Radiology of the Musculoskeletal System
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
only the area of interest
When taking a radiograph of the musculoskeletal system, it is important to center the image on what?
it should span from the joint proximal to the bone to the joint distal to the bone
-several images may be necessary to capture this entire distance
What should the image of a long bone include?
should be centered on the joint of interest and include a short length of the bones proximal and distal
What should the image of a joint include?
1.) craniocaudal or dorsopalmar/plantar
2.) lateral
Three views that are always taken:
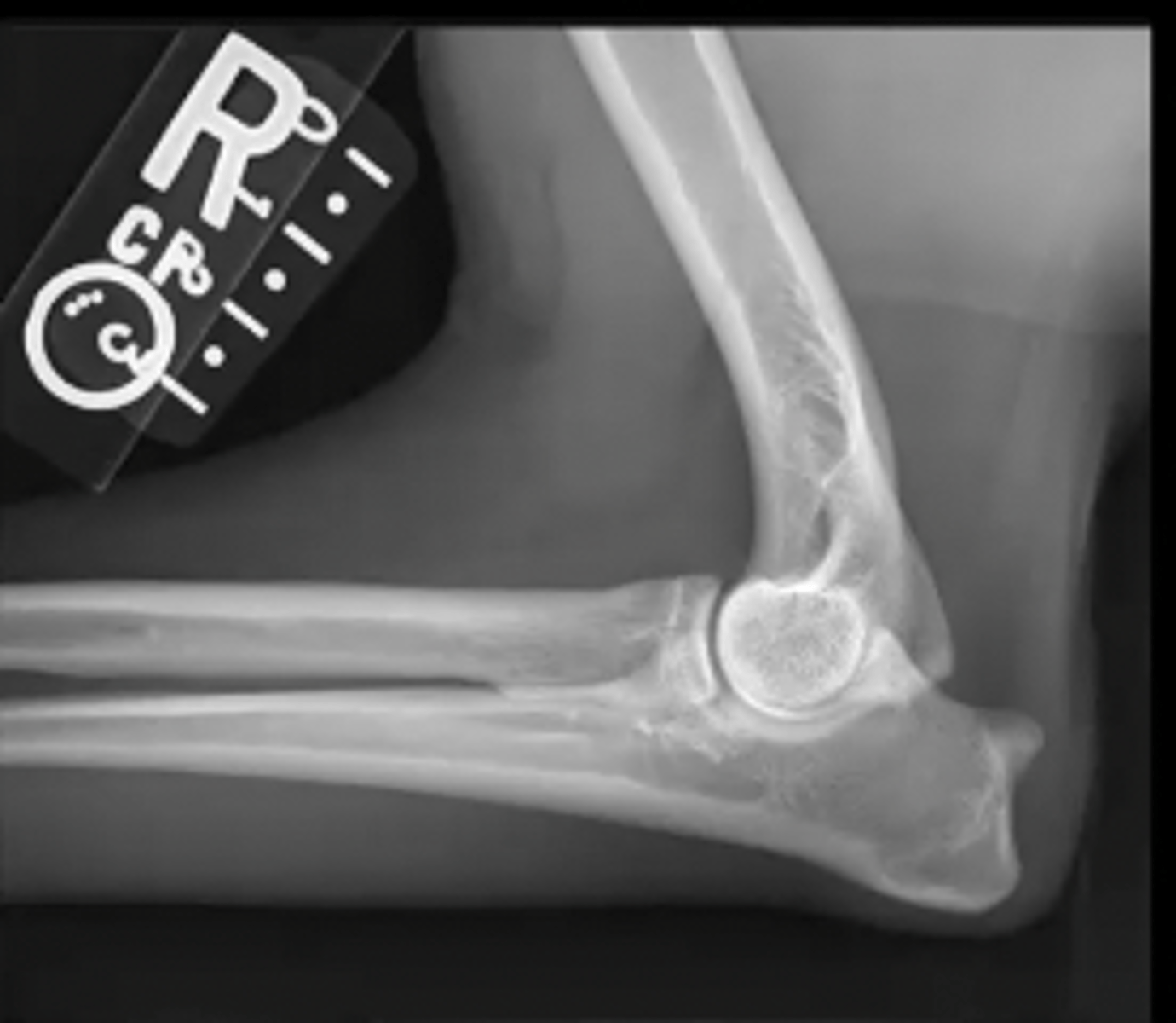
lateral canine elbow
What is the view of this image?
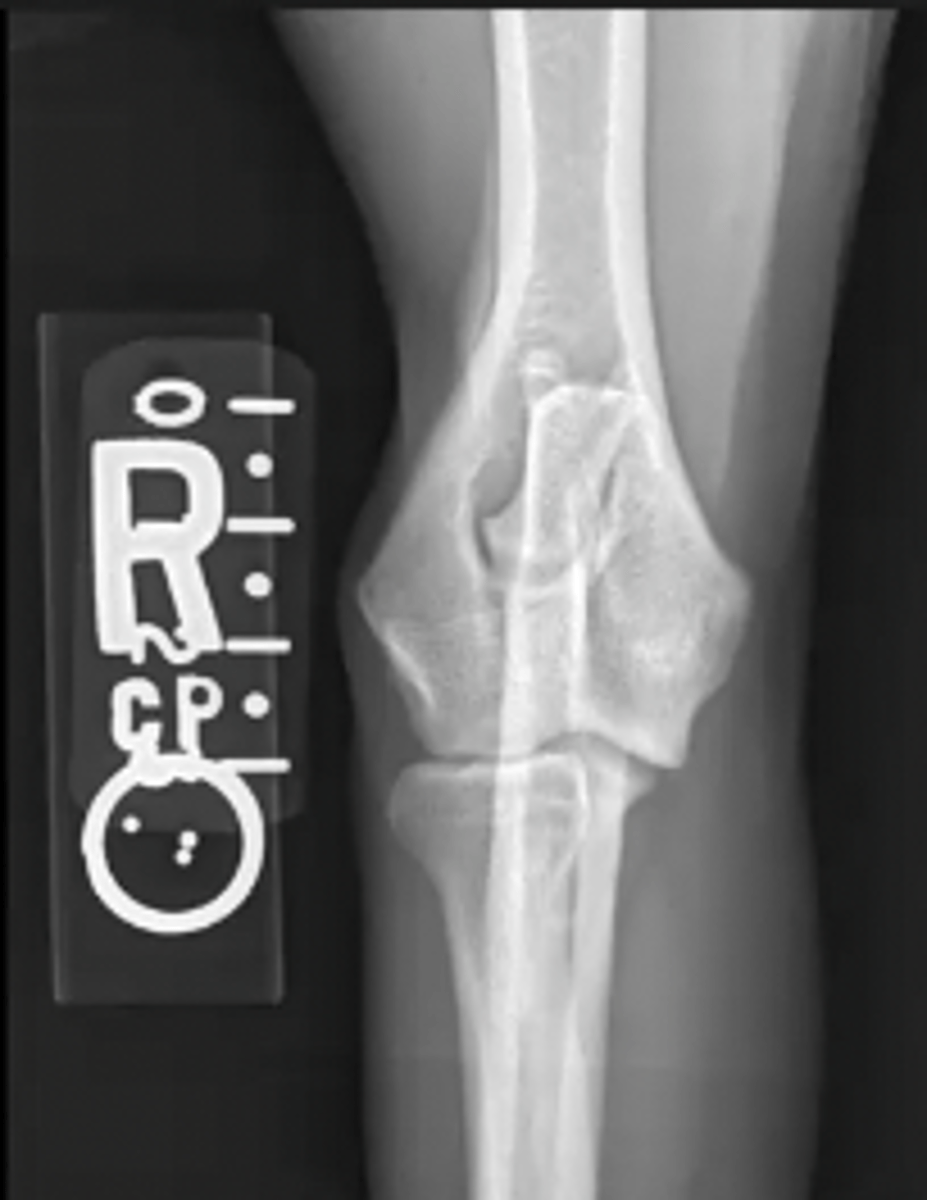
craniocaudal canine elbow
What is the view of this image?
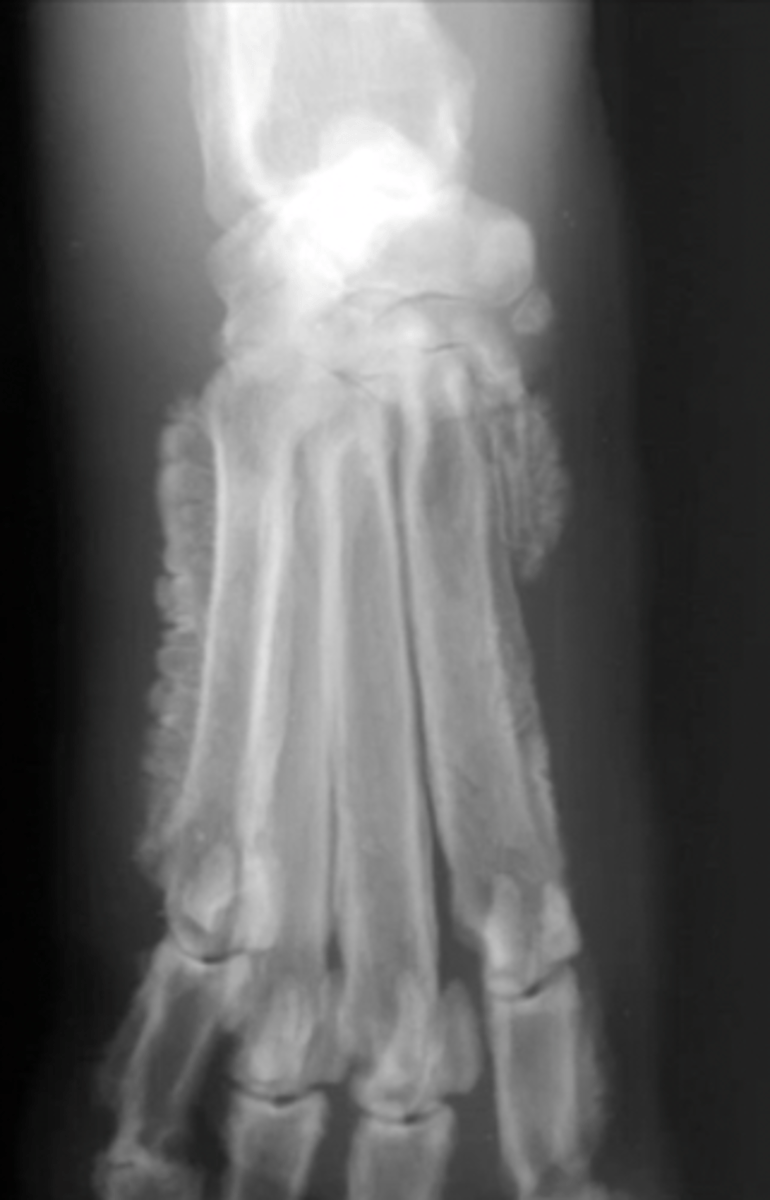
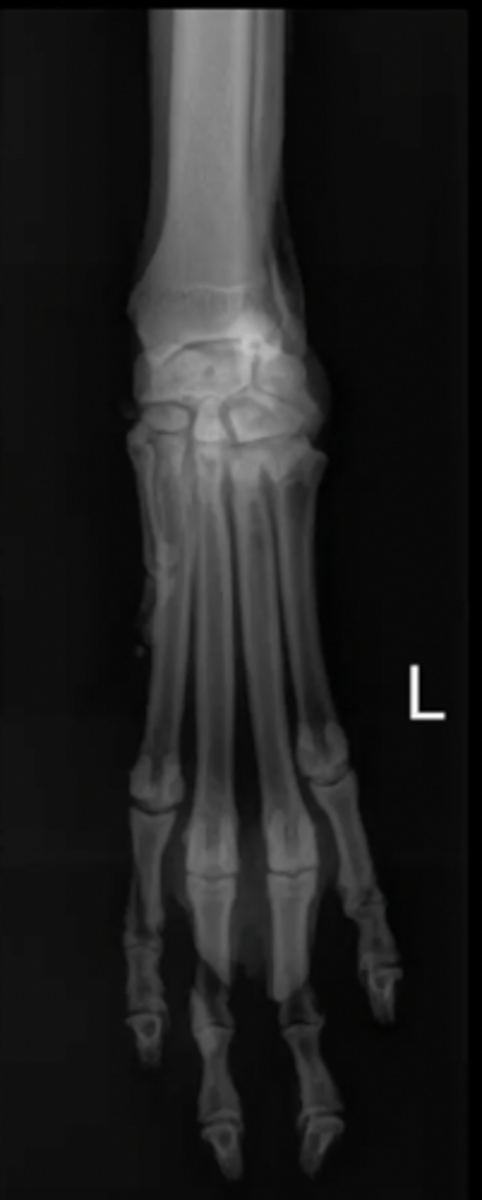
carpus/tarsus/digits
What type of bones might require oblique images?
overexposed
Is this image overexposed or underexposed?
lateral aspect
What aspect is the marker always placed?
limb; left or right
A marker must indicate what _______ you are looking at and if it is _______ or ______
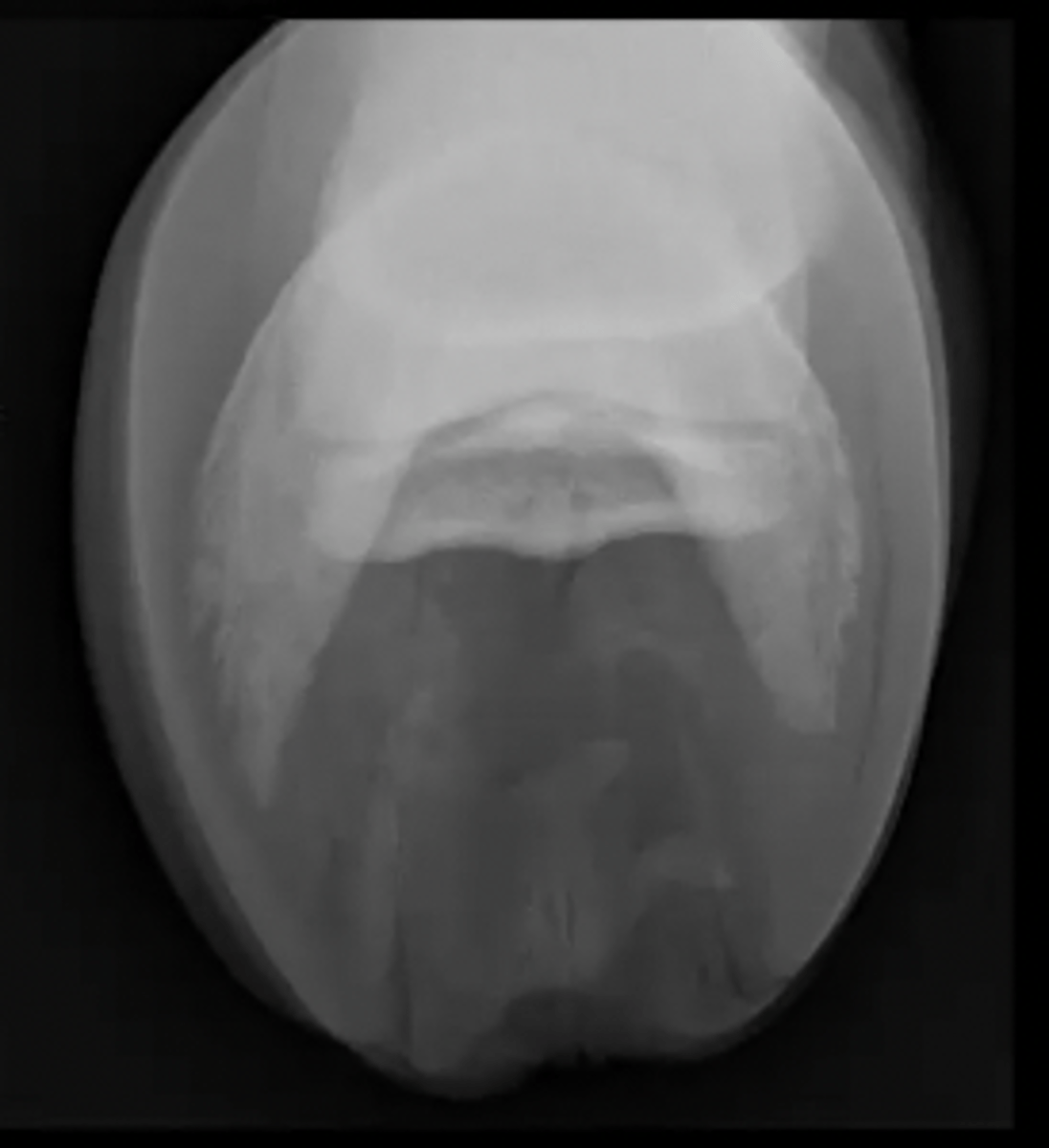
navicular flexor skyline view
What special equine view is this?
1.) always put L where the marker is
2.) place M across from L
3.) D always on the top
4.) read clockwise starting with D
Trick to naming oblique images
DLPMO
What is the name of this oblique image?
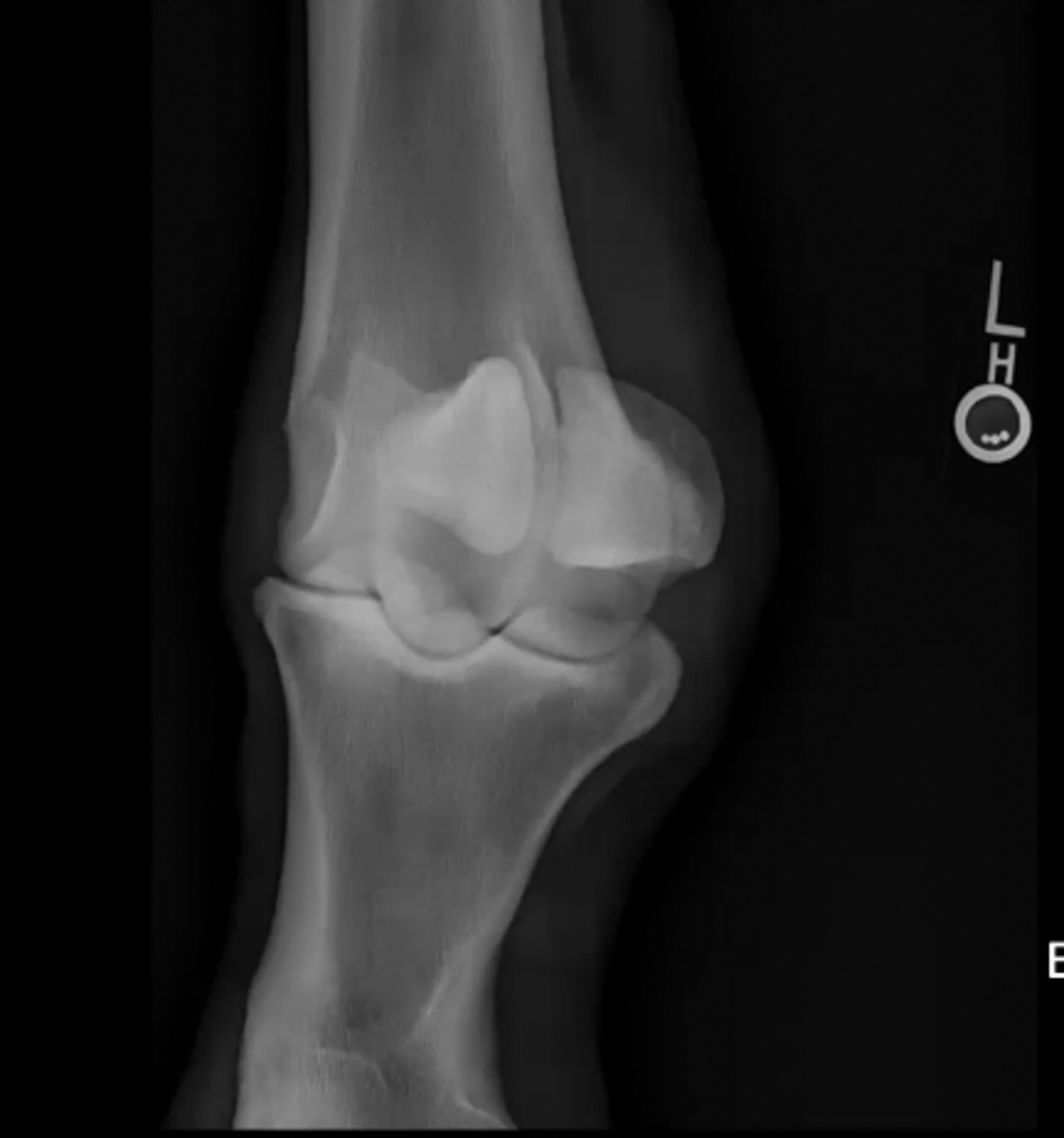
hind limb
What does the "H" label on this image indicate?
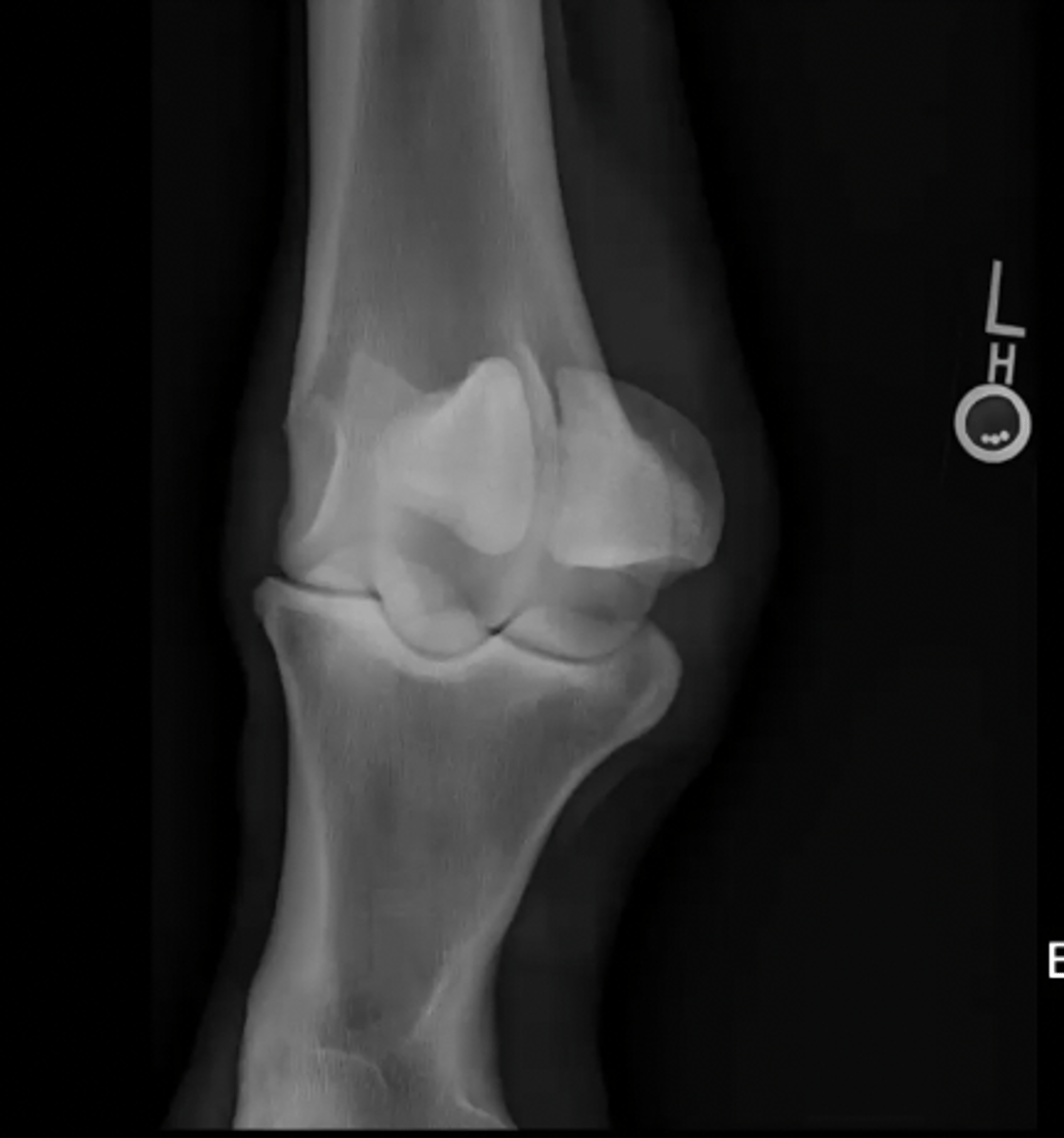
front limb
What does the "F" label on this image indicate?

diaphysis
1
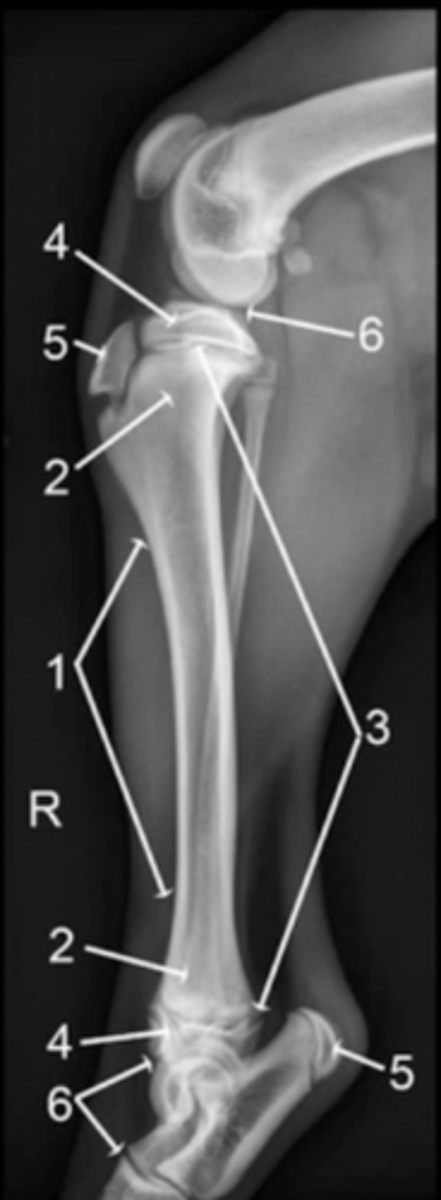
metaphysis
2
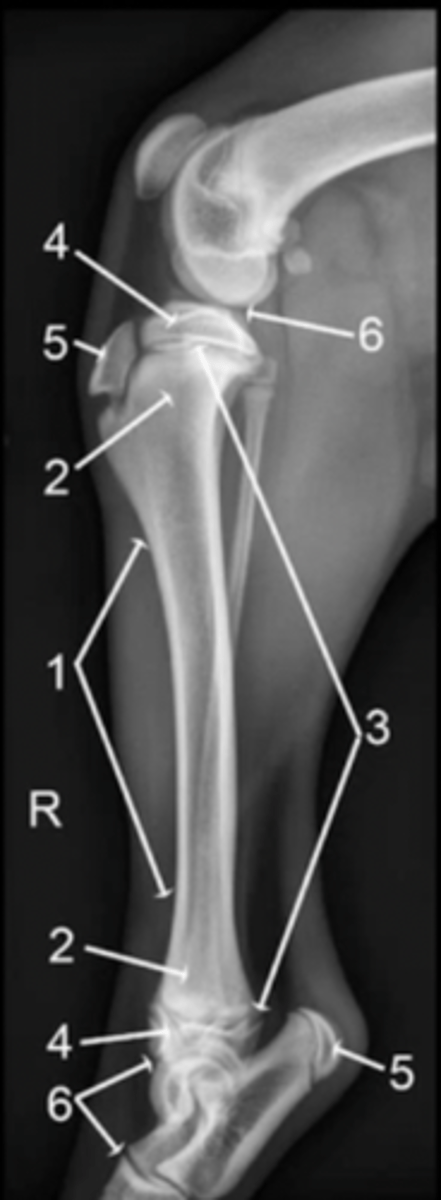
physis
3
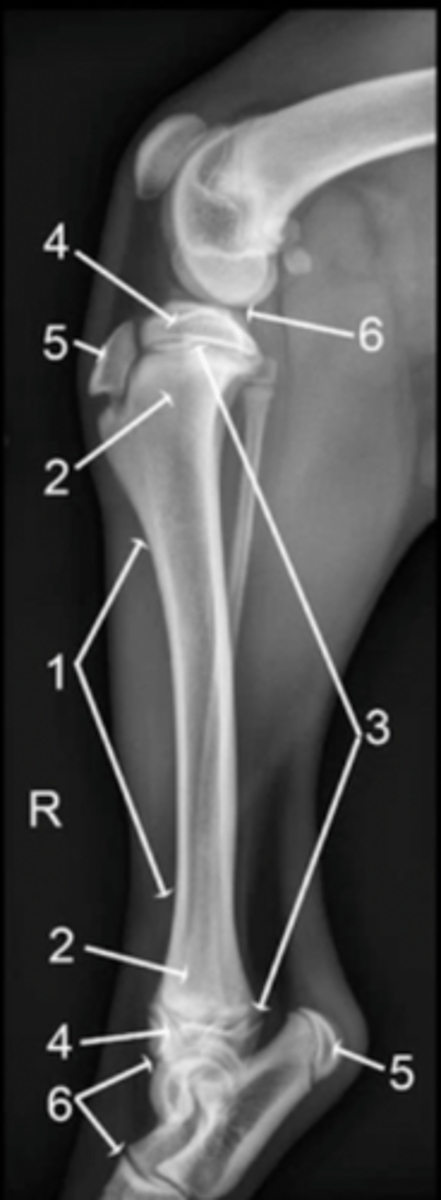
epiphysis
4
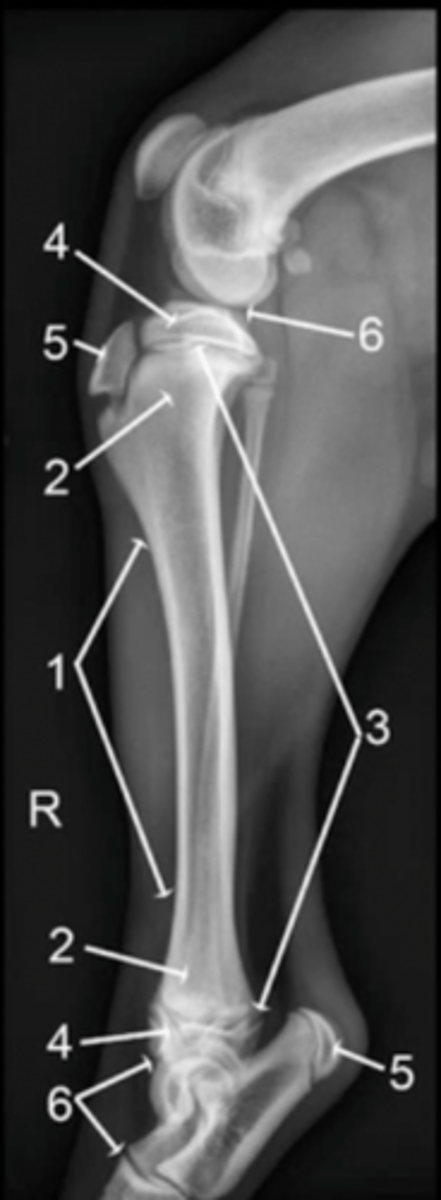
apophysis
5
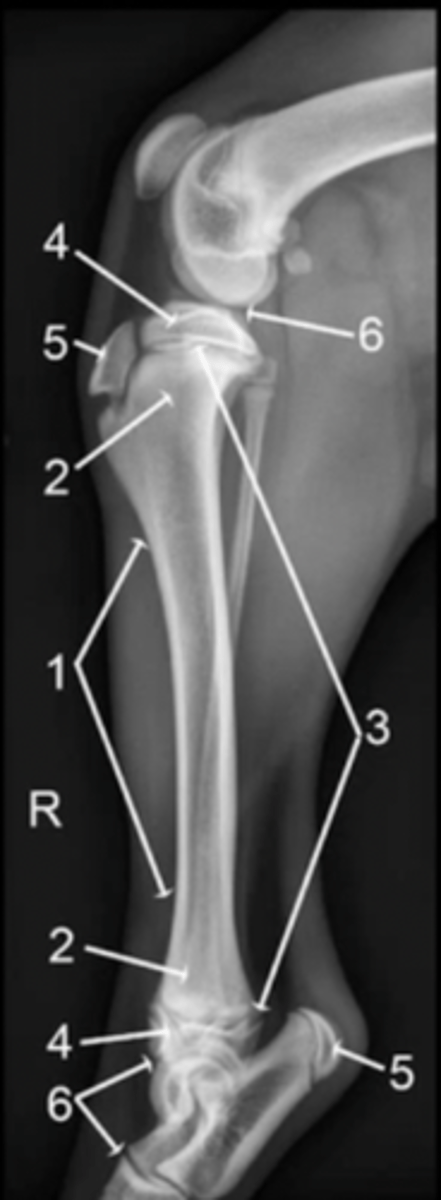
joint
6
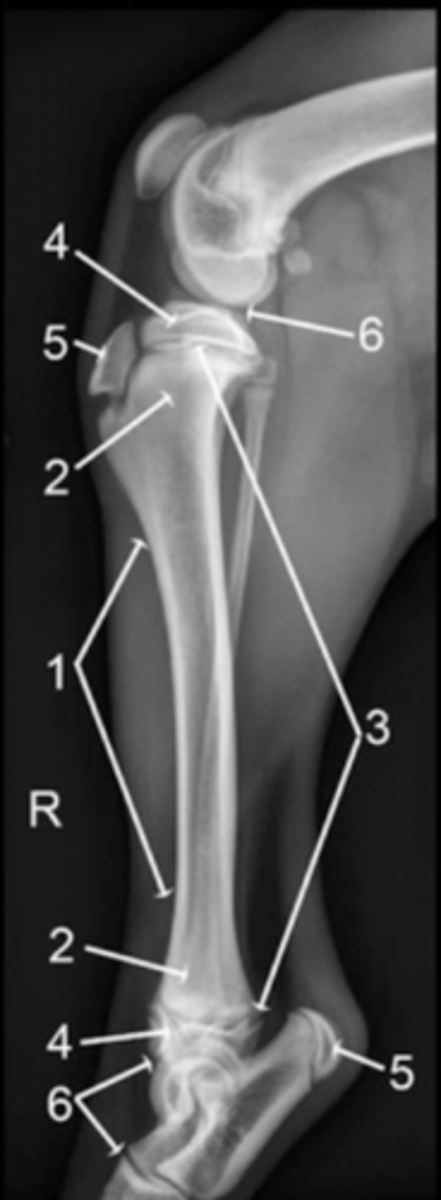
epiphysis (or apophysis) from the metaphysis
The physis separates the ___________ from the __________
well-defined lucent line compared to surrounding bone
How will a physis appear radiologically?
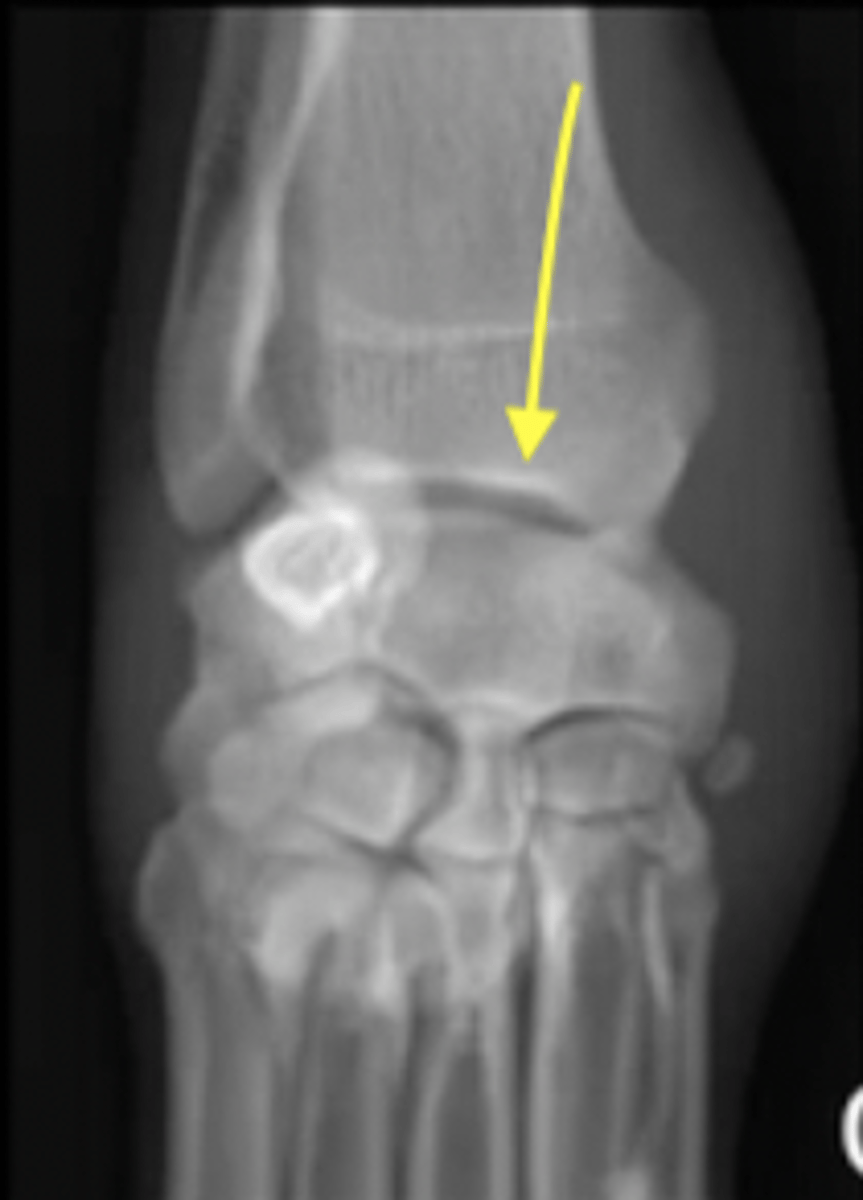
physis
What are the arrows pointing to?
foramen for a nutrient blood vessel
*importnant to know where they are so they are not mistaken for a fracture
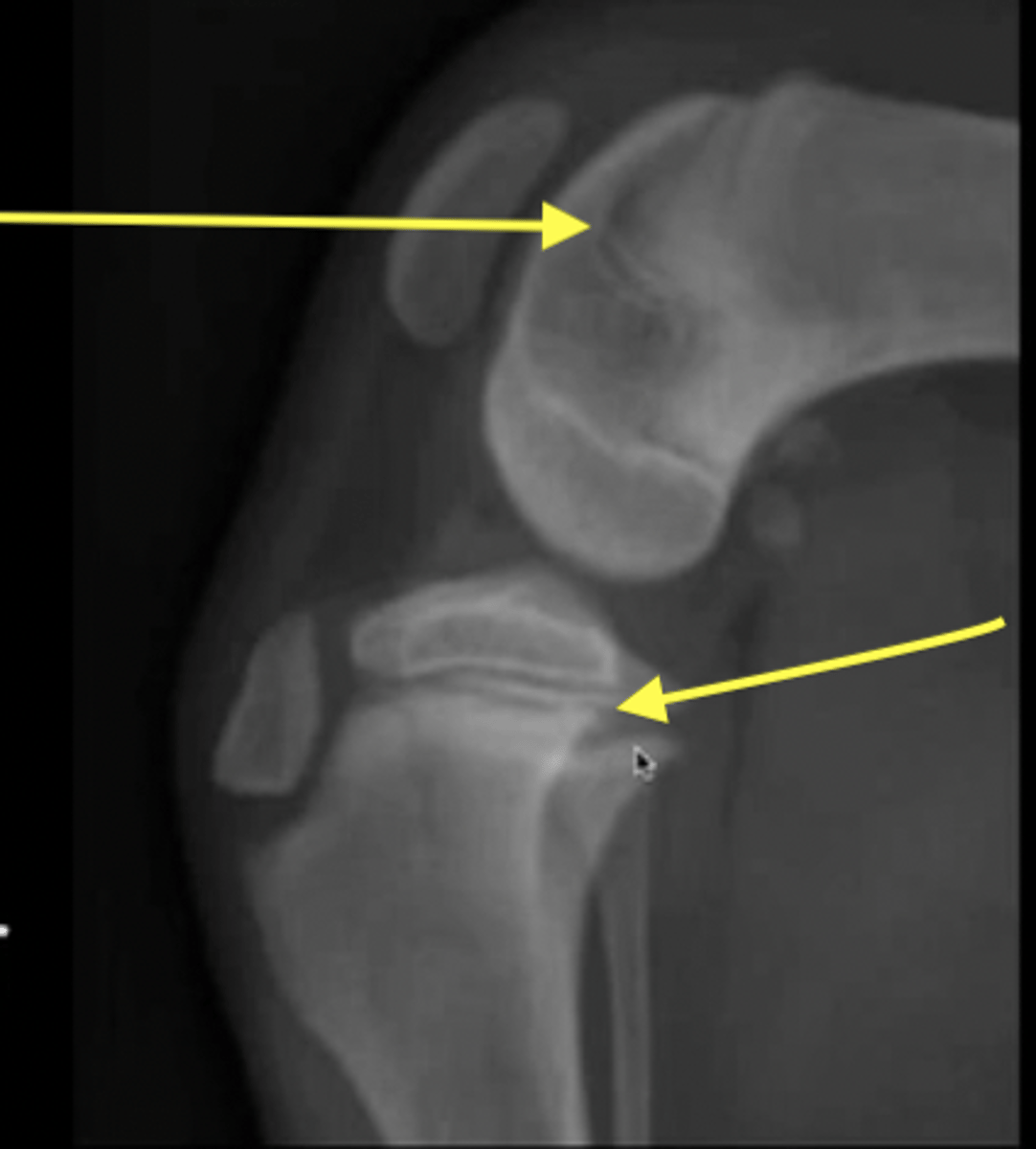
What is the arrow pointing to?
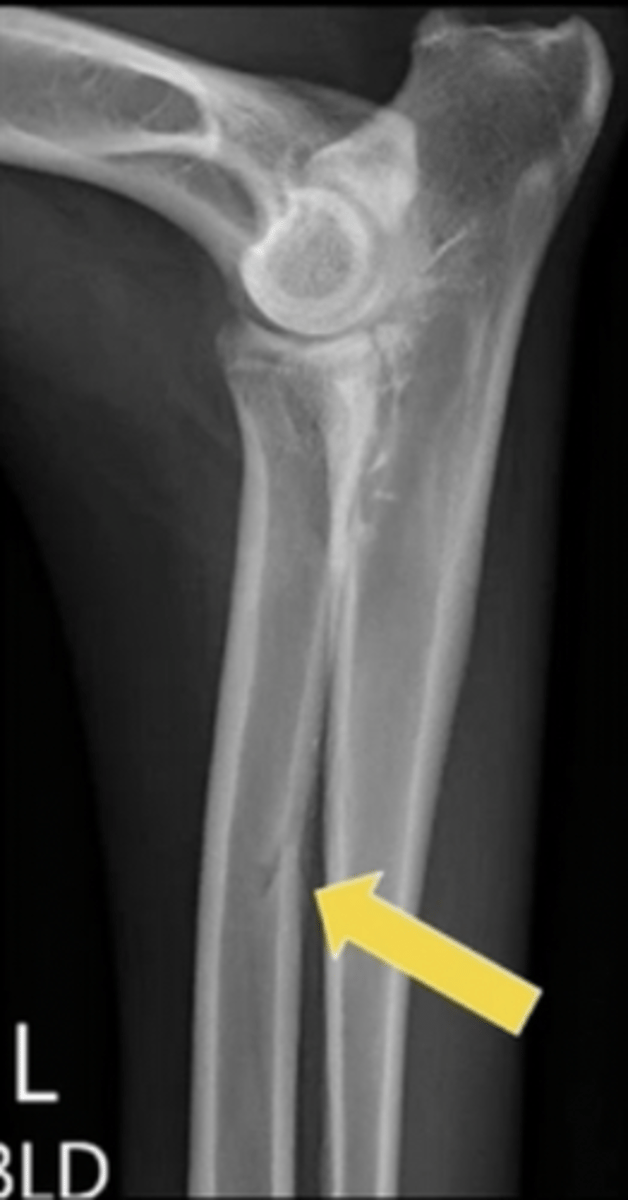
foramen for a nutrient blood vessel
What are the arrows pointing to?
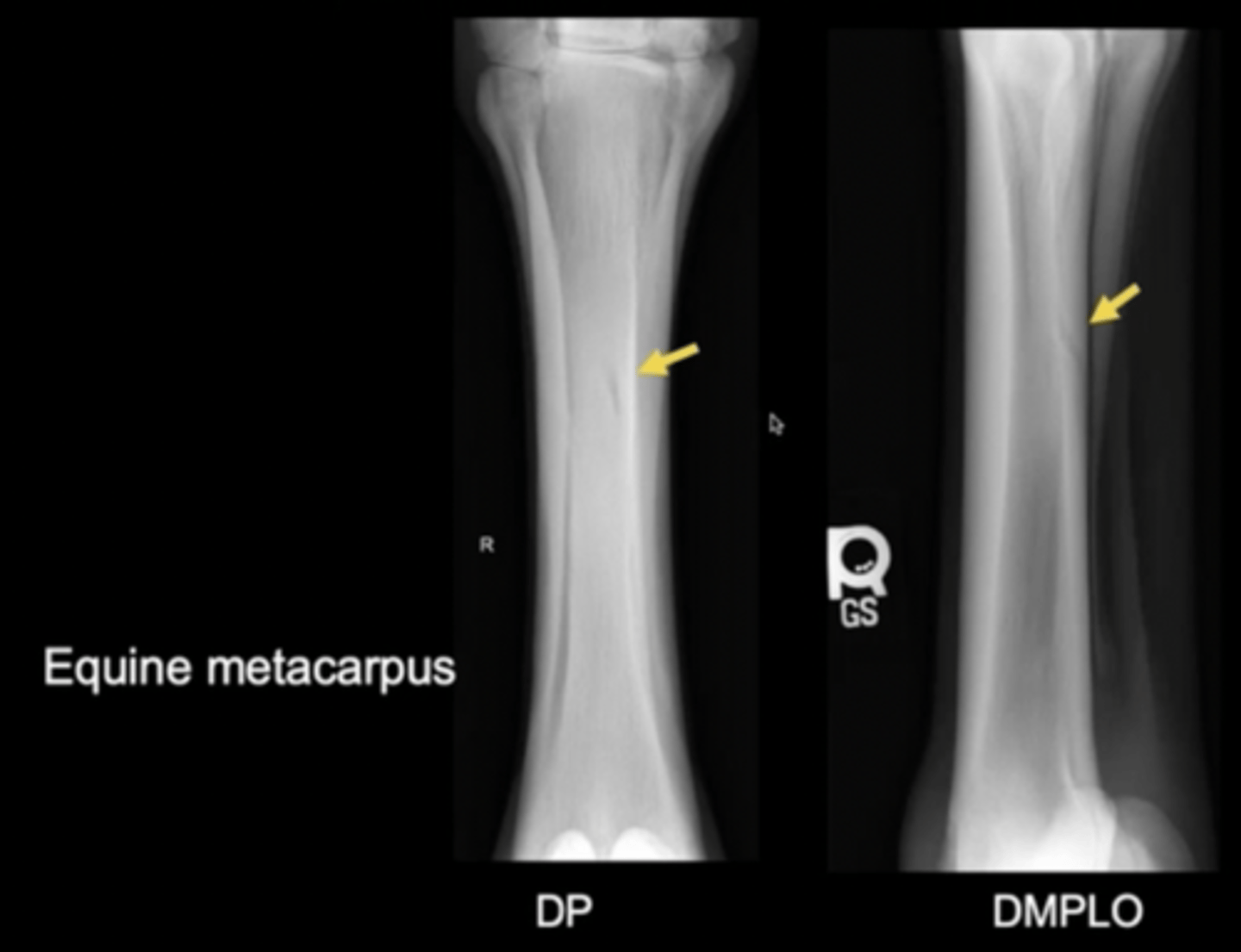
sutures of skill, periodontal ligament of the teeth
Examples of fibrous joints
mandibular symphysis, pelvic symphysis
Examples of cartilaginous joints
stifle, shoulder, elbow, carpus, hips
Examples of synovial joints
synovial
What type of joint is pictured?
fibrous
What type of joint is pictured?
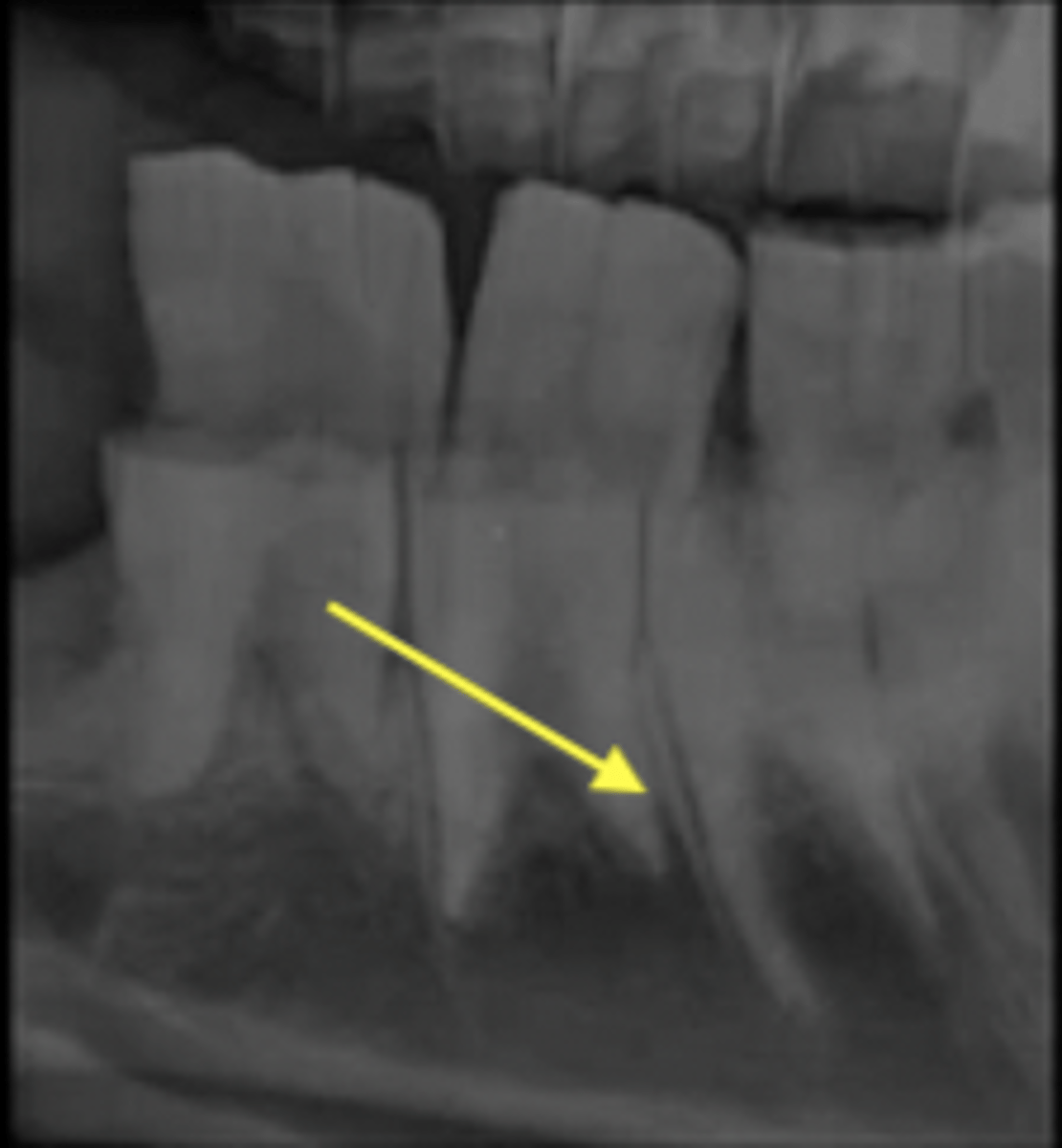
cartilaginous
What type of joint is pictured?
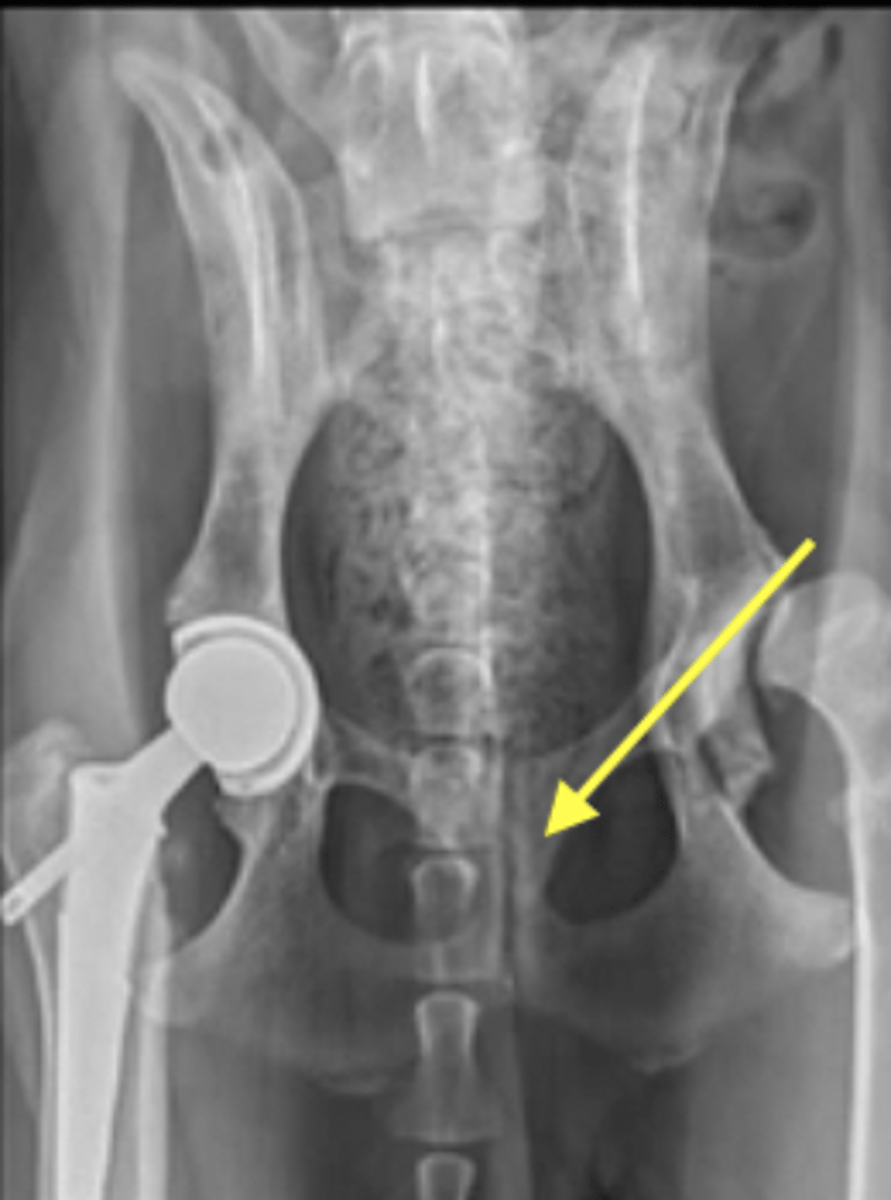
radiolucent
Compared to bone, articular cartilage of joints is ____________
not seen on radiographs but we know its there
radiolucent
1.) geographic
2.) moth-eaten
3.) permeative
Three patterns of destruction
have very sharply defined margins
geographic pattern of destruction
likely benign
Are geographic patterns of destruction are usually benign or aggressive?
small, irregular, poorly defined holes
moth-eaten pattern of destruction
likely aggressive
Are moth-eaten patterns of destruction usually benign or aggressive?
numerous, small, ill-defined holes (sponge like)
permeative pattern of destruction
very aggresive
Are permeative patterns of destruction usually benign or aggressive?
moth eaten
Which pattern of destruction is this?
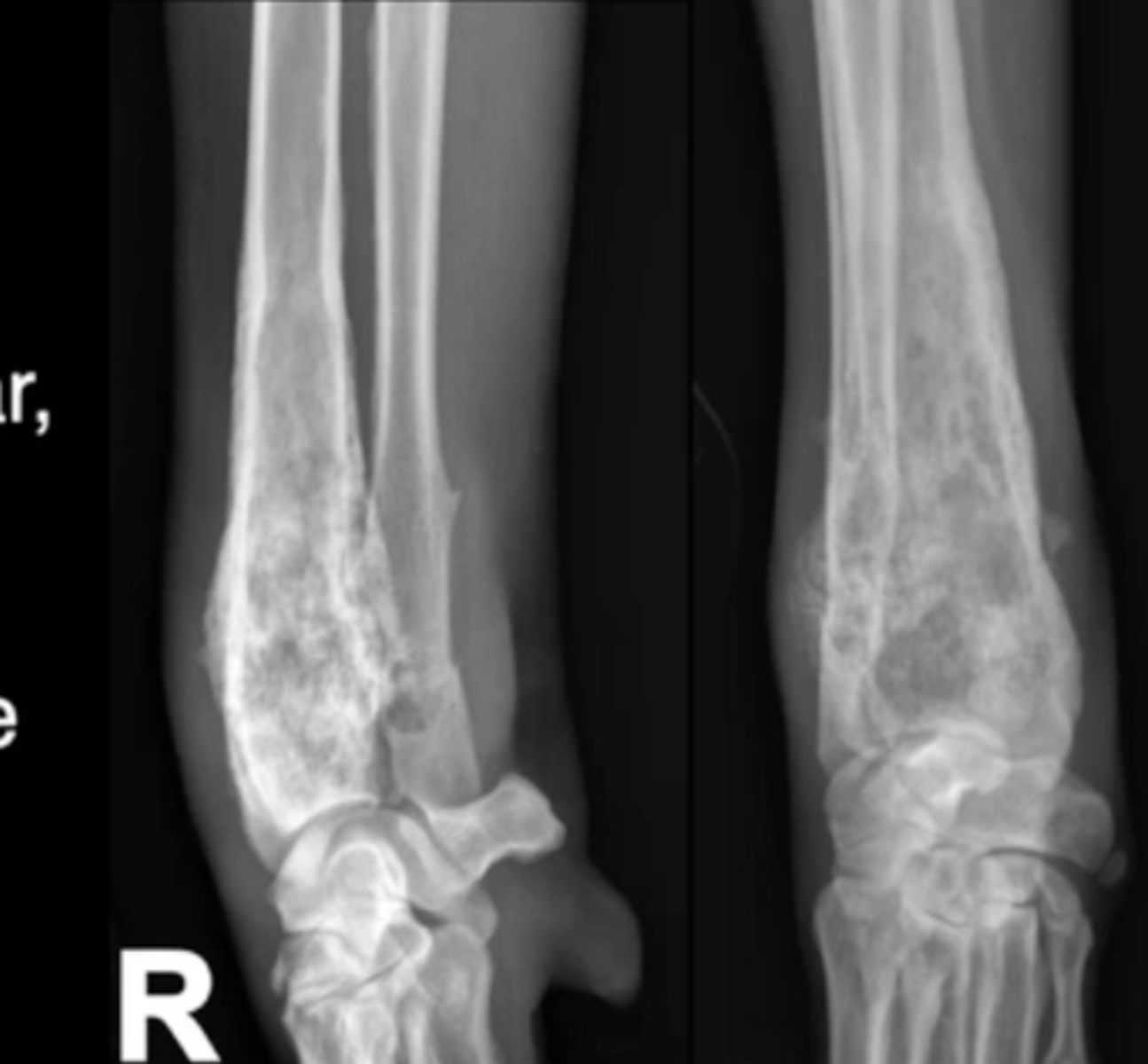
geographic
Which pattern of destruction is this?
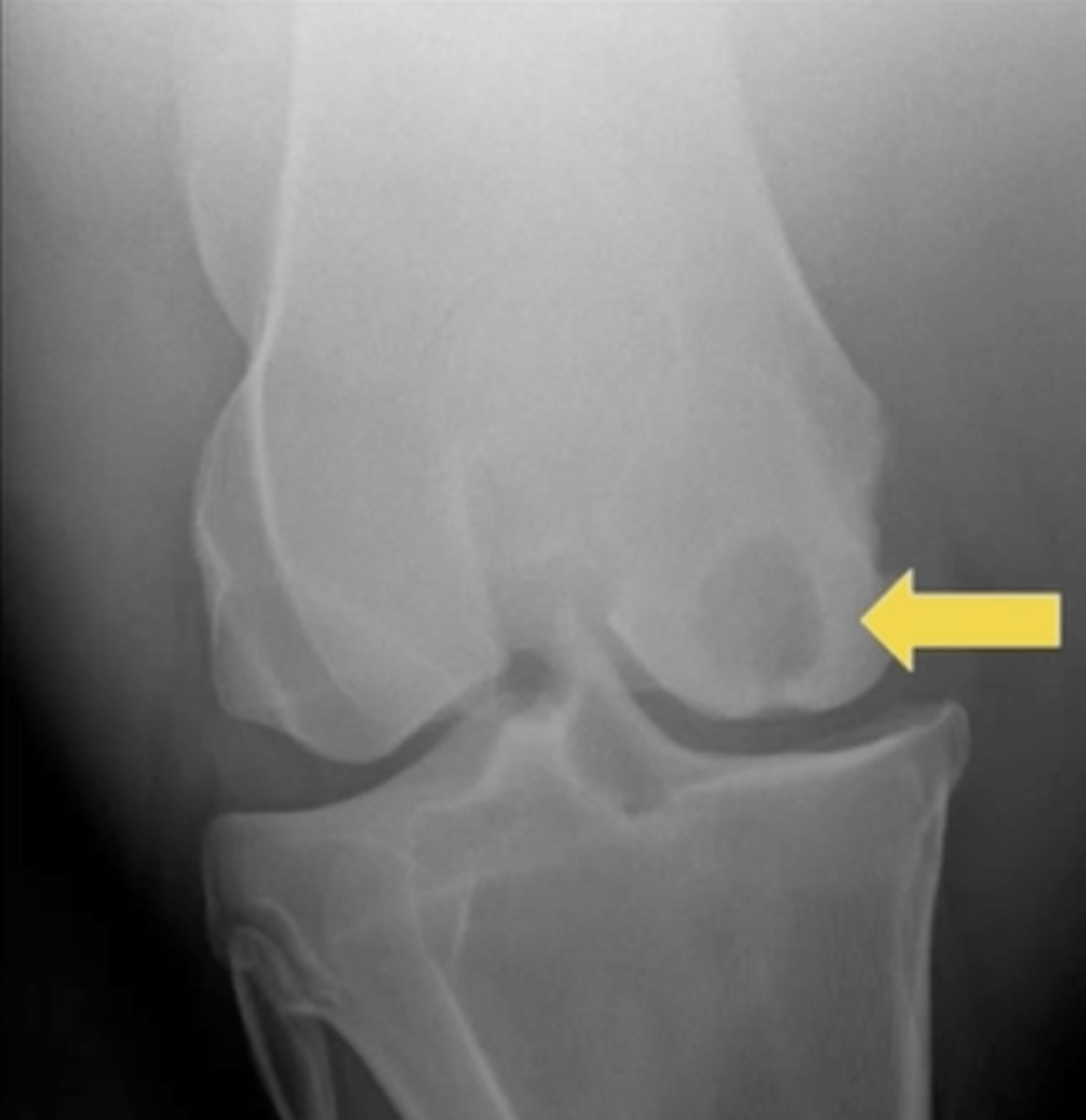
permeative
Which pattern of destruction is this?
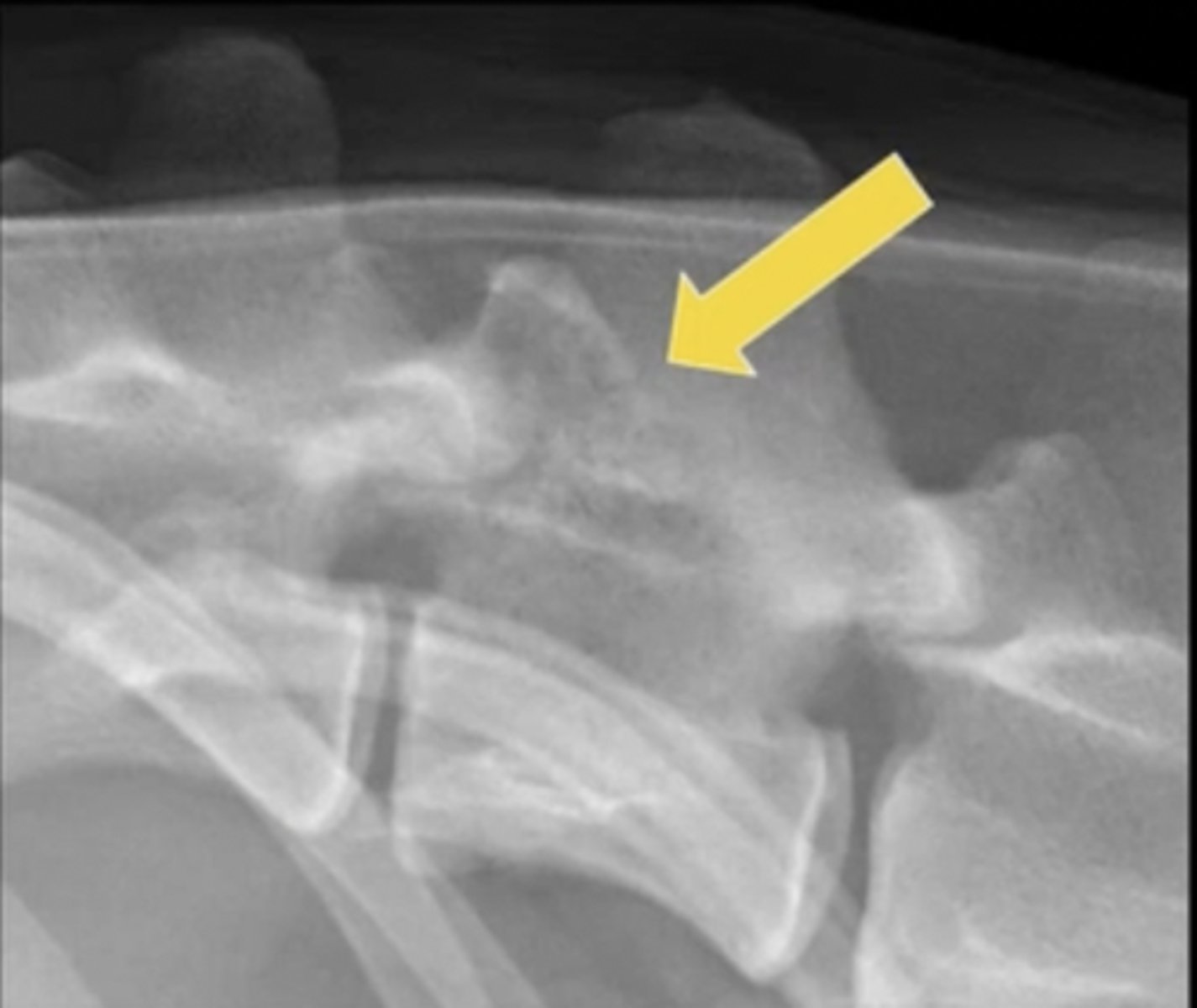
gradual change from an abnormal finding to normal; more likely to be aggressive
Long zone of transition
short change from an abnormal finding to normal; more likely to be benign
Short zone of transition
1.) smooth, lamellar
2.) pallisading
Two types of new bone formation
smooth, lamellar
What type of new bone formation is this?
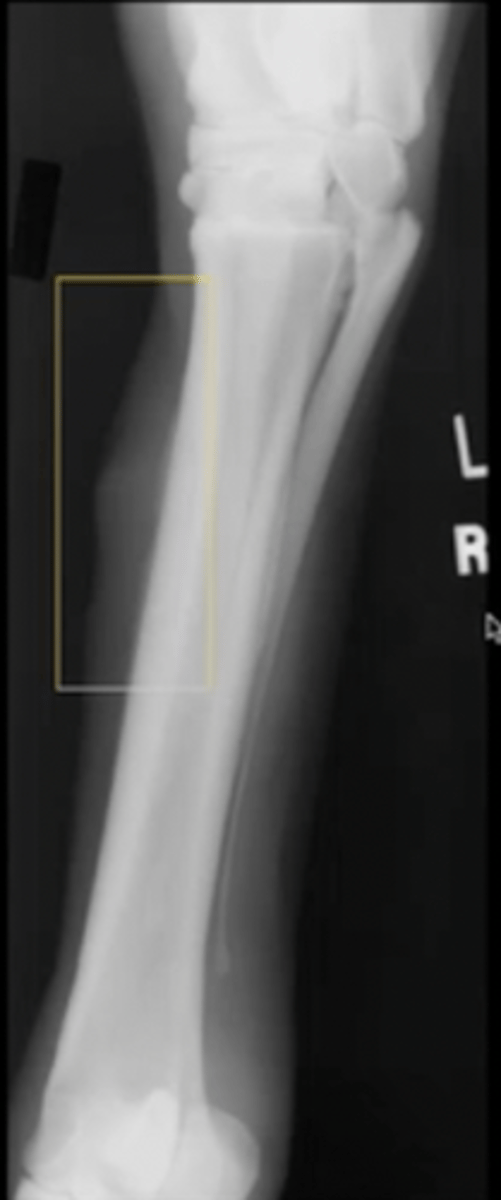
pallisading
What type of new bone formation is this?
