GEN 141 Unit 1 Test
1/200
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
201 Terms
anatomical position
upright, feet parallel, eyes and palms forward
prone
lying face down
supine
lying on the back
dorsal
toward the back
ventral
toward the belly
anterior
front
posterior
back
midline
divides body into left and right
medial
toward the midline
lateral
to the side, away from the midline of the body
inferior
below
superior
above
cephalic
toward the head
caudal
toward the tail
proximal
closer to point of attachment
distal
further from point of attachment
deep
away from surface
superficial
near surface
sole/plantar
bottom of foot
parietal
outer wall of body cavity
visceral
internal organs
coronal plane
divides body into anterior and posterior
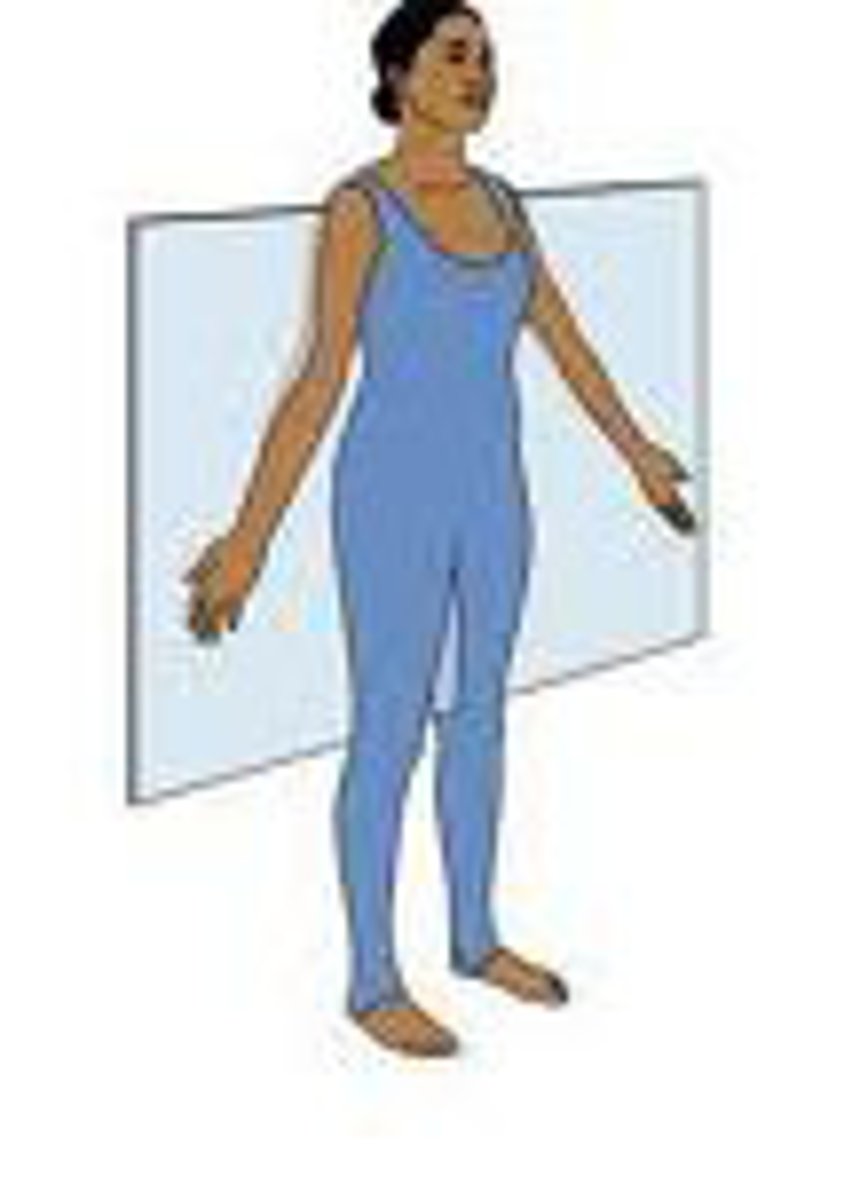

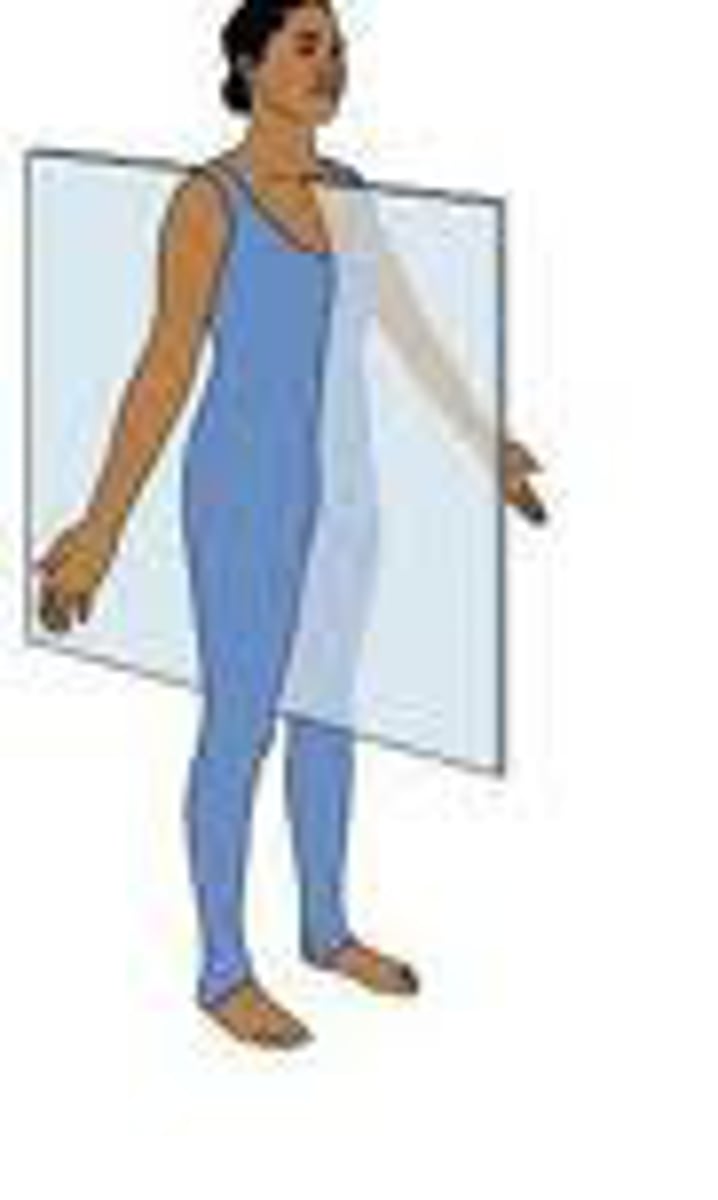
sagittal plane
divides body into left and right
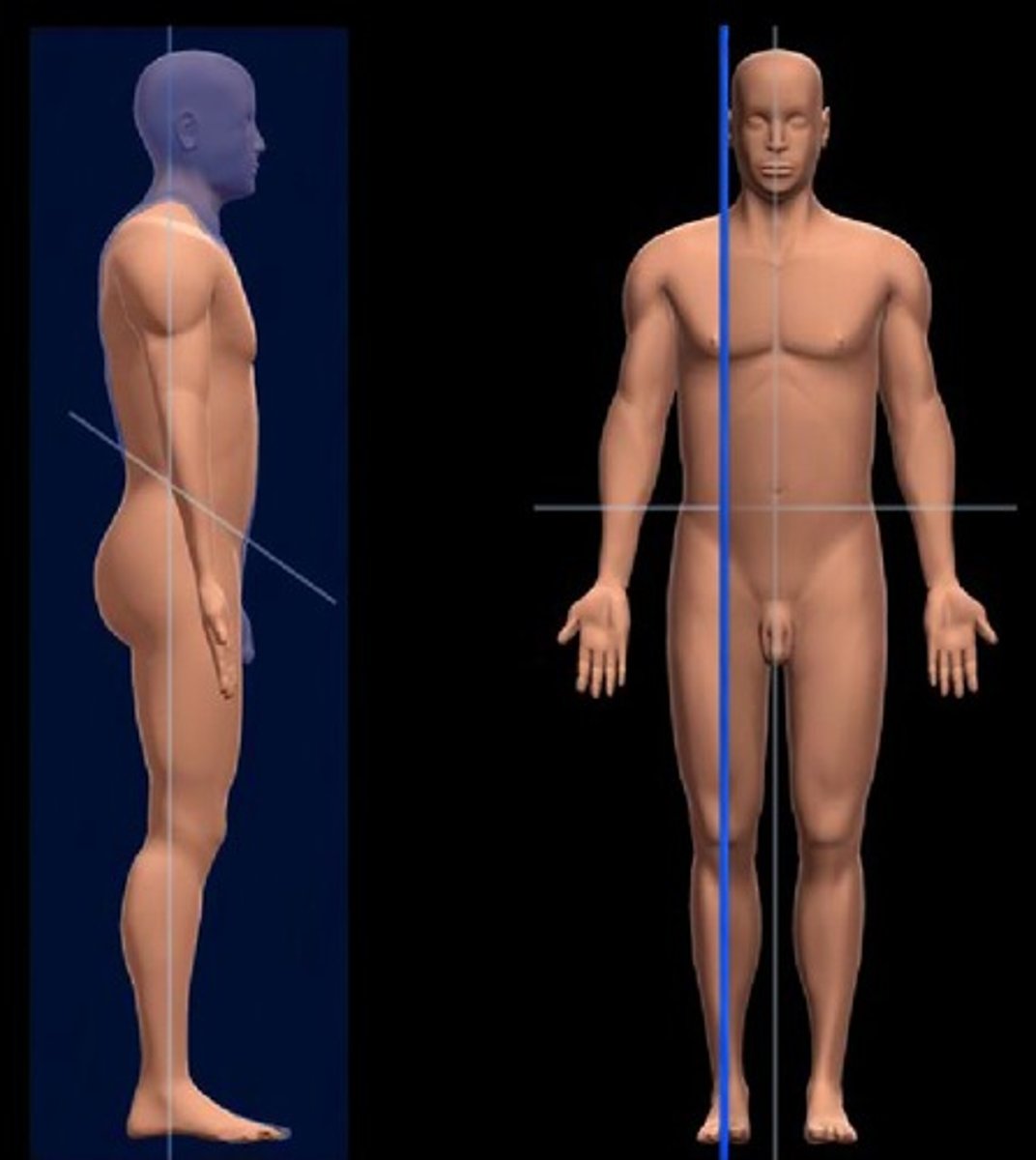
midsagittal plane
divides the body into equal right and left sides
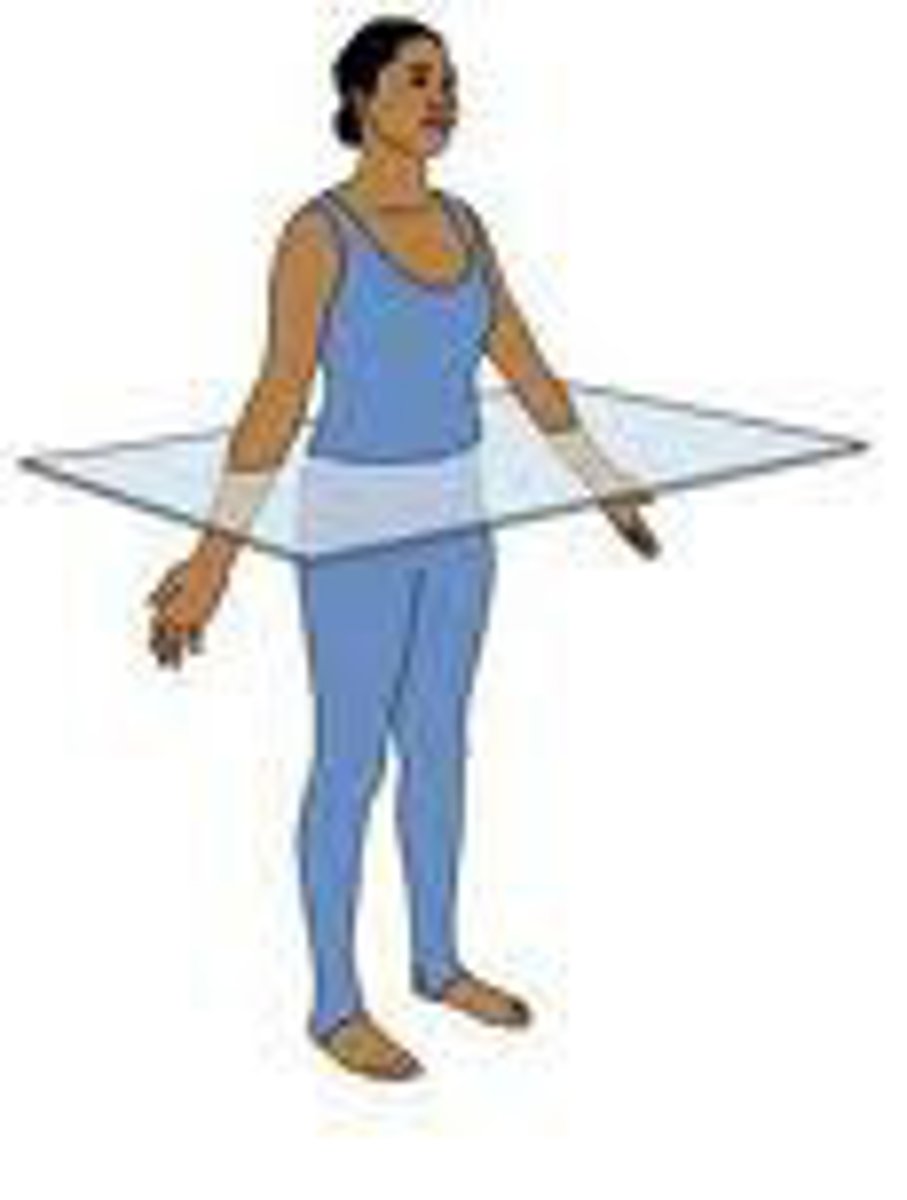
transverse plane
divides the body into superior and inferior parts
oblique plane
divides body at an angle
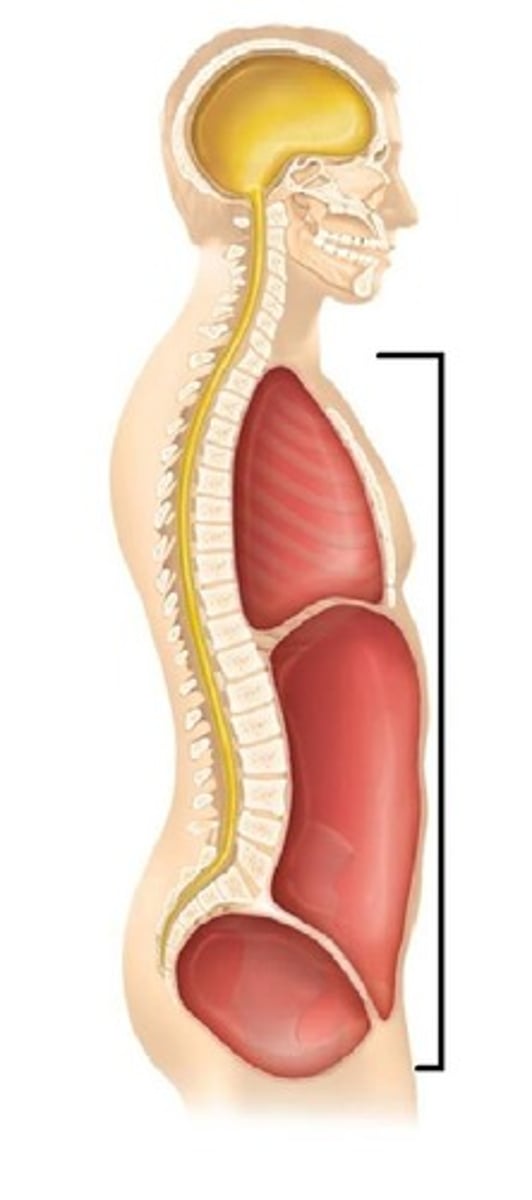
body cavities
protect organs
serous membrane (serosa)
lines body cavities + covers organs
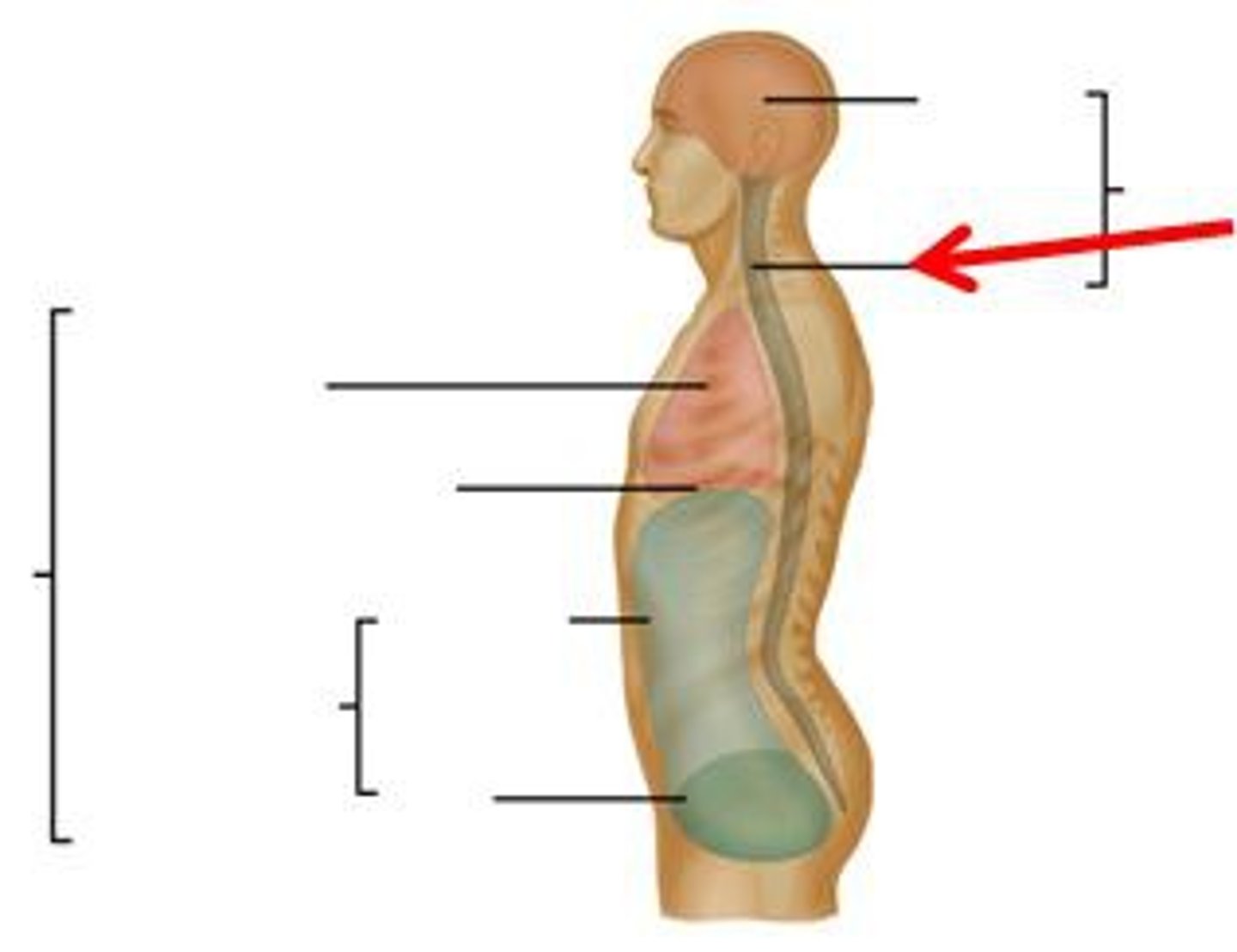
ventral cavity
thoracic cavity(sup.) and abdominopelvic cavity(inf.); divided by diaphragm
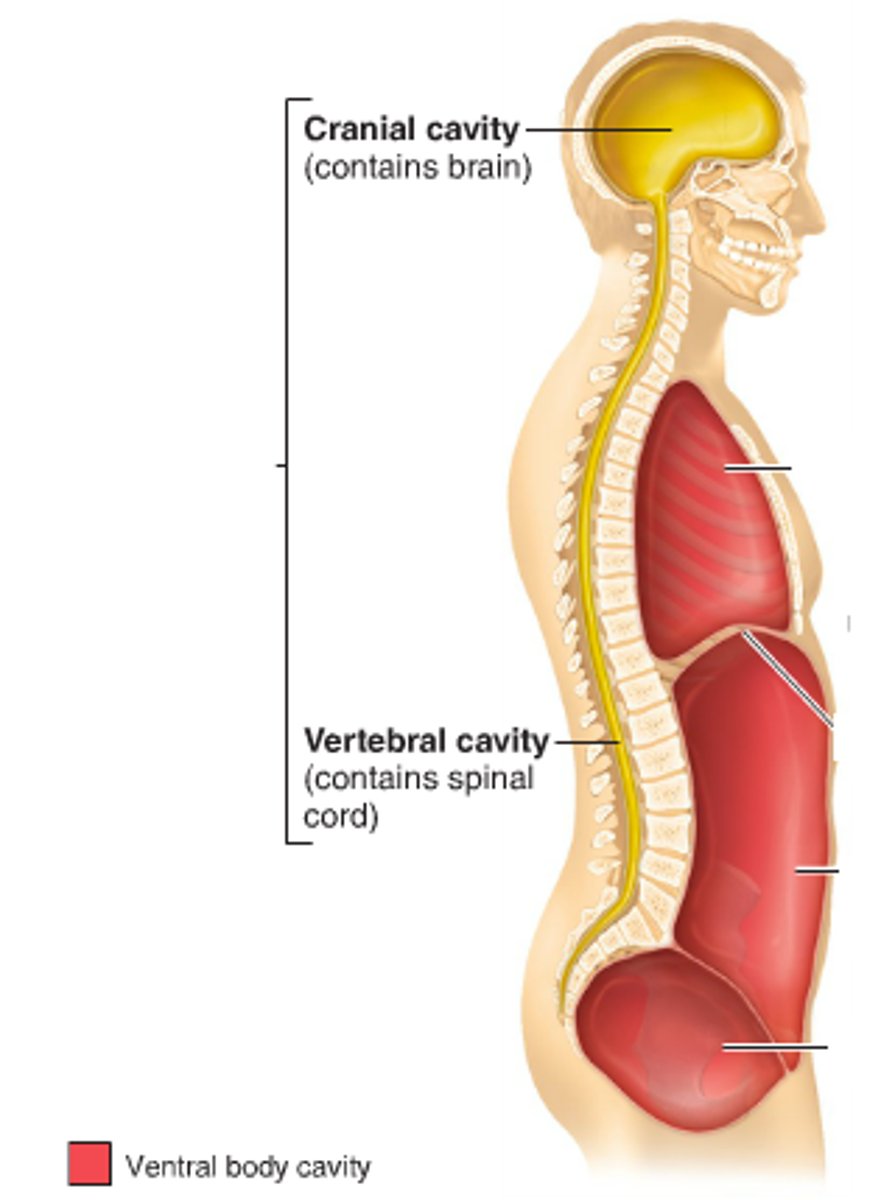
dorsal cavity
cranial cavity + vertebral canal
thoracic cavity
2 pleural cavities (lungs; lined w/ pleurae); 1 pericardial cavity (heart; lined w/ pericardium)
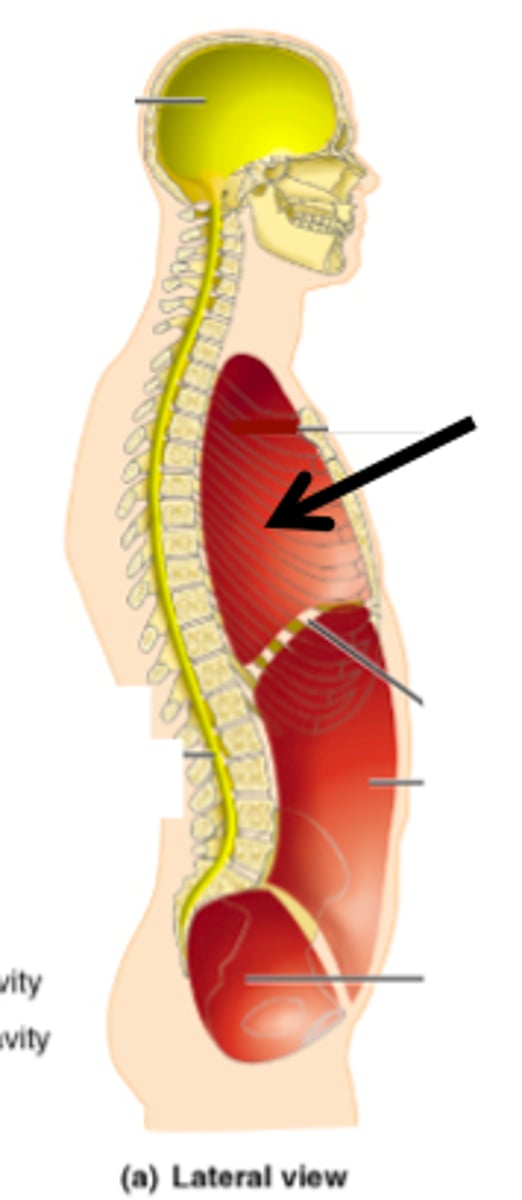
abdominopelvic cavity
abdominal cavity (digestive organs, spleen, kidneys, ureters; lined w peritoneum); pelvic cavity (bladder, rectum, reproductive; peritoneum)
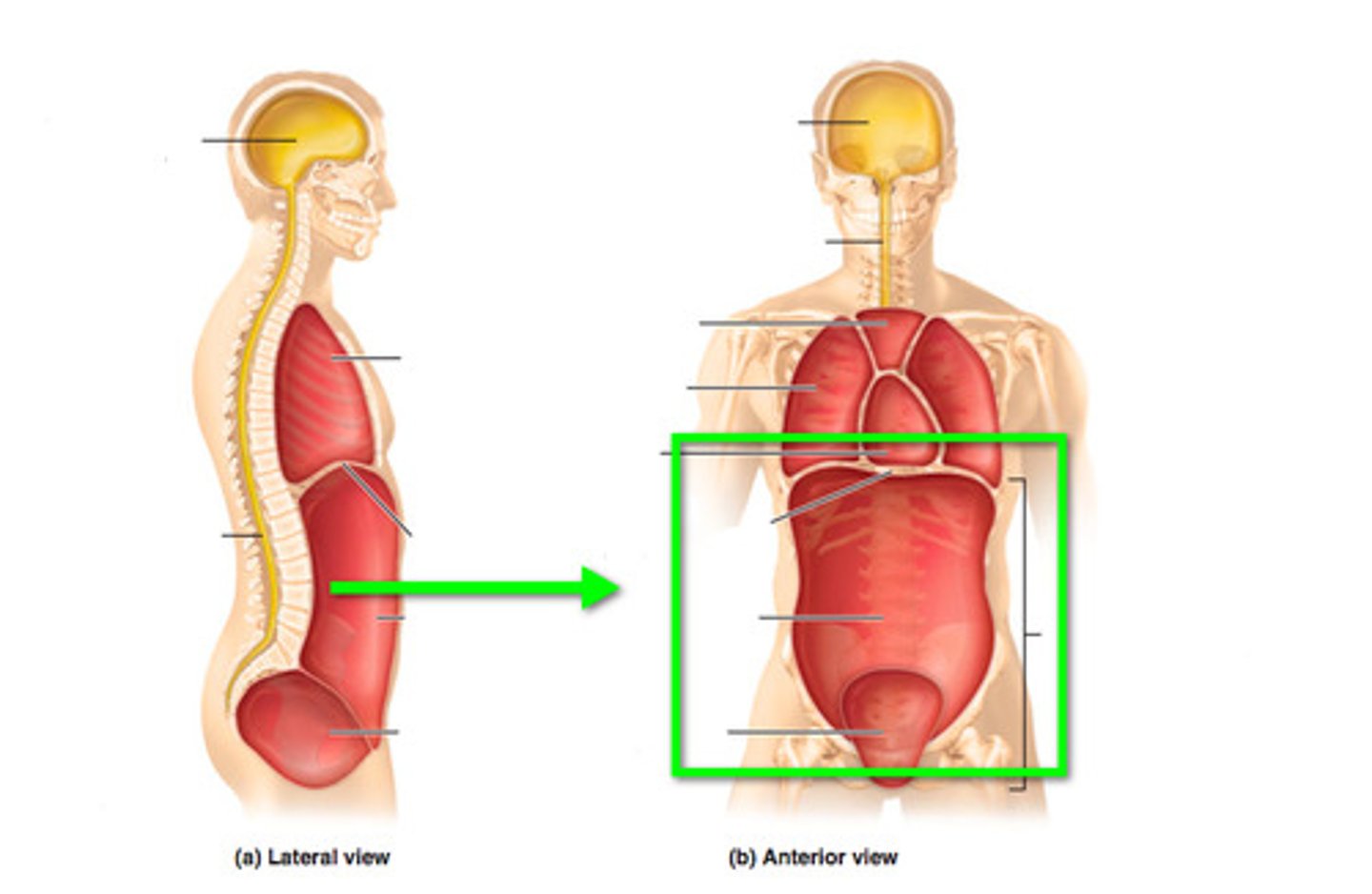
cranial cavity
brain; lined by meninges
vertebral canal
contains spinal cord; lined by meninges
right upper quadrant (RUQ)
right lobe of liver, gallbladder, right kidney, portions of stomach, small and large intestine
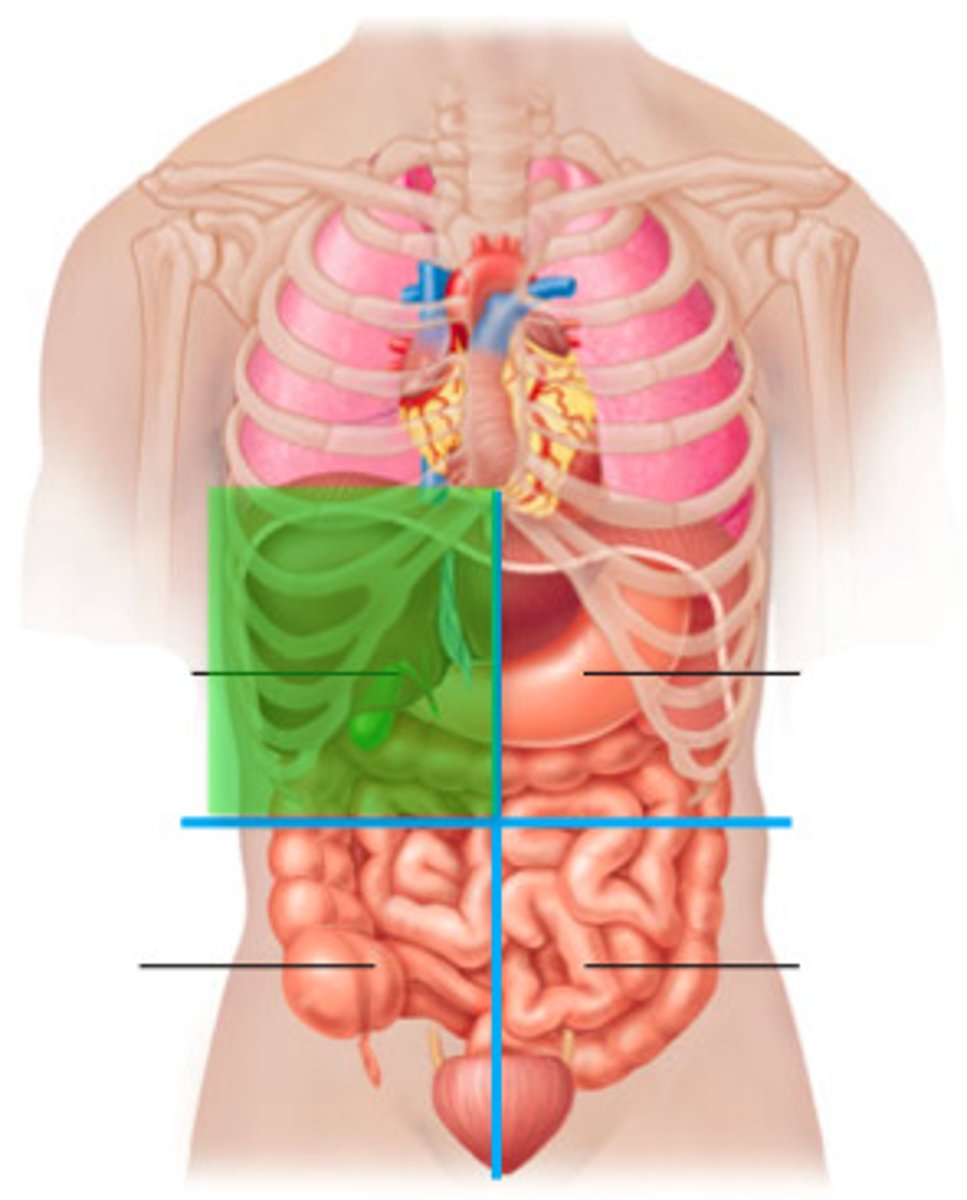
left upper quadrant (LUQ)
left lobe of liver, stomach, pancreas, left kidney, spleen, portions of large intestine
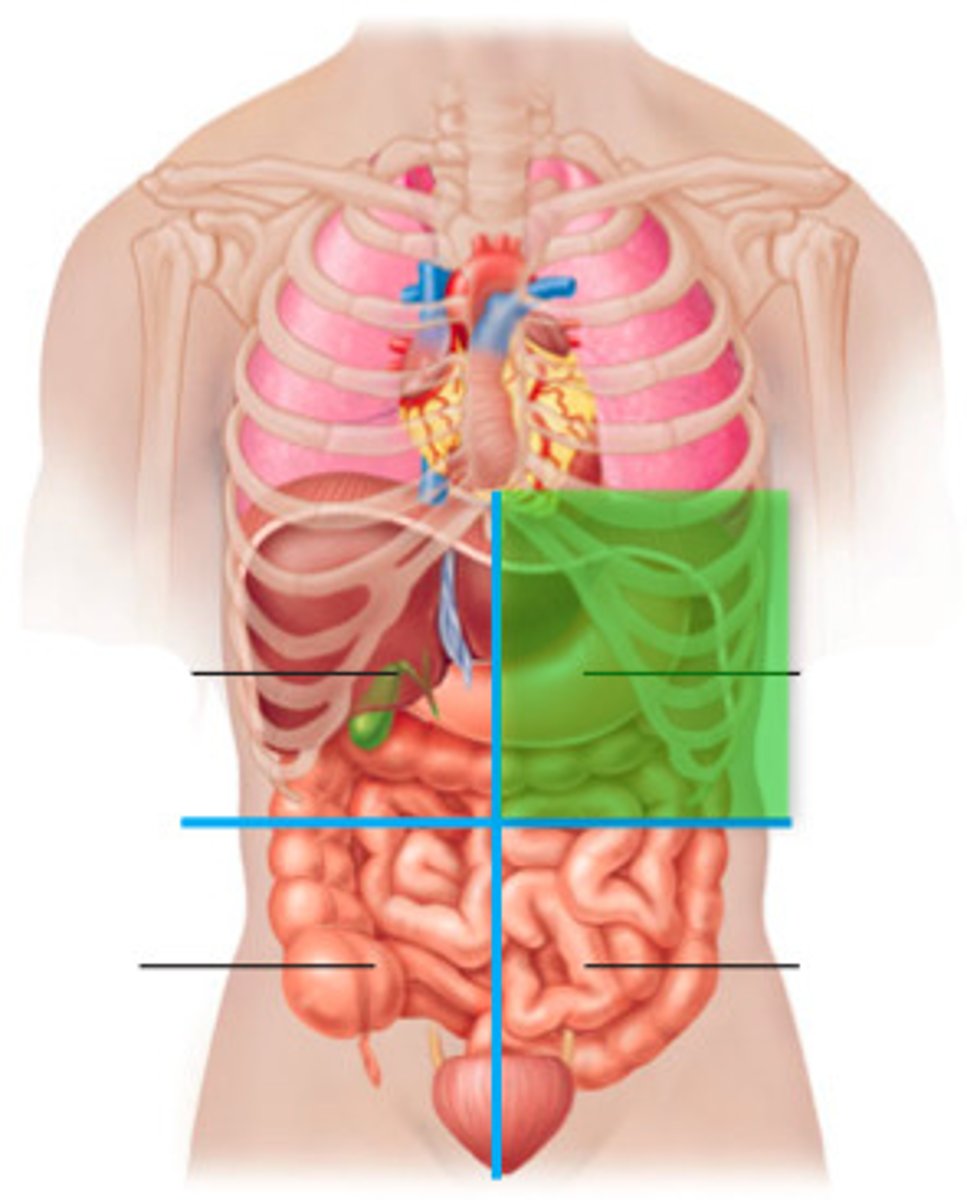
right lower quadrant (RLQ)
cecum, appendix, right ovary and tube, right ureter, right spermatic cord
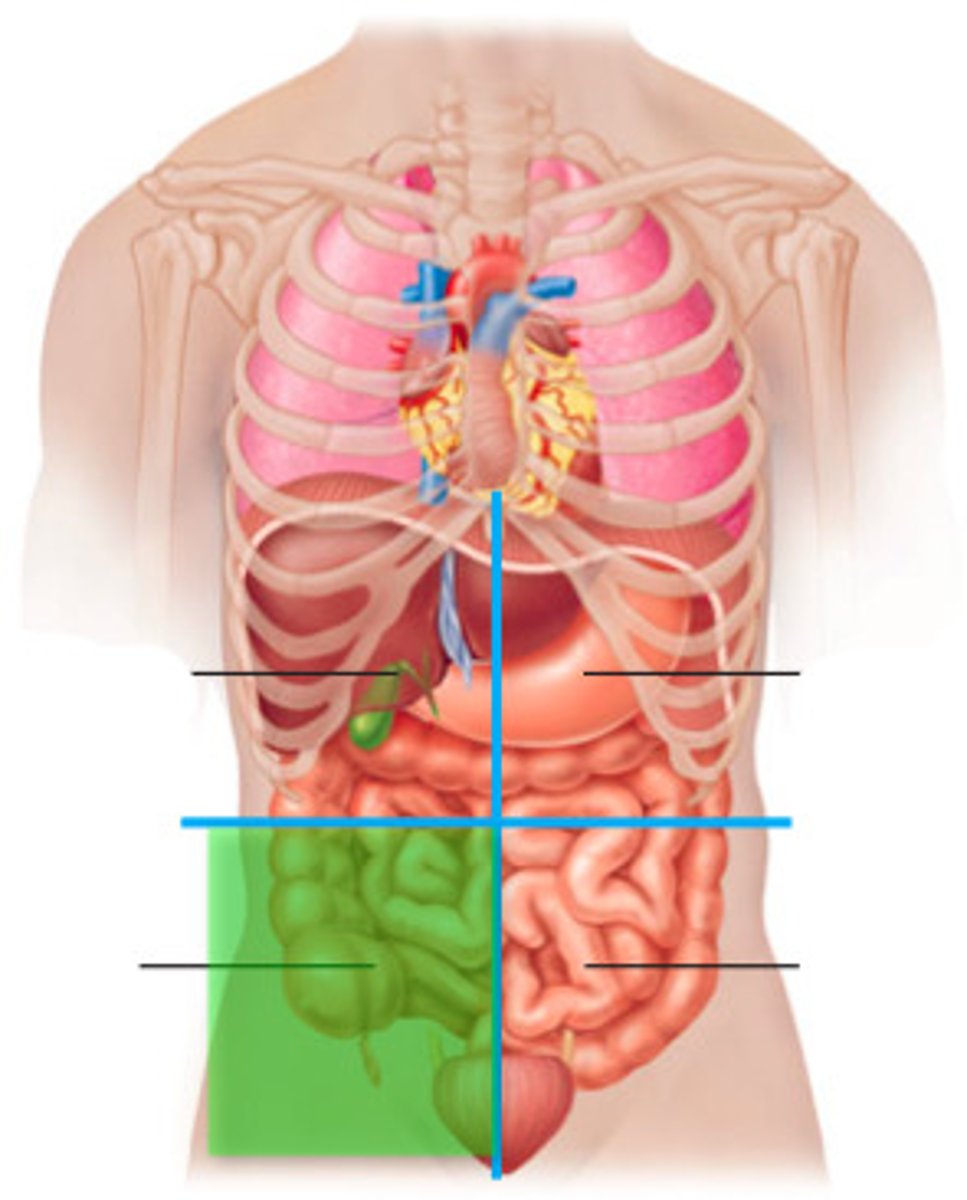
left lower quadrant (LLQ)
contains parts of the small and large intestines, left ovary, left fallopian tube, left ureter
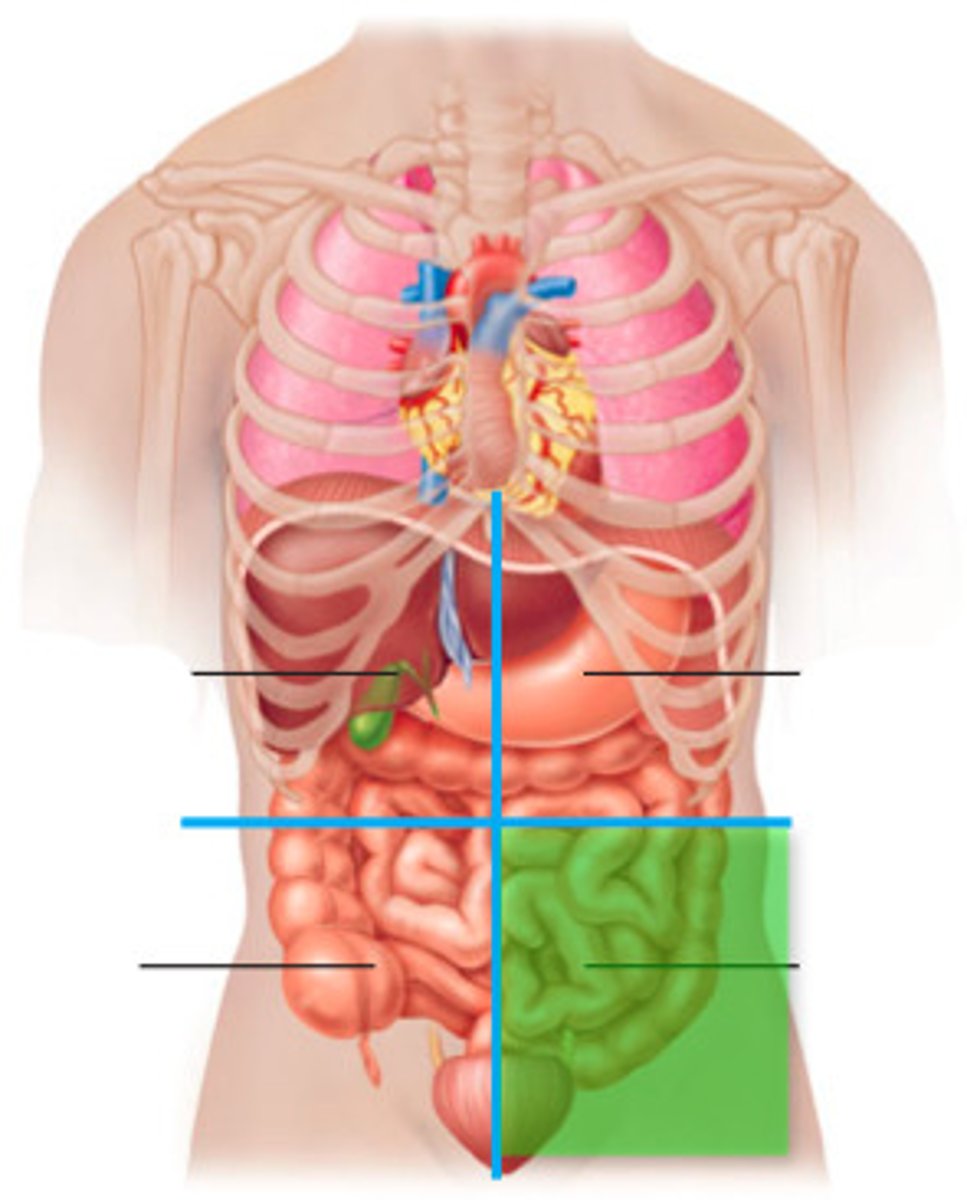
right hypochondriac region
liver, gallbladder, right kidney
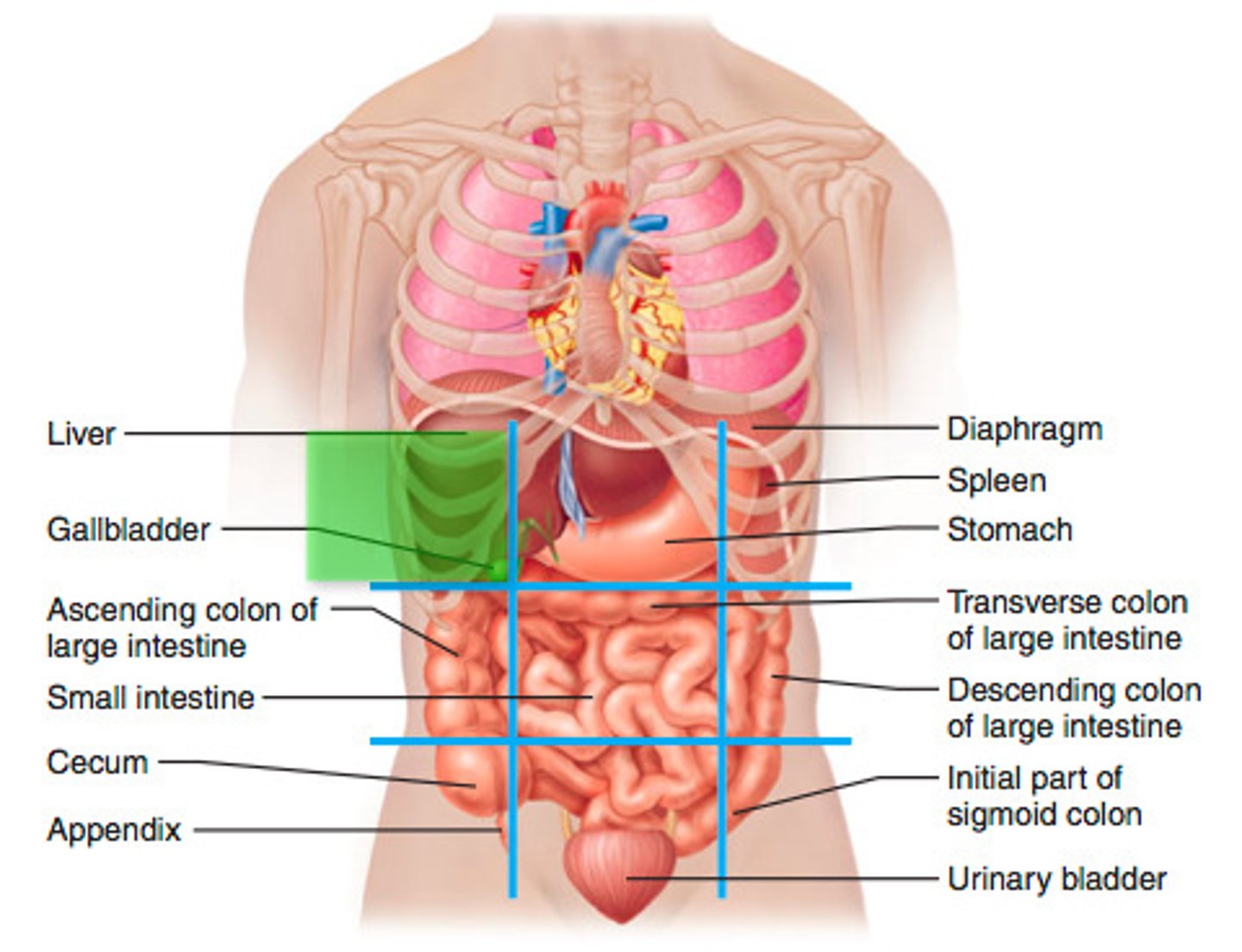
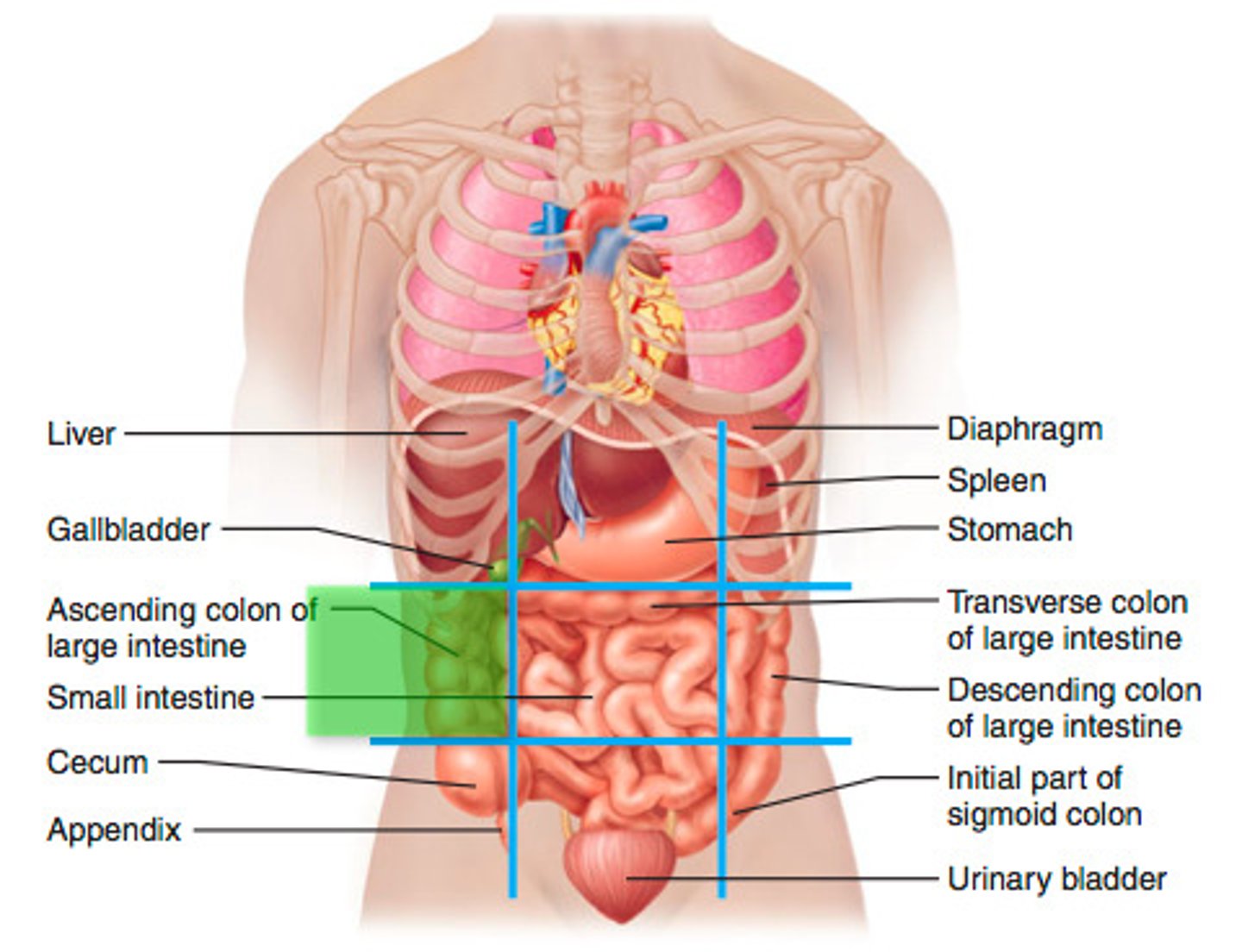
right lumbar region
ascending colon of large intestine
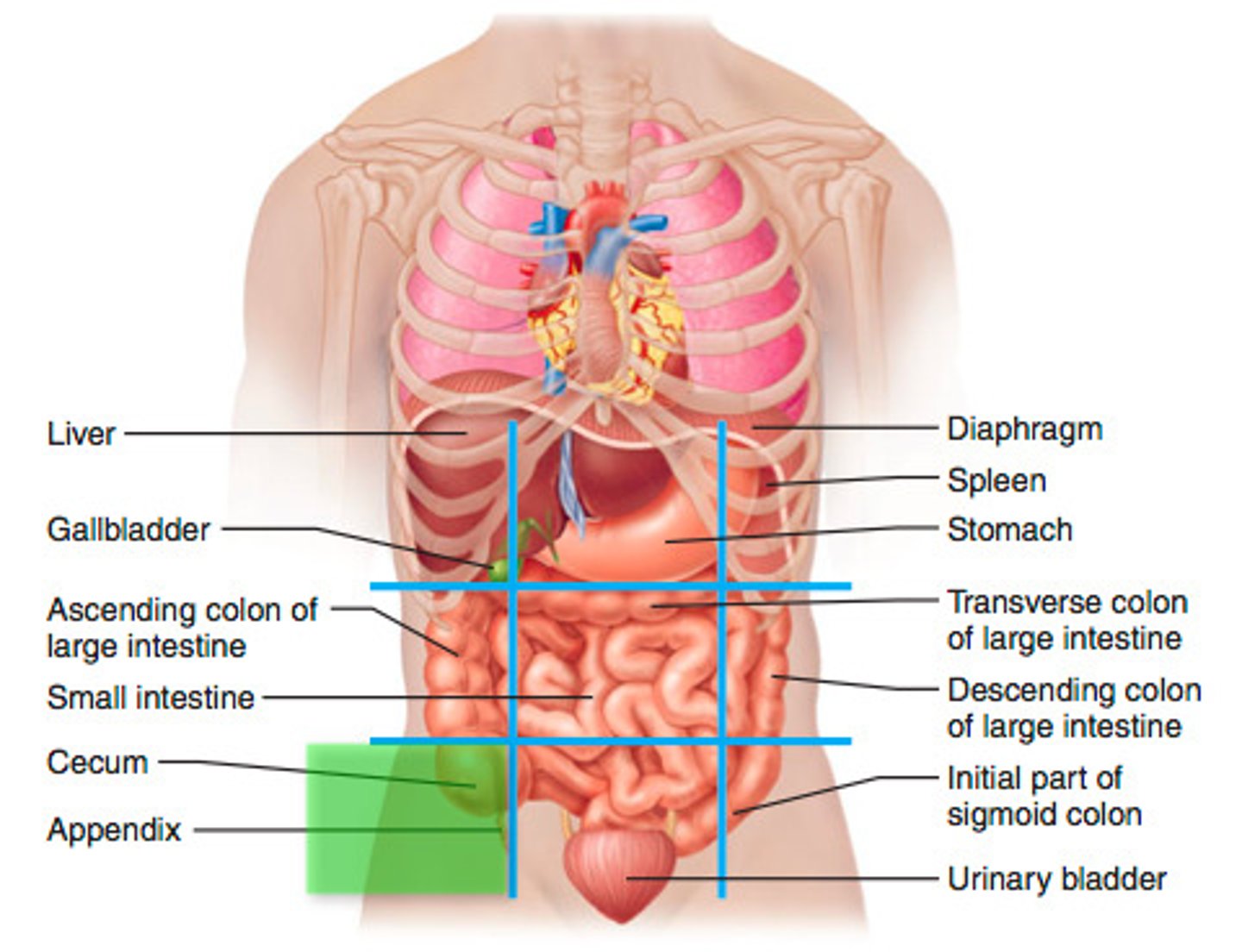
right inguinal region
cecum, appendix
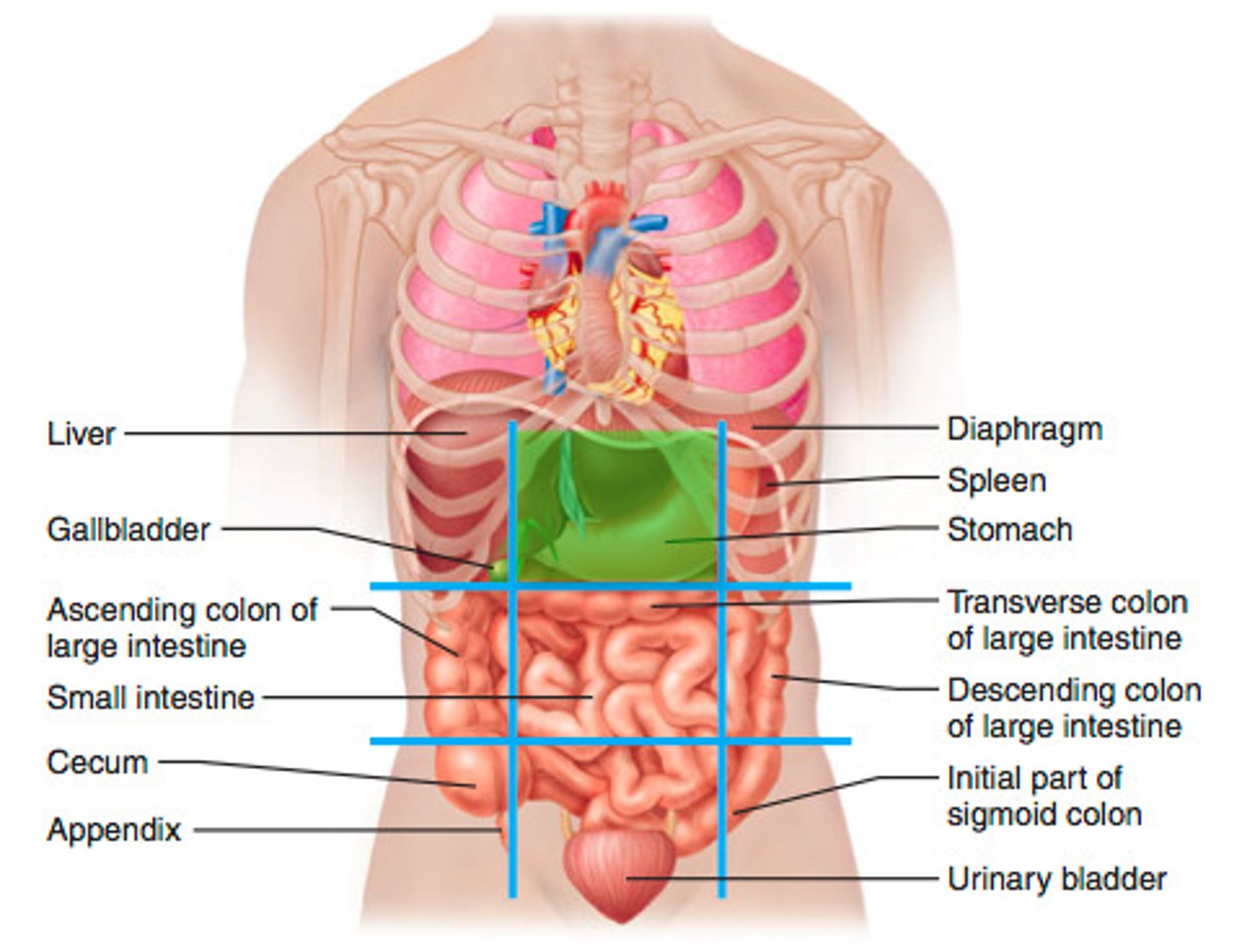
epigastric region
stomach, liver, pancreas, right and left kidneys
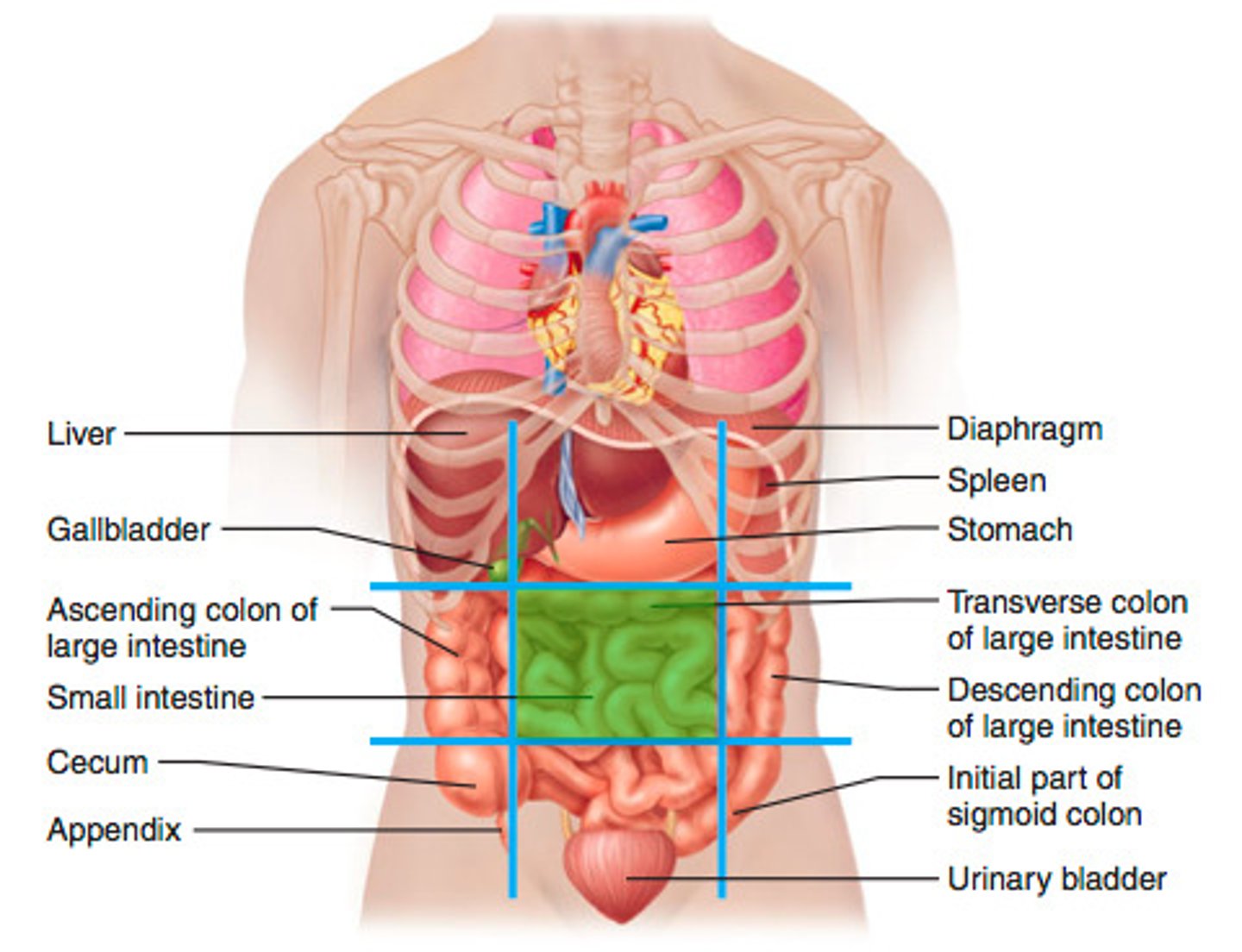
umbilical region
small intestine, duodenum
hypogastric region
bladder, colon, reproductive organs
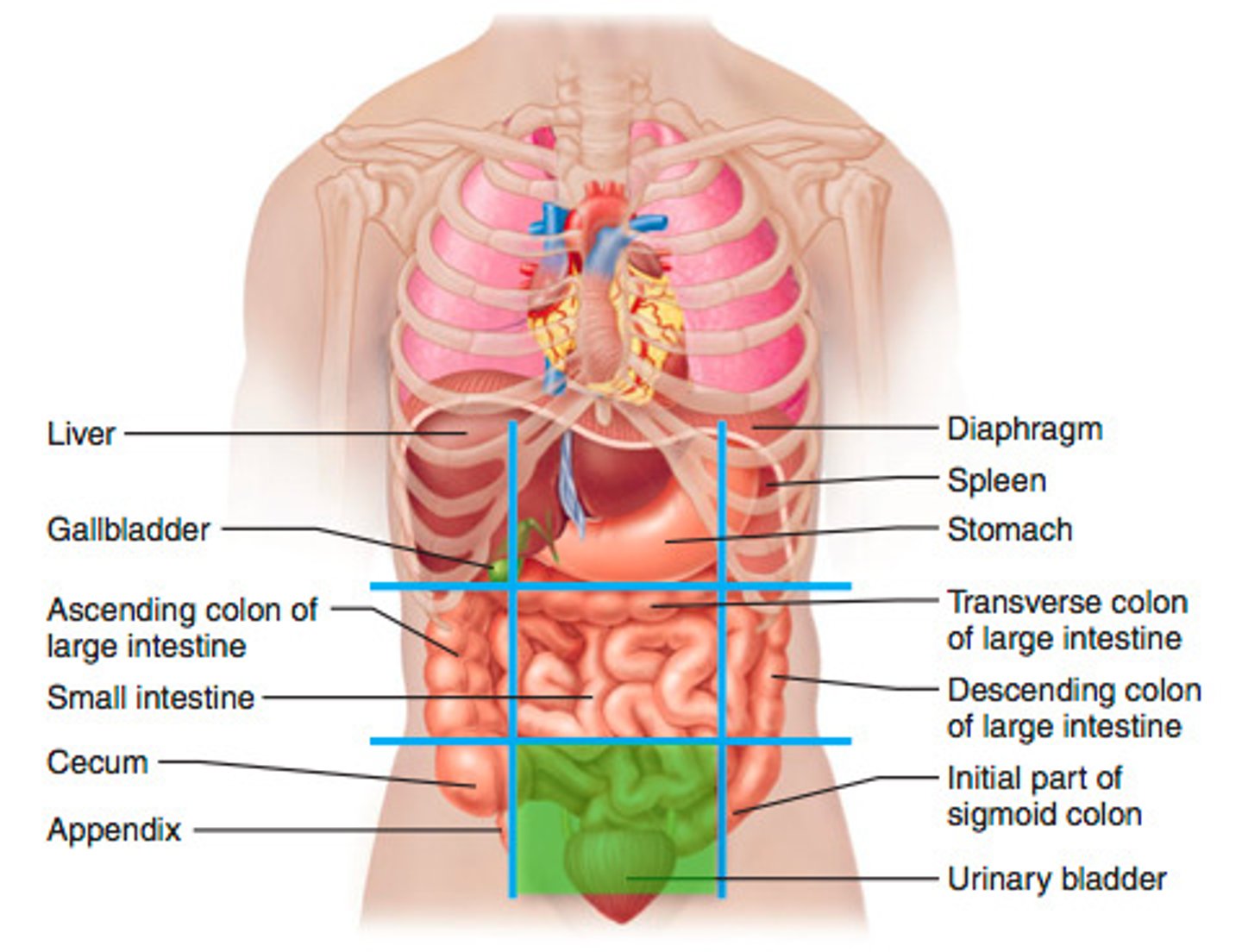
left hypochondriac region
spleen, colon, left kidney, pancreas
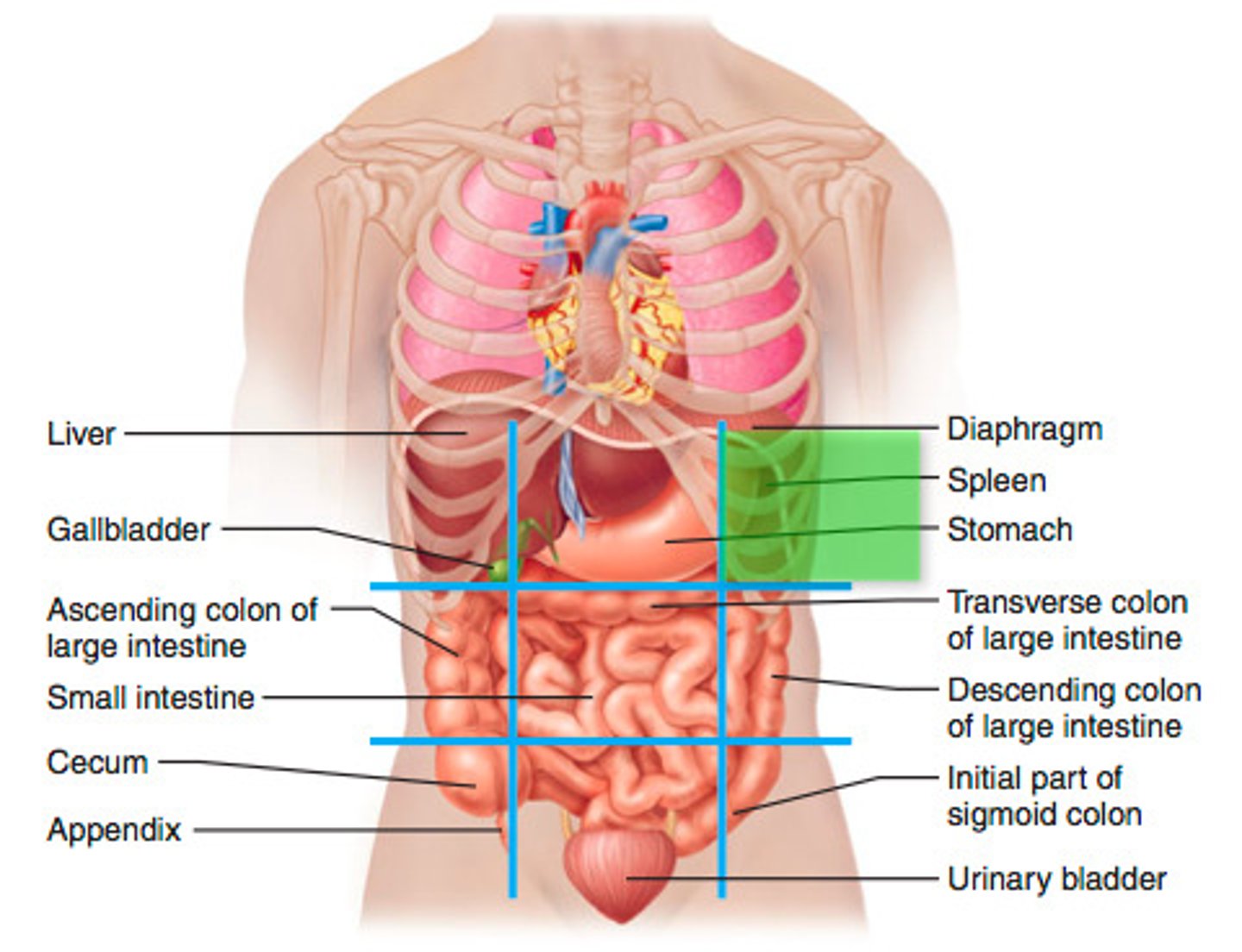
left lumbar region
large intestine
left iliac region
large intestine, colon
hierarchy of structure
atom
molecule
organelle
cell
tissue
organ
organ system
organism
homeostasis
state of equilibrium
dynamic equilibrium
narrow range of homeostasis
negative feedback
change detected, body acts to negate/reverse (ex: sweat)
positive feedback
change detected, body amplifies change (ex: labor/childbirth)
integumentary system
skin, hair, nails, cutaneous glands
--
protection, thermoregulation, water retention

skeletal system
bone, cartilage, ligaments
--
support, movement, protection
muscular system
muscles
--
movement, stability, communication, body openings, heat
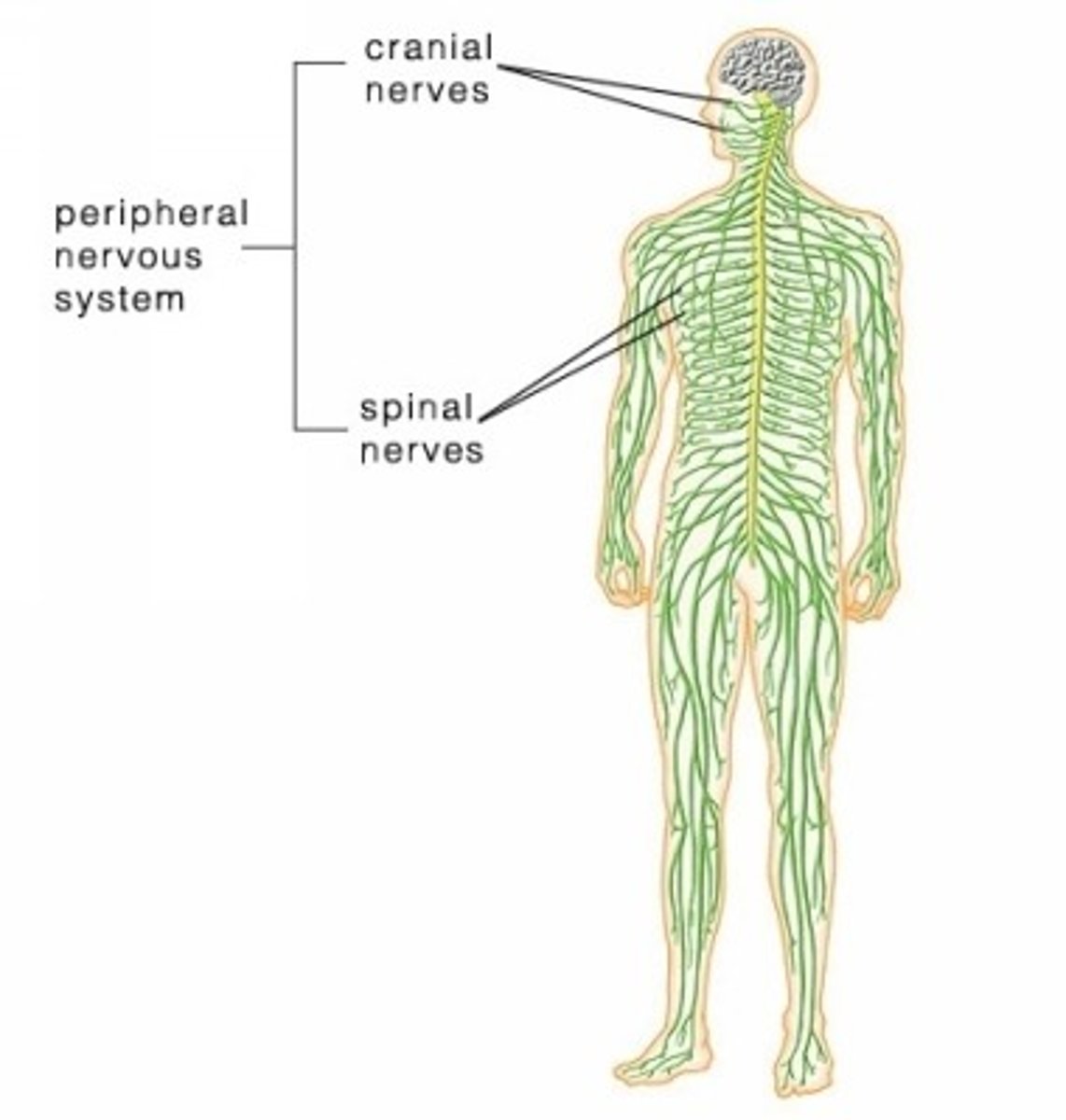
nervous system
brain, spinal cord, nerves
--
communication, coordination, motor control, sensation
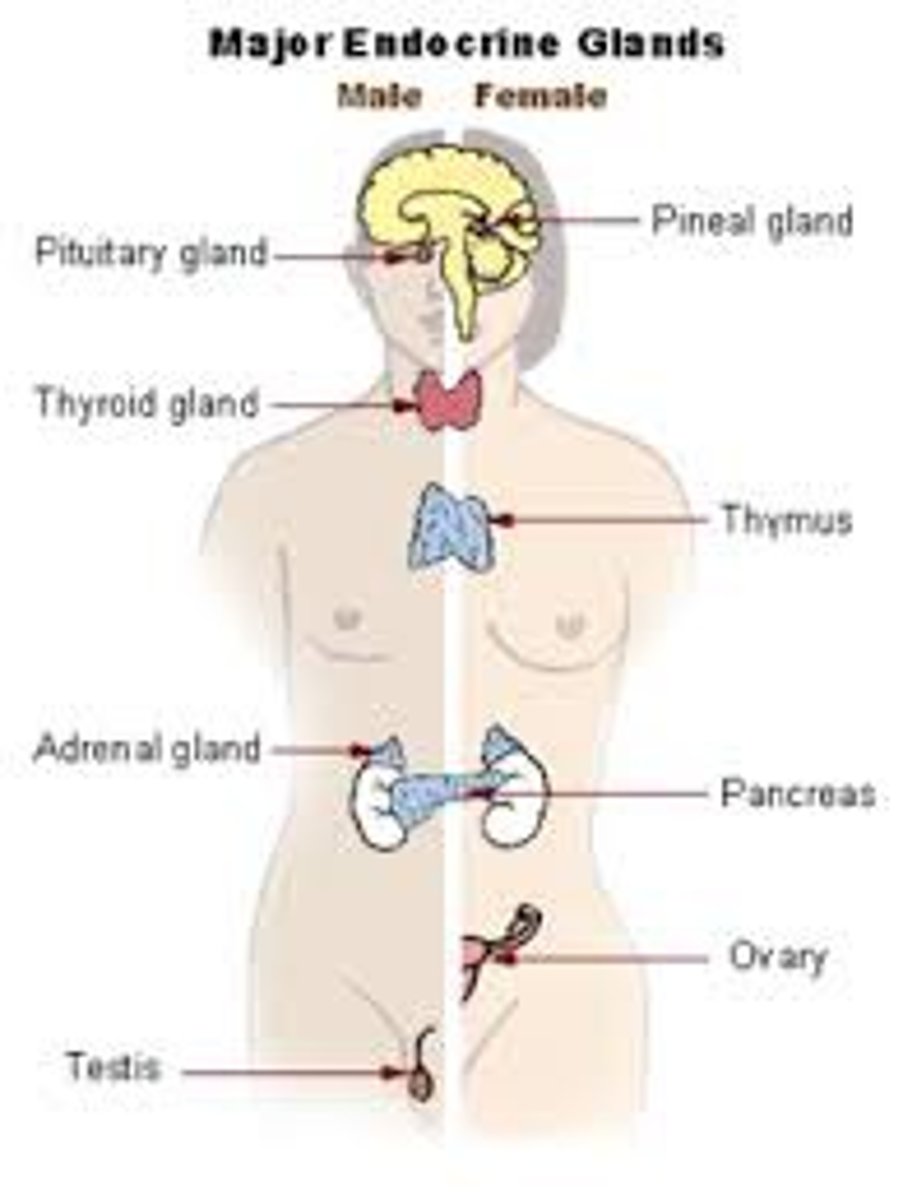
endocrine system
pituitary, pineal, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus, adrenal glans, pancreas, testes + ovaries
--
hormones + chemical communication
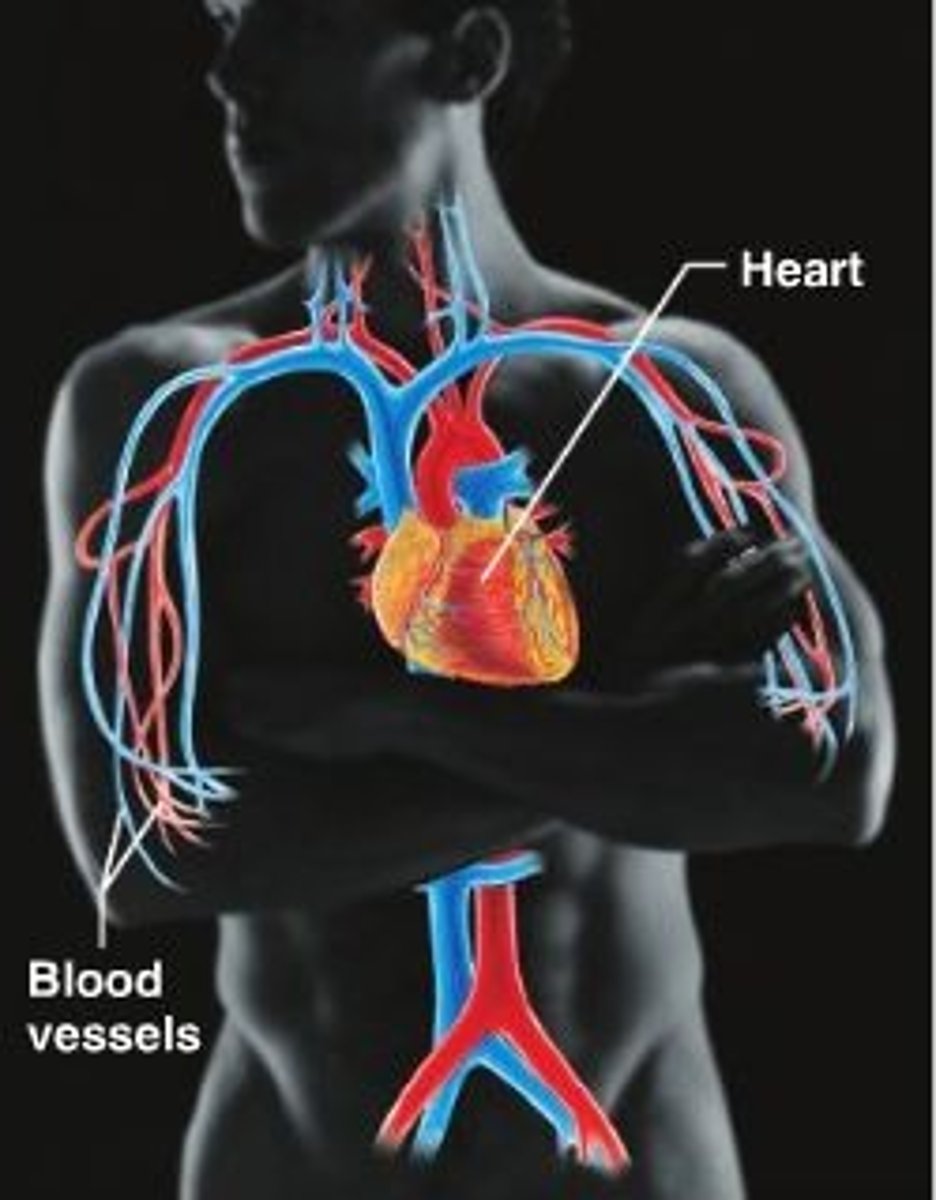
cardiovascular system
heart + vessels
--
nutrient + oxygen distribution, wastes, immunity, acid/base, fluid, electrolyte
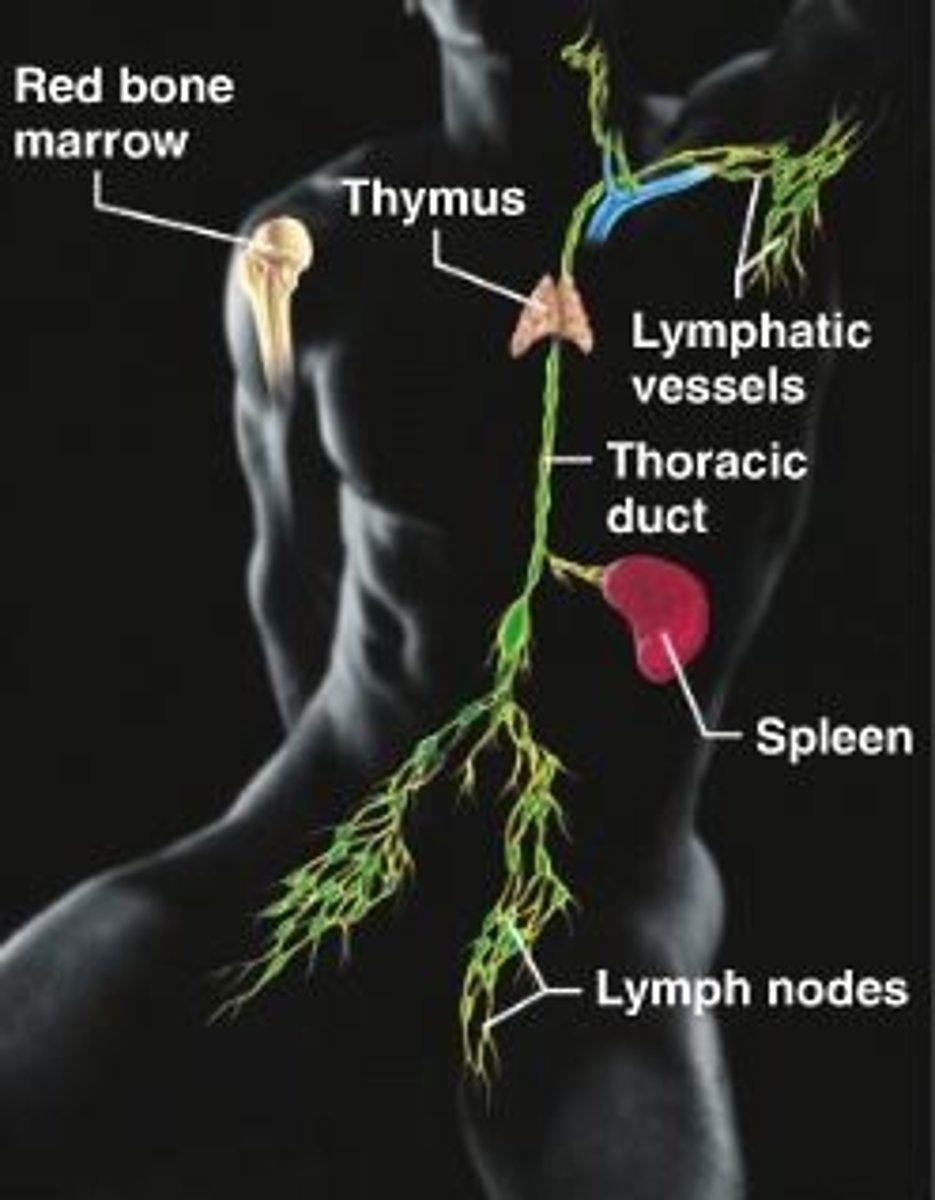
lymphatic system
thymus, spleen, tonsils, lymph nodes + vessels
--
excess fluid, pathogens, immunity
respiratory system
nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs
--
oxygen<->carbon dioxide, speech

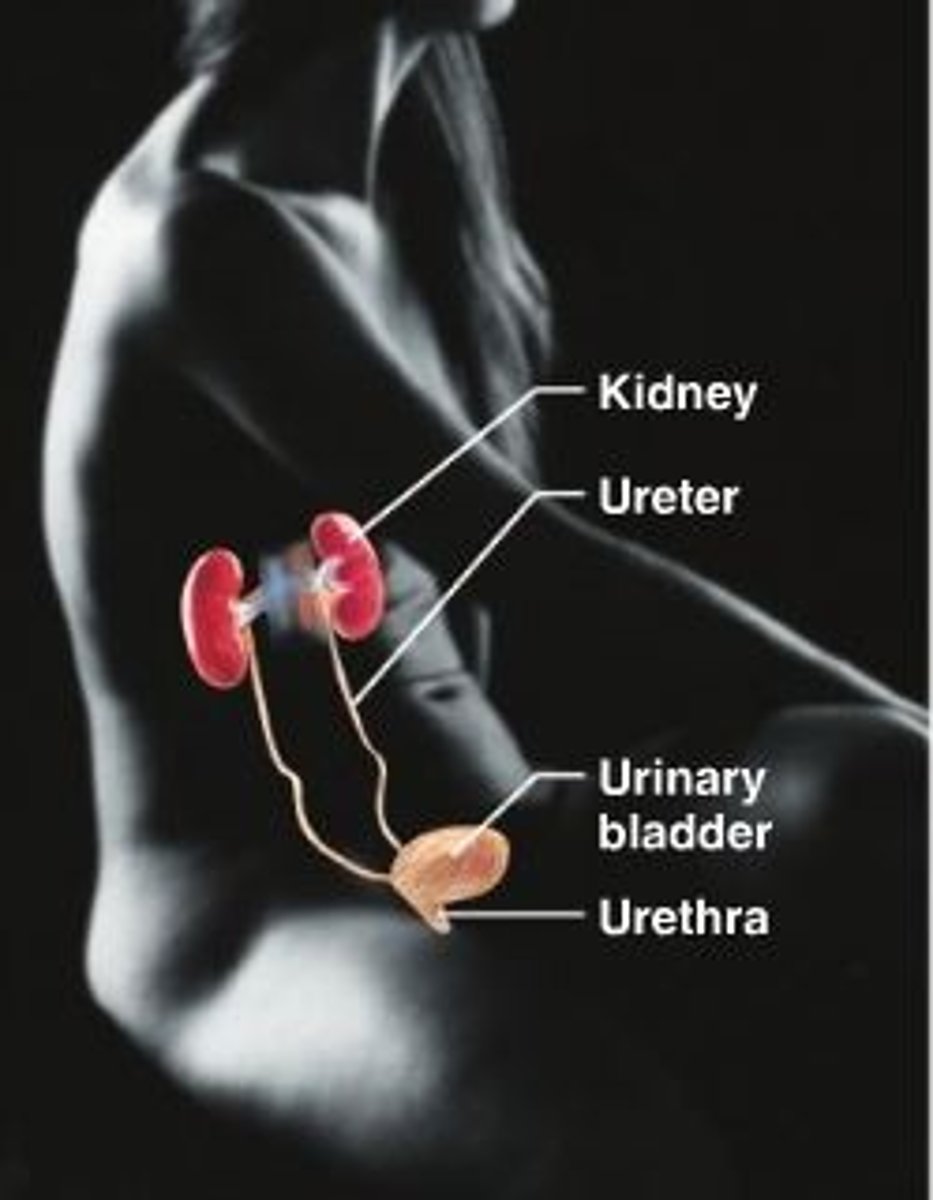
urinary system
kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra
--
waste elim, blood volume + pressure
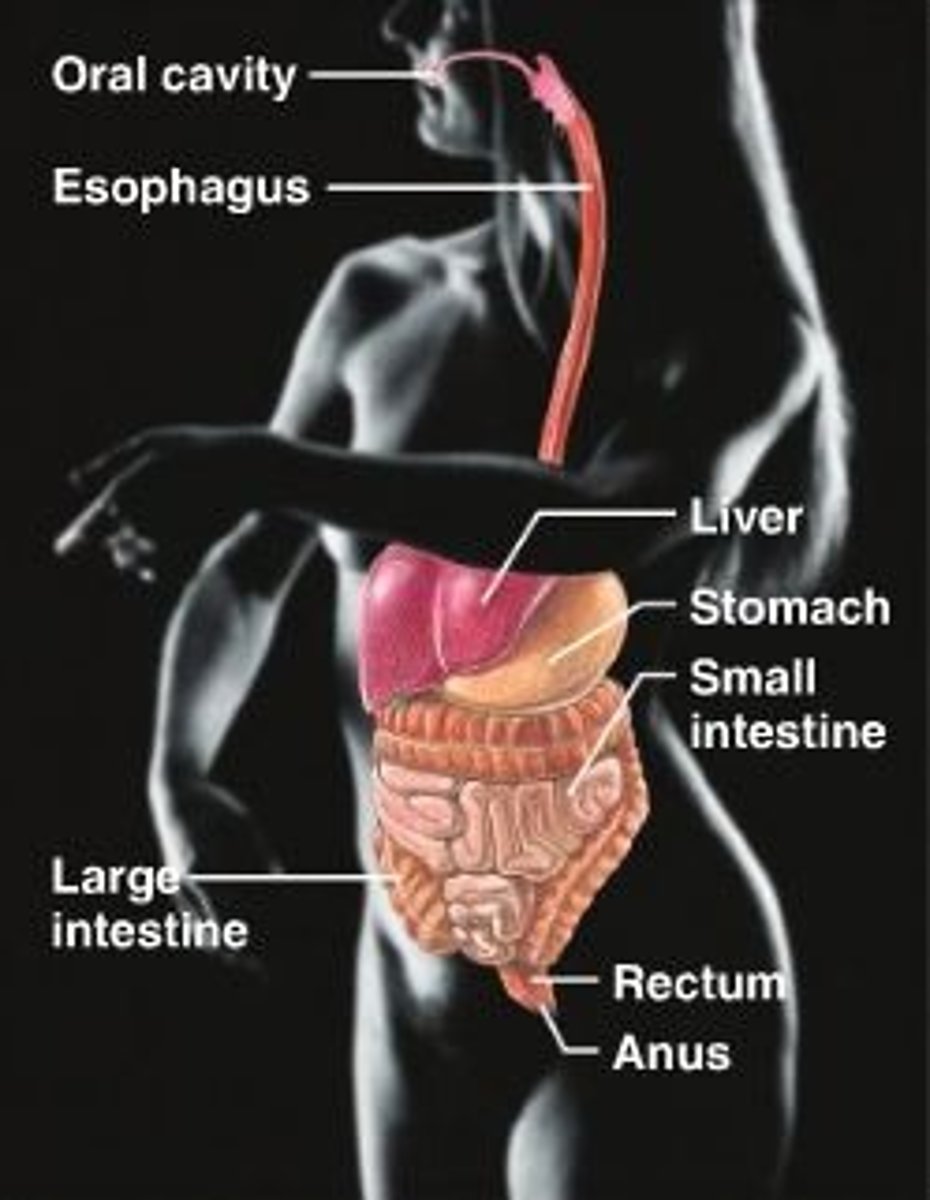
digestive system
mouth components, stomach, esophagus, intestines, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
--
nutrient breakdown + absorption
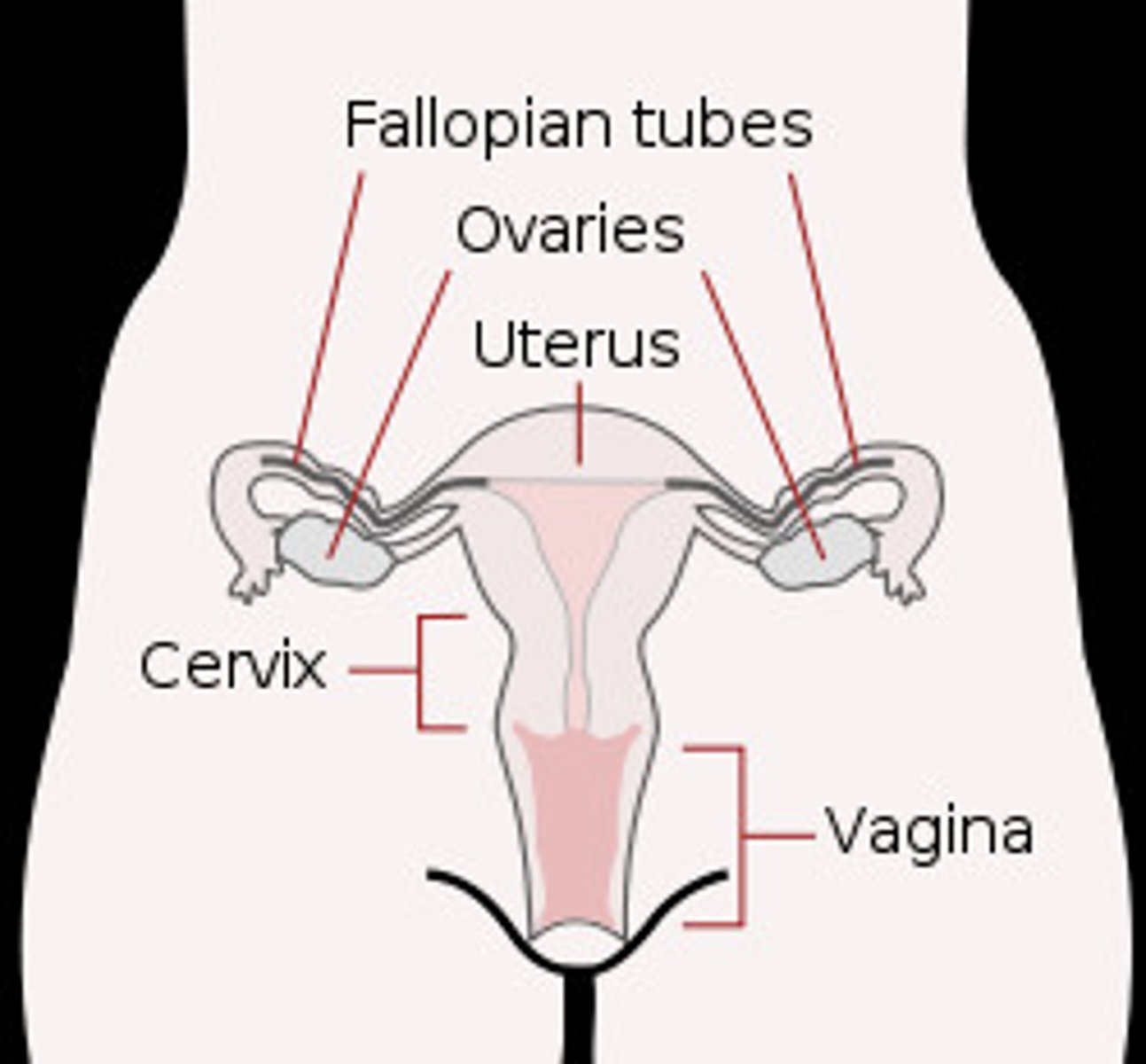
reproductive system (female)
ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, mammary glands
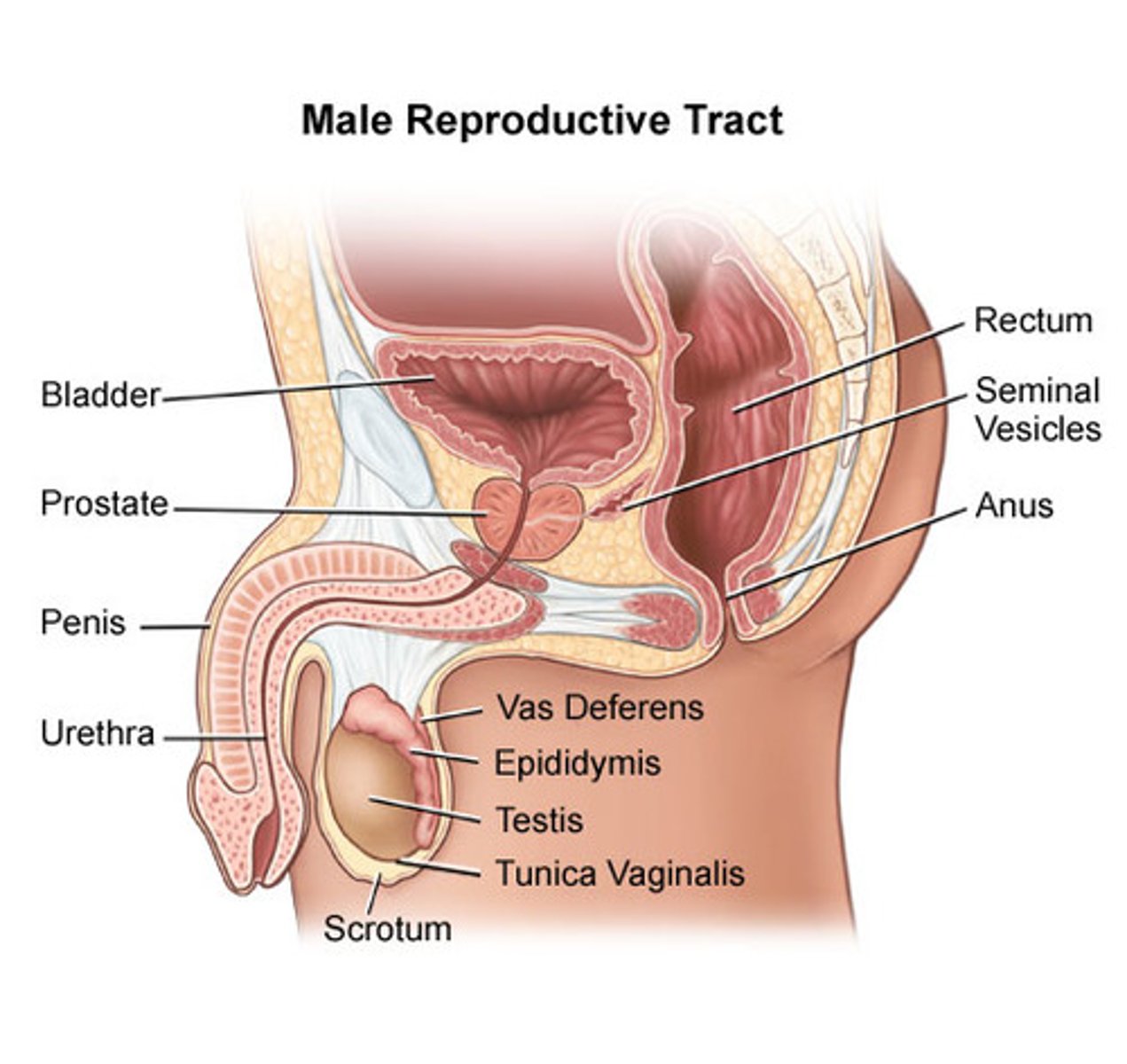
reproductive system (male)
prostate gland, ductus deferens, testis, penis
neutron
no charge, 1 mass unit
proton
+ charge, 1 mass unit
electron
- charge, no significant mass
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
atomic weight
protons + neutrons; mass of single atom
element
simplest form of matter w/ unique chemical properties
atom
smallest particle of an element with the properties of that element
isotope
element with different number of neutrons
radioisotopes
unstable; decays until stable
ionizing radiation
high energy radiation
ion
charged particle; unequal number of protons and electrons
ionization
transferring electrons between atoms
physical half life
the time required for 50% of its atoms to decay to a more stable state
biological half-life
time it takes for 1/2 of radioisotope to disappear from body
anion
negative ion
cation
positive ion
electrolyte
substance that ionizes in water; reactive
molecule
2+ atoms chemically combine
compound
2+ atoms of different elements combine
ionic bond
the attraction between oppositely charged ions; weak -- dissolve in water
covalent bond
sharing of 1 or more pairs of electrons
nonpolar covalent bond
a covalent bond in which the electrons are shared equally by the two atoms
polar covalent bond
A covalent bond in which electrons are not shared equally
hydrogen bond
weak attraction between polarized molecules
van der waals force
brief attraction of adjacent atoms that are neutral
adhesion
tendency to cling to another substance
cohesion
tendency to cling to self
acid
<7 -- proton donor, more H+
base
>7 -- proton acceptor, more OH-
human pH
7.35-7.45
buffers
chemicals that resist a change in pH
metabolism
all chemical reactions in body
catabolism
breaking down
anabolism
building up
reaction rate factors
concentration, temperature, catalysts
oxidation
loss of electrons, energy release