Ultrasound Orientation and Terminology (Vocabulary)
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of vocabulary flashcards covering directional terms, planes, image orientation concepts, echo terminology, image controls, and transducer types relevant to ultrasound orientation and interpretation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
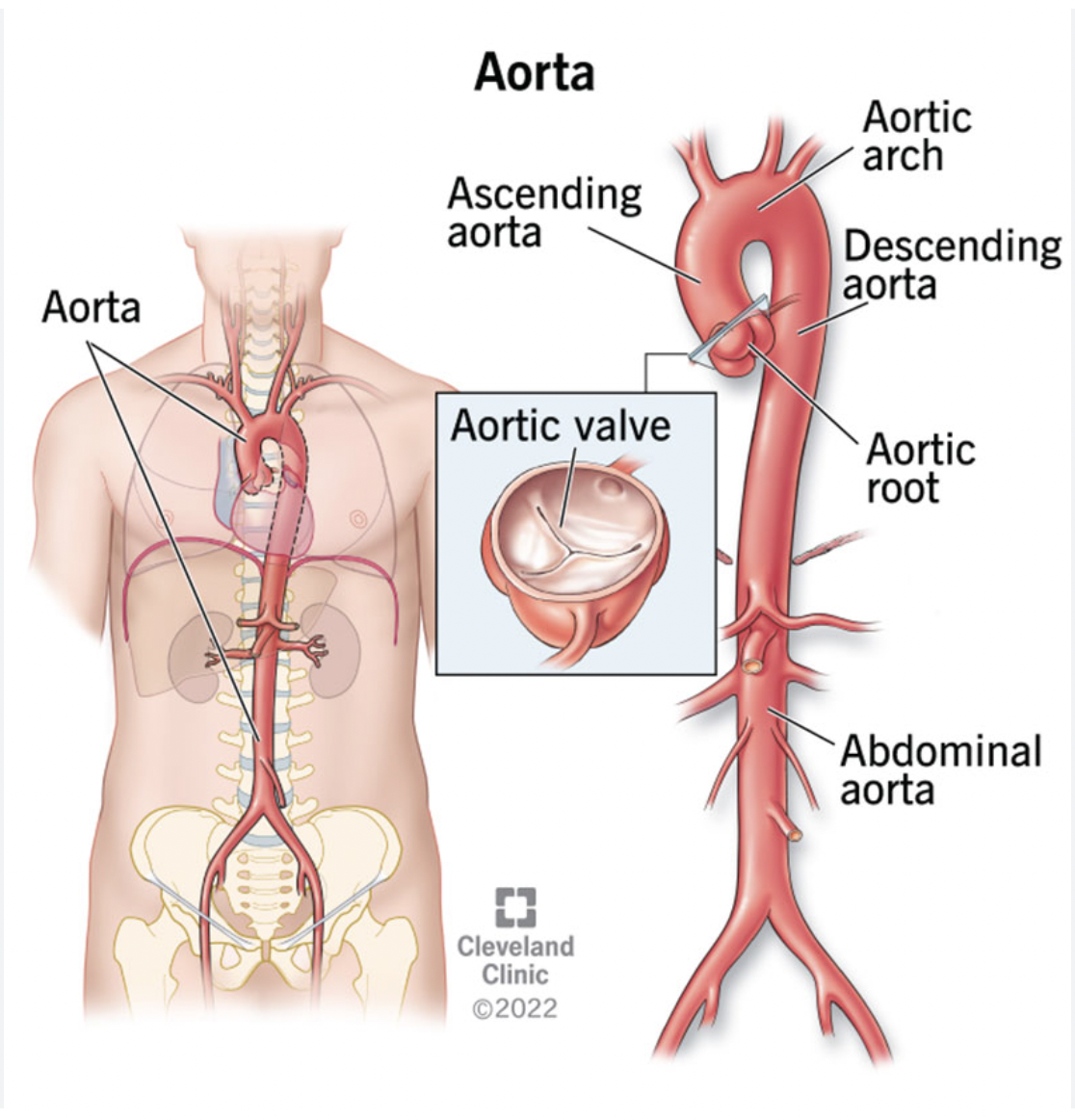
Ventral
Toward the front or belly
EX: the aorta is ventral to the spinal column
Dorsal
Toward the back or spine
EX: The spinal column is dorsal to the aorta
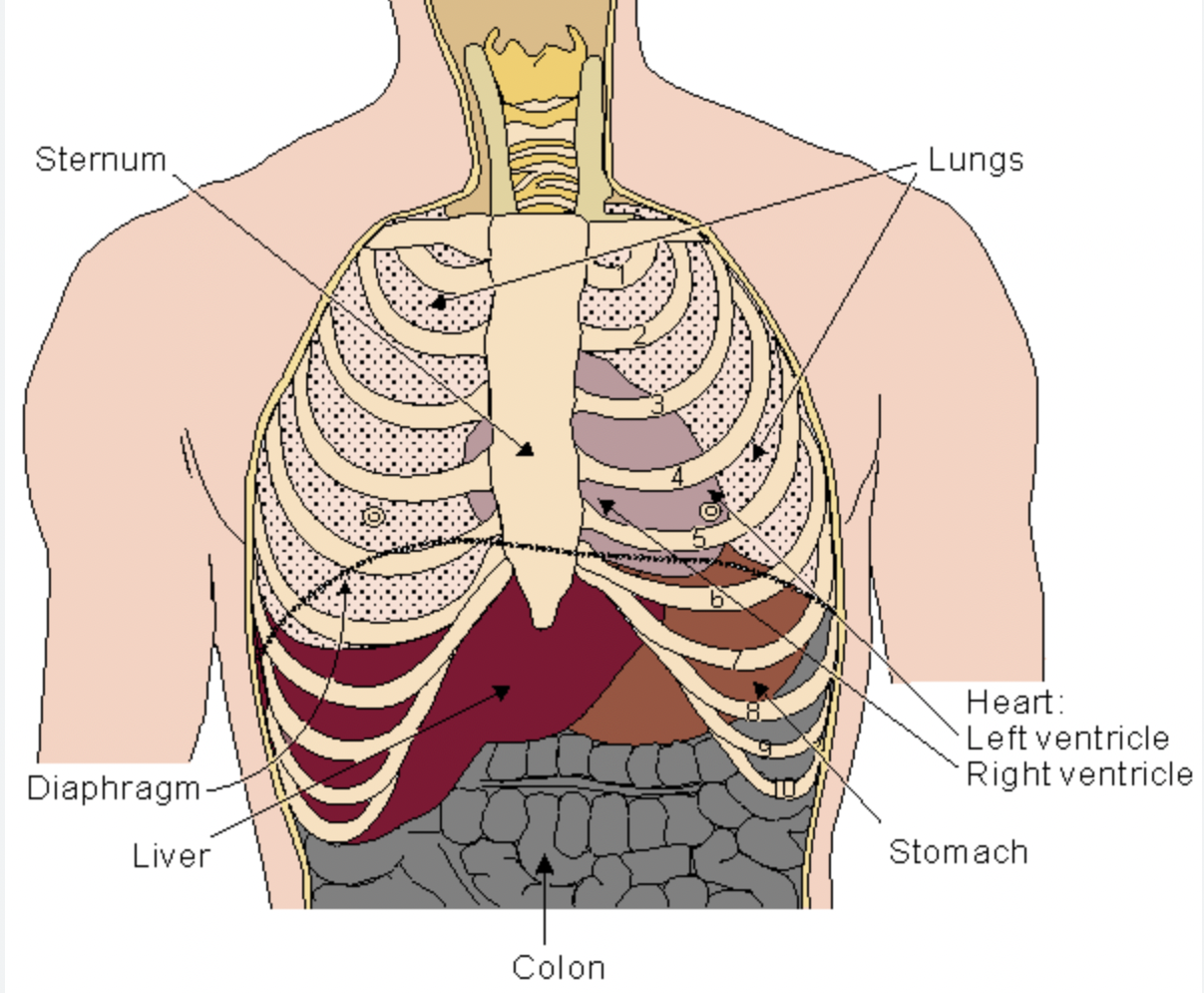
Anterior
Toward the ventral/front side
ex: The sternum is anterior to the heart
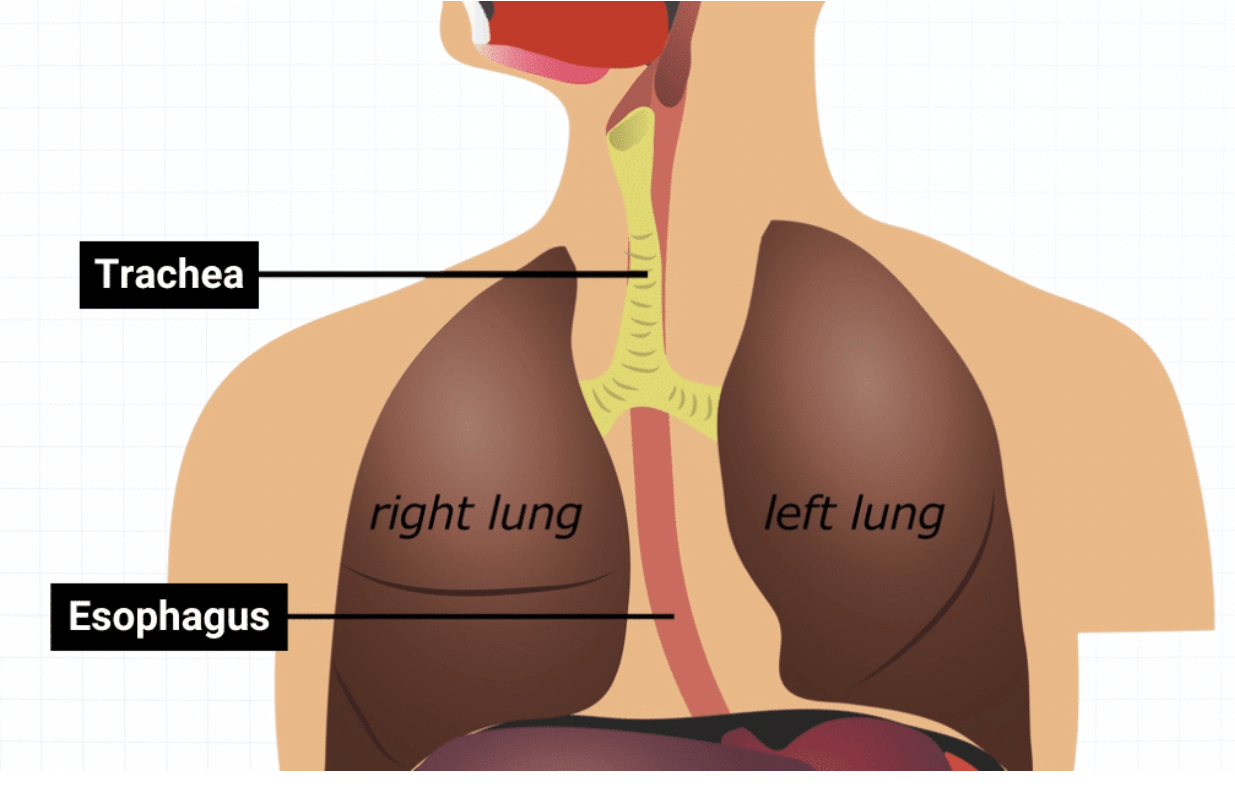
Posterior
Toward the dorsal/back side
ex: The esophagus is posterior to the trachea
Superior
Above (towards the head)
ex: The heart is superior to the diaphram
Inferior
Below (towards the feet)
ex: the liver is inferior to the diaphragm
Medial
Toward the midsagittal plane
midsagittal plane: straight down the middle of body
ex the heart is medial to the lungs
Lateral
Away from the midsagittal plane (away from the middle)
ex: the clavicles (collarbone) are lateral from the sternum
Proximal
Closer to the point of attachment or origin (above)
ex: the elbow is proximal ^^^ to the wrist
Distal
Farther from the point of attachment or origin (below)
ex: the fingers are distal to the shoulders
Central
Near or toward the midline of the body
ex: the brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system
Peripheral
Away from the midline or center of the body
ex: peripheral nerves lead from the spinal cord to the skeletal muscles blood drawn from a fingerstick is peripheral blood
Superficial
Closer to the body surface
ex: the skin is superficial to the muscles
Deep
Farther from the body surface
ex: the bones are deep to the muscles
Ipsilateral
on the same side of the body
ex: the right arm is ipsilateral to the right leg
Contralateral
on opposite sides of the body
ex: the left arm is contralateral to the right leg
Anechoic
No internal echoes; appears black; typical of fluid-filled structures.
ex blood vessels, urine, bile
Echogenicity
The brightness or strength of echoes
hyperechoic = more echogenic than surrounding structures
hypoechoic = less echogenic than surrounding structures
isoechoic = same echogenicity
anechoic = no internal echoes
Hypoechoic
Low amount of echoes (varying shades of darker gray)
ex: the liver is hypoechoic to the pancreas
meaning the liver is darker shades of gray when compared to the pancreas
Hyperechoic
Greater amount of echoes (varying shades of lighter gray)
the pancreas is hyperechoic to the liver
meaning the pancreas is lighter shades of gray when compared to the liver
Isoechoic
Having similar echogenicity to a neighboring structure
Homogeneous
Uniform grayscale echo pattern throughout the structure
ex: liver is homogeneous (looks normal)
Heterogeneous (inhomogeneous)
grayscale echo pattern is Irregular or mixed echo pattern within a structure.
ex: liver is inhomogeneous (non uniform texture pattern)
Gray Scale
The range of grays used to display echoes in ultrasound imaging
anechoic, hypoechoic, hyperechoic, echogenic
Posterior enhancement
Increased brightness behind a fluid-filled structure due to low attenuation.
Sound or posterior attenuation
Dark, no echoes beyond a structure due to attenuation.
Cyst
A fluid-filled structure that is anechoic and often shows posterior enhancement.
Cholelithiasis
Gallbladder with gallstones
stones are echogenic and may cast posterior shadow.
Gallbladder is anechoic
Anechoic cyst
A fluid-filled structure with no internal echoes, showing posterior enhancement.
Focal point
level at which the ultrasound beam is most focused to improve resolution at that level.
Time Gain Compensation (TGC)
Controls (near (top) /far (bottom) and overall gains) that compensate for depth-related attenuation.
Gain
Overall brightness control of the ultrasound image; includes near and far gain.
Depth
How deeply the sound beam penetrates
18cm
toggle up for decrease ( more superficial structures)
toggle down for increase (deeper structures)
Transducer
The ultrasound probe; converts electrical energy to sound waves and vice versa.
Convex transducer
Curved-array transducer; larger footprint; suitable for deeper structures.
Micro-convex transducer
Small curved-array transducer; good for limited spaces and pediatrics.
Phased array transducer
Small-footprint transducer, often used for cardiac imaging; beam is electronically steered.
Linear transducer
Flat, high-frequency array; ideal for superficial structures and vessels.
Curvi-linear / Curved transducer
Large footprint, ability to penetrate deep structures large variation in frequencies available
Suboptimal for superficial structures
Endocavitary / Transvaginal transducer
Placed inside the vagina for detailed views; used only for pelvic first trimester or early second trimester exams measuring cervical length
Sagittal plane
A vertical plane dividing the body into left and right sections (midline reference).
Transverse plane
A horizontal plane dividing the body into superior and inferior parts.
Coronal plane
A plane dividing the body into anterior and posterior portions.
Supine
Lying with face and torso UP (flat on back)
Left lateral decubitus
lying on the left side
upright
sitting elevated with head and upper body raised at an angle between 60-90 degrees
Prone
laying with face and torso facing DOWN
Sagittal imaging Plane
midline sagittal plane (Notch toward the head)
Transverse imaging plane
imaging sideways —— Notch right shoulder
right left
Oblique imaging plane
criss cross X
Coronal imaging plane
sliced in half but laying on back
Echoes
reflected sound waves displayed as varying shades of gray
Echogenic
the ability of a structure to produce echoes
“bright” or white on ultrasound
ex: stone, calcification, bone