GENTICS
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Genetics
The study of genetics material and heredity
Genes
Hereditary factors responsible for traits
Genome
the collection of DNA molecules that is characteristic of an organism
Alleles
Different forms of genes
Genome
The entire set of DNA molecules found in a cell
When did Mendal discover the genes and the rules of inheritance?
1866
What year was the structure of DNA founded
1953 by Waston, Crick
What year was the first human genome sequenced?
2003
What year was the first trans genetic organism made?
1973
When did crisper become popularized?
2012
The first plant and insect species got their genome published in what year?
2000
Prokaryotes have how many chromosomes?
one
How many chromosomes do eukaryotes have?
Many
Chromsomes are?
Double stranded DNA that is associated with proteins
What is the shape of prokaryotic cells?
Long like a tampon
Eukaryotic cells look like?
a pad with a nucleus
What are gametes?
They are reproductive/ sex cells that help to allow reproduction
Are somatic cells haploid or diploid.
Diploid, bc they have 2 copies of each chromosome
Are gametes hapless or diploid?
They are haploid because they contain half of what the cell needs to be completed
What are centromeres?
The point within a cell where the spindle fibers attach during cell division.
What is fission?
How prokaryotes split and divide into multiple cells for division.
What is mitosis
Cell division of somatic tissue, that results din growth and tissue repair
What is meiosis?
The cell division of germ lines cells to for gametes.
What is cytokinesis?
The process of cell division that occurs after mitosis
What are the steps of mitosis?
Interphase
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
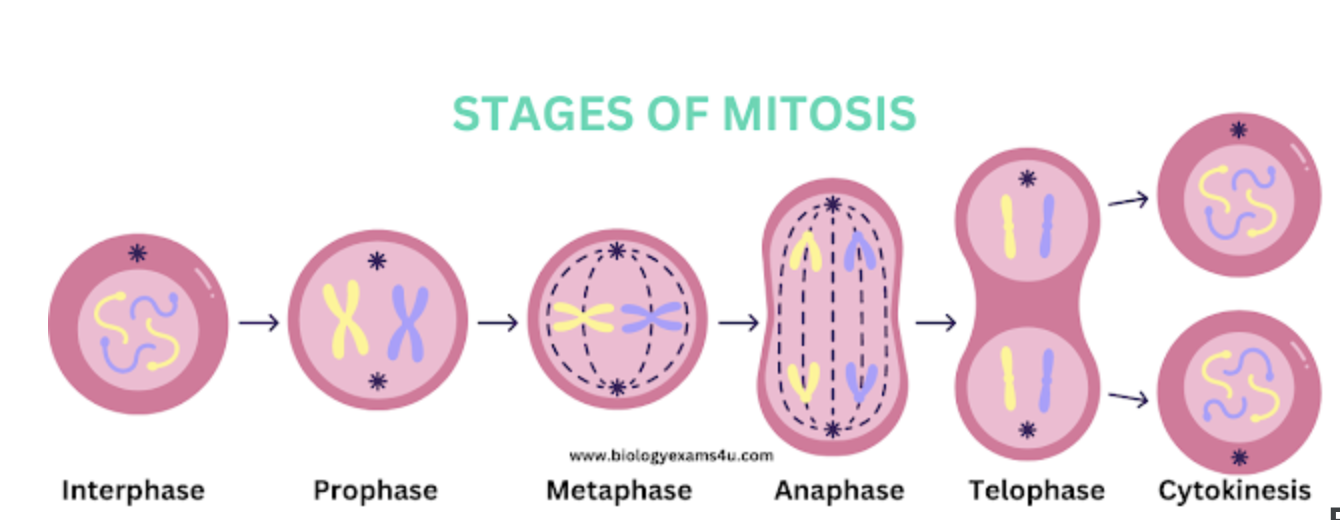
In diploid organism, what type of cells are produced from meiosis?
Haploid Cells/ Haploid gametes
How many divisions does meiosis have?
two divisions within the cell
What is a homologues cell?
A daughter cell from meiosis that is a copy of its twin
What happens in meiosis 2?
Sister chromatics disjoint from one another
Cross- fertilize ( cross-pollinate) is when?
You mix one plant with the pollen from another.
What is true breeding?
Plants that are identical from one germination to the next.
what does filial mean and stand for?
It stands for progeny generations and is denotes after the cross.
What can chi-square test be used for?
To determine if the predictions of a genetic hypothesis agree with the data from an exmoeriment
What is a pedigree?
A drawing that shows the relationship among relatives
What is the principle of independent assortment?
Mendles law saying that the traits associated with a gene will not effect other genes leading too to new genetic diversity.
( ie, hair color won’t effect eye color)
What does inheritance of a dominant trait mean?
That the dominant gene is likely to show up.
Do all alleles of a gene affect phenotype in the same way?
No, they do it in different ways.
What is incomplete dominance
When genes are a mixture of how everyman traits.
If red and white flower the offspring would be pink.
What is codominace?
When the phenotype of the organism is expressed phenotypically in both homozygotes.
Red and white flowers mixing would create a red and white flower hybrid instead of one or the other.
What is the wildtype of a gene?
The most common alleles of a gene that occur in nature
What is the mutant form of a gene?
the mutant form of the gene is the less likely form
What is an allelic series?
The hierarchy of multiple genes within as series when discussing dominance
What is allelism?
a mutation
What are encoded in most genes? DNA and what else?
Polypeptides
Can dominate traits ever mess with polypeptides?
Yes, think inbreeding
Penetrance is?
the proportion of individuals with a specific genotype that express the associated phenotype.
Incomplete penetrance means?
Not every individual with the appropriate genotype expresses the trait
Complete penetrance means?
Every individual with the appropriate genes type expresses the trait.
Variable Expressivity means?
The amount of the trait that comes across for a trait
Gene Interactions means?
different combinations of alleys from two genes that result in different phenotypes
What does epistasis mean?
That an allele of one gene overpowers the other gene.
Just a different word for dominant
A gene that effects many genes is?
Pleiotropic gene
What is inbreeding?
When offsprings are produced from parents with a high degree of relatedmness or common ancestry
What is heterosis?
When two inbreaded lines are crossed
Haploids are?
the basic chromosomes number
What symbol represents haploids?
n
What is a diploid organism
a cells or organisms that contain two sets of chromosomes
What are diploid cells denoted in?
2n
What is chromatin?
The complex of DNA and protein that make up chromosomes
What is euchromatin?
Lightly packed chromatin genes, meaning they are more often expressed
what is heterochromatin?
Tightly packed chromatin genes that are less often expressed
Sex chromosomes differ from autosomes because they?
they come in two different forms
what is heterogametic?
different sex chromosomes
What is nondisjunction
When chromosomes do not properly disjoin during meiosis
What does homozygous mean?
Only one copy of the gene is present within the cell
Anisogamy is?
when gametes have size dimorphism
What is isogamy?
all of the gametes are the same size
mosaicism is when?
inactivation of x linked genes