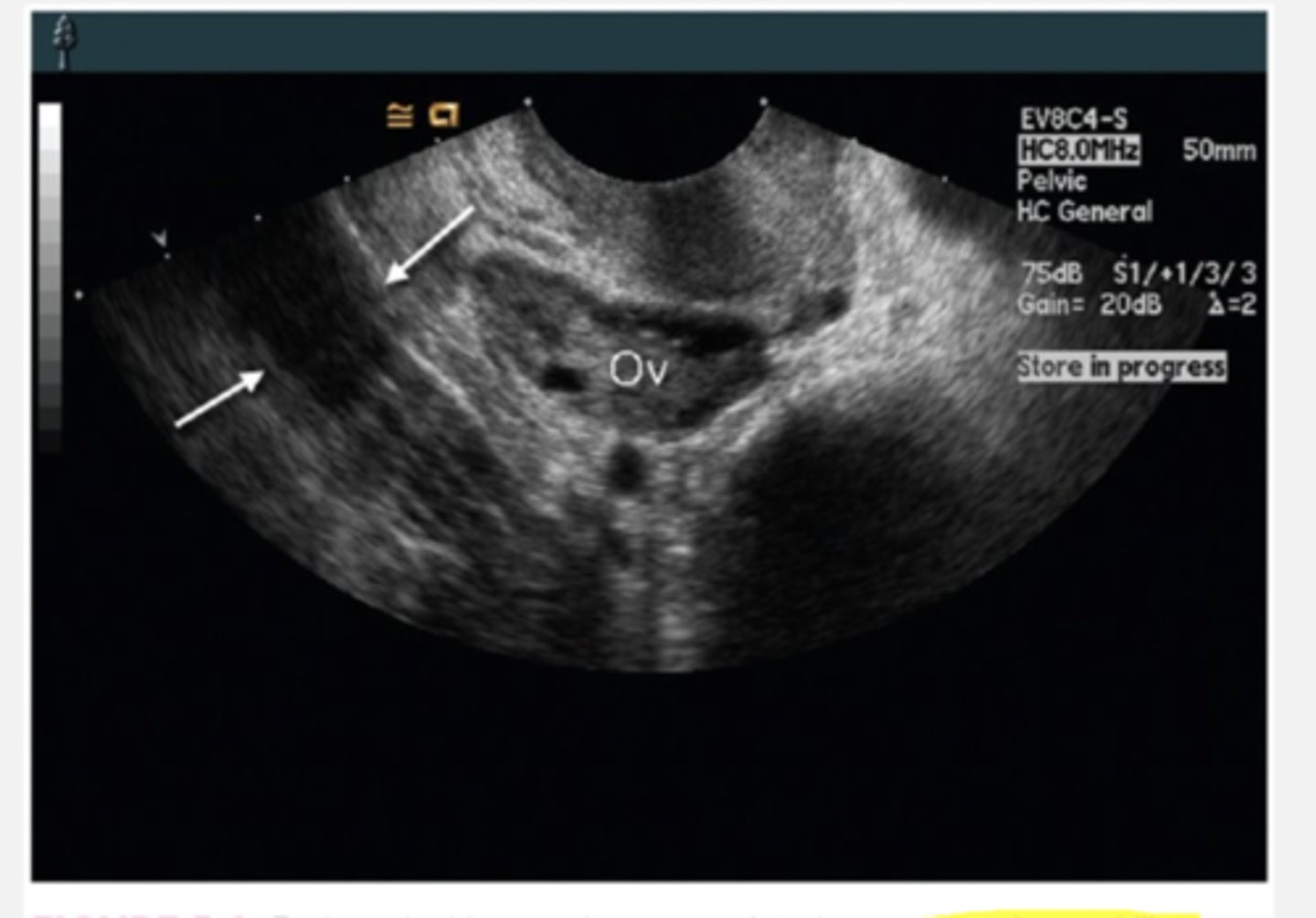
the psoas muscles can be mistaken for
an adnexal mass. make sure to elongate.
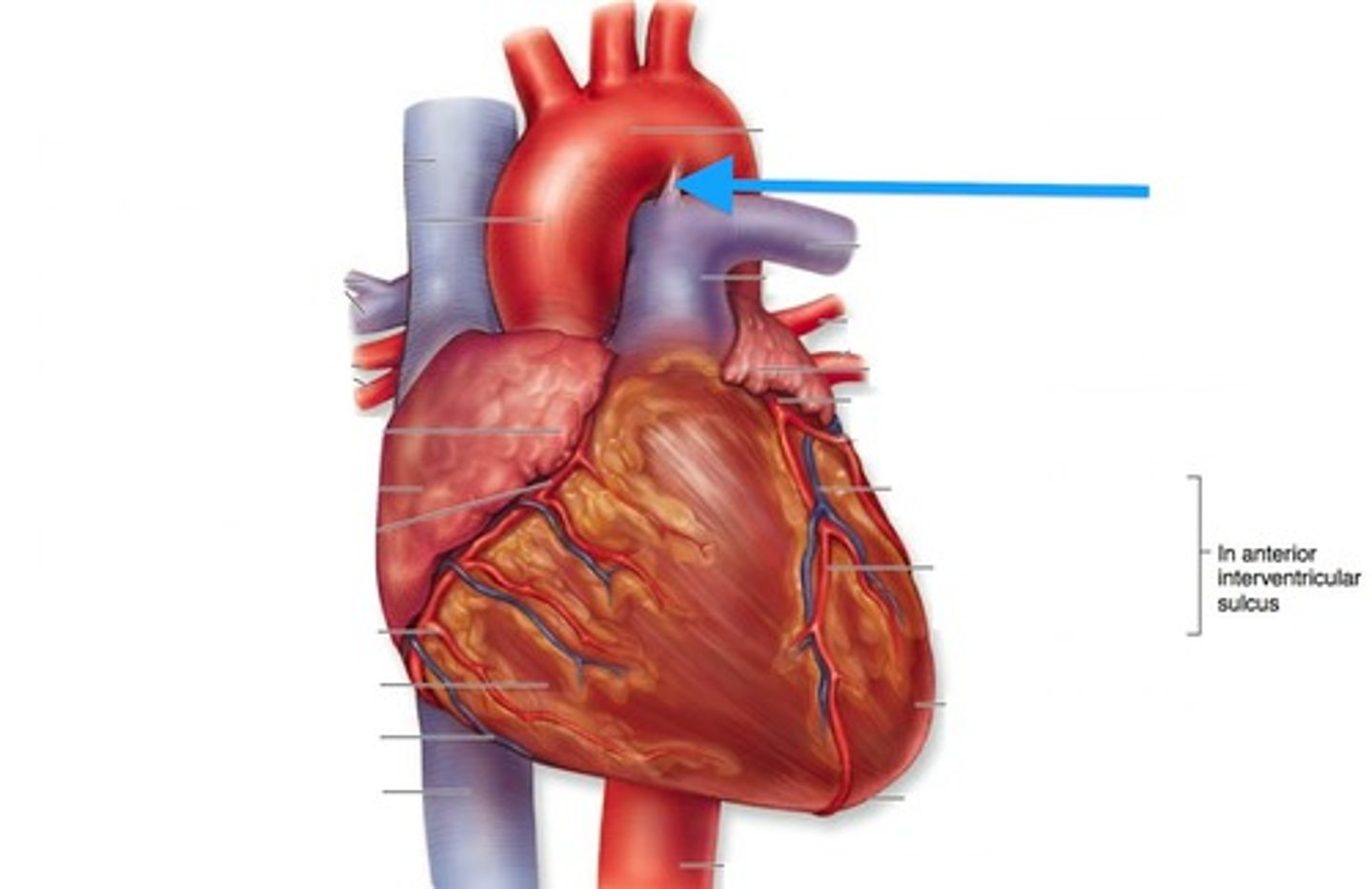
What is the Ductus arteriosus?
It connects the pulmonary artery to the aortic arch.
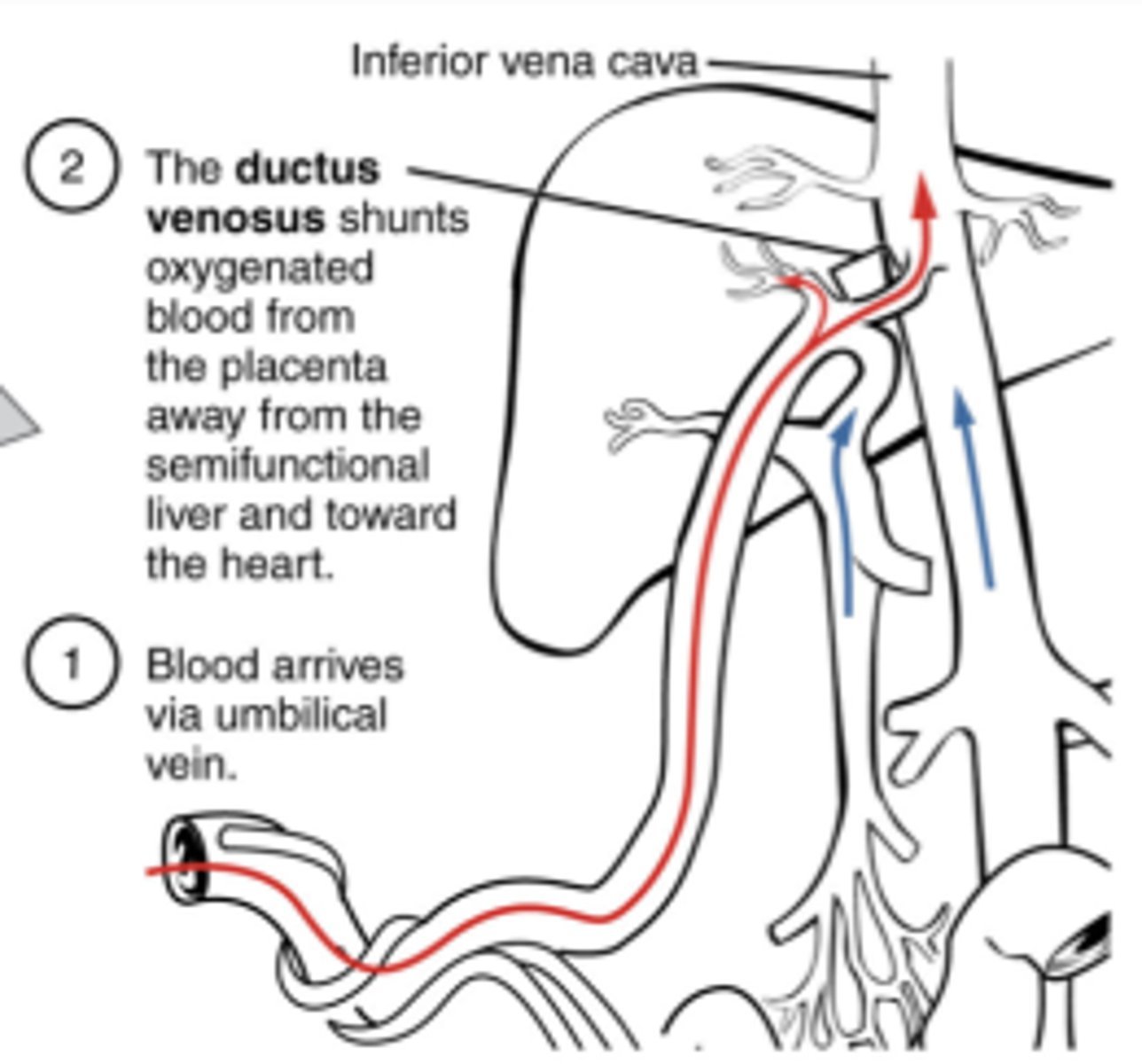
What is the Ductus venosus?
It connects the umbilical vein to the inferior vena cava (IVC).
What does BPP stand for and what does it assess?
Biophysical Profile; it assesses fluid, trunk movement, tone, and breathing, excluding heart rate from the score.
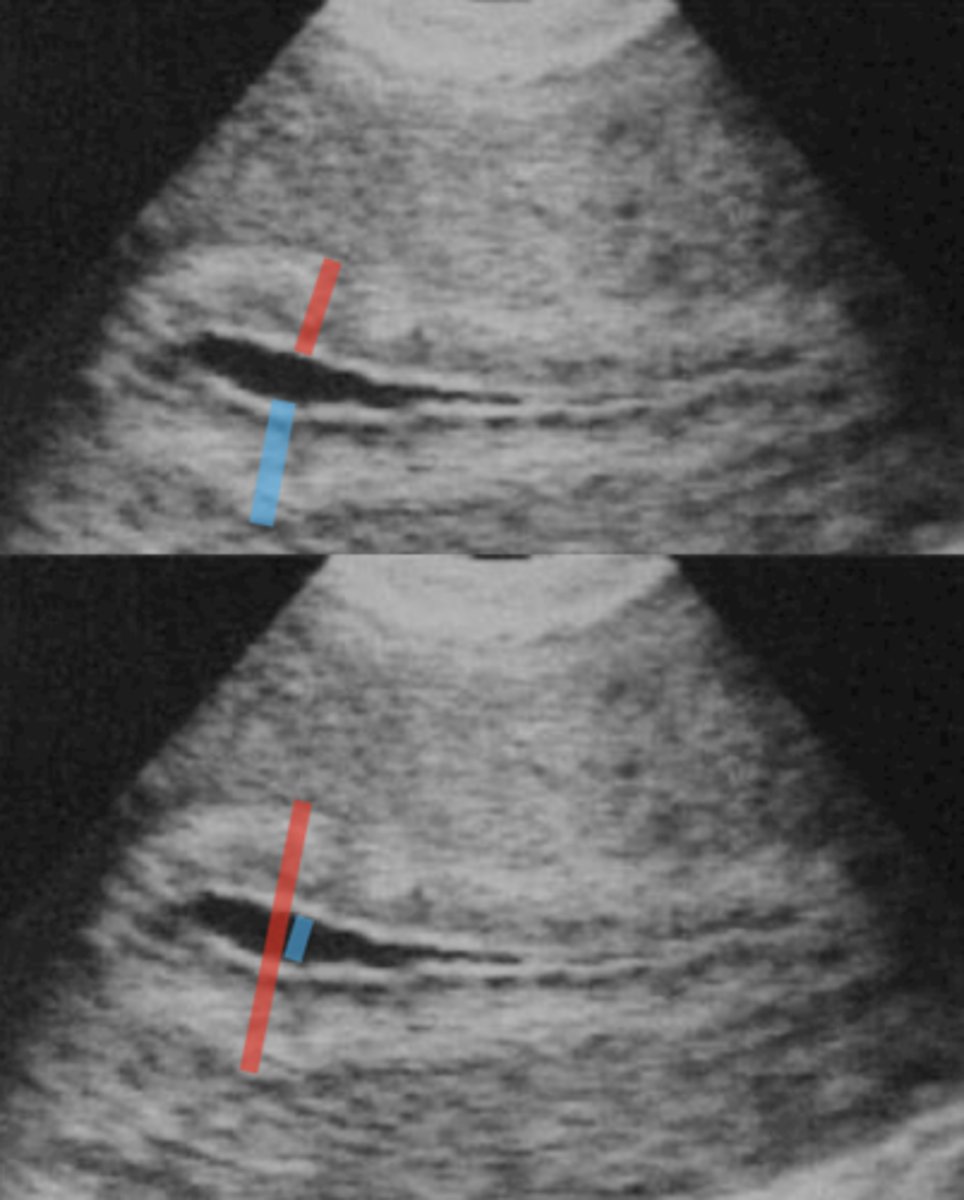
How to measure endo with fluid
measure endo as 2 separate measurements
Ectopic pregnancy; most dangerous location and most common location
Most dangerous place in FT: Interstitial.
Most common location:Ampulla of FT
Esophageal atresia
Nothing goes to stomach/stomach not seen. Nostomach seen if any problem with swallowing; neurological, cleft palate
What is the most dangerous location for an ectopic pregnancy?
The interstitial part of the fallopian tube.
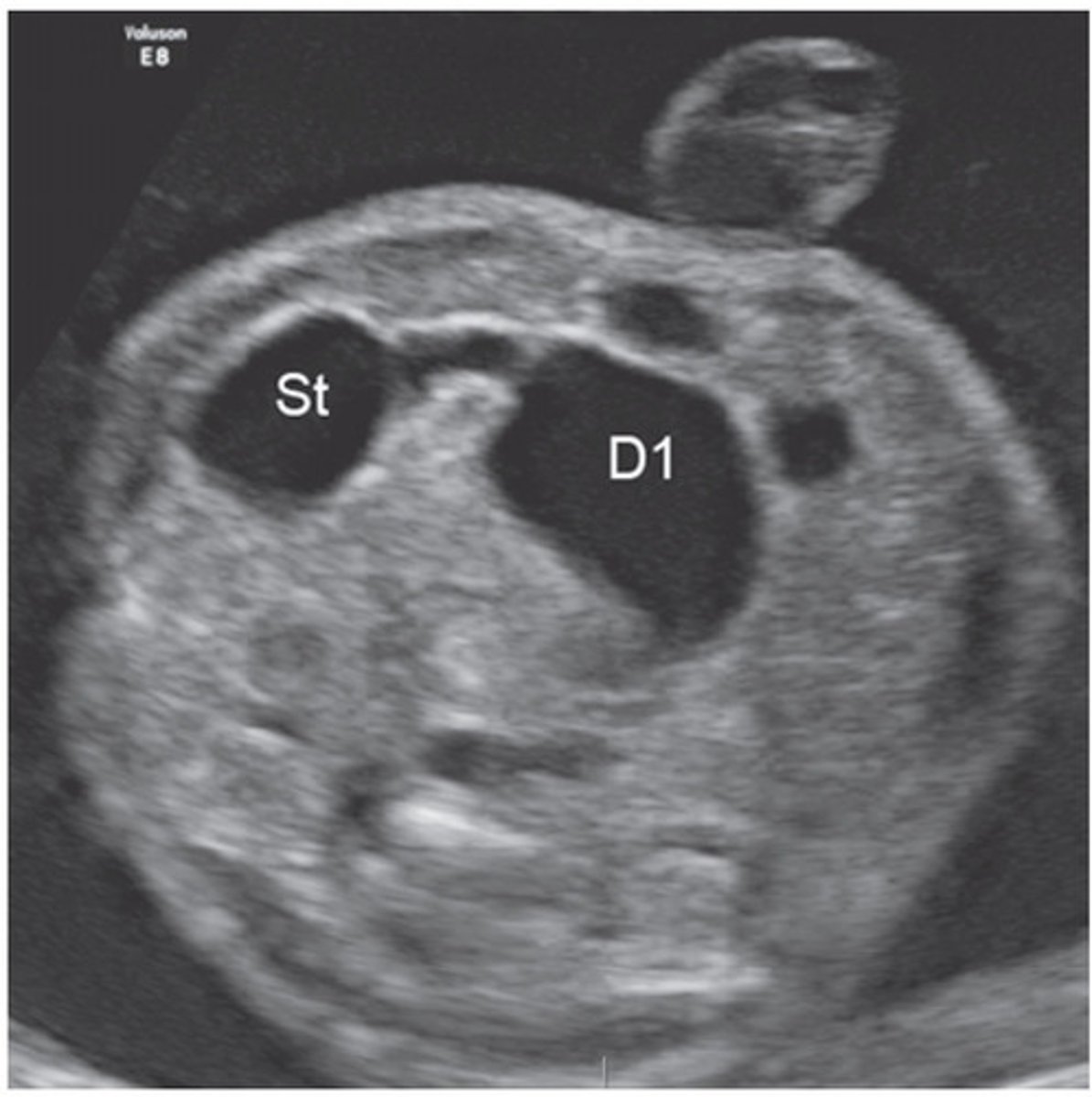
What is Duodenal atresia associated with?
Down syndrome, but can also occur as an isolated condition, will have a double bubble sonographic appearance
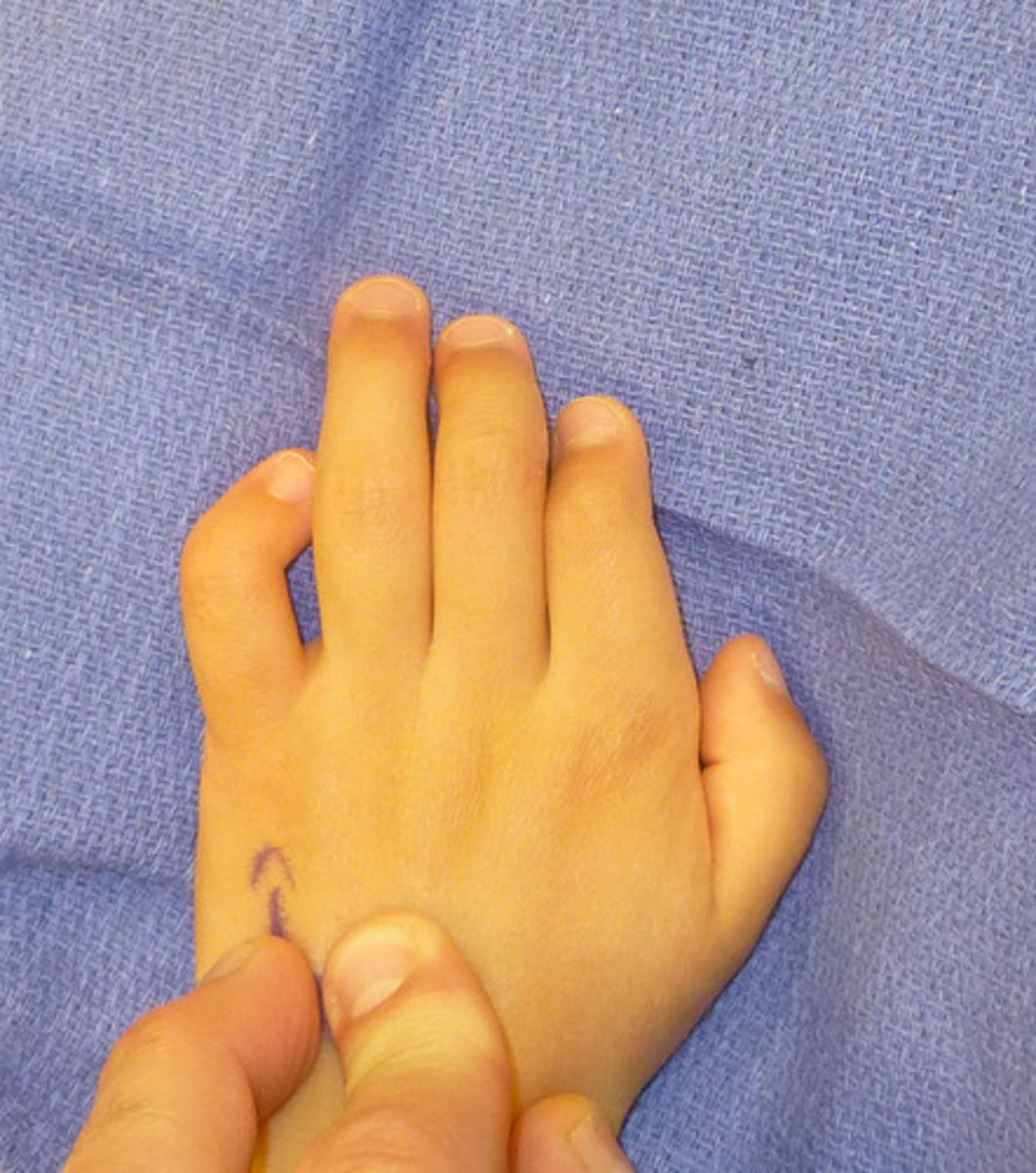
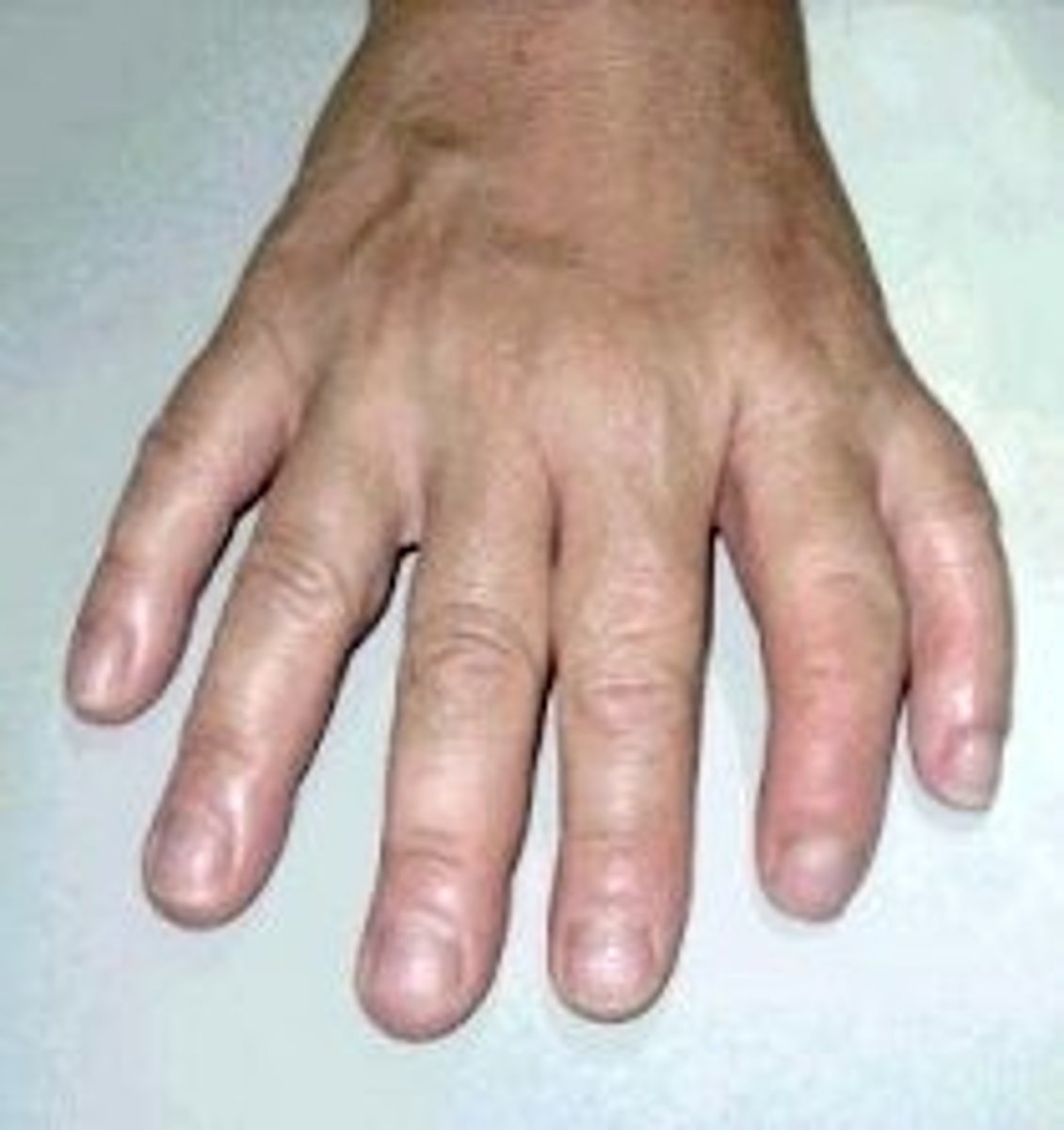
Clinodactyly
Deviation of a finger
Syndactyly
webbed fingers or toes
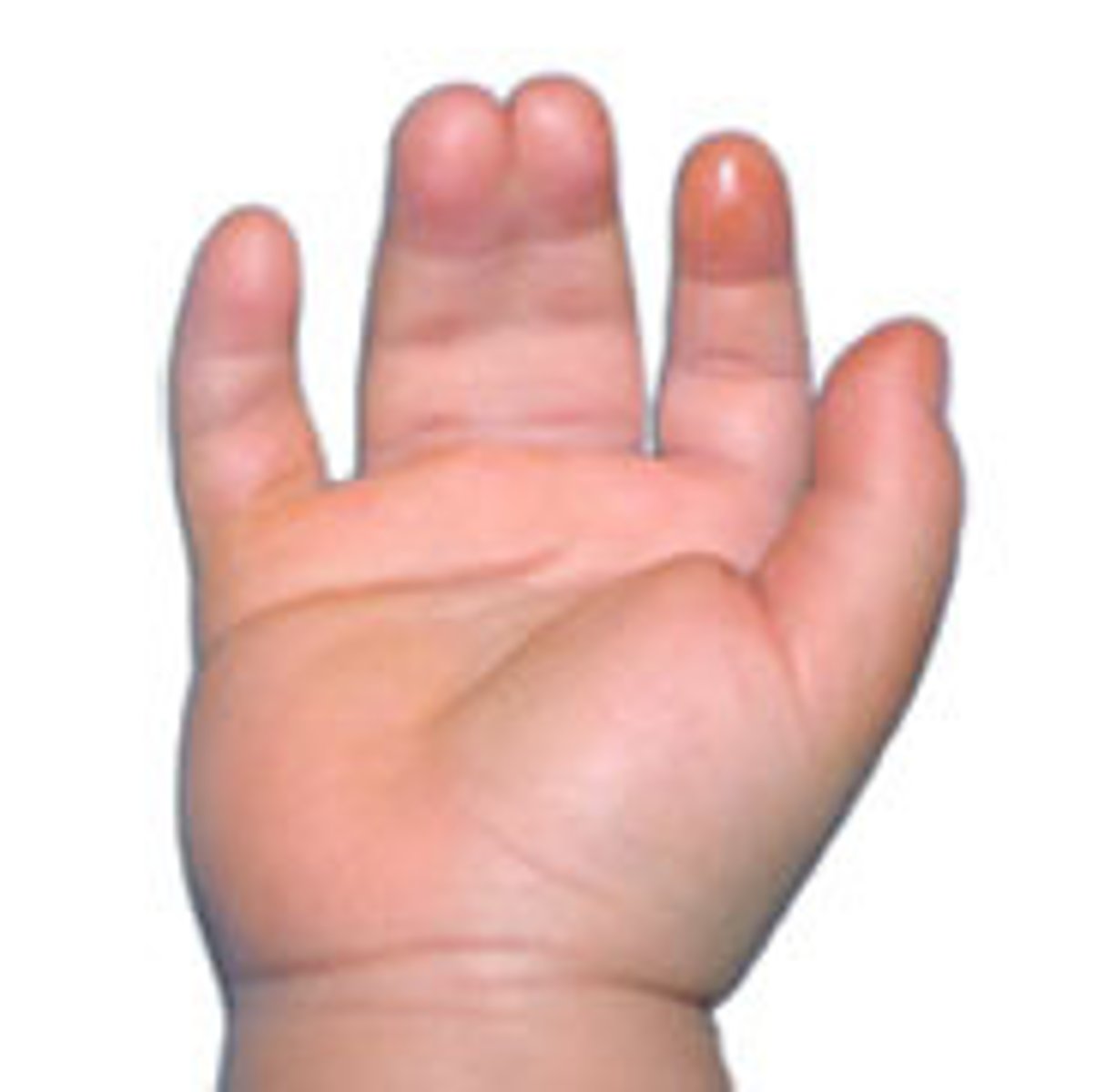
Polydactyly
extra digits
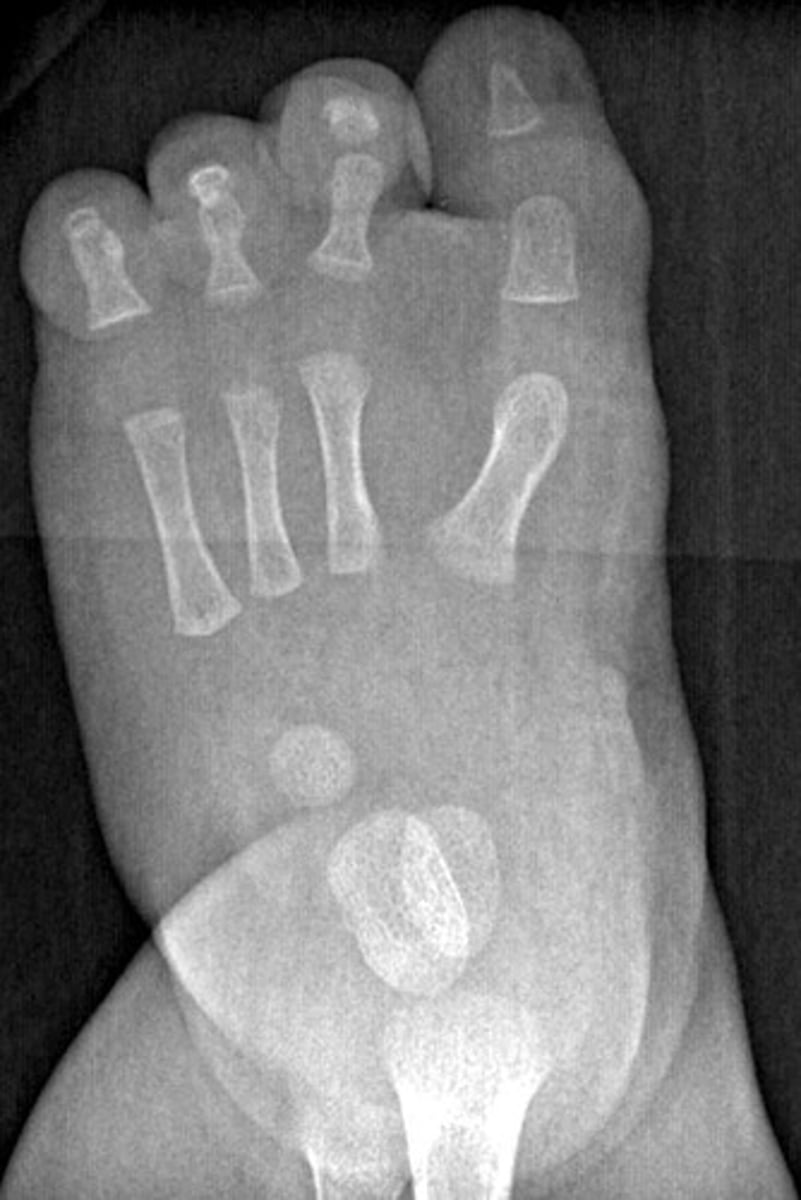
Oligodactyly
missing digits
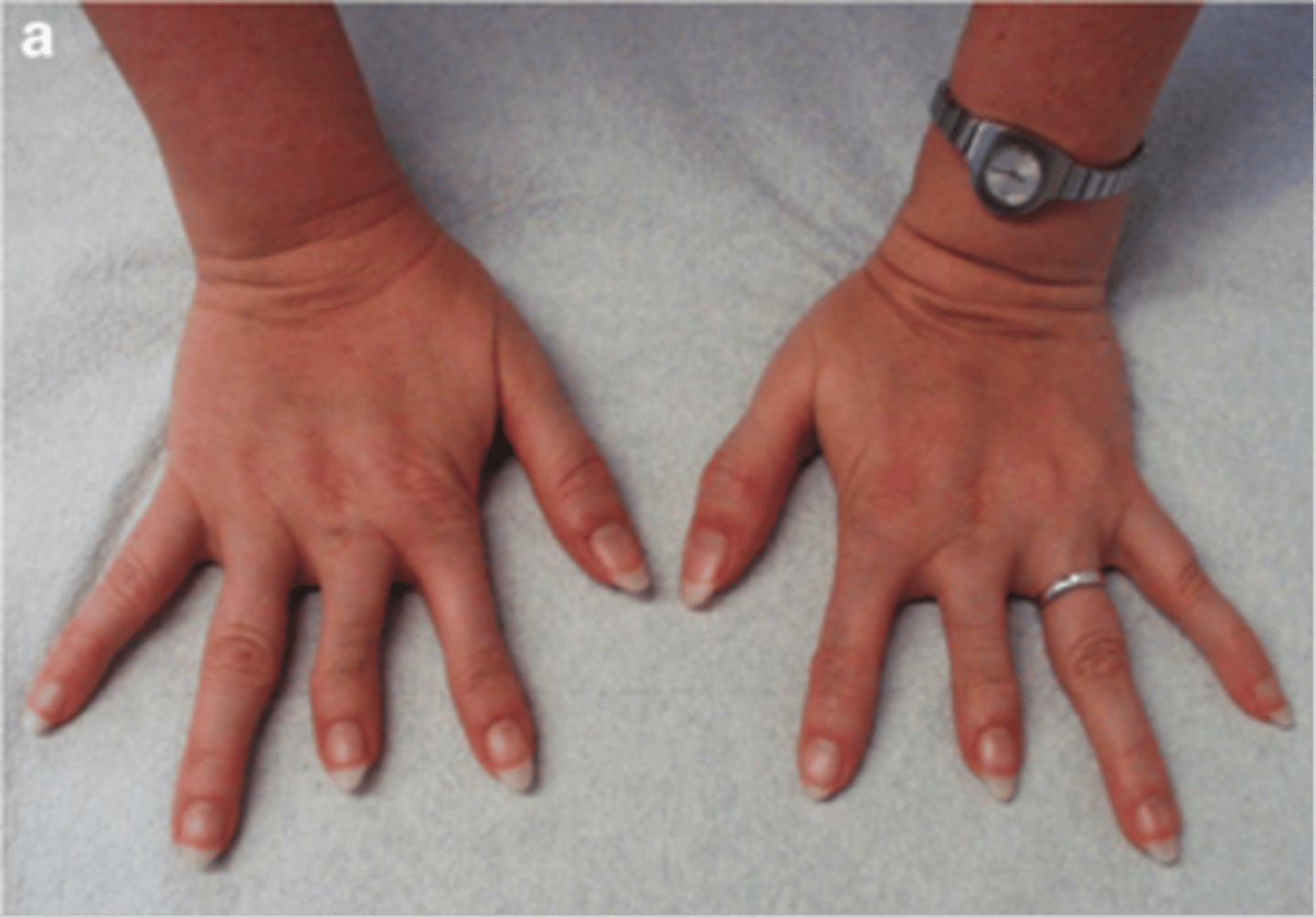
Brachydactyly
short fingers
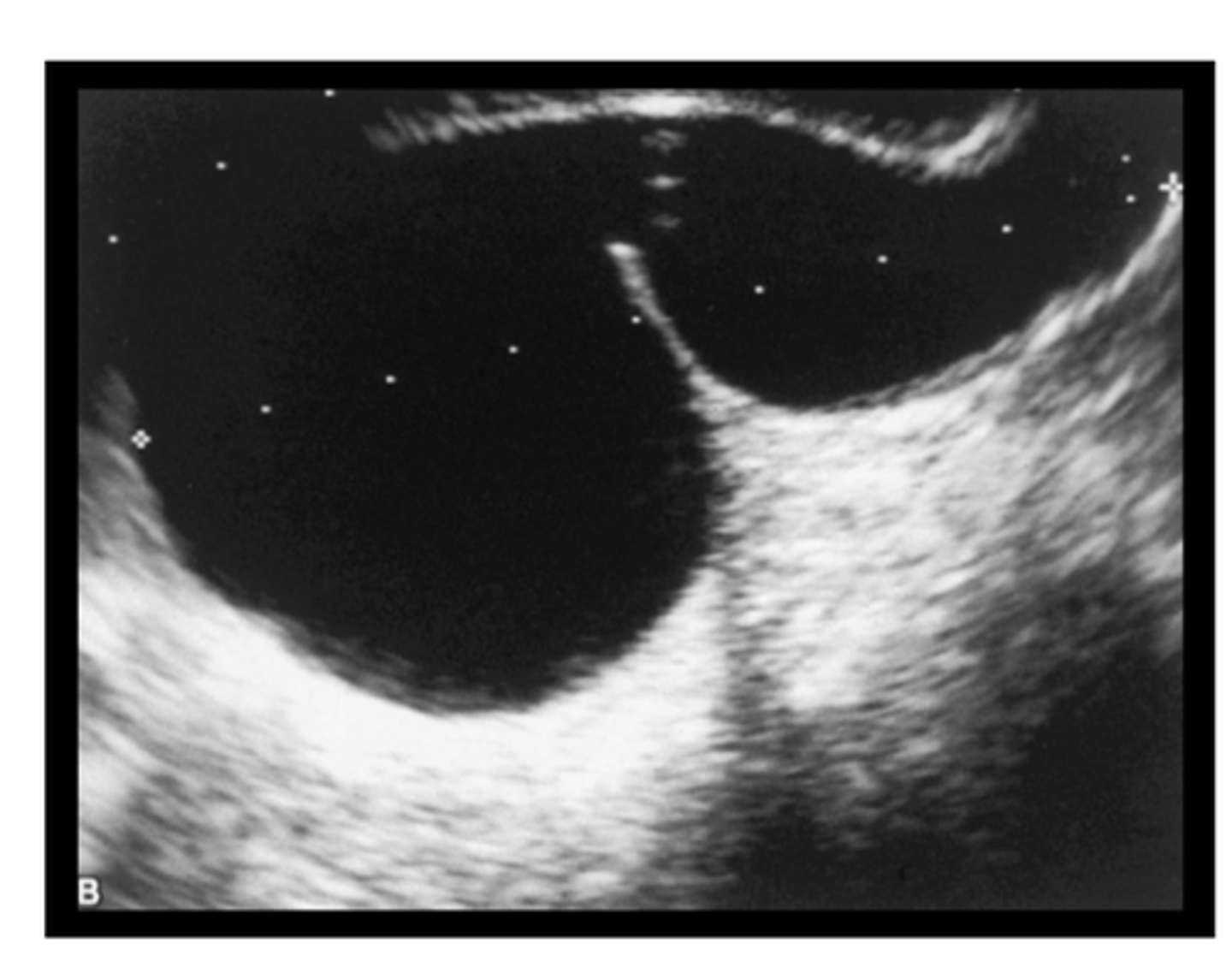
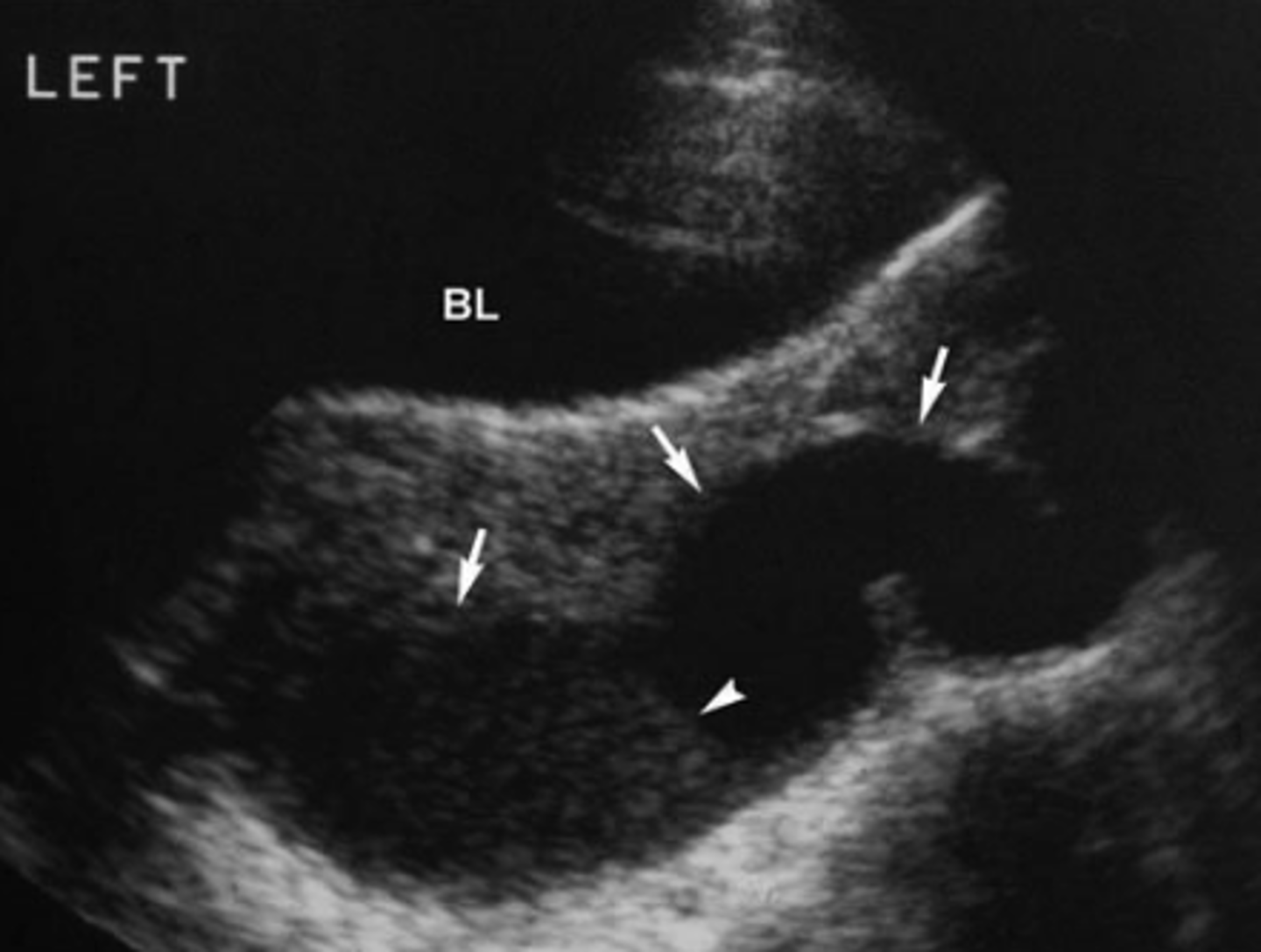
Hydrosalpinx
Anechoic tubular adnexal structure, can be chronic conditionafter recovery from PID
Hematosalpinx
Blood in FT, likely to have echoes/heterogeneous
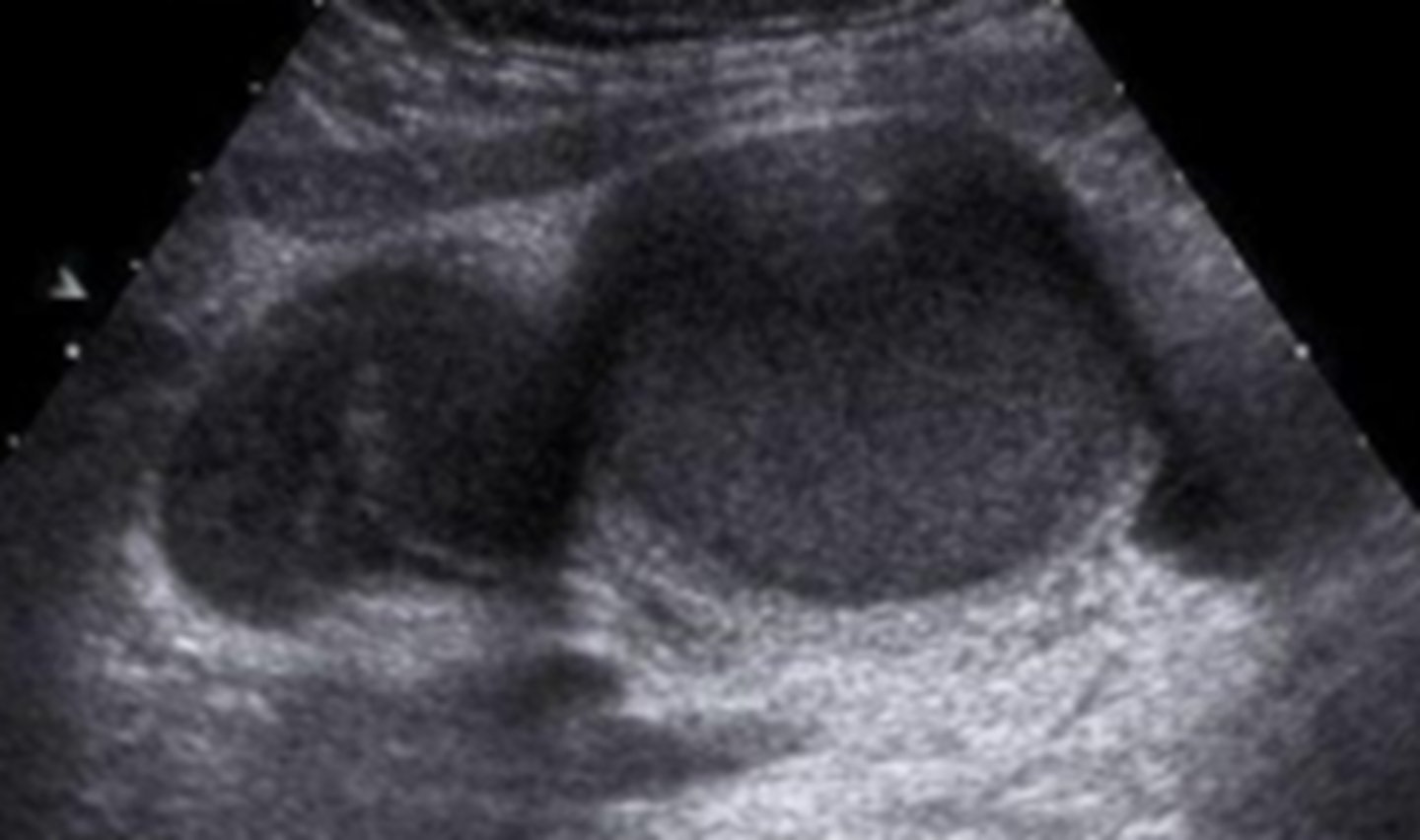
Pyosalpinx
Elevated WBC, fever, pain, may have internal echoes
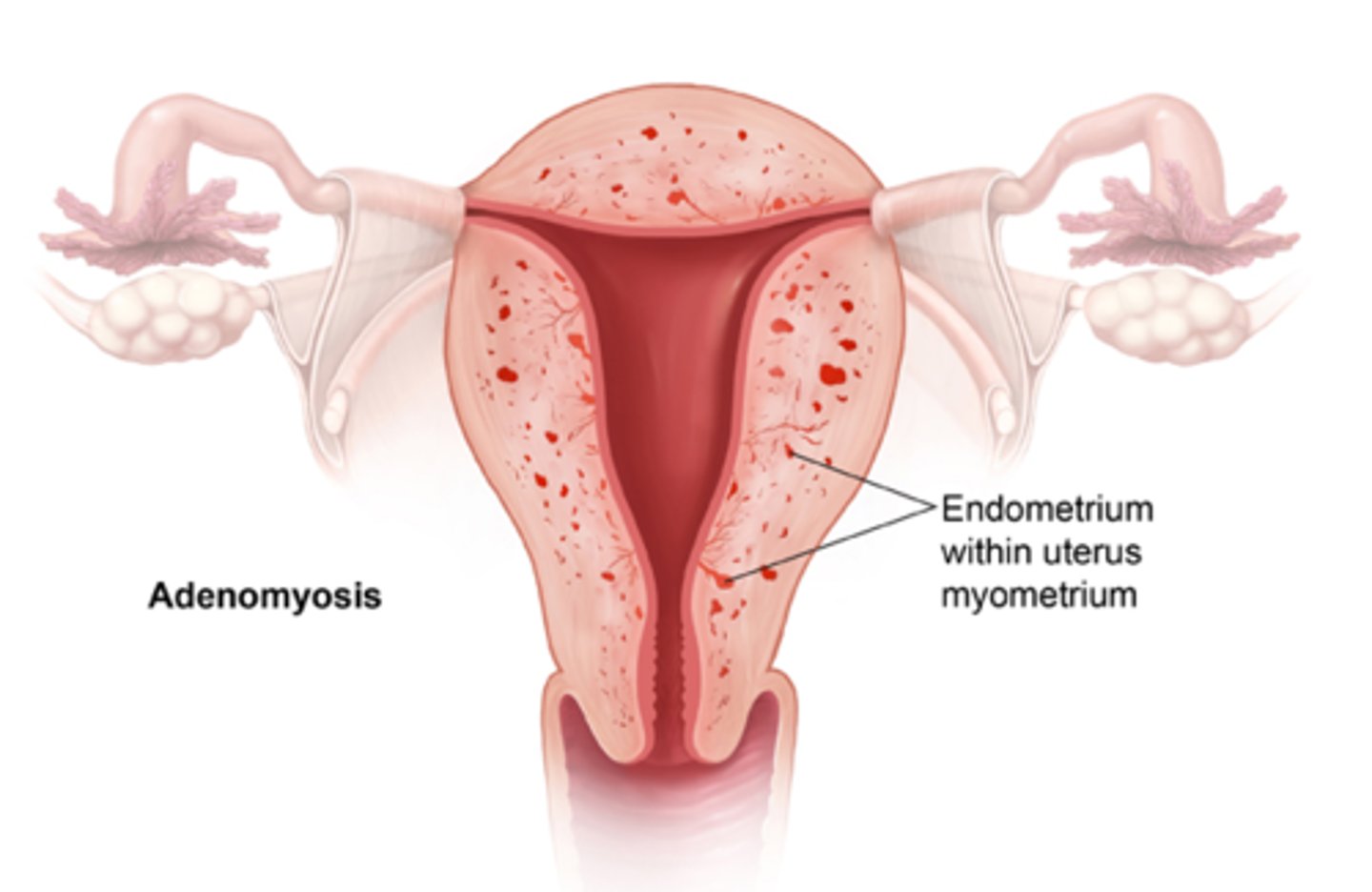
Adenomyosis
growth of endometrium into the muscular portion of the uterus
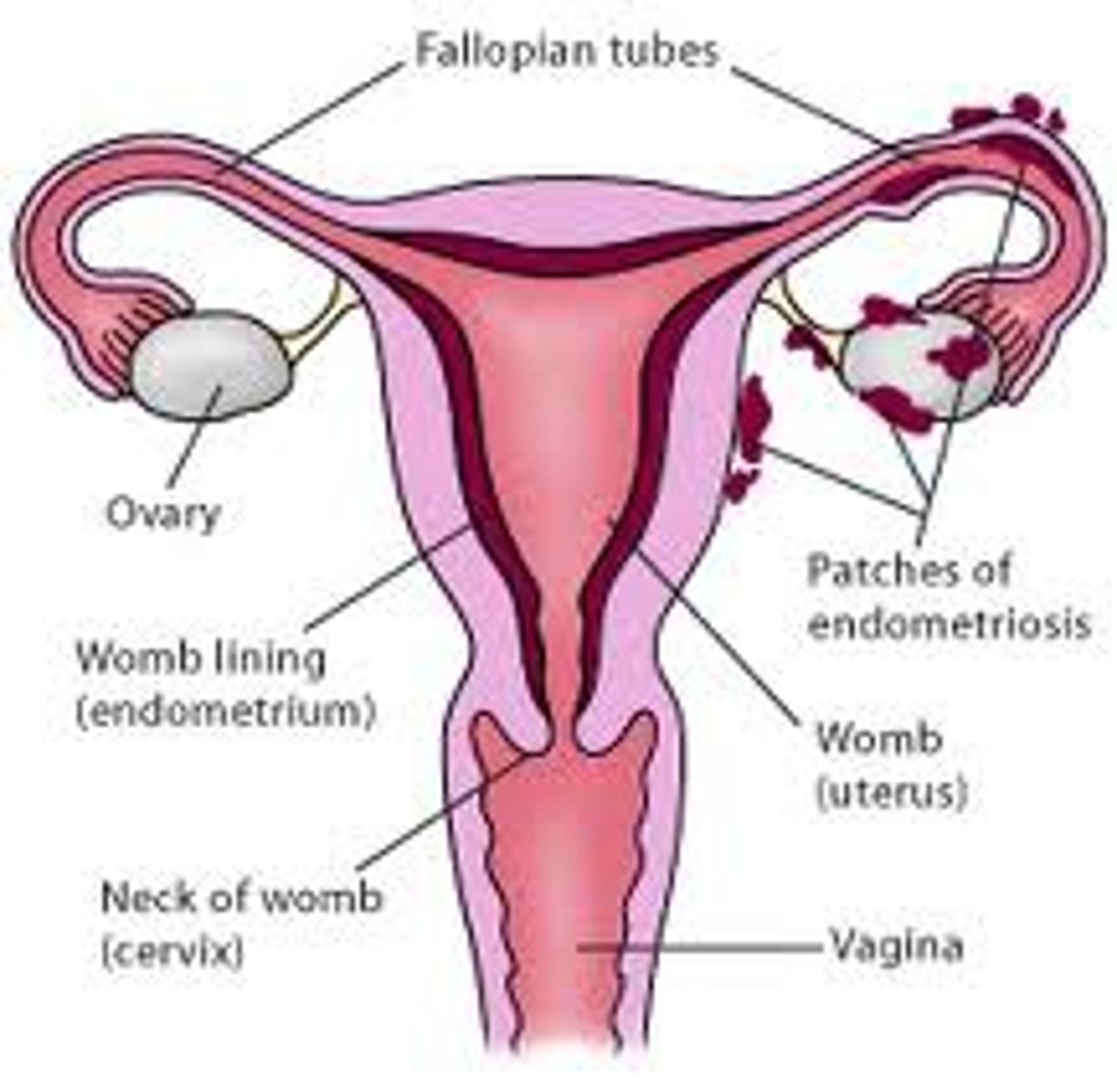
Endometriosis
endometrial tissue located outside the uterus
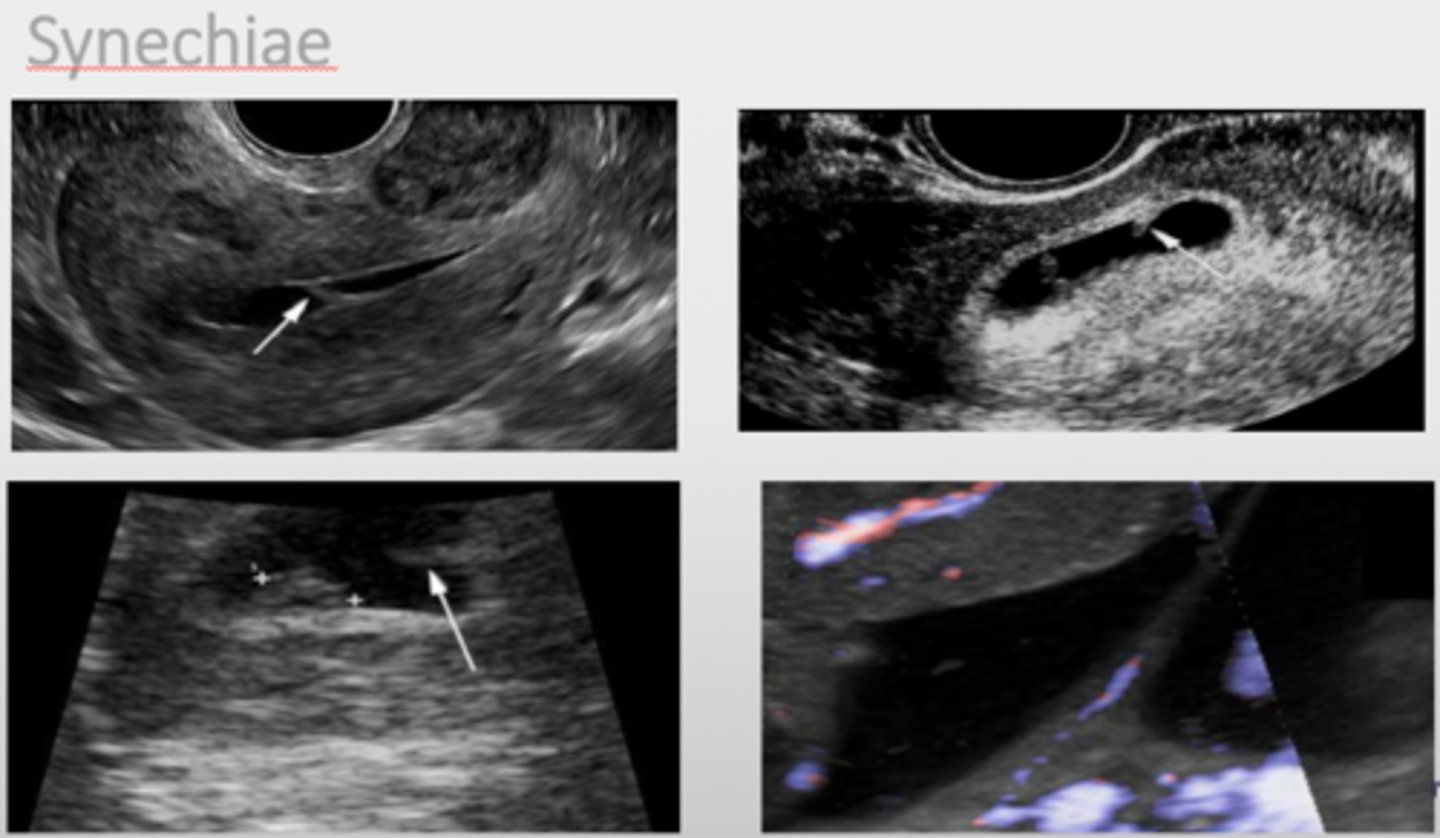
Asherman syndrome/synechiae
Adhesions of the endometrium develop as a result of trauma to the uterine lining.
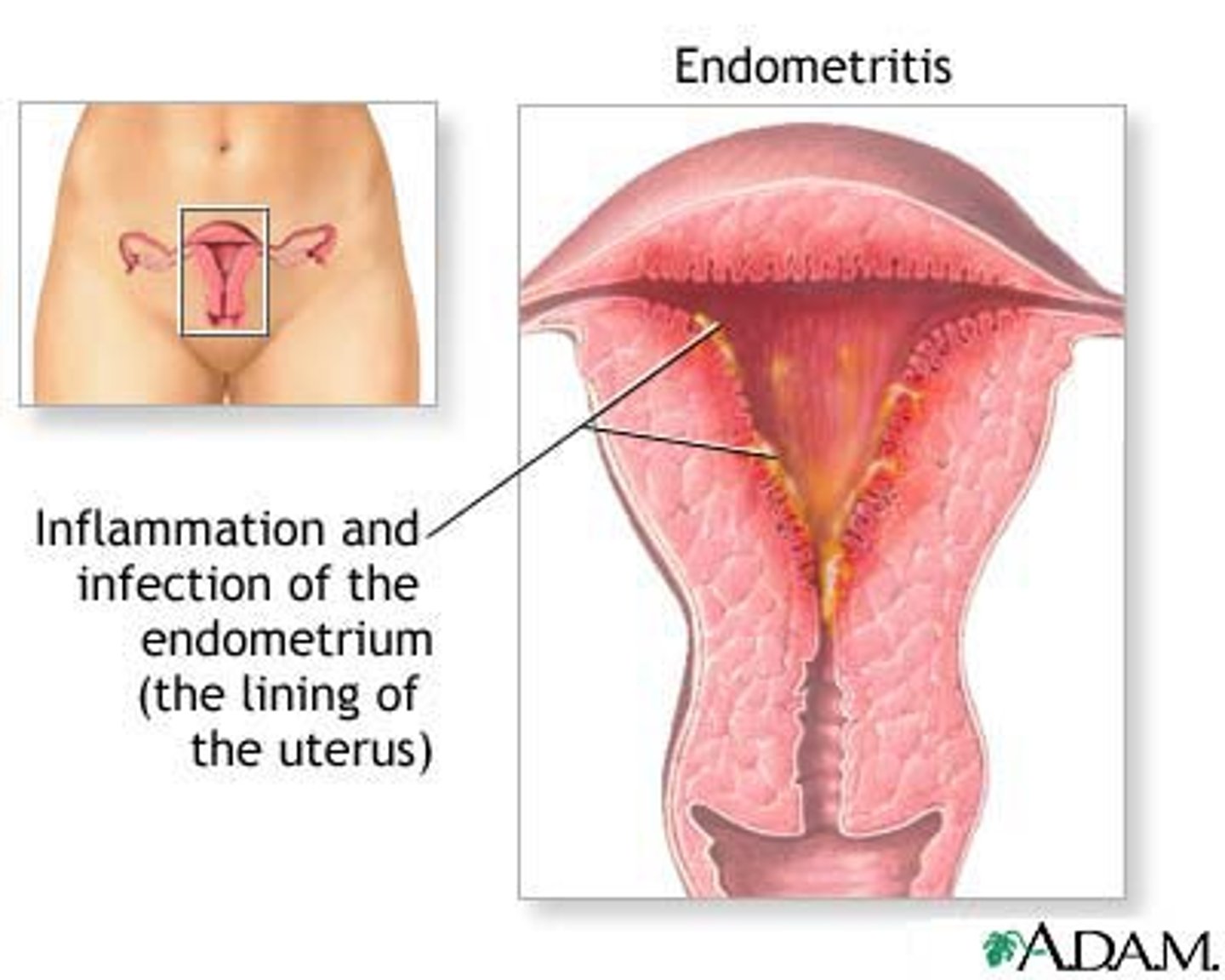
Endometritis
inflammation of the inner lining of the uterus
Trophoblastic Disease
Molar pregnancy. Larger than normal for dates,high hCG, hyperemesis, cystic/grapelike mass in endometrium, theca luteincysts
Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART)
Hormones can cause ovarianhyperstimulation syndrome/theca lutein cysts
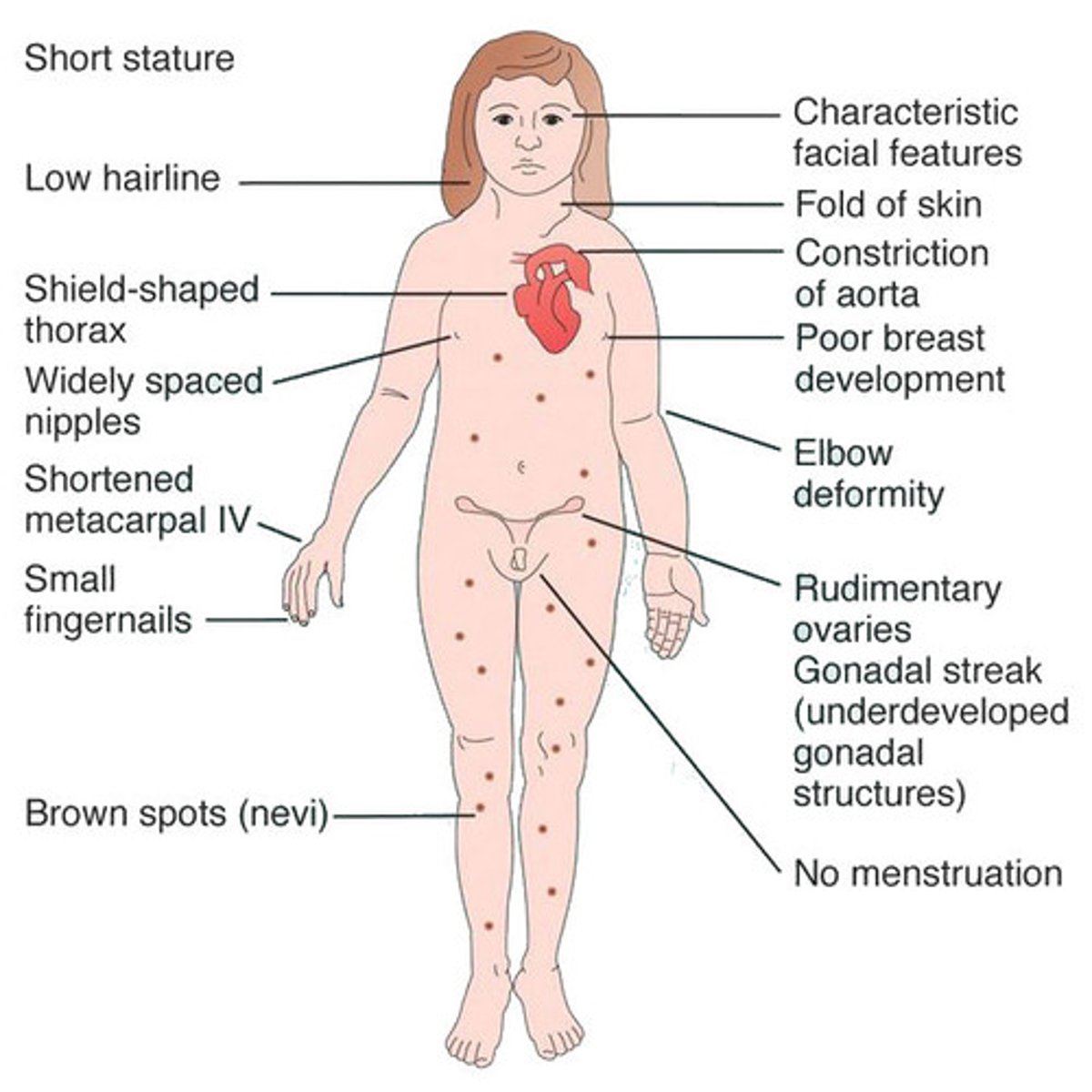
Turner syndrome
Missing "X" chromosome, 45 X0. Cystic hygroma, shortstature, short, webbed neck, non-immune hydrops, ovarian dysgenesis,nevi
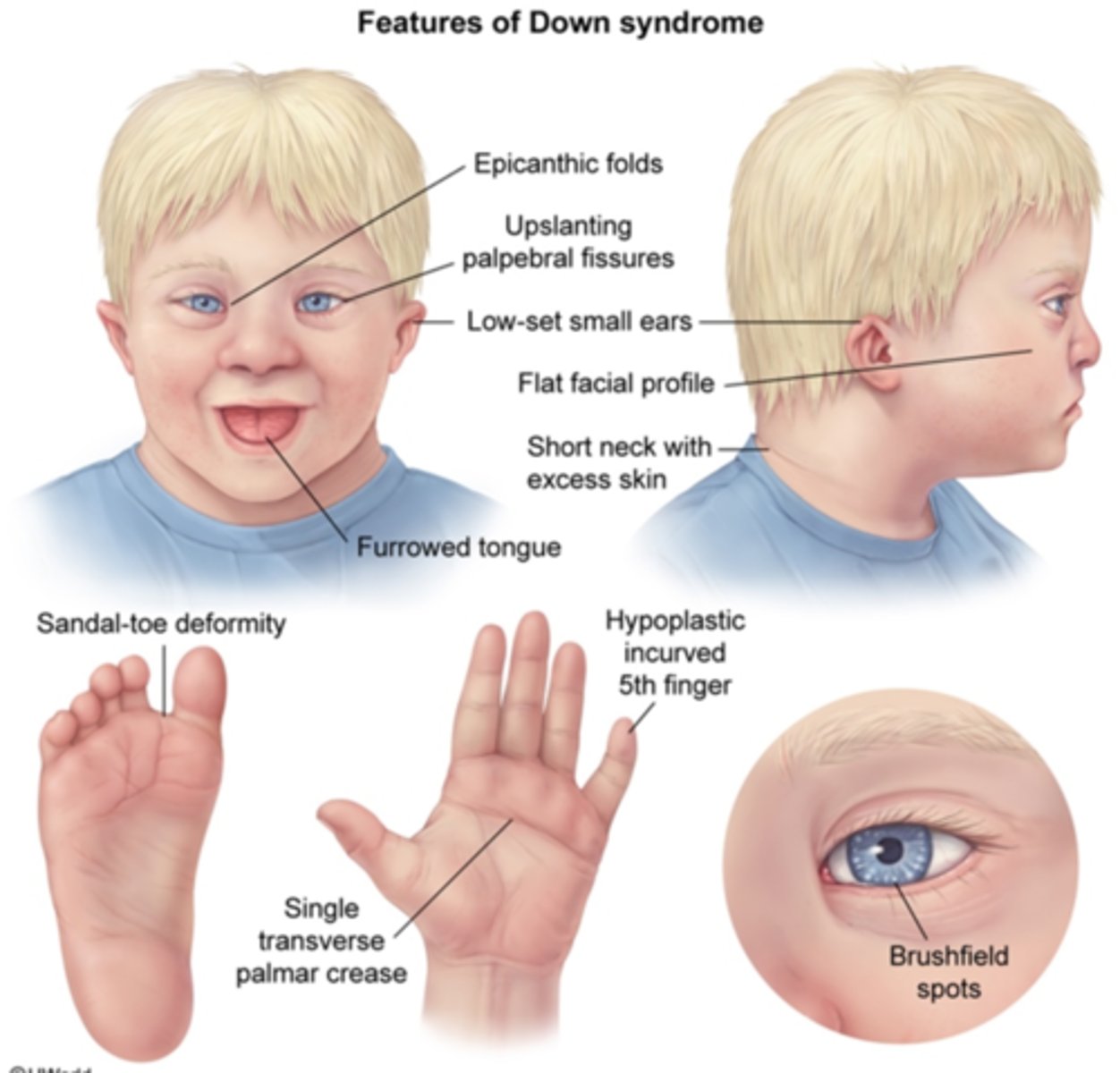
Down/Trisomy 21
Echogenic bowel, thickened nuchal fold, short or absentnasal bone, heart defects, duodenal atresia. High hCG, low AFP, Estriol,PAPP A
Trisomy 13/Patau:
Holoprosencephaly, ethmocephaly, cyclopia, cleftpalate, small head, low-set ears, heart defects
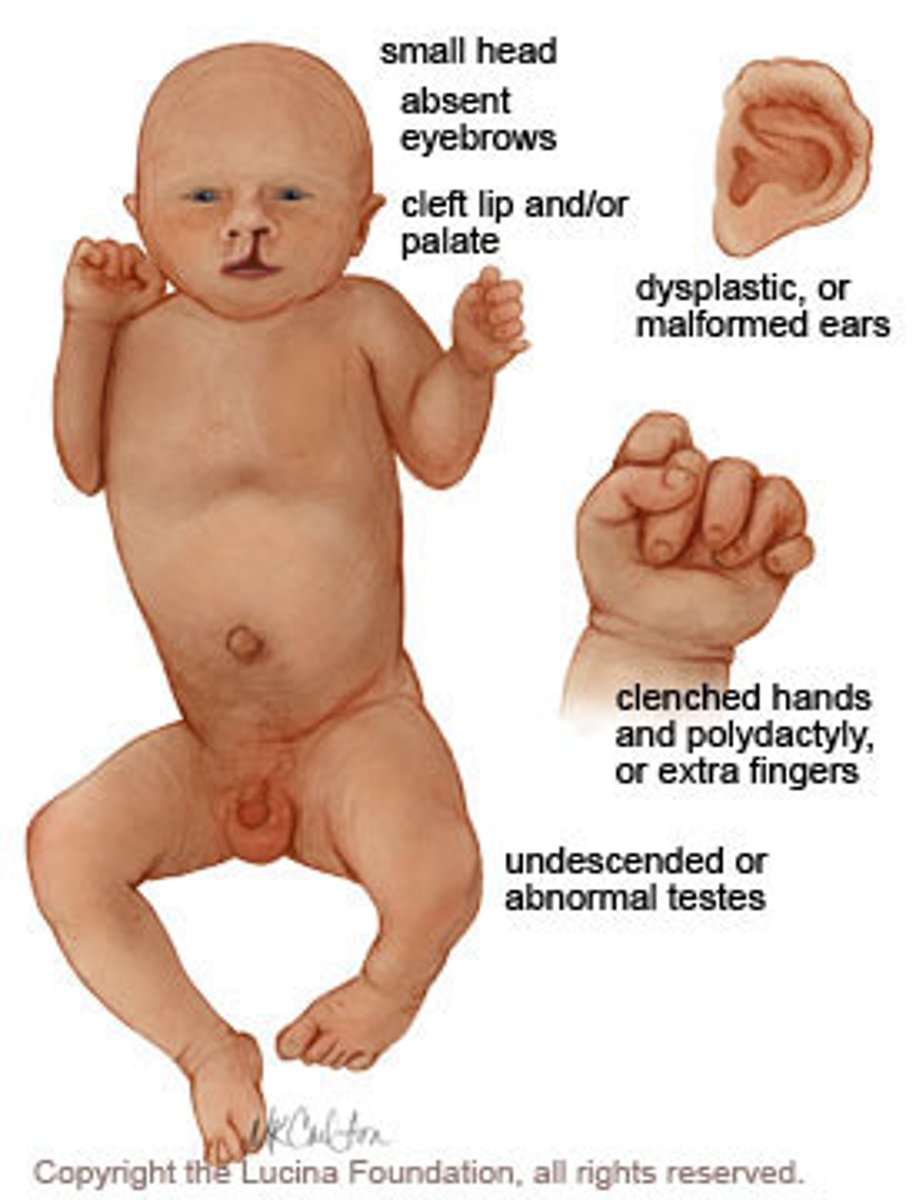
Trisomy 18/Edward
Micrognathia, choroid plexus cysts, rocker bottom feet,omphalocele, clenched hands, low-set ears, heart/lung abnormalities
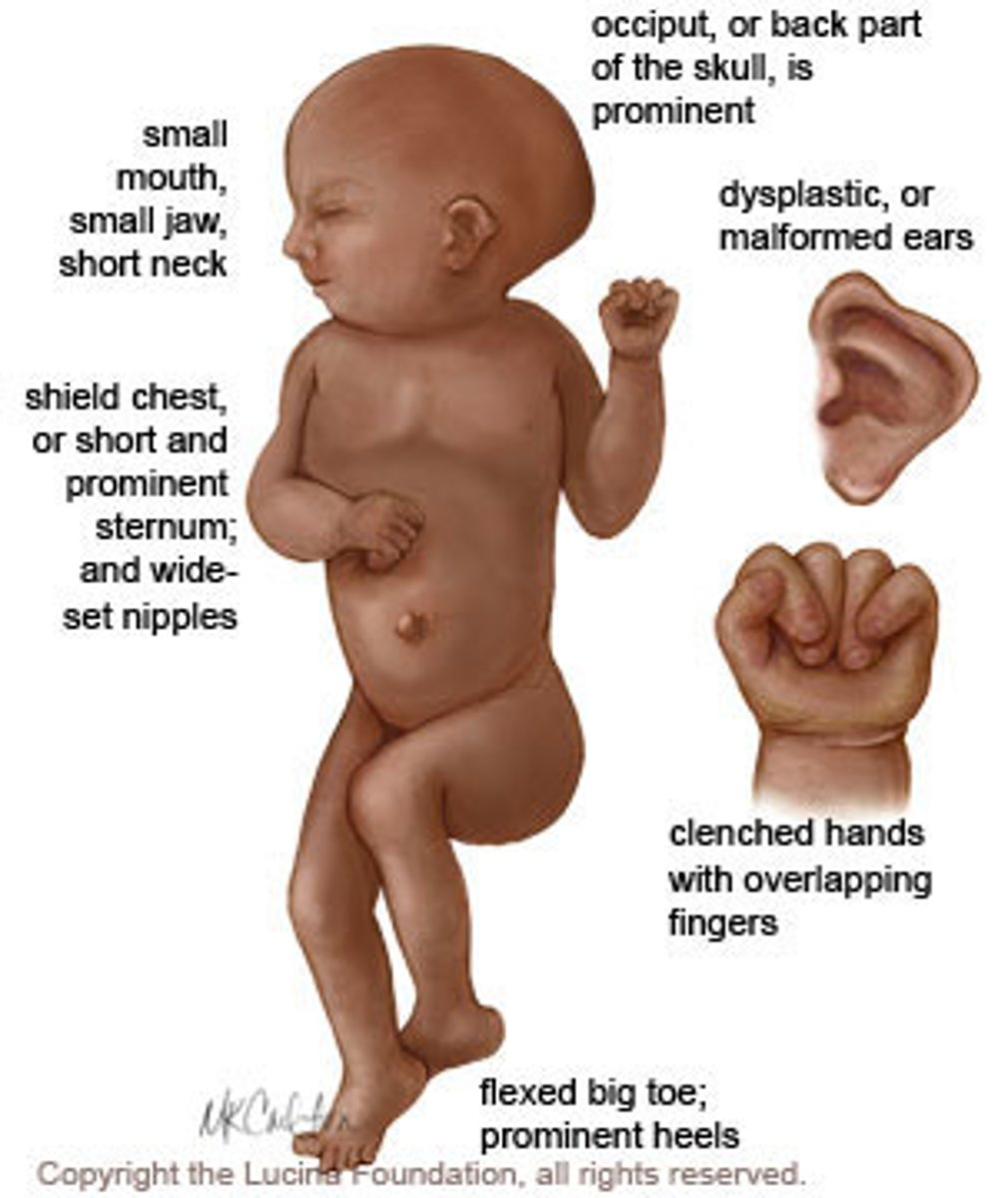
Triploidy
Assoc w/molar pregnancy. Often lethal. Omphalocele, low-setears, IUGR, oligohydramnios, enlarged placenta, heart, GI/GU, CNS,cardiac, facial
Cystic Fibrosis
Echogenic bowel, problems with digestion and lungs due tomucus
Dandy Walker
absence or dysplasia of cerebellar vermis, splayedcerebellum, high-riding 4th ventricle
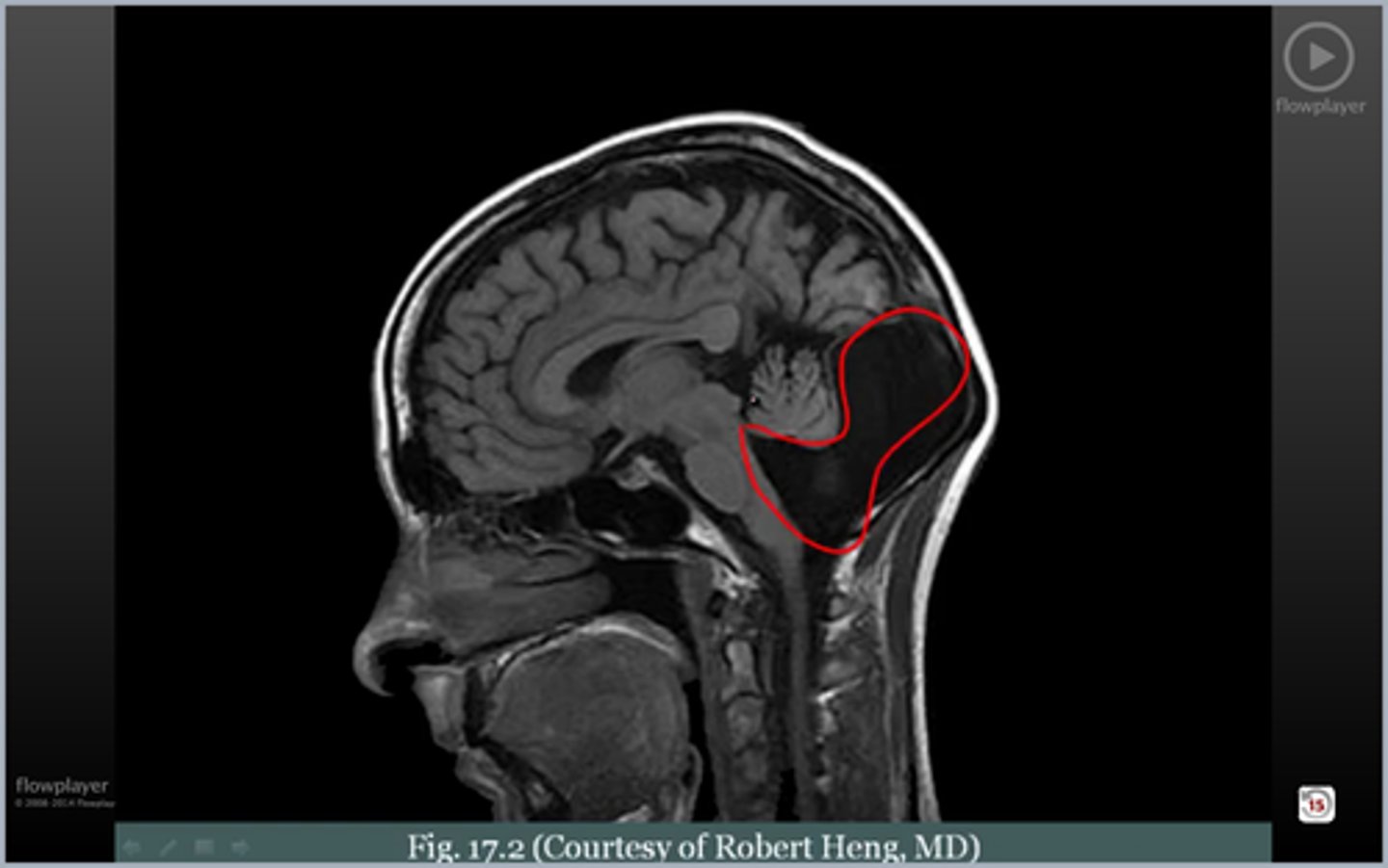
Agenesis of the CC
Absent CSP. Enlarged 3rd ventricle
Hydrocephalus
Excess CSF in brain, lateral ventricles >15 mm, causeshead enlargement. Can be caused by spina bifida and other neural tubedefects, in utero infections
Posterior urethral valves
Males. Keyhole sign, megacystis, bilateralhydroureter, hydronephrosis
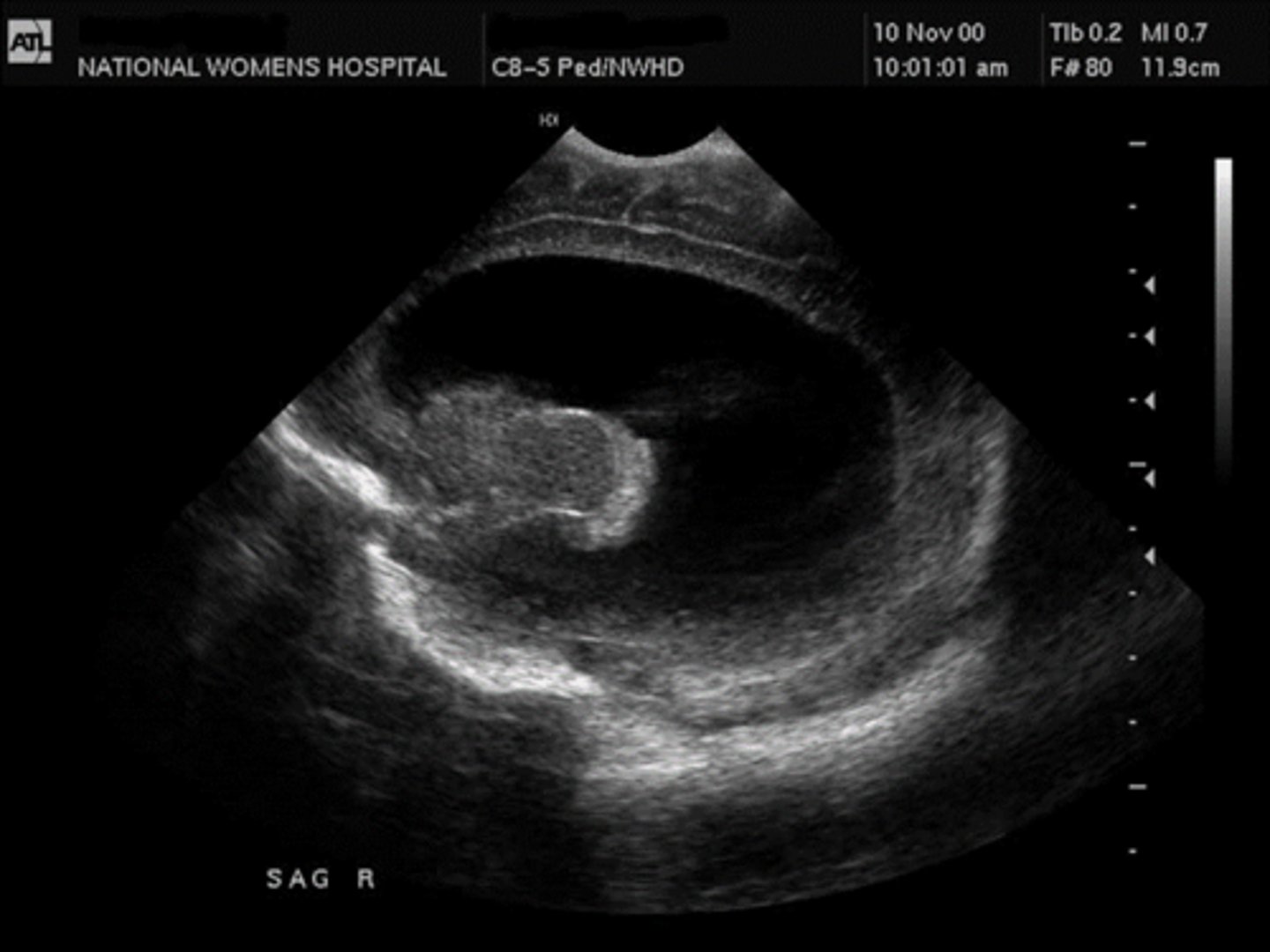
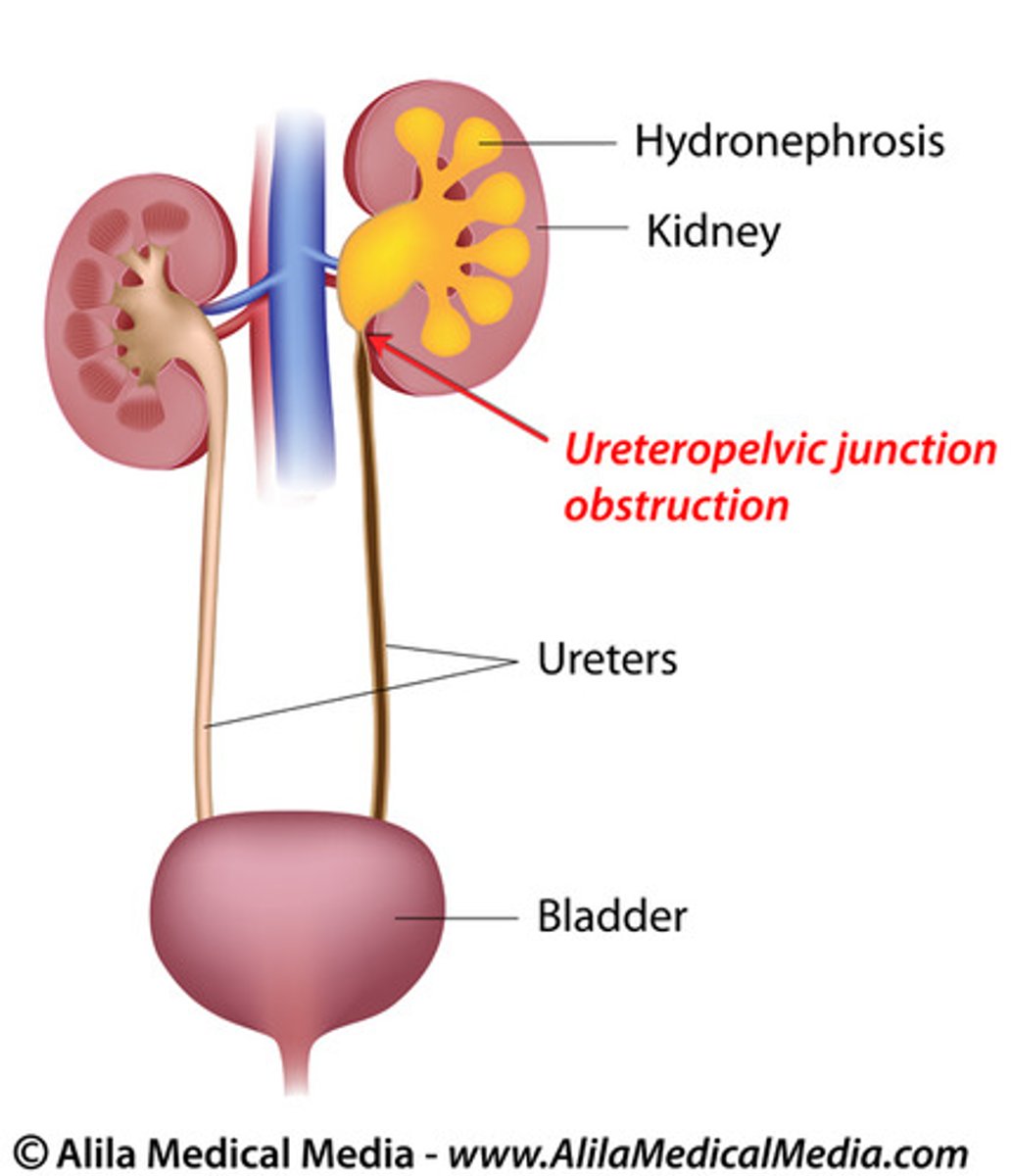
UPJ Obstruction
Unilateral, hydronephrosis, most common obstruction location
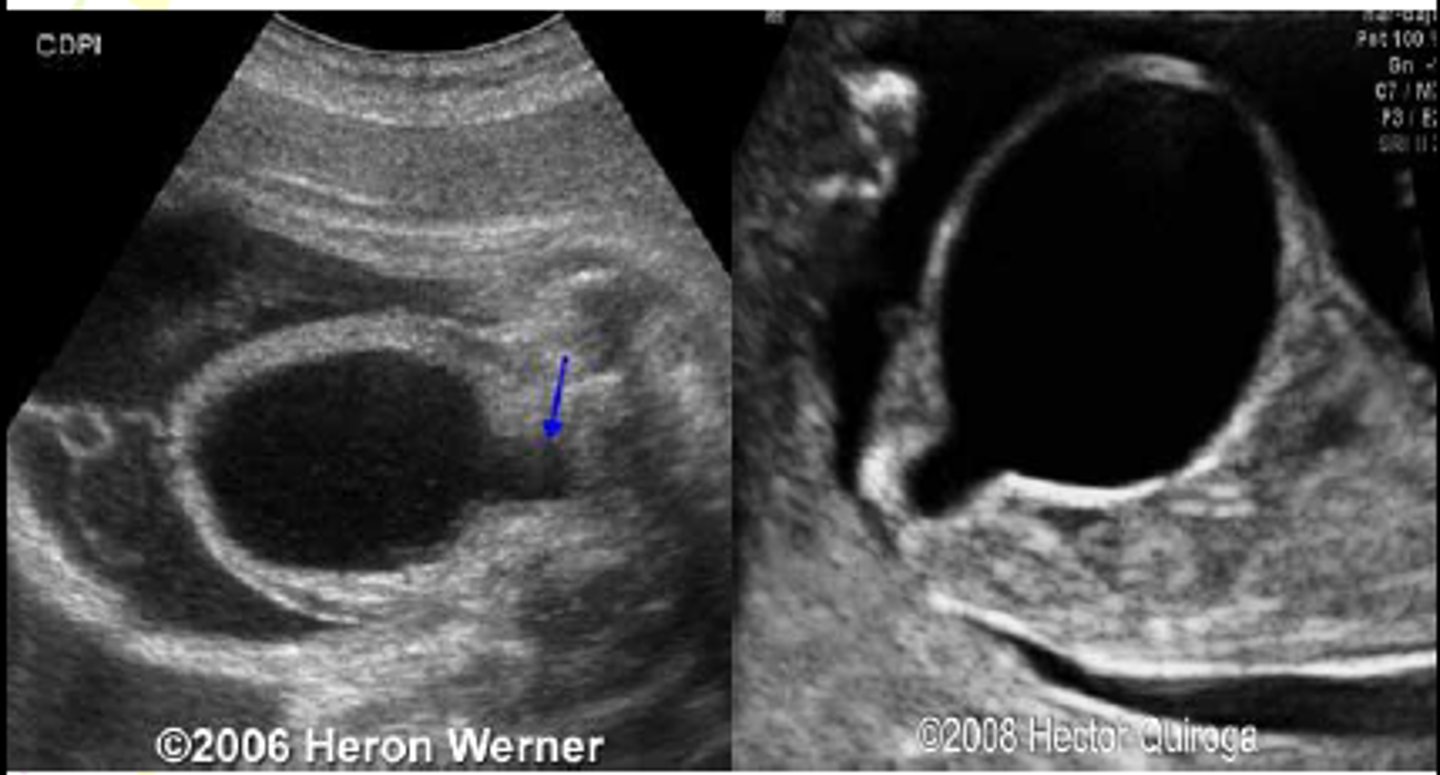
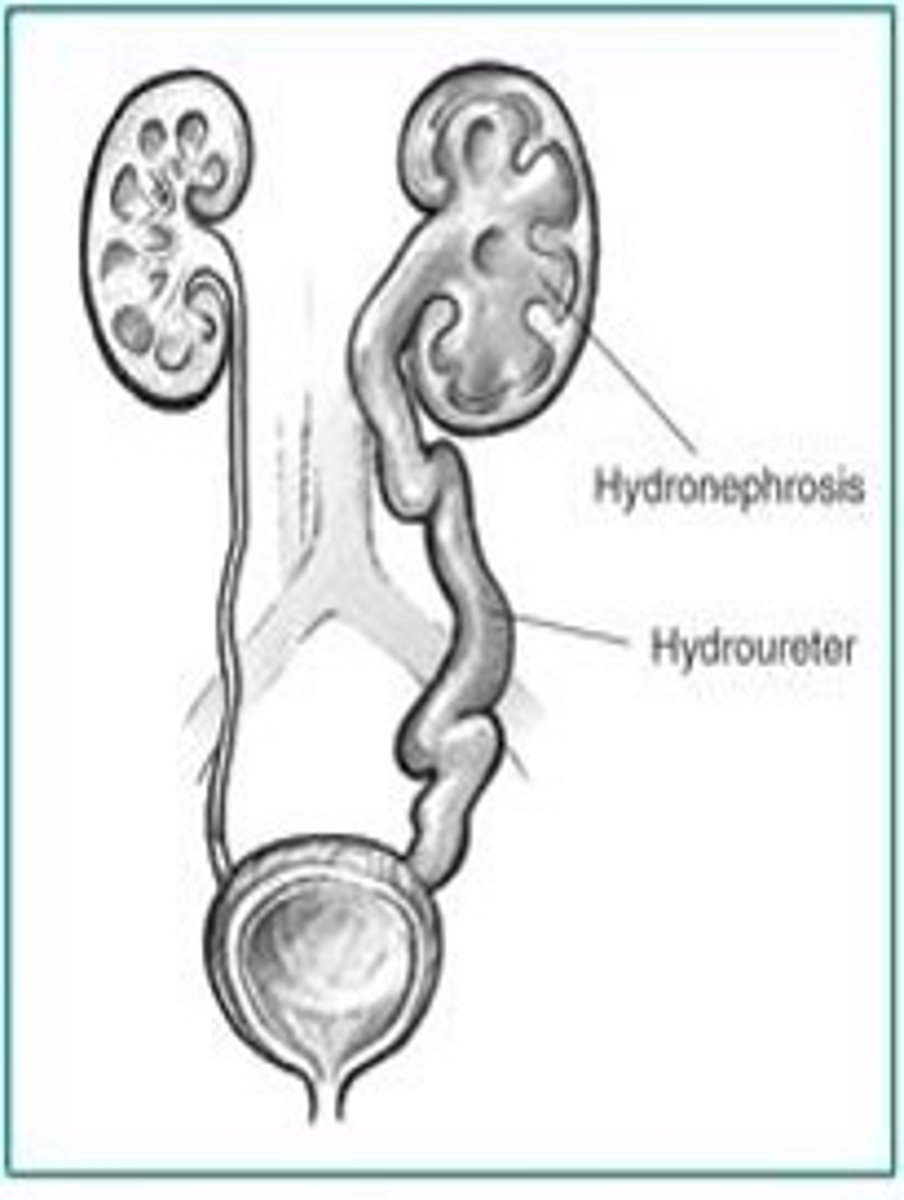
UVJ Obstruction
Unilateral, hydroureter, hydronephrosis
urethral obstruction
Megacystis, bilateral hydroureter, hydronephrosis
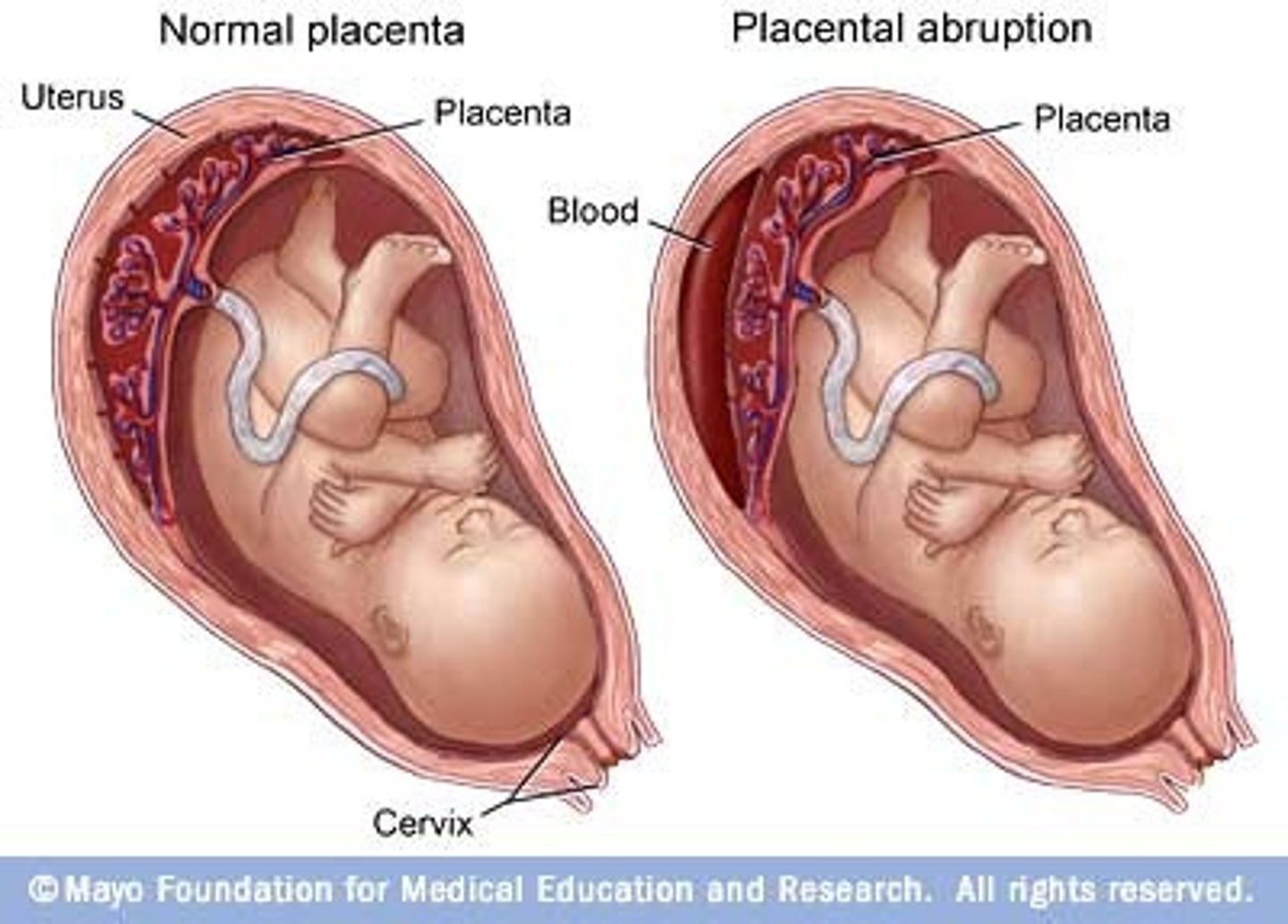
placental abruption
Serious and urgent condition due to bleeding/damageto placenta. May necessitate immediate delivery
What is the most common gynecological malignancy?
Endometrial carcinoma.
What is Meigs syndrome?
A condition associated with fibromas, less often with granulosa cell tumors, characterized by ovarian tumor, ascites, and pleural effusion.
Benign tumors
fibroma, thecoma (estrogen), cystic teratoma (mostcommon), cystadenoma
Malignant tumors
choriocarcinoma, dysgerminoma, yolk sac, cystadenocarcinoma, granulosa cell (estrogen)
Malignant neoplasm flow
low resistance (high diastolic flow)
truncus arteriosus
Aorta and pulmonary trunk are one great vessel instead of 2 separate
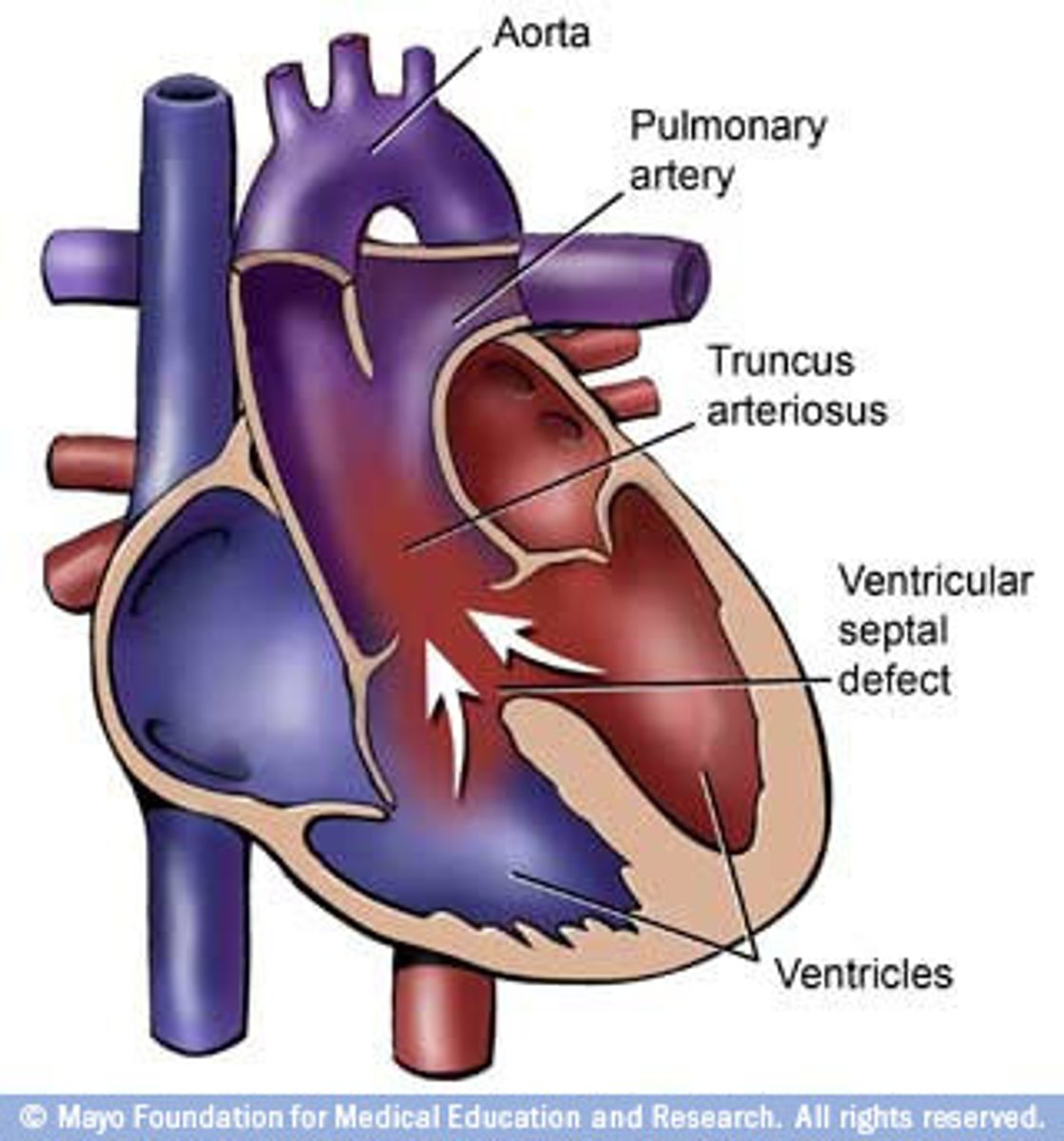
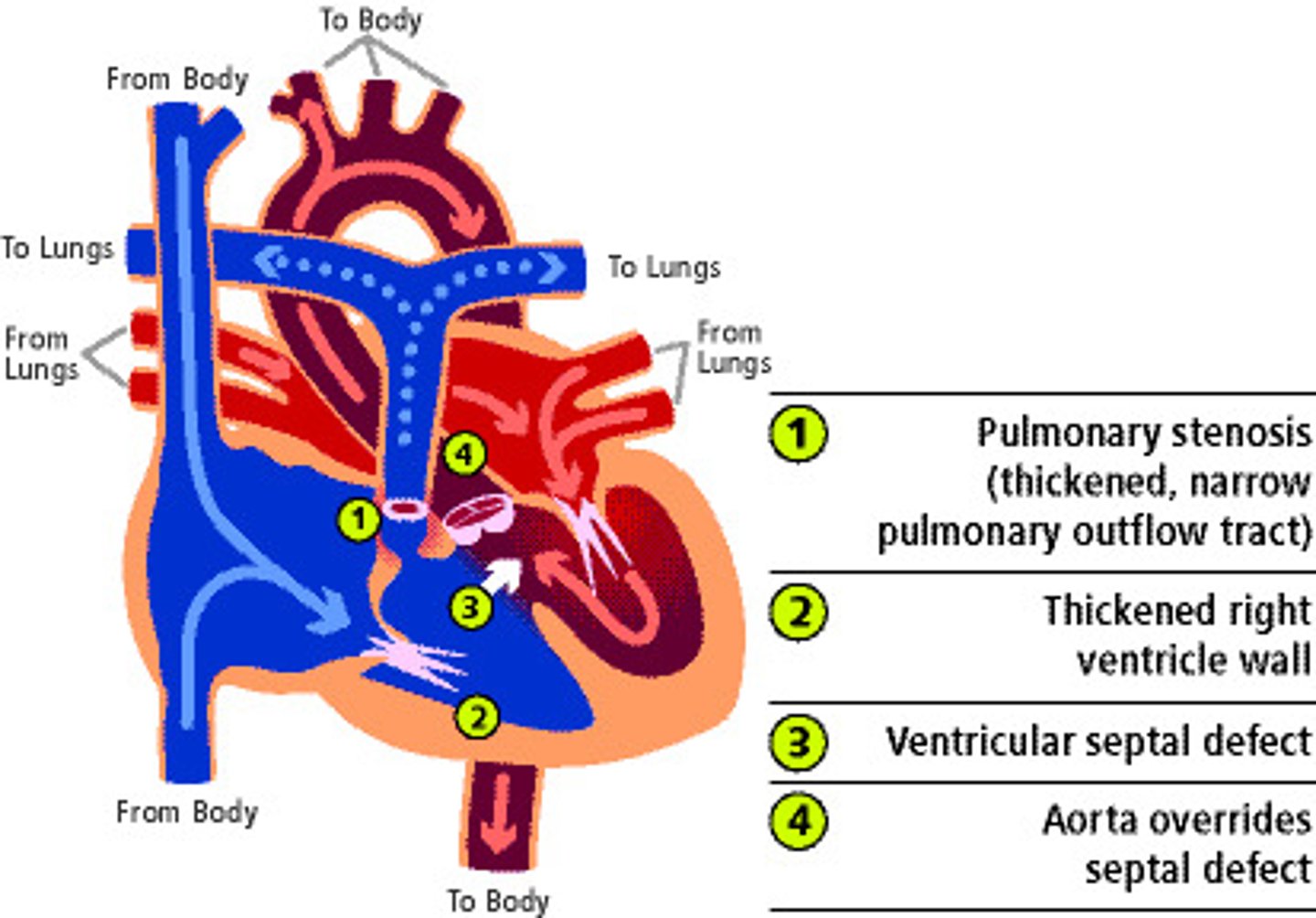
tetralogy of fallot
congenital malformation involving four distinct heart defects (pulmonary stenosis, rt ventricular hypertrophy, VSD, overriding aorta)
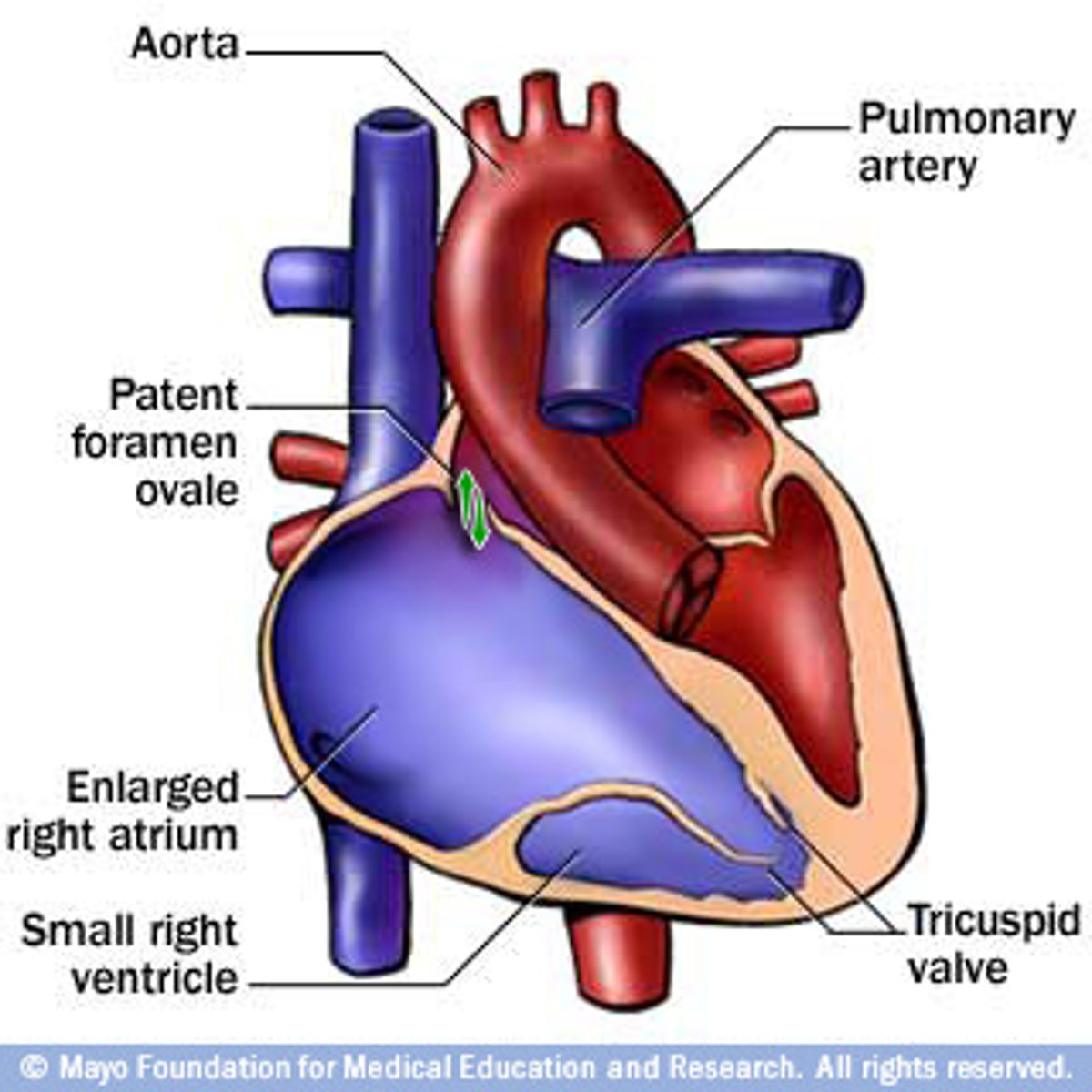
Ebstein's anomaly
Tricuspid flaps fused to inside of right ventricle; creates constant opening between atrium & ventricle
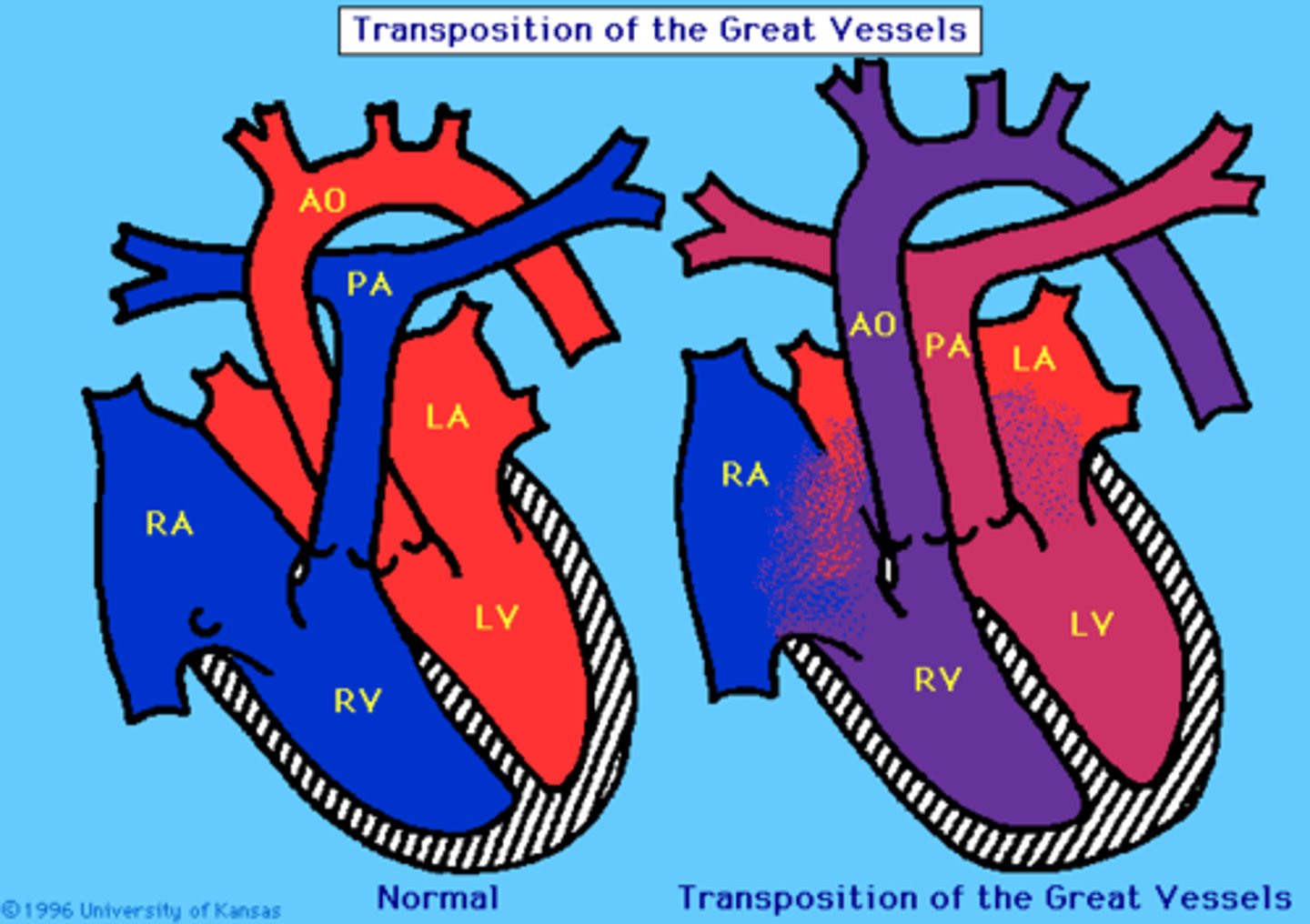
Transposition of great arteries
Aorta and pulmonary artery are switched.
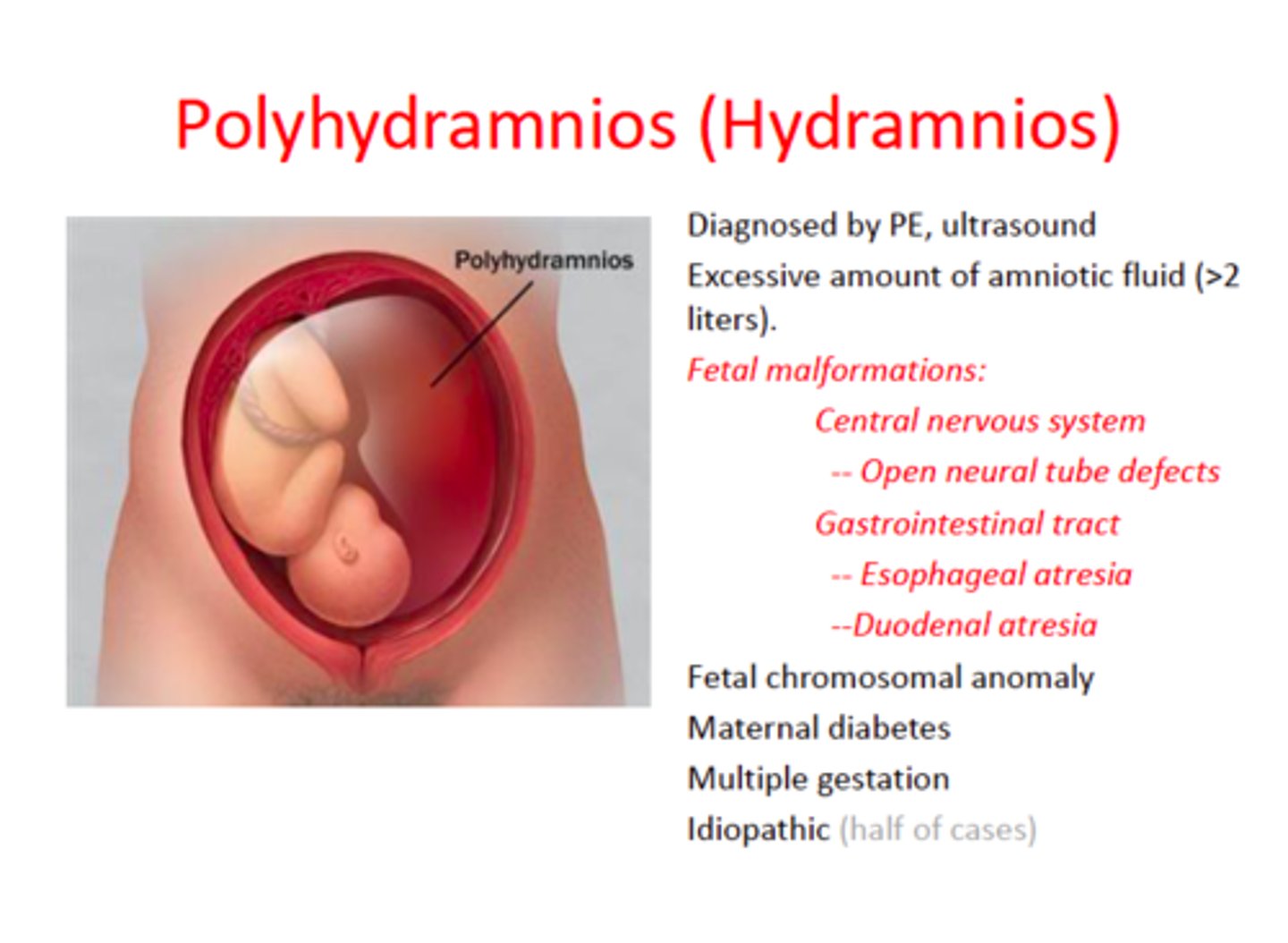
What can signify polyhydramnios?
Inability to swallow due to digestive anomalies, maternal diabetes, and twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS).
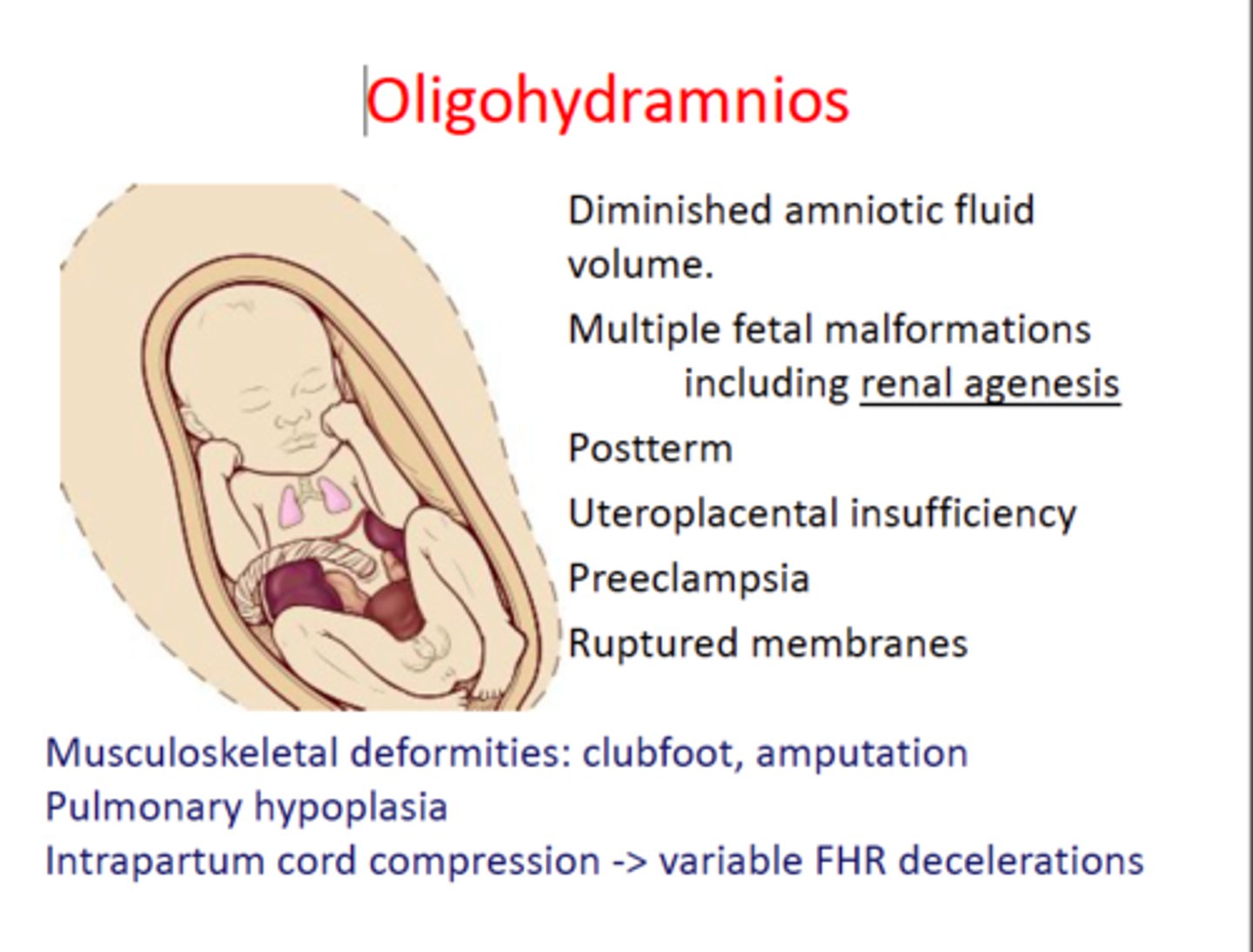
What can oligohydramnios signify?
Renal failure/agenesis, urinary tract obstruction, and placental insufficiency.
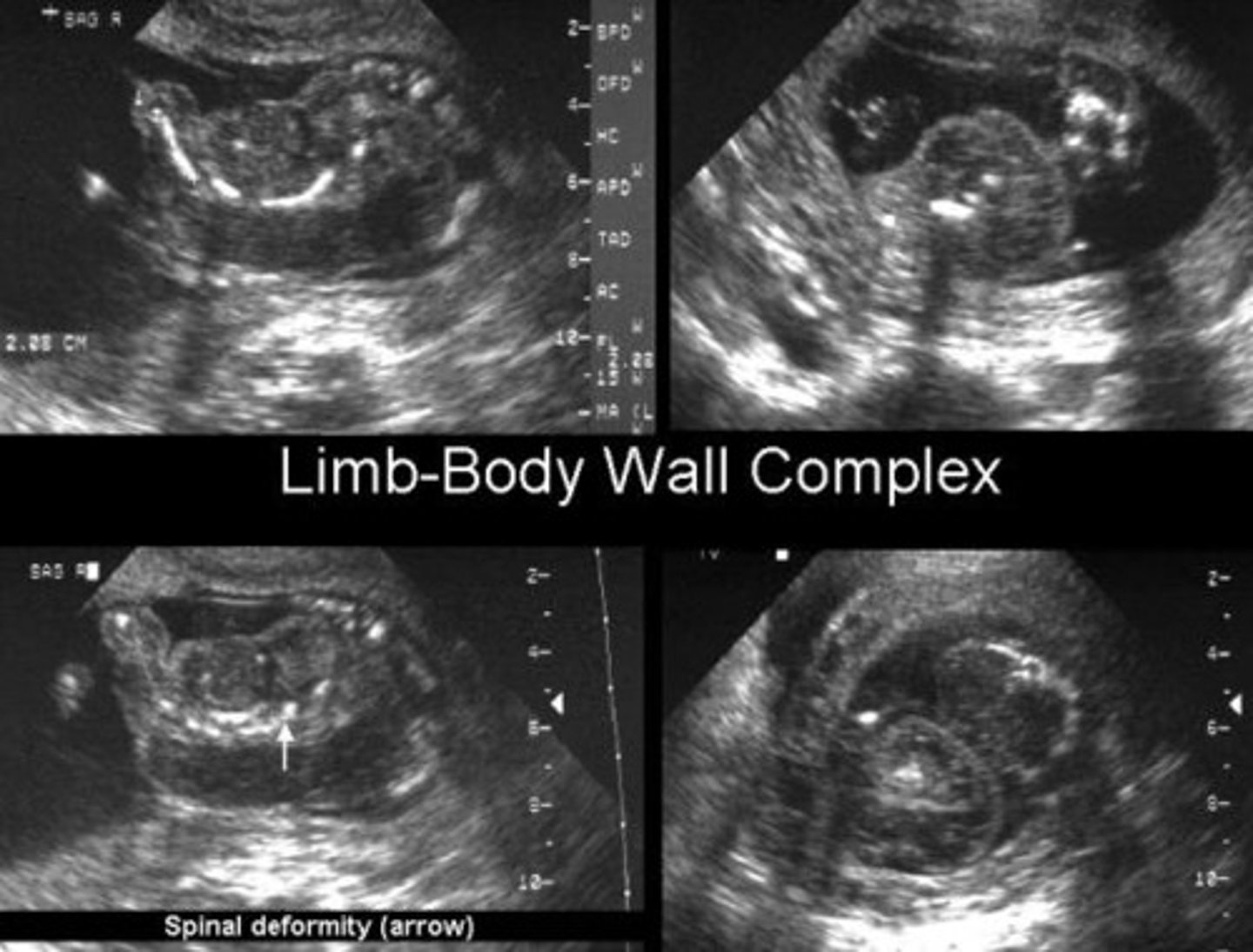
Body stalk anomaly
The most severe form of limb-body wall complex, where organs are outside the body and attached directly to the placenta.
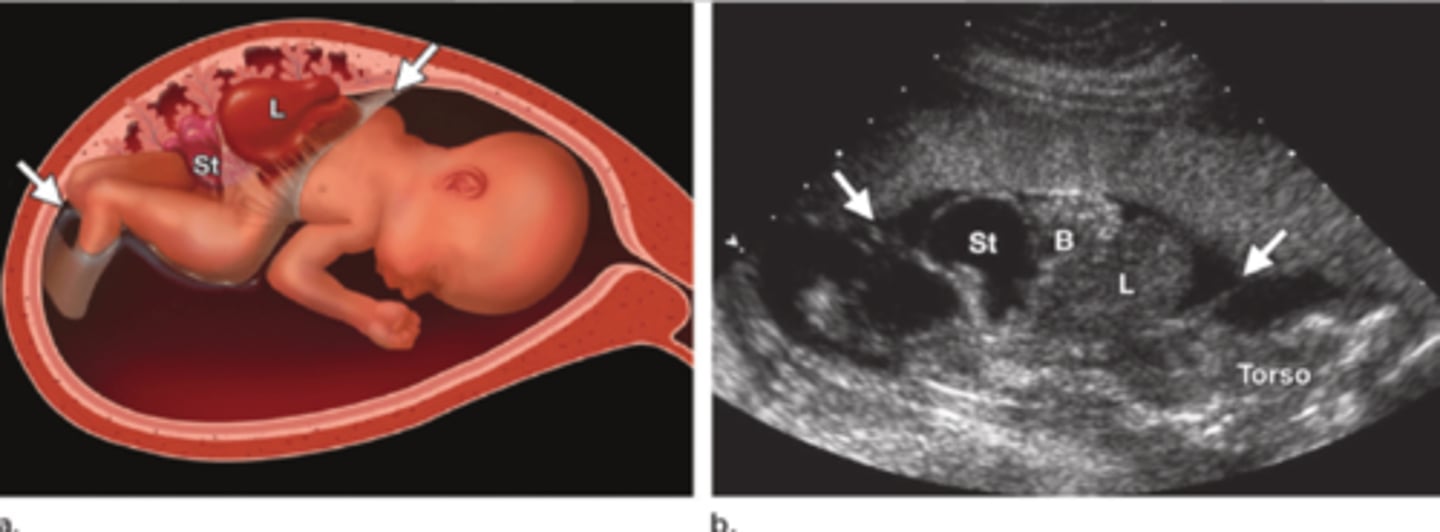
Limb body- wall complex
Thoracoschisis, abdominoschisis, limbdeformities, craniofacial defects, spinal anomalies/scoliosis, urogenitalabnormalities
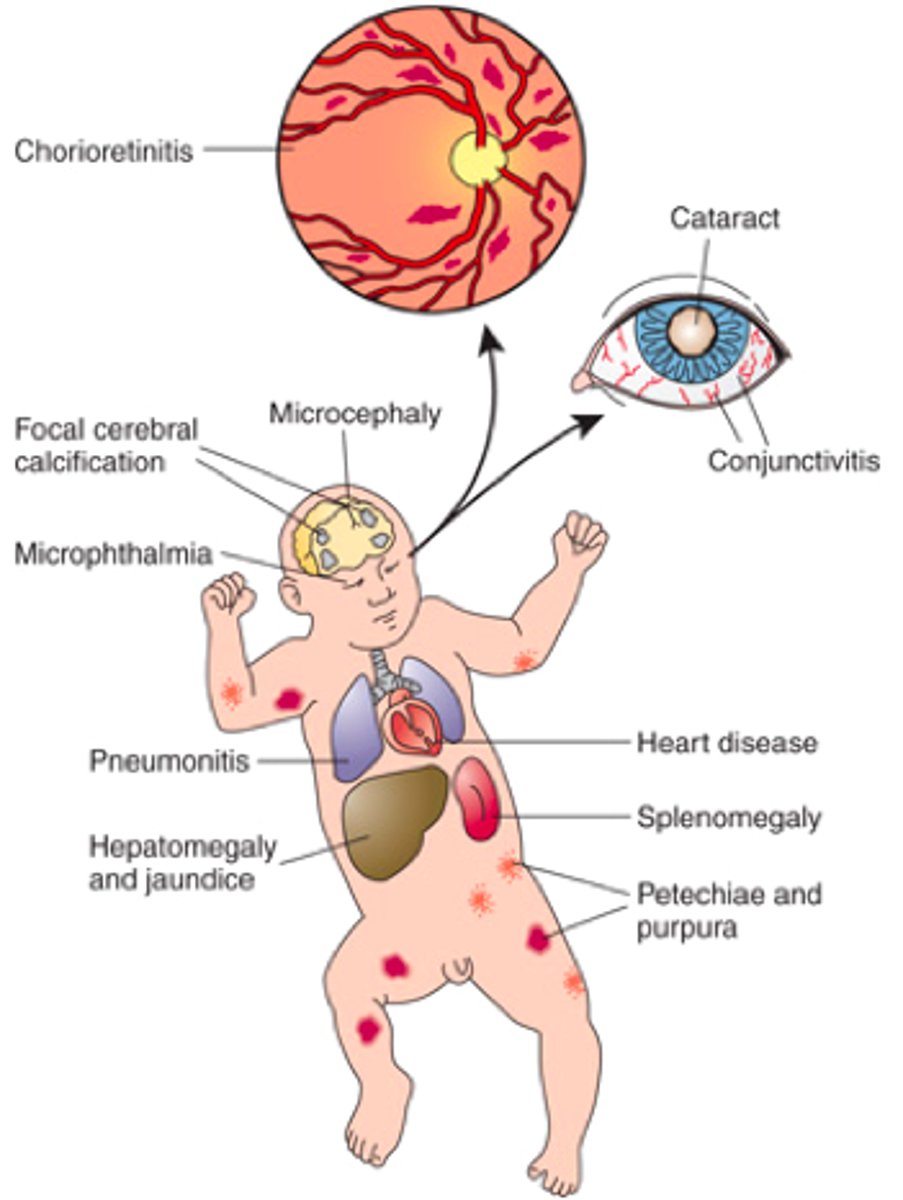
What is the TORCH complex?
A group of infections (Toxoplasmosis, Other, Rubella, Cytomegalovirus, Herpes) that can cause severe fetal anomalies.