CHEM - LIPIDS 2.0
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
What is a lipid?
class of naturally occurring organic molecules
categorized based on similar solubility characteristics:
insoluble in water
soluble in organic solvents (ie. other lipids)
What is the significant of lipids in saliva?
contains fatty acids, triglycerides, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and cholesterol
these rations can change during times of disease
What is the significance of lipids in dental calculus (hardened plaque)?
lipids make up 10% of calculus (proteins make up 50)
What is the significance of lipids to caries?
High levels of triglycerides in children’s saliva is correlated to early childhood caries
What are the functions of lipids?
Structure of Membranes - separates aqueous cellular environments, binds cells together
Storage - storing metabolic fuel → specialized fat storing cells: adipocytes
Transport of Metabolic Fuel
Insulation - heat loss, injury prevention, nerve impulses
Chemical Signalling - steroids/hormones
What are the 4 types of lipids?
Fatty Acids -
long chain carboxylic acid
free + esterfied
Lipids with Glycerol
mono/di/tri-glycerols
glycerophospholipids
Lipids w/o Glycerol
sphingolipids - cermides, sphingomyelin
steroids
vitamins
Lipids attaches to other molecules
lipoproteins (LDL, HDL, ect)
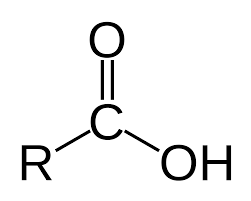
What functional group is this?
Carboxyl
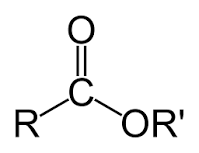
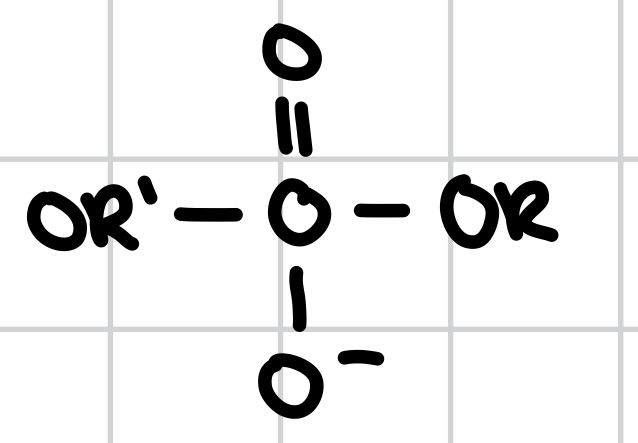
What functional group is this?
an Ester
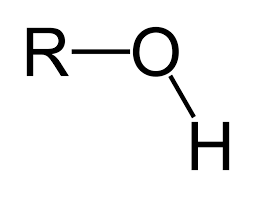
What functional group does this image correspond to?
an alcohol
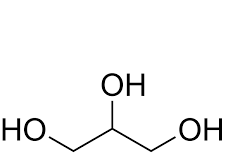
What molecule is this?
Glycerol (prop-1,2,3-triol)
What are simple lipids?
fatty acids
fatty acid esters
triglycerides
What are the 2 categories of complex lipids?
→ Phospholipids - sphingolipids and glycerophospholipids
→ Glycolipids (have glucose/galactose)
What are complex lipids?
typically amphipathic
have polar/non-polar groups
often present in membranes
What are fatty acids?
long chain carboxylic acids
What lipid has the ratio 16:0?
plamic acid
What lipid has the ratio 18:0?
stearic acid
What lipid has the ratio 18:1?
Oelic acid
Saturated vs. Unsaturated
SATURATED -
has single bonds
increased saturation = increased BP
usually solid (can pack tight)
UNSATURATED -
has double bonds
lower melting points
rigid bonds (prevents tight packing)
How does carbon chain length affect solubility?
The longer the carbon chain, the less soluble the molecule becomes
How does saturation affect solubility?
More saturated molecules typically have lower water solubility
What is the optimal temperature for a human being?
37 degrees
What types of fatty acids are animal fats and vegetable oils?
triglycerides (fatty acid tri-esters → have 3 ester bonds)
Why do animals store energy as lipids and plants as carbohydrates?
Lipids allow animals to store more energy per/g (9kcal/g) than carbohydrates. This allows them to move energy easier without being weighted down
Plants do not need to move and therefore store energy as carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are also water soluble allowing for easy transport of energy
What type of linkages occur in DNA, RNA and nucleotide molecules (ATP)?
phosphoester linkages between phosphate groups
glycosidic linkages between the base and the sugar
(phosphoric anhydride bonds?)
How much ATP does the heart typically use per day?
35kg of ATP/day
What are triglycerides?
most abundant lipids in human
3 fatty acid molecules attached to a glycerol by ester linkage
(aka treaclyglycerols)
Where are triglycerides commonly found?
→ Deposition Lipids (storage) - adipocytes
→ Dietary Lipids - >90% of lipids
→ Transport lipids - chylomicrons
What are oils?
triglycerides rich in unsaturated fatty acids
usually liquid at room temp
What are fats?
triglycerides rich in saturated fatty acids
usually semi-solid @ room temp
What are lipases?
enzymes that hydrolyze and release fatty acids (hydrolysis)
Where do variation in dietary fatty acids occur (ie. beef tallow vs. olive oil)?
in the saturation and amount of cholesterol
What are phosphoglycerides?
the second most abundant group of naturally occurring lipids
contain glycerol and phosphate
What is Lecithin?
the most abundant glycerophospolipid
a natural supplement found in eggs and soy beans
rich in choline
What is the most abundant lipid in cell membranes?
phospatidylcholine (phosphoric acid + choline w/ flexible HC chains)
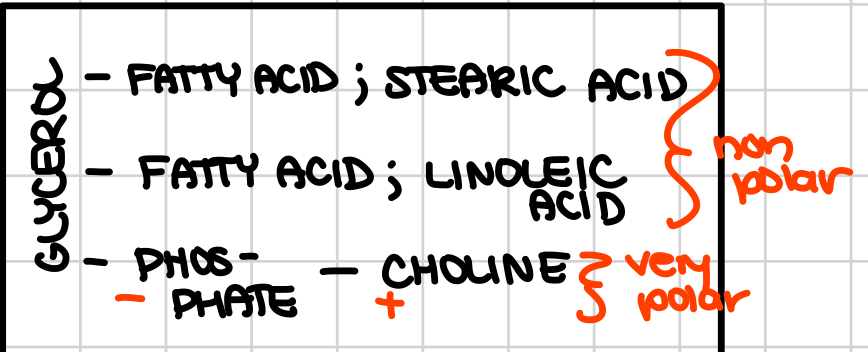
What molecule is this?
Lecithin
What functional group is this?
Phosphate
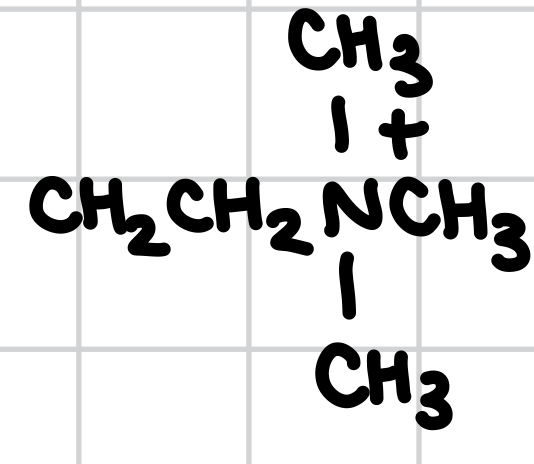
What functional group is this?
Choline
What is the physiological pH of the body?
What are Sphingolipids?
long chain amino alcohols → sphingosine
may be found in the coating of nerve axons (myelin sheath)
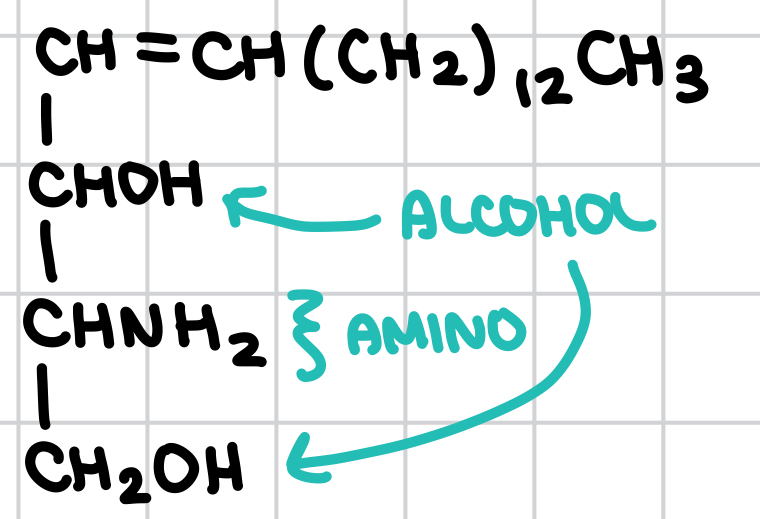
What is this molecule?
Sphingosine
What are glycolipids?
complex lipids that contain a carbohydrate (glucose/galactose) and a sphingosine
ex. Cerebrosides
What are cerebrosides?
glycolipids commonly found in brain cell membranes and myelin of oligodendrocytes
accounts for 7% of dry brain mass
ceramide monosaccharides
What is the function of Sphingomylein, cerebrosides and cholesterol?
Increase electrical resistance across the bilayer (ie. increase insulation)
What is white matter?
region of the CNS that contains myeline sheath (insulating coating)
majority of the coating is sphingomyelin
What do Shwann cells do?
produce myelin
What is MS?
The demyelination of white matter, causing decreased nerve transmission
What are steroids?
lipid
derivative of perhydrocyclopentaphenanthrene (tetracyclic ring structure)
most are biological regulator compounds, especially hormones
ex. testosterone, cholesterol, dianabol, estrogen
What are hormones?
substance produces by a cells system and is delivered by the bloodstream to a remote target system
What are androgens?
male sex hormone
matures 2nd male sex characteristics
What are Estrogens?
female sex hormones
matures 2nd sex characteristics
controls the menstrual cycle
What are Adrenocorticoid Hormones?
glucocorticoids
regulation of carbohydrate metabolism
synthesized in the adrenal cortex
mineralocorticoid - K+, Na+ regulation
What is signal transduction?
a set of biochemical mechanisms which transmit extracellular signals inside the cell and target the proteins which control either metabolic or gene expression
What does the Agonist do in Signal Transduction?
binds to receptors to activate:
→ Endogenous (hormones)
→ Exogenous (drugs)
What does the Antagonist do in Signal Transduction?
binds to a receptor to block agonist and reactive the receptor
What is the purpose of second messengers?
relay signals between receptor proteins and target proteins
produced by hydrolysis of glycerophospholipids
amplifies messages
What is Catabolism?
Breakdown of macromolecules
What is anabolism?
Buildup of macromolecules
What are nutrients?
Set components in an organisms diet required for growth, replacement and energy
What are macronutrients?
molecules necessary for energy
ex. carbohydrates, fats (oils), proteins
What are micronutrients?
essential minor dietary compounds
ex. Vitamins (organic compound)
Minerals (inorganic compounds)
Which Vitamins are lipids soluble?
→ Vitamin A - for vision
→ Vitamin D3 - regulates calcium and phosphorous metabolism
→ Vitamin E - serves as an antioxidant, aids in reproduction
Which vitamins are water soluble?
→ Vitamin C
→ Vitamin B3
What is Vitamin A?
unsaturated hydrocarbon with a polyene
lipid soluble
forced from beta-carotene
retinal is an aldehyde derivative of Vitamin A bound to a protein opsin in the rod cell of the eye
deficiency = night blindness (enamel hypoplasia)
rec 1mg/day otherwise toxic
What is Vitamin D3?
steroid derived molecule
lipid soluble
formed from cholesterol + UV from the sun
presence of D3 increase synthesis of Ca2+ binding protein = increase absorption of dietary calcium (increased calcium uptake by the teeth)
deficiency = softening of the bones → Rickets and Enamel Defects
rec. 5ug/day
What are Low Density Lipoproteins (LDL)?
remains in the plasma for 2-3 days and carries cholesterol to the cells
most of the cholesterol in the blood is carried by LDL - has about 175mg cholesterol/ 100ml of blood
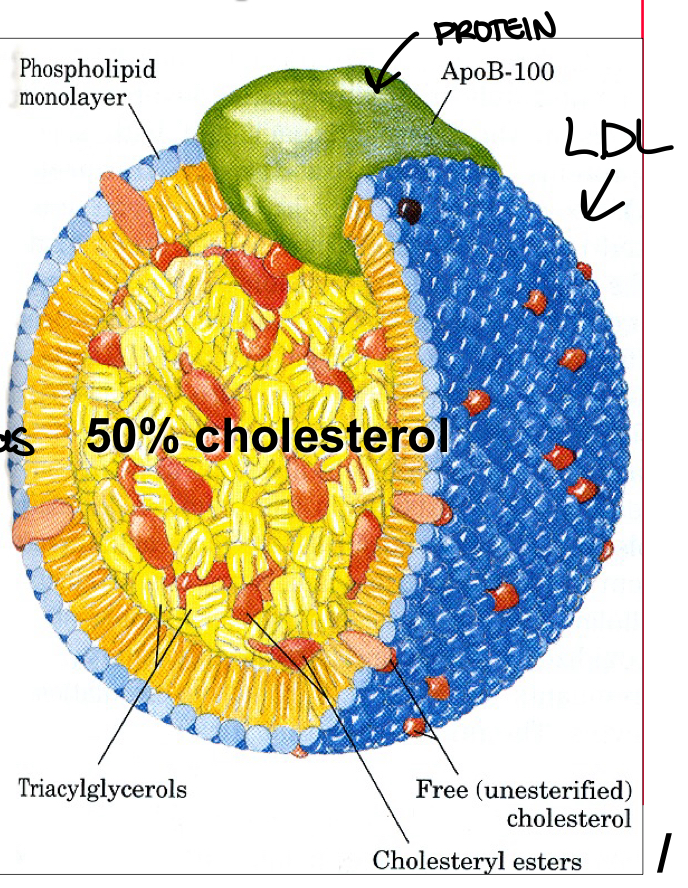
APOLIPOPROTEIN (APOB-100)
LDL
single peptide chain
core = hydrophobic
surface = hydrophilic
peripheral proteins allow LDL to be recognized by the cells
allows cells to obtain cholesterol