classifying organic compounds
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
aldehyde
a carbon atom shares a double bond with an oxygen atom and a single bond with a hydrogen atom & with another atom or group of atoms
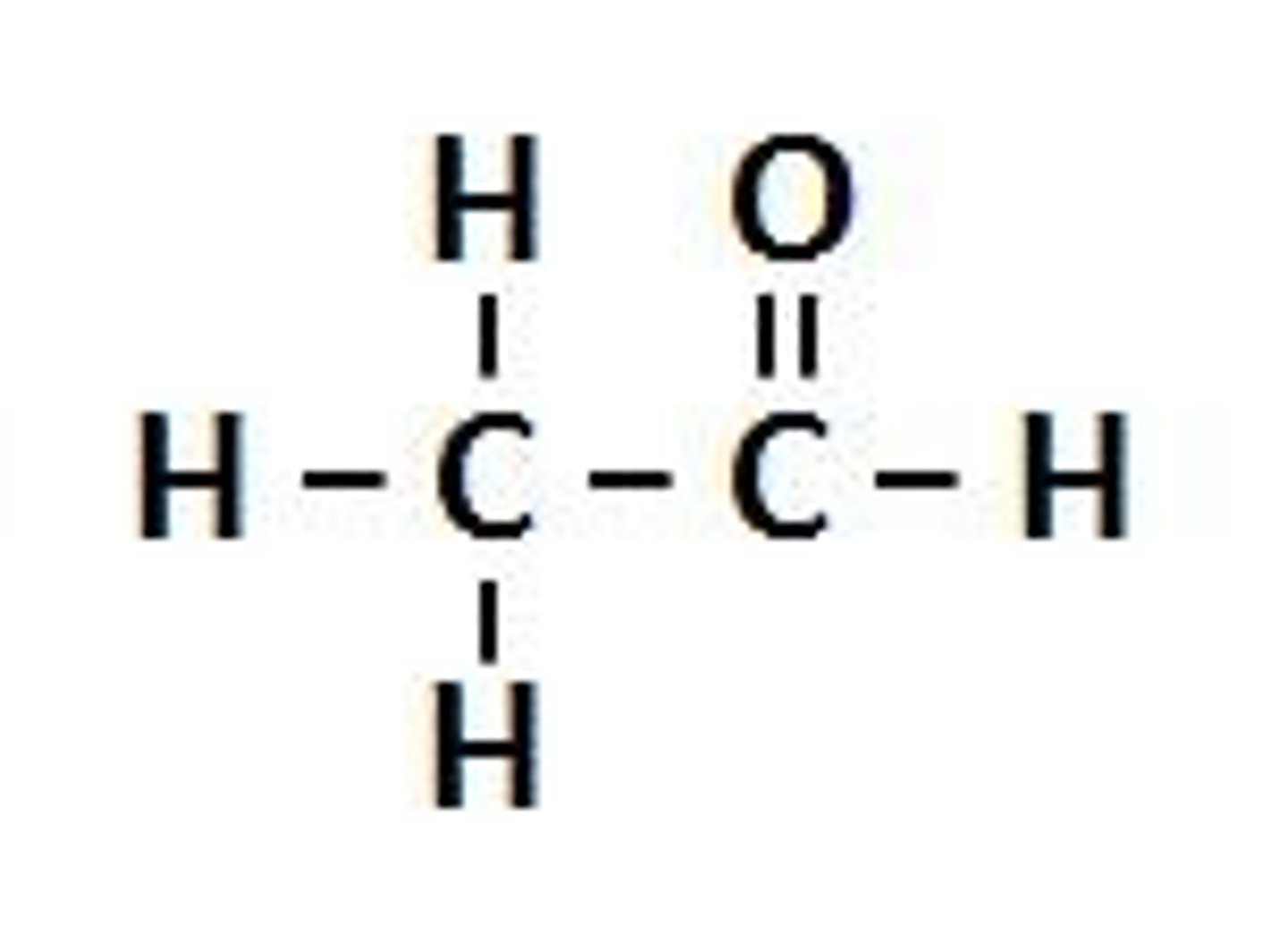
carbonyl group
chemically organic functional group composed of a carbon atom double bonded to an oxygen atom; C=O
ketone
carbon atom that shares a double bond with an oxygen atom. the remaining two bonds are either to other carbon atoms or hydrocarbon radicals (R)
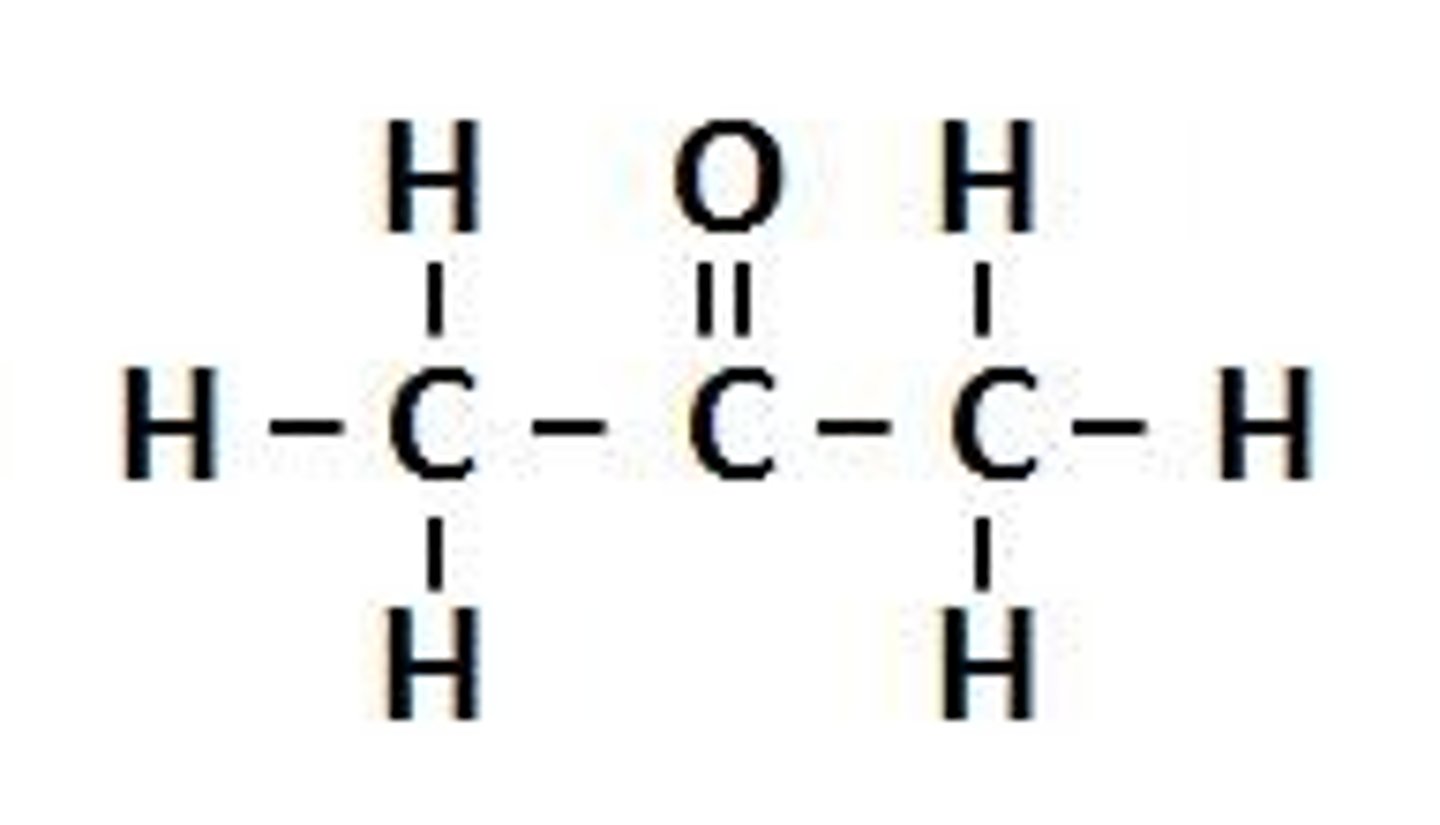
what is a key difference between aldehydes and ketones?
an aldehyde has at least one hydrogen connected to the carbonyl group whereas, ketones have two carbon groups connected to the carbonyl carbon.
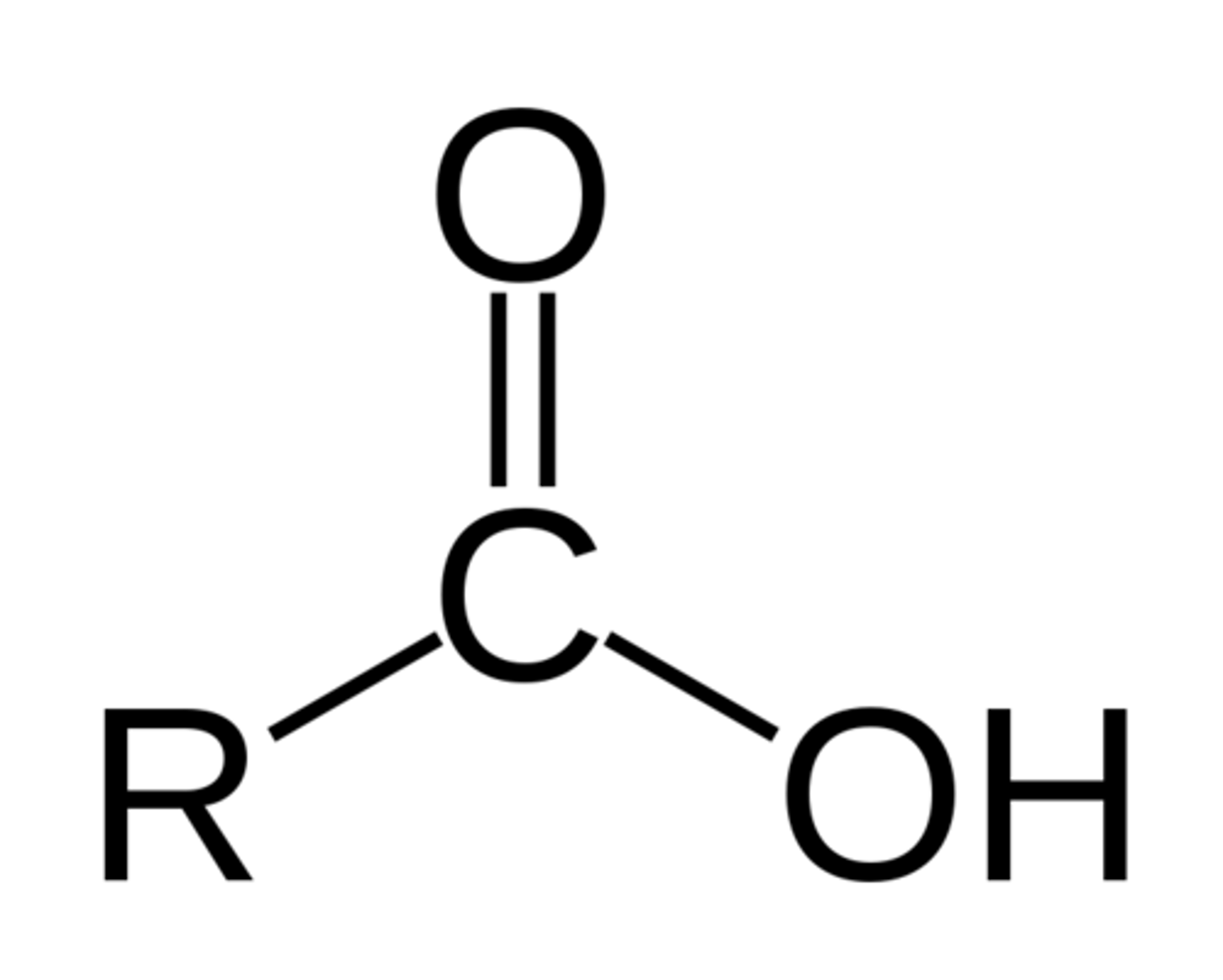
carboxylic acid
a carbon atom is bonded to an oxygen atom and to a hydroxyl group (-OH) by a single bond & a fourth bond links a carbon atom to a hydrogen atom
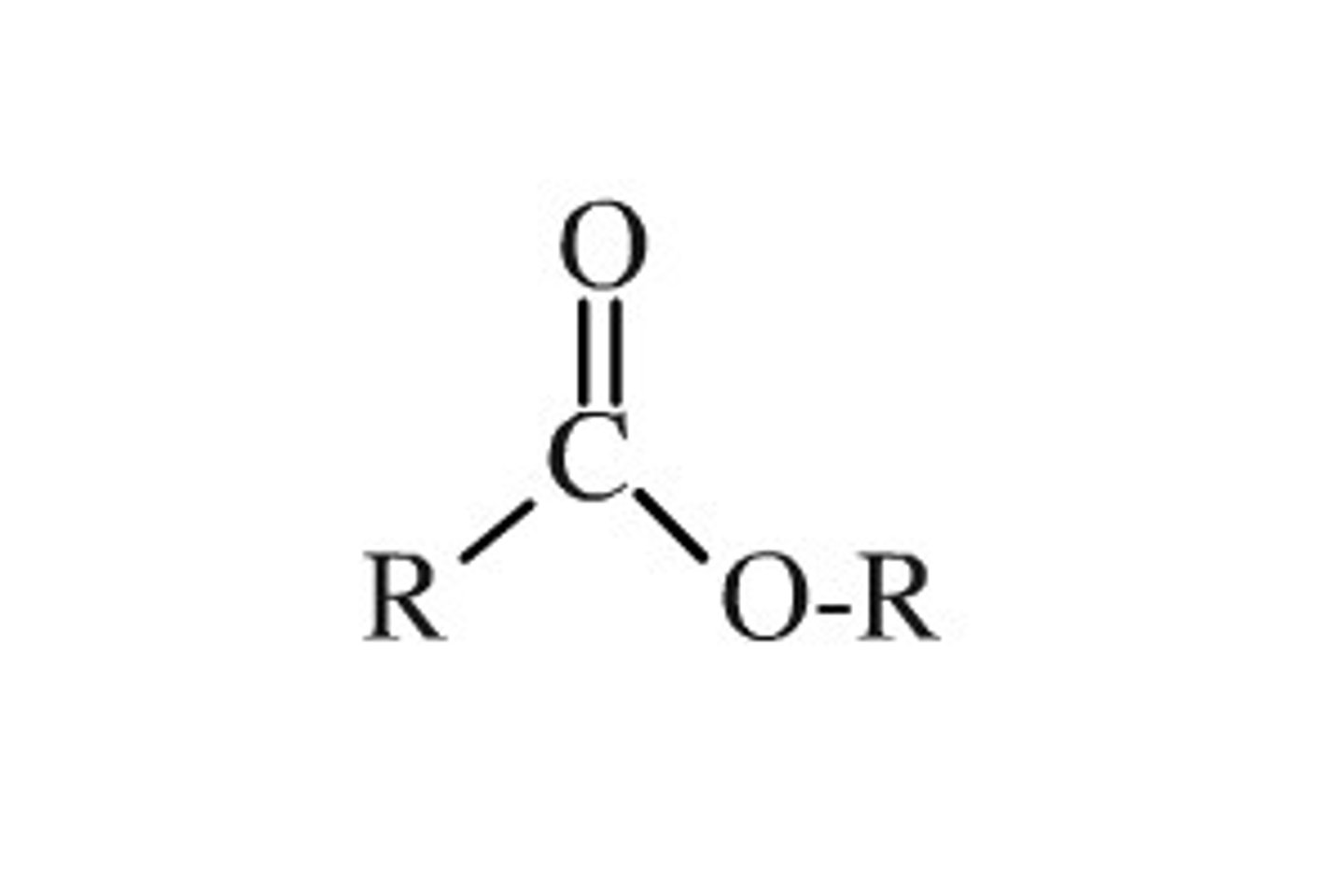
ester
characterized by a carbon bonded to three other atoms: a single bond to carbon, a double bond to oxygen, and a single bond to oxygen. The single oxygen is bonded to another carbon.
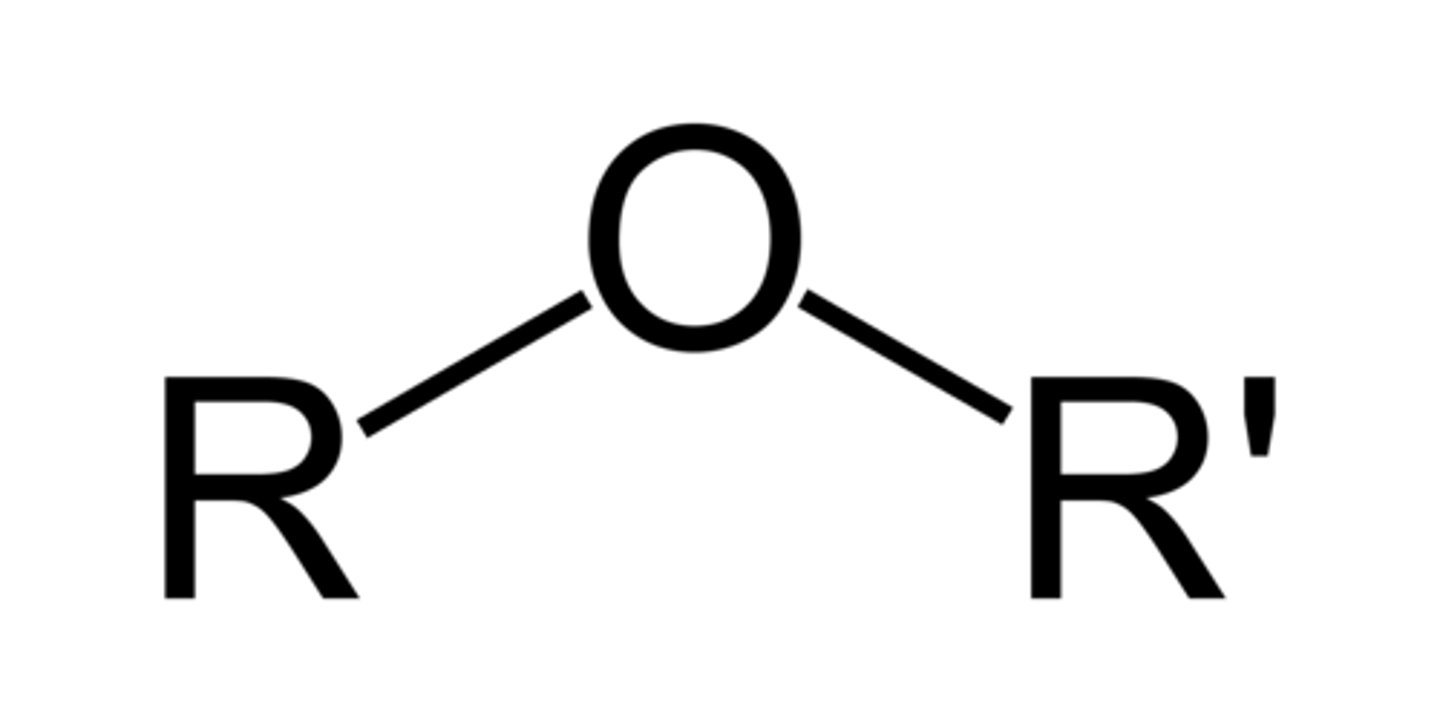
ether
characterized by an oxygen atom bonded to two alkyl groups or aryl groups
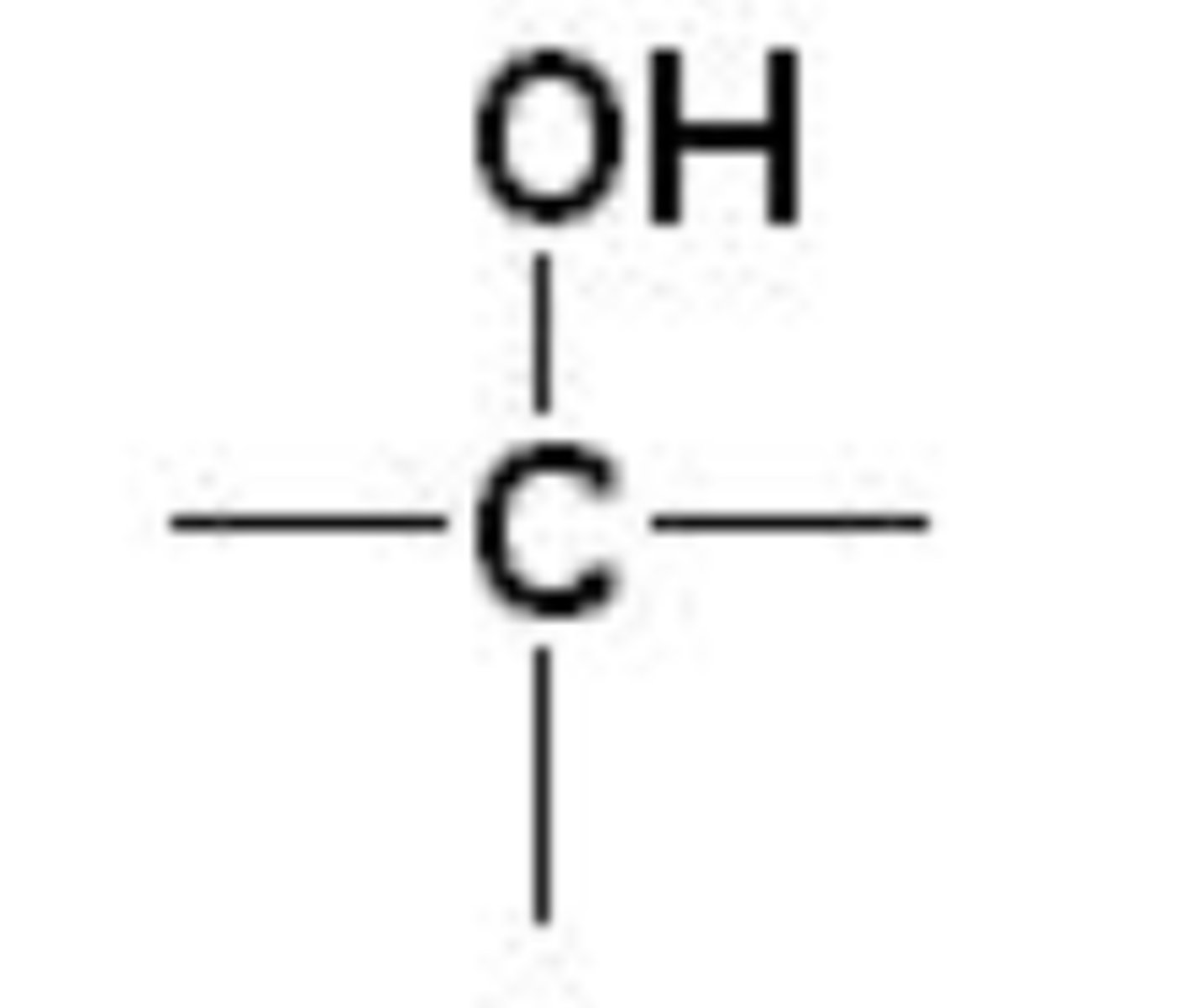
alcohol
one or more hydroxyl (-OH) groups attached to a carbon of an alkyl group
structural formulas for organic molecules
- carbon forms 4 covalent bonds
- can form single, double, and/or triple bonds
- carbon has no unshared pairs of electrons (most stable)
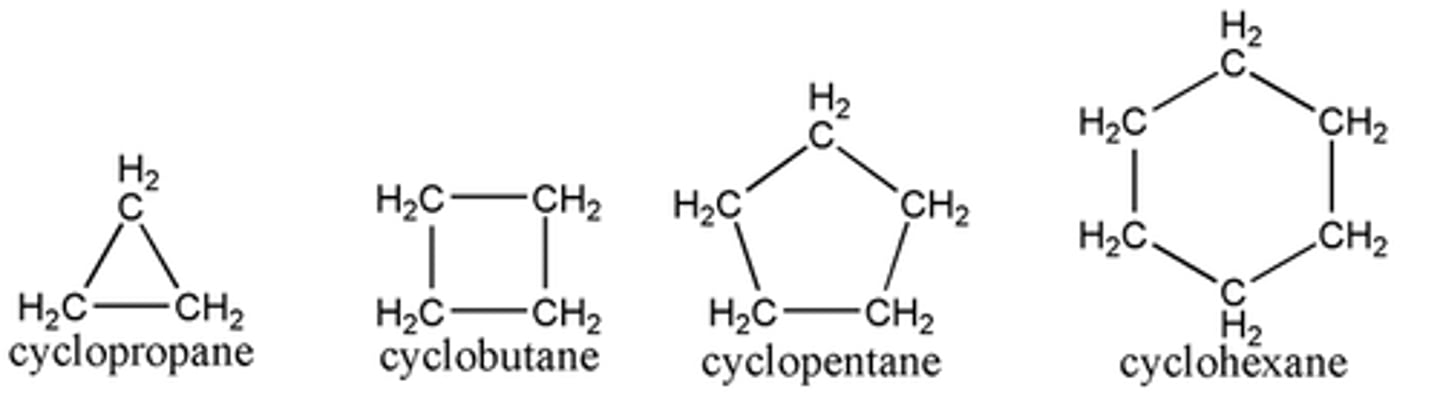
cycloalkanes
organic molecules with carbon connected with single bonds and at least one ring structure.
name constructed by prefix cyclo followed by the name of the open-chain alkane
ring restricts-no free rotation
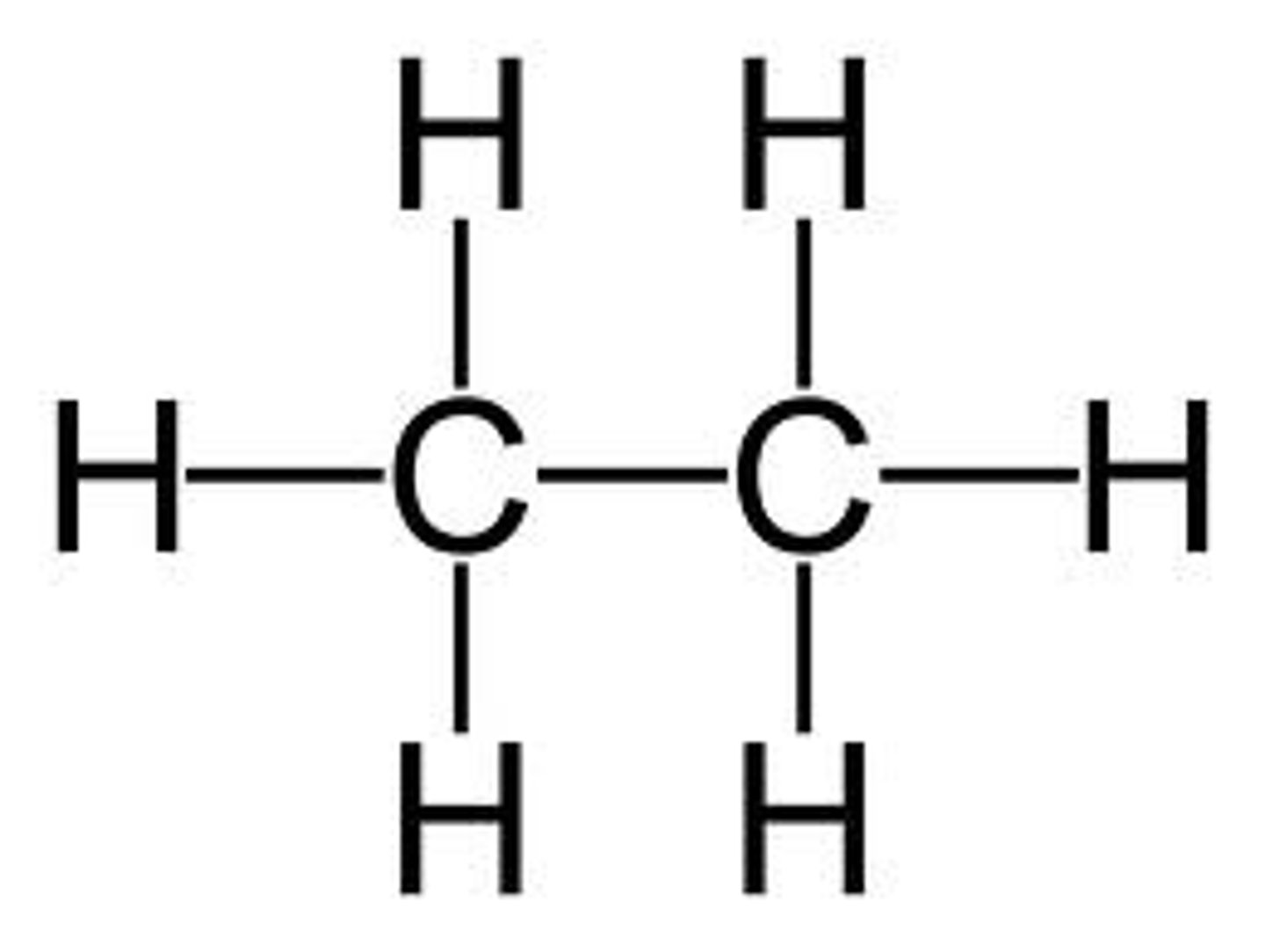
alkanes
only single bonds between carbon and hydrogen atoms; referred to as saturated hydrocarbons
alkenes
carbon-carbon double bond; unsaturated hydrocarbons
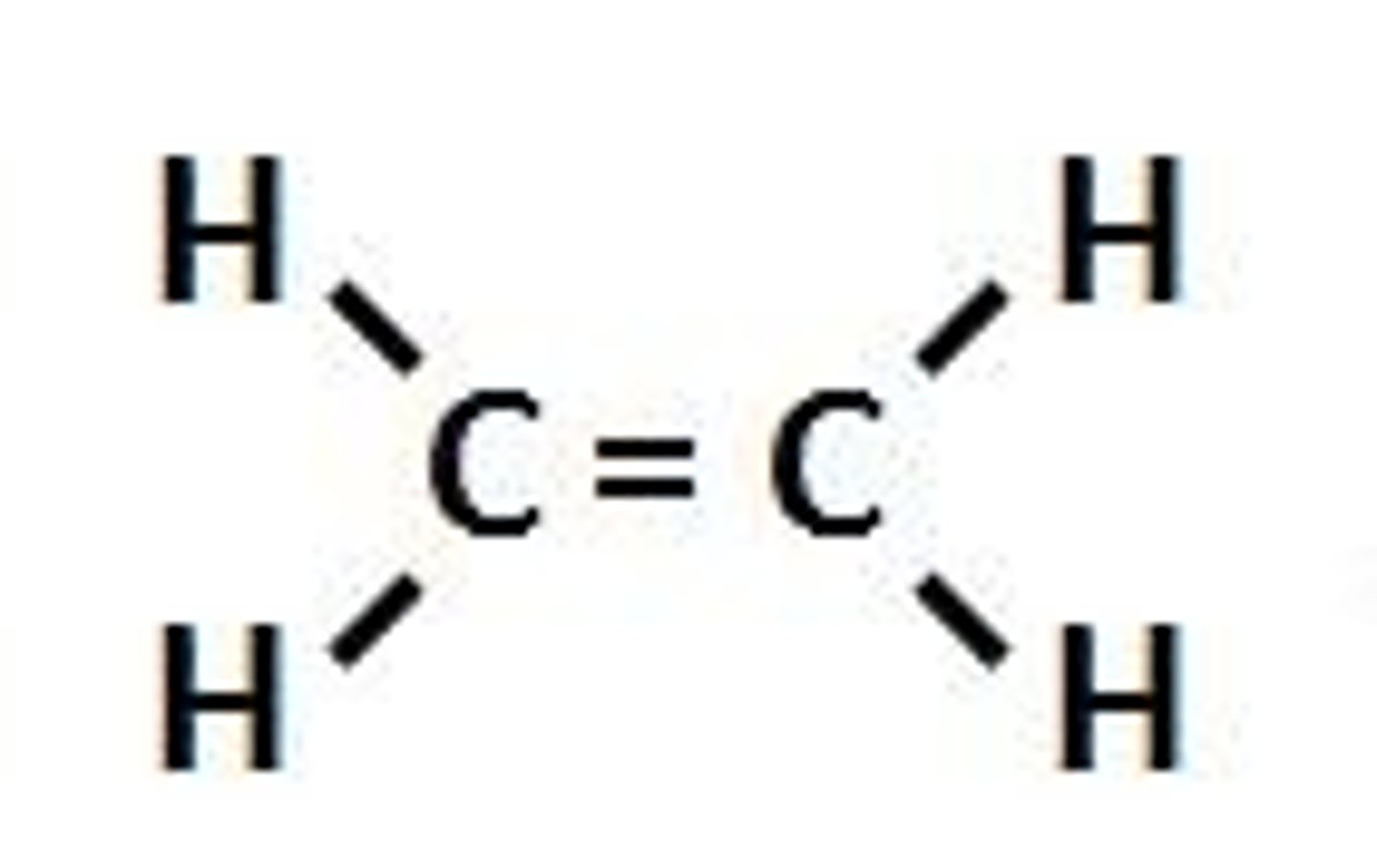
alkynes
a carbon-carbon triple bond; unsaturated hydrocarbons
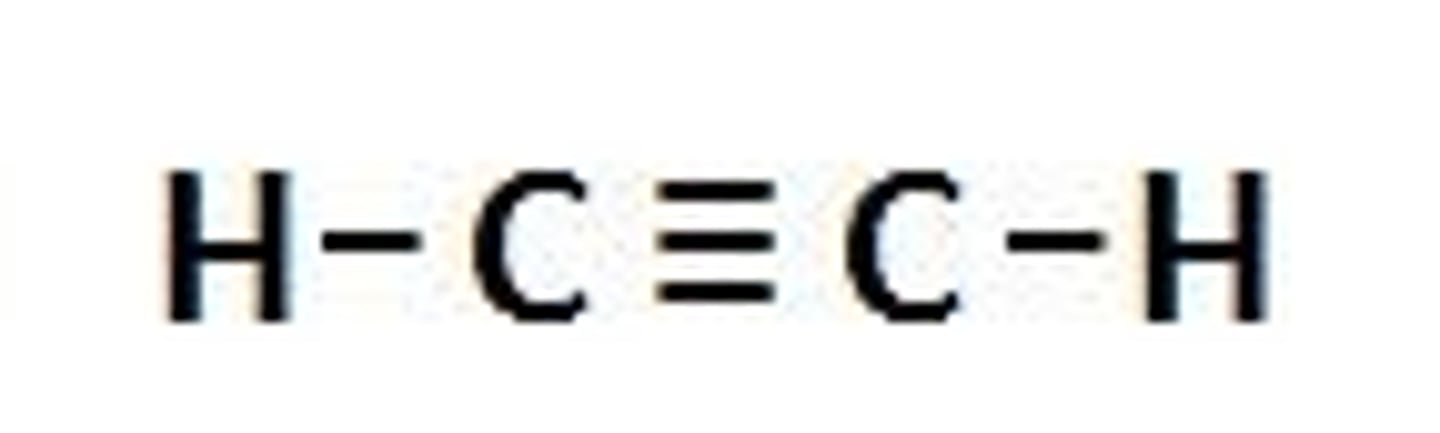
arenes
benzene-like ring; all arenes are aromatic
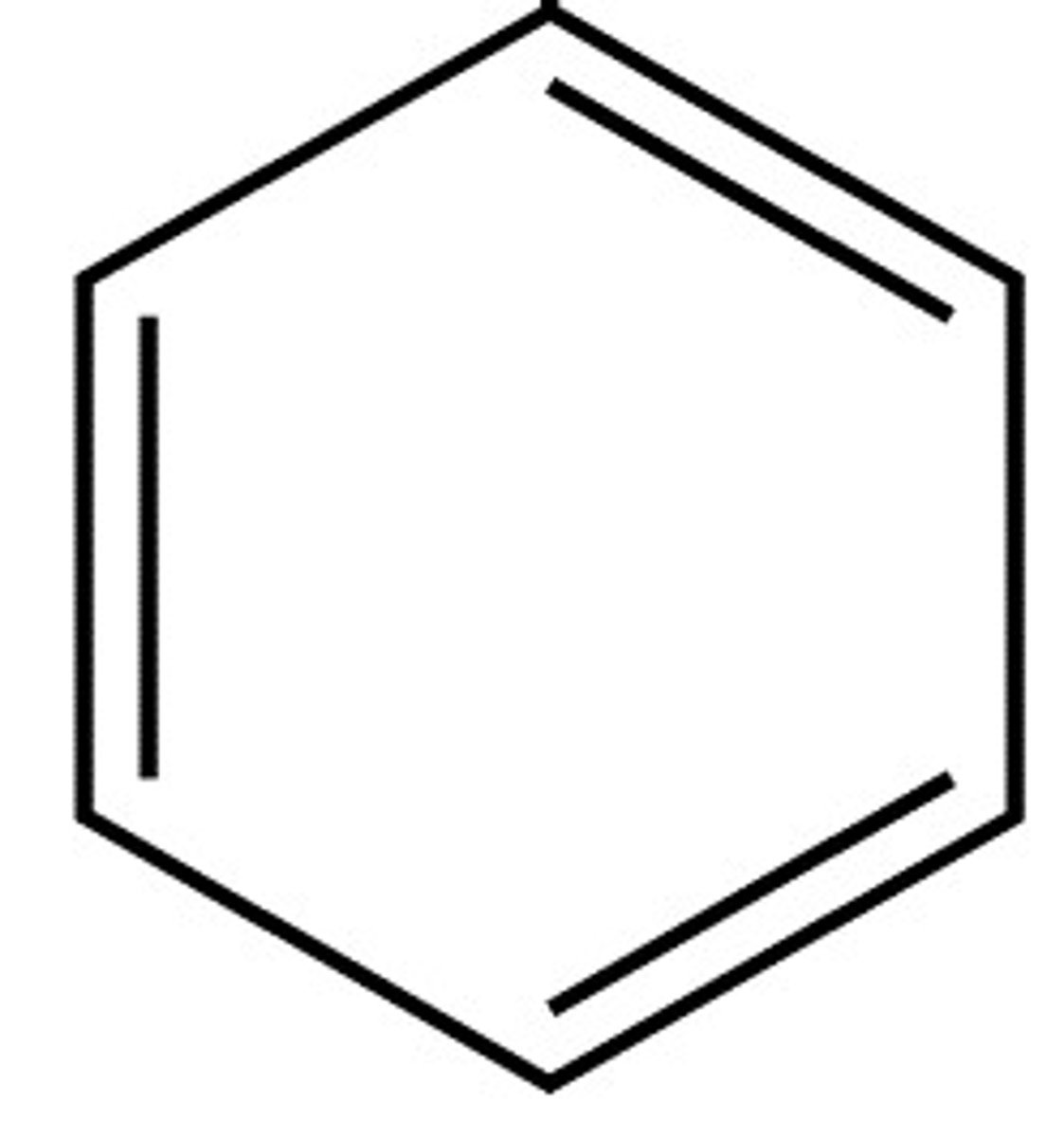
hydrocarbon
an organic molecule consisting only of carbon and hydrogen.
saturated
compounds consisting of only single bonds
heteroatoms
atoms in an organic compound other than carbon and hydrogen
functional group
a group of atoms bonded in a particular way
carbonyl group
C=O
unsaturated hydrocarbons
hydrocarbons with more than one bond between two carbon atoms, which means those carbons are no longer saturated with hydrogen atoms

terpenes
compounds contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond and are a multiple of 5 carbons (5, 10, 15, 20, and so on)
aromaticity
a term used to describe the unexpected stability of aromatic compounds
alkanas polar or nonpolar?
the electronegativities of carbon and hydrogen are so similar that when these two elements form covalent bonds, the electrons are shared equally = the bond is nonpolar
what functional group makes good fuel sources? explain
alkanes; they readily undergo a reaction with oxygen, called combustion
monosaturated fats
one double bond
polyunsaturated fats
more than one double bond
lipids
energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
saturated fatty acids
long, straight-chain alkane-like compounds that do not contain double bonds and have a carboxylic acid functional group at one end
branched-chain alkanes
alkanes that do not have all their carbon atoms connected in a single continuous chain
structural isomers vs. conformational isomers
structural involves different molecules while conformational involves the same molecule (different arrangements/connectivity)
stereoisomers
compounds with the same structural formula but with a different arrangement of the atoms in space.
the prefix "cis" means
same side
the prefix "trans" means
across