Lecture 13 - Chromosomal Basis Inheritance
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Hereditary Factors
Another name for Genes
Chromosome Theory of Inheritance
Genes occupy specific loci on chromosomes
Chromosomes undergo segregation and independent assortment during meiosis
Mendel’s Laws of inheritance
The behavior of non-homologous chromosomes can account for the independent assortment of alleles for two or more genes located on different chromosomes.— law of independent assortment
law of segregation — Two alleles for the same gene are separated randomly during meiosis, this id due to the separation of homologous chromosomes in meiosis I
Sex Chromosomes
X and Y
Autosomal Chromosomes
Non-sex chromosomes (22 of them)
X-linked Genes
around 1,100 on found on the X chromosome
If an X-linked trait is due to a recessive allele, a female will express the phenotype only if she is homozgyous for that alelle
Heterozygous females are carrier for recessive trait
Female phenotypes between heterozygous and homozygous X-linked genes
Hemizygous
Refers to a male only needing one recessive X-linked gene in order to exhibit that phenotype
Males are more likely to exhibit X-linked recessive disorders
males are hemizygous so.
X-linked disorders
color blindness
muscular dystrophy
Hemophilia
Barr Body
Genes on ___ X-chromosome are not expressed. One X-chromosome is condensed into a compact _____.
Linked Genes
Genes that tend to be inherited together because they are located near each other on the same chromosome — crossing over is unlikely to happen, no independent assortment
Wild Type
Generally the dominant trait, but more specifically the more common trait found in nature. (Not on a sex chromosome)
Mutant Allele
Typically the recessive trait, less commonly found in nature (not on a sex chromosome)
Parental Phenotype
The phenotype of offpsirng match that of the parent
Non-parental phenotypes
Phenotype of offspirng is different than parent, this is due to genetic recombination
Crossing over
accounts for the recombination of linked genes — these recombination of genes provides new variation for natural selection
This genetic variation provides the “raw material” on which natural selection works.
•
If the traits conferred by particular combinations of alleles are better suited for a given environment, organisms possessing those genotypes will leave more offspring, and thereby pass the better suited genes on in greater quantities (percentages)
Genetic map
Ordered list of the genetic loci along a particular chromosome
Recombination Frequency
percentage of a recombinant offpspring, ______, depends on the distance between genes on a chromosome
the farther apart two genes are, the higher the probability that a crossover will occur between them and, therefore, the higher the recombination frequency.
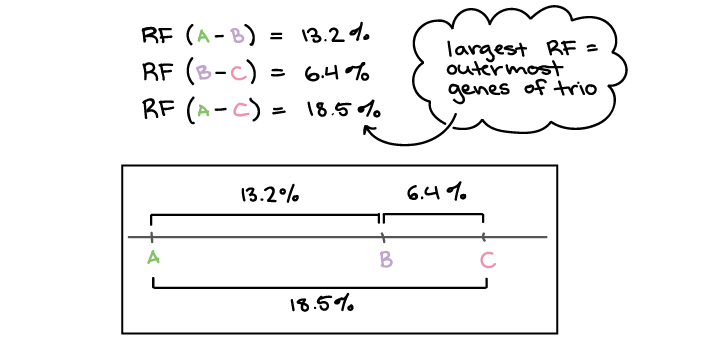
Linkage Map
Genetic map based on the recombination frequencies
dsistance between genes are map units
Nondisjunction
Leads to abnormal chromosme number — occurs when members of a homologous chromosome do not separate properly during meiosis I or sisster chromatids fail to separate during meiosis II. — results in aneuploidy
Trisomic vs Monosomic
Cell thats have three copies of a particular chromosome type… vs cells that have only one type of a particular chromosome
Deletion
Occurs when a chromosome segment is lost - missing a certain gene
Duplication
When a segment becomes repeated within a chromosome
producti of an unequal crossover are one chromosome with a deletion and one with a ____.
Inversion
Chromosomal fragments reattaches to the original chromosome but in the reverse orientation
Translocation
Chromosomal fragment joins a non-homologous chromsome
Down Syndrome
Three copies of chromosome 21 result in…
Klinefelter Syndrome
XXY male