Annelids and Arthropods: Structure and Evolution
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Prostomium
First segment of annelids' body structure.
Peristomium
Second segment following the prostomium.
Pygidium
Last segment of an annelid's body.
Growth Plate
Structure after pygidium for growth.
Parapodium
Lateral extensions from segments, non-jointed.
Triploblastic
Organism with three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm.
Closed Circulatory System
Blood contained within vessels, no direct contact.
Ocelli Eyes
Light-sensitive organs for detecting light.
Metanephridia
Excretory organs for ammonia removal.
Hydrostatic Skeleton
Support structure using fluid pressure.
Dorsal Blood Vessel
Main vessel pumping blood anteriorly.
Ventral Blood Vessel
Vessel pumping blood posteriorly.
Clitellum
Band structure secreting cocoons in earthworms.
Monoecious
Organisms having both male and female reproductive organs.
Typhlosole
Fold increasing surface area in earthworm intestines.
Spermathecae
Organs storing sperm for later fertilization.
Subclass Oligochaeta
Class of annelids including earthworms.
Subclass Hirudinea
Class of annelids including leeches.
Hirudin
Anticoagulant secreted by leeches.
Hemocoelic System
Body cavity filled with blood, not segmented.
Ecdysone
Hormone triggering molting in nematodes.
Eutelic
Organisms with a fixed number of cells.
Malpighian Glands
Excretory structures in tardigrades for osmoregulation.
filters the blood and dumps wastes into the gut for elimination
Lobopod
Jointed appendages in onychophorans.
ecdysozoan clade
- open circulatory system
- must molt to grow
- extensive hemocoel
- heart with openings to hemocoel (ostia)
- spiders use blood pressure to jump
- striated muscle lets things fly
Phylum Nematoda Characteristics
- triploblastic
- unsegmented but with annotations
- All free living live in the water due to permeability of the cuticle
- Body is turgid (limitations in movement)
- Only longitudinal muscles
- eutelic
- Pseudocoelom
- Nonexistent respiratory / excretory systems
- dioecious
- must shed cuticle to grow
Phylum Tardigrade Characteristics
- Loss of heart
- Loss of nephridia
- Eutelic development
Striated muscles
- Hemocoelic body cavity
- Malpighian glands (Osmoregulatory structures)
Phylum Onycophora (velvet worms)
- No blood pigment
- To feed they Shoot glue from slime glands and bite prey injecting material to liquefy prey
- Free living Protostome coelomates
- Slime glands
(Discharge glue that helps digest material through openings in the oral papillae)
Subclass Oligochaeta Characteristics - EARTHWORMS
- Parapodia absent (spiky looking things that help with movement)
- Prostomium is small
- Has typhlosole
- has spermathecae
Crop
- storage of food
gizzard
- grinding of food
Tergum
Dorsal Plate for arthropods
Sternum
Ventral plate for arthropods
Pleuron
holds dorsal and ventral body plates together (flexible)
Resilin
- insect rubber
- inprocuticle
- substance that stores energy and releases efficiently
Arthropod Gut characteristic
- straight, differentiated for special functions
foregut
- ingestion, "chewing", and storage of food, lined with cuticle
midgut
- site of enzyme production, digestion and absorption
hindgut
- function in absorption of water and formation of feces
Arthropod excretory system
1. Malpighian tubules
- filters blood and dumps waste into gut for elimination
2. saccules
- paired, open to the outside of body next to an appendage
- derived from coelom
- filter surrounding blood
Arthropod Digestive system
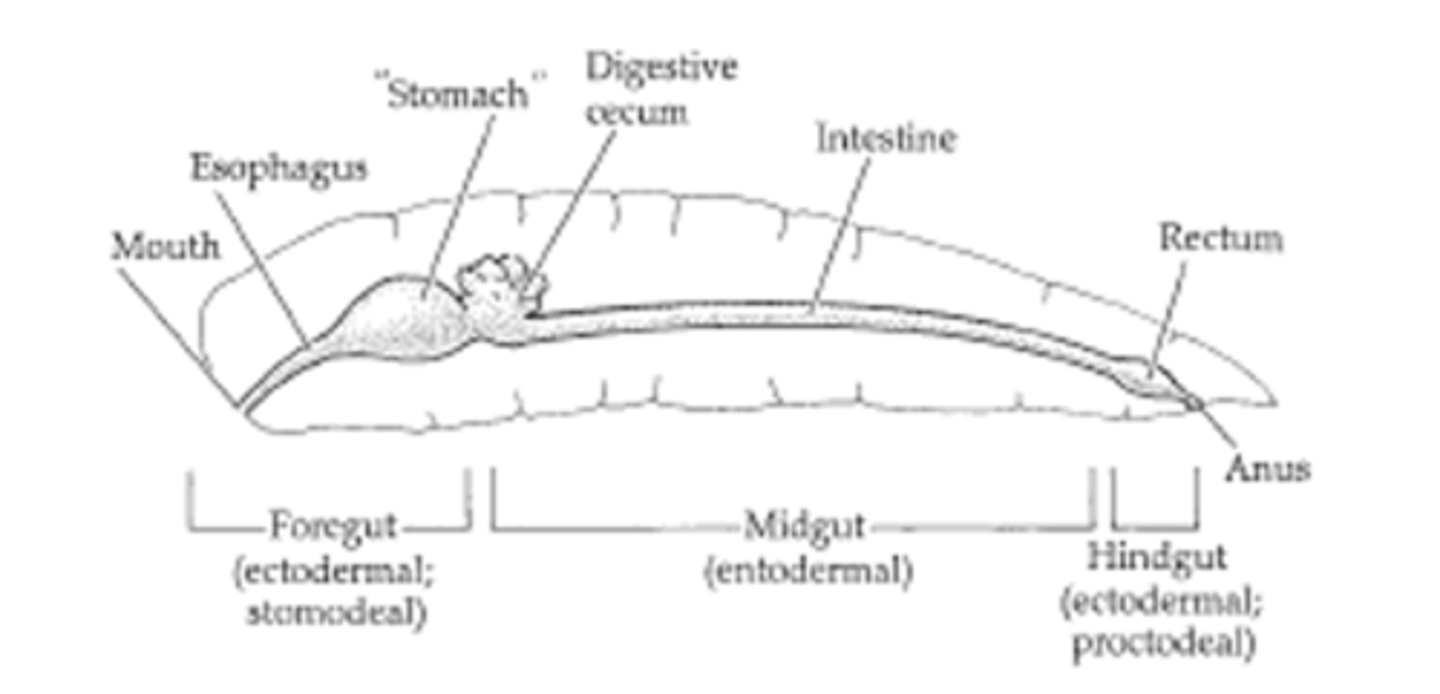
metamer
“rings” that divides body into segments
hydrostatic skeleton
uses pressure of coelomic fluid as support for movement
heteronomous
some segments are specialized
pereopod
used for walking
Telson
end of abdomen, where the rectum is
Hemocoel
body cavity filled with hemolymph
What type of body cavity is found in nematodes?
Pseudocoelom
What structure provides nematodes with structural support?
Hydrostatic skeleton
What is the composition of the nematode cuticle and a second character shared with one other phylum?
Multilayered collagen fibers that must be shed to grow
How is nematode development characterized in terms of cell division?
Eutely, where each species has a fixed number of cells at maturity
What is unique about the muscle structure in nematodes?
Nematodes have only longitudinal muscles, lacking circular muscles
How are nematode muscles innervated?
Muscles send out processes to the nerve cords
What type of circulatory system is characteristic of arthropods?
Open circulatory system
Arthropods' coelom is primarily used for which function?
Surrounding the gonads and excretory organs
Arthropods' excretory system primarily consists of
Malpighian tubules
The molting process in arthropods is also referred to as
Ecdysis
The arthropod exoskeleton is unique from other phyla in that this structure contains what unique material
Chitin
The main function of arthropods' hemolymph is
Nutrient distribution and waste removal
What type of circulatory system do annelids typically have?
Closed
What structure is used by annelids for excretion?
Metanephridia
What is the primary function of the annelid's coelom?
Hydrostatic skeleton
How do annelids primarily respire?
Through the skin or parapodia
What is the main role of setae in annelids?
To aid in locomotion and defense
Which statement is true about annelid reproduction?
Some are hermaphroditic, and others are dioecious.