bio 109- CHAPTER 11- sexual reproduction and meiosis
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
meiosis
creating gametes from germ cells
karyotype
total number of chromosomes in a cell
homologous chromosomes
chromosomes with same genes (may be different alleles)
ploidy
number of homologous chromosomes (how many sets)
synapsis
joining of homologous chromosomes
cross-over
transfer of alleles between homologous chromosomes
how many chromosomes do diploid cells have per set
2 (ex. human somatic cells)
how many chromosomes do haploid cells have
1 (human gametes)
how many homologues do offspring inherit from parents
2
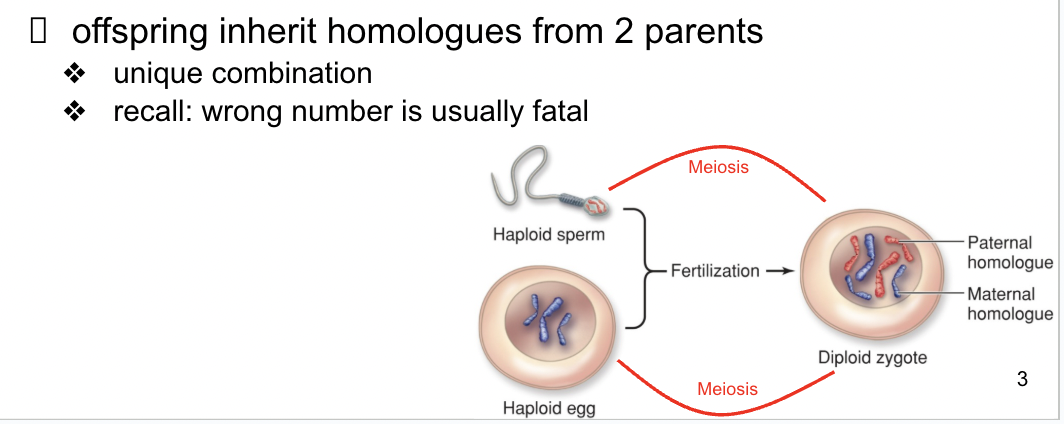
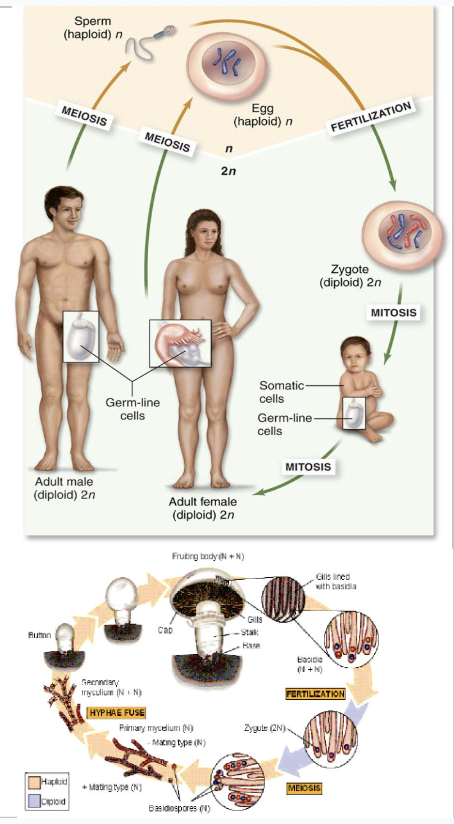
sexual life cycles
alternation of haploid and diploid stages
sometimes diploid phase is longer (most animals)
sometimes haploid phase is longer (mosses, fungi, some invertebrates)
features of meiosis
1 round of S phase (like mitosis)
2 rounds cell division
1st separates chromosomes
2nd separates chromatids
synapsis
homologous chromosomes pair up (not in mitosis)
early prophase I
form tetrads (a.k.a bivalents)
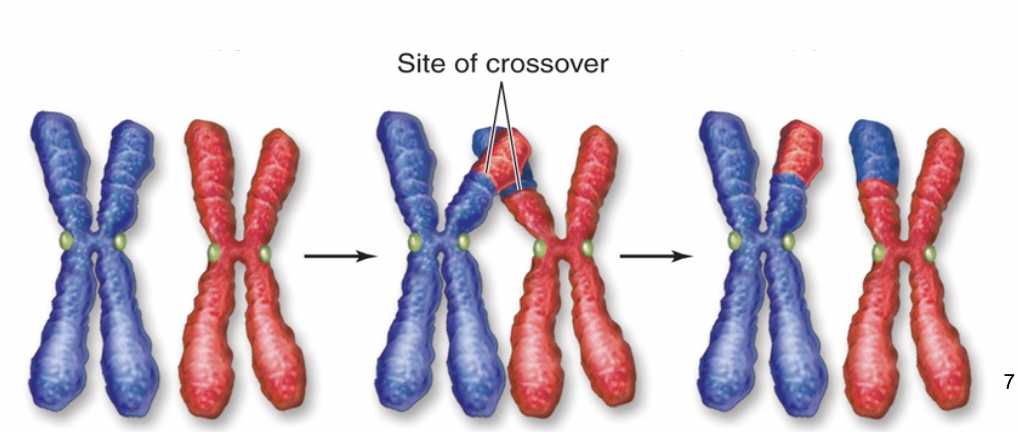
cross over
exchange DNA between homologous chromosomes
DNA from maternal now on parental (and vice versa)
sister chromatids are no longer identical
process of meiosis I and II
prophase I
prometaphase I
metaphase I
anaphase I
telophase I
NO S PHASE BETWEEN
prophase II
prometaphase II
metaphase II
anaphase II
telophase II
what are 3 sources of genetic variation
1) crossover
2) alignment of chromosomes
3) alignment of chromatids
meiosis I vs mitosis
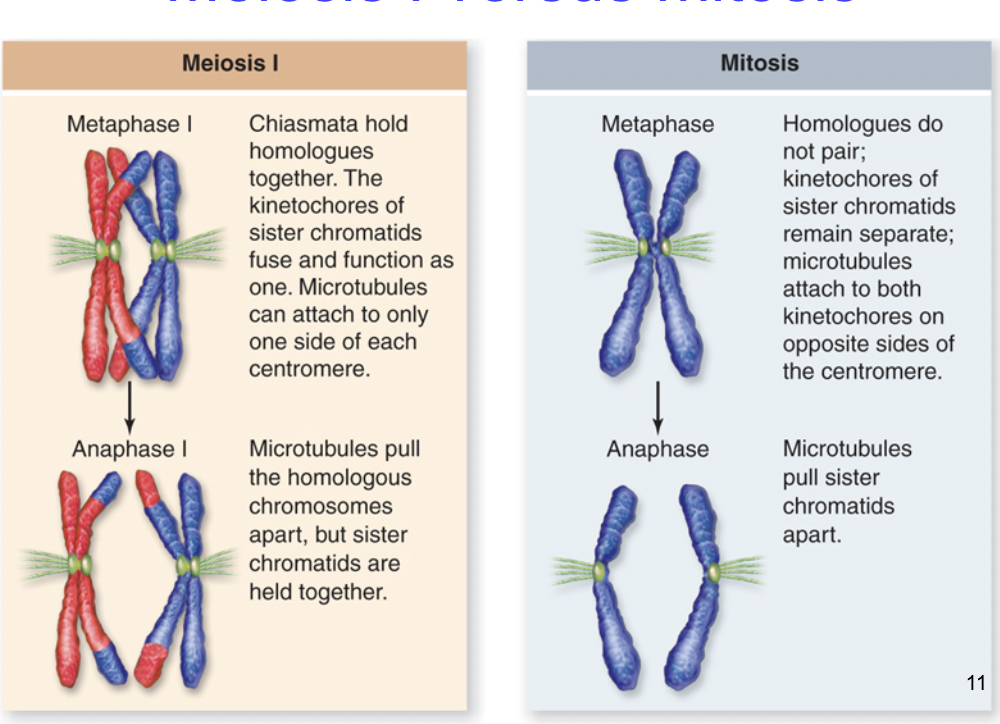
3 key features of meiosis
1) synapsis and cross-over, makes unique chromatids (recombine maternal and paternal genes)
2) sister chromatids remain joined in meiosis I, go to the same pole during anaphase I
3) DNA replication is suppressed between meiosis I and meiosis II, half as much DNA in gametes compared to start.
final result of meiosis
four cells containing different half set of original karyotype
in animals, develop directly into gametes
in plants, fungi and many protista, then divide by mitosis
produces greater number of gametes
nondisjunction
failure to separate
produces aneuploid gametes (missing or extra chromosomes)
most common cause of miscarriage in humans