Energy-Converting Organelles & Endosymbiosis (2A)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Mitochondria Function
carry out cellular respiration in nearly all eukaryotic cells
converts the chemical energy in foods to chemical energy in ATP
ATP
adenosine triphosphate
primary energy carrier in cells
stores and transfers energy for cellular processes
Mitochondria Structure
have 2 membranes - outer & inner (2 internal compartments)
intermembrane space (between the 2 membranes)
mitochondrial matrix
enclosed by the inner membrane
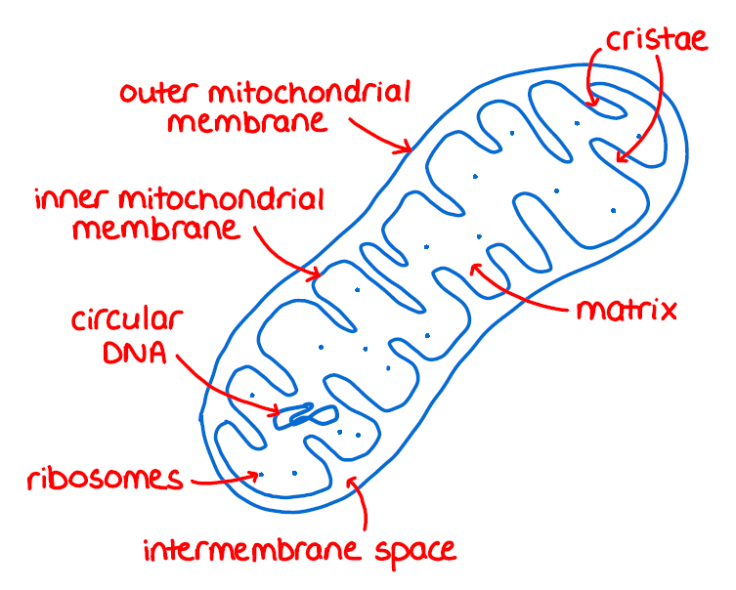
The Matrix Contains…
mitochondrial DNA, ribosomes, and enzymes for cellular respiration
Mitochondria’s Inner Membrane
contains many embedded protein molecules that function in ATP synthesis
has folds (cristae)
increases its surface area, enhancing the mitochondrion’s ability to produce ATP
Chloroplast Function
the photosynthesizing organelles of plants and algae
Photosynthesis
photosynthesis is the conversion of light energy from the sun to the chemical energy of sugar molecules
Chloroplasts Structure
ALSO have an outer and inner membrane separated by an intermembrane space
Stroma
enclosed by the inner membrane
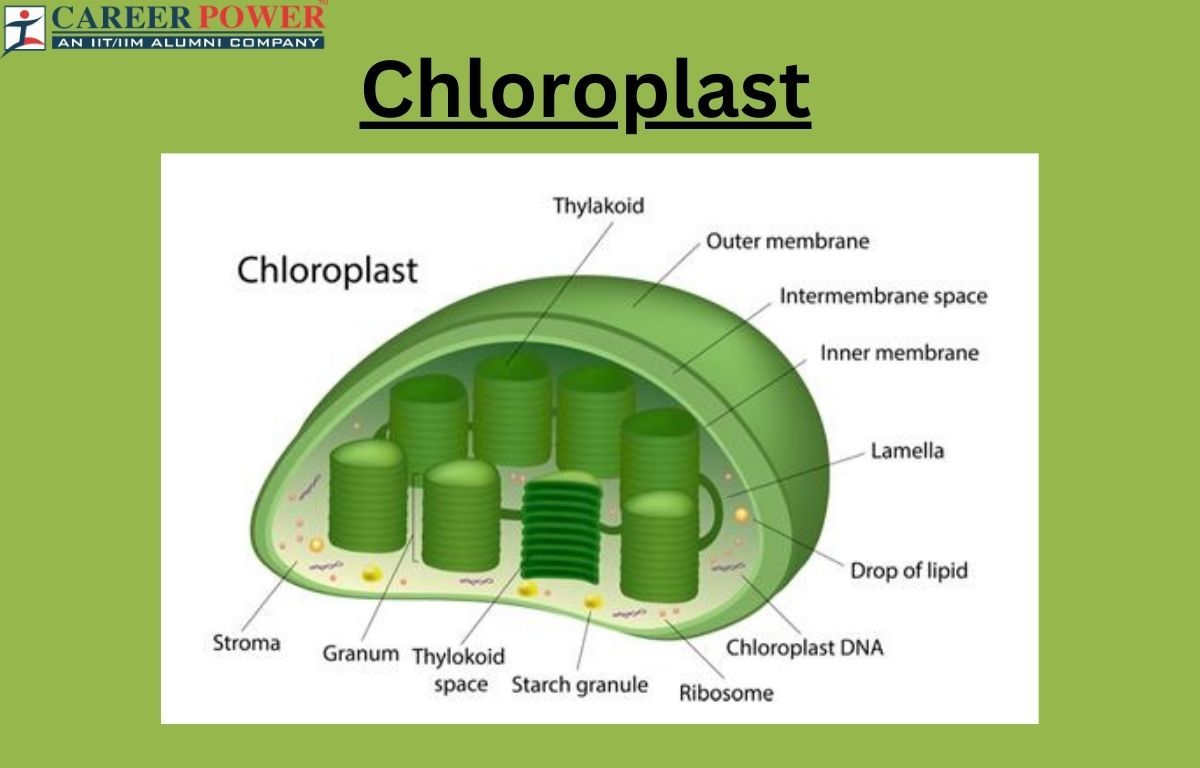
The Stroma Contains…
thylakoids, chloroplasts DNA, ribosomes, and enzymes for photosynthesis
Thylakoids
a network of interconnected sacs that contain chlorophyll
Granum
a stack of thylakoids
Endosymbiosis Theory
mitochondria and chloroplasts were formerly small prokaryotes that began living within larger cells
an endosymbiont is one organism that lives inside of another one
Evidence for the Endosymbiosis Theory
divide by binary fission (as do all prokaryotes)
contain their own DNA - with genes more like those from prokaryotes
membrane lipids are similar to those of modern prokaryotes
ribosomes that are the same size of prokaryotic ribosomes (smaller than ribosomes of eukaryotes)