CNM - C3
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
my_list = [1, 7, “hi”, 3, 5]
write a for loop to list this list
remember colon and 4 spaces to be included in loop

write a while loop to produce 0,1,2,3,4,5
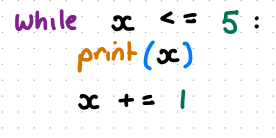
symbols for
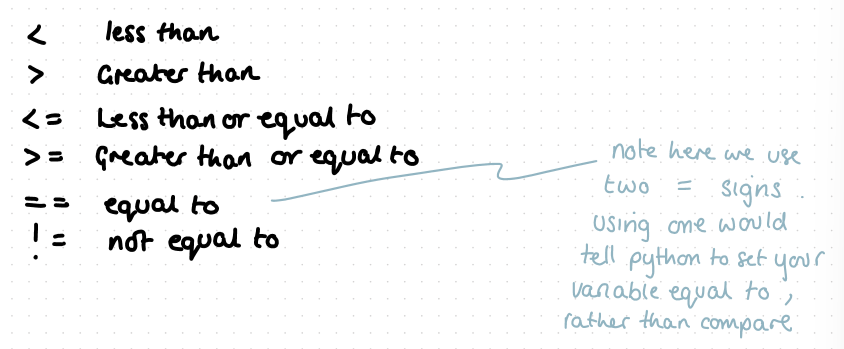

whats will be printed if at the beginning
x=1
x=2
x=3
if x=1 printed: 1
if x=2 printed: -8888
if x=3 printed: -9999
what code can you use to avoid error and move forward with code
try and except
it will try the try code and if this won’t work it will run the except code

what can you use to test for potential issues and stop the code
if —→ raise Exception()
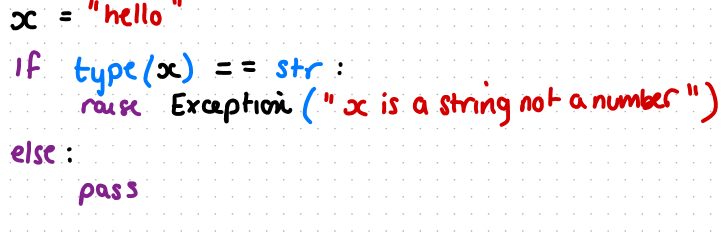
words used to halt or proceed with a loop
break - terminates the nearest loop it is in
continue - continues to the next iteration of the loop
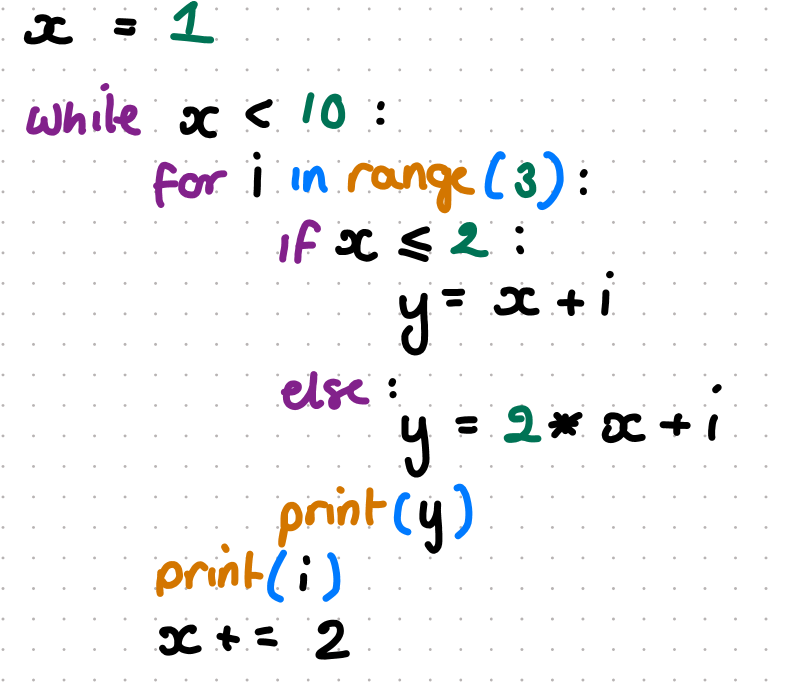
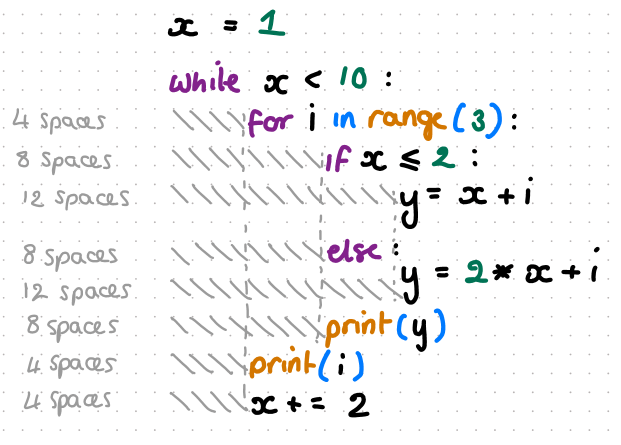
what does this code do and what should the spacing be
figure out the code
text = input("enter a string:")
if ___________
print("even")
else:
print("odd")
fill the gap after even to create a programme which prints even if the number of letters in the string is even and odd if it isn’t
text = input("enter a string:")
if len(text) %2 == 0:
print("even")
else:
print("odd")
this divides by 2 and gives the remainder - if the remainder is 0 it is even
how do you denote a dictionary in python and give an example dictionary with some personal info
it should have curly brackets, “speech marks” colons in between key and variables and commas in between information:
information = {"Name" : "Daisy", "Location": "Sheffield"}
print(information[“Name”]) gives Daisy
you can change and add info
What is the output from the following section of code?
try:
x = int("100")
print(x)
except:
print("Error")
is it '“100”, 100, or Error
100
what will this code return
d = {"a": 1, "b": 2}
for key in d:
print(d[key])
1
2
Which Python feature can combine two lists into a dictionary without using a manual loop?
zip() is used followed by dict()
eg:
keys = ['a', 'b', 'c']
values = [1, 2, 3]
d = dict(zip(keys, values))
what does this code print
my_dict = {"a": 1, "b": 2}
for key in my_dict:
print(key)
a
b
What is the output of this code?
for i in range(2):
for j in range(2):
print(i, j)
(0,0) (0,1) (1,0) (1,1)
What is the output for the following section of code?
keys = ["a", "b", "c"]
values = [1, 2, 3]
result = {}
for i in range(len(keys)):
result[keys[i]] = values[i]
{"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": 3}
What is the output of this code?
varA = True
varB = False
if varA:
print("TRUE")
if not varB:
print("TRUE")
TRUE
TRUE
What will happen?
if 0:
print("Hello")
else:
print("Goodbye")
prints goodbye
What's the output for the following section of code?
nums = {"x": 10, "y": 20}
nums["x"] += 5
print(nums["x"])
15
What's the output for the following section of code?
d = {"x": 1, "y": 2, "z": 3}
print("y" in d)
True
change this so it prints 2
d = {"x": 1, "y": 2, "z": 3}
print("y" in d)
d = {"x": 1, "y": 2, "z": 3}
print(d[“y”])
What type of data is always returned by input()?
String - always.
What is an exception in Python?
An error detected during program execution