(CIE A2 Biology) Phenotypic variation (based on SaveMyExams revision notes)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Phenotype
The observable characteristics of an organism.
Phenotypic variation
The difference in phenotypes between organisms of the same species.
Genotype
The genetic constitution of an organism.
Genetic variation
The small differences in DNA base sequences between individual organisms within a species population.
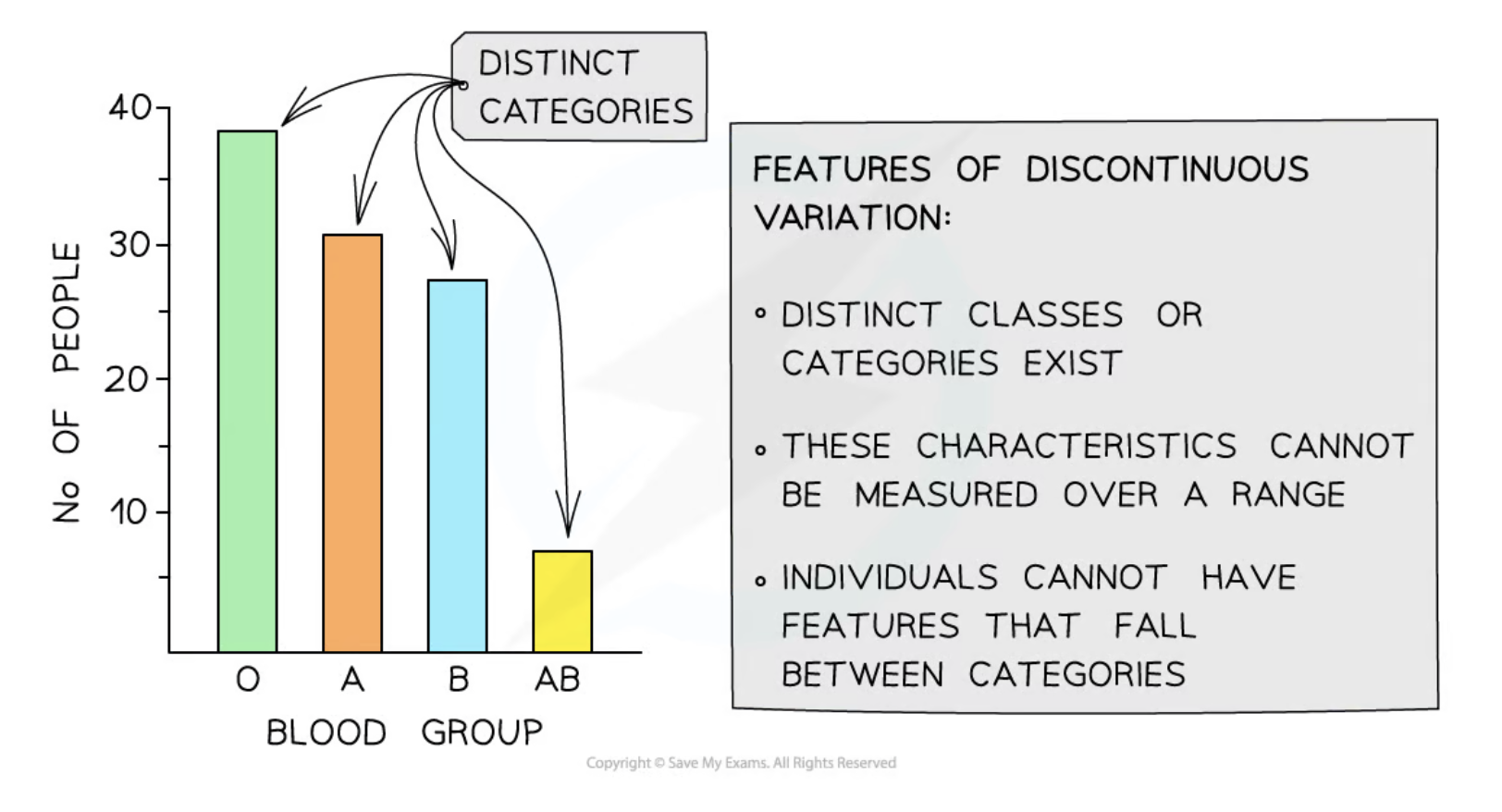
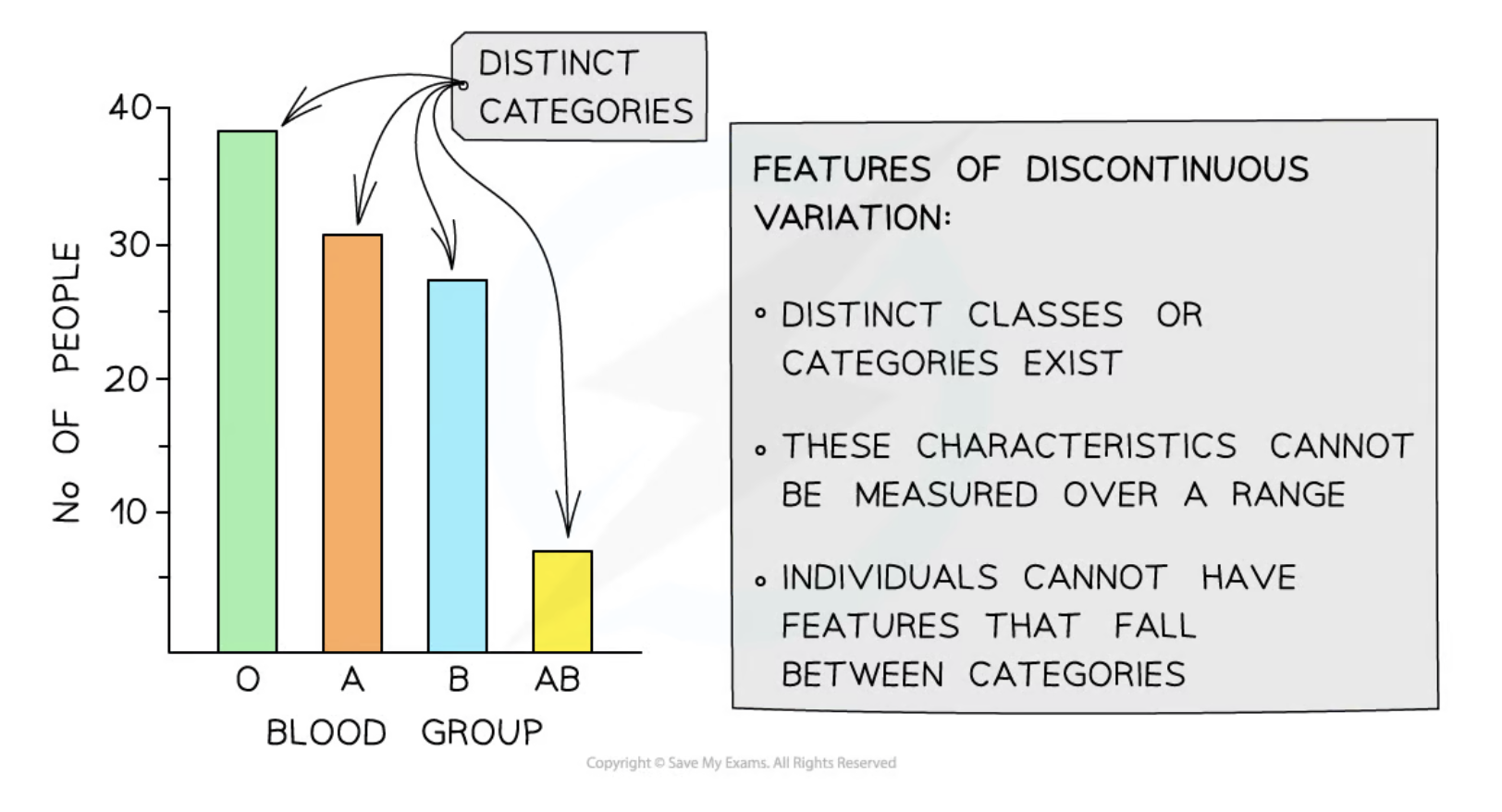
Discontinuous variation
Variation that occurs where qualitative differences fall into distinct, non-overlapping categories.
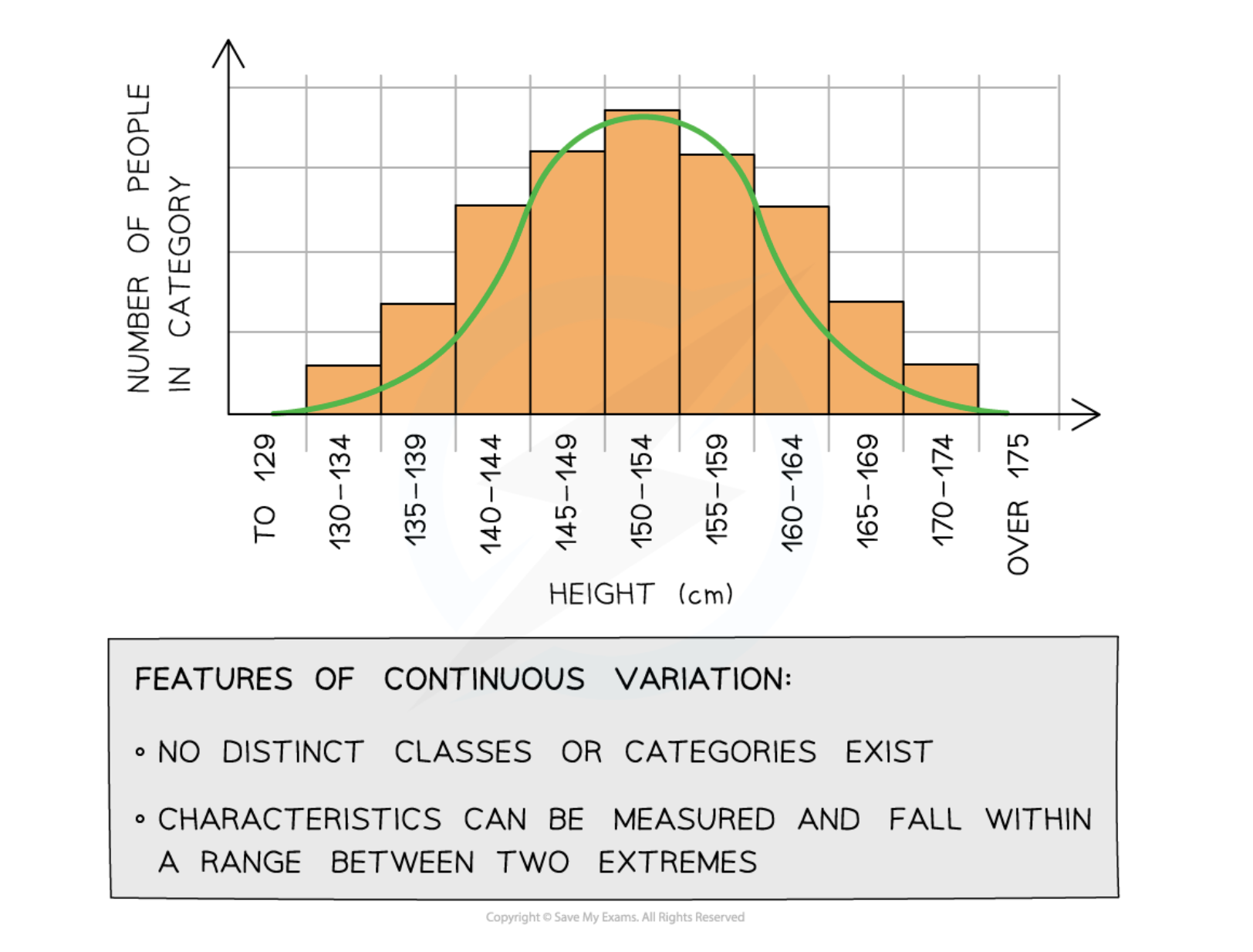
Continuous variation
Variation characterized by quantitative differences that form a range of values between two extremes.
Independent assortment
The random alignment of chromosomes during metaphase I leading to different combinations of alleles in gametes.
Crossing over
The exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids during prophase I.
Mutation
A random change in the DNA base sequence that generates a new allele.
Polygenes
Multiple genes that together influence a phenotype in a cumulative manner.
Additive effect of genes
When different alleles at various loci combine to produce a cumulative effect on a phenotype.
Homozygous
An organism with two identical alleles for a given gene.
Heterozygous
An organism with two different alleles for a given gene.
ABO gene
The gene that determines blood group in humans.
Sickle cell anaemia
A genetic condition caused by a recessive allele that affects the shape of red blood cells.
Environmental factors
External conditions, such as sunlight, nutrients, and temperature, that can affect an organism's phenotype.
Gamete
A reproductive cell (sperm or egg) that carries genes to the next generation.