Unit 6 Honors Biology: Energy in Cells
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
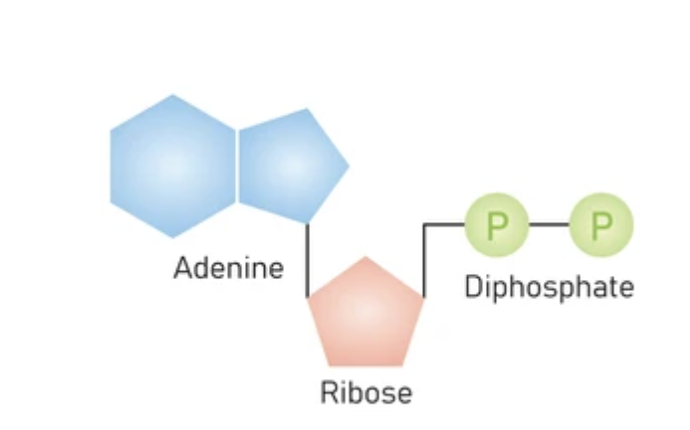
adenosine diphosphate
ADP
combined with a phosphate to make ATP
C10H15N5O10P2
one adenine, one ribose sugar, two phosphate group
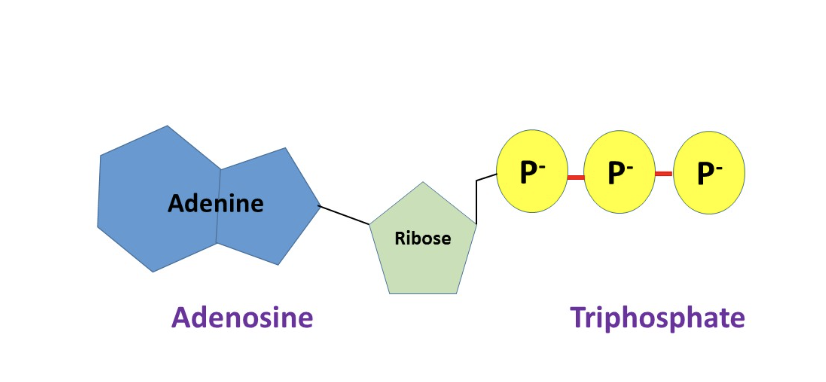
adenosine triphosphate
ATP
molecule used for energy
like a battery
three phosphate
fully charged battery
used in chemical, mechanical, and transport work
aerobic
with oxygen
anaerobic
without oxygen
autotroph
an organism that is able to form nutritional organic substances from simple inorganic substances such as carbon dioxide
heterotroph
an organism deriving its nutritional requirements from complex organic substances
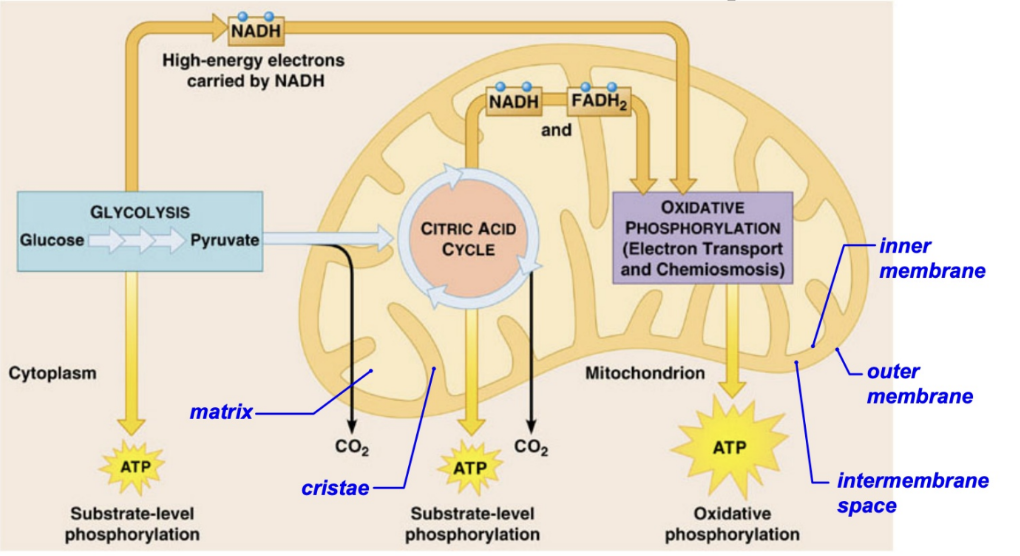
mitochondria
the powerhouse of the cell
in which respiration and energy production occur
has a double membrane and cristae
cellular respiration
C6H12O6 + 6 (O2) → 6 (CO2) + 6 (H2O)
ADP + P → ATP(s)
the point is to break apart the sugar in a controlled way to release energy that can be captured to store in ATP by bonding ADP +P together with the energy coming from the sugar
the energy stored in glucose by photosynthesis is released by cellular respiration and repackaged into the energy of ATP
chlorophyll
the natural compound present in green plants that gives them their color
chloroplast
where photosynthesis occurs
green
plastid
contains chlorophyll
glucose
sugar
C6H12O6
glycolysis
glucose → pyruvate
a series of reactions that extract energy from glucose by splitting it into two-three carbon molecules called pyruvates
grana/um
a stack of thylakoids
inner chloroplast membrane
phospholipid bilayer
inner mitochondrial membrane
the active site for the electron transport chain and ATP production
its integrity is crucial for mitochondrial function and depends on the supply of proteins and phospholipids
outer chloroplast membrane
chloroplast envelope, contains porins and is therefore freely permeable to small molecules
outer mitochondrial membrane
separates the intermembrane space from the cytosol
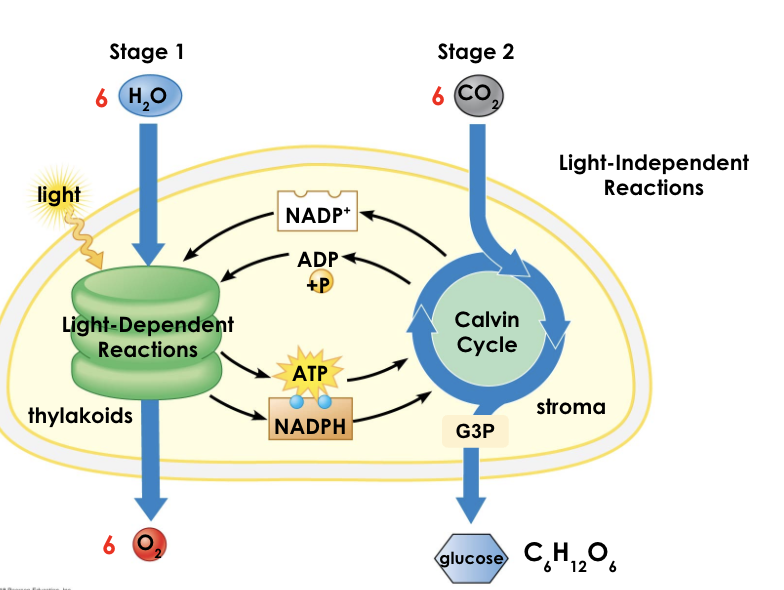
light reactions
use light energy to make two molecules needed for the next stage of photosynthesis
calvin cycle
a process that plants and algae use to turn carbon dioxide from the air into sugar, the food autotrophs need to grow
mitochondrial matrix
the space within the inner membrane, viscous
phosphorylation
ATP energizes molecules by phosphorylating them (transferring a phosphate group to the molecule)
pigment
absorb specific wavelengths of light and reflect other wavelengths
chlorophyll = green
flavonoids = yellow
carotenoids = orange
anthocyanins = red
stoma/ata
allow for transpiration and gas exchange
if water is plentiful, guard cells retain water in the center vacuole to swell = open stoma, more transpiration & photosynthesis
if water is scarce, guard cells shrivel = closed stoma, less water loss & less photosynthesis
stroma
the colorless fluid surrounding the grana in the chloroplast
thylakoid
each of the flattened sacs inside a chloroplast
stack is a granum
function is to trap light energys and the transduction of energy into chemical energy
photosynthesis
endergonic
takes in atmospheric CO2 and turns it into food
happens in the mesophyll layer of the leaf
light energy + 6 (CO2) + 6 (H2O) → C6H1206 + 6 (O2)
light energy
kinetic energy with the ability to make types of light visible to human eyes, emitted by hot objects and the sun
chemical energy
energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules, released when a chemical reaction takes place
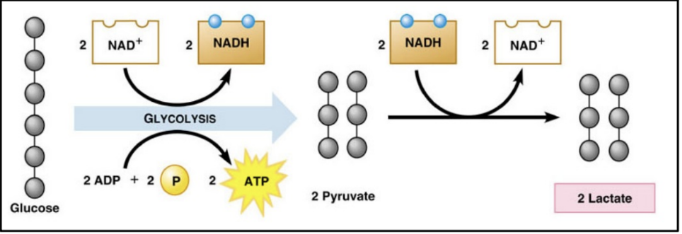
lactic acid fermentation
humans and some microorganisms
when our muscle cells run out of oxygen, we can produce ATP briefly by performing this
lasts for only about 1-3 minutes
lactic acid will build up in the muscle cells and cause soreness
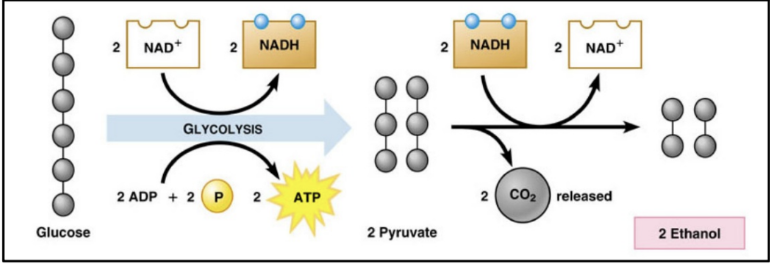
alcoholic fermentation
anaerobic
transfomation of fructose and glucose into ethanol and CO2
converts sugars into cellular energy, ethanol, and carbon dioxide