Gravitational Fields
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What is a force field?
A region where an object experiences a non contact force
They cause interactions between particles or objects
What do gravitational fields act on?
Any object with a mass
Larger masses experience a greater force
Force of gravity equation
(GM1M2)/r^2
Always attractive
What is a point mass?
A theoretical object that has a mass but no dimensions
What does it mean when an object/sphere acts as a point mass?
We assume all their mass is concentrated in their centre
What shape is the gravitational field of earth?
Radial field
However if we are close to the ground it is almost exactly uniform so we can assume this
Fields lines are almost parallel
Law of universal gravitation
An inverse square law
F proportional to 1/r^2
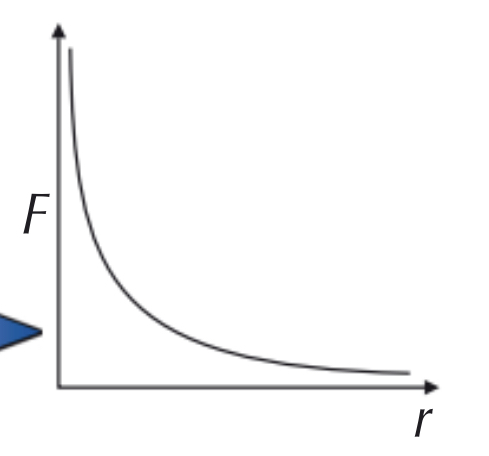
Gravitational field strength
Force per unit mass
g = Fm
this changes depending on where you are in the field
At the earth’s surface = 9.81N/kg
g = Fm → F = mg = ma
In a radial field g is inversely proportional to the square of r
Combine F equation and g equation you get GM/r^2 = g
How does the gravitational field strength change with distance from the centre of the earth?
from the centre to the surface, g is proportional to distance (linear relationship)
from the surface outwards, g is inversely proportional to r^2
Gravitational potential
Work done to move a unit mass from infinity
at a point = GPE/ m
In a radial field V(grav)= -Gm/r
It is negative as you do work against the field to move the object out of it
just think of it as the work need to pull something away from the other to infinity
further away it is easier to as the strength of gravity is less
Similarities between gravitational and electric fields
they both follow inverse square laws
the negative radial field is the same as the radial field of gravity
gravitation potential and electric potential are both 0 at infinity
Differences between gravitational and electric fields
gravitational fields act on masses while electric fields act on charges
gravitational forces are always attractive, electric can be attractive or repulsive
objects can be shielded from electric fields but not gravitational fields
the magnitude of an electric force depends on the medium between the two charges whereas gravitational forces don’t
Orbits
Speed depends on the radius of the orbit and the mass of the larger body
Circular motion caused by a centripetal force of gravity
The orbiting object will constantly change direction so it is accelerating
How can you find the speed of an orbit?
combine the centripetal force equation with the gravitational force equation
Rearrange to find v
V = square root of GM/r
How can you find the period of an orbit?
Use the equation T=2(pi)r/v from circular motion
Combine with v = square root of GM/r
You get
T^2 = (4(pi^2)/GM)r^3