Midterm Review for Understanding Human Communication
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Communication
Transfer of meaning between individuals or groups.
Types of Communication
Includes intrapersonal, interpersonal, small group, public, organizational, mass.
intrapersonal communication
with in ourselves
interpersonal communication
one to one
organizational
with in a community
Principles of Communication
Symbolic, a process, irreversible, relational.
Linear Model of Communication
Describes communication as a one-way process.
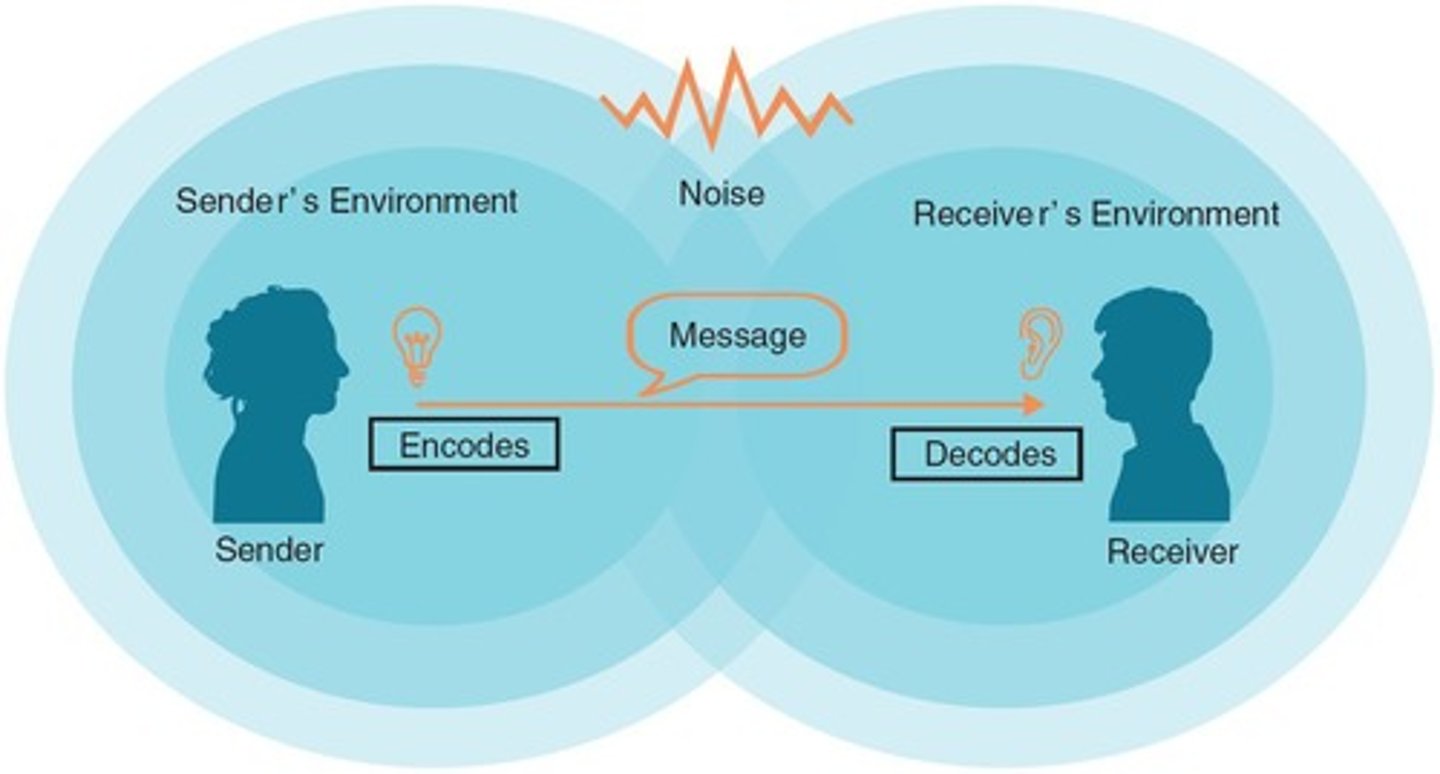
Senders and Receivers
Participants in the communication process.
Encoding
Transforming ideas into communicable messages.
Decoding
Interpreting the received message.
Channels
Medium through which messages are transmitted.
Mediated Communication
Communication through technology or media.
Noise
Interference that distorts communication.
Environment
Context in which communication occurs.
Feedback
Responses from receivers to senders.
Self Concept
Stable perception individuals have of themselves.
Self Esteem
Evaluation of one's self-worth.
Self-fulfilling Prophecy
Beliefs that influence outcomes.
Attributions
Explanations for behavior of oneself or others.
Halo Effect
Judging someone based on one positive trait.
Stages of Perception
Selecting, organizing, interpreting, retrieving, responding.
Nature of Language
Symbolic, meanings reside in people, not words.
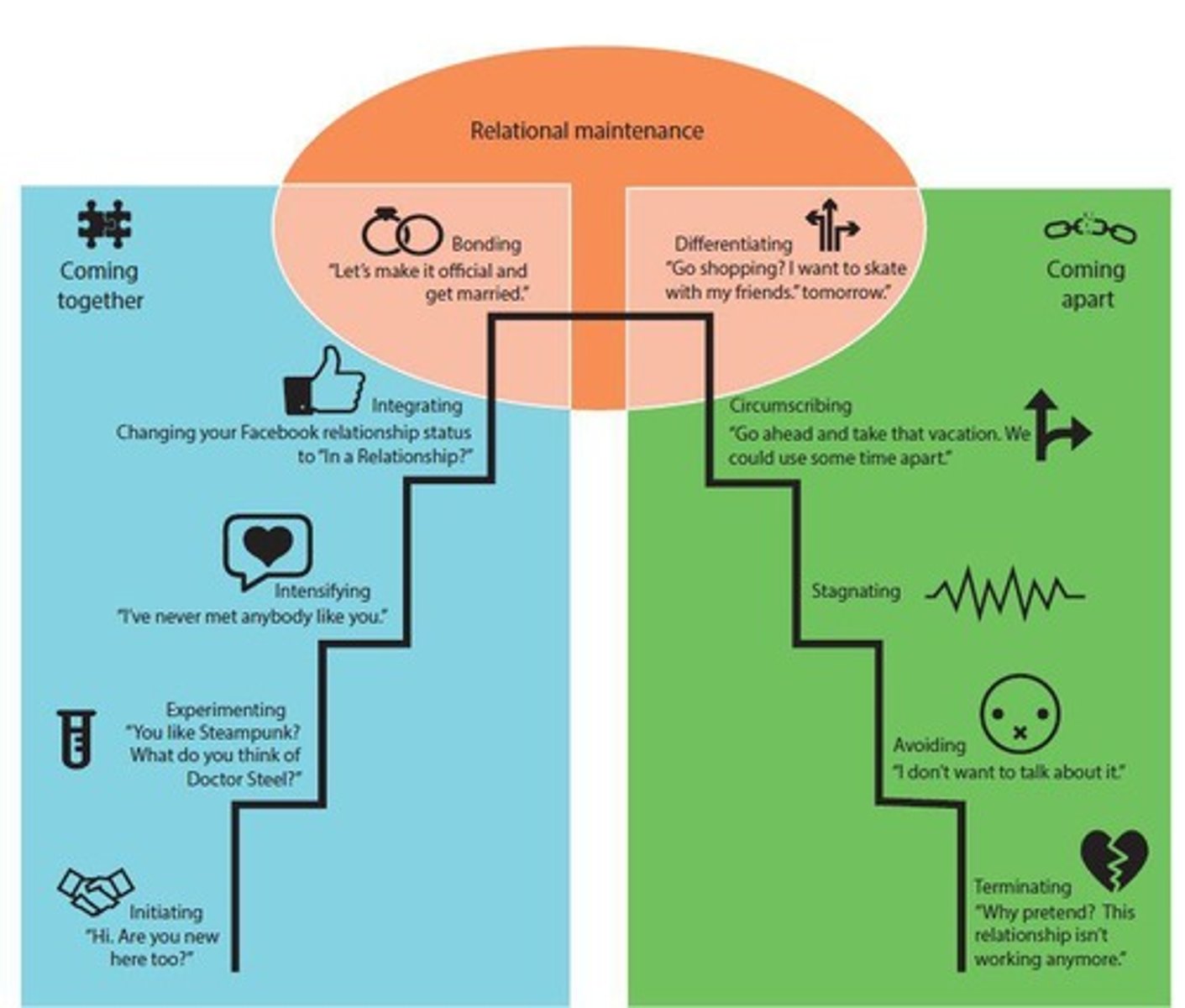
Romantic Relationships
Evolve through escalating, navigating, and deteriorating stages.
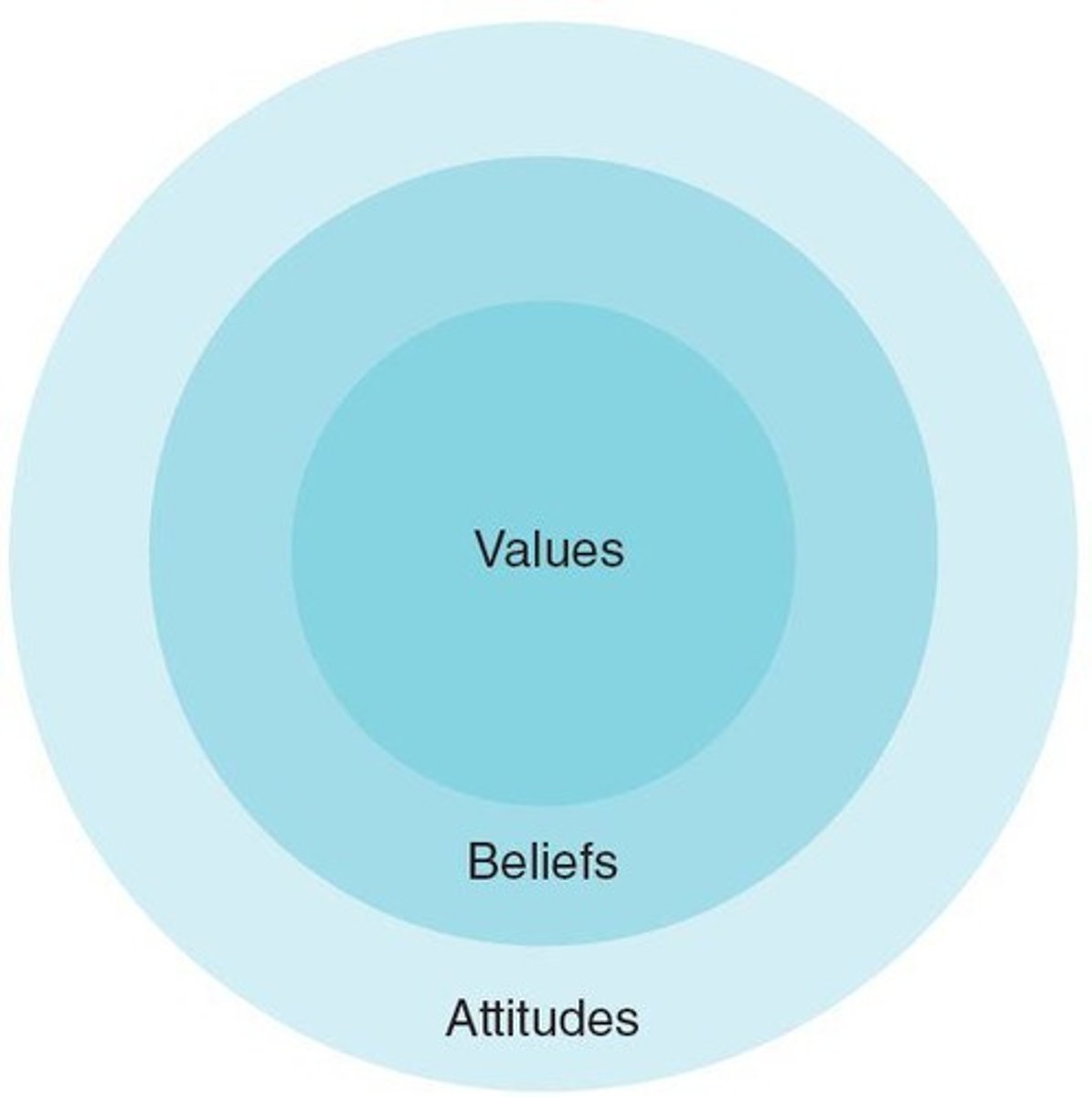
Audience Analysis
Understanding demographics, attitudes, beliefs, and values.
Types of Delivery
Extemporaneous, impromptu, manuscript, memorized.
Informative Speeches
Aim to provide information, not change attitudes
types of informative speech
explanation, description, definitions, narrative
when making informative speech look at
information hunger, audience analysis, attention getting devices, create and maintain interest, information overload or under load