Central concepts
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Biodiversity
The variety of life in the world, including the different species of plants, animals, and microorganisms. It is essential for ecosystem health and resilience.
Evolution
Biological, the process whereby populations of organisms accrue gradual genetic changes over generations that lead to differences between them
DNA location
In the nucleus, also in the cytoplasm and other areas of cell
Chromosomes
Organisation of DNA into structures that carry genetic information, found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.
Human Karyotype
A complete set of chromosomes typically consists of 46 chromosomes arranged in 23 pairs, including 22 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes. Diploid.
DNA composition
Chain of sugar-phosphate backbone and DNA nucleotides that include adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine.
DNA Nucleotides
Phosphate group, sugar and nitrogenous base
DNA strand
Phosphate bonds and hydrogen bonds form a double helix of anti-parallel strands
3’ end
-OH group
5’ end
-P group
Genome
The complete genetic constitution if an individual (3,000,000,000 base pairs in humans, of which 1% codes for proteins)
Locus
A physical position on a chromosome. Refers to a segment of DNA that may be a gene, or simply defined as a point or region of interest - can be single nucleotide
Allele
An alternative genetic form at a locus
Genotype
The genetic composition of an individual at a locus
Homozygote
An individual with the same allele at a locus (i.e. the alleles are the same on two homologous chromosomes)
Heterozygote
An individual with two different alleles at a locus (i.e. the allele is different on the two homologous chromosomes)
Heterozygosity
A measure of the number of individuals within a population who are heterozygotes at a single locus, OR the number if heterozygote genotypes across multiple loci within an individual
Central Dogma
The process by which genetic information flows from DNA to RNA and gets translated into proteins
Transcription
The process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA using RNA polymerase
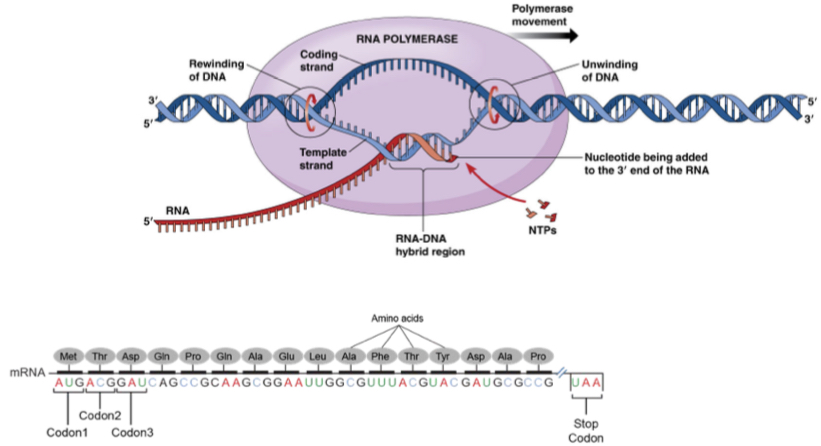
Translation
The process by which the sequence of nucleotides in mRNA is decoded to produce a specific polypeptide or protein
