Bone Tissues
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Osteoprogenitor cells
unspecialized undergo mitosis and develop into osteoblasts, found in periosteum, endosteum, and canals that contain blood vessels
Osteoblasts
cells that form bone but don’t divide, secrete collagen and other organic bone components, derived from osteoprogenitor cells
Osteocytes
mature, derived from osteoblasts, don’t divide, trapped in bone matrix, don’t secrete matrix material, maintain cellular activities of bone, exchange of nutrients and waste with blood
Osteoclasts
believed to develop from circulating monocytes, settle on bone surface and function in bone reabsorption
Bone tissue matrix
contains mineral salts of tricalcium phosphate (hydoxyapatite) and calcium carbonate, with small amounts of magnesium hydroxide, sulfate, and fluoride
Calcification
process in which salts are deposited in the frame work formed by collagen fibers, salts give the bone hardness and fibers give it tensile strength
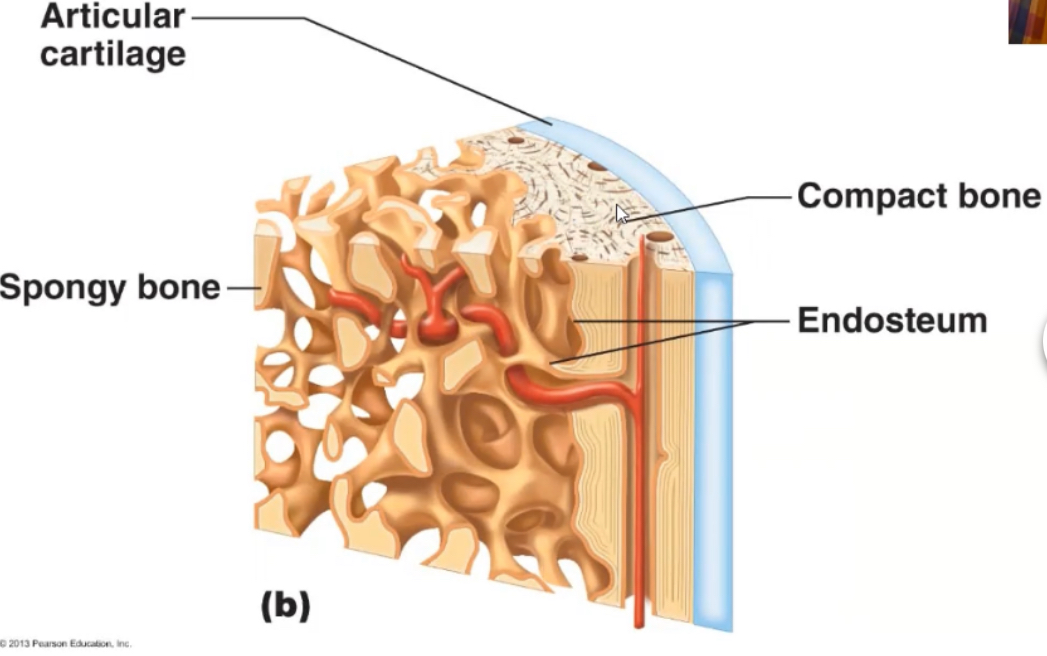
Compact (dense) bone tissue
few spaces, make up bulk of diaphysis, gives long bones strength, forms concentric ring structure
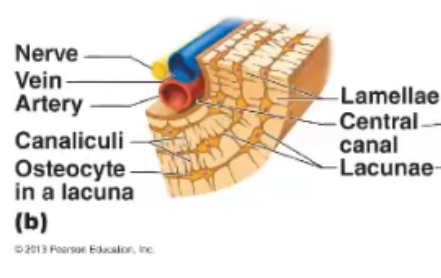
Osteon
the basic structural unit of compact bone, target shaped structures made of rings of bone
Haversian (central) Canal
a hole at the center of the osteon, contains blood vessels, lymphatic vessels and nerves

Concentric lamellae
rings of bone around the central canal, make up the osteon
Lacunae
small spaces within the lamellae that house osteocytes
Canaliculi
are small channels which radiate away from the lacunae; they are filled with extracellular fluid and processes from osteocytes
Interstitial lamellae
Arches of bone that fill up the spaces between the osteons
Circumferential lamellae
Arches of bone around the surface of the bones, make the bones surface smooth
Perforating canals
Tubes in the sides of the bones that allow blood vessels, lymphatic vessels and nerves to reach the central canals of the osteon
Spongy bone tissue
does not contain osteons, made of irregular lattice of bone plates called trabeculae, spaces between trabeculae are filled with red bone marrow, in trabeculae are osteocytes in lacunae, radiating from lacunae are canaliculi
Long bones
greater length then width, curved for strength, mostly made of compact bone, but with some spongy bone, ex. thigh, leg, arm, forearm, finger and toes

Short bone
cube shaped, made of spongy bone except at the surface where there is thin layer of compact bone, ex. wrist and ankle bones
Flat bone
thin, composed of two parallel plates of compact bone enclosing a layer of spongy bone, provide protection and places for muscle attachment, ex. cranial bones, sternum, ribs
Irregular bone
complex shape, vary in amount of spongy and compact bone tissue, ex. vertebrae
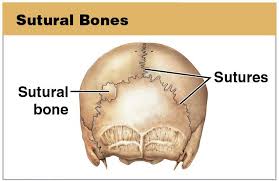
Suturas bone
small bones found in the sutures of certain cranial bones, vary in number between people not all people have them
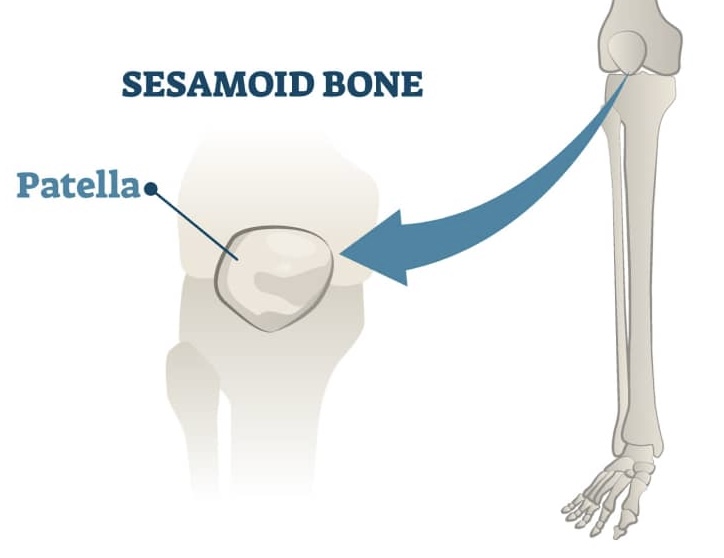
Sesamoid bone
small bones warped in tendons where pressure develops, ex. wrist, variable in number, knee caps are sesamoid
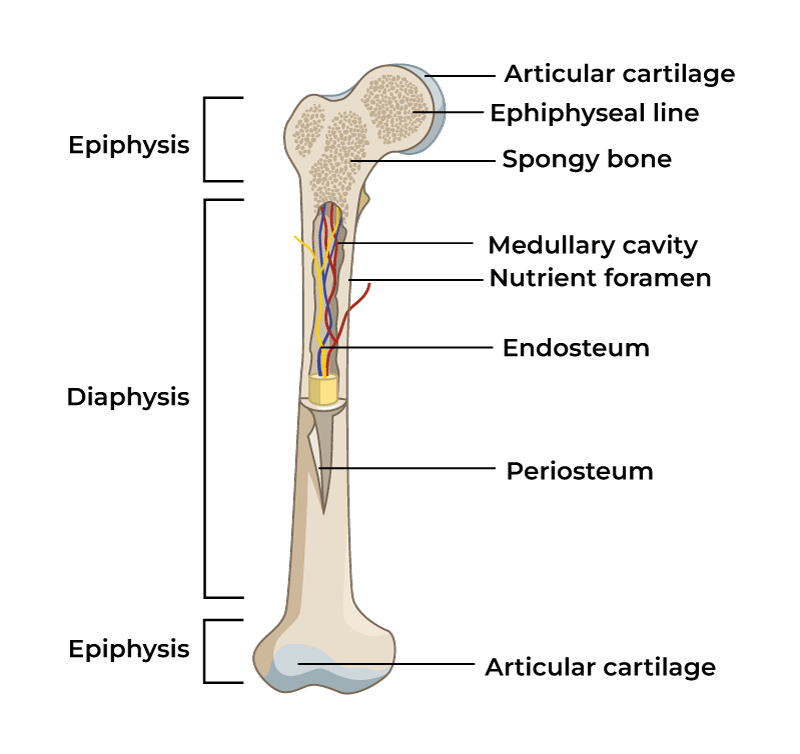
Diaphysis
Main shaft of a long bone
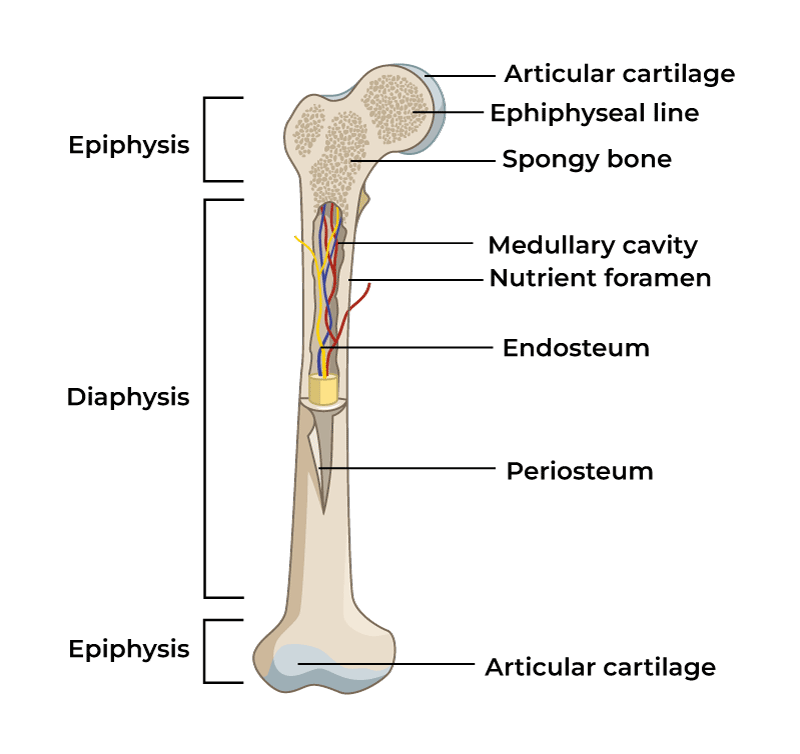
Epiphysis
End of bone of a long bone
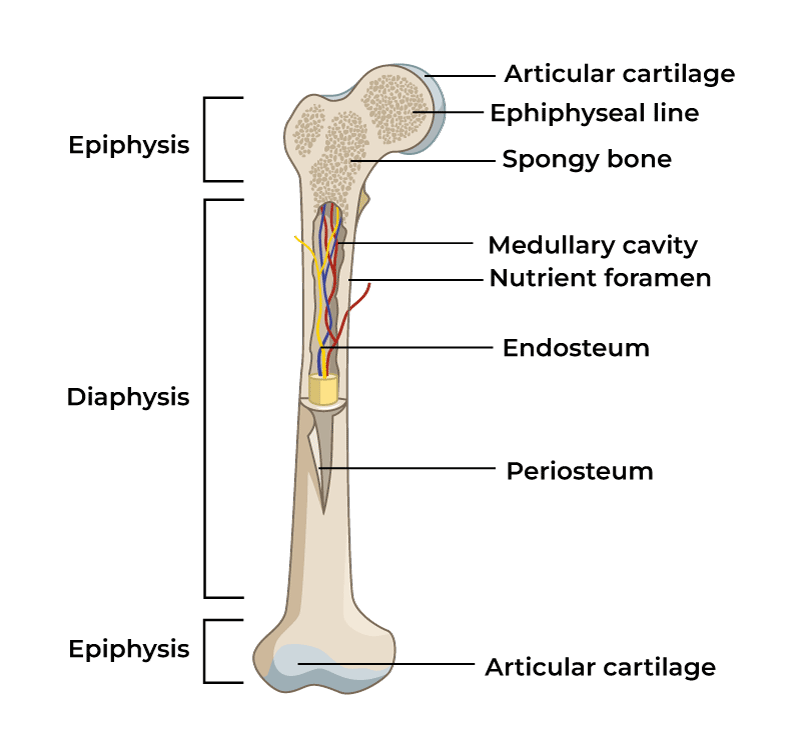
Metaphysis
in mature long bone where epiphysis meets the diaphysis, in growing bone it contains the epiphyseal plate
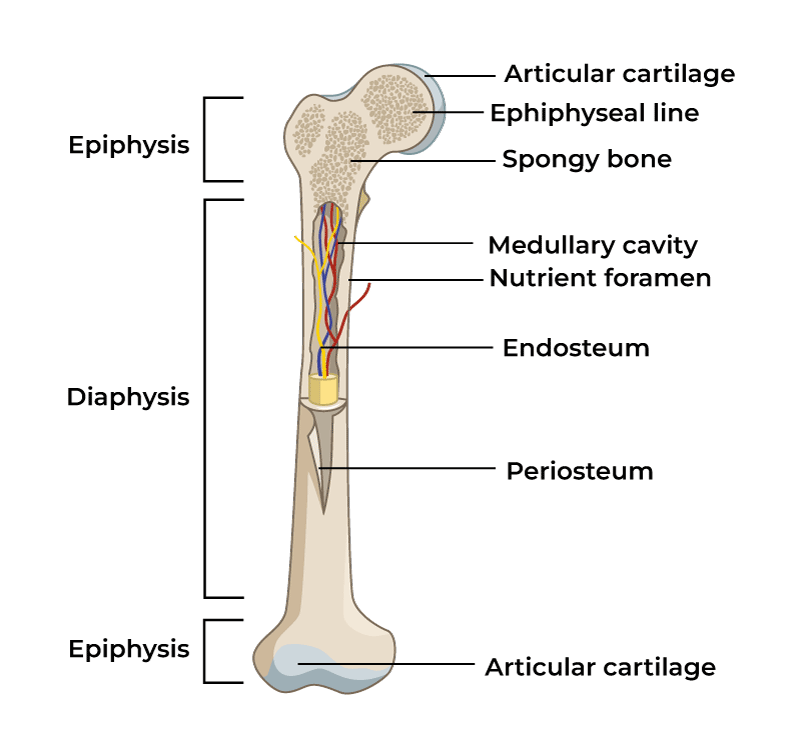
Articular cartilage
Thin layer of hyaline cartilage where the bone articulates with another bone
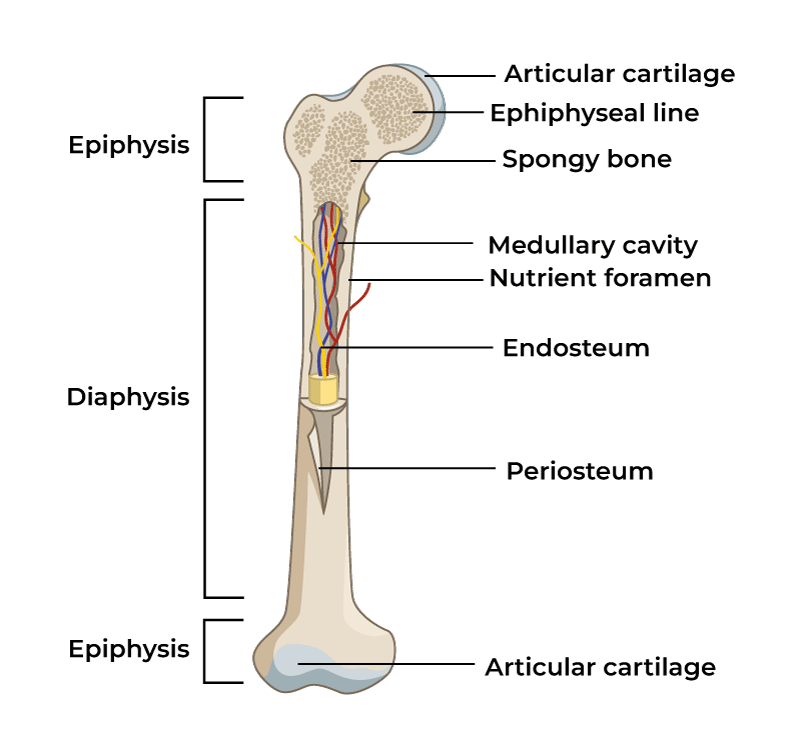
Periosteum
Membrane around the surface of bone not covered by articular cartilage; has two layers
Fibrous layer
(Part of periosteum) made of dense irregular connective tissue, contains blood vessels, lymph vessels and nerves
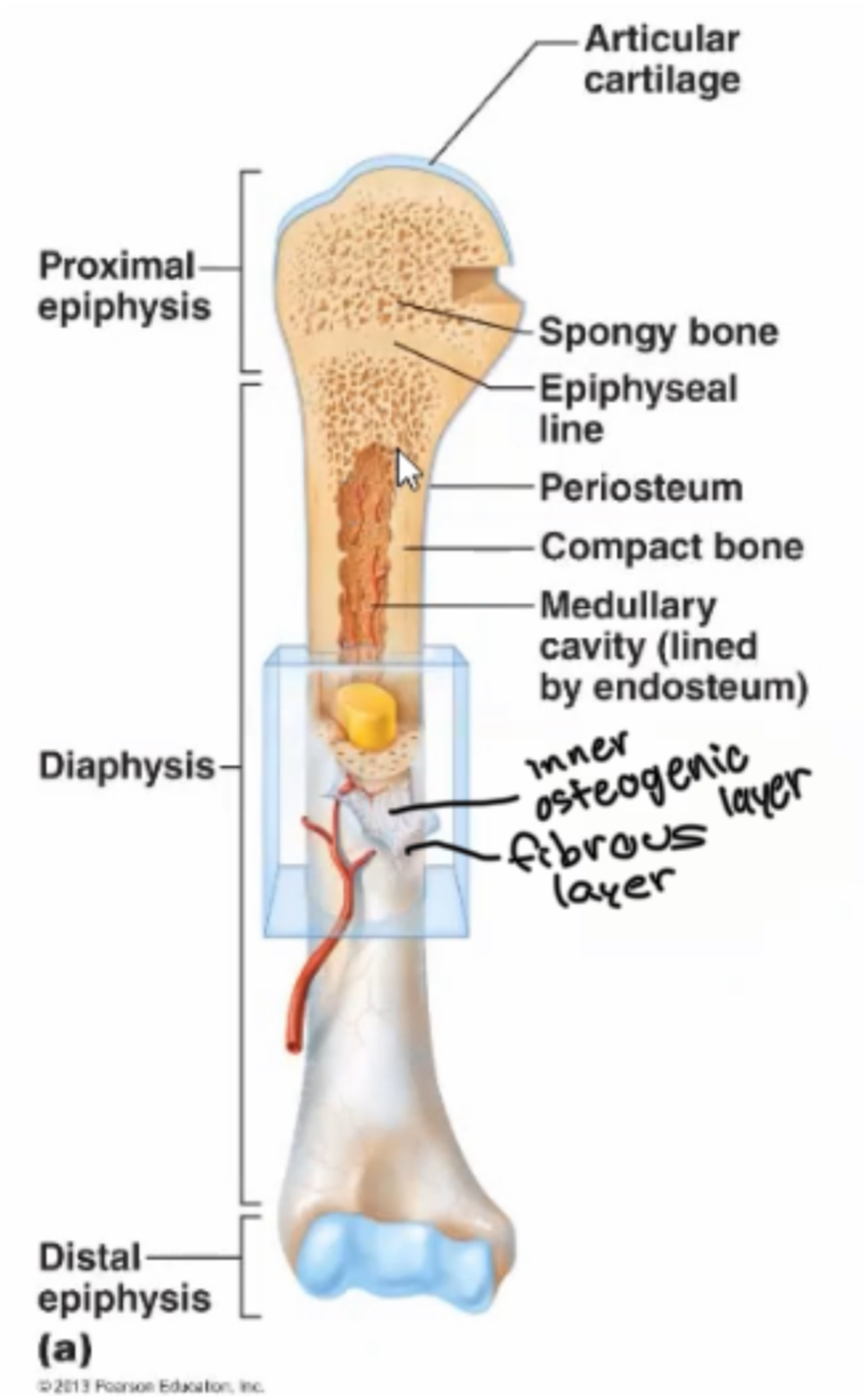
Inner osteogenic layer
(Part of periosteum) has elastic fibers, blood vessels and various types of bone cells, periosteum necessary for bone growth in diameter, repair, and nutrition, present in all bone types
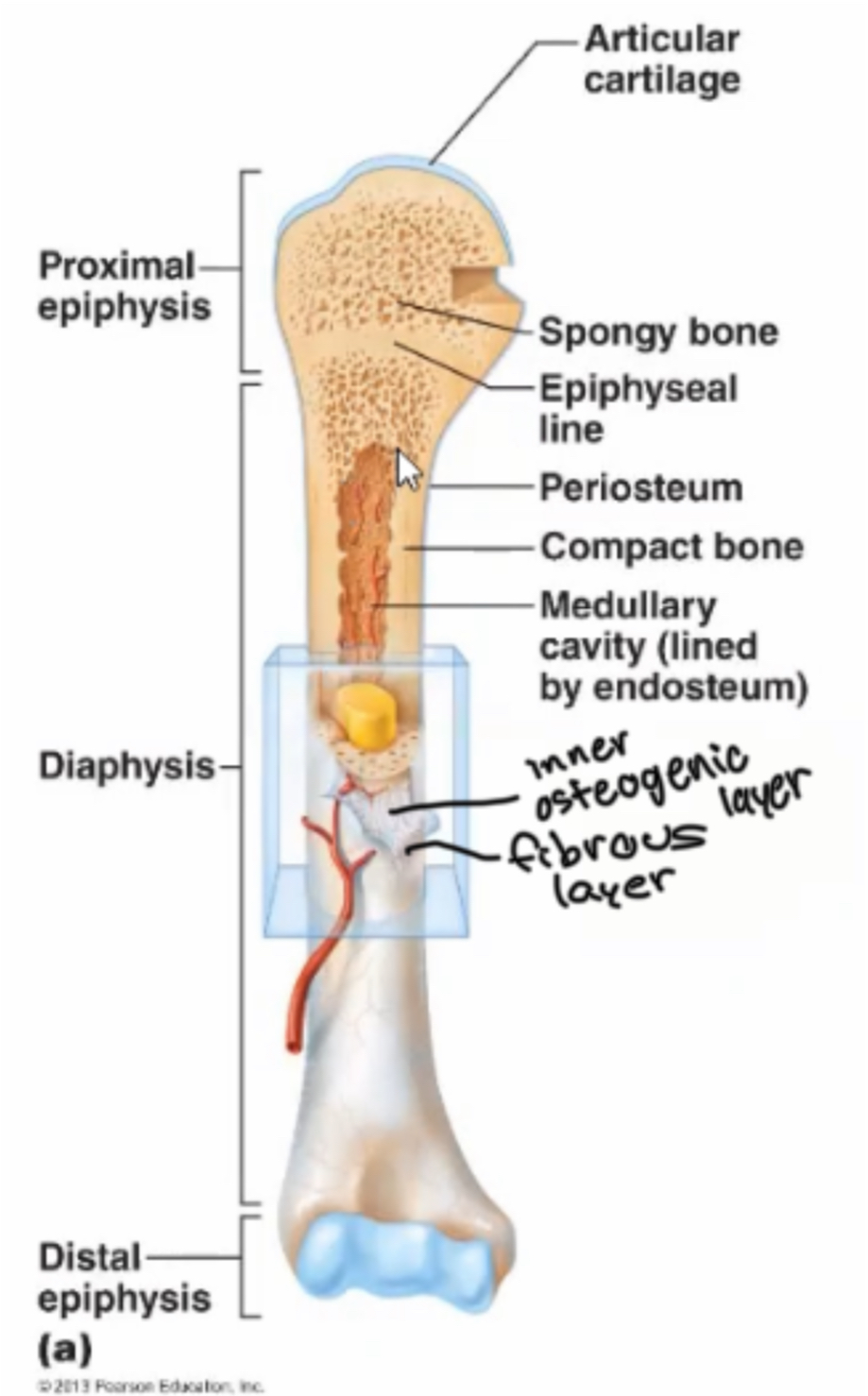
Medullary
marrow cavity, space in diaphysis filled with yellow bone marrow, present in all bone types
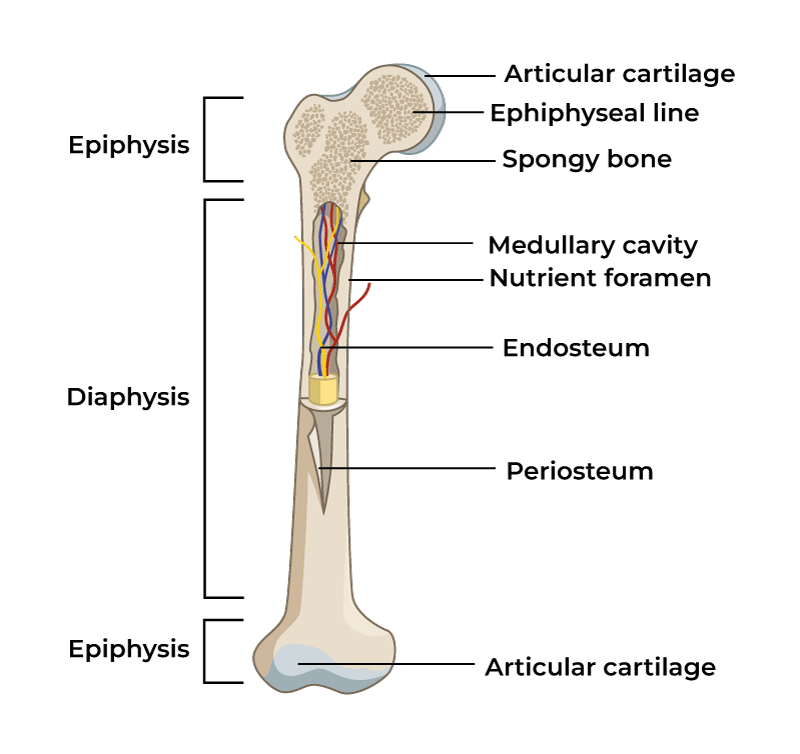
Endosteum
membrane that lines the medullary, contains osteoprogenitor cells and osteoclasts, present in all bone types