Pharmacy Practice- Consultation Skills
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Consultation
meeting to discuss or get advice, goal of discovering course of action
Person-centred approach
committing to putting the people at the centre of healthcare
- increases choice and decision making processes, all parties benefit
- underpins care principles
advising -> supporting -> coaching
Holistic view
taking into account social, physical, psychological and behavioural aspects during a consultation
Golden minute
letting the patient speak for the fist minute of the consultation without interruption
- for history taking
Clinical reasoning
evidence based, dynamic process combining scientific knowledge, clinical experience and critical thinking
Factors affecting clinical reasoning
- epidemiology- some conditions are more common than others
- age and sex- elderly more likely to have polypharmacy, gender-specific conditions
- general appearance of a patient
Medicines optimisation and adherence
meds are used sub-optimally and are not taken as intended, HCP duty to help increase med adherence
Compliance
extent to which a person's behaviour matches prescriber's recommendations
Concordance
nature of prescribing, relationship and med taking behaviour
- actively discussed with patient
Persistence
length of time person continues to take meds
Adherence
extent to which a person's behaviour matches agreed recommendations from the prescriber
Non-adherence
failure to comply fully with treatment recommendations for modification of a health habit or an illness state
- impairs health outcomes, increases risks, treatment failure/disease progression
- can be (un)intentional (demographics, age, gender, no support or care, beliefs)
Unintentional non-adherence
forgetfulness, unable to open or operate meds/apparatus/devices, swallowing issues, doesn't match lifestyle, child in school
Intentional non-adherence
active decision not to take meds
- due to concern about risks, health benefits, felt not listened to, unconvinced by meds, personal beliefs (e.g. vegetarian)
Informed adherence
accept that the patient has the right to decide not to take meds (as long as they have the capacity to decide)
Improving non-adherence
1- unintentional or intentional
2- consider support options
3- address beliefs and concerns
4- tackle practical problems (monitor, simplify treatment plan)
5- side effects, refer back to prescriber
Interventions on non-adherence
no 'one size fits all' strategy
- first explore the person's perspectives and attitudes towards change, dis/advantages, negotiate, shared decision making
- alter formulation, compliance aids, monitored dosage systems, change regime, reading aids
Age, ability and mental health on adherence
- encourage people of all ages to participate in therapy discussions
- be aware of different abilities
- people with mental health conditions may struggle to adhere with meds, so be patient, awareness
Communication skills
incorporating verbal and non-verbal methods of language to vocalise emotions and listen effectively
- building and maintaining rapport
Effective listening
receiver involved in listening experience by paying attention to visual cues, watching body language, asking relevant questions
Transactional analysis model
refers to states of mind, 'ego states'
- adult- 'here and now', appropriate response to stimuli
- child- echo the past, natural child (playful) or adaptive child (adapted by conforming)
- parent- reflected the behaviours of paternal figures (authoritative, paternalistic or caring)
consultations should aim to be A to A
Sharing expertise
each person is their own expert in their care, diagnosis and treatment
Barriers during consultations
lack of communication skills, time, personal/language/organisational barriers, inadequate knowledge, telephone restricted to verbal, blocking behaviours
Blocking behaviours
HCP- advice too soon, distress as 'normal' (dismissing), physical aspects only, changing topic, 'jollying' along
person- refusal, belief that nothing can be done, burden, pathetic or ungrateful, uncomfortable, fear
Taking a history in a consultation
considered the best way to obtain relevant info and accurate diagnosis (promotes empathy, understanding, learning)
- identify patient, encourage description one problem at a time, how effective is treatment, recent life changes, past illness, meds taken, family disease, social history, interpret
RESPECT all info
History of consultation theory
1800- bio-medical- concentrates solely on disease and physical issues
1950- Balint- psychological problems related to physical
1960- transactional analysis- states of mind
1970- health beliefs- factors influencing and predicting behavioural outcomes from person's viewpoint
1980- anthropological 'folk'- people ask themselves questions
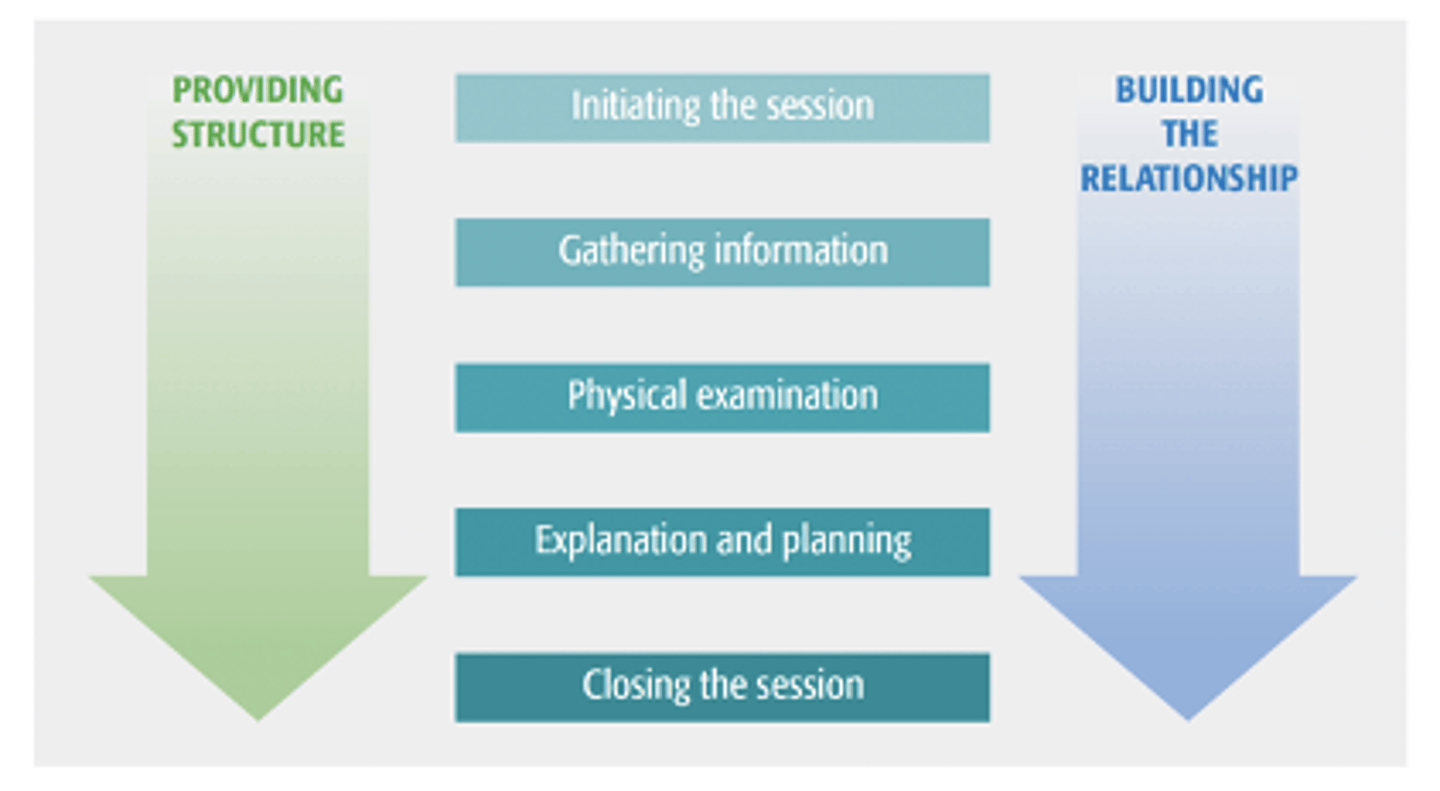
Calgary-Cambridge model
1- initiating the session (prep, intro, rapport, agendas)
2- gathering information (LICEF)
3- physical examination (where and when appropriate)
4- explanation and planning (info, aids, discuss action plan)
5- closing the session (summarising, teach back, safety net)
Pendleton's framework
more person-centred approach:
- discuss reason for attendance, consider other problems, choose appropriate action, achieve shared understanding, involve person in management, appropriate time and resources, establish and maintain relationship
Neighbour's inner consultation
cultivating HCP ability to act on info-rich moments
- connect, summarise, handing over, safety-net, housekeeping (am I in good enough state for next person)
BARD
considers whole relationship and personality, will influence consultation
- behaviour, aims, room, dialogue
Medicines related consultation assessment tool (MR-CAT)
global assessment tool for identifying strengths and weaknesses to improve technique (based on Calgary-Cambridge)
LICEF
lifestyle, ideas, concerns, expectations, feelings
Shared decision making
patient and HCP work together to decide on a treatment plan
- "no decision about me, without me"
- awareness of balance of power
- active listening, working together, discussing opinions, making inferred decisions
Active listening
paraphrasing- restating info
summarising- concisely reiterating main points
clarifying- clearing up any misunderstanding in both parties
reflection- mirror and relay info
Types of questions
open- broad in nature (how, where, when, what)
closed- yes or no
leading- used when the patient is unsure ("does it get worse when XYZ?")
probing- "tell me more" (TED- tell, explain, describe)
Health coaching
HCP encourage to empower patients into their own decision making to take control of their healthcare (own insight, self-aware health goals)
- improves med optimisation, responsibility
- mutual partnership, balanced discussion, believing in potential, appropriate level of challenge, support behavioural changes
Pillars of healthcare coaching
patient activation, motivational interviewing, positive psychology
Grow model
goal, reality, options, way forward
Four E's model
explore, educate, empower, enable
OARS
open-ended questions, affirmations, reflective listening, summaries (leads to more exploratory questions)
Scaling questions
solution-focused
- subjective statement -> objective measure