Chapter 8: Carbohydrates
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Carbphydrates
The most abundant biological molecules. Many, but not all have the empirical formula (CH2O)n, where n>/ 3 is the number of carbon atoms:
Carbohydrates occur in four main size classes:
Monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides
Monosaccharides
Simplest form of carbohydrates. They are are aldehyde or ketone derivative of straight chain polyhydroxy (multiple OH groups) with at least 3 Carbon atoms. Its backbone is unbranched C chain.
If the C=O is at the end of the chain, it is called?
aldose
If the C=O bond is at any other position, it is called?
ketose
The C=O group is most commonly at C2 and the position of their carbonyl group gives ketones…?
one less symmetric center than their isomeric aldoses.
All monosaccharides except ______ contain one more chiral carbon atoms
dihydroxyacetone (DHA)
Monosaccharides, such as Glyceraldehyde, contain one chiral center, and therefore have two different isomers, or ___.
enantiomers
D-Sugars have its OH on the ___ and farthest from their carbonyl group.
right
L-Sugars have its OH on the ___ and farthest from their carbonyl group.
left
In general, a molecule with n chiral centers can have ____ (where n=number of chiral centers) stereoisomers.
2^n
What is the predominant form in nature?
D-Form
How are carbons numbered?
Beginning at the end of the chain nearest the carbonyl group.
Epimers
Two sugar molecules that differ only by the configuration around one chiral center.
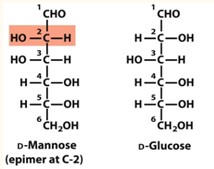
D-Glucose and D-Mannose are epimers at?
Carbon 2
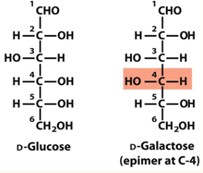
D-Glucose and D-Galactose are epimers at?
Carbon 4
Aldotetetroses and all monosaccharides with 5 or more Carbon atoms occur predominantly as ______, which the carbonyl group has formed a covalent bond with oxygen of a hydroxyl group along the chain.
cyclic ring structures
Alcohols react with carbonyl groups of aldehydes to form?
Hemiacetals
Alcohols react with the carbonyl group of ketones to form?
Hemiketals
Cyclization of glucose (formation of hemiacetal)
(1) Free hydroxyl group at C5 reacts with the aldehyde at C1.
(2) Hydroxyl group adds to the carbonyl carbon.
a. The attack is either from the front or back.
(3) The reaction produces two stereoisomeric configurations, denoted alpha and beta.
(4) These isomeric forms, which differ only in their configuration on the hemiacetal carbon atoms, are called anomers.
Cyclization of Hemiketals
The hydroxyl group at Carbon 5 reacts with the keto group at Carbon 2 forming a ring containing a hemiketal.
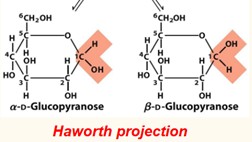
In the alpha anomer, the OH substituent of the anomeric carbon is _____ of the sugar ring from the CH2OH group.
opposite side
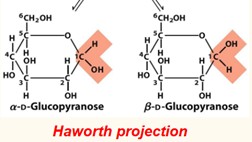
In the beta anomer, the OH substituent of the anomic carbon is _____ of the sugar ring from the CH2OH group.
same side
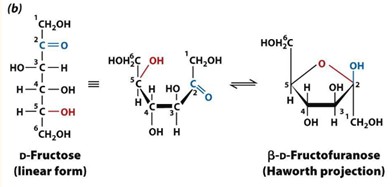
Mutarotation
The alpha and beta anomers of D-Fructose interconvert via the linear form in aqueous solution.
Pyranoses
A six-membered monosaccharide ring compounds. They are named after pyran (hexagon).
Furanoses
A five-membered monosaccharide ring compounds. They are named after furan (pentagon).
Both pyranose and furanones are not planar. To depict their structures, they are represented in?
chair conformations.
In one form, bulkiest ring substituents occupy equatorial positions. The other form occupies axial positions. The predominant form is?
the equatorial form.
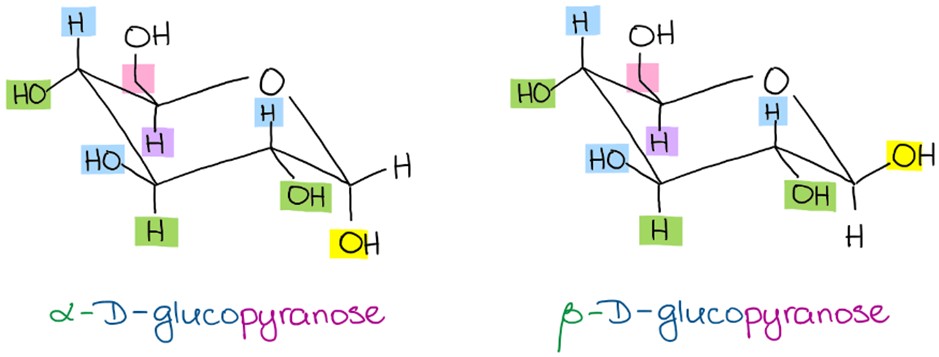
Which glucose is the predominant form?
Beta-D-Glucopyranose
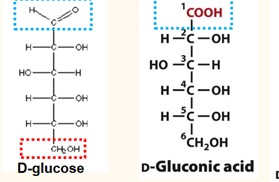
Formation of Aldonic acid
The oxidation (loss of H) of an aldose converts its aldehyde group to a carboxylic acid group.
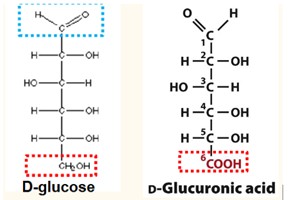
Formation of Uronic Acid
The oxidation of the primary alcohol group to a carboxylic acid.
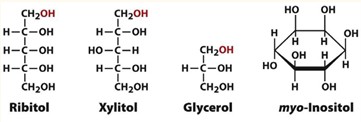
Formation of Alditols
Aldoses and ketoses can be reduced (gain a H) under mild conditions by treatment with NaBH4.
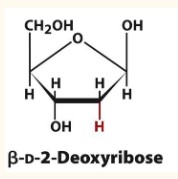
Formation of Deoxy Sugar
Monosaccharide units in which an OH group is replaced by H.
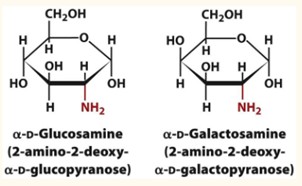
Formation of amino sugars- acetylated
In amino sugars, one or more OH groups have been replaced by an amino group which is often acetylated (CH3C=O).
formation of disaccharides
By two D-configuration monosaccharides (ex. two D-glucose molecules). One D-monosaccharide OH group condenses with he intramolecular hemiacetal of the other D-monosaccharide.
during the formation disaccharides, h2o molecule is eliminated (condensation) creating a ________. The reversal is hydrolysis using diluted acid.
glycosidic bond.
reducing sugars
monosaccharides or disaccharides that can reduce other compounds by donating electrons due to a free aldehyde or ketone group. Only aldoses and hemiacetals can do this.
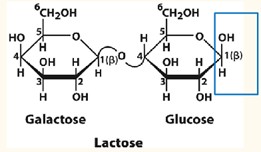
Lactose
Composed of beta-D-galactopyranose and beta-D-glucopyranose.
β glycosidic bond links Carbon 1 β anomer of galactose to Carbon 4 of the glucose
Hydrolyzed by β-D-galactosidase/ lactase
Reducing sugar
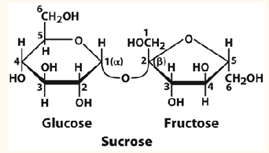
Sucrose
Composed of alpha-D-glucose and Beta-D-glucose.
The most abundant disaccharide
Alpha glycosidic bond links C1 alpha anomer of glucose to C2 in fructose.
Hydrolyzes by sucrase.
Not a reducing sugar
polysaccharides
Medium to high molecular weight. also called glycans. they can differ based on monosaccharide units, lengths of their chains, types of bonds linking mono units, and degree of branching
Homopolysaccharides
Contain only a single monomeric species
Heteropolysaccharides
Contain two or more different types of monomeric units.
Starch (Plant Storage)
A mixture of glycans that plants synthesize as their principal energy reserve.
Reducing sugar
Glucose repeating units
Composed of: alpha-amylose and amlopectin
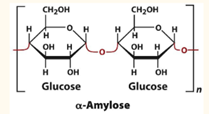
Alpha-Amylose
A linear polymer of several thousand glucose residues linked by alpha(1—>4) bonds. Amylopectin contains up to 106 glucose residues.
Amylopectin