ch07 rg astro solar system
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
geller
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
View of the solar system from above
Orbits are nearly circular
View of the solar system from the side
Orbits are all in nearly the same plane
Terrestrial planets
Four small inner planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars) Resemble Earth
Have hard, rocky surfaces with mountains, craters, valleys and volcanos.
Jovian planets
Four large outer planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune) Resemble Jupiter
The materials that make up these planets are mostly gaseous or liquid.
Visible “surface” features of a jovian planet are actually cloud formations in the planet’s atmosphere
Are terrestrial or jovian planets bigger?
Jovian planets
Have masses that range from tens to hundreds of times greater than the mass of any of the terrestrial planets.
Density definition
The mass of an object divided by its volume.
What does chemical differentiation suggest on density?
Low-density materials rise to the surface, high-density materials sank deep into Earth’s interior
Do terrestrial planets or jovian planets have a higher density?
Terrestrial planets —> Have dense iron cores
Which elements do the giant outer planets are composed primarily of?
Light elements such as hydrogen and helium
Which planets have interiors made mostly of gas and liquid and NO solid surface?
Jovian planets
Which planets DO NOT have moons?
Mercury and Venus
Small planets with low gravity can’t hold onto hydrogen and helium gasses.
A given planet’s size and mass has a corresponding ESCAPE SPEED.
Atoms or molecules moving at speeds ABOVE the escape speed simply leave the atmosphere of the planet. This prevents small planets from accumulating hydrogen/helium, which are the most abundant materials. (In fact, to keep a gas, its average molecular speed should be LESS than 1/6th of the ESCAPE SPEED)
Temperature of gas determines the average speed, and this temperature is determined by distance from the Sun
The largest moons
Moon
Io
Europa
Ganymede
Callisto
Titan
Triton
Moon, Io and Europa have relatively high average densities, indicating that these moons are made primarily of rocky materials.
By contract, the average densities of Ganymede, Callisto, Titan, and Triton are all relatively low
—> Contain substantial amounts of water ice (LESS DENSE THAN ROCK)
Jupiter’s satellite Io is the most geologically active world in the solar system FOR WHAT reason?
Due to its numerous volcanoes that continually belch forth sulfur rich compounds
The fractured surface of Europa, another one of Jupiter’s large satellites, was an early clue that…
That a worldwide ocean of liquid water lies beneath its icy surface.
Titan (Saturn’s moon) fun facts
Liquid methane and ethane —LAKES
Has a “methane cycle” analogous to Earth’s hydrological cycle
In Titan’s low gravity, GRAPE-SIZED rain drops would slowly fall to the ground!
With light-weight wing attachments to arms, humans could FLY around in Titan’s low-gravity and thick atmosphere!
Titan has ICE VOLCANOES
Cryovolcanism
Titan has 100 km “sand” dunes with grains of?
Water-ice mixed with hydrocarbons
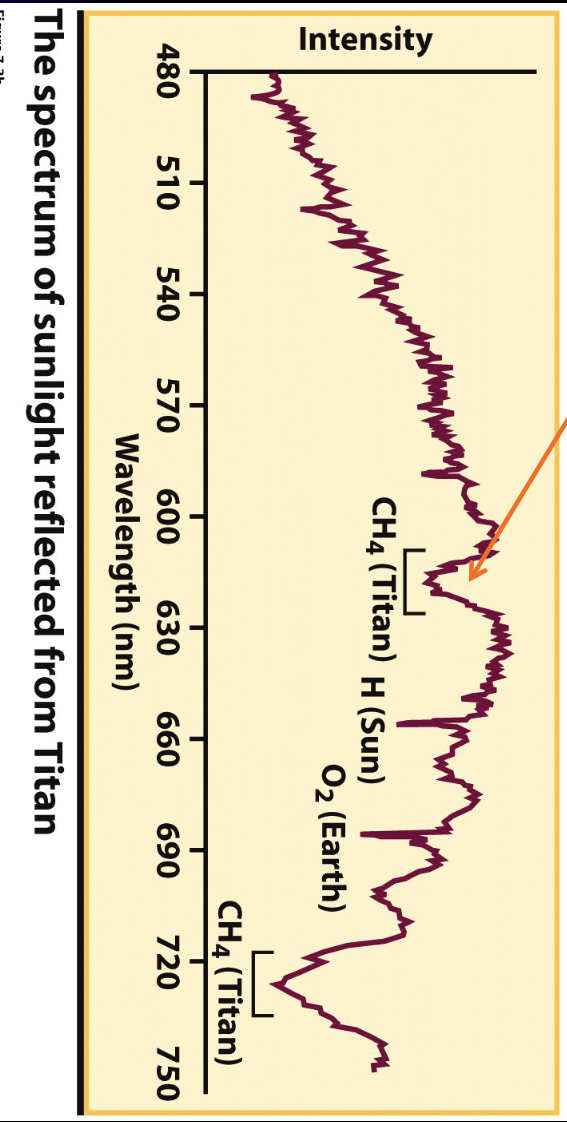
The absorption lines of methane (CH4) are produced in
Titan’s atmosphere
The absorption line of oxygen (O2) is produced in
Earth’s atmosphere
The absorption line of hydrogen (H) is produced in
Sun’s atmosphere
Titan lines Doppler shifts back and forth
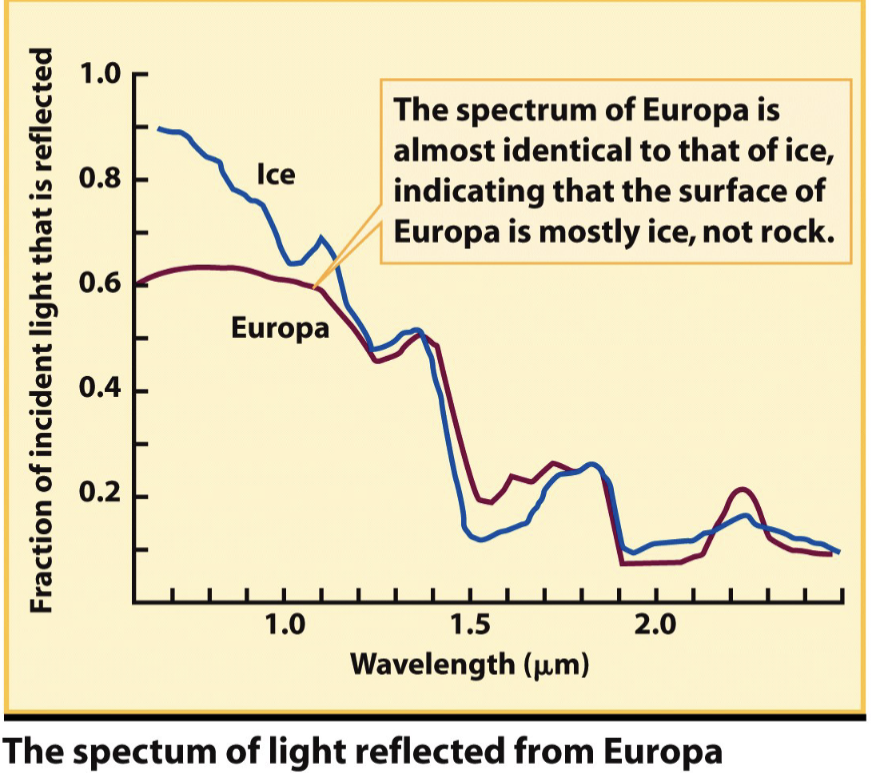
The spectrum of Europa is almost identical to that of ice, indicating that its surface is MOSTLY ice, not rock
While Jupiter and Saturn lack a solid surface, their many moons contain
A rich variety of features
On Earth, spectroscopy is a very useful tool for assessing
vegetation and greenhouse gases in our atmosphere
How does spectroscopy help us determine the atmosphere of a planet?
Look at particular wavelengths absorbed AND the amount of light absorbed at these wavelengths
Both of these depend on the kinds of chemicals present in the planet’s atmosphere and the abundance of those chemicals.
What molecules are dominant in Titan’s atmosphere?
Titan’s ultraviolet spectrum shows nitrogen molecules (N2) are dominant
Titan’s spectral lines includes a variety of molecules that contain carbon and hydrogen
What heavy elements are the terrestrial planets made of?
Iron
Oxygen
Silicon
Magnesium
Nickel
Sulfur
Distance from the Sun (Terrestrial VS Jovian)
Terrestrial —> LESS than 2 AU
Jovan —> MORE than 5 AU
A planet’s surface temperature is related to its distance from the Sun
H2 (hydrogen) and He (helium) are gaseous EXCEPT at extremely LOW temperatures and extraordinarily HIGH temperatures
Rock-forming substances such as iron and silicons are SOLIDS except at temperatures ABOVE 1000 K.
Why do massive and slow moving molecules such as CO2, N2, O2, and water vapor (H2O) surround the terrestrial planets?
Atmospheric temperatures are HIGH, low-mass hydrogen molecules and helium atoms move so SWIFTLY that they can ESCAPE from the WEAK gravity of the planets.
Asteroids
Found in the inner solar system
Trans-Neptunian objects
Found beyond Neptune in the outer solar system and contain BOTH rock and ice
Comets
Mixtures of rock and ice that originate in the outer solar system that can venture close to the Sun
BLUISH tail of GAS
WHITE tail of DUST
TRANS-NEPTUNIAN
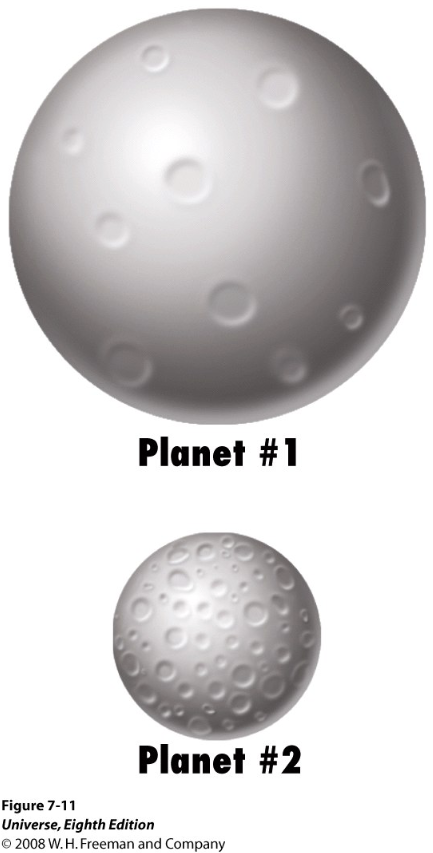

What determines how smooth versus cratered a planet or moon surface appears?
Big planets had longer period of volcanism to erase craters!
—> expect “big = smooth” and “small = cratered”
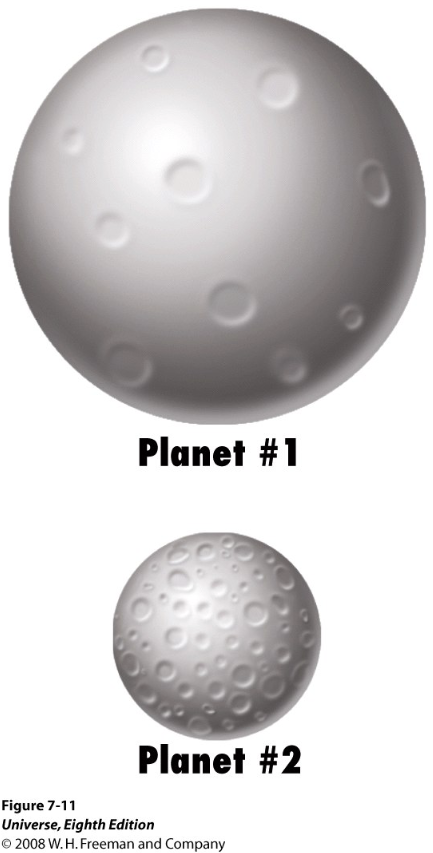

Compared to planet #1, planet #2:
Has ½ the radius
Has ¼ the surface area (so it can lose heat only ¼ as fast)
But has only 1/8 the volume (so it has only 1/8 as much heat to lose)
Hence compared to planet #1, planet #2:
Will COOL OFF MORE rapidly
Will sustain LESS geologic activity
Will have MORE CRATERS
Where is the asteroid belt located?
Between Mars and Jupiter
Kuiper Belt
Extends from around the orbit of Pluto to about 500 AU from the Sun
Most Trans-Neptunian objects orbit here
Oort Cloud
Forms a spherical “halo” around the solar system, extends to 50,000 AU from the Sun
Meteroids
Smaller craters
What do magnetic fields tell us about a planet?
A planet (or moon’s GLOBAL magnetic field comes from electrical currents flowing in a molten interior!
This allows use to measure magnetism on the outside and learn about the inside.
Unexpected magnetism on Mars
Suggests (past) plate tectonics!
Magnetic fields for terrestrial planets
Mercury —> WEAK magnetic field
Venus —> NO magnetic field
Earth —> MODERATE, due to liquid iron core
Mars —> NO magnetic field
Atmosphere for terrestrial planets
Mercury —> NO atmosphere
Venus —> Carbon Dioxide
Earth —> Nitrogen, Oxygen
Mars —> Carbon Dioxide
Magnetic field for Jovian planets
Jupiter —> STRONG, due to liquid metallic hydrogen
Saturn —> STRONG, due to liquid metallic hydrogen
Uranus —> MODERATE, due to dissolved ions
Neptune —> MODERATE, due to dissolved ions
Layout of Solar System
Inner terrestrials
Asteroid belt
Outer-giants
Trans-Neptunian objects
Kuiper-belt ice balls
Oort Cloud

The most intense planetary magnetic field in the solar system is that of ?
Jupiter
Liquid metallic hydrogen
Hydrogen compressed to such a density that it behaves like a Liquid Metal