Chapter 10 Review Sheets - Biochemistry of the Genome
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What did Gregor Mendel work with instead of DNA?
Why did he not work with DNA itself?
What form of science did his experiments lay the groundwork for?
Gregor Mendel worked with Garden Peas
He did not work with DNA because he did not know what it was
His experiments laid the groundwork for the science of Inheritance
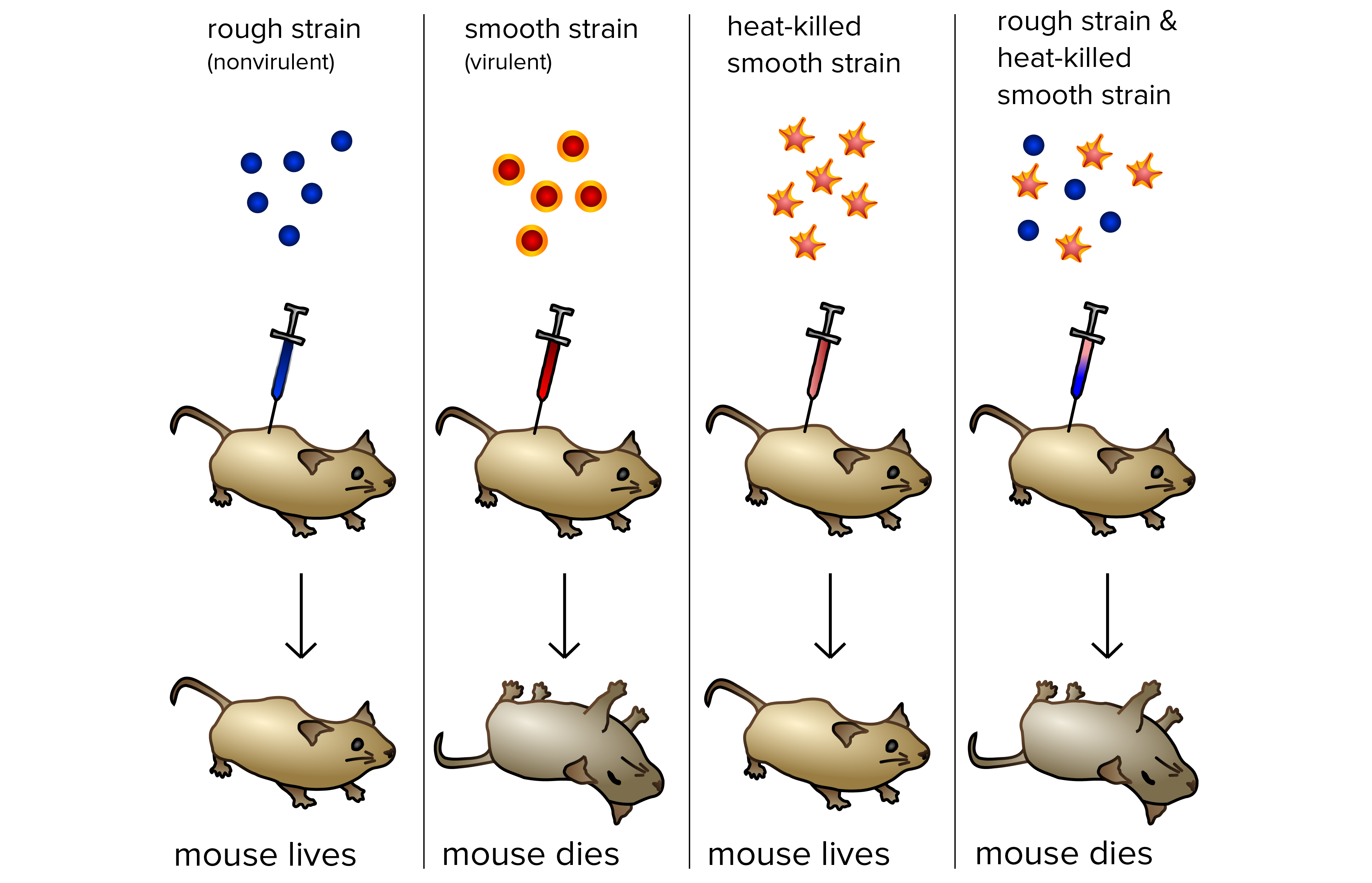
What was the experiment performed by Frederick Griffith?
What is the Transforming Principle?
Is this an example of Vertical Gene Transfer?
* See picture.
Griffith’s Transforming Principle was that a non-pathogenic strain of a bacteria was able to “transform” into a pathogenic strain.
No, this experiment was an example of Horizontal Gene Transfer
Nucleic acids are _______, which means they are made up of many monomers. What is the monomer of nucleic acids?
Polymers
The monomer of nucleic acids is called a Nucleotide
What are the three components of a Nucleotide?
The three components are:
A Phosphate group (attached to 5’ carbon)
A Sugar molecule (deoxyribose in DNA, ribose in RNA)
Nitrogenous Base (Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine, or Uracil)
What is the certain order of the nucleotides in the DNA of a cell referred to as?
The Base Sequence
Which carbon is the Phosphate Group attached to in a single nucleotide?
Which carbon does the Phosphate group attach to when covalently attaching to other nucleic acids?
ThePhosphate group in a single nucleotide attaches to the 5’ Carbon
When forming a nucleic acid strand, the Phosphate Group attaches to the OH group on the 3’ carbon of the other nucleic acid
List the five Nitrogenous Bases. Which are purines and which are pyrimidines?
Purines:
Adenine
Guanine
Pyrimidines:
Cytosine
Thymine (DNA)
Uracil (RNA)
What is the special name for the covalent bond formed via dehydration between two nucleic acids?
Phosphodiester Bond
What are the complementary base pairs?
How many Hydrogen bonds are there between each pair?
(Purine - Pyrimidine)
Adenine - Thymine / Uracil —> Two Hydrogen Bonds
Guanine - Cytosine —> Three Hydrogen Bonds
What is the significance of complementary base pairing?
Allows for us to make a complementary copy of a DNA strand
What two types of bonds can take place in DNA that were identified in class?
The two bond types are:
Covalent Bonding
Hydrogen Bonding
What is the relative strength of the two bonds that take place in DNA?
Hydrogen Bonding < < < Covalent Bonding in strength
(Inter- MF is weaker than Intra- MF)
If heat is applied to DNA, what happens to the molecule?
The Hydrogen bonds break apart and the double-stranded helix begins to denature into single-stranded DNA
Describe the contributions of the following individuals:
Rosalind Franklin / Maurice Wilkins
Erwin Chargaff
Watson / Crick
Rosalind Franklin / Maurice Wilkins
Used X-Ray Differentiation to take photos of DNA displaying its double-helix structure
Erwin Chargaff
Found that in the base composition, A = T and C = G; Chargaff’s Rule
Watson / Crick
Put together the previous two findings and proposed the structure of DNA as being Double-Helical
What is the overall charge of DNA?
Negatively Charged
What is the function of DNA?
DNA stores the information needed to build and control the cell
How are DNA and RNA similar? How are they different? Compare these factors:
Monomer
Sugar Component of the Nucleotide
Nitrogen Containing Bases
Complementary Base Pairs
Single or Double Stranded
Relative Length
Relative Stability
RNA:
Monomer —> Nucleotides
Sugar Component —> Ribose
Nitrogen Bases —> A, G, C, U
Base Pairs —> A - U and G - C
Usually Single-Stranded
Short (linear)
Less Stable
DNA:
Monomer —> Nucleotides
Sugar Component —> Deoxyribose
Nitrogen Bases —> A, G, C, T
Base Pairs —> A - T, G - C
Usually Double-Stranded
Long (linear or circular)
More Stable
What are the functions of RNA?
Four main functions:
Structural RNA
Informational
Catalyst (Ribozymes)
Synthesis
Which process involves the three major types of RNA?
Protein Synthesis
Briefly describe the function of the three types of RNA
mRNA (Messenger) —> provides a template for protein synthesis during translation
rRNA (Ribosomal) —> structural and catalytic (Peptidyl transferase activity)
tRNA (Transfer) —> brings Amino acids and reads the genetic code during translation
What is a gene?
A gene is a distinct unit of DNA that codes for proteins or functional RNA
What does it mean if a gene is said to be transcribed “constitutively”?
“Constitutively” means that the gene is being transcribed at all times
What does it mean if a gene is either upregulated or downregulated?
Upregulated —> Gene is being transcribed (On)
Downregulated —> Gene is NOT being transcribed (Off)
Define the terms Genotype and Phenotype
Which of the two can change and which stays the same?
Genotype —> full collection of genes a cell contains in its genome
Phenotype —> observable characteristics expressed by genes / genotype
Phenotypes can change, while Genotypes remain the same / constant
Compare the structures of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic chromosomes using:
How many and what shape
How many copies
Supercoil or No Supercoil
Enzymes
Histones or No Histones
Eukaryotes:
How Many & What Shape —> Multiple, linear chromosomes
How Many Copies —> Diploid (two copies)
Supercoiled
Topoisomerase
Has Histones
Prokaryotes:
How Many & What Shape —> Single, circular chromosome
How Many Copies —> Haploid (one copy)
Supercoiled
Topoisomerase (Unique, DNA Gyrase)
No Histones
How is DNA, which is relatively large, able to be stored in the cell?
What is the function of Topoisomerases in this process?
DNA supercoils on itself inside the cell at ~10 bp / turn
Topoisomerases facilitate the supercoiling process
What is noncoding DNA?
How does the amount of noncoding DNA differ between Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes?
Noncoding DNA is DNA that does not code for proteins or stable structural RNA
Noncoding DNA is much more abundant in Eukaryotic Cells
Is noncoding DNA important or is it just “junk”?
Noncoding DNA is not junk; it can serve a regulatory role during transcription
What are Plasmids?
How are they transferred between organisms?
What types of genes might be found on a Plasmid?
Plasmids are smaller loops of DNA that may contain one or a few genes that are not essential for normal growth
They are transferred between organisms via Horizontal Gene Transfer
Genes that provide organisms with a competitive advantage may be found on a Plasmid
How does the size of chromosomes vary amongst organisms?
Is the complexity of an organism directly related to the size of the chromosome?
Size of chromosomes vary greatly amongst organisms
The complexity of an organism is NOT related to the size of the chromosome