Chapters 3-4 :Gene Mapping and Linkage
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
gene linkage
genes so close to one another that the ability for
alleles located on them to recombine is inhibited
NRC
Parental type
RC
recombinant, the result of crossing-over or fertilization
SCO
Single cross over, recombination of region 1 vs region 2. (region 1 = first and second gene, region 2 = 2 and 3rd gene0
DCO
recomb happens in both region 1 and 2
middle gene
n ‘3 point’ data (with 3 linked genes, one is in the middle position
interference
(closeness of genes inhibits the ability to recombine with a homolog)
What ratio is expected in a trihybrid test cross if genes assort independently?
1:1:1:1:1:1:1:1 (8 phenotypes total for 3 genes)
In a trihybrid cross, how many phenotype pairs appear when genes are linked?
4 reciprocal pairs (8 total phenotypes)
Which phenotypes represent parental (non-recombinant) types?
The two largest numbers in the data set
Which phenotypes represent double crossovers (DCOs)?
The two smallest numbers in the data set
Which phenotypes represent single crossovers (SCOs)?
The intermediate numbers, forming two sets (region 1 and region 2)
How do you identify the middle gene?
Compare a parental and a DCO, the allele that changes is the middle gene
What does a greater number of recombinants between two genes indicate?
those genes are farther apart on the chromosome
Formula to calculate map distance between two genes?
(SCO + DCO) / Total progeny × 100 = distance in cM
What are the steps to analyze trihybrid test cross data?
Pair reciprocals
Identify parentals (largest)
Identify DCOs (smallest)
Compare to find middle gene
Assign regions (SCO1, SCO2)
Calculate map distances
What does a “cross-over” mean in genetics, and how do single and double crossovers differ?
A cross-over is an exchange of DNA between homologous chromosomes during Prophase I of meiosis.
A single crossover (SCO) breaks the DNA once, producing two reciprocal recombinant types.
A double crossover (DCO) breaks the DNA twice, producing two reciprocal DCO types.
Because it’s harder to break DNA twice when genes are close together, DCOs always appear least frequently among recombinant offspring.
Gene map
A unidimensional chromosome map that indicates gene positions (loci). Can be a recombination map (shows loci of genes identified by phenotypic recombinations using linkage analysis) or a physical map (shows a gene as a DNA segment produced using sequencing). Can only make a map using linked genes
What does gene mapping show and what affects crossing-over frequency?
Gene mapping shows the specific locus of a gene on a chromosome. The closer two genes are, the less likely crossing-over occurs between them during Prophase I. The centromere is where kinetochores form, and chromosomes have short (p) and long (q) arms ending at telomeres (p-ter, q-ter).
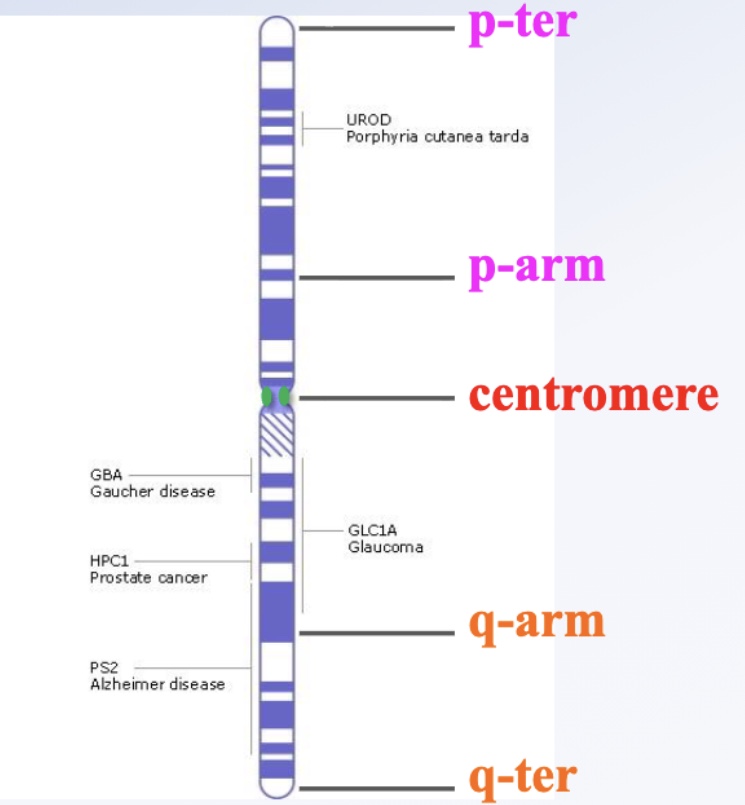
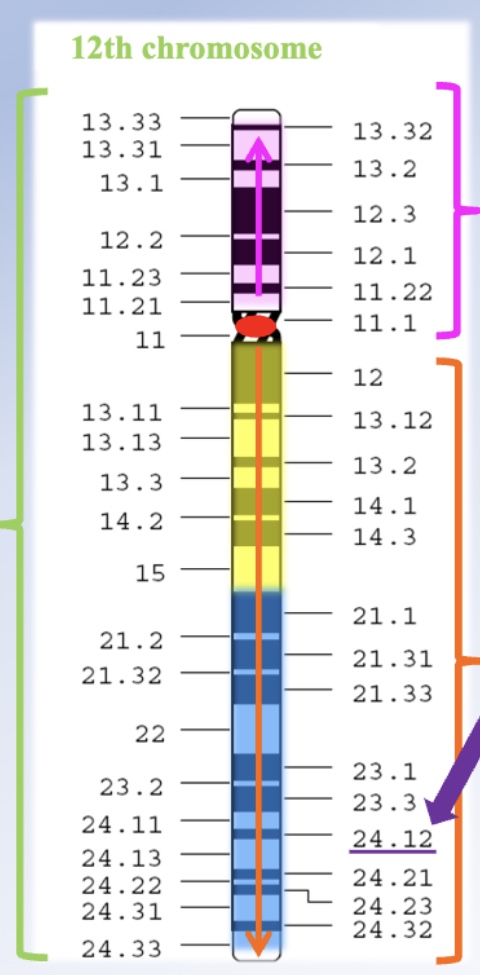
How are loci numbered on chromosomes?
Loci are numbered from the centromere outward toward the telomeres. Larger numbers mean farther from the center. For example, on chromosome 12: the 12p arm has one region, and the 12q arm has two regions (1 = yellow, 2 = blue). The locus 12q24.12 is read as “twelve Q two-four point one-two,” pinpointing a precise location on the q arm.
What happens when genes are located close together on the same chromosome?
: Their alleles are inherited together more often because crossing-over between them is less likely. Fewer recombinants mean the genes are closer together.
If AaBb × aabb returns 4 phenotypes at 25% each (AB, Ab, aB, ab), what does this show?
Independent assortment, the genes are on separate chromosomes.
What is interference during crossing-over?
Interference occurs when genes are close together, reducing the chance of recombination between them.
How is interference ranked?
From 0 to 1 — 0 = no interference (independent assortment), 1 = complete interference (no recombination)