Week 1: Classification of Pain
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is pain?
An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. It is subjective and doesn't occur in isolation but is influenced by psychosocial, economic and cultural contexts.
What does pain warn us of and what is its progression?
Warns us of injury, but usually gets better with time and may not need to be treated.
What is all pain affected by?
How we are feeling at the time.
What are the 3 types of pain classification?
1. Duration - acute vs. chronic
2. Cause - cancer vs. non-cancer
3. Mechanism - nociceptive, inflammatory, neuropathic, dysfunctional
Give features of acute pain. (6)
1. Recent onset
2. Limited duration and predictable time course (no longer than 3mo)
3. Obvious tissue injury (operation, burn)
4. Varying severity
5. Intensity linked to extent of injury
6. Successful treatment.
Give features of chronic pain. (6)
1. Lasts for >3mo
2. Lasts after normal healing
3. Sometimes no identifiable cause or no obvious pathologic process
4. Intensity not linked to tissue injury
5. Unpredictable time course (flare-ups)
6. Difficult to treat.
Why isn't symptom duration a good discriminator between acute and chronic pain?
Acute pains can go on for a long time eg. burns dressings, sickle cell disease, or RA flares.
How may pain be complex from initial presentation? (6)
Presents as acute but clearly complex -
1. Multiple somatic complaints (varying IBS symptoms)
2. -ve test results
3. Emotional burdens
4. Unsatisfied with care and lack of collaborative working
5. Feeling that there is little to offer
6. Poor therapeutic relationship
What is cancer and non-cancer pain?
Cancer: progressive and acute/chronic.
Non-cancer: multiple causes, acute/chronic.
Give features and examples of cancer pain - duration, mechanism. (4)
1. Progressive (if left untreated).
2. Mixture of acute and chronic.
3. Mixed nociceptive and neuropathic pain.
4. Eg. uterine, cervical, breast cancer, bone metastases and nerve compression.
Give features of acute non-cancer pain - duration, symptoms, mechanism. (4)
1. Multiple causes
2. Usually nociceptive but sometimes neuropathic (eg. sciatica)
3. Symptoms of tissue injury or illness
4. Eg. fracture, appendicitis, MI.
Give features and examples of chronic non-cancer pain - cause, mechanism, treatment. (4)
1. Not obvious cause
2. Complex mechanism - mixed nociceptive + neuropathic
3. Multiple treatments may be needed
4. Eg. chronic back pain, arthritis.
What are different mechanisms of pain? (4)
1. Nociceptive - 'good'
2. Inflammatory - 'good'
3. Neuropathic
4. Dysfunctional
What is nociceptive pain?
A 'good' pain - sensation linked with detecting potentially damaging noxious stimuli (likely to cause tissue damage). Acts protectively.
Results in an autonomic response and withdrawal reflex.
Nociceptive pain is protective pain that is felt when sensory nerve endings (nociceptors) detect tissue damaging stimuli
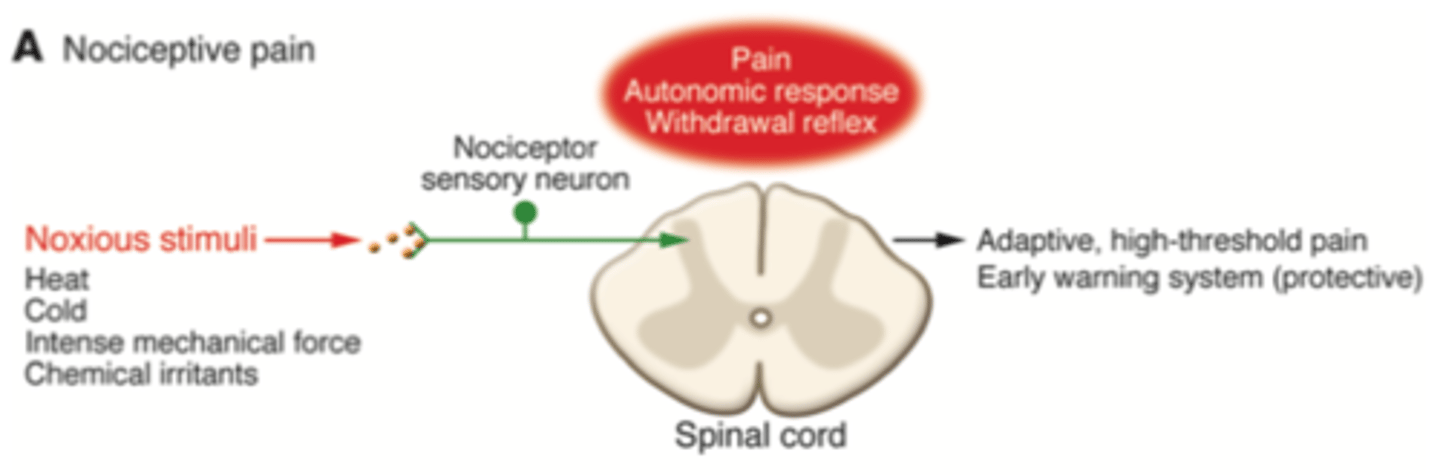
What is inflammatory pain?
Obvious tissue injury/illness linked with tissue damage and immune cell infiltration. Releases mediators that promote repair via pain hypersensitivity (making the area tender) until healing can occur.
Also has a protective function.
Is well-localised - close to area of tissue damage.
Is maladaptive
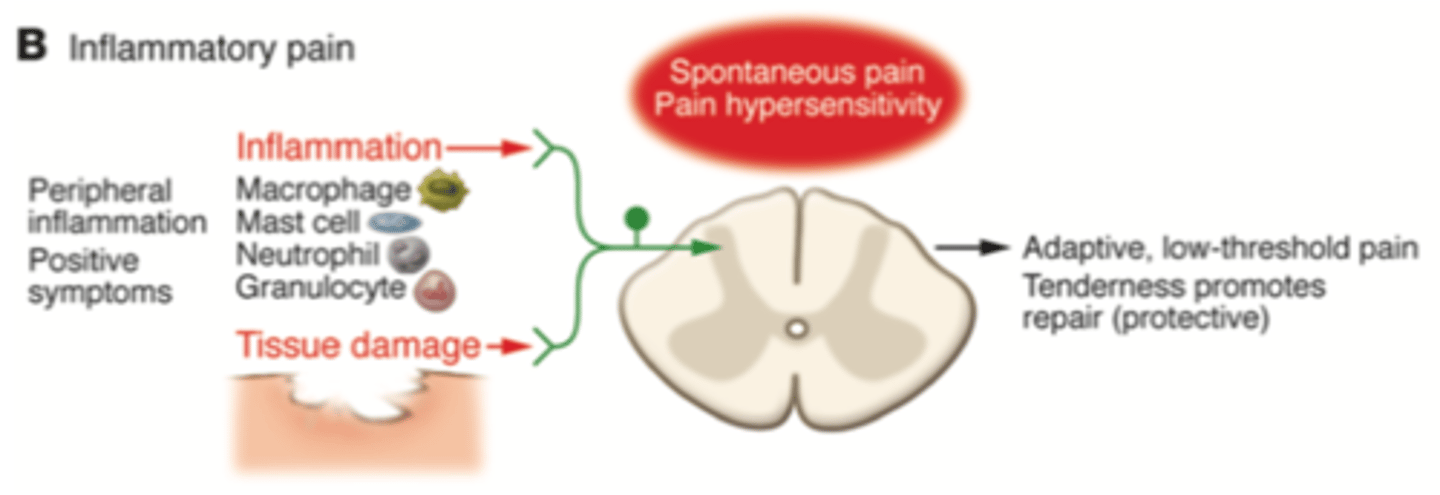
How can inflammatory pain be described? (3)
1. Sharp and/or dull
2. Aching
3. Throbbing
What is pathological pain and what can it be due to?
Maladaptive pain due to abnormal function in NS. Can be due to:
- damage to nervous system (neuropathic)
- or by its own abnormal function (nociplastic).
-Does not have a protective function
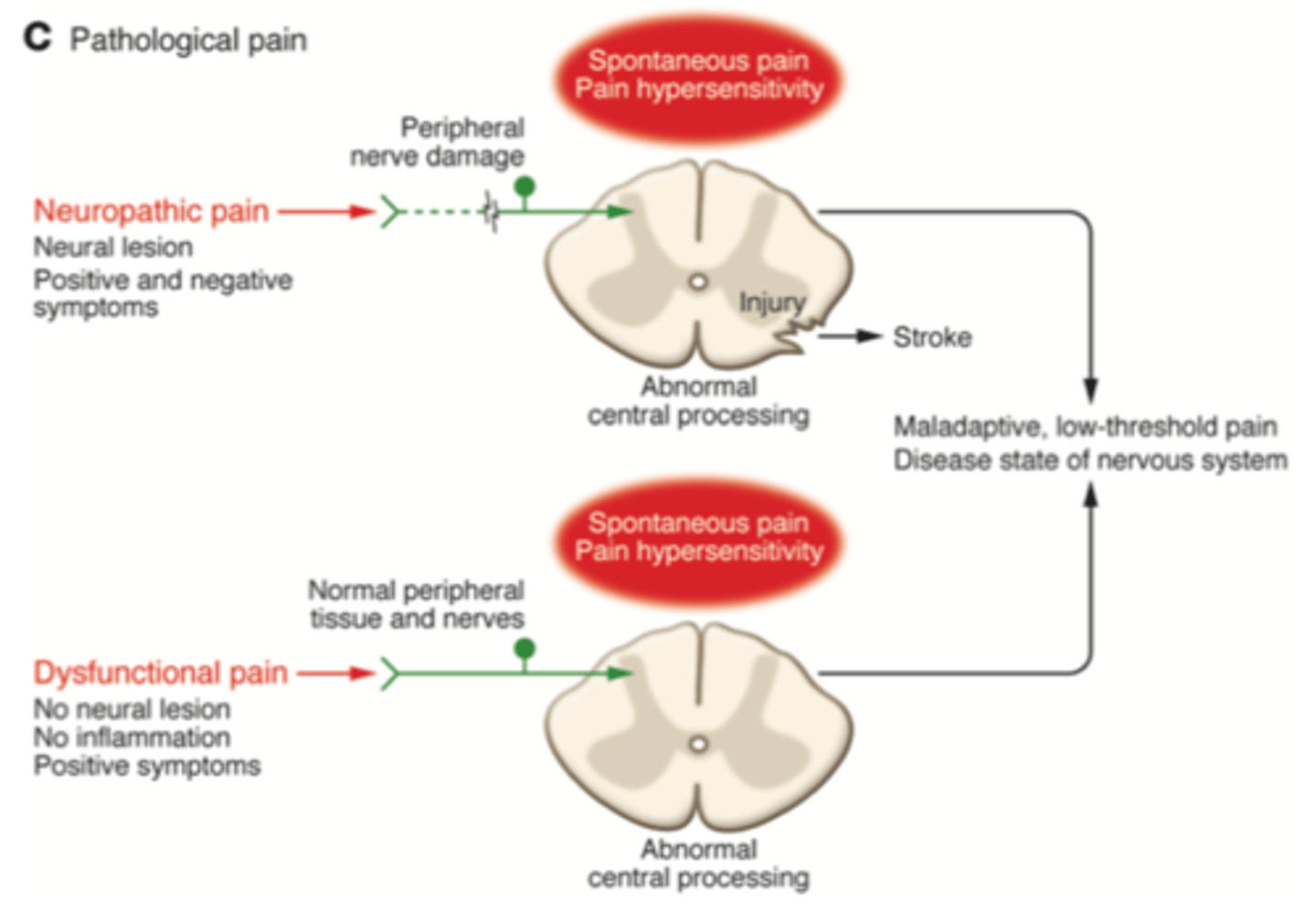
What is neuropathic pain? Give its features. (4)
- Due to lesion or disease of sensory nervous system.
- Tissue injury may not be obvious
- There is no protective function
- Less well-localised than inflammatory.
How can neuropathic pain be described? (2)
1. Burning, shooting, pins/needles
2. Numbness
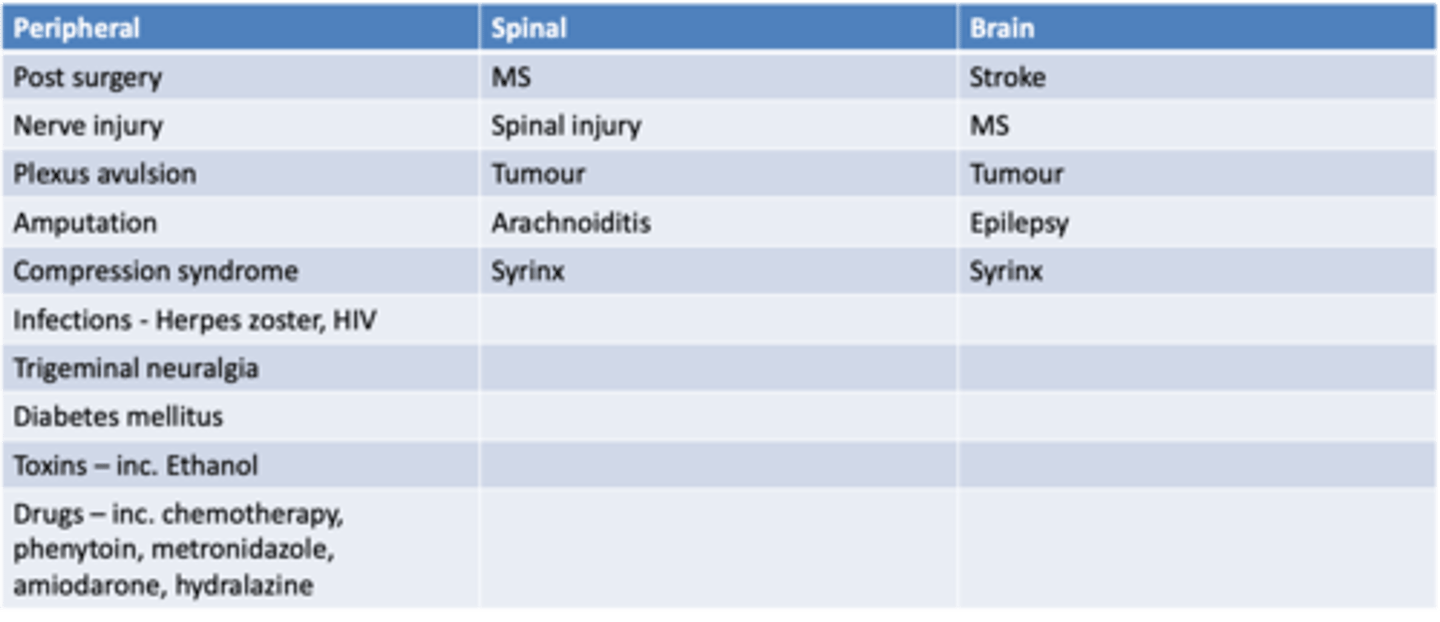
What are different types of neuropathic pain?
3 areas - peripheral, spinal, or brain. Study table.
What is nociplastic (dysfunctional) pain? Give features and examples. (3)
- A substantial pain with no noxious stimulus and none or minimal peripheral inflammatory pathology.
- There is no functional issue (i.e. no neuronal damage).
- Eg. fibromyalgia, IBS, tension-type headache, TMJ disease, interstitial cystitis, MSK diseases.
Give burdens and impact on individuals living with long-term pain. (6)
1. Depression
2. Sleep disturbances
3. Fatigue
4. Impaired concentration
5. Less active, time off work
6. Impaired physical functioning
Why can pain be a burden
Cause
Depression
Sleep disturbances
Fatigue
Impaired physical functioning
Impaired concentration
Time off work - less active