Energy Changes and Rates of Reaction - Standard Formation & Rxn Rates
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Standard Enthalpy of Formation
change in enthalpy that accompanies the formation of 1 mole of a compound from its elements
All elements in the equation (not the substance formed) must be in their standard states
Standard State
the most stable form of the substance under standard conditions (25oC and 100 kPA)
elements w gas as their standard state
noble gases and diatomic elements (except bromine, which is liq)
elements w liq as their standard states
bromine and mercury
stan state for substance in sol is at a concen of
1 mol / L
most elements are ______ in standard state
solid
standard formation formula
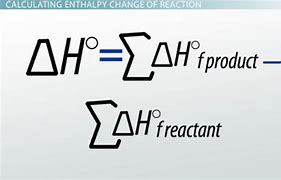
writing formation equations
1. Write 1 mol of product in the state that has been specified.
2. Write the reactant elements in their standard states.
3. Balance the equation so that it yields 1 mol of product.
Elementary Step
a step involving one, two, or three collisions that cannot be explained by simpler reactions
Reaction Mechanism
a series of elementary steps by which a chemical reaction occurs
Rate-Determining Step
the slowest step in the reaction – determines the overall rate at which a reaction can proceed
Reaction Intermediate
an entity that is neither a reactant or a product, but is formed and consumed in during the reaction sequence
differences between intermediate and catalyst
intermediate: made and consumed DURING rxn seq
catalyst: present before and after rxn seq
Requirements for Plausible Reaction Mechanisms
Summing the elementary steps in the reaction mechanism must give the overall balanced equation for the reaction. (hess’s law)
The reaction mechanism must agree with the experimentally determined rate law
in an pot en diagram, the rxn step that makes the highest peak is the
slow reaction, therefore the rate determining step
the top of a peak
transition state
chemical kinetics
study of REACTION RATES and REACTION MECHANISMS (events at molecular level that control the speed and outcome of a reaction)
rxn rate
a measure of how fast a reaction proceeds and is measured by how fast a reactant is used up, or a product is formed.
i.e. a change in the concentration of a reactant or product over time
units of rxn rate
mol/L•s
for rxn rate, if you are measuring the disappearance/consumption/decomposition etc of a compound, you need a ____ sign in front
neg
for rxn rate, if you are measuring the appearance/formation etc of a compound, you need a ____ sign in front
pos / no sign
concentration of reactants goes _______ over time
down → neg slope
concentration of products goes ______ over time
up → pos slope
rxn rate is typically not ____________
constant
avg rate of rxn
draw a secant line btwn two points on a concen - time graph and the slope would equal the avg rate of rxn
avg rate of rxn fromula
rate A = (concentration of A at a time t2 – concentration of A at time t1) / t2 – t1
simplified avg rate of rxn formula
rateA = Δ[A] / Δt
where [A] rep the concen in mol / L, Δ[A] is the change in mol / L and Δt is the change in time
instantaneous rate of rxn
the rate of reaction at a particular time during the reaction (x point on a concen time graph)
to find instantaneous rate
1. Plot the concentration - time graph
2. Draw a tangent to the curve at the specified time
3. Find the slope of the tangent (equal to instantaneous rate
initial rate of rxn
the speed of the reaction the instant the reactants are mixed (t = 0) (tangent line starting from origin
writing stoichiometric relationships for rxn rates
use fractions lol
ways to measure rxn rates experimentally (4)
a measurement of the amount of gas produced
a measurement in the change of conductivity of a solution (for reactions that involve ions)
a measurement in the change in pH
a measurement of a change in colour
rxns that produce a gas
measure change in volume or pressure of gas produced
measure change in mass (products or reactants)
rxns that involve ions
measure change in conductivity of solution or change in pH
rxns that change colours
measure change in intensity of colour (concentration) using a spectrophotometer
spectrophotometer
an apparatus for measuring the intensity of light in a part of the spectrum, especially as transmitted or emitted by particular substances.
five key factors of the speed of a rxn rate
chem nature
temp
concen
s.a
catalyst
collision theory
for a reaction to occur, the reactant particles must first collide with one another
concepts of collision theory (3)
a system consists of particles in constant motion at speeds proportional to the temp of sample.
chemical rxn must involve particle collisions...with each other and with the walls of the containers.
rate of rxn depends on frequency of collisions and the fraction of collisions that are effective
requirements for an effective collision
correct orientation → collide in a way that the reactive site is involved
sufficient en
particles have to collide
activation en
the minimal en needed for a collision to be effective (to break the bonds in the reactant molecule)
diff btwn n the initial energy of the reactants and the energy of the activated complex at the transition state.
transition state theory involves the
activation en (Ea)
activated complex
transition state
activated complex
an unstable molecule containing partially broken and partially formed bonds representing the maximum potential energy point in the change (top of peak)
trans state
energy maximum where the activated complex is formed
rate of a rxn depends on 2 criteria:
freq of collisions
frac of collisions that are effective (suff en, correct orien)
chem nature : a factor of rxn rates
more bonds a compound has, the more en it needs to break all the bonds, thus a slower rxn
stronger bonds would also slow the rxn
therefore complicated molecules are less reactive and since the collision must be at the right orientation, it would take longer for the rxn to occur
temp : a factor of rxn rates
increase in temperature causes an increase in collision frequency and the fraction of collisions that are effective
particles collide more often and with more force
concen : a factor of rxn rates
higher concen → more collisions bc more particles are occupying the fixed space
s.a : a factor of rxn rates
only the particles at the surface, where the substances are in contact, can react
the amount of exposed surface area, where the two reacting phases are in contact, affects the reaction rate.
more surface area → higher rxn rate
catalyst : a factor of rxn rates
can either quicken or slow a rxn
works by lowering the activation en needed for a rxn to occur
turns the “slow” rxn steps into fast ones
inhibitor
a catalyst that slows a rxn
homogeneuous vs heterogenous catalyst
hetero → diff state of matter than the reactants and is usually a solid
homo → same phase as the reactants usually gas or liq
biological catalysts
catalysts produced by living organisms to help with biological processes
temp and how it specifically affects rates of rxn
doubled for every 10 celcius degree increase and halved for every 10 celcius degrees decrease (SEE EXAMPLES)