Vascular Thrombosis and Embolism
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Thrombus
An aggregate of coagulated blood containing
platelets, fibrin, and cellular elements
Thrombosis
The process of blood clot formation (Thrombus) in the vessels, obstructing the blood flow
Pathogenesis of Thrombosis- virchow’s triad
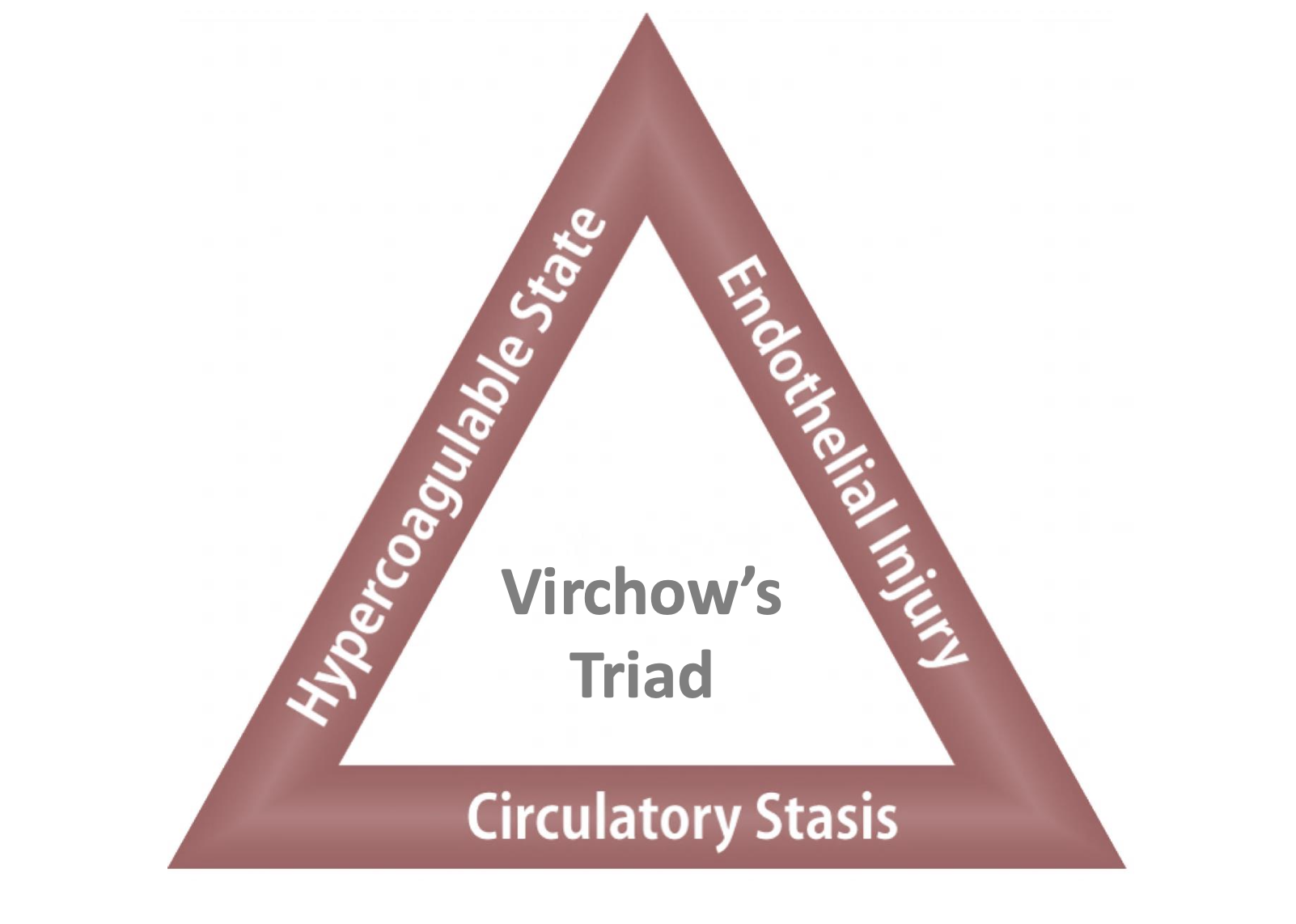
Endothelial Injury
Injury in the Endothelial Cells of blood vessel leads to the release of tissue factors
Fibrin and platelets will be recruited to stop the bleeding of the Endothelial Cells leading to aggregation hence formation of thrombus.
Circulatory Stasis
laminar flow vs turbulent flow
laminar flow
Platelets and other cells flow centrally in the lumen, separated from the endothelium by a clear zone of plasma.
turbulent flow
Platelets flow into contact with the ECs. Promote endothelial cell activation and thrombus formation.
Hypercoagulability
Alteration of the coagulation pathways that predispose to thrombosis
can be primary (Genetic)
can be secondary (acquired)
primary (Genetic) Hypercoagulability
Factor V Mutation
Prothrombin Mutation
Antithrombin III Deficiency
Protein C or S Deficiency
acquired (acquired) Hypercoagulability
Prolonged bed rest/immobilization
Myocardial infarction
Tissue damage (Surgery, Fracture, Burns)
Cancer
Prosthetic Cardiac Valve
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
Atrial Fibrillation
Contraceptive pills
Sickle Cell Anemia
Types of Thrombus
Pale Thrombus
Red Thrombus
Mixed Thrombus (Lines of Zahn)
Pale Thrombus formed from
• Mainly platelets
Pale Thrombus characteristics
(Chicken Fat)
Firm, pale, gray, tan
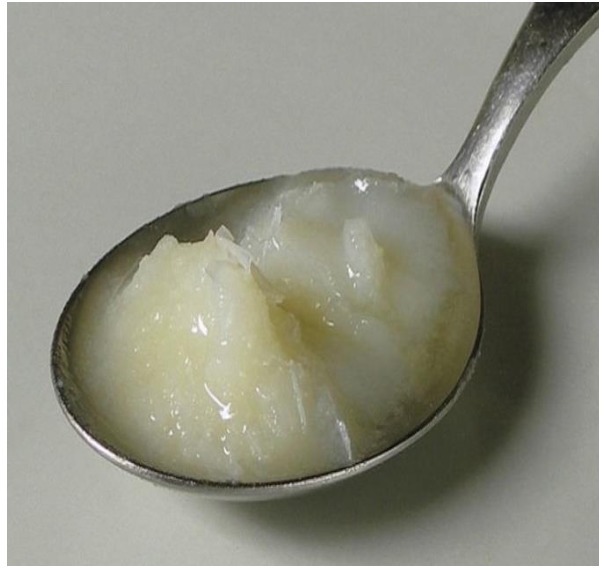
pale thrombus location
seen in Cardiac chambers or arteries
red thrombus contains
• Fibrin, RBCs, WBCs and platelets
red thrombus characteristics
currant jelly
Soft dark red and gelatinous
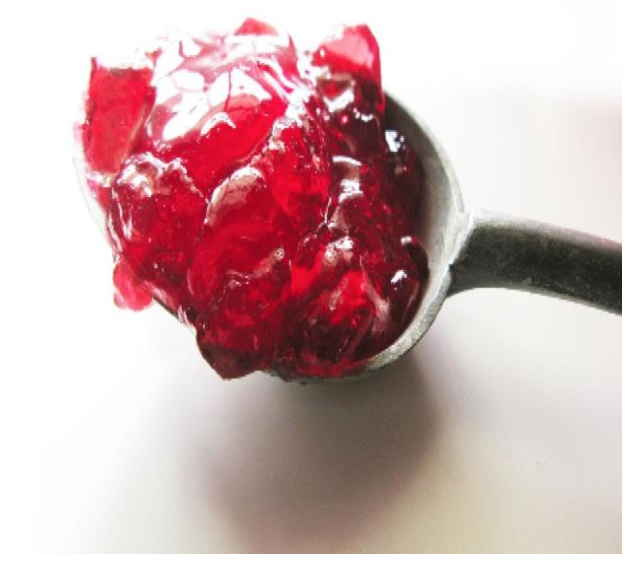

red thrombus location
as a result of Stagnant blood in veins
Mixed Thrombus (Lines of Zahn) contains and looks like
• Alternating layers of platelets, fibrin, RBCs
-appears as Alternating red and pale layers
Mixed Thrombus (Lines of Zahn) location
in heart or aorta
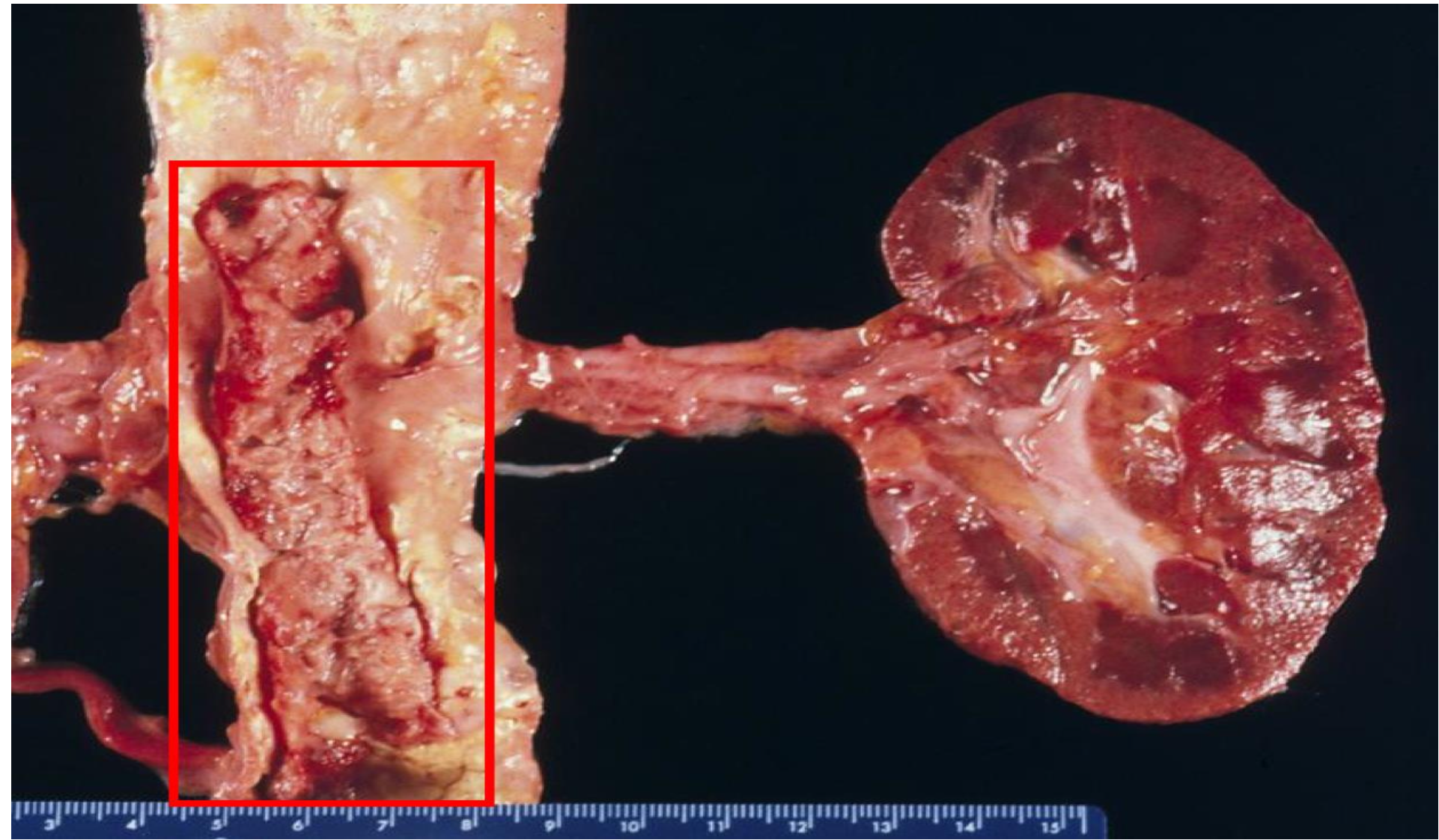
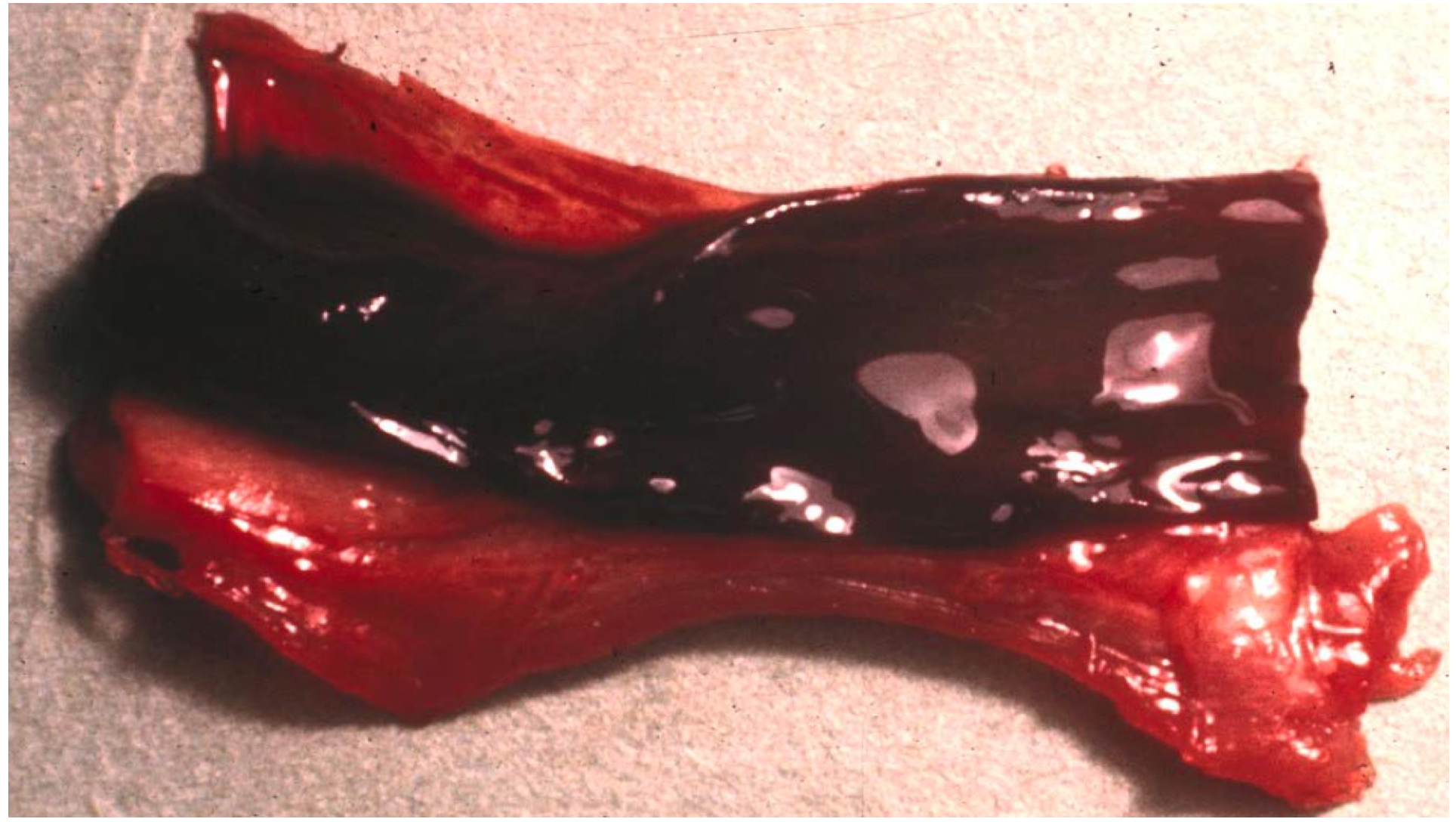
aorta at level of kidney
-mixed thrombus (lines of zahn)
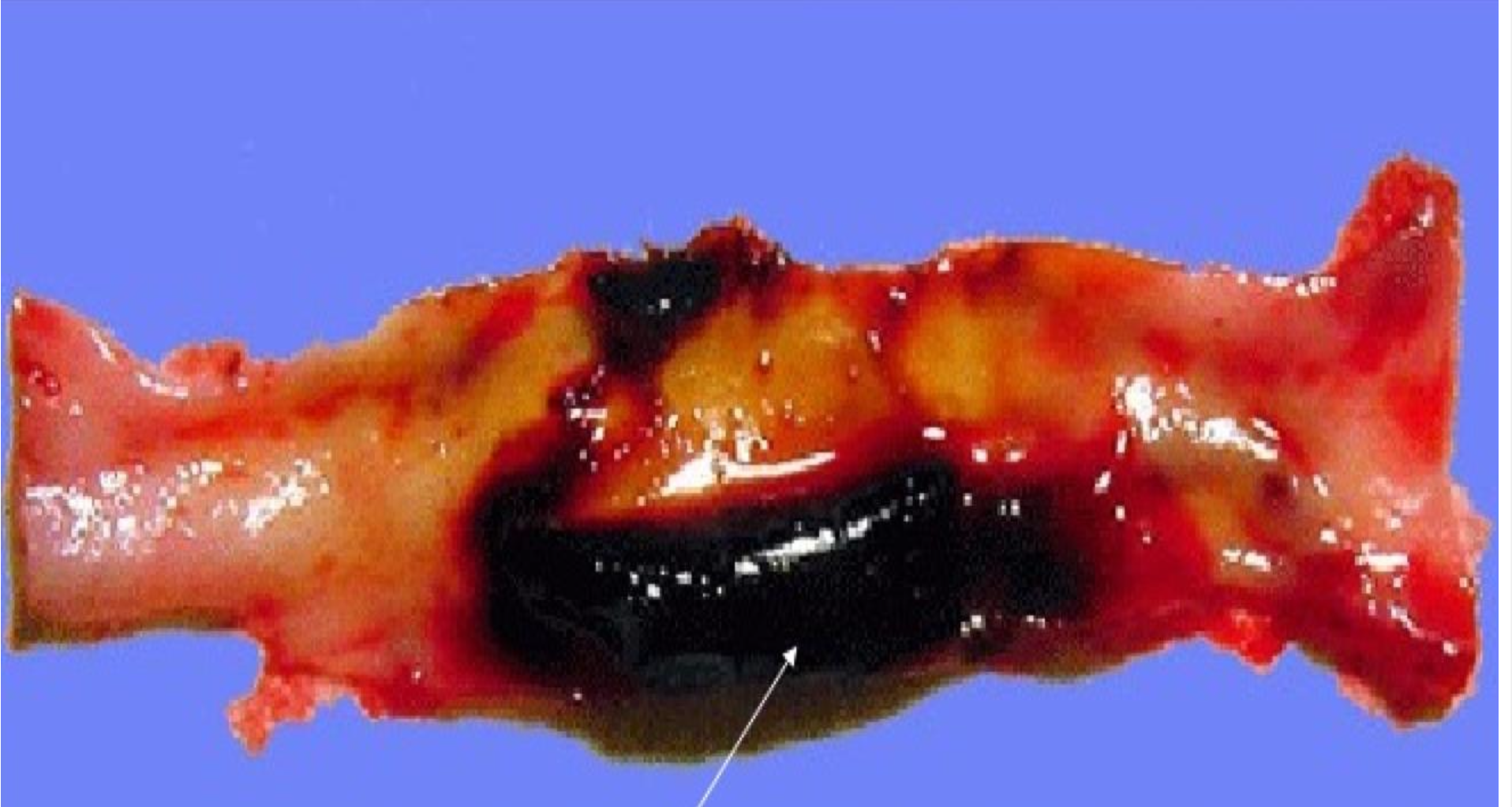
red thrombus
-in vein
red thrombus
-vein
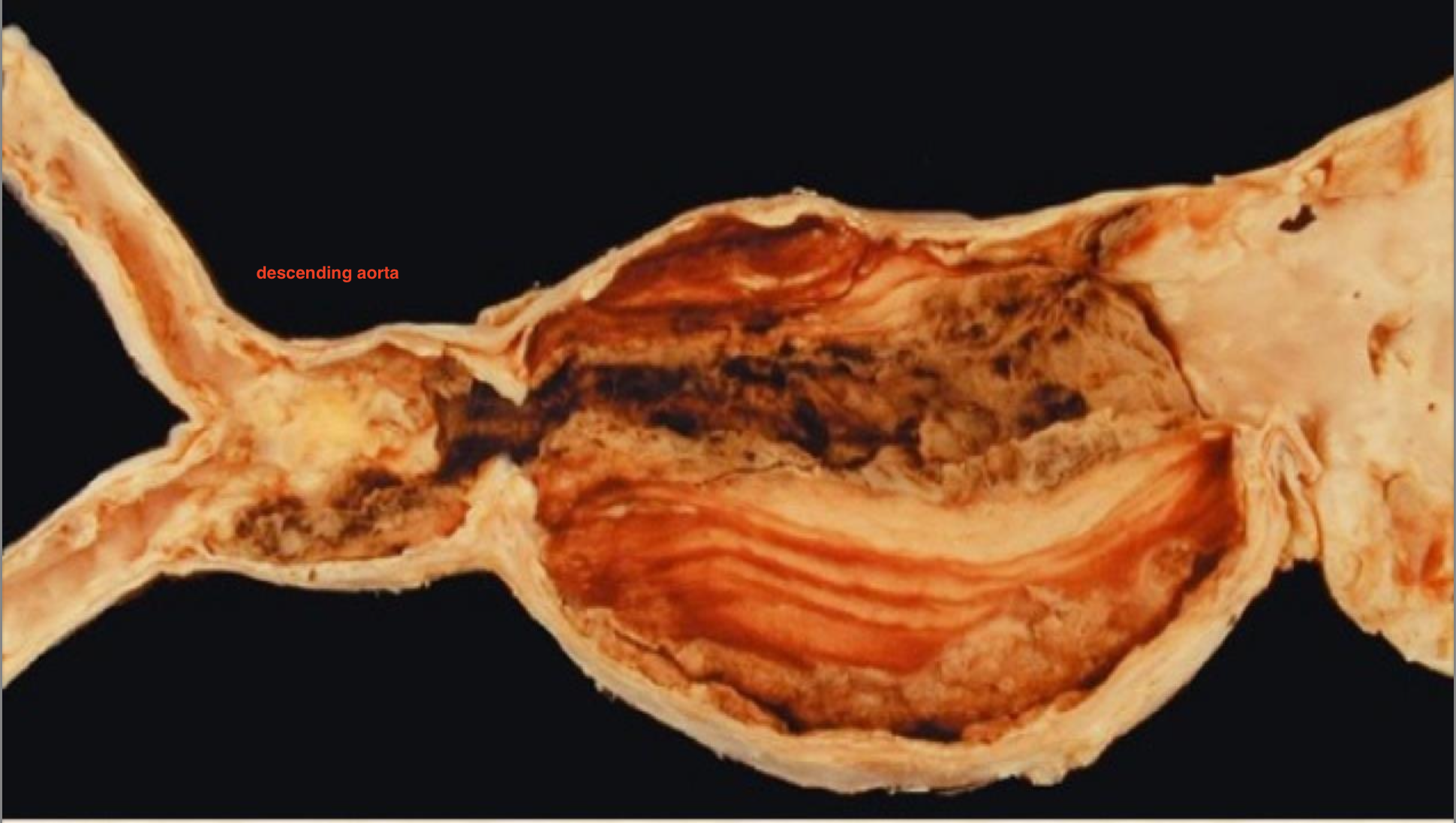
-mixed
-in aorta

mixed
-LV
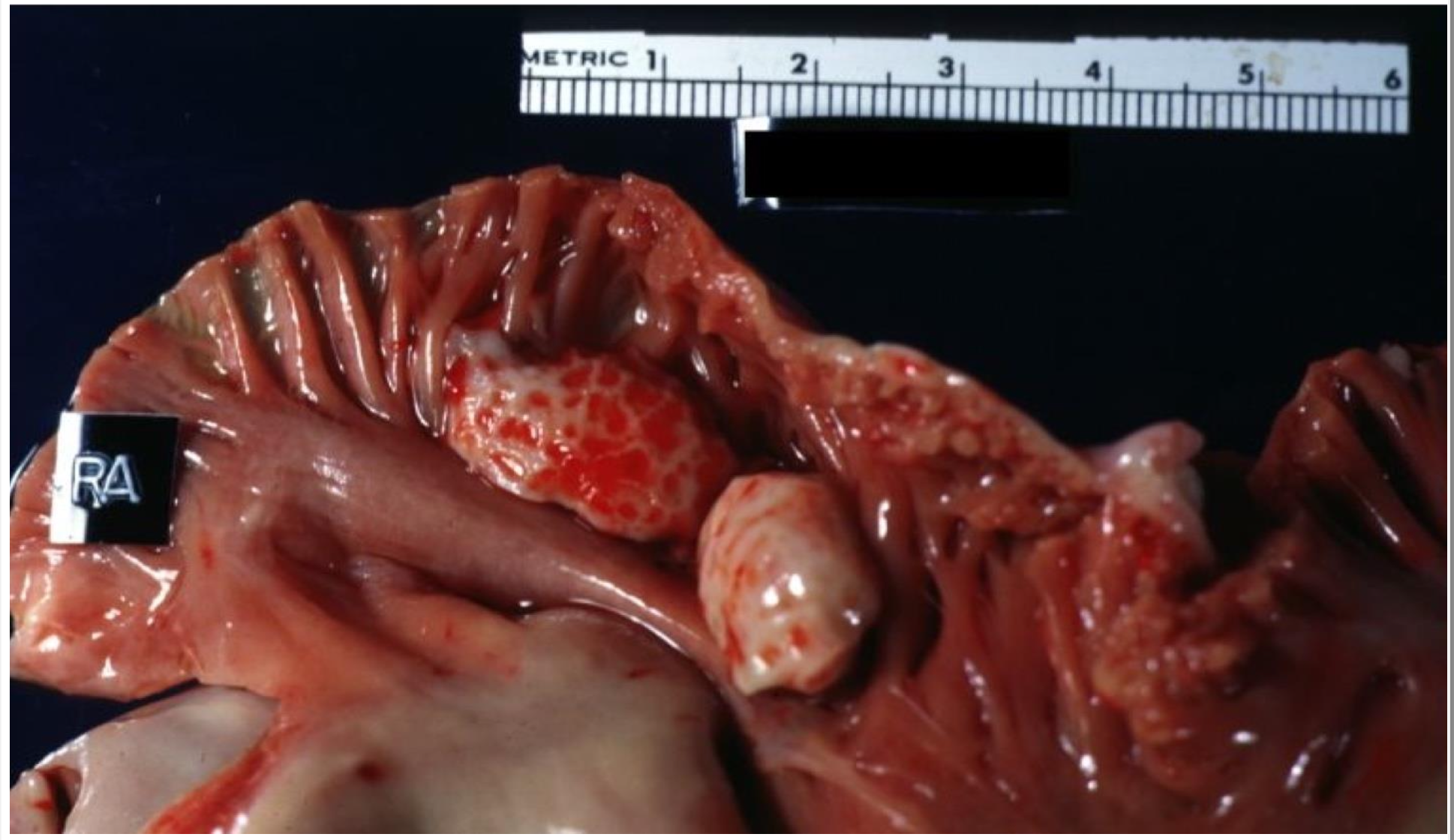
mixed
right atrium
thrombosis
Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system.
Arterial and Cardiac thrombosis
• Occur in site of endothelial Injury or turbulance e.g. atherosclerosis
• Pale or mixed thrombus
Venous thrombosis
• Occur in sites of stasis
• Tail of thrombus is prone to fragment creating an embolus (can move to the lung)
• Red or dark thrombus
arterial thrombosis leads to in different locations
Renal Infarction
Stroke
Intestinal Infarction
Myocardial Infarction
Gangrene
-due to blockage of oxygen delivery to those regions
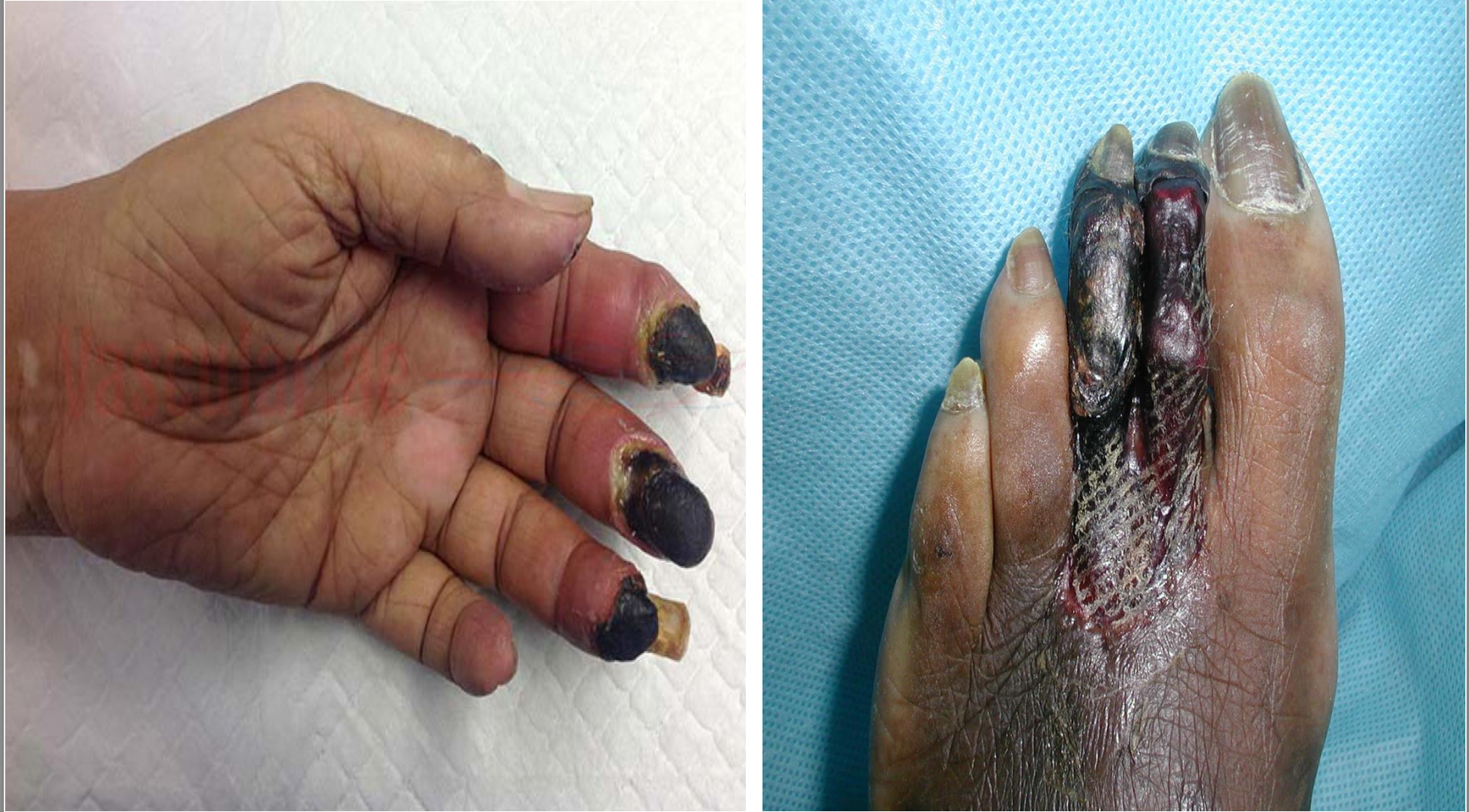
gangrenous necrosis
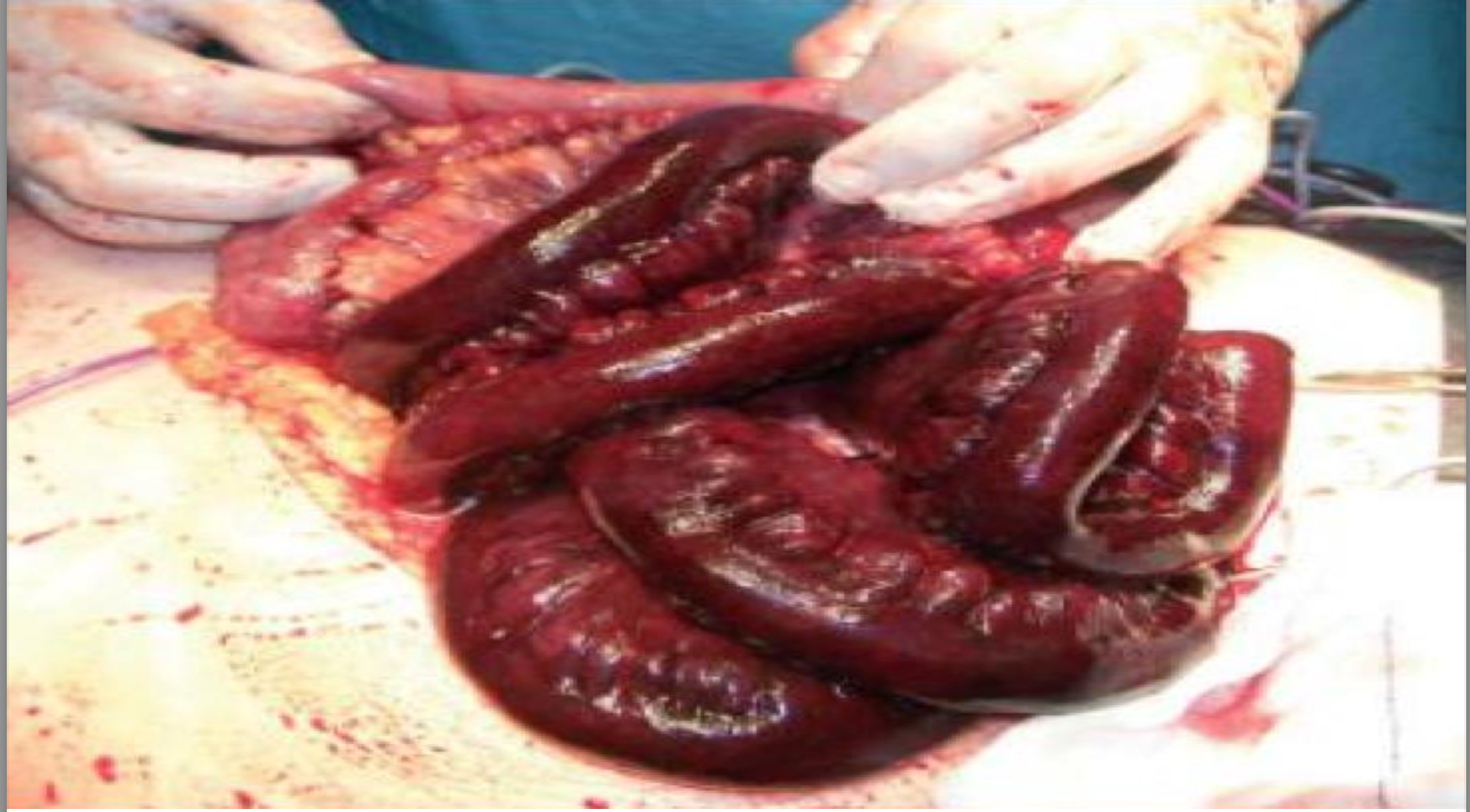
Intestinal Infarction
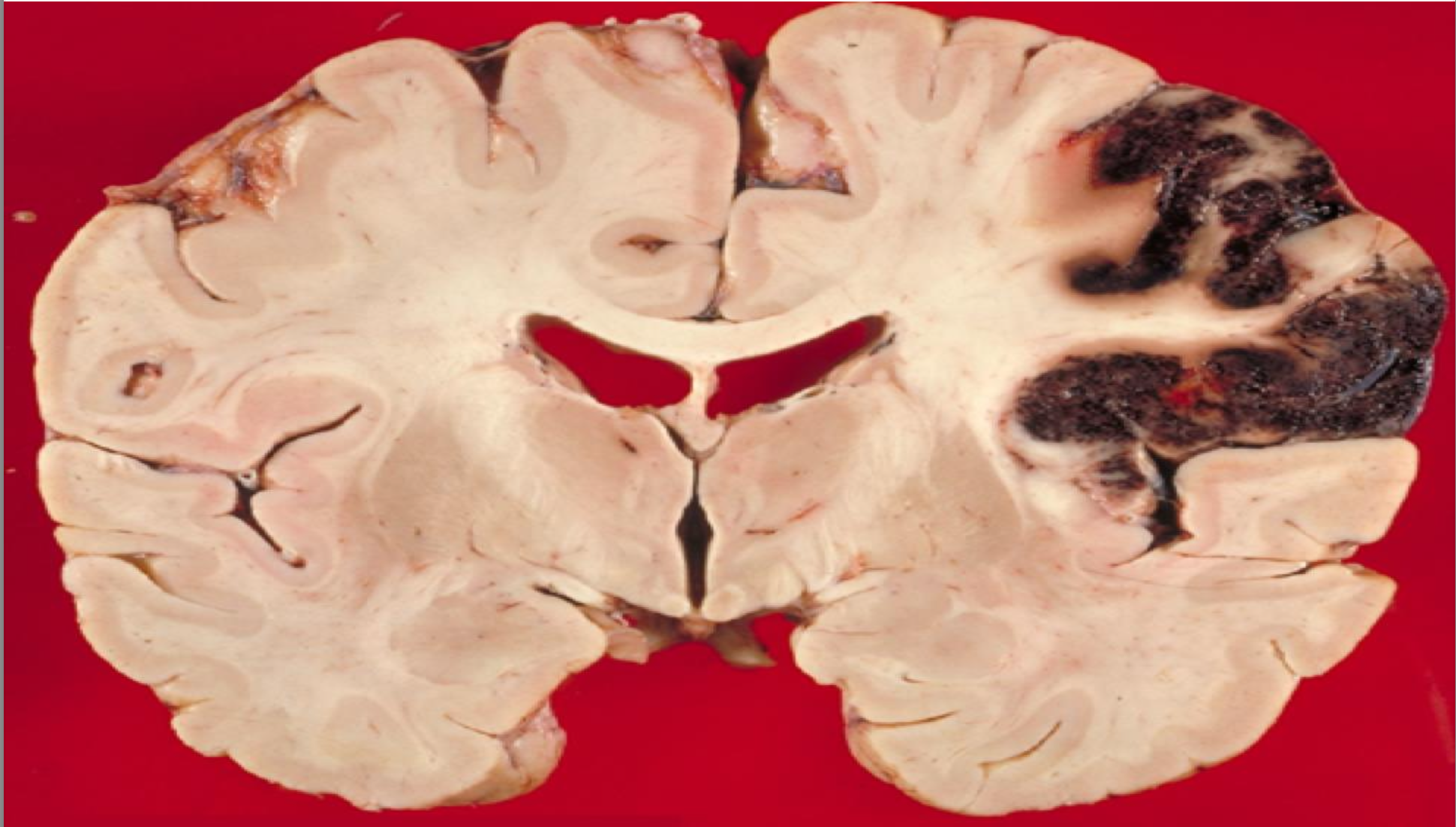
stroke
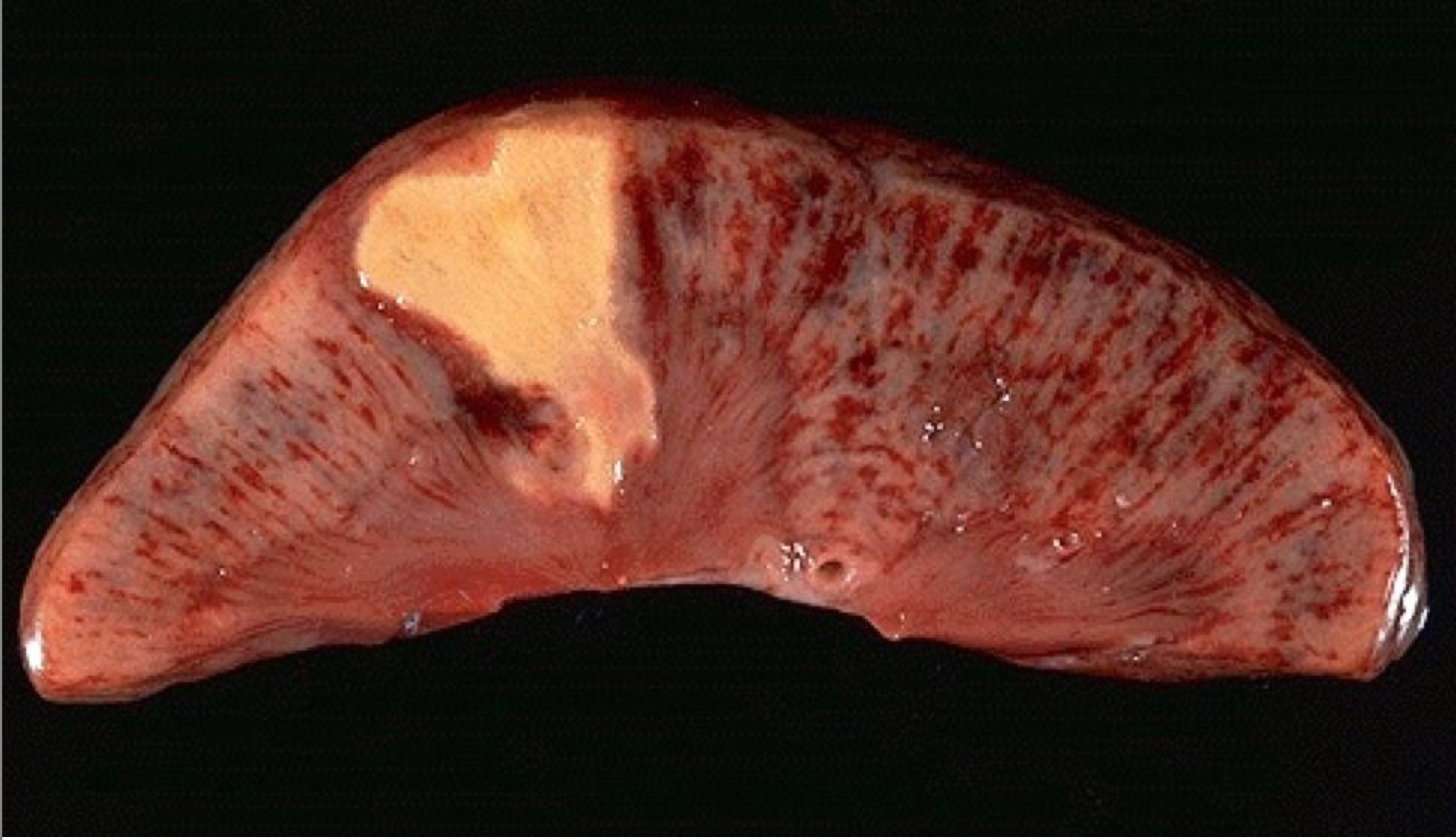
renal infarction
-coagulative necrosis
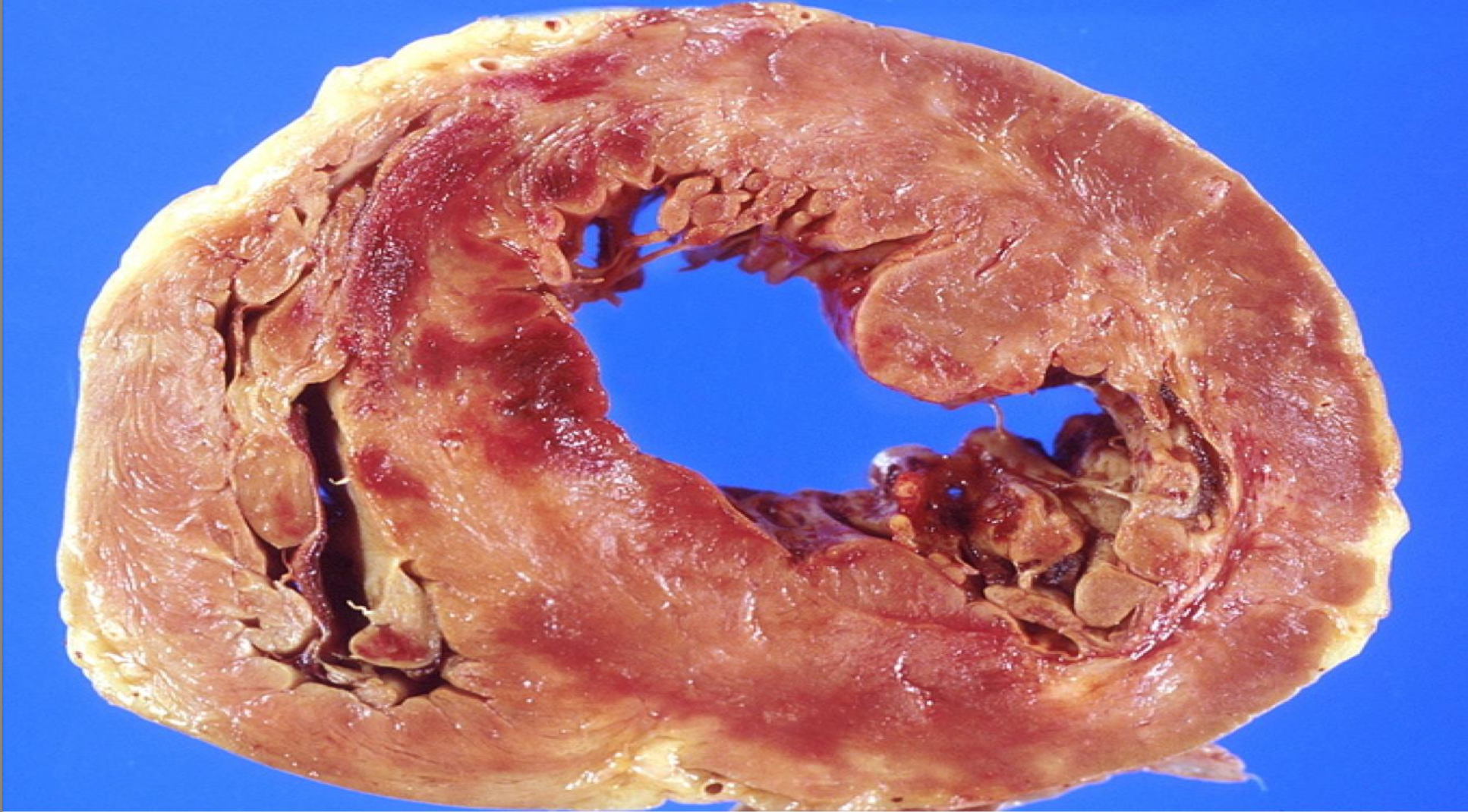
myocardial infarction
-coagulative necrosis
Cardiac Thrombosis common causes
• Myocardial infarction: Mostly the left ventricle, part of muscle wall not working so not all blood pumped out so remenant blood can lead to thrombus formation
• Endocarditis: Vegetation(fibrin, platelets, bacteria) may develop on cardiac valve
usually mitral or aortic that are damaged by bacterial
infection. Vegetation can detach leading to embolism
• Atrial fibrillation: Disorganized electrical signals leads to slower blood flow.
how does atrial fibrillation lead to a stroke
Atrial Fibrillation
Atrium do not empty completely
Blood in the atrium may stagnate
Blood clot formation
Clot may detach (Emboli)
Emboli may pass into Brain vessels
Block the vessels
Stroke
If a blood clot forms in the left atrium, it can dislodge and enter the systemic circulation through the left ventricle. From there, it can travel up the carotid arteries to the brain. If the clot lodges in a cerebral artery, it can block blood flow, leading to an ischemic stroke.
most common venous thrombosis
-swelling of leg due to blockage
-congested with blood and engorged
-redness at that area
-warm on touch due to accumulation of the blood
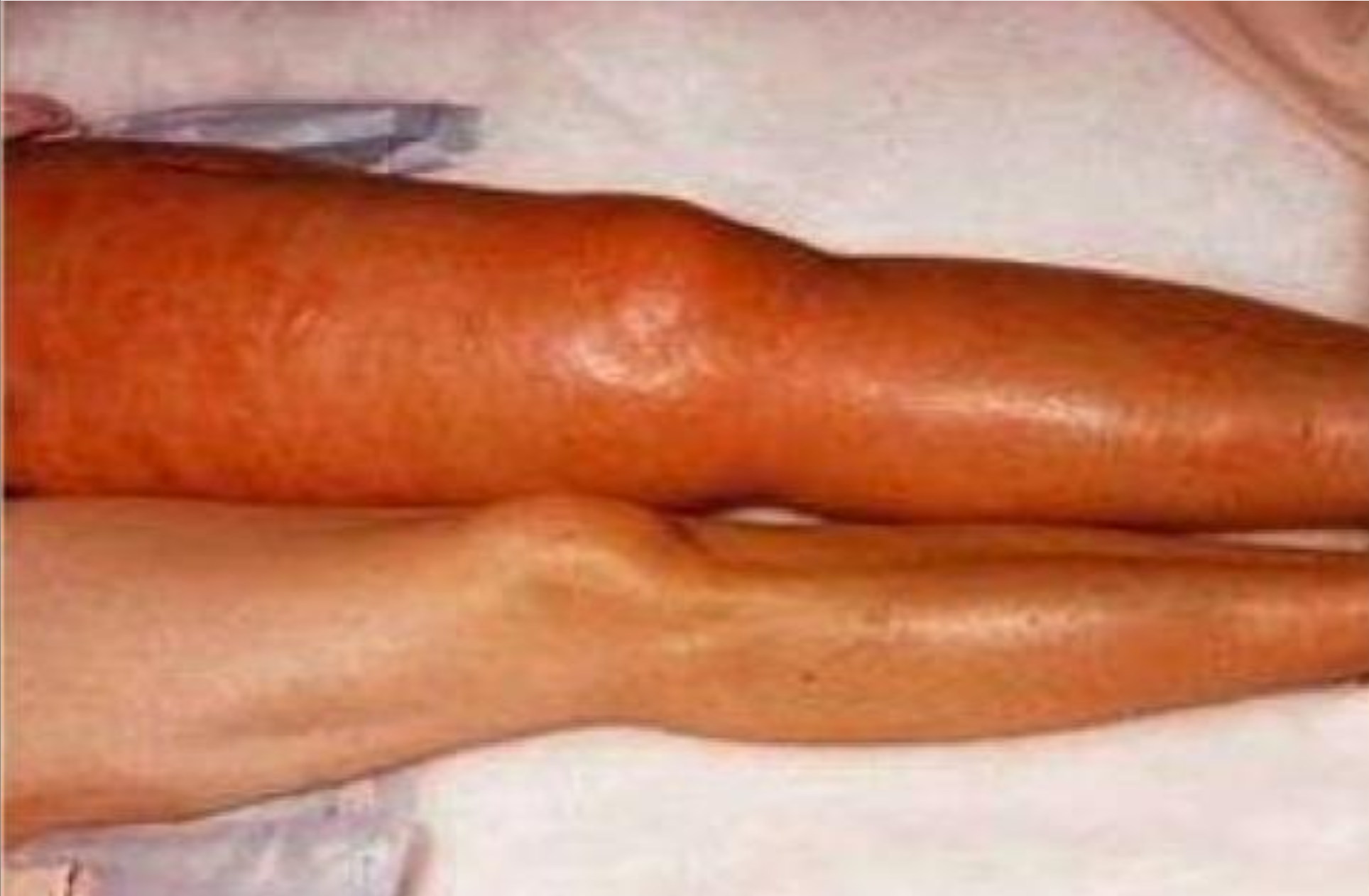
DVT findings
-Leg engorged, red, swollen and warm
-usually in one leg
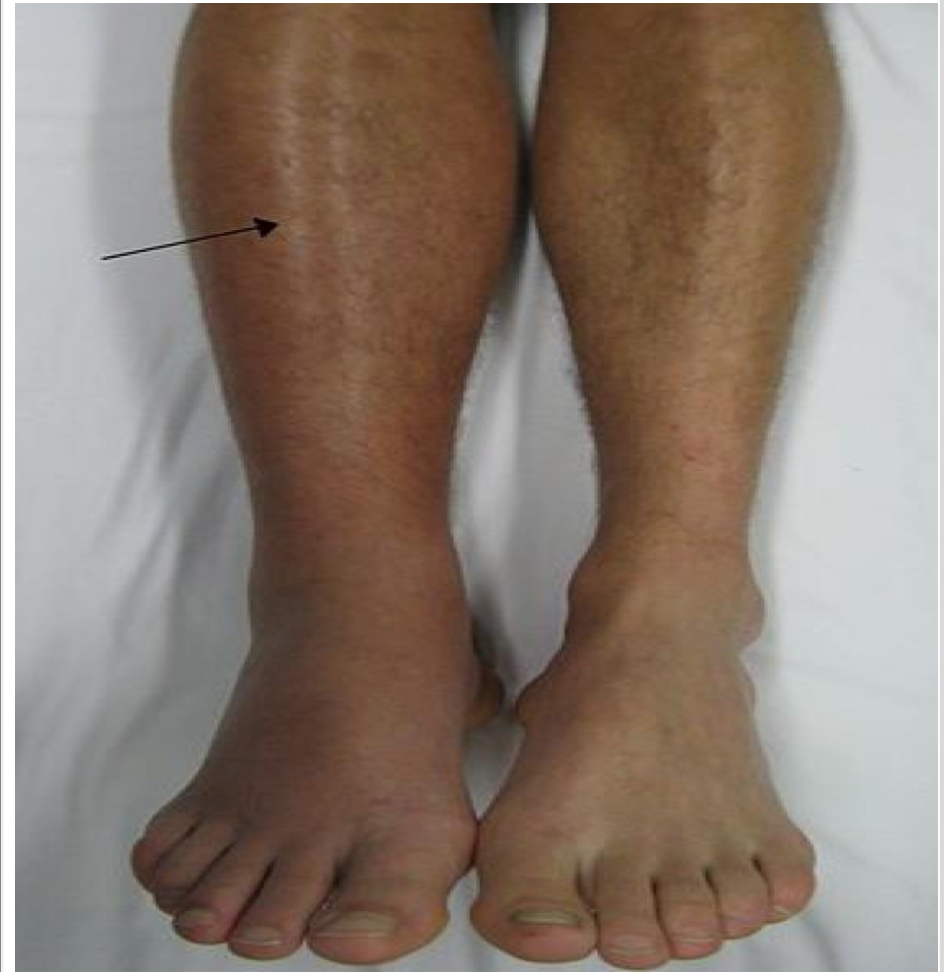
what is Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
arterial thrombosis in the leg
PAD clinical findings
• Arterial block leads to ischemia
• Leg looks pale-bluish-gangrene
• Leg is cold because there is no blood
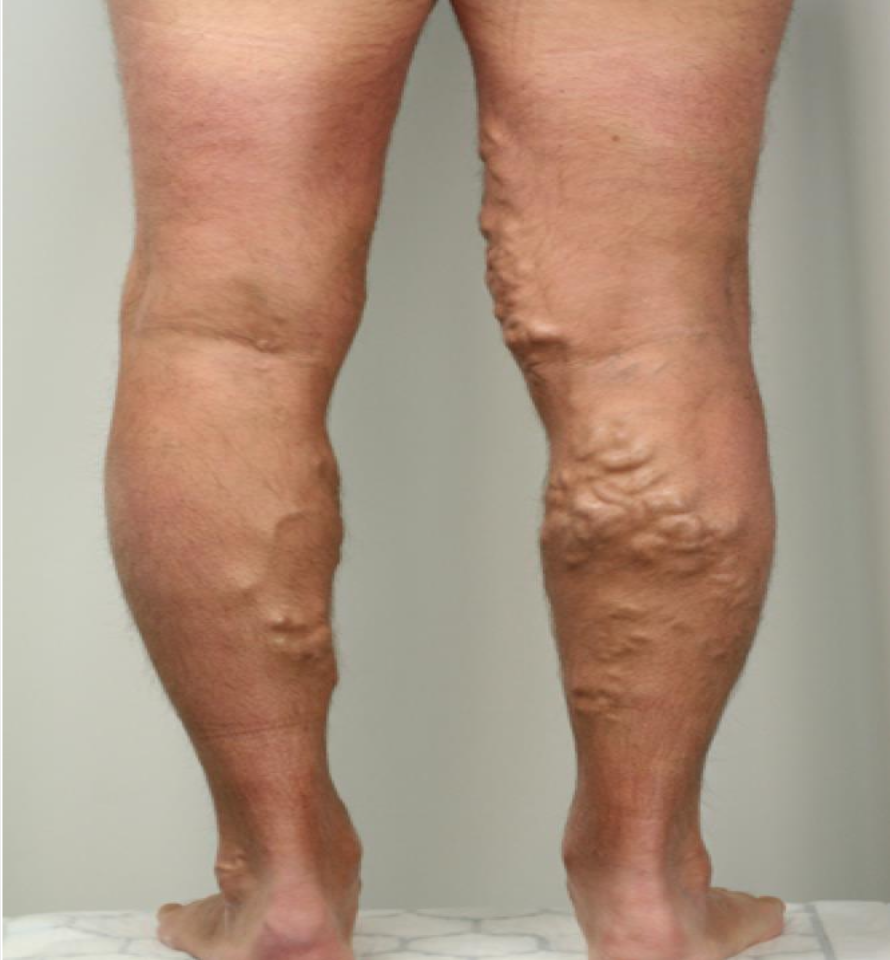
Varicose Veins
Venous valves are weak
• Affect superficial small veins
• dilated veins are blue
-doesnt block the veins
fate of the thrombus
-resolution: body removes the clot
-embolization to the lung
-organization and recanalization
-propagation: blood clot grows
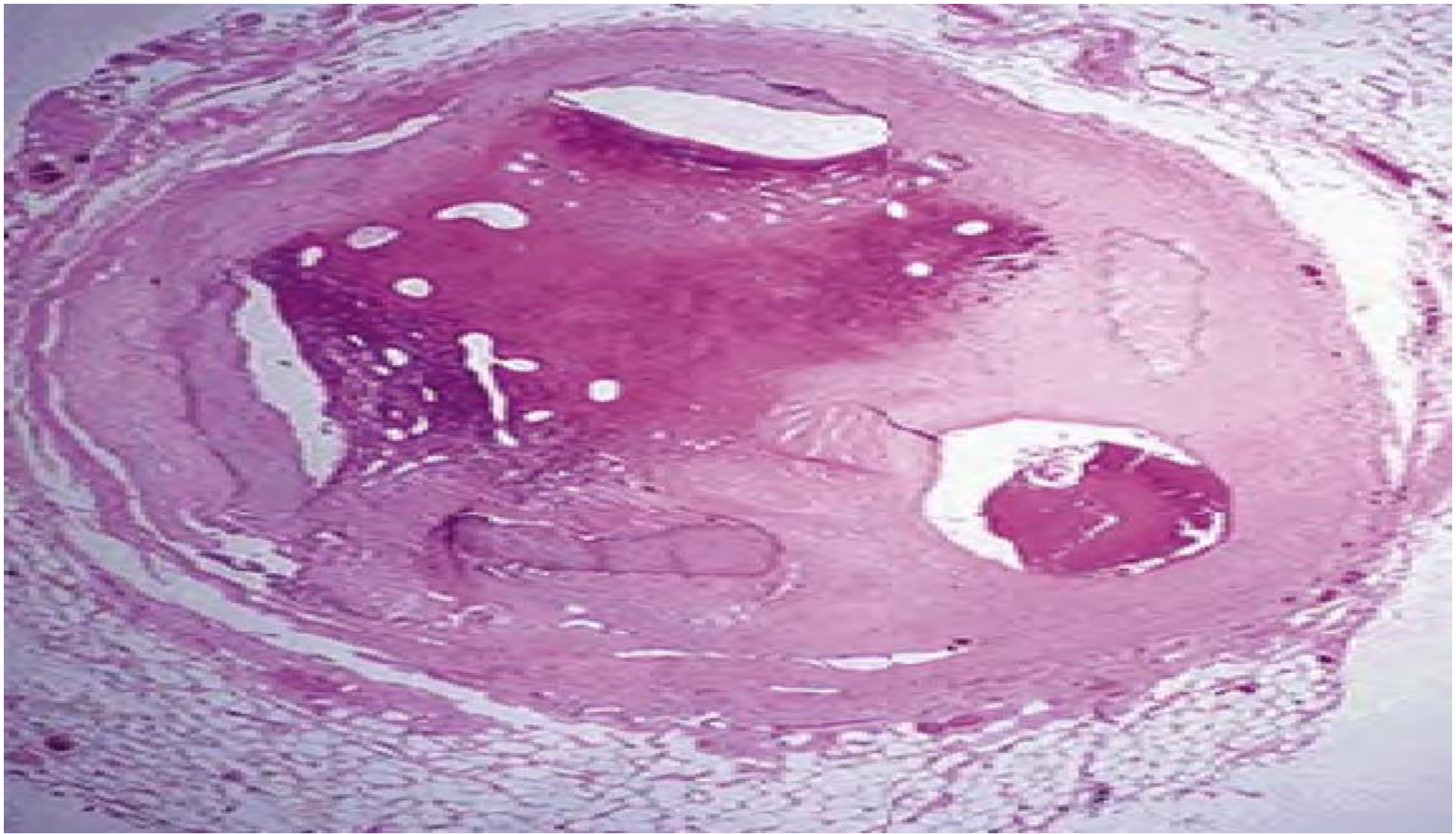
A cross section of coronary artery at autopsy showing one of the fate of a thrombus which is the organization and recanalization.
Embolus
A detached intravascular solid or gaseous mass that is carried by the blood from its point of origin to a distant
site, where it often causes tissue dysfunction or
infarction
Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
part of the DVT detaches and goes to left side of the heart into the pulmonary artery into the lungs causing lung infarction
lung infarction symptoms
shortness of breath, cough, dyspnea, orthopnea
DVT and ASD/VSD
In ASD/VSD, emboli can enter the arterial circulation (Paradoxical Embolism) and lead to stroke
Emboli in ARTERIAL circulation mostly from
– 60% left ventricular wall infarcts
– 25% left atrial dilation or fibrillation
– 15% aortic aneurysms and valvular vegetations
Consequences of arterial embolism depend on what
Consequences depend on caliber of occluded vessel and wether a collateral blood supply exist.
total blockage --> infarction
-collateral blood supply: other blood supply going to the same area
Types of Embolism
-Fat and marrow embolism
-Air Embolism
-Amniotic Embolism
Fat and marrow embolism
-when fracture happens part of marrow or fat pass through the small veins and do same as DVT and can lead to pulmonary embolism.
-mostly tibial or femoral fracture
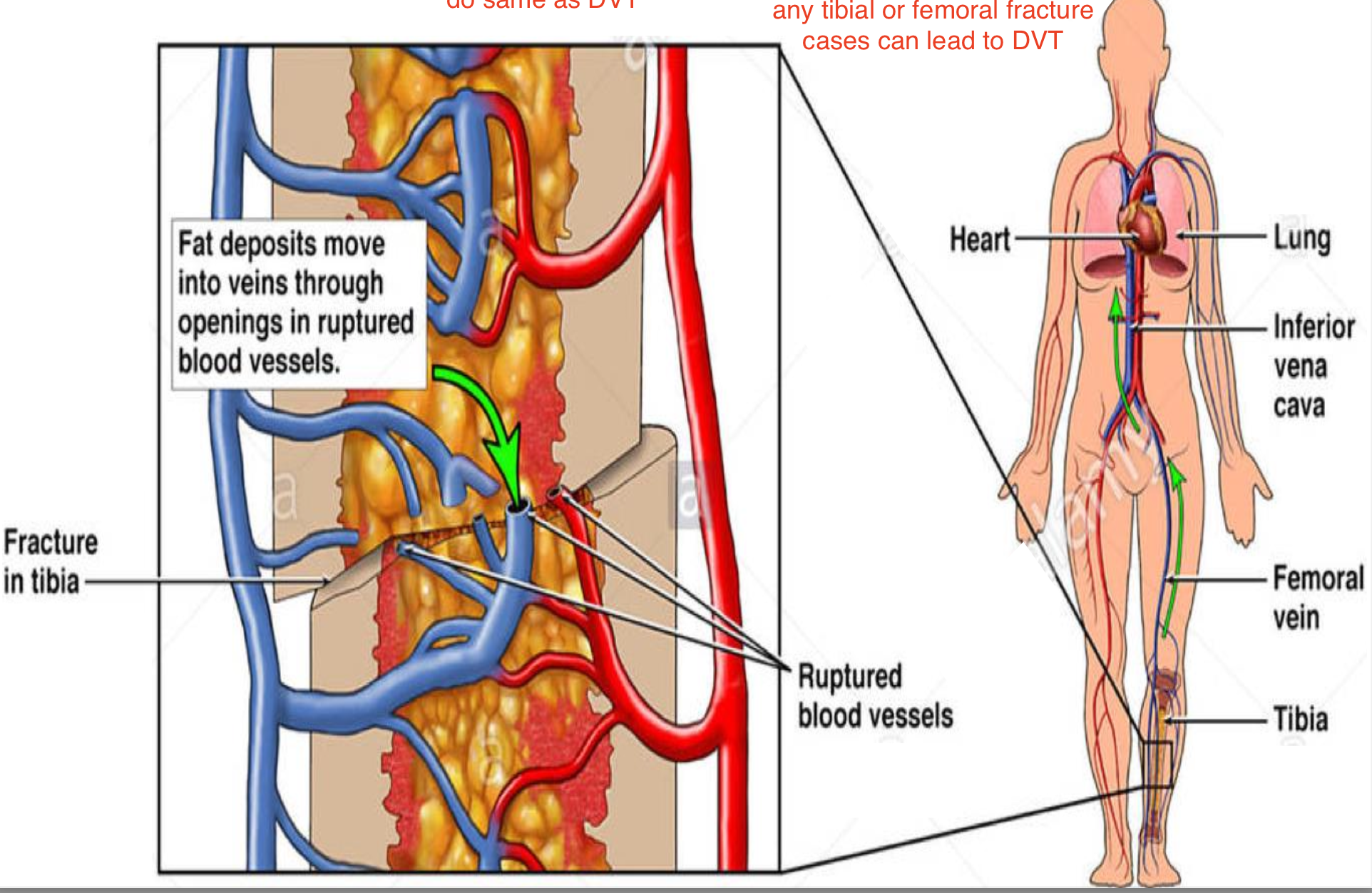
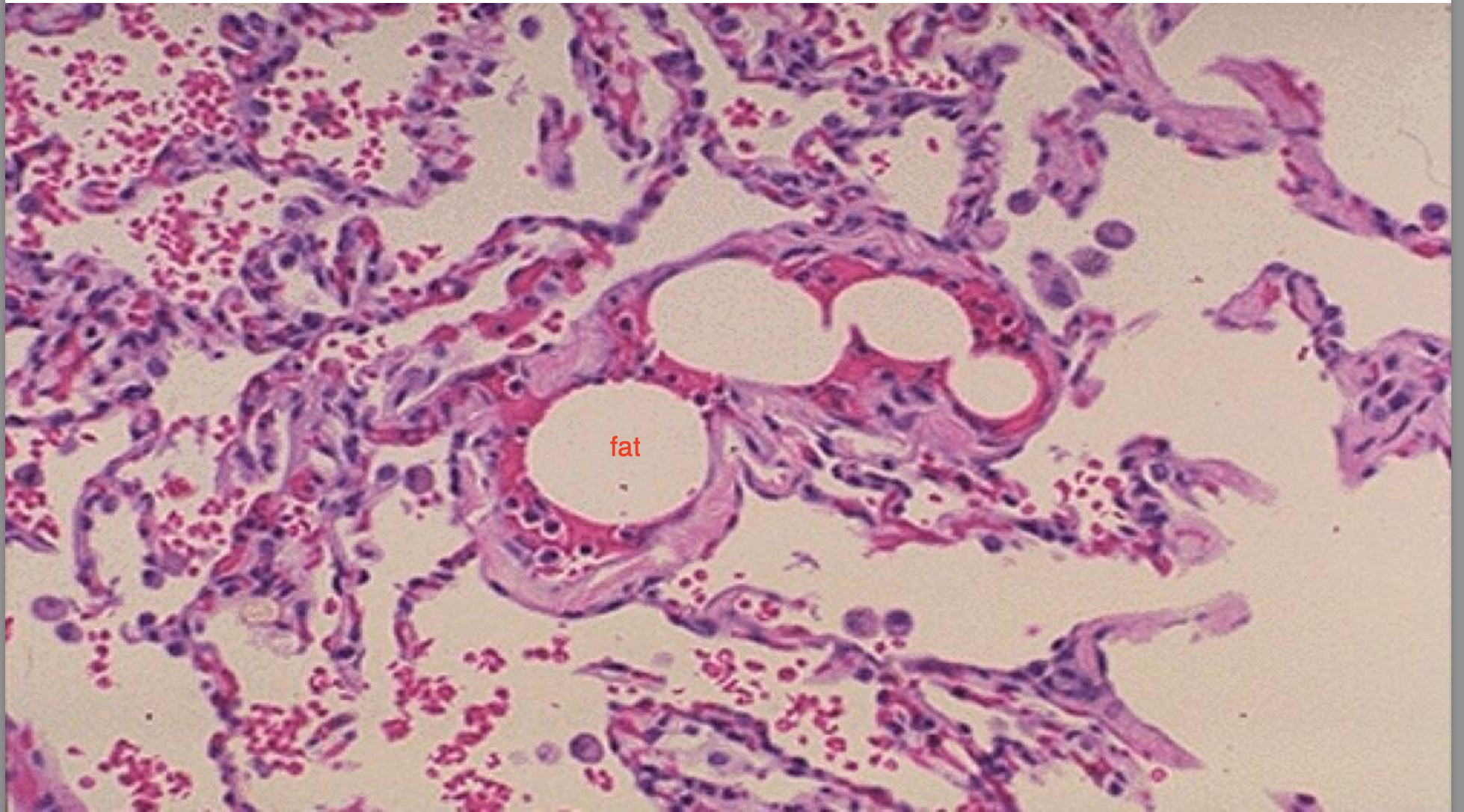
A cross section of pulmonary vessels at autopsy showing the presence of fat embolism blocking the the vessels.
Air Embolism occurs in what sickness
decompression sickness
-dive in deep sea levels, sudden drop in atmospheric pressure leads to rupture of alveoli, the air moves from ruptured alveoli to the capillaries and go to the brain, block those vessels and lead to stroke.
-also why u remove air bubbles from injections
Amniotic Embolism
when placenta is detached, the uterine veins rupture and some amniotic fluid or fetal tissue can pass into the mothers circulation leading to an embolism
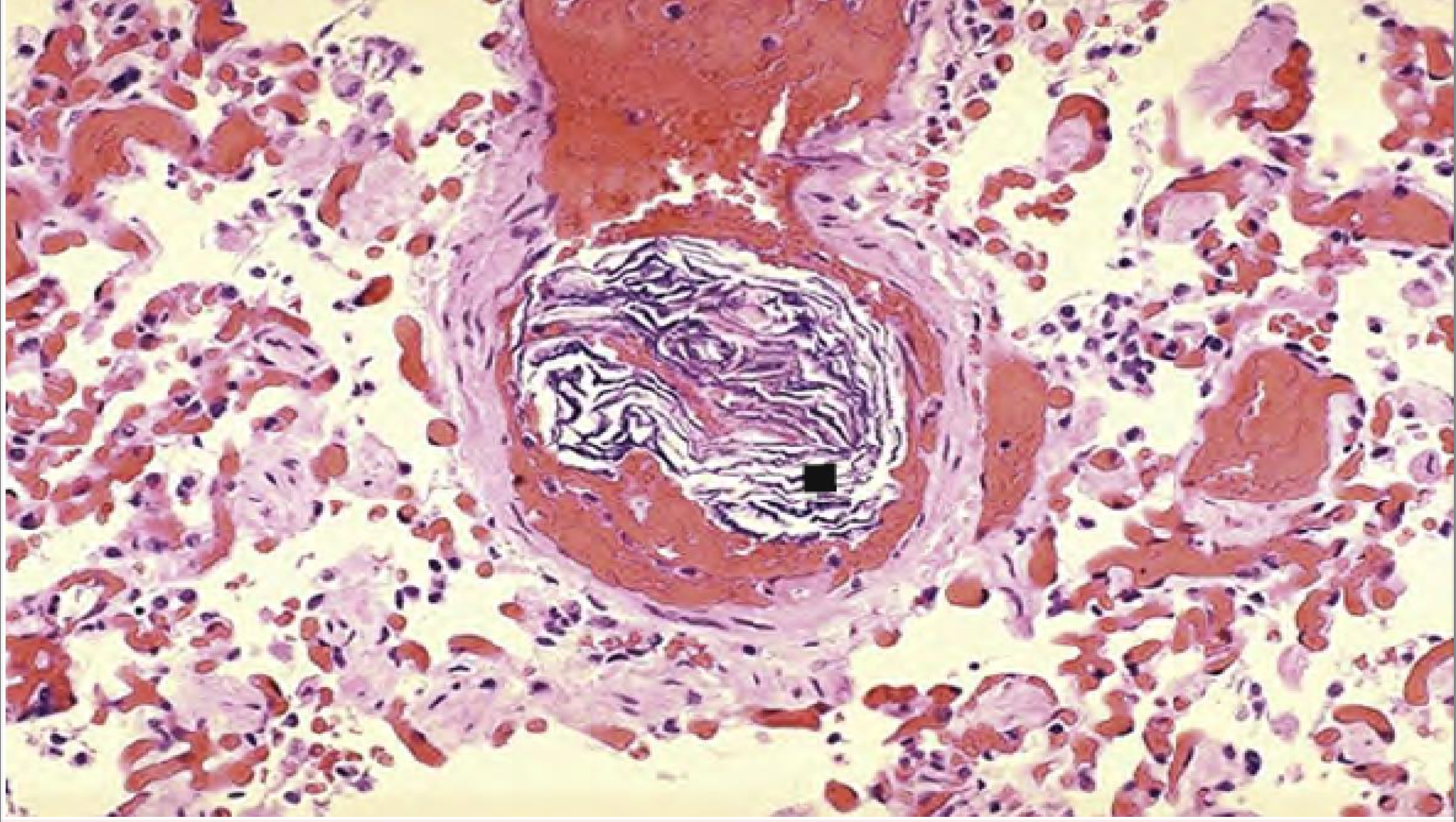
A cross section of pulmonary vessel at autopsy showing the presence of squamous cells shed from fetal skin.