AP World History Unit 6 (LHS)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
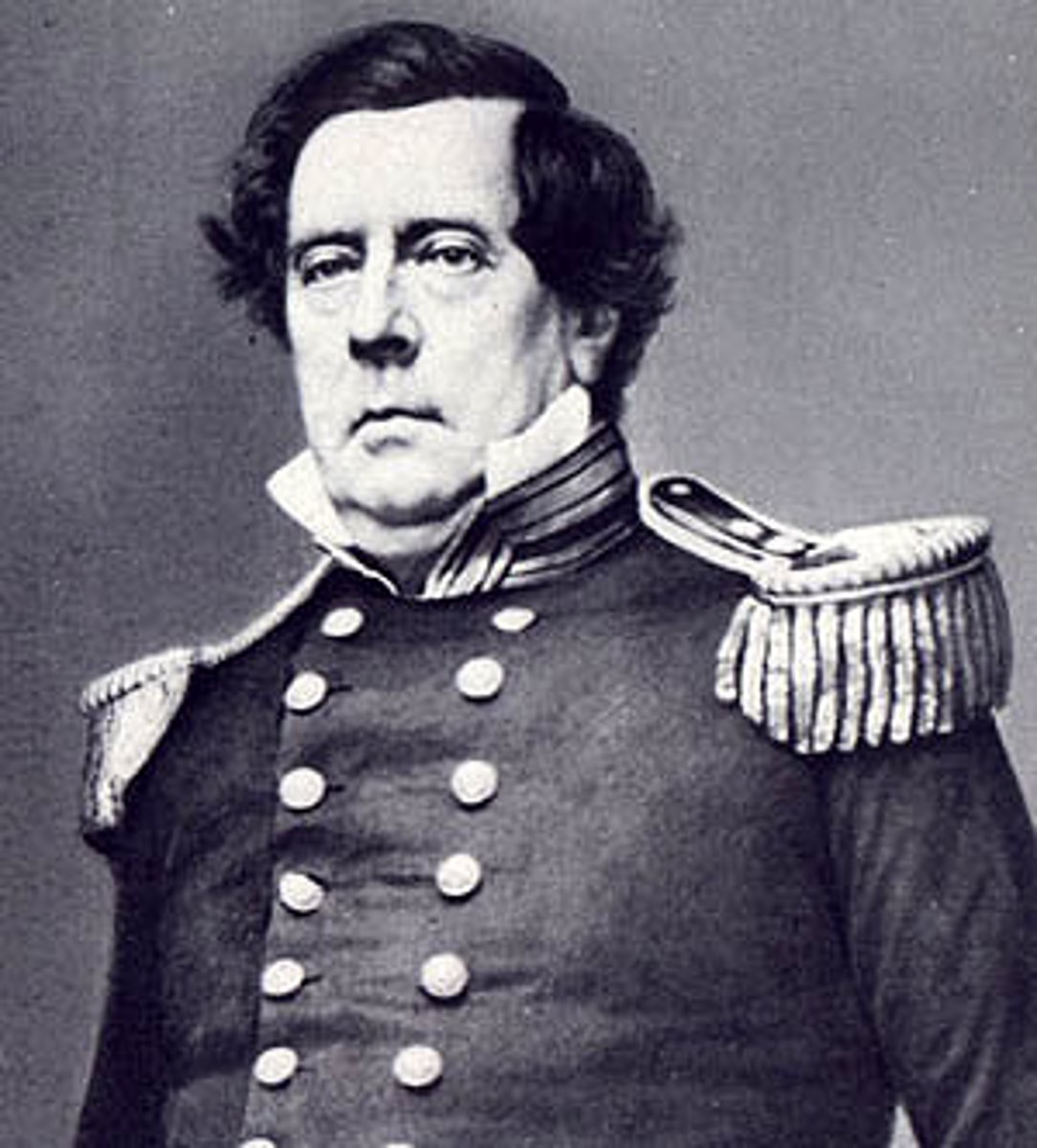
Commodore Matthew Perry
A U.S. naval officer who forced Japan to open its ports to Western trade in 1853, ending centuries of isolation under the Tokugawa shogunate. (He * the US wanted to be 'friends' with Japan)

Nationalism
A political ideology emphasizing loyalty to one's nation and often leading to movements for independence or unification, as seen in Germany and Italy in the 19th century.
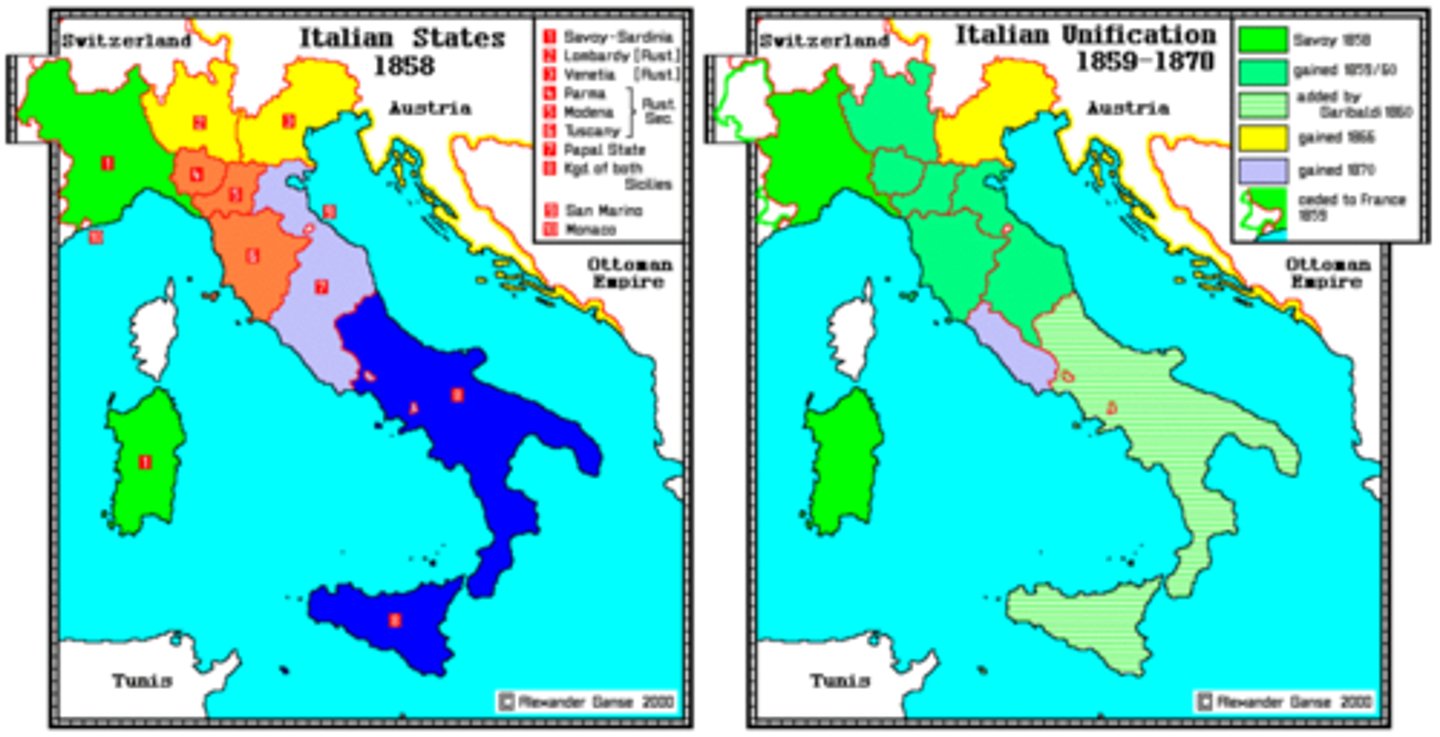
Imperialism
The expansion of a nation's influence over other territories through military force, diplomacy, or economic control, as demonstrated by European colonization of Africa and Asia.

Social Darwinism
A belief that applied Charles Darwin's theory of natural selection to human societies, justifying European imperial expansion by arguing that stronger nations were meant to dominate weaker ones.
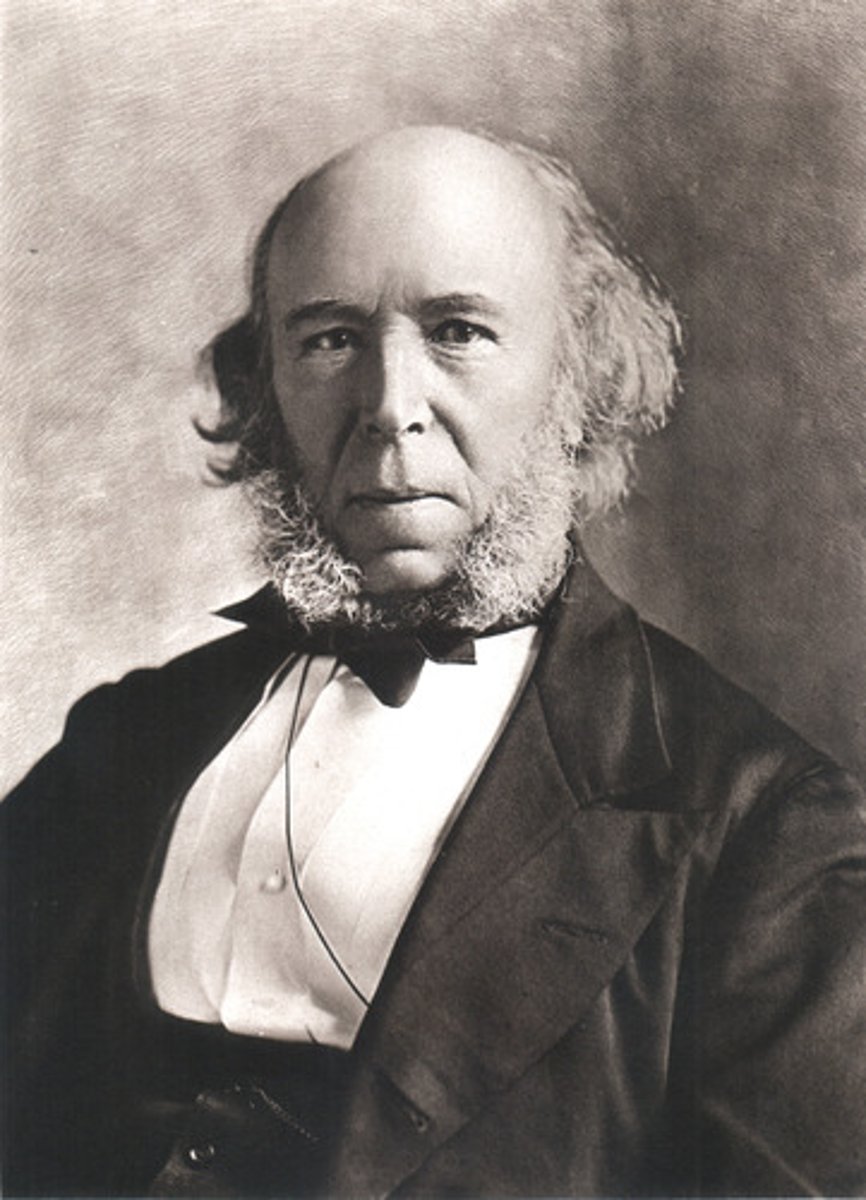

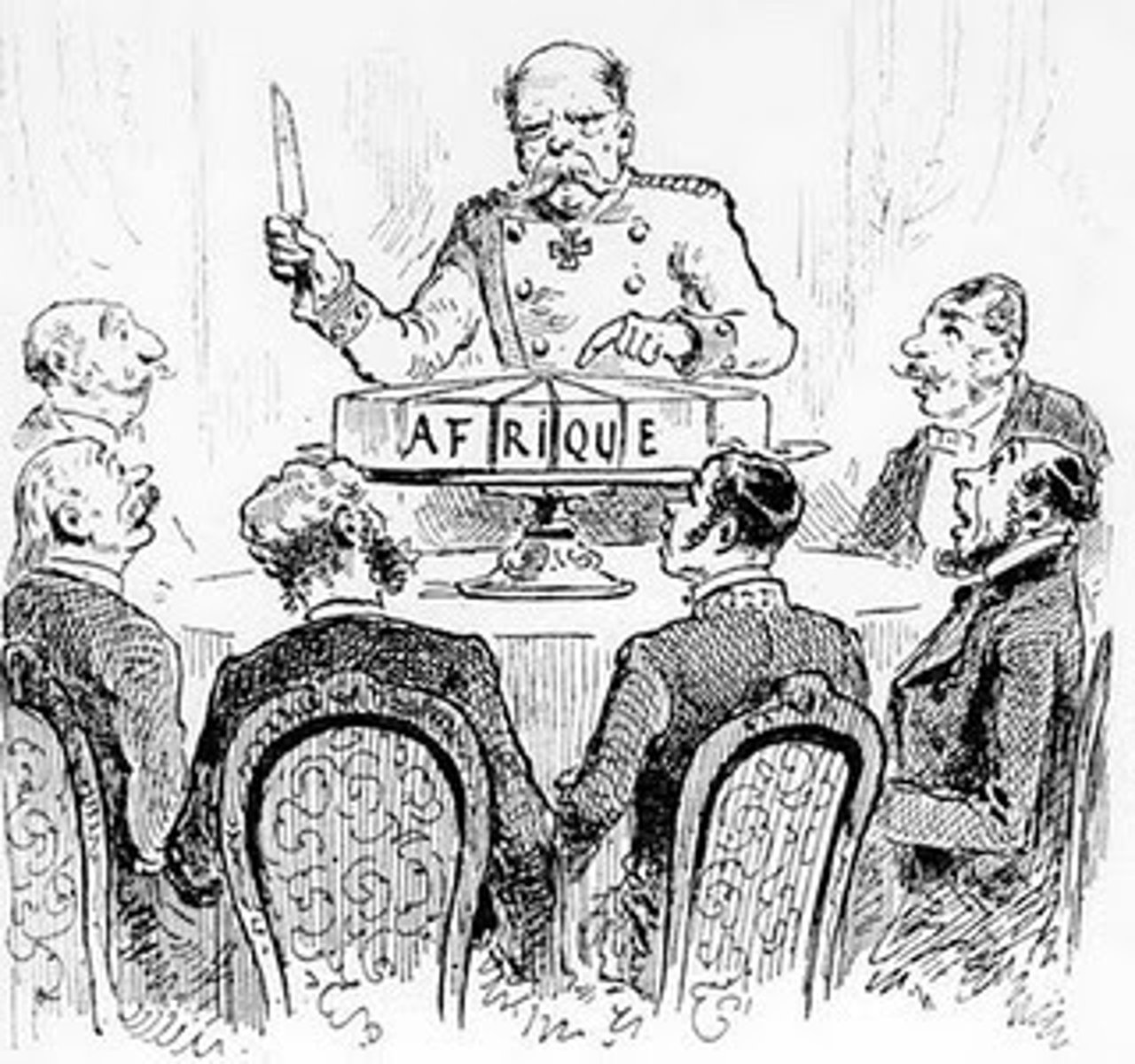
Otto von Bismarck
The Prussian chancellor who unified Germany through strategic wars and diplomacy, using Realpolitik to strengthen German power. He also led the Berlin Conference (1884-1885), where European powers divided Africa to avoid conflicts while securing Germany's colonial interests.
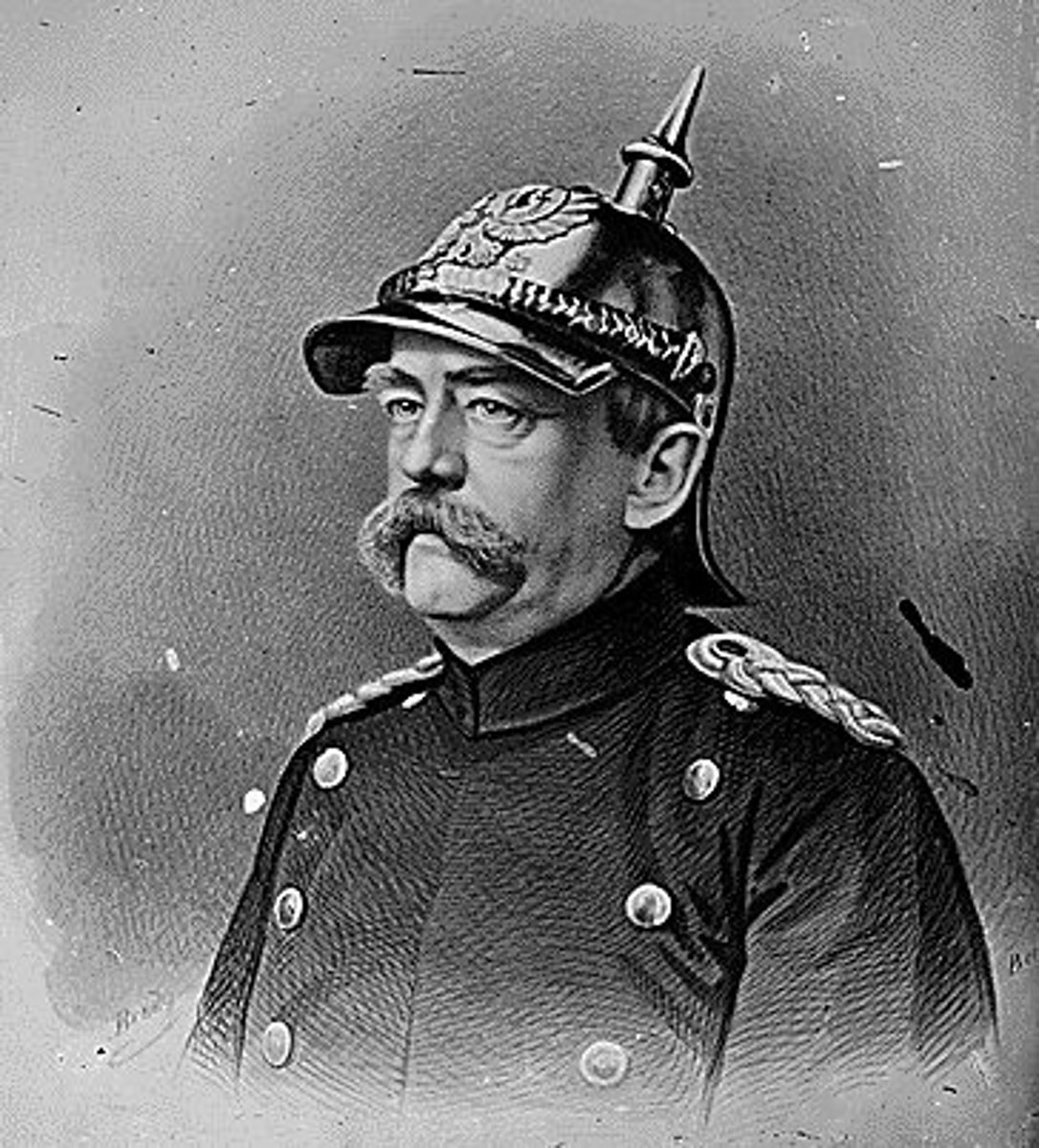

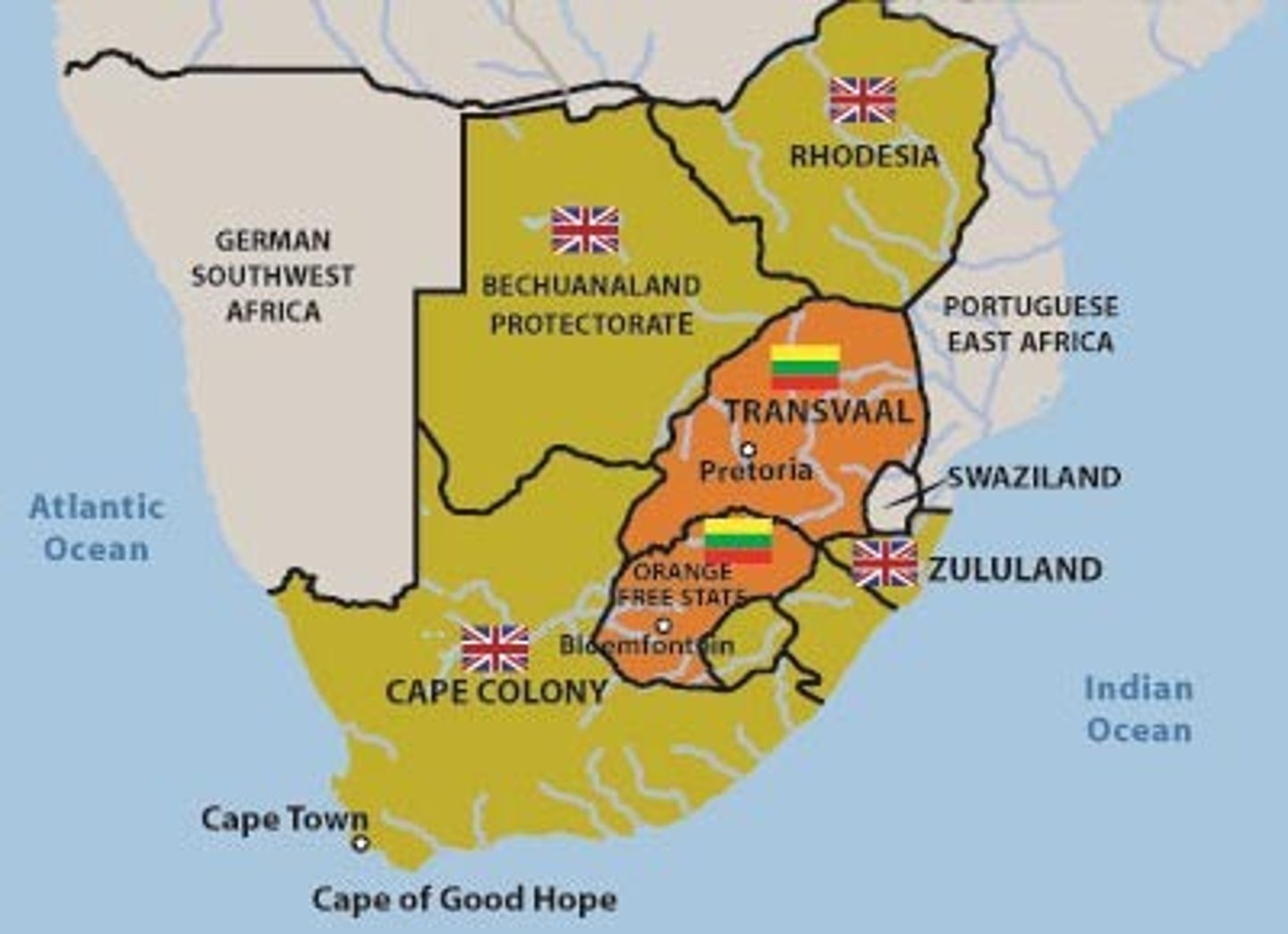
Zulu
A powerful African kingdom in southern Africa that resisted British and Boer encroachment under leaders like Shaka.

Afrikaners
Descendants of Dutch settlers in South Africa who clashed with the British and indigenous groups over land and political control.
King Leopold II
The Belgian king who exploited the Congo for rubber and ivory, infamously using brutal forced labor that resulted in millions of deaths and maiming of Africans (limb removal, etc).
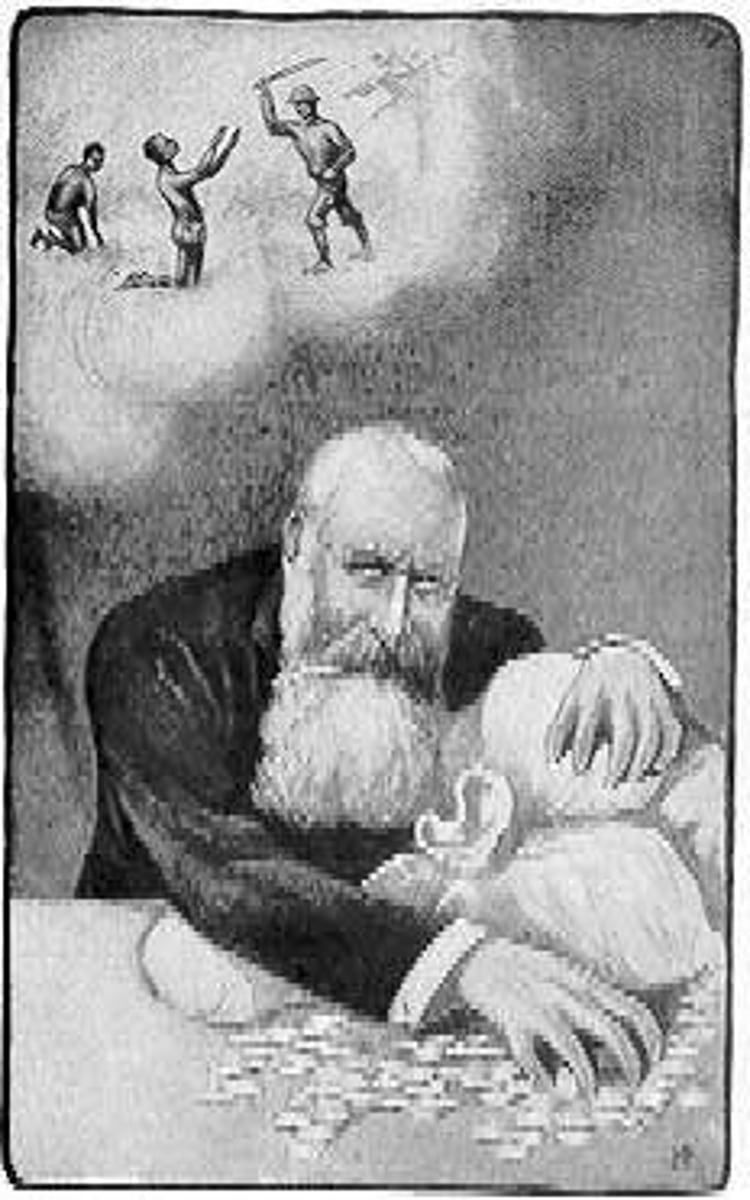
Berlin Conference (1884-1885)
A meeting of European powers from 1884-85 that diplomatically established rules for the colonization of Africa, dividing the continent without consideration for indigenous cultures.

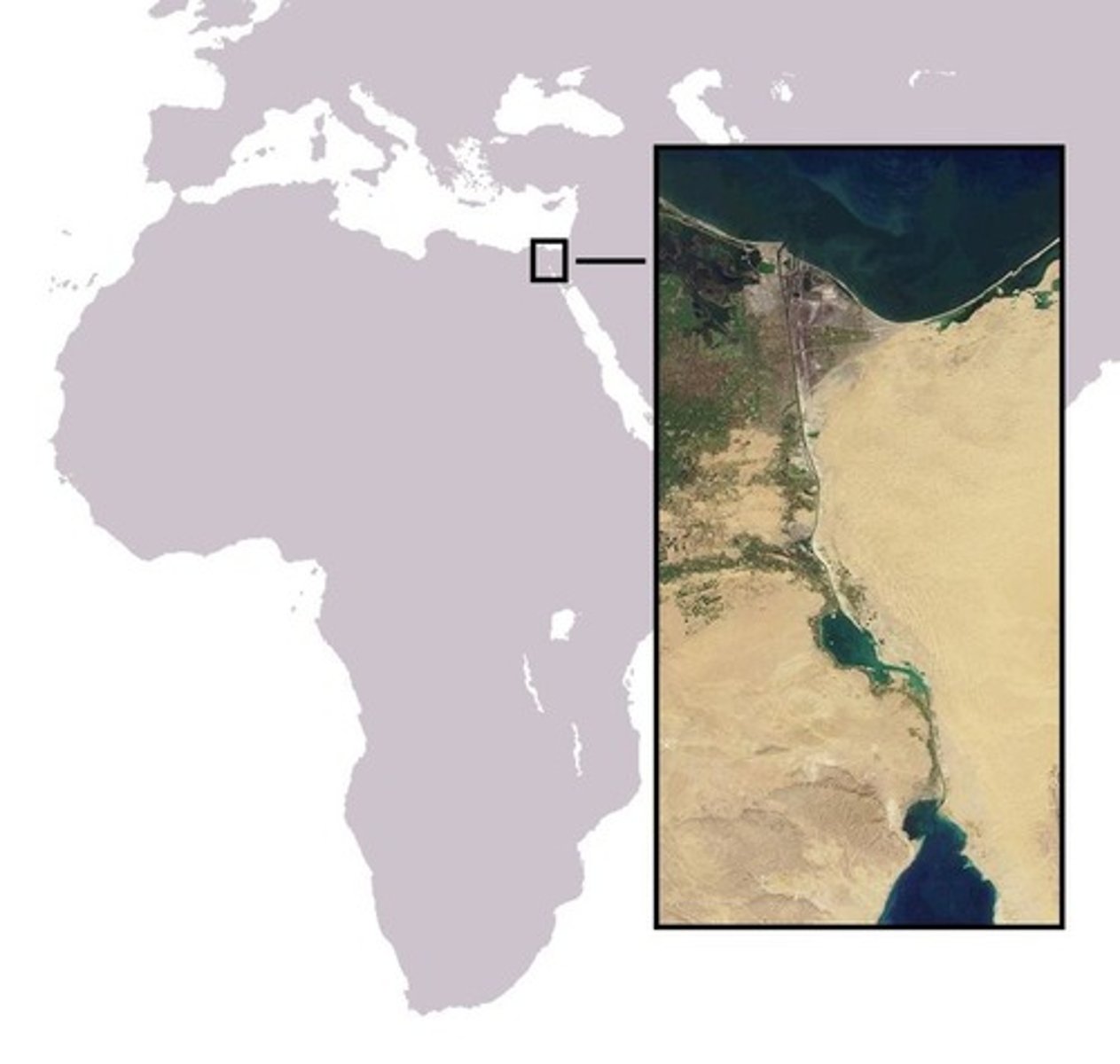
Suez Canal
A strategically important waterway connecting the Mediterranean and Red Seas, constructed by Egypt and later controlled by the British for trade and military purposes.
Recaptives
Enslaved Africans who were freed by British naval patrols and resettled in places like Sierra Leone in the 19th century.

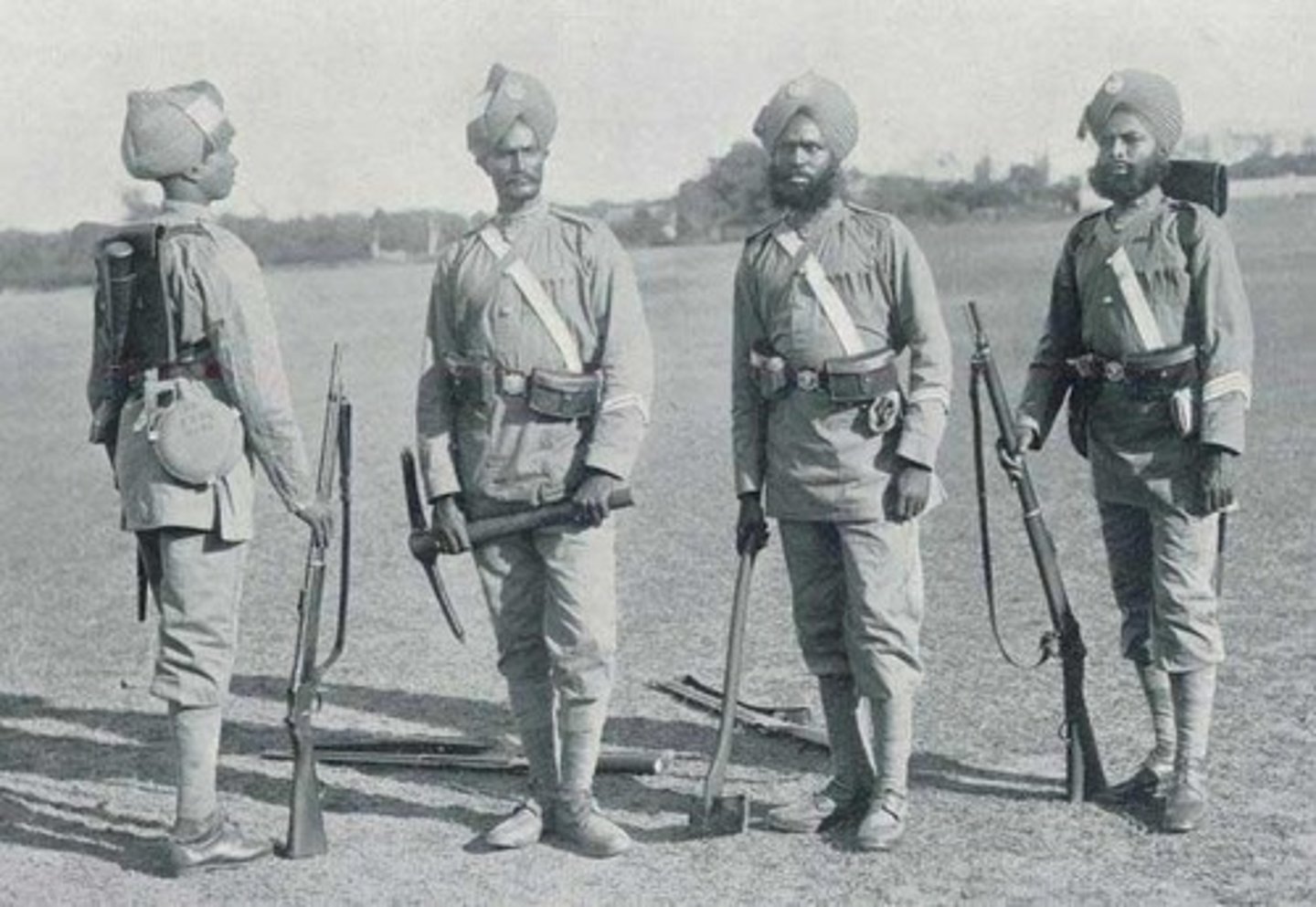
Sepoy
Indian soldiers employed by the British East India Company, many of whom rebelled in 1857 due to grievances over cultural insensitivity and harsh policies.

British Raj
The period of direct British rule in India from 1858 to 1947, following the dissolution (end) of the British East India Company.

Sepoy Rebellion (Indian Rebellion of 1857)
a widespread but ultimately unsuccessful uprising against British rule, sparked by resentment over cultural insensitivity, high taxes, and political control. Indian soldiers (sepoys) in the British army rebelled after rumors spread that rifle cartridges were greased with cow and pig fat, offending both Hindu and Muslim soldiers. The British brutally suppressed the revolt, leading to the dissolution of the Mughal Empire and the official establishment of the British Raj, bringing India under direct British control.

Indian National Congress (INC)
A political organization founded in 1885 to advocate for greater Indian self-rule, which later became a driving force for independence in the mid 20th c.

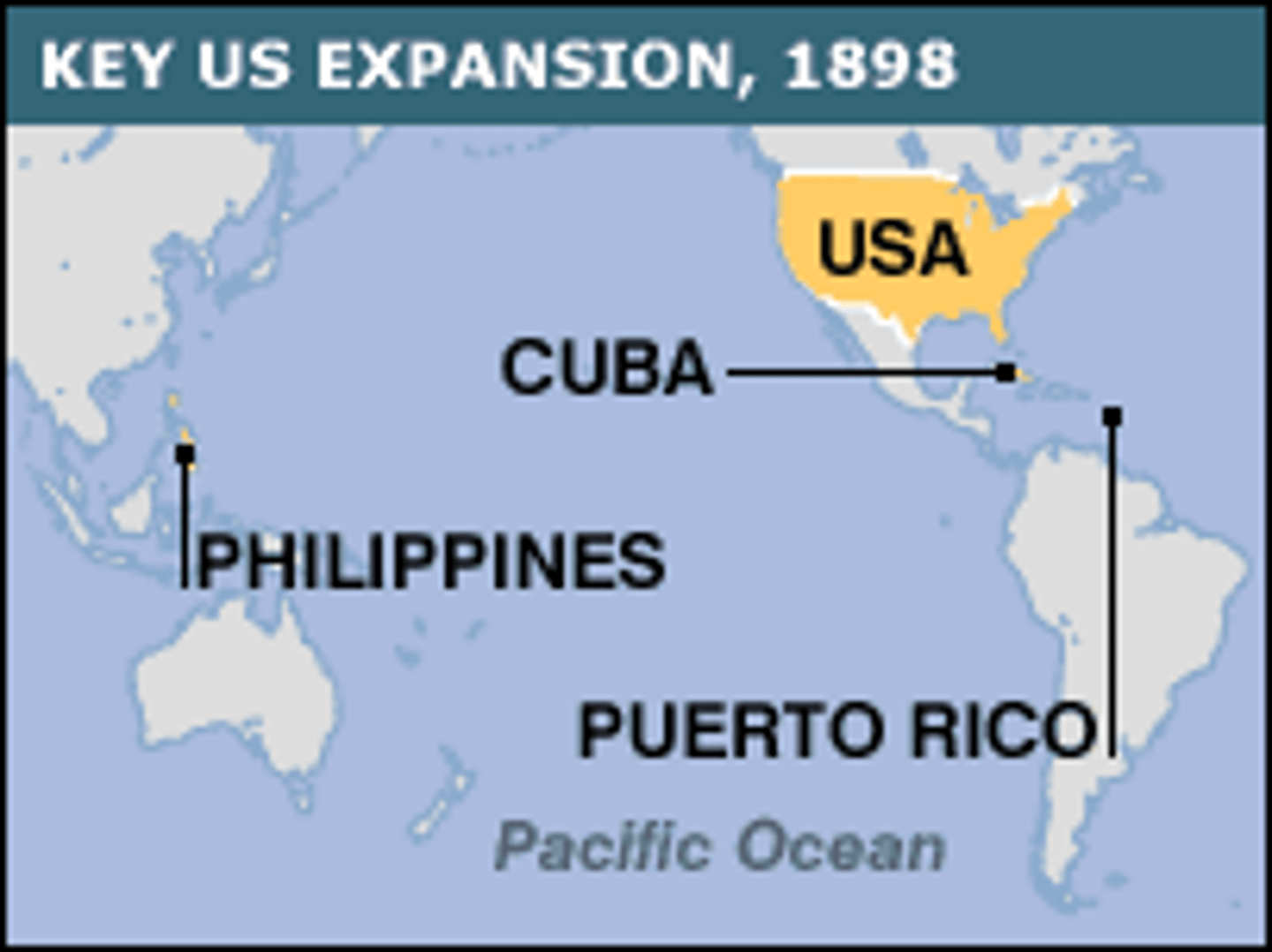
Spanish-American War (1898)
A conflict in the late 19th c between the U.S. and Spain that resulted in U.S. acquisition of former Spanish colonies, including the Philippines, Guam, and Puerto Rico.
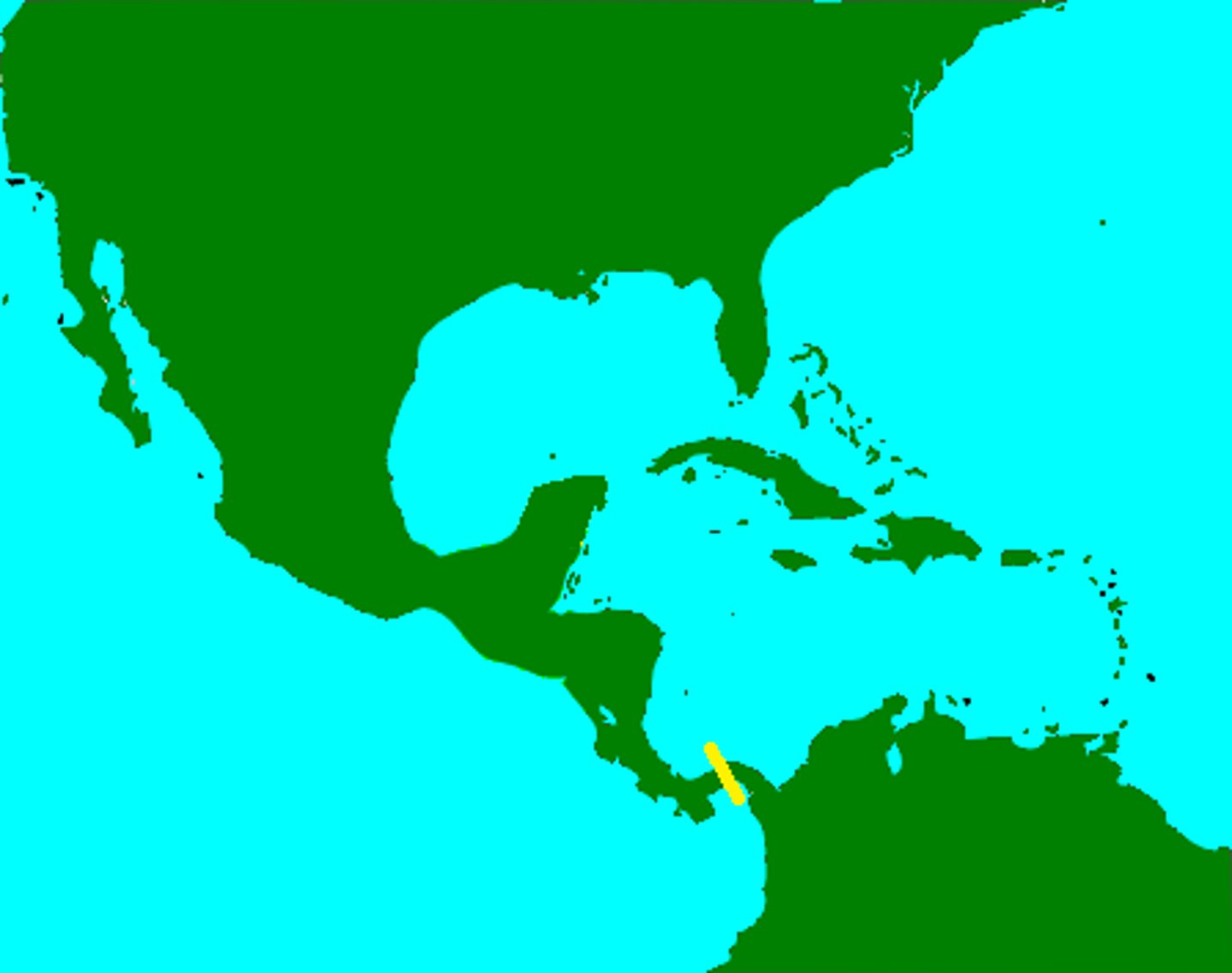
Panama Canal
A crucial canal built by the U.S. to connect the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, greatly enhancing global trade and military movement. Construction occurred from 1904-1914.
Crimean War (1853-1856)
A war between Russia and an alliance of Britain, France, and the Ottoman Empire in the mid 19th c, highlighting the declining power of the Ottomans and the modernization of European warfare.

Taiping Rebellion (1850-1864)
A massive Chinese civil war in the mid 19th c led by Hong Xiuquan, who claimed to be the brother of Jesus, seeking to overthrow the Qing dynasty and establish a utopian Christian state.

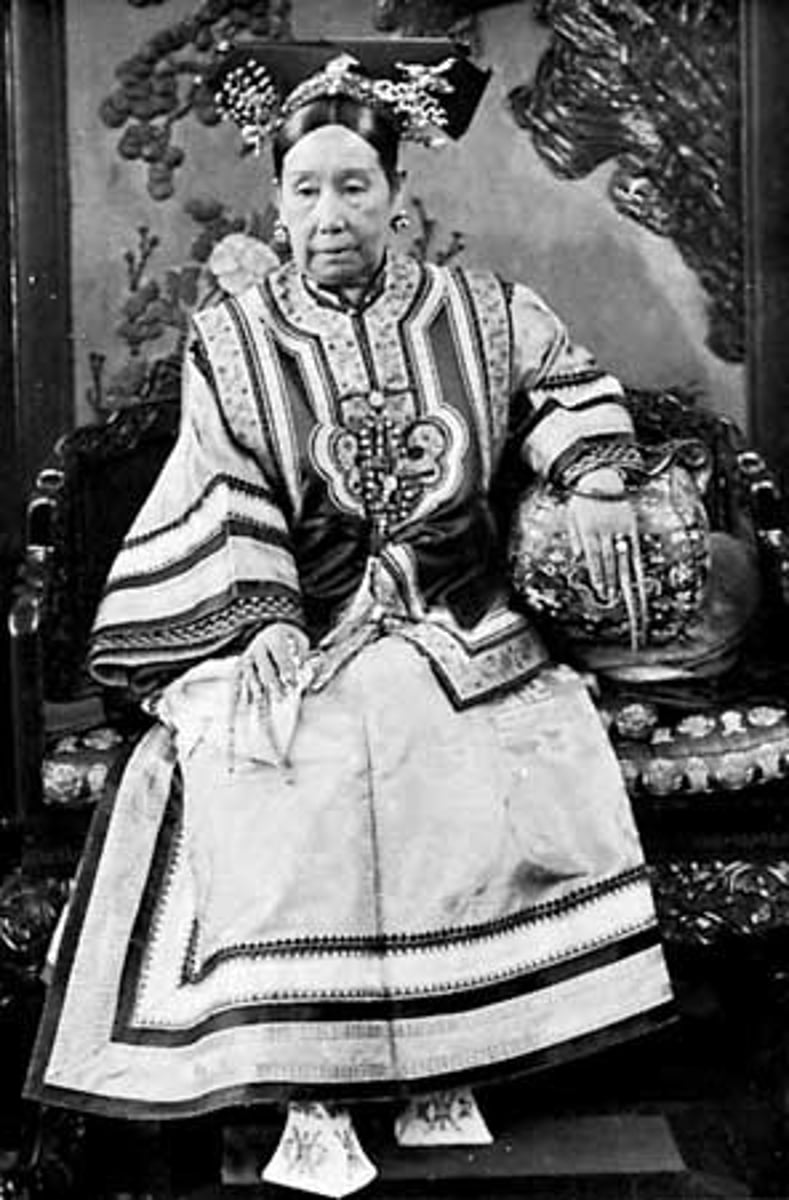
Empress Dowager Cixi
A conservative Qing ruler who opposed reforms and modernization, contributing to the weakening of China in the face of Western imperialism.

Boxer Rebellion (1899-1901)
An anti-foreign, anti-Christian uprising in China, where the 'Boxers' sought to expel Western influence, ultimately crushed by foreign military intervention at the turn of the 20th c.
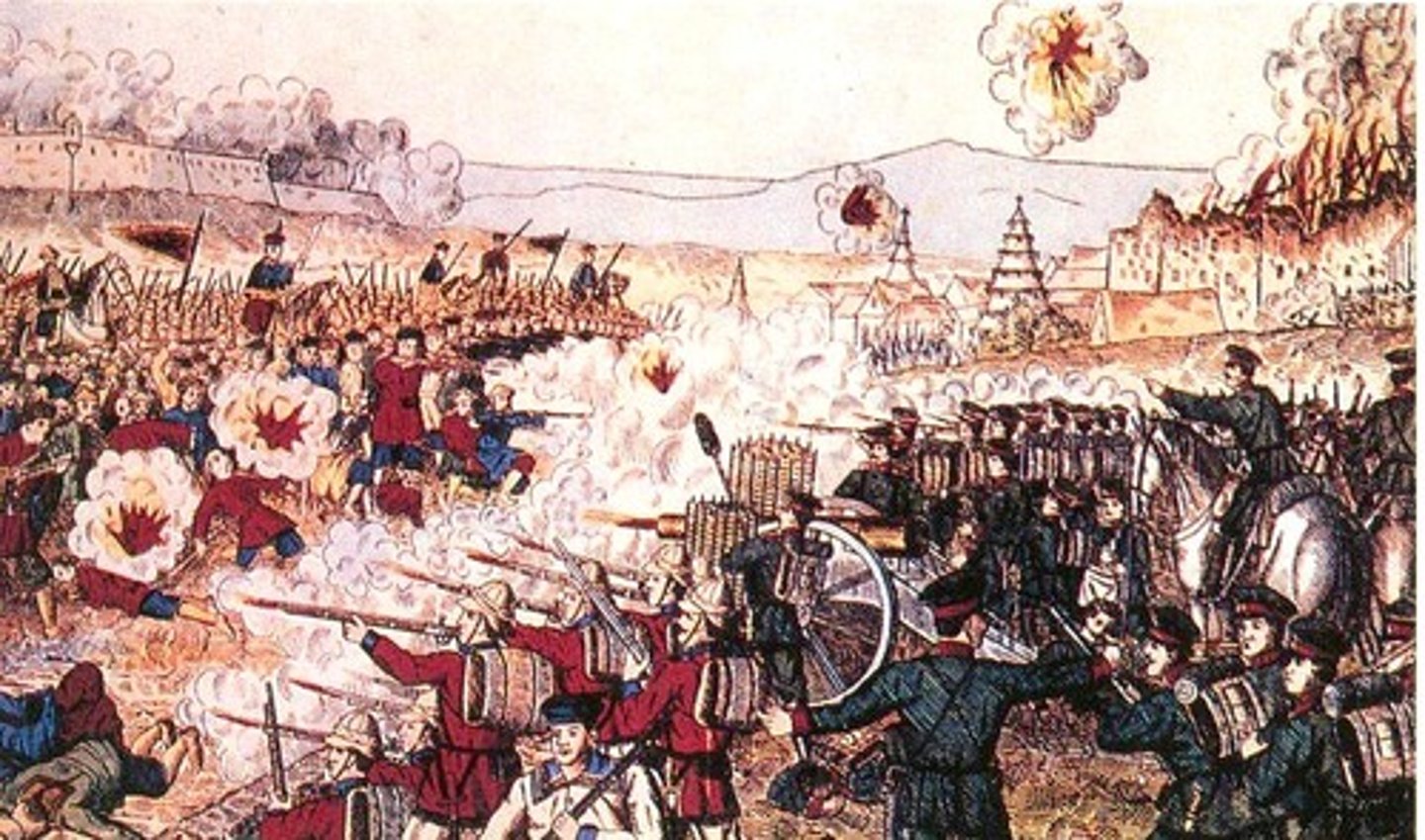

Túpac Amaru II
A Peruvian indigenous leader who led a major rebellion against Spanish colonial rule in 1780, inspired by grievances over forced labor and high taxes. Ultimately, the revolt was unsuccessful, resulting in the deaths of himself/family and continued Spanish rule.
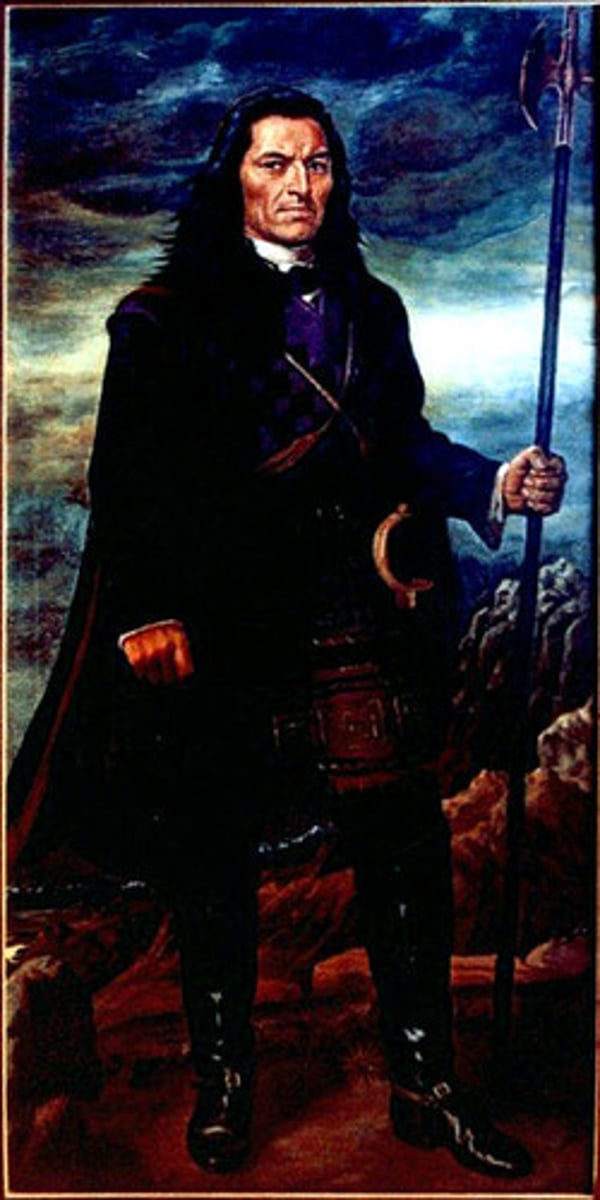

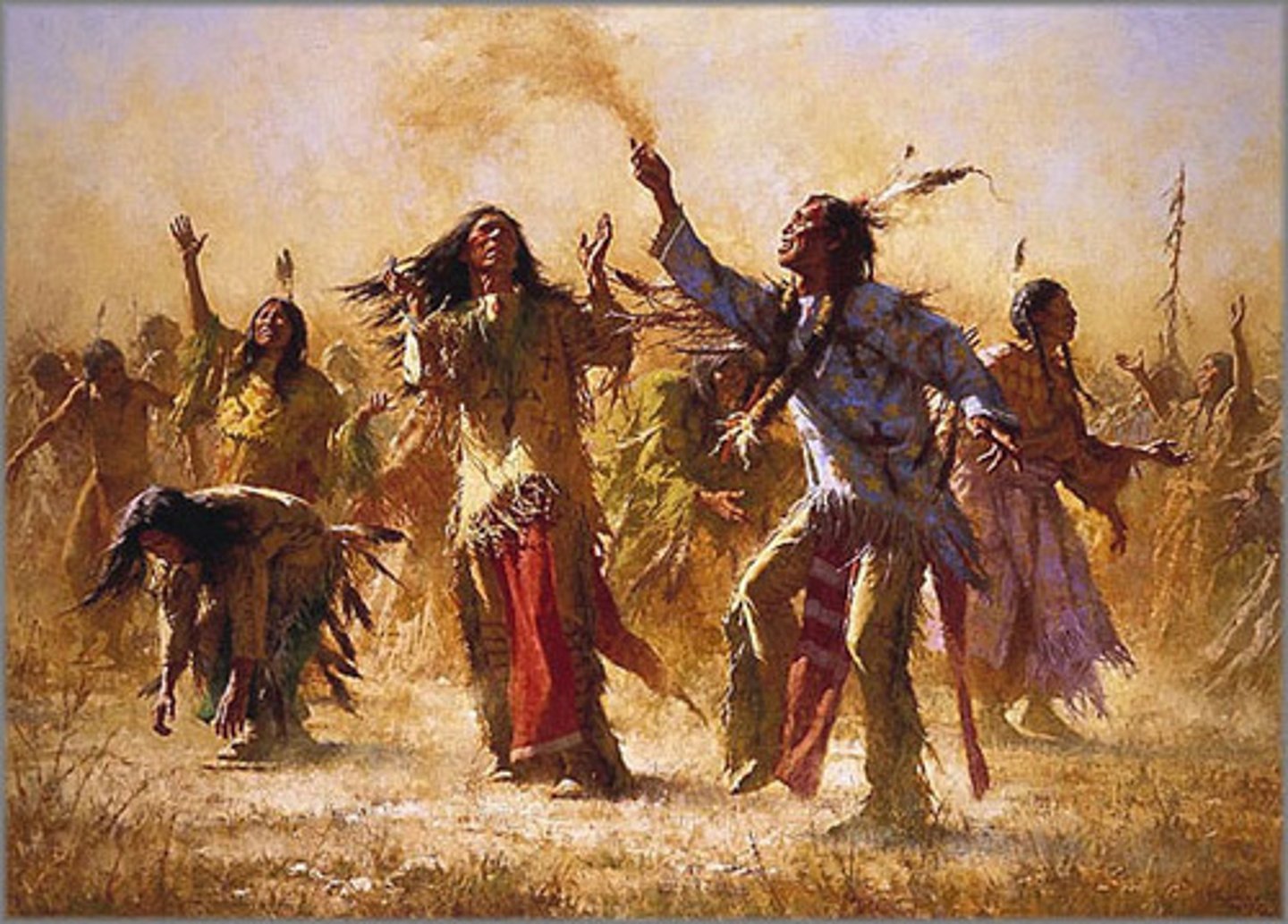
Ghost Dance
A Native American spiritual movement in the late 19th century that sought to restore indigenous ways of life and resist U.S. expansion, leading to conflicts like the Wounded Knee Massacre. This was an example of religious resistance to imperialism.

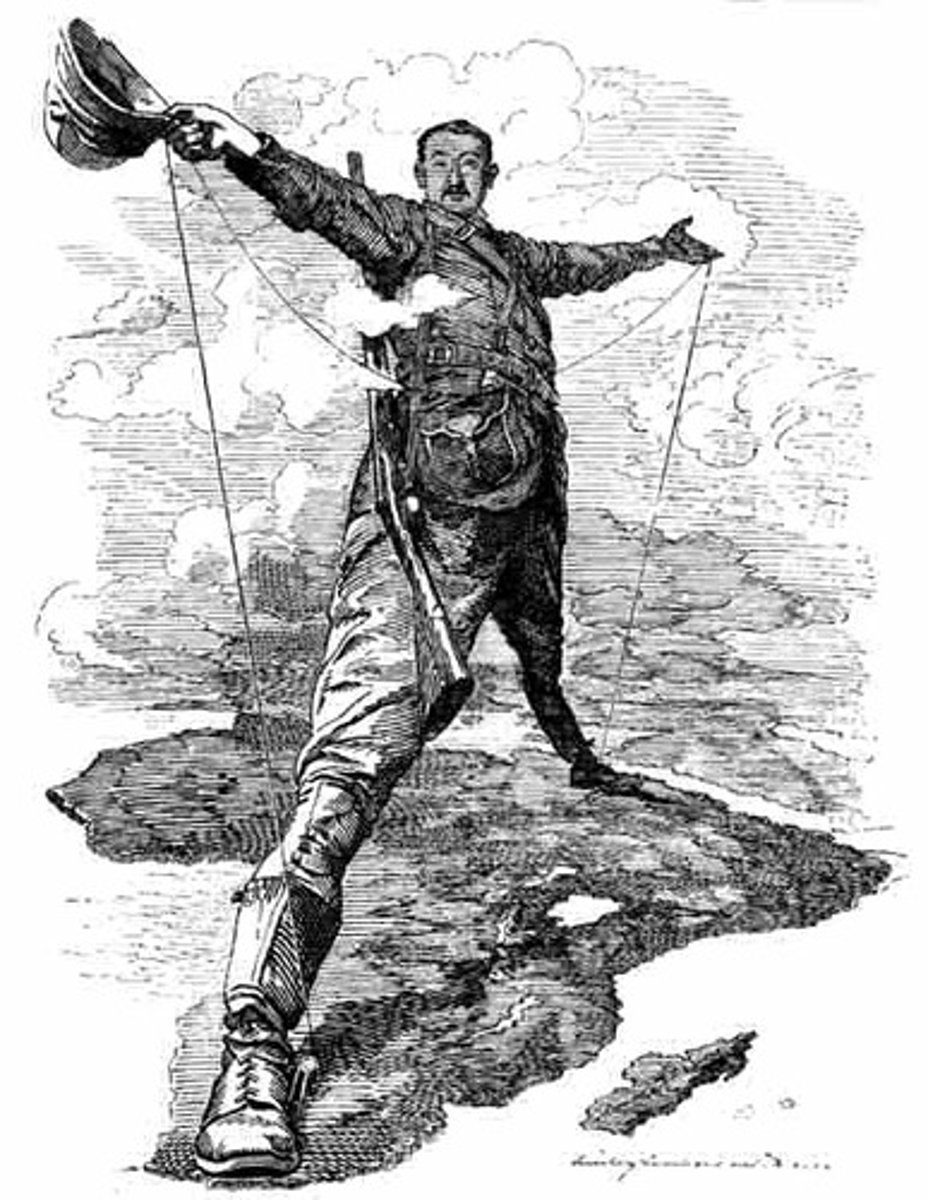
Cecil Rhodes
A British imperialist and businessman who played a key role in expanding British influence in southern Africa and envisioned a transcontinental railroad.

Boer War (1899-1902)
A conflict at the turn of the 20th c between the British and Afrikaners in South Africa over control of land and resources, leading to British victory and harsh policies against the Afrikaners.

Extraterritoriality
A policy where foreigners were exempt from local laws and subject only to their own nation's laws, commonly enforced in China and the Ottoman Empire by Western powers.

Opium War (1839-1842, 1856-1860)
Conflicts between China and Britain over the British trade of opium, leading to China's defeat and forced concessions (loss of economic power) to Western powers through the Treaty of Nanking.

Treaty of Nanking (Nanjing) (1842)
A treaty that ended the First Opium War, forcing China to cede (give up) Hong Kong to Britain, open treaty ports, and grant extraterritorial rights to foreigners.

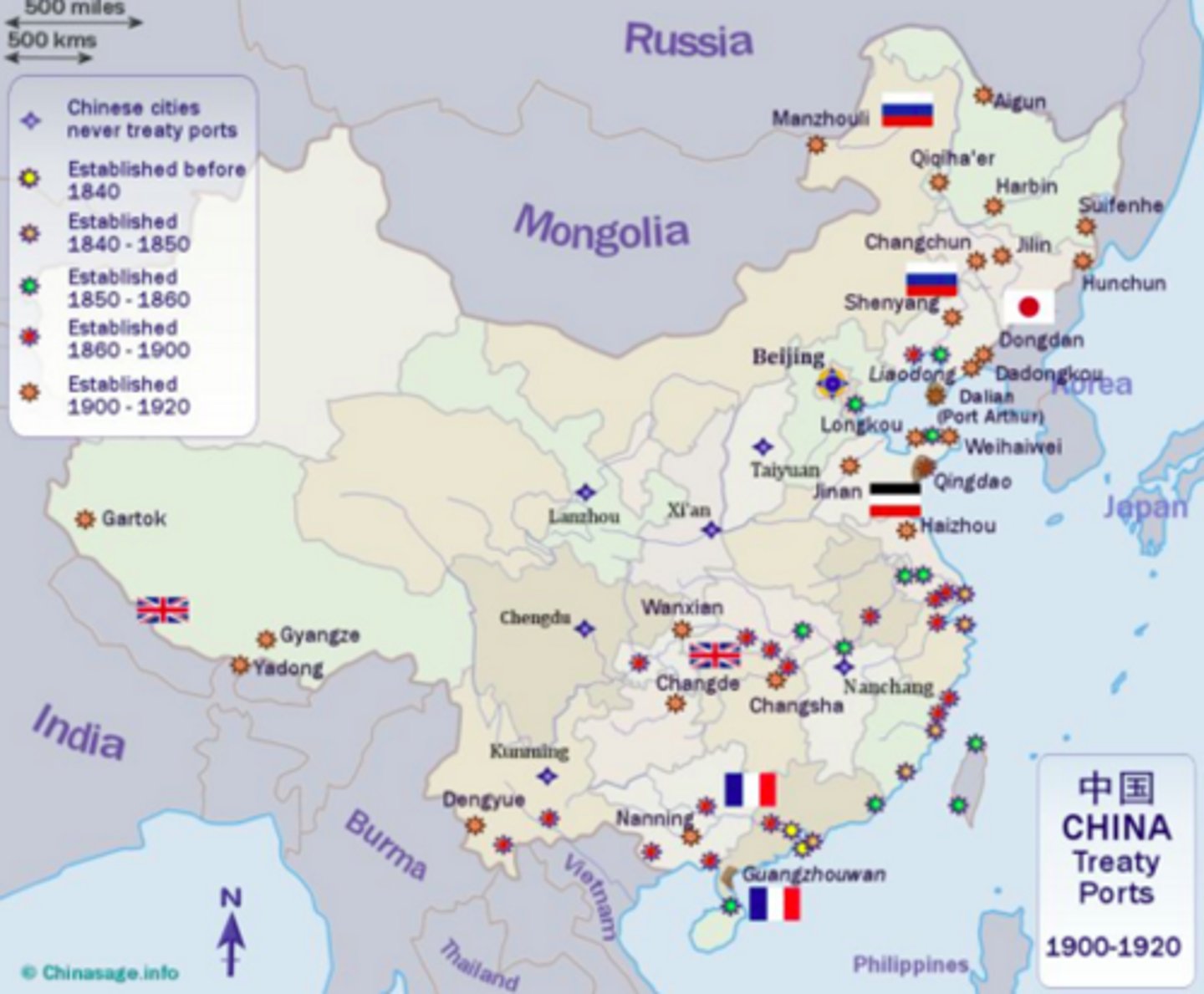
Treaty Ports
Chinese coastal cities that were forcibly opened to foreign trade under unequal treaties following the Opium Wars.
Acculturation
The process by which one culture adopts aspects of another, often seen in immigrant communities adapting to new societies.

Chinese Exclusion Act (1882)
A U.S. law that restricted Chinese immigration, reflecting growing anti-Asian sentiment and racial discrimination in the late 19th century.

White Australia Movement
A series of policies aimed at restricting non-European immigration to Australia, particularly targeting Asian laborers at the turn of the 20th c.
