Chem 1610 Midterm 1 Memorization
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
Prefix for one
Mono-
Prefix for two
di-
Prefix for three
tri-
Prefix for four
tetra-
Prefix for five
penta-
Prefix for six
hexa-
Prefix for seven
hepta-
Prefix for eight
octa-
Prefix for nine
nona-
Prefix for ten
deca-
Acetate
CH3COO-
Carbonate
CO32-
Hydrogen carbonate or bicarbonate
HCO3-
Cyanide
CN-
Hypochlorite
ClO-
Chlorite
ClO2-
Chlorate
ClO3-
Perchlorate
ClO4-
Dichromate
Cr2O72-
Chromate
CrO42-
Permanganate
MnO4-
Azide
N3-
Ammonium
NH4+
Nitrite
NO2-
Nitrate
NO3-
Hydroxide
OH-
Peroxide
O22-
Phosphate
PO43-
Hydrogen phosphate
HPO42-
Dihydrogen phosphate
H2PO4-
Disulfide
S22-
Sulfate
SO42-
Hydrogen sulfate or bisulfate
HSO4-
Sulfite
SO32-
Hydrogen sulfite or bisulfite
HSO3-
Thiocynate
SCN-
Hydrofluoric acid
HF
Hydrochloric acid
HCl
Hydrobromic acid
HBr
Hydroiodic acid
HI
Carbonic acid
H2CO3
Nitric acid
HNO3
Nitrous acid
HNO2
Phosphoric acid
H3PO4
Sulfuric acid
H2SO4
Sulfurous acid
H2SO3
Hypochlorous acid
HClO
Chlorous acid
HClO2
Chloric acid
HClO3
Perchloric acid
HClO4
Alcohols
a hydroxyl group attached to an R group
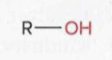
Ethers
an oxygen atom single-bonded to two separate R groups
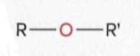
Adehydes
a carbonyl group (C=O) where the carbon atom is bonded to at least one hydrogen atom and the rest to an R group
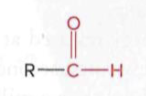
Ketones
a carbonyl group (a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom) with R groups attached to the carbonyl carbon
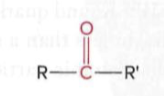
Carboxylic acids
a carbonyl group (C=O) and a hydroxyl group (–OH) bonded to the same carbon atom, R group is attached to the carboxylic carbon
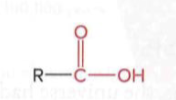
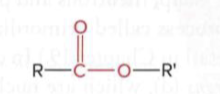
Esters
a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to an oxygen atom, which is in turn bonded to an R group
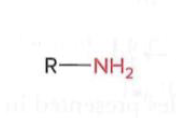
Amines
A nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms (derivative of Ammonium)
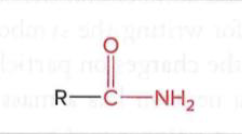
Amides
a nitrogen atom is bonded to a carbonyl carbon atom (a carbon double-bonded to an oxygen), forming a C-N bond that links a carbonyl group and an amine group
Alkanes
carbon bonds that contain only single bonds between (carbon) atoms
Alkenes
carbon bonds that contain double bonds between (carbon) atoms
Alkynes
carbon bonds that contain triple bonds between (carbon) atoms
Is Hydrofluoric acid (HF) a strong or weak acid?
Strong
Is Hydrochloric acid (HCl) a strong or weak acid?
Strong
Is Hydrobromic acid (HBr) a strong or weak acid?
Strong
Is Hydroiodic acid (HI) a strong or weak acid?
Strong
Is Carbonic acid (H₂CO₃) a strong or weak acid?
Weak
Is Nitric acid (HNO₃) a strong or weak acid?
Strong
Is Nitrous acid (HNO₂) a strong or weak acid?
Weak
Is Phosphoric acid (H₃PO₄) a strong or weak acid?
Weak
Is Sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) a strong or weak acid?
Strong
Is Sulfurous acid (H₂SO₃) a strong or weak acid?
Weak
Is Hypochlorous acid (HClO) a strong or weak acid?
Weak
Is Chlorous acid (HClO₂) a strong or weak acid?
Weak
Is Chloric acid (HClO₃) a strong or weak acid?
Strong
Is Perchloric acid a strong or weak acid?
Strong
Which cations are always soluble?
Group I ions (alkali metals: Li⁺, Na⁺, K⁺, etc.) and NH₄⁺ (ammonium).
Which anions are always soluble?
NO₃⁻ (nitrate) and CH₃COO-/C2H3O2- (acetate).
Which halides (Group 17) are soluble?
Cl⁻, Br⁻, I⁻ are soluble except with Ag⁺, Cu⁺, Pb²⁺, Hg₂²⁺.
Which sulfates (SO₄²⁻) are soluble?
All sulfates except those of Pb²⁺, Hg₂²⁺, Ca²⁺, Ba²⁺, Sr²⁺.
Which hydroxides (OH⁻) are soluble?
All are insoluble except Group IA (Alkali Metals) hydroxides, Ca(OH)₂, Sr(OH)₂, and Ba(OH)₂.
Which sulfides (S²⁻) are soluble?
Group IA (Alkali Metals), NH₄⁺, CaS, SrS, BaS.
(All other sulfides are insoluble.)
Which carbonates (CO₃²⁻) are soluble?
Only those of Group IA (Alkali Metals) and NH₄⁺.
(All others are insoluble.)
Which phosphates (PO₄³⁻) are soluble?
Only those of Group IA (Alkali Metals) and NH₄⁺.
(All others are insoluble.)
strong acids make ____ electrolytes
strong
weak acids make ____ electrolytes
weak