Pharmacology of Smoking Cessation
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
nicotine
Nicotinic cholinergic receptor (nAChR) agonist with dose-dependent pharmacologic effects. Most affinity for the alpha 2 beta 2 type
effects of nicotine
-sympathomimetic
-catecholamine release by adrenal medulla
-increased BP, HR, CO, and oxygen consumption
low doses
What doses of nicotine can increase alertness and improve cognitive functioning?
higher doses
What doses of nicotine stimulate "reward pathway" in limbic system?
reward pathway
-initial pleasure
-after continued use, pleasure diminishes (used only to avoid withdrawal)
alpha 2 beta 2
predominant in the brain and the main receptor mediating nicotine dependence
reinforce behaviors that promote the survival of a species
What is the purpose of the reward pathway?
DA (pleasure)
What is the primary NT?
ventral tegmental area (VTA)
-in midbrain
-rewarding stimulus induces DA release from VTA projection neurons into NAc and prefrontal cortex
Nucleus accumbens (NAc)
helps regulate survival drives like food and thirst
amygdala
emotions, memory
prefrontal cortex
part of frontal lobe involved in many cognitive functions (memory, language, planning, decision making)
VTA
Nicotine from smoking acts in the _______ causing DA release in the NAc, amygdala, hippocampus, prefrontal cortex.
pre and post
Through the lungs, nicotine is absorbed into the systemic circulation, crosses BBB, and reaches _________-synaptic nACh receptors (in about 7 seconds!!).
nAChR
When nicotine binds the _________, it opens and allows entry of cations → depolarization →opening of voltage-gated calcium channels →release of NT, including dopamine (DA).
Physical dependence
When someone tries to quit smoking, they suffer insomnia, irritability, anxiety, weight gain, depression, difficulty concentrating, etc. This is called WITHDRAWAL, and it is an indicator of:
a. Addiction
b. Substance use disorder
c. Physical dependence
d. Reinforcement
e. Tolerance
substance use disorder
at least 2 of the symptoms in a given yr:
-impaired control
-social impairment
-risky use of substance
-pharmacological criteria
genetics
40-60% of the risk of SUD is mediated by ___________
addition
chronic, relapsing disorder characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use despite adverse consequences
pathology of SUD
involves functional changes to brain circuits involved in reward, stress, and self control
tolerance
-Decreased effect with repeating dose (pharmacological
adaptation)
-Expected biological phenomena with many drugs (abused and not)
physical dependence
if stopped, adaptive responses are now unopposed -> withdrawal
SUD
Engages in compulsive repetition of the experience despite negative long-term consequences (drug seeking)
SUD depends on:
-user (genetics, psychiatric disorders)
-environment
-drug (reinforcement and onset)
reinforcement
neuronal activation in reward areas with compulsive use
aversive conditioning
creating aversion to the addicted drug, bringing consequences or punishment closer to the reinforcement of drug use
neurotransmitter manipulation
manipulating NT in the reward pathway to modify cravings/withdrawal symptoms (antidepressants)
pharmacological substitution
substituting one substance that stimulates the brain reward pathway with another less addictive/less harmful (NRT and Varenicline)
1) reduction of cravings and withdrawal symptoms (anxiety, irritation, depression, ect.)
2) inhibition of the reinforcing effects of smoking
What are the goals of pharmacotherapy for smoking cessation?
first line therapies
-Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT)
-Varenicline (Chantix)
-Bupropion (Zayban)
second line therapies
-Clonidine
-Nortriptyline
Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT)
-less addictive and less harmful than smoking
-no immediate spike (most addictive admin)
constant
The patch provides the same net dose of nicotine, but time release results in ________ blood levels.
makes less reinforcement (spike) and craving (dip)
What does the constant moderate levels of DA in the brain from Nicotine Replacement Therapy do?
NRT MOA
-Selective nAChR agonist: activates α4β2 receptors in the VTA → DA release in the NAc.
-Mimics/replaces the effects of nicotine from tobacco → relief of withdrawal symptoms without the spike reinforcements
-Desensitizes nAChR → reduced effect of nicotine from cigarettes
admin of NRT
Absorbed through skin, mucous membranes, and lungs → Several dosage forms (gums, lozenges, transdermal patches, oral inhalers, nasal spray)
AEs of NRT
-nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, hypertension, and tachycardia
-Nausea and lightheadedness may indicate nicotine overdose.
-Patch: skin irritation (not due to nicotine) and sleep disturbances
CI with NRT
patients with unstable coronary artery disease, arrhythmias, recent MI or stroke, or active peptic ulcers
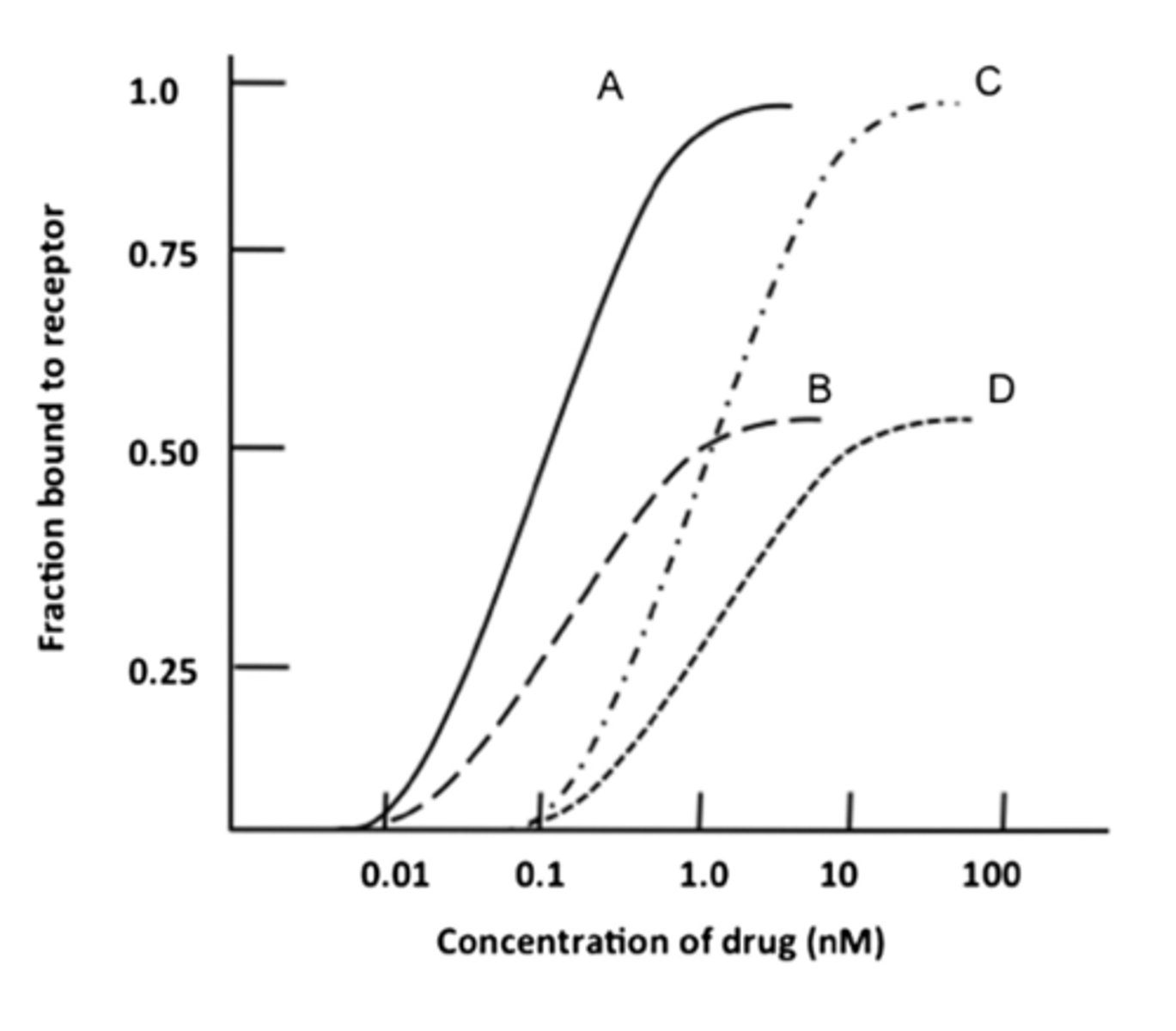
1.0 nM
What is the Kd of Nicotine?
0.1 nM
What is the Kd of Varenicline?
C
Which curve corresponds to nicotine?
A
What curve corresponds to Varencicline?
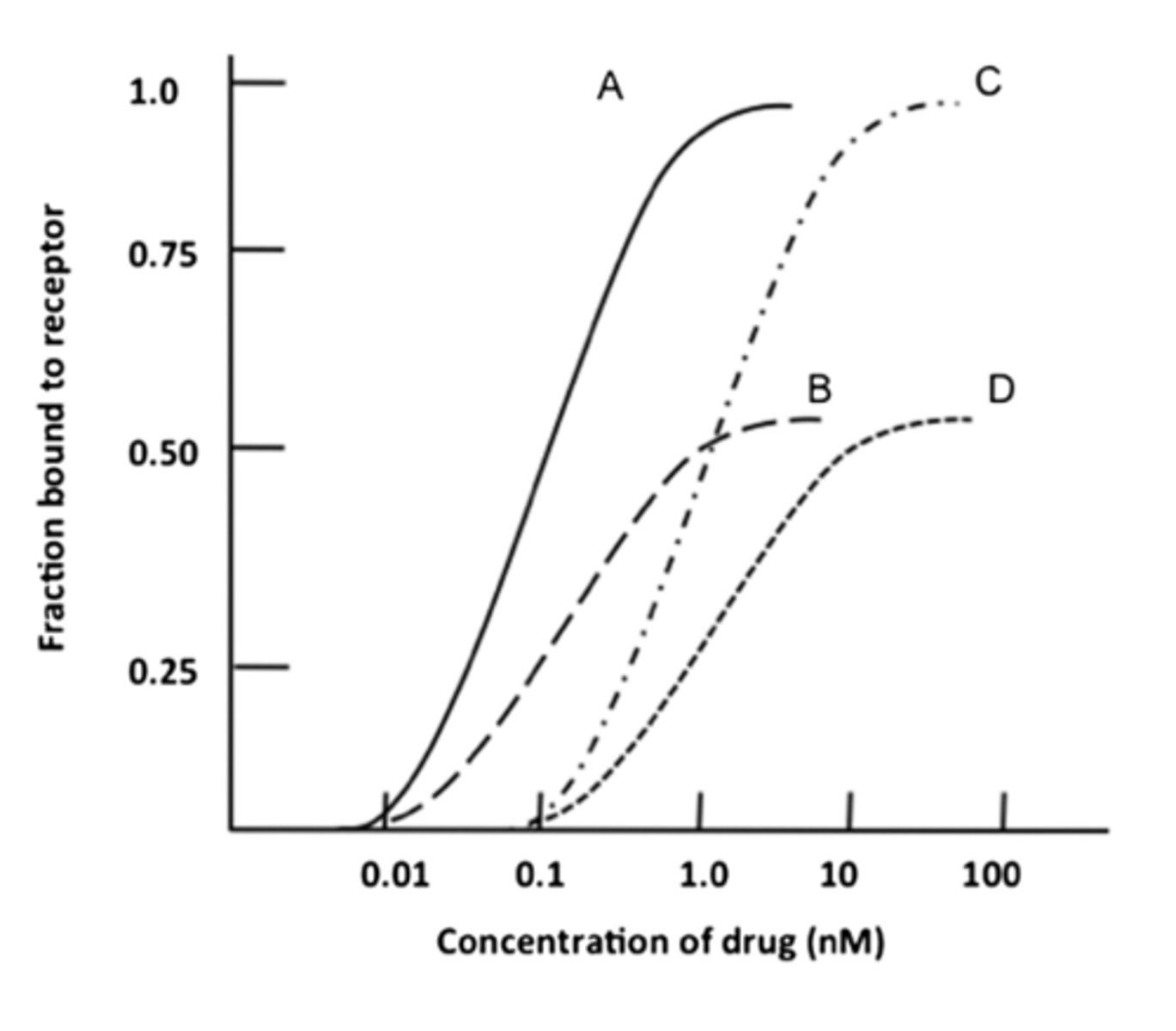
Kd
The concentration of drug that binds 50% of the receptors in the system
Varenicline MOA
-Partial agonist at α4β2 neuronal nAChR, highly selective, high affinity
-Causes the release of DA, and prevents binding of nicotine to alpha 2 beta 2 receptors (competition)
Increases DA release in the NA and prefrontal cortex (although to a lower extent than nicotine)→pleasure
How does Varenicline reduce craving and withdrawal?
relieve physical withdrawal symptoms and decrease the rewarding properties of nicotine
What is the goal of Varenicline?
AEs of Varenicline
-Nausea & headache (dose-dependent)
-Abdominal pain (minimized by taking w/ food & water), acne, agitation, insomnia, constipation, vivid dreams
-Caution: Serious psychiatric events, seizures
Bupropion
Norepinephrine Dopamine Reuptake Inhibitor (NDRI) -Unicyclic antidepressant
Bupropion MOA
-poorly understood
-Weak inhibition of neuronal reuptake of 5HT, NE, and DA
-Parent compound also acts presynaptically increasing catecholamine release (NE>DA; no 5-HT effects)
-Major metabolites (hydroxy) - inhibitor of NE and DA reuptake
increased dopaminergic and noradrenergic signaling
How does Bupropion mimic nicotine's effects?
non-competitive antagonist of nicotinic receptors
How does Bupropion diminish reinforcement of nicotine?
effects of Bupropion
-attenuates the fluctuations between pleasure and dysphoria → attenuates physical effects of nicotine withdrawal
-reduces cravings
-fewer mood symptoms and possibly less weight gain while withdrawing
-substitute for antidepressant effects
yes
Even though Bupropion is about as effective as nicotine patches can it be combined with nicotine patches?
PK of Bupriopion
-As with many antidepressants, takes weeks to reach steady state → start before quit date (at least 1 week).
-Metabolized by CYP2B6
AEs of Bupropion
-Activity on DA, 5-HT, and NE; → high BP, tachycardia, tremors, insomnia, weight loss, dry mouth, and headache.
-more pronounced in the first days if dose titration is not utilized
-Seizures in OD
-Serious psychiatric events (BW in young on antidepressants)
CIs with Bupropion
-pts on MAOis
-pts with seizure disorders
Nortriptyline and Clonidine
What are the off label smoking cessations?
Nortriptyline (Pamelor) MOA
Tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) → 5-HT & NE reuptake inhibition
PK of Nortriptyline
takes weeks to reach SS -> begin before quit date
AEs of Nortriptyline
Many!
-Although less than TCAs as a class.
-Anticholinergic and antihistaminergic effects:
• Sedation.
• Dry mouth.
• Blurred vision.
• Urinary retention.
• Lightheadedness
BP and HR prior and during therapy in elderly pts
What do you monitor with Nortriptyline?
CI with Nortriptyline
in pts taking or received MAOi in preceding 14 days
Clonidine (Catapres) MOA
-Centrally-acting agonist of presynaptic alpha 2 -R
- ↓ catecholamine output (DA, NE)→ ↓ sympathetic stimulation → hypotension and in general less catecholaminergic response
PK of Clonidine
oral or transdermal admin
Clonidine
-may reduce withdrawal symptoms
-6 trials which showed increase 9% smoking cessation rates
-increase chances of quitting but dose dependent rise in AE
AE of Clonidine
dose dependent
-dry mouth, sedation, fatigue, dizziness, constipation, hypotension
-abrupt discontinuation causes rapid increase in BP and symptoms of sympathetic overactivity
-gradual withdrawal is needed
-need to monitor BP, mental status, HR
alpha 4 beta 2 type nAChR
Nicotine causes addiction by stimulating the _____________ and inducing release of DA in the NAc.
pharmacological substitution and neurotransmitter manipulation
What are the 2 pharmacological strategies in smoking cessation?
pharmacological substitutions
-NRT
-Varenicline
neurotransmitter manipulation
-Bupropion
-Nortriptyline, Clonidine