Science - Tectonic plates
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
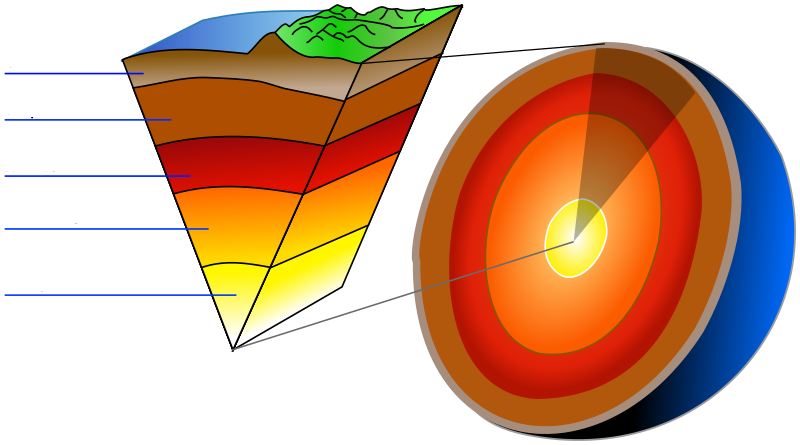
Order of layers of the Earth
crust, upper mantle, lower mantle, outer core, inner core
Crust
Outermost layer of the Earth, is made out of thin rock. 2 types: continental and oceanic
Upper/Lower mantle
Earth’s middle layer
Outer core
Fluid layer outside the inner core made of iron and nickel
Inner core
Innermost layer of inner and outer core, is solid due to high pressure
Lithosphere
Earth’s outer zone made up of rock. Consists of the crust and upper mantle
Asthenosphere
The thin zone just below the lithosphere, is hotter and weaker and acts like magma
Continental drift
The movement of continents due to tectonic plates seperating over time
The man who published the theory of continental drift
German meteorologist Alfred Wegner
Origins of Alfred Wegner’s theory
In 1912, Alfred noticed that South America’s and Africa’s Eastern coasts fit like a puzzle
Urkontinent
Super continent
Pangea
All-Earth, continents were connected for 160,000,000 years
Mountains that are about 500,000,000 years old
Highlands, Little Atlas mountains and Appalachian mountains
When did Himalayas begin forming
50,000,000 years ago
Convection
The motion of a fluid in response to heat. As a liquid gets hotter, it rises while cooler liquid floats down
Seafloor spreading
When the seafloor starts to seperate, molten magma rises from the mantle and creates new oceanic crust
What happens when 2 oceanic plates seperate
Rifts and valleys form along ocean ridges
Subduction
When 1 tectonic plate converge underneath another, due to converging plates. Oceanic is more dense and sinks underneath
What forms when 2 oceanic plates/continental-oceanic plates collide
Forms volcanoes
Types of subduction
Continental-oceanic or oceanic-oceanic
Convergant boundary
When 2 plates collide towards each other
Properties of convergent boundaries
Can be subduction, slow movement, can create mountains, high areas of earthquakes
Divergent boundary
When 2 tectonic plates get pulled and seperated
Properties of divergent boundary
Can be seafloor spreading, can create volcanoes, weak earthquakes
Rift
The zone where divergent boundaries occur
Transform boundary
When 2 tectonic plates slide across each other
Properties of transform boundary
Can cause earthquakes, areas are also called faults
Volacno
A rupture in the Earth’s crust which can release magma, volcanic rock, ash and gas
Ring of fire
75 volcanoes around the boundary of the Pacific Plate
How many volcanoes are around the world
600+ volcanoes, 50 erupt per year
Earthquakes
A buildup of pressure and release of energy at the Earth’s crust
Epicentre
The point on the Earth’s surface above the focus
Focus
The point under the crust where Earthquakes originate
Intensity
Measure of destruction of an earthquake
Magnitude
Measure of energy released of an earthquake
Moment magnitude scale
A logarithmic scale used to compare energy released by earthquakes
Tsunami
A long, high sea wave caused from earthquakes
Seismogram
A record of the seismic from an earthquake, measured with a seismograph or seismometer
Properties of primary waves
Fastest seismic wave, longitudinal, travels through solids, liquids and gases