Agriculture
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Except Abiotic and Biotic Factors
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Name the 2 ways to manipulate food species to increase productivity:
Increasing the stocking/crop density
Monocultures
What is stocking/crop density?
Stocking density refers to the number of animals per unit of land.
Crop density refers to the number of plants grown per unit of land.
Advantages of increased density
Efficient land use
Easier management (controlled feeding, irrigation, harvesting)
Maximises productivity
Disadvantages of increased density
Overcrowding can lead to resource competition and disease spread.
Soil degradation (overplanting)
What are monocultures?
The cultivation of a single crop in a given area.

Advantages of Monocultures
Efficient (easier to manage, harvest)
Consistent quality (all crops grown under same conditions)
Disadvantages of Monocultures
Soil degradation
Loss of biodiversity
Dependency on fertilisers and pesticides
Pest and disease vulnerability
Definition of Genetic Manipulation
Manipulation of an organism's genes using biotechnology
What are the 3 examples of genetic manipulation?
Selective breeding
Asexual reproduction
Genetic engineering / Transgenics / Genetic Modification
What is selective breeding?
The selection of plants or animals with the desired characteristic by the farmer/breeder and are bred together so that the offspring have the desired trait.
What’s the disadvantage of selective breeding?
There’s an increased risk of inbreeding
Examples of Selectively Bred Animals
Highland Cow - Even temper, few stress problems
Large white - Good quality bacon
Merino - Good quality wool

How do plants reproduce asexually?
Via vegetative propagation
Advantages of Plants Asexual Reproduction
Uniform phenotype
Disadvantages of Plants Asexual Reproduction
No genetic variation
Uniform disease susceptibility
Fewer offspring produced
How do animals reproduce asexually?
Via cloning
Outline the Method of SCNT
The animal to be cloned donates a somatic body cell
The nucleus from the somatic cell is removed
An unfertilised egg cell is extracted from the female egg donor
The unfertilised egg cell is enucleated
The nucleus from the somatic body cell is fused with the enucleated egg cell using an electric current
The hybrid zygote cell is now treated to encourage it to divide by mitosis
The embryo is implanted into the surrogate mother for gestation and birth
What are the potential applications of artificial asexual reproduction?
Valuable animals that die can be replaced with genetically identical animals
Herds culled due to a disease outbreak can be replaced with genetically identical animals
Large numbers of animals with desirable characteristics can be produced
Definition of Genetic Engineering
The direct manipulation of an organism's DNA to change its traits.
Definition of Transgenics
The transfer of DNA from one species to another
Examples of GM crops:
GM rice varieties
Bt crops
What are Bt crops?
Soya is genetically modified to produce Bt proteins.
Bt proteins are toxic to many pests and resistant to weed killer.
This means farmers don’t need to spray insecticides, and can spray weed killer to get rid of weeds and don’t kill the soya.
What are the disadvantages of Bt crops?
Pollinators and predators may be damaged by the toxins from the Bt protein
Insects might become resistant to the toxic Bt protein
Genes might spread to wild populations, creating "superweeds"
Reduces biodiversity
Claims that GM foods can increase food allergies
Why are GM crops costly for farmers, especially in LEDCs?
IP rights and patents for specific GM crops are owned by specific companies that control the prices and availability of the seed.
GM seeds need to be purchased each year, rather than harvesting seeds from an existing crops.
Name the 5 ways in which agricultural energetics can be quantified:
Productivity
Efficiency
Intensive/Extensive systems
Energy Subsidies
Energy ratios
What is productivity?
Measures the amount of output per unit of input
What is efficiency?
Measures how effectively energy is converted into useful agricultural output. It focuses on the energy ratio (output vs. input).
What is intensive agriculture?
Agriculture that involves increasing the amount of artificial inputs (like fertilisers, pesticides) to increase and maximise agricultural yield per unit of land.
What is extensive agriculture?
Agriculture whereby agricultural effort is spread over a larger land area
There is lower productivity per unit of land area, but overall global productivity is higher due to more areas being farmed.
Lower input farming techniques are used.
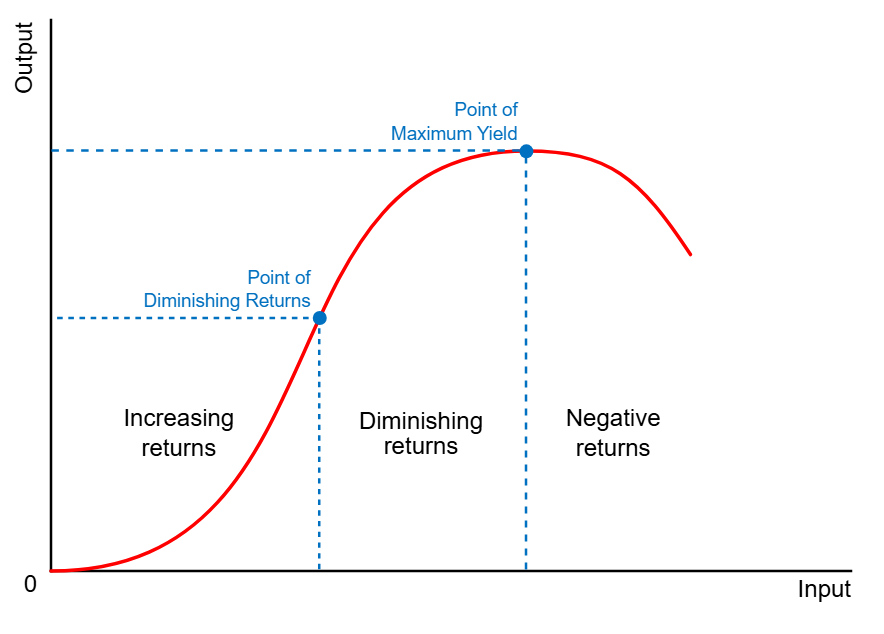
Explain the Law of Diminishing Returns.
At a certain point, any further increase in inputs is inefficient, because outputs will not increase by an equivalent amount.
Beyond the certain point, increasing inputs leads to smaller increases in production, and efficiency declines
What are energy subsidies and can you give some examples?
Any input that aids productivity, but requires the use of energy to do so.
Examples include:
Machinery - Fuel is needed for machinery for ploughing
Fertilisers - Manufacture of nitrate fertilisers
Pesticides - Manufacture of pesticides
Transport - Transporting food to customers
Processing - Heat for drying harvested grain
Why does intensive agriculture have higher energy inputs? What’s the energy used in?
Energy is used in:
fertiliser manufacture
fuel for ploughing
pumped irrigation
the artificial control of temperatures
artificial lighting
What are energy ratios?
These compare energy inputs and outputs.
It is the number of units of food energy produced per unit of energy input.
Energy Ratio Calculation
Energy Output / Energy Input
Suggest 2 reasons why poultry farming has a higher energy input than beef farming?
Energy is used for artificial lighting
Energy is used for heating
Energy is used for machinery
Material is used for the coop
Production/growth of chicken feed
The higher the energy ratio...
...the more efficient food production (more food energy for less input)
What are Food Conversion Ratios?
A measure of the efficiency with which an organism converts its food into its own increasing biomass.
(the mass of food needed to produce one unit of new tissue)
The lower the food conversion ratio...
...the better the conversion of food into animal biomass.
Outline the 3 main environmental impacts of agriculture:
Impacts on habitats
Increased pollution
Changes to the hydrological cycle
Name the 6 impacts agriculture has on habitats:
Habitat clearance
Wetland drainage
Ploughing of grassland
Reduced biodiversity
Genetic contamination
Soil degradation and erosion
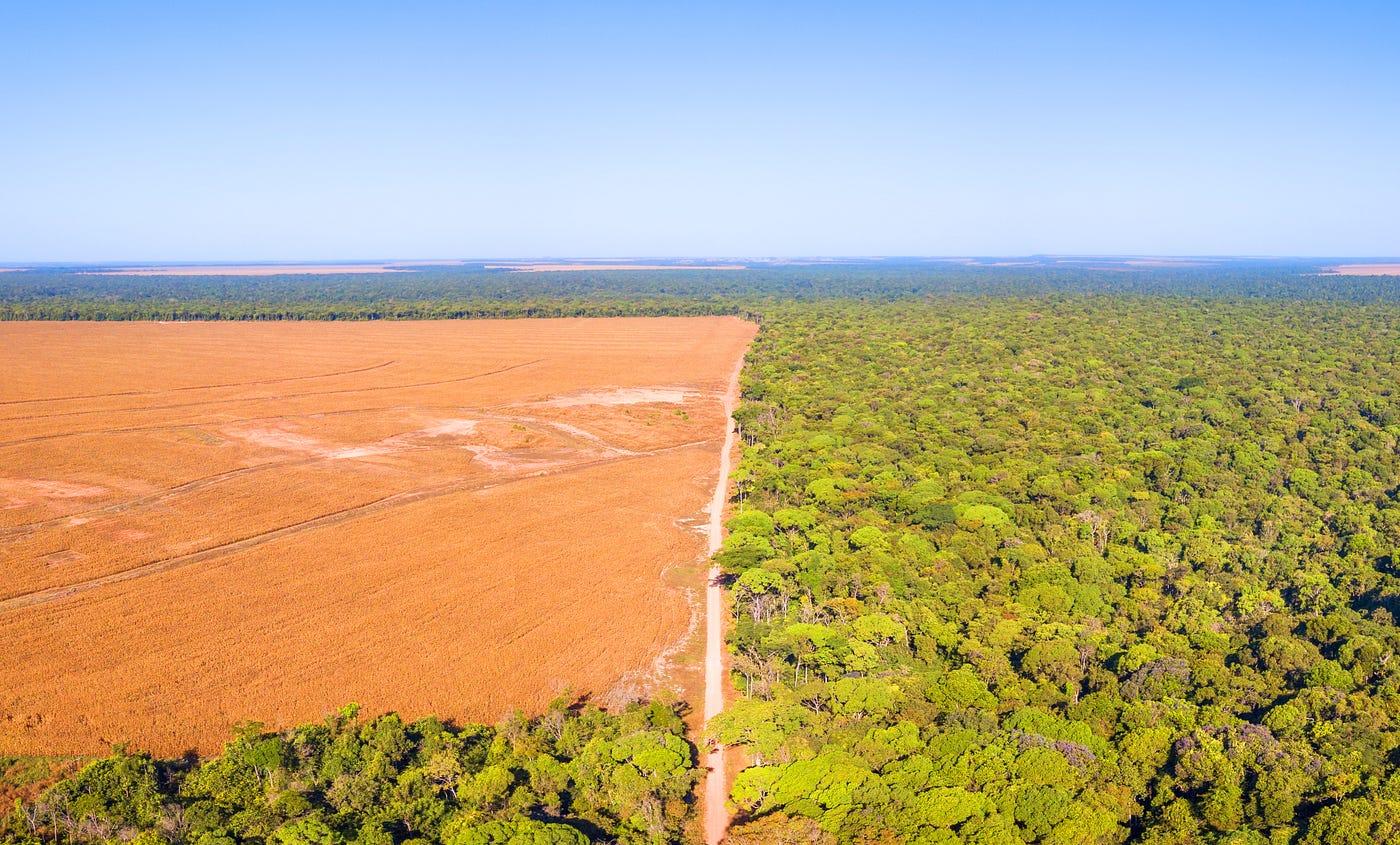
Why does habitat clearance take place and why is it bad?
Large areas of land are cleared to produce farmland
This is done in areas where climate is favourable and soils are fertile, like where the natural biomes are (forests or grasslands)

Why does wetland drainage take place and why is it bad?
Farmland is drained to produce more aerobic soils.
Wetland species and the supported ecosystem may not be able to survive the changes

Why is ploughing grassland bad?
Removes native plant cover and disrupts food chains
Exposes topsoil to wind and water, leading to loss of nutrients
Loss of grassland species due to them losing their habitat
How do agroecosystems reduce biodiversity?
Agroecosystems replace the diverse communities of indigenous species with a community of fewer species, many of which may not be indigenous.
The indigenous species will not be able to survive the new conditions, or may be removed as they are prey to new competitors
What is genetic contamination and why is it bad?
The unintended spread of genes from GM crops to wild relatives or traditional crop varieties.
It can lead to wild plants getting the gene for herbicide resistance, making them harder to control
What does soil degradation and erosion lead to?
Fertile land turns into desert, reducing biodiversity.
Eroded soil washes into rivers, causing siltation and harming fish.
Less fertile soil means lower yields, requiring more fertilisers.
Name the 3 ways agriculture leads to pollution:
Pesticide Usage
Nutrient Leaching
Emissions of Greenhouse gases
How do pesticides pollute?
They leach into water bodies, killing non target species
How do inorganic and organic nutrients pollute?
Leached inorganic nutrients cause eutrophication
Leached organic nutrients cause deoxygenation and pathogen spread
Example of Nutrient Pollution:
Nitrates can be leached from farmland into water bodies that are used as sources of potable water for human consumption.
High nitrate levels can cause blue baby syndrome (methaemoglobinemia) and nitrates may be a human carcinogen
How is methane released by agriculture?
Microbial anaerobic digestion
Livestock intestines
Rice padi fields
How is CO2 released by agriculture?
Fossil fuel use
Ploughing increases soil aerobic respiration
How Is NOx released by agriculture?
Livestock manure
Nitrogen fertilisers
What are the 2 changes to the hydrological cycle that agriculture cause?
Depleted aquifers
Changes in evapotranspiration.
How does agriculture lead to depleted aquifers?
Through unsustainable irrigation
How does agriculture lead to changes in evapotranspiration?
Changes depend on the ecosystem present before farming began.
Evapotranspiration is increased in arid areas
Evapotranspiration is reduced in areas where forests were removed
Name the 3 economic influences on agriculture:
Subsidies
Guaranteed Prices
Quotas
What are subsidies?
Governments pay farmers to limit yields or diversify
How did subsidies come about and what do they do?
Post WW2, farmers in Europe could not afford to invest in more productive methods because they were unsure they would earn enough to repay their loans taken out
To solve this, grants were made available so farmers could get financial assistance for a wide range of projects to increase food production
What were the grants/subsidies used for?
- Hedgerow removal (to increase field size)
- Use of machinery
- Drainage of wetlands
- Beetle banks (to increase habitat)
- Organic farming (reduced pesticides, so reduced nutrient leaching)
- Skylark plots
What are guaranteed prices?
Government set the price of a product
Why were guaranteed prices introduced?
Increasing production meant that if output exceeded demand, then the market price would drop, and the farmers could make a loss, despite the high yield. Therefore, to solve this issue, a guaranteed market provides a price support system.
Creates financial stability for farmers and consumers
Food production was raised
If there was a surplus harvest, how did guaranteed pricing work?
The government would buy some of the harvest from the farmers to create an artificial market shortage and raise the price to an agreed level that had been set earlier in the year
If there was a poor harvest, how did guaranteed pricing work?
To prevent raised prices, the government would sell the surplus food from previous years (milk powder, grain, cheese) to bring the market price down to the agreed level
What are quotas?
Farmers are given limits on what they are allowed to produce
(For example, dairy farmers are given a limit on the amount of milk they can sell)
Why were quotas introduced?
By the 1970s, food production had increased to the level where there were more surpluses than shortages in MEDCs
Surplus food in one country couldn't be sold to other MEDCs, because they also produced surpluses
Countries of Eastern Europe and the USSR needed food but could not afford to pay the full price
Selling the surplus food in LEDCs would undercut local producers, put them out of business, and reduce long term food production
Therefore, quotas prevents the overproduction of food
Political influences also include subsidies, guaranteed prices, and quotas. Name the 2 other political influences on agriculture:
Trade controls
Economic controls
What are trade controls?
Government put tariffs on the trading of particular products
What do trade controls do?
Protects local farmers from cheaper foreign imports
Ensures food security by controlling exports
During the war, Europe could not produce enough food to feed everyone. Without a major change in food availability, there would have been serious food shortages, possibly famine. Food aid from the USA helped reduce these issues.
What are economic controls?
Government policies that regulate the agricultural market to maintain stable prices and production.
Outline 3 reasons why economic controls good
Prevents price volatility that harms farmers and consumers
Controls food inflation
Ensures affordable food supply
Issue: Decreasing nutrient supply
Current supplies of rock phosphates to produce phosphate fertilisers are non renewable.
What are the 2 ways to reduce the issue of decreasing nutrient supplies?
Use natural processes
Increase the natural nutrient supply
How to use natural processes to increase nutrient supply:
• Nitrogen-fixing bacteria. These bacteria naturally convert nitrogen from the air into a form plants can use.
• Decomposition. The breakdown of dead organic matter naturally releases nutrients back into the soil.
• Crop rotation. Planting different crops in a cycle helps maintain soil nutrients back into the soil.
What are 5 ways to increase increase natural nutrient supply?
• Recycling of organic matter - Using plant and animal waste to return nutrients to the soil
• Crop rotation
• Permaculture - A farming system that mimic natural ecosystem to maintain soil health and nutrient cycling
• Growth of legumes
• Conservation of soil biota
Issue: High amounts of Energy inputs
The manufacture of nitrate fertilisers requires large energy inputs from fossil fuels
What are the 2 sustainability strategies to minimise energy inputs?
Using natural processes instead of artificial fertilisers
Low tillage techniques
Issue: Decreasing Water Supplies
There is an overexploitation of rivers and groundwater reserves.
Soil salination is also caused by using saline irrigation water.
What are the sustainability strategies to conserve water supplies?
Cultivating low water use crops
Maintaining soil and soil organic matter
Use of reservoirs and aquifer recharge
Drip irrigation rather than overhead sprays
Issue: Atmospheric Pollution
Atmospheric CO2 levels increased
Increased methane production in agriculture
How to reduce the atmospheric pollution from agriculture?
Low tillage farming to reduce the decomposition of soil organic matter
Reduced use of machinery
Retain natural and semi natural ecosystems such as hedgerows, ditches, ponds, woodlands
How to make cattle produce less methane?
Feed them a high carb diet and grind their food first
Issue: Pesticide Usage
A reliance on chemical pesticides may be unsustainable.
The use of some pesticides has been banned or restricted due to their impacts on non-target species
Many pests have developed resistance to pesticides
What are 3 sustainable strategies to control pests?
Cultural pest control
Integrated control
Reduced use of antibiotics
Name the cultural pest control techniques
• Weeding
• Mulching
• Crop rotation
• Barrier crops
• Biological control
• Predator habitats
• Polyculture / companion crops.
What is integrated control?
An ecological approach to pest management, combining biological, cultural, and chemical control.
Name some integrated control techniques:
Cultural pest control
Growing pest resistant species
Why is the overuse of antibiotics bad?
Exposure to a high dose of an antibiotic may kill all of a pathogen population
However, exposure to a lower dose of antibiotics may kill only the most sensitive individuals, so the surviving population will be less easily controlled by the antibiotic
Also, increases in antibiotic resistant bacteria is an issue. Antibiotic resistant bacteria may be zoonoses, which cause disease if transferred to humans (E.coli)
Therefore, antibiotic use should be reduced.
What are the 4 factors influencing consumer choice?
• Social factors
• Cultural factors
• Religious factors
• Ethical factors
• Social factors
Those with higher incomes may choose organic food, whilst others opt for budget friendly options
Vegetarian/vegan diet
• Cultural factors
Horsemeat is not popular in the UK but is widely eaten in other European countries

• Religious factors
People with religious convictions may avoid certain foods
Muslims do not eat pork
Hindus do not eat beef

• Ethical factors. What are the 5 reasons?
A desire to reduce the environmental or social impact of food production can influence food choice.
Local food / food miles
Seasonal food
Free range livestock
Organic food
Fairtrade
Local food / food miles
Buying food that was produced nearby reduces the energy involved in transport and the pollution that would have been emitted
Seasonal food
Choosing food that is grown when the local weather is suitable has a lower environmental impact than eating out of season food that needs heating, lighting, or transporting from another area with a suitable climate
Free range livestock
Some consumers choose to buy eggs and meat from animals that are kept under conditions close to their natural conditions
The animals have the freedom to move around and search for food.
They often consider the conditions of intensive rearing to be cruel

Organic food
Some consumers choose to buy food that was produced using natural processes wherever possible, rather than those using artificial processes for pest control and nutrient supply

Fairtrade
Fairtrade food is produced in a way that provides an income for producers which means that they can afford basic human rights such as water, education, healthcare, and food