Scrotum notes
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
Testicles arise in the upper fetal abdomen near the developing kidney. By what month of gestation the testicles move to the level of the bladder?
4th month
Descend into the scrotum around the ________ of gestation through the inguinal canal.
7th month
True/False: Descent, on occasion, may be delayed until the first few weeks of neonatal life.
true
The scrotum is a sac of cutaneous tissue that supports the testicles, or testes and ____________ the paired organs of reproduction.
the epidydimis
The testicles (testes) are the male gonads and are classified as both endocrine and exocrine glands. Why?
• At the onset of puberty, the testes produce testosterone, which causes growth in the male sex organs and development of secondary male sex characteristics such as body hair and voice deepening (endocrine function).
•The testes also produce sperm, which are transported through a network of ducts (exocrine function) that store and transport the sperm.
What is layer of muscle fibers beneath scrotal skin and divides scrotum into 2 chambers?
Dartos
What is scrotal raphe?
Division of the chambers in the scrotum
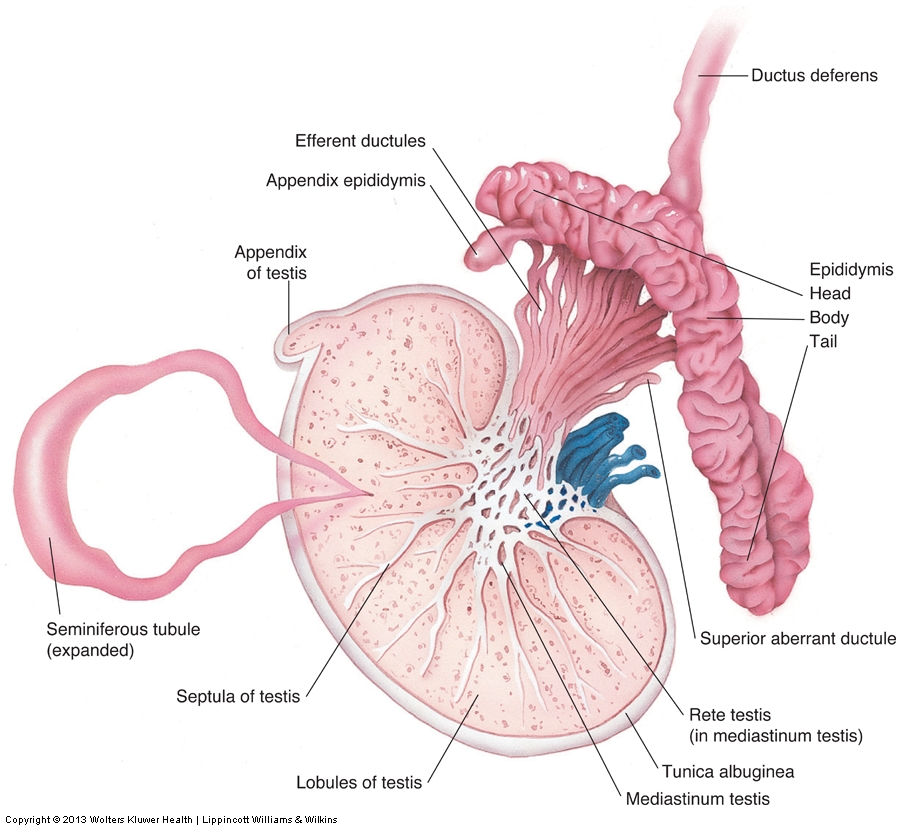
What is the anatomy of the testis?
•Symmetric, oval-shaped glands residing in the scrotum
•When a male is between the ages of 12 and 17 years, the testicle undergoes rapid growth.
•Prior to age 12, the average testicular volume is less than 5 mL.
•After the male reaches maturity, the average testicular volume is approximately 25 mL, with the testicle weighing between 10 g and 15 g.
•The testicle gradually decreases in size with advancing age.
What is the average adult size of testis?
measures 3-5 x 2-4 x 3 cm
Each testis divided into what?
250 to 400 conical lobules containing the seminiferous tubules
Seminiferous tubules converge at apex of each lobule and anastomose to form ___________ in mediastinum.
rete testis
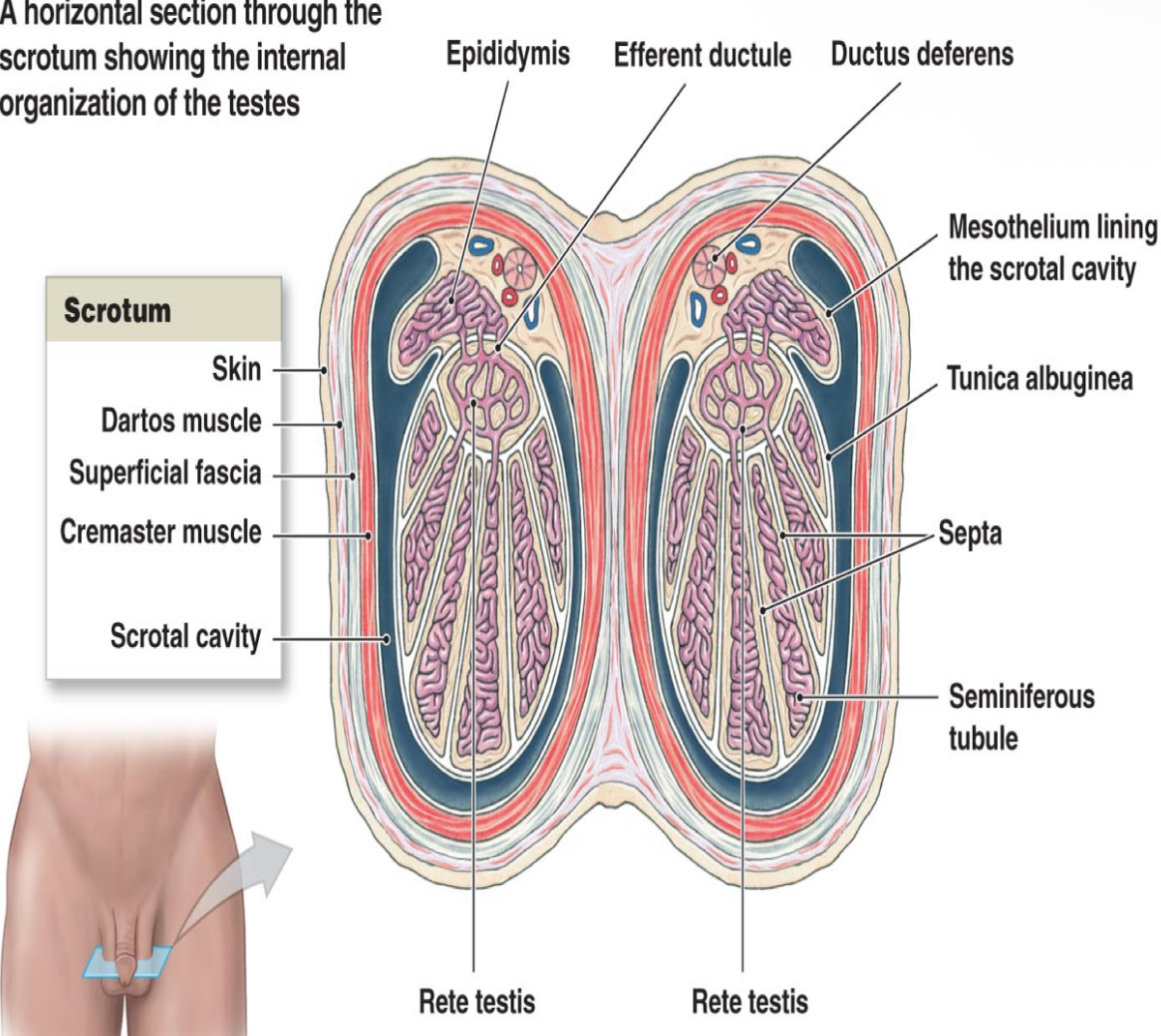
Rete testis drains into head of epididymis through ________. They carry seminal fluid from testis to epididymis.
efferent ductules
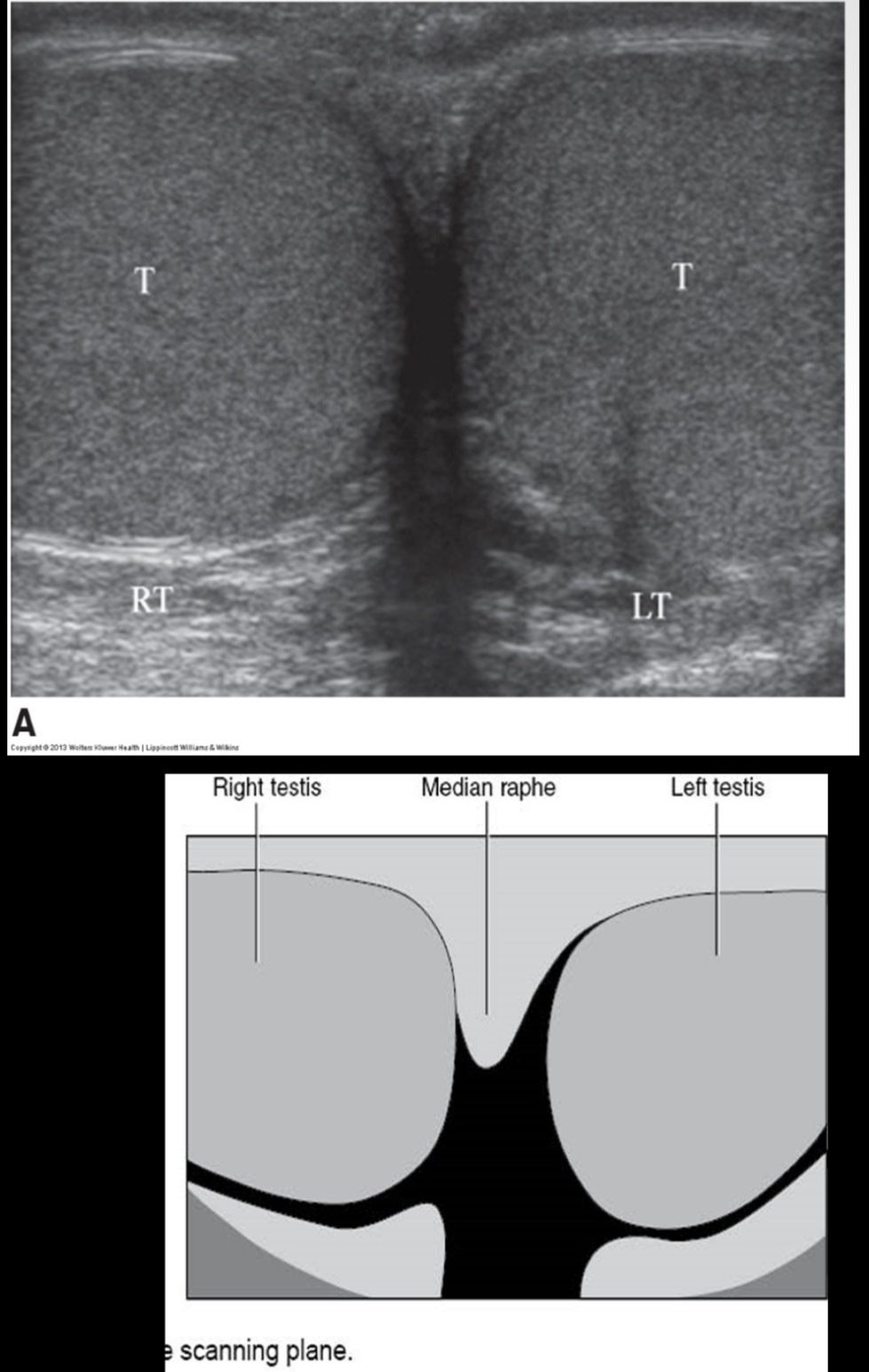
How do the testes normally appear sonographically?
testes appear as smooth, medium gray structures with fine echo texture (similar to the liver)
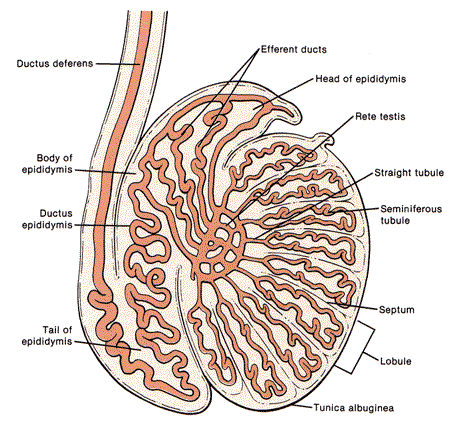
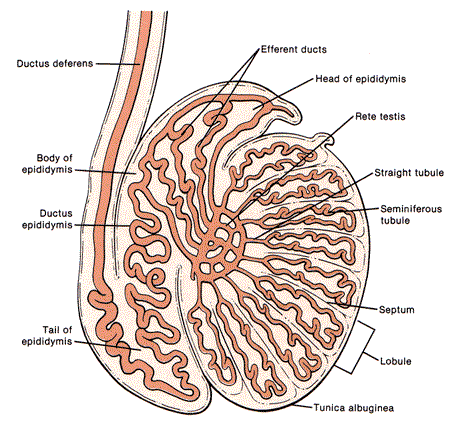
What does the following describe?
• is curved, 6-7 cm in length, posteriolateral to testis
–Head – AKA globus major – adjacent to superior pole of testis and largest portion of epididymis
–Body – AKA corpus – adjacent to the posterolateral margin of testis
–Tail – AKA globus minor – loosely attached to lower pole of testis by areolar tissue
anatomy of Epididymis
What formed by 10-15 efferent ductules from rete testis that join to form a single convoluted duct, duct forms the body and majority of the epididymis, measuring 600 cm long
ductus epididymis
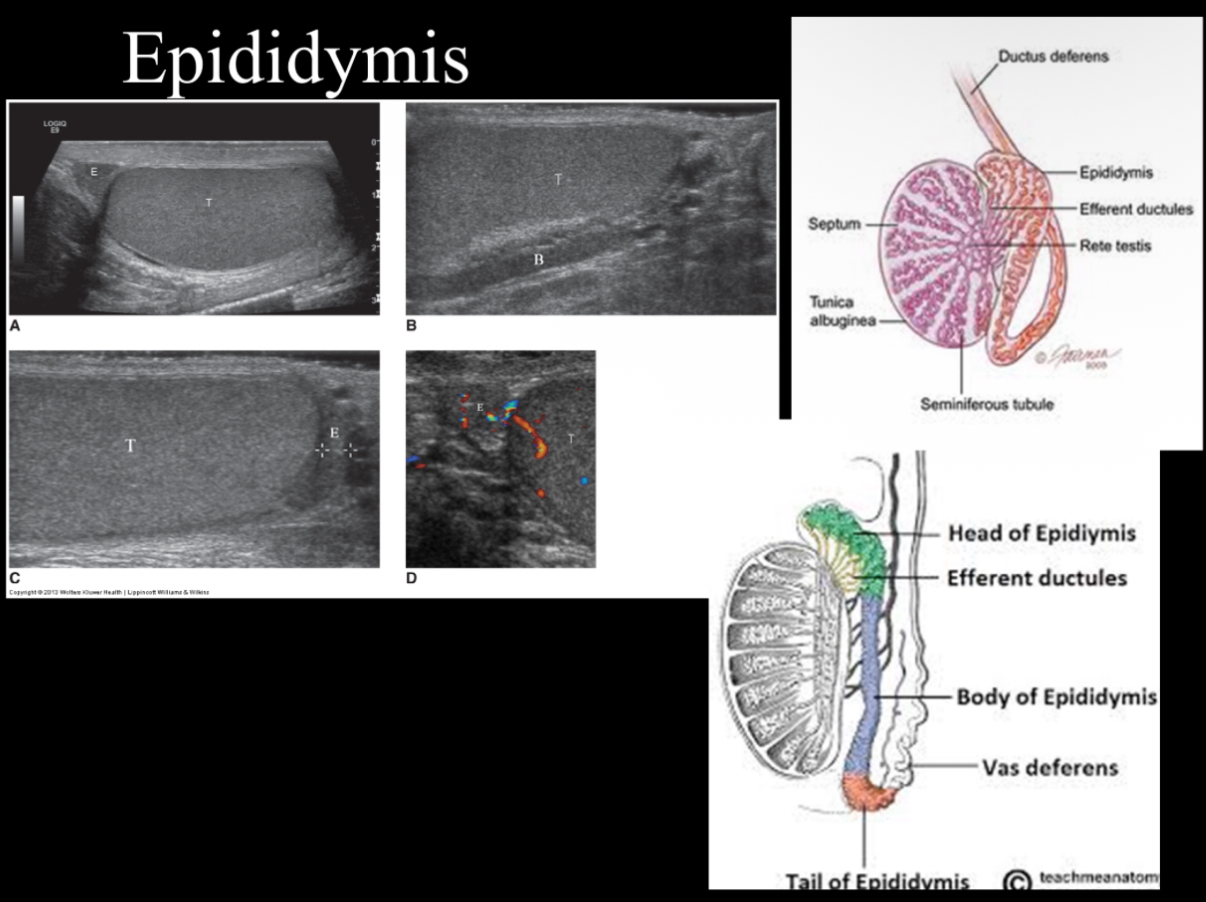
Body tends to be isoechoic or slightly less echogenic than globus major and testis. What does epididymis look sonographically?
isoechoic or hypoechoic than the testis with a coarse echotexture
Globus major measures ____________ in diameter and lies lateral to superior pole of testis
10-12 mm
True/False: Body measures less than 4 mm in diameter, usually 1-2 mm
true
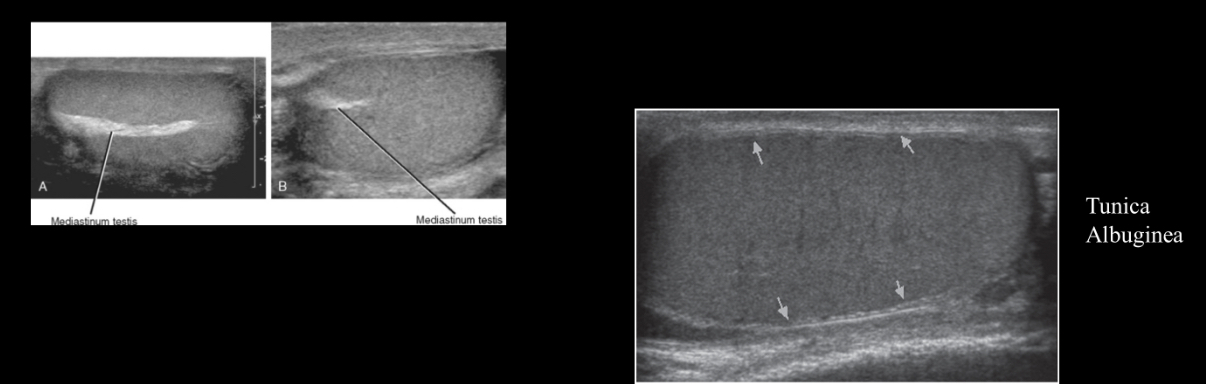
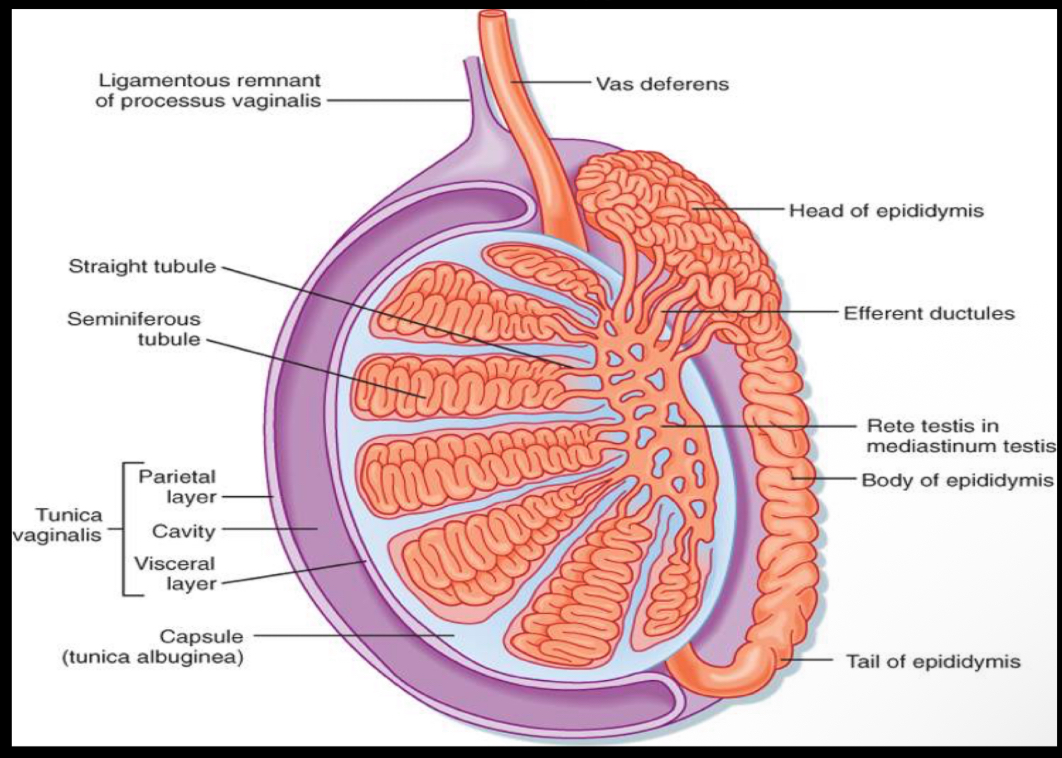
What fibrous capsule surrounds the testicles?
tunica albuginea
Septations arise from tunica albuginea to form what, which is seen as an echogenic linear band extending longitudinally within the testicle?
(hint: it forms the support for the testicular vessels and ducts entering and exiting the testicle)
mediastinum testis
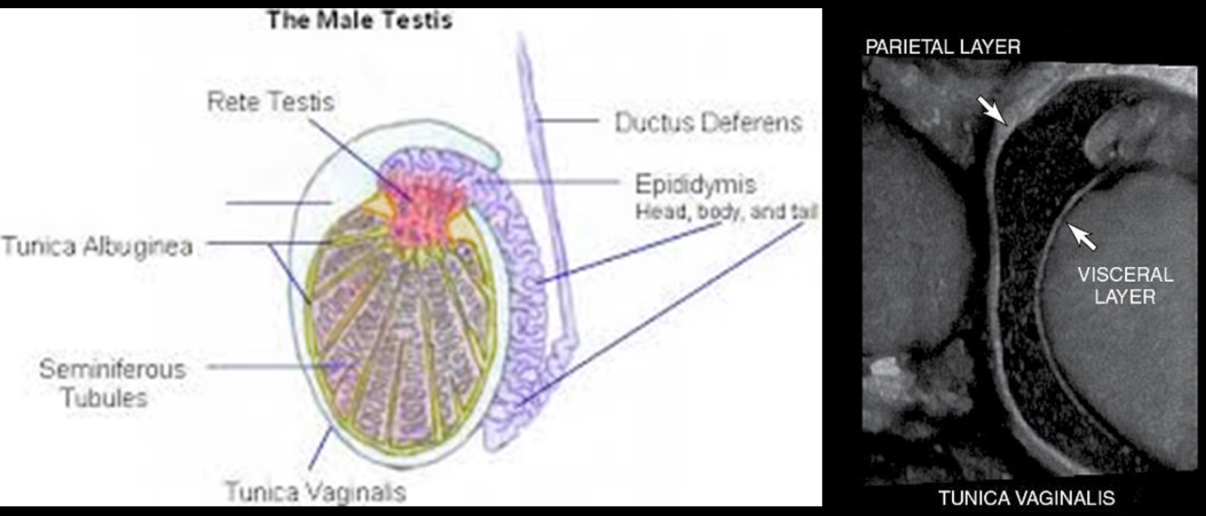
What is a saccular extension of peritoneum in chambers?
–Inner, visceral layer covers testis and epididymis
–Outer, parietal layer lines chamber
tunica vaginalis
What is the path of sperm?
(Santa Took Rudolph’s Eggs Down the Vent)
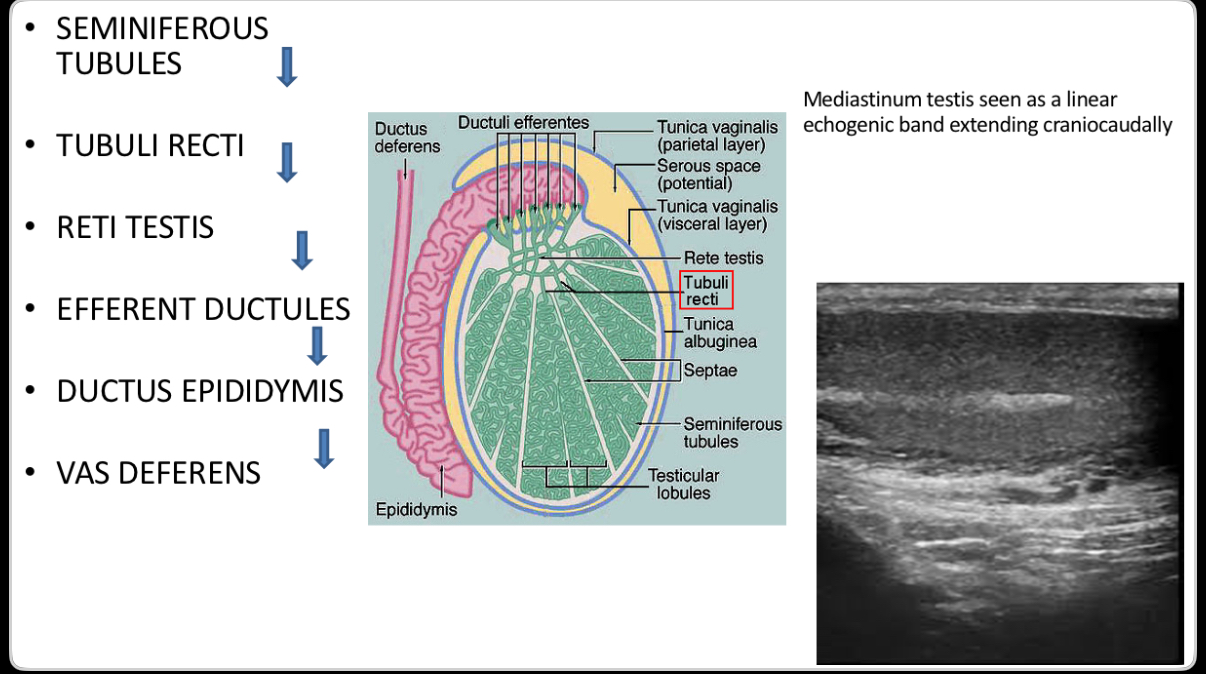
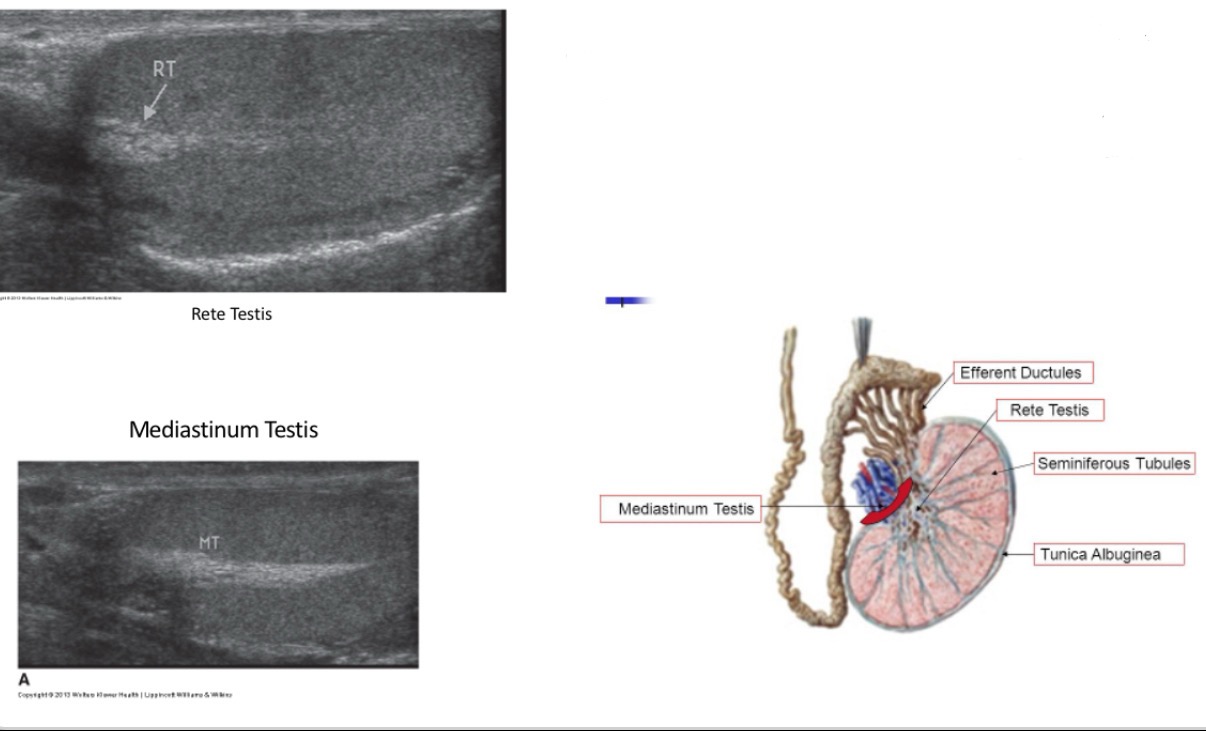
The _______ is an anastomosing network of delicate tubules located in the hilum of the testicle (mediastinum testis) that carries sperm from the seminiferous tubules to the efferent ducts. The efferent ductules carry the seminal fluid from the ______ to the epididymis.
rete testis
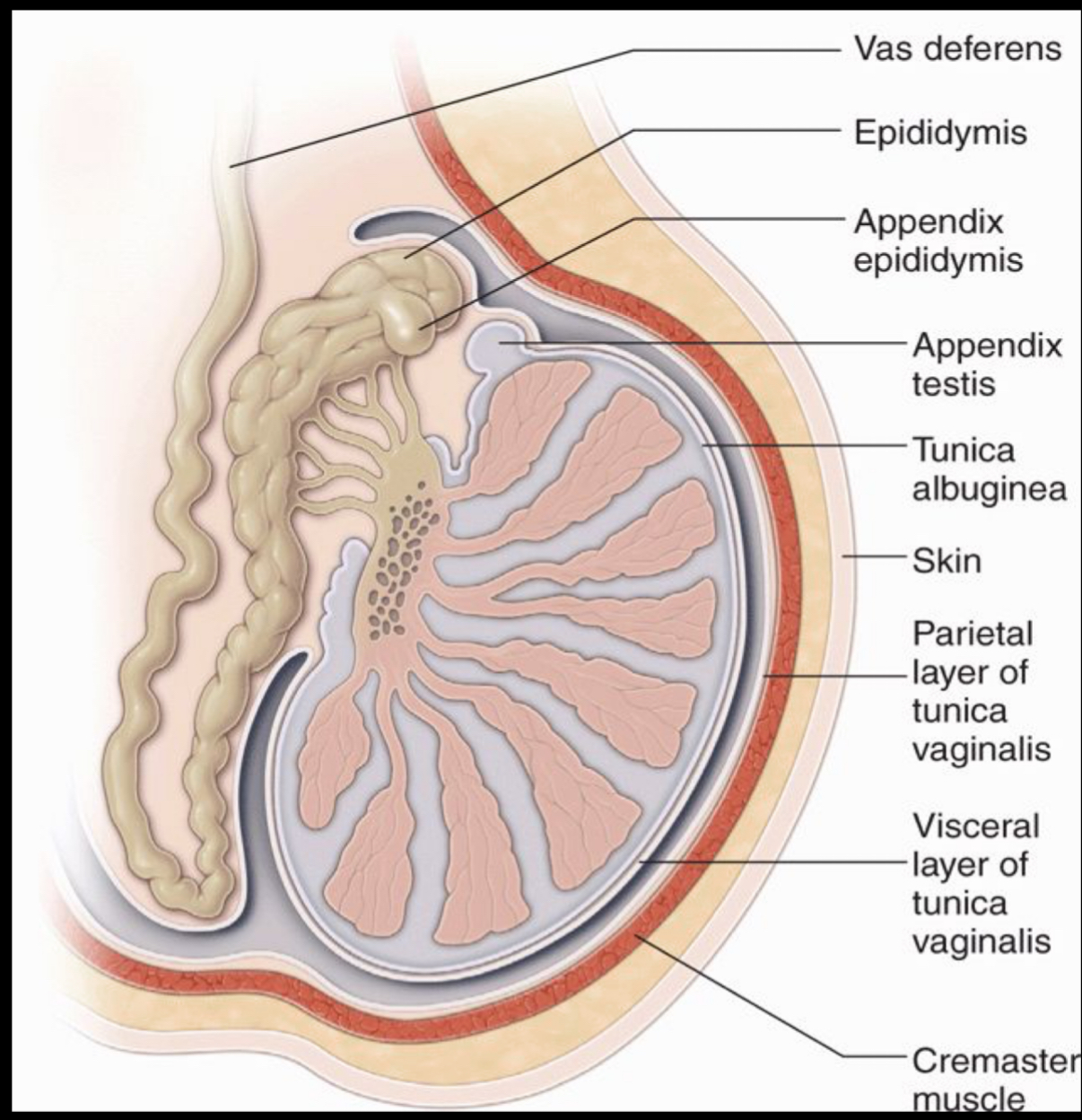
What is remnant of Mullerian duct, small ovoid structure beneath head of epidydmis?
–More easily seen when hydrocele is present.
–Torsion of this appendage can occur in boys aged 7- 12 years resulting in a blue dot sign
appendix testis
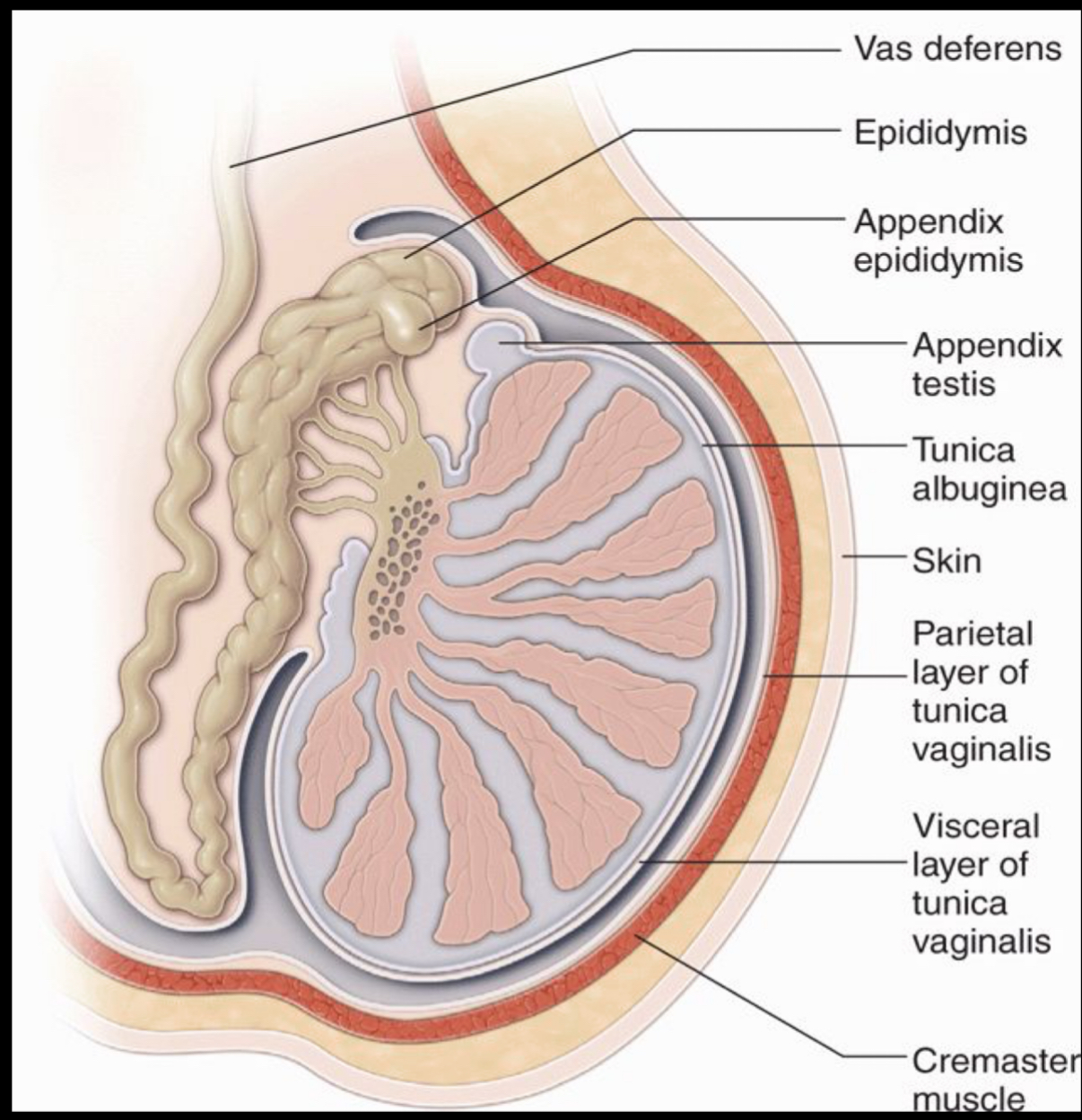
What represents a detached efferent duct, a small stalk projecting off epididymis?
–Derived from Wolffian duct.
appendix epididymis
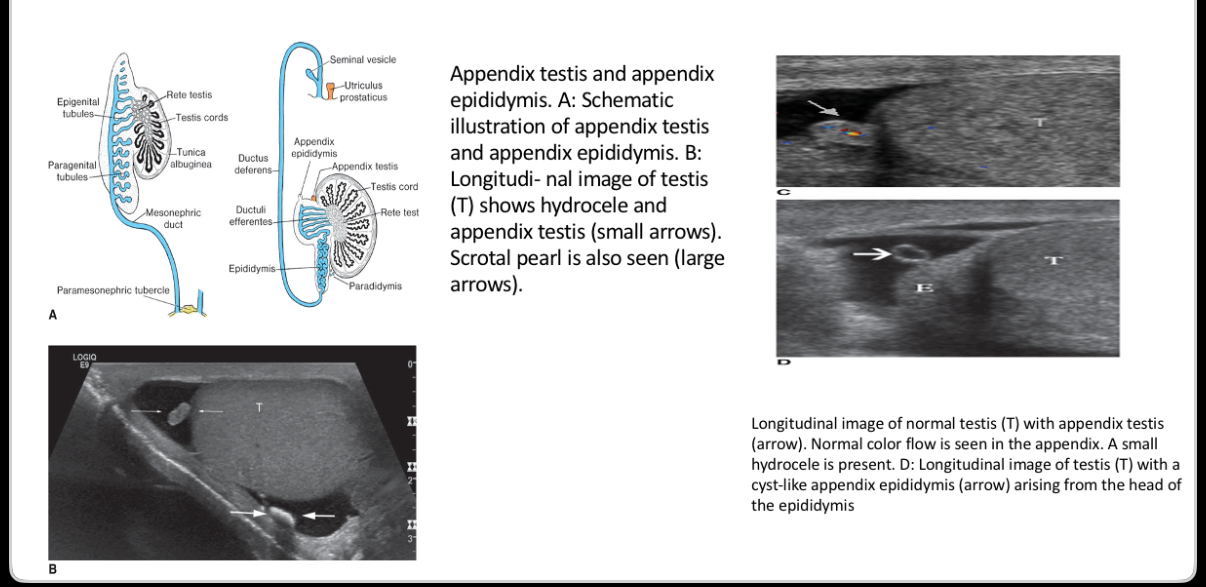
What is the following an image of?
Appendix Testis and Appendix Epididymis
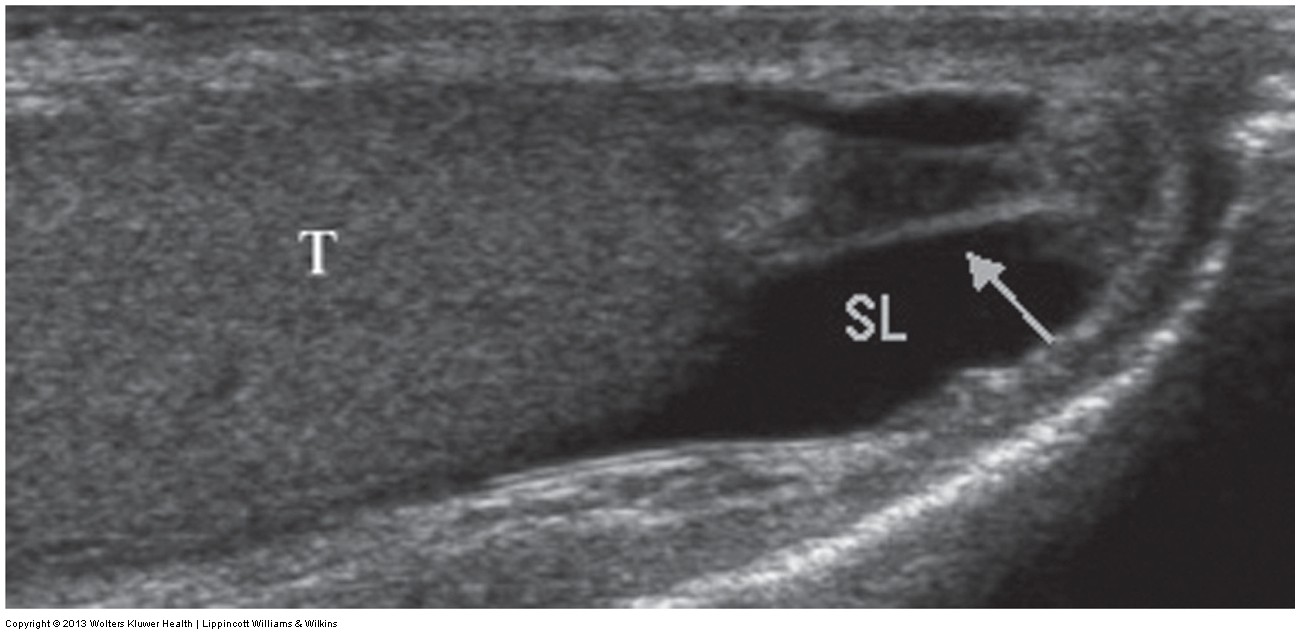
What does the following describe?
extends from the inferior pole of the testis and tail of the epididymis to the skin of the scrotal wall.
It secures the testis, tethering it in place and limiting the degree to which the testis can move within the scrotum.
can be seen in the presence of a hydrocele.
The sonographic appearance is an echogenic band extending from the caudal end of the testis to the scrotal wall.
scrotal ligament
What originate from aorta feeds testis and have low resistance flow?
Right and Left Gonadal Arteries
originates from internal iliac and feeds epididymis and vas deferens
deferential artery
What originates from external iliac artery; feeds peritesticular tissues?
Cremasteric Artery
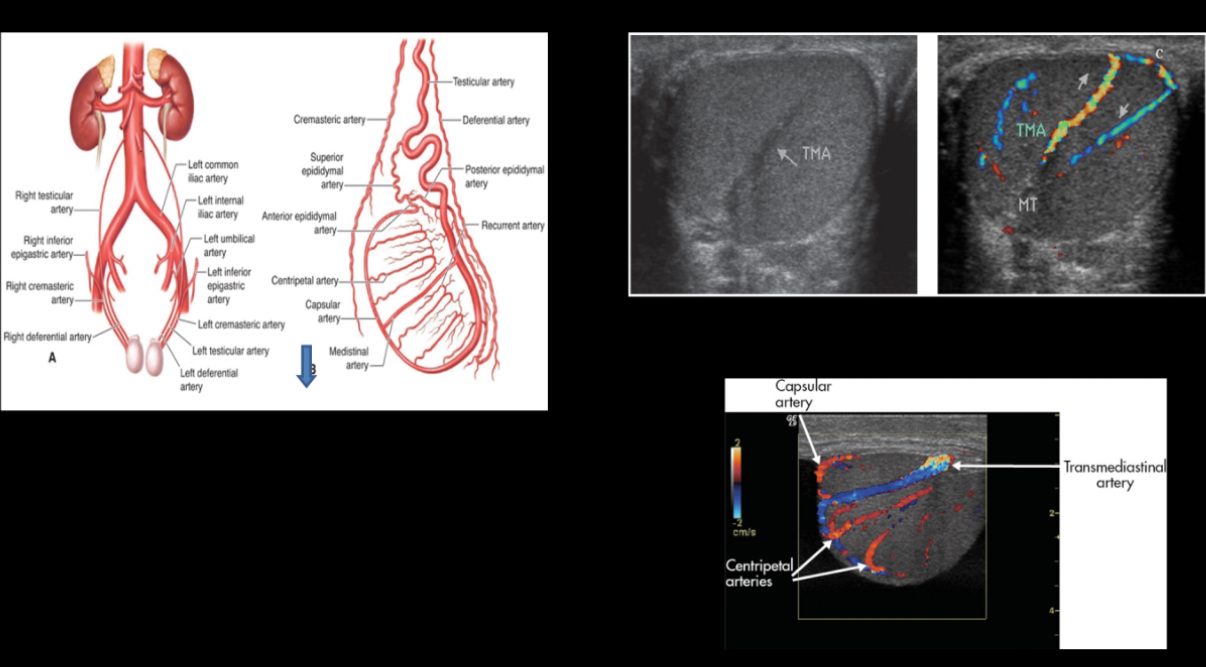
What courses along testicle periphery and produces branches called centripetal arteries?
Capsular artery
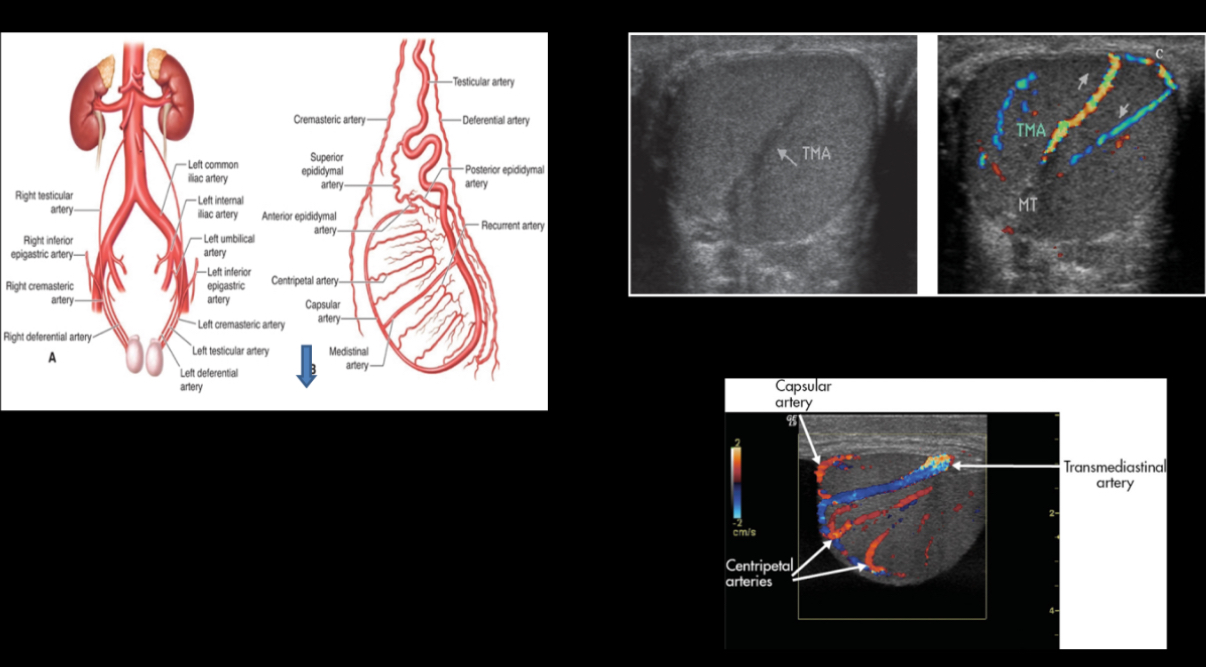
What course through the parenchyma to deliver oxygenated blood to the tissues; these arteries are sampled with Doppler?
Centripetal arteries
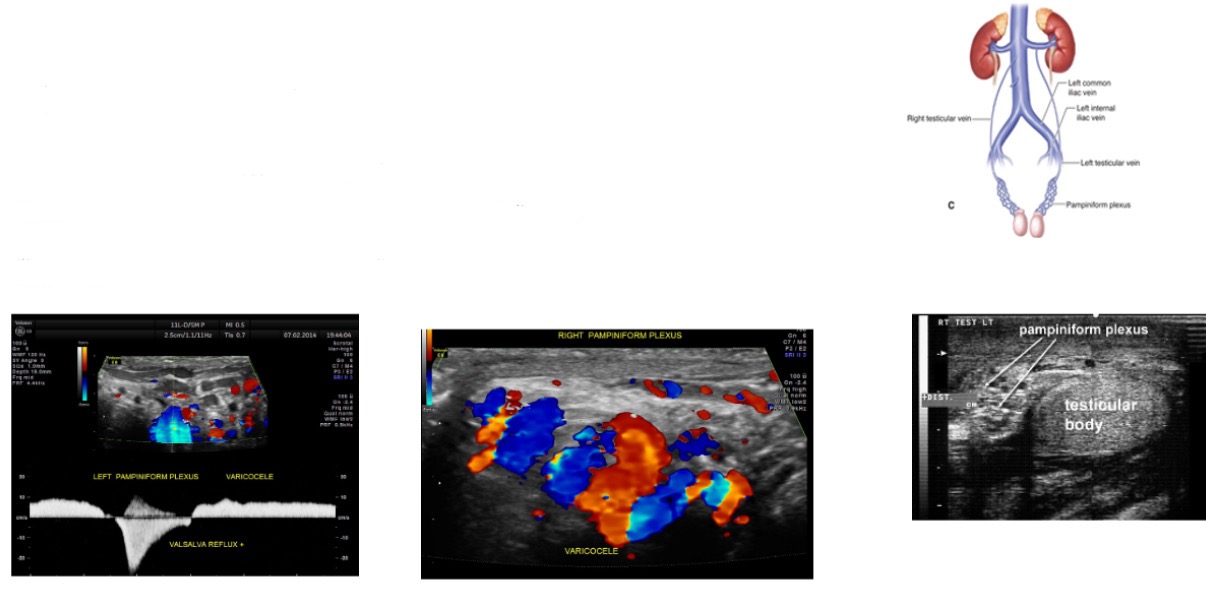
Venous drainage of the scrotum occurs through _________. Pampiniform plexus exits from mediastinum testis and courses in spermatic cord.
veins of Pampiniform plexus.
What slightly increases venous flow in a normal patient?
valsalva maneuver
Right testicular vein drains into….
Inferior vena cava (IVC)
Left testicular vein joins….
left renal vein
What drains into pelvic veins?
Deferential vein
What drains into tributaries of epigastric and deep pudendal veins?
Cremasteric vein
Normal veins of the pampiniform plexus measure less than _____ in diameter.
2 mm
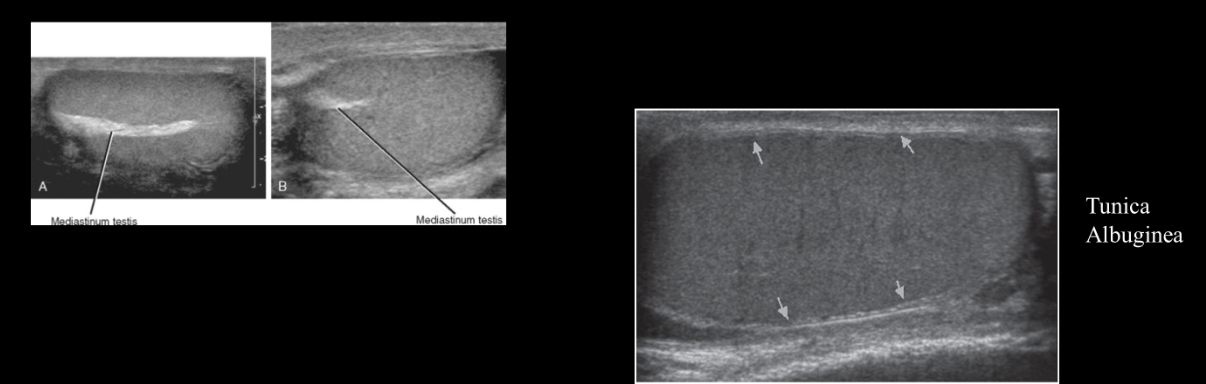
What is the dense fibrous capsule that surrounds the testis?
tunica albuginea
Septula arise from the tunica albuginea to form the ___________ which provides support for testicular vessels
mediastinum testis
Each testis contains approximately 840 seminiferous tubules that converge to form 20-30 larger _________ which form channels called the rete testis that carry the seminal fluid from testis to epididymis
efferent ducts
What layer does the following describe?
•Extension of the peritoneum into the scrotal sac
•Visceral Layer-inner layer covering the testes, epididymis and lower part of the spermatic cord
•Parietal Layer-lines the walls of the scrotal pouch
•Small amount of fluid in the space between the layers to assist in movement
Tunica Vaginalis
What layer does the following describe?
Thin layer of tissue that is in direct contact with the testicular tissue
Folds of this layer form sections within the testes; forms the mediastinum testis (similar to a hilum)
The rete testes is a series of channels within the mediastinum
Blood vessels and ductules enter/exit the testicle at the mediastinum
The visceral layer of the tunica vaginalis covers the tunica albuginea
Tunica Albuginea
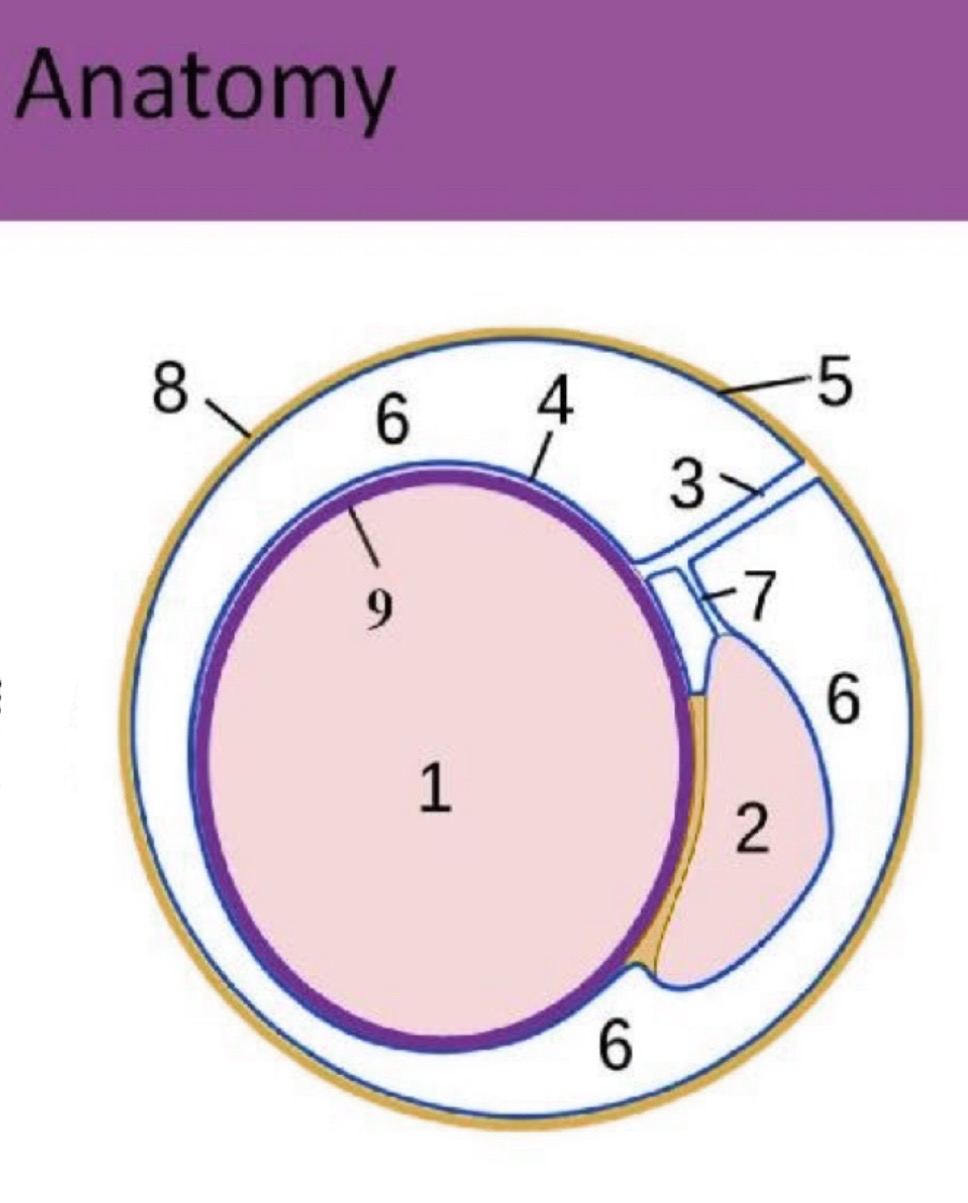
What is #1?
testicle
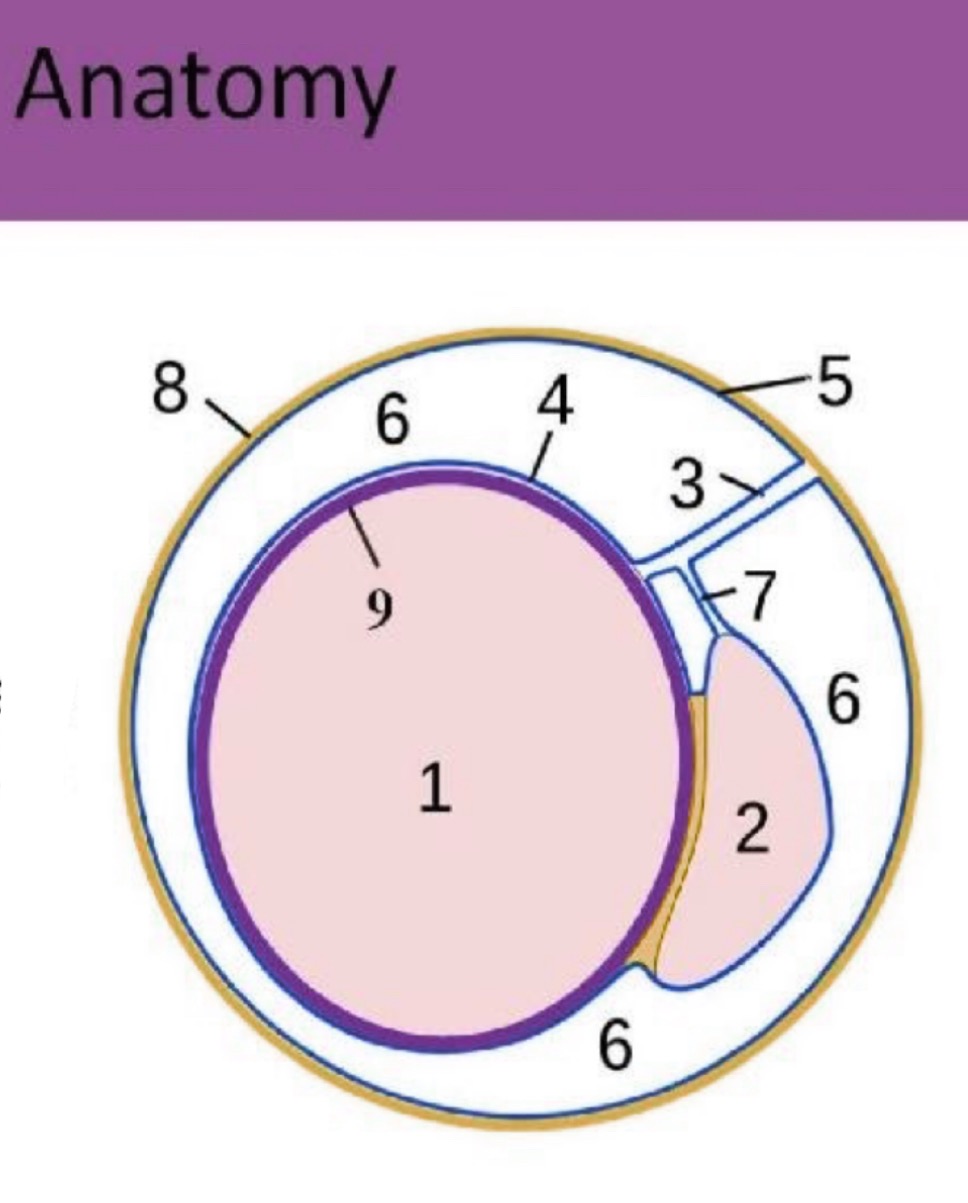
What is #2?
epididymis
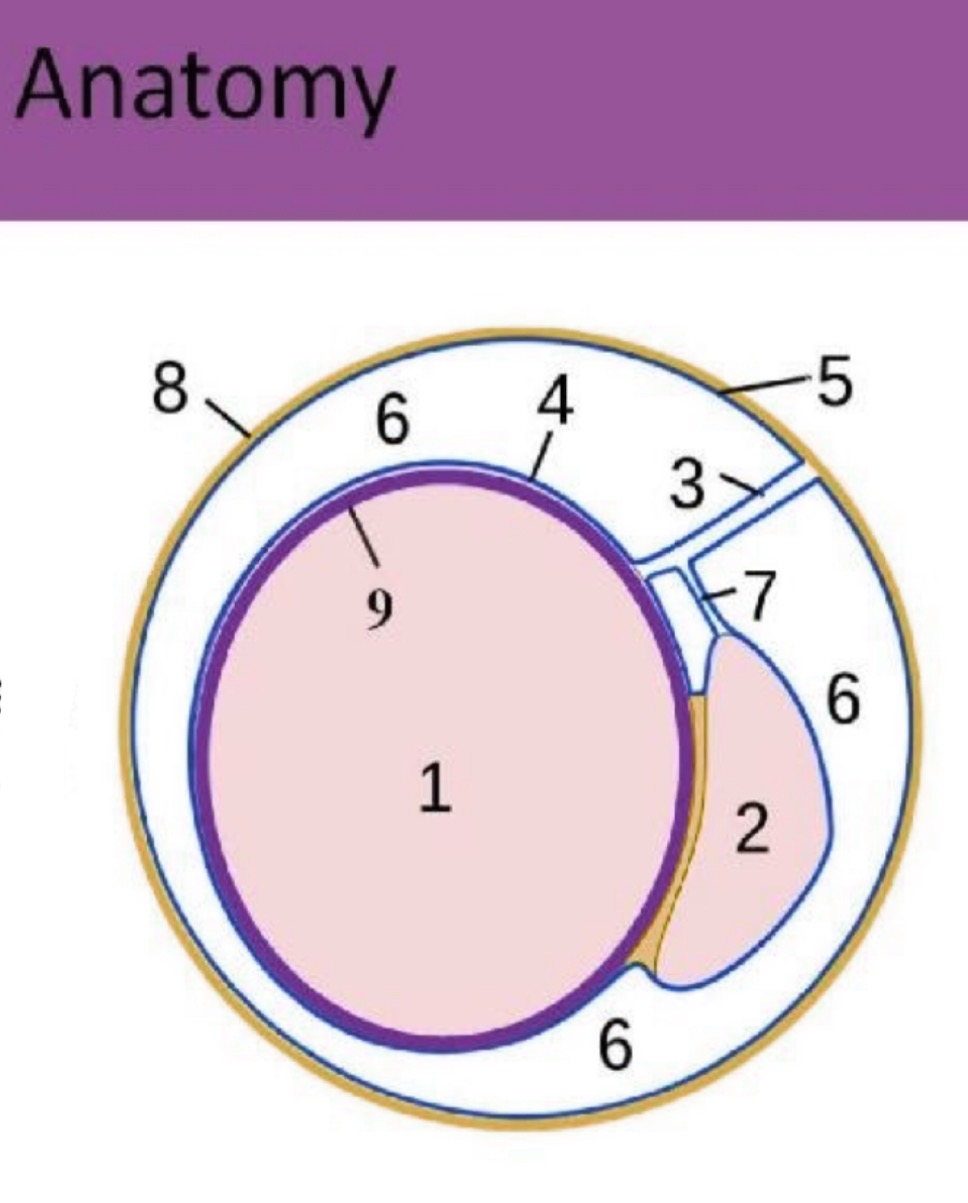
What is #3?
spermatic cord
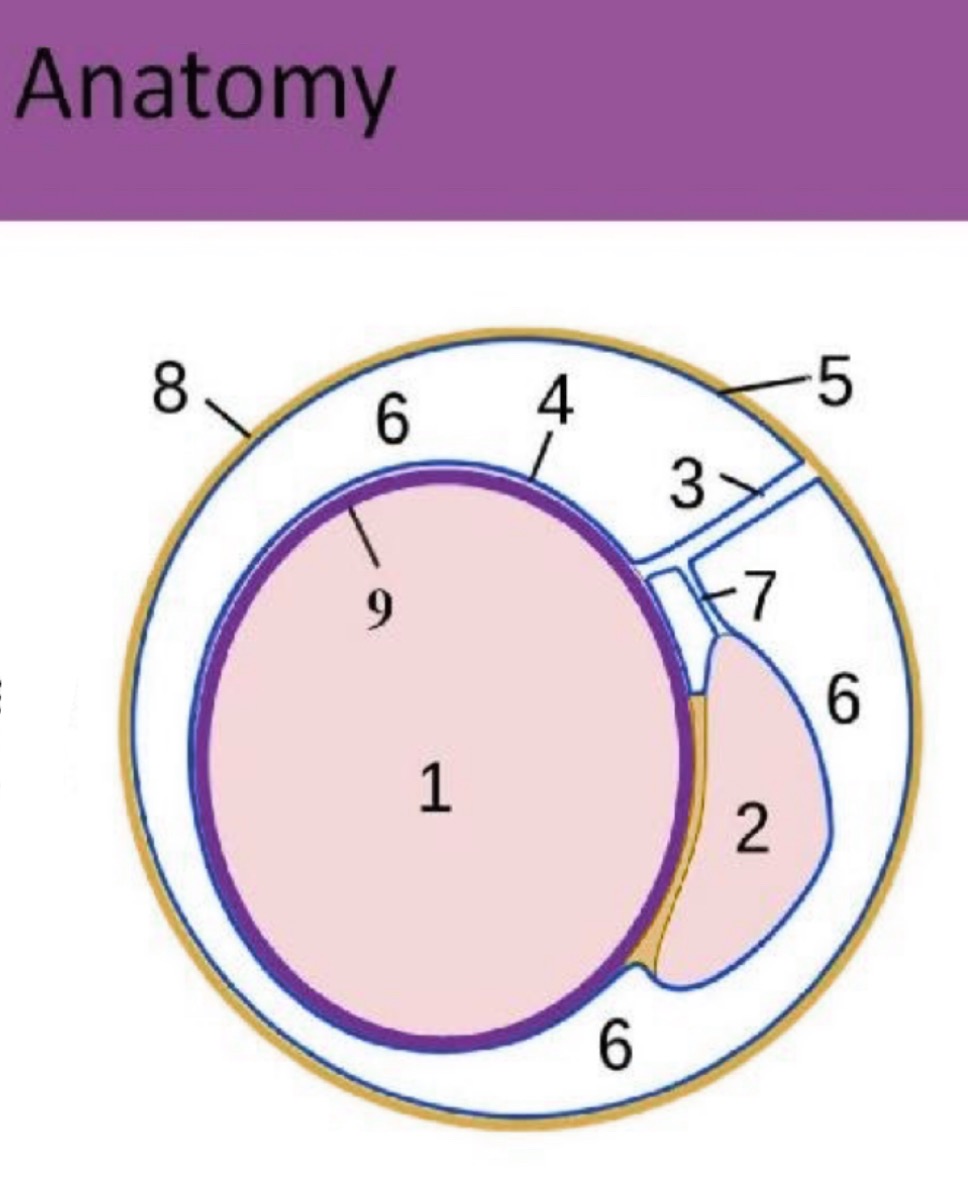
What is #4?
Visceral tunica vaginalis
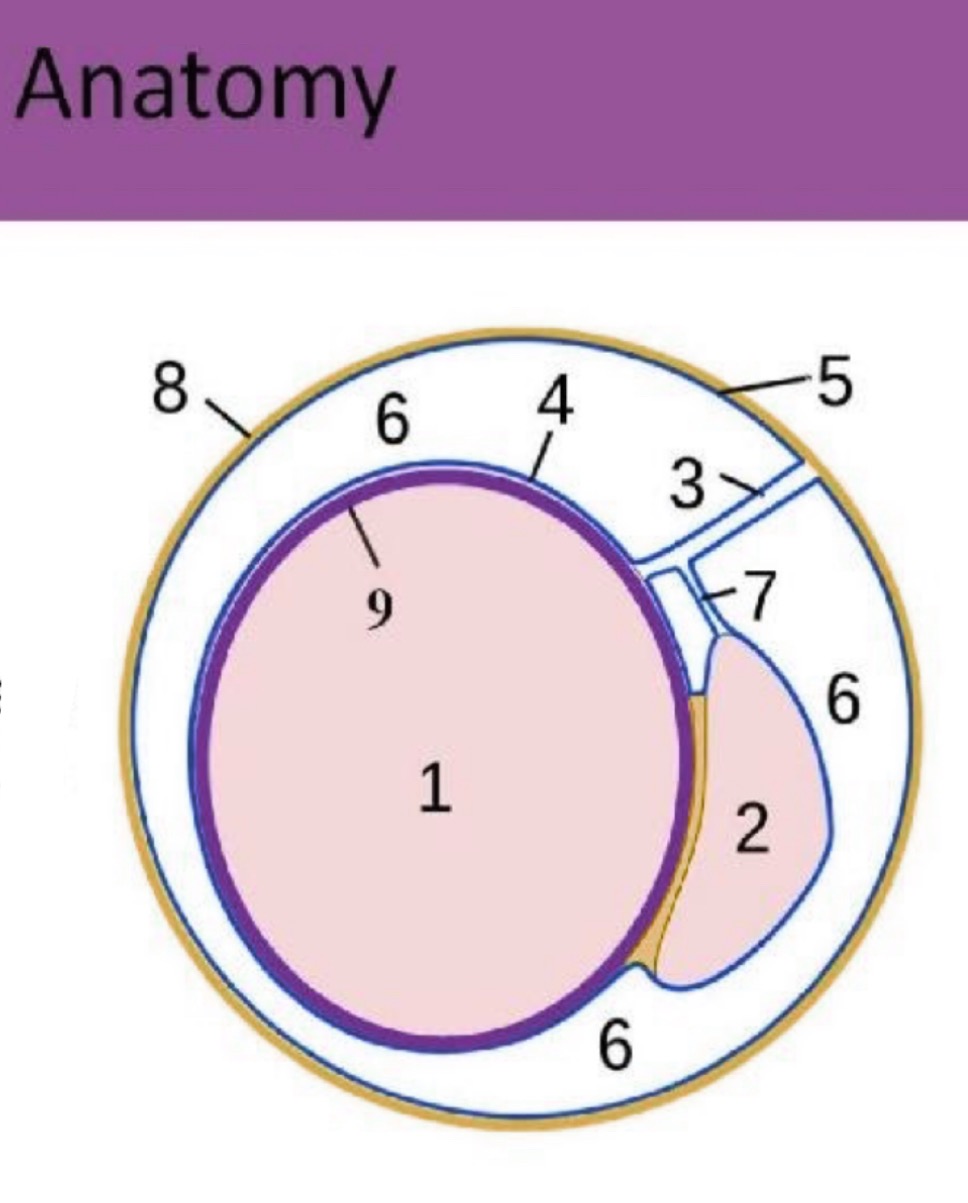
What is #5?
Parietal tunica vaginalis
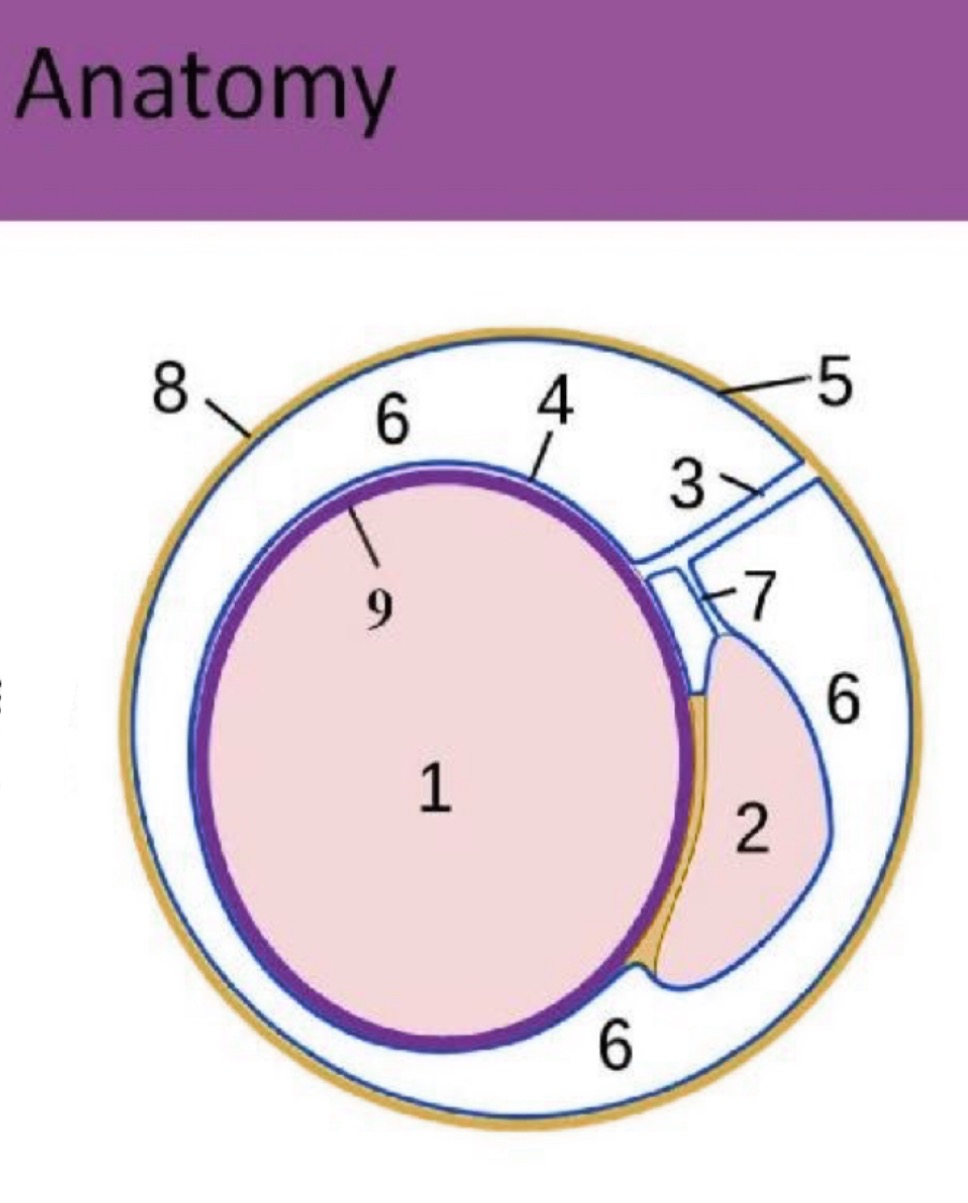
What is #6?
scrotal sac space
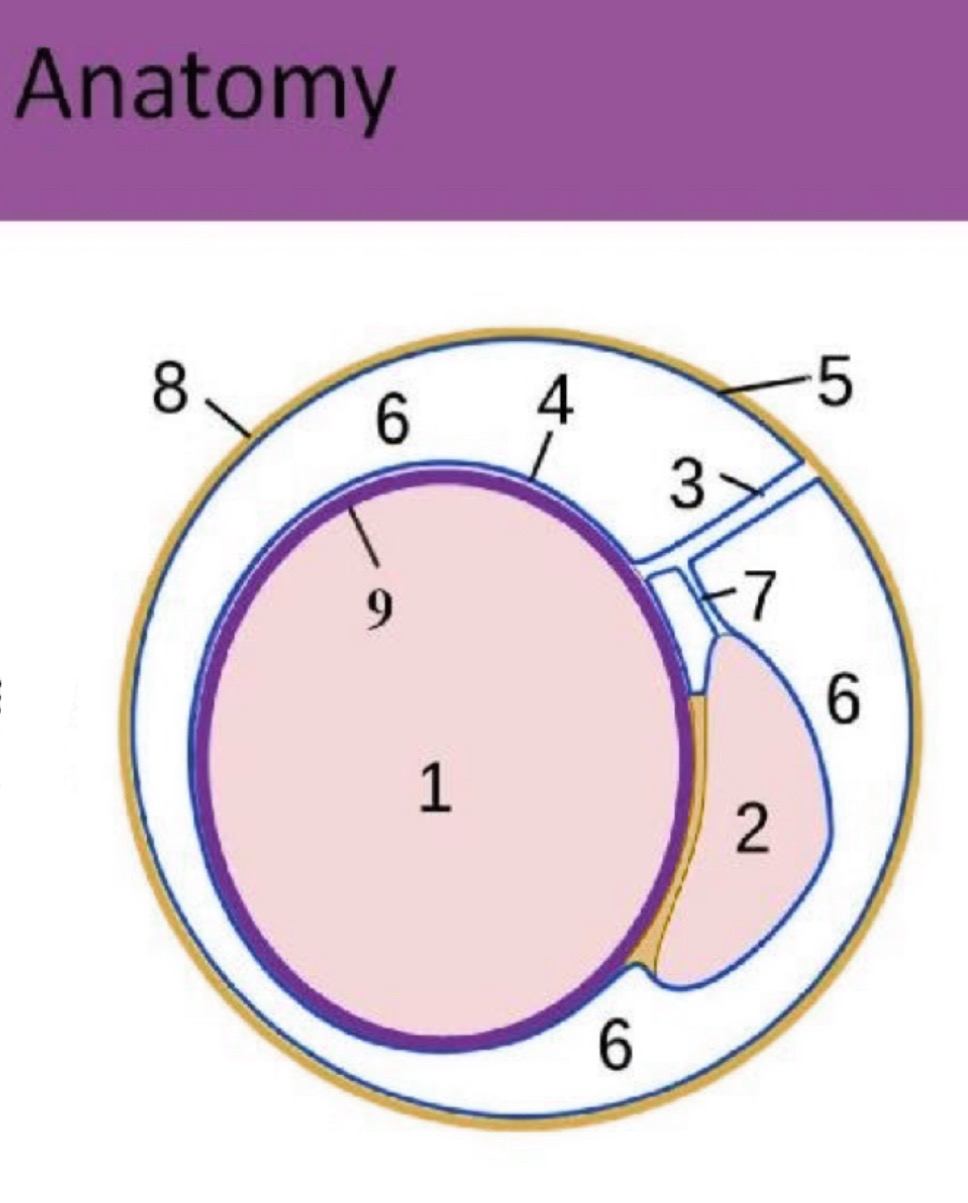
What is #7?
accessory duct
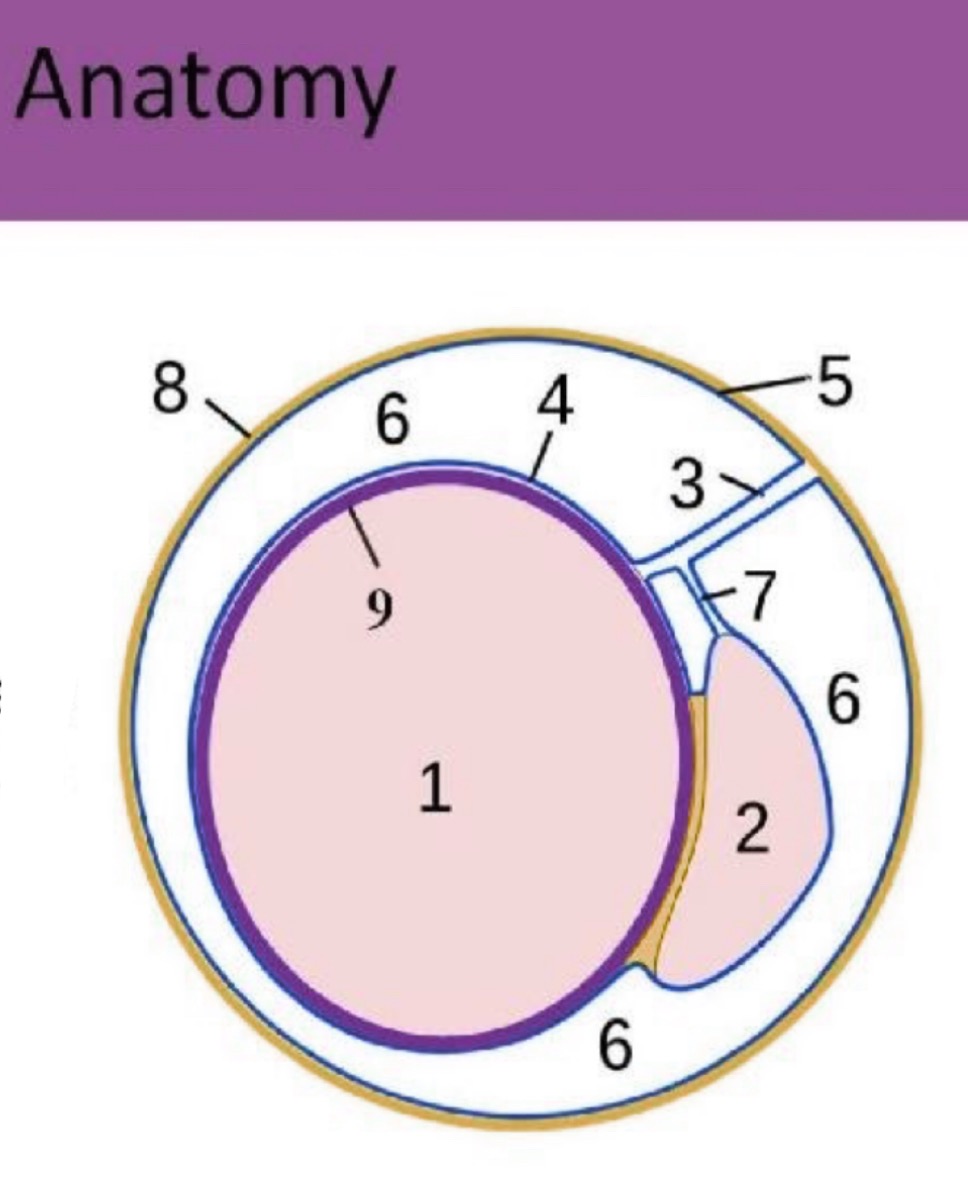
What is #8?
scrotal sac
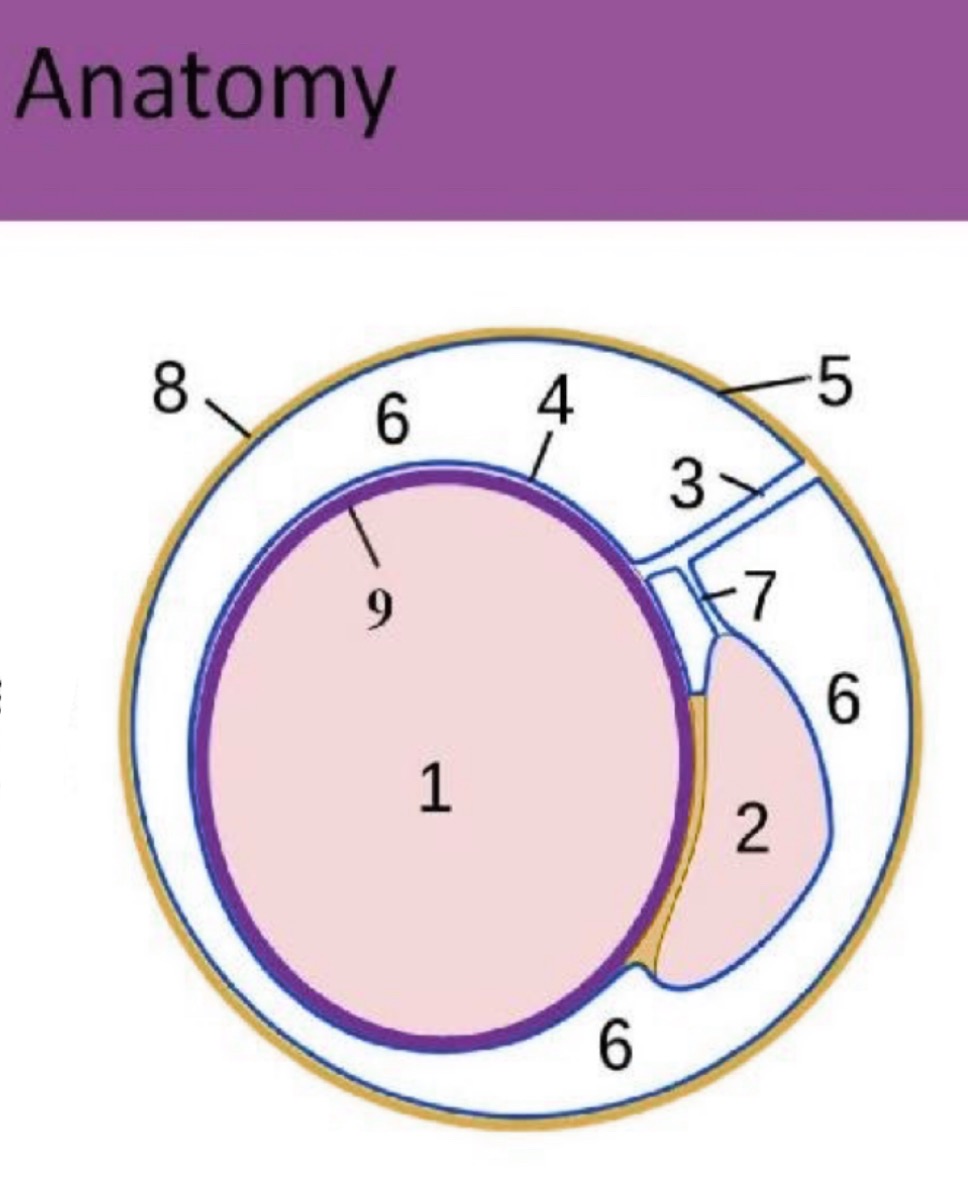
What is #9?
Tunica albuginea
What does the spermatic cord consist of?
Consists of vas deferens, cremasteric, deferential and testicular arteries, pampiniform plexus of veins, lymphatics and nerves
What manipulates the position of the testicles in the scrotum?
Cremasteric muscle
What does sperm production and testosterone secretion?
testis
Where does sperm maturation?
Epididymis
What does sperm and seminal vesicle fluid go through?
Ejaculatory duct
What is the drainage channel for semen, sperm and urine?
Urethra
What secretes alkaline component of semen and nutrients for sperm?
Seminal Vesicle
What secretes alkaline fluid into semen?
prostate
What secretes mucous for lubrication?
Cowper's gland
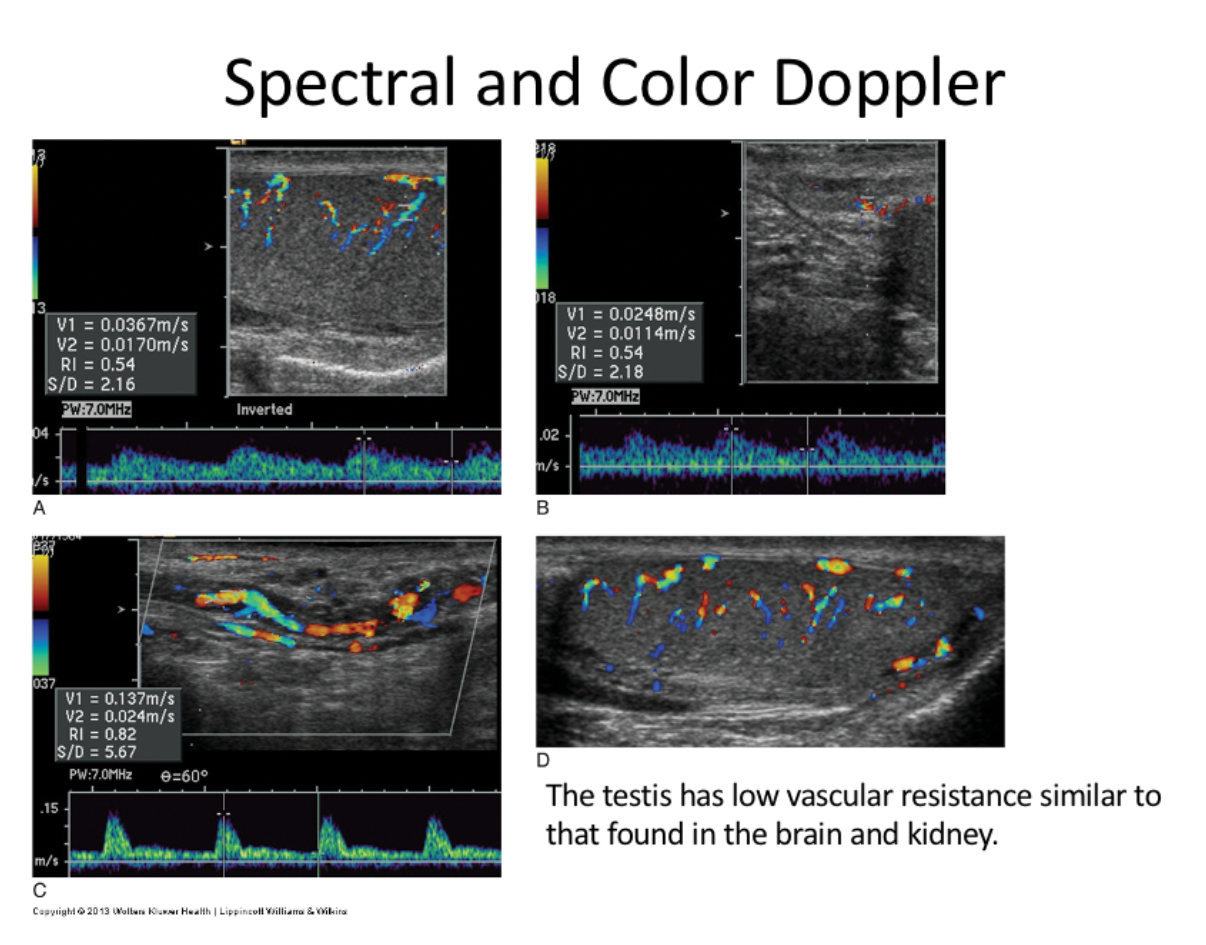
With high-frequency probes (10 to 14 MHz), what is the sonographic appearance of the testicles?
Homogeneous, uniform, medium level echoes
Mediastinum testis seen as a linear echogenic band within testicle
Tunica albuginea not normally visualized
Epididymis normally isoechoic or mildly hypoechoic to the testicle.
Testes offer low vascular resistance
What is some technical considerations?
(Hint: A lower line density is useful in cardiac applications as it allows significantly higher frame rates.)
Gain- high gain
PRF-low
Wall filter- low filter
Line density- high line density
Packet size- High The number of ultrasound pulses per line of color
(ENSEMBLE LENGTH)
Typically (8-30)
What could an acute painful scrotum mean?
TORSION, EPIDIDYMITIS, AND EPIDIDYMO-ORCHITIS
Decrease in the size of a testis may be a cause of ________ . The sonographic appearance of testicular atrophy is a small or shrunken heterogeneous testis displaying increased echogenicity due to fibrosis.
infertility
What does the following describe?
•AKA Undescended Testicle – usually descends from abdomen at birth, but sometimes in first year of life
•Orchioplexy is treatment of choice, performed within 2 years of age
•Complications – carcinoma and infertility
– Increased risk of developing malignancy if not treated, in one or both testicles
•Most common location is inguinal canal
– < 10% in abdomen
CRYPTORCHIDISM
What is a congenital absence of testicle?
•Rare, accounts for only 4% of pts with cryptorchidism
•May need patient to have full bladder to aid in finding an undescended testicle
–MRI and CT help
Anorchia
Undescended testes are at increased risk for _____ and commonly associated with __________
torsion, malignancy
(Congenital inguinal hernia is also associated with undescended testis)
Failure to close the processus vaginalis, which forms the scrotal sac, increases the chance of ______ herniating into the scrotum.
•Approximately, 90% of patients with undescended testes have herniated sacs
bowel
What is twisting of the spermatic cord on itself, obstructing the blood vessels supplying the epididymis and testis?
Clinical findings---Sudden onset of groin or scrotal pain, lower abdominal pain, Nausea/vomiting and Scrotal swelling
Sonographic appearance- Hypoechoic parenchyma and enlarged testes(acute)
-Hetergeneous parenchyma (chronic)
-Markedly absent or decreased intra testicular blood flow
-Hydrocele
Typically testicle is attached to tunica vaginalis.
torsion
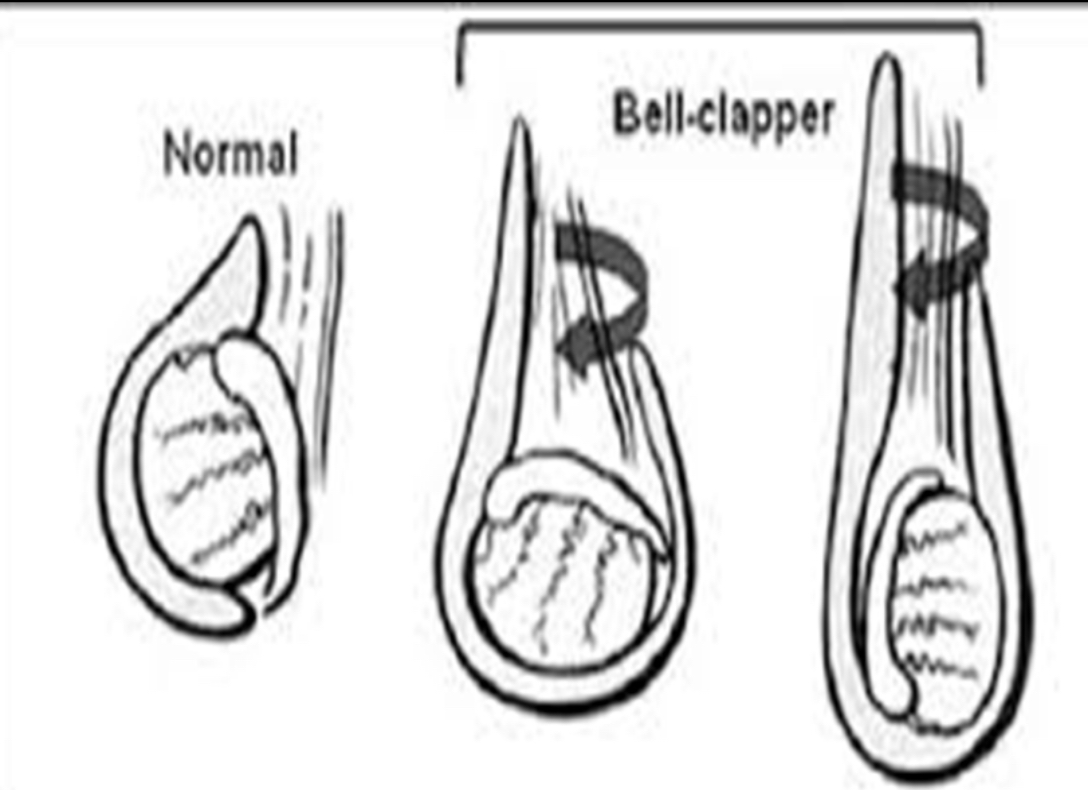
What is a predisposing factor in testicular torsion in which the tunica vaginalis joins high on the spermatic cord, leaving the testis free to rotate, ____ predisposes to intravaginal torsion of the testis?
•Without this attachment, testicle can rotate freely on spermatic cord (bell clapper deformity)
bell clapper deformity
Sudden onset of unilateral pain could mean…
torsion
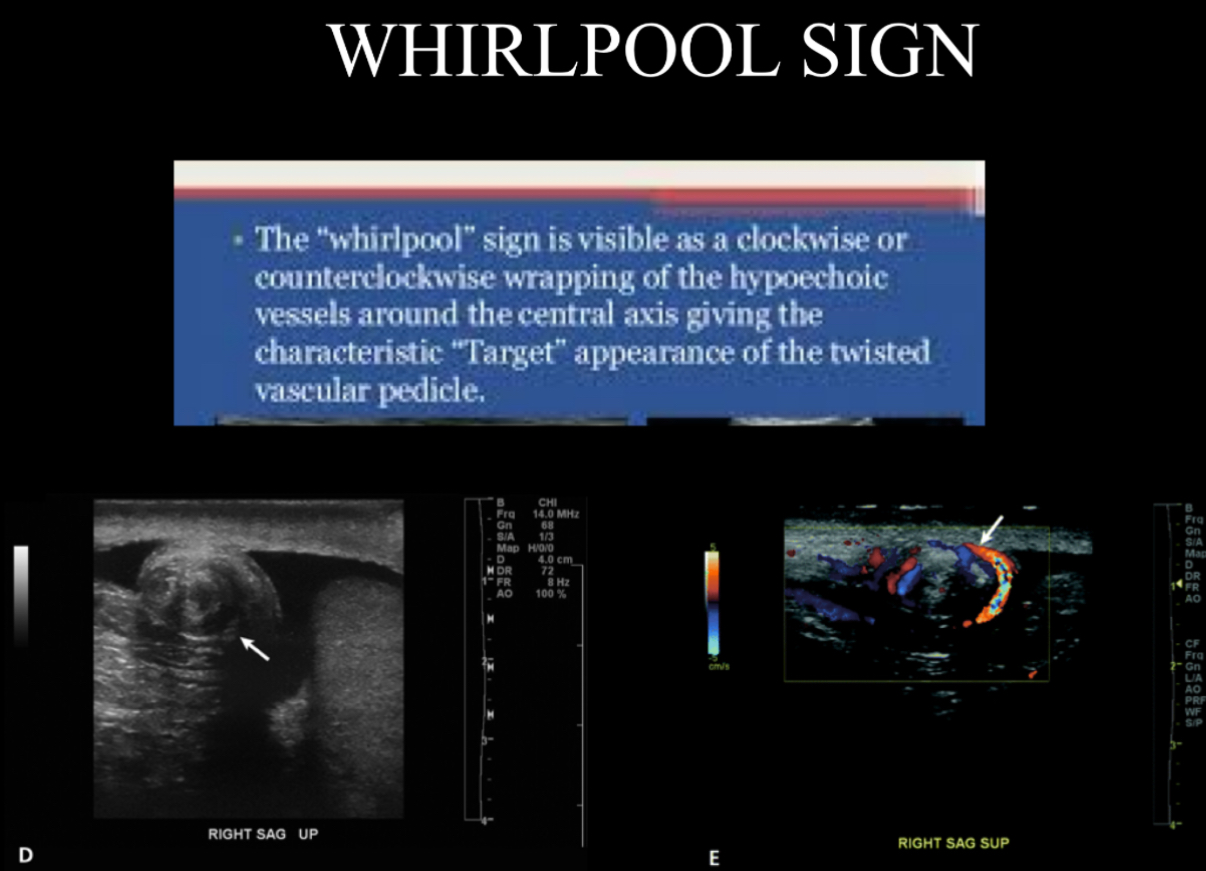
The torsion knot or whirlpool sign is a sonographic indicator of what?
torsion
Torsion of __ degrees or more is required for complete arterial occlusion. Salvage of testicle optimal at ______ hours from symptom onset
540, <6
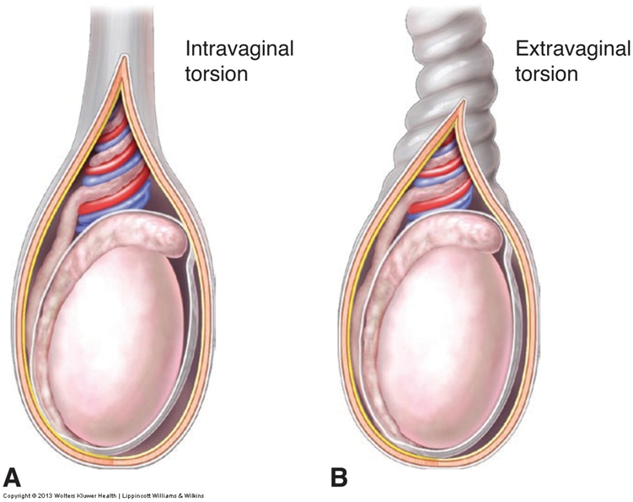
Describe the two types of torsions?
Intravaginal:Testis rotates freely within the tunica vaginalis by a long stalk of mesorchium. (Intravaginal torsion is the most frequent type of testicular torsion and is seen in 80% of cases.)
Extravaginal: Occurs exclusively in newborns. This type of torsion occurs outside the tunica vaginalis when the testes and gubernacula are not fixed and are able to freely rotate
Acute and intermittent sharp testicular pain and scrotal swelling, interspersed with long asymptomatic intervals, are characteristic of what?
torsion–detorsion
What does the following describe?
can cause acute scrotal pain mimicking testicular torsion
More than 90% of torsed appendages involve the appendix testis
The peak incidence is between the ages of 7 and 14 years
A testicular appendage larger than 5.6 mm with increased periappendiceal color flow is suggestive of torsion.
Torsion of the appendix testis and appendix epididymis
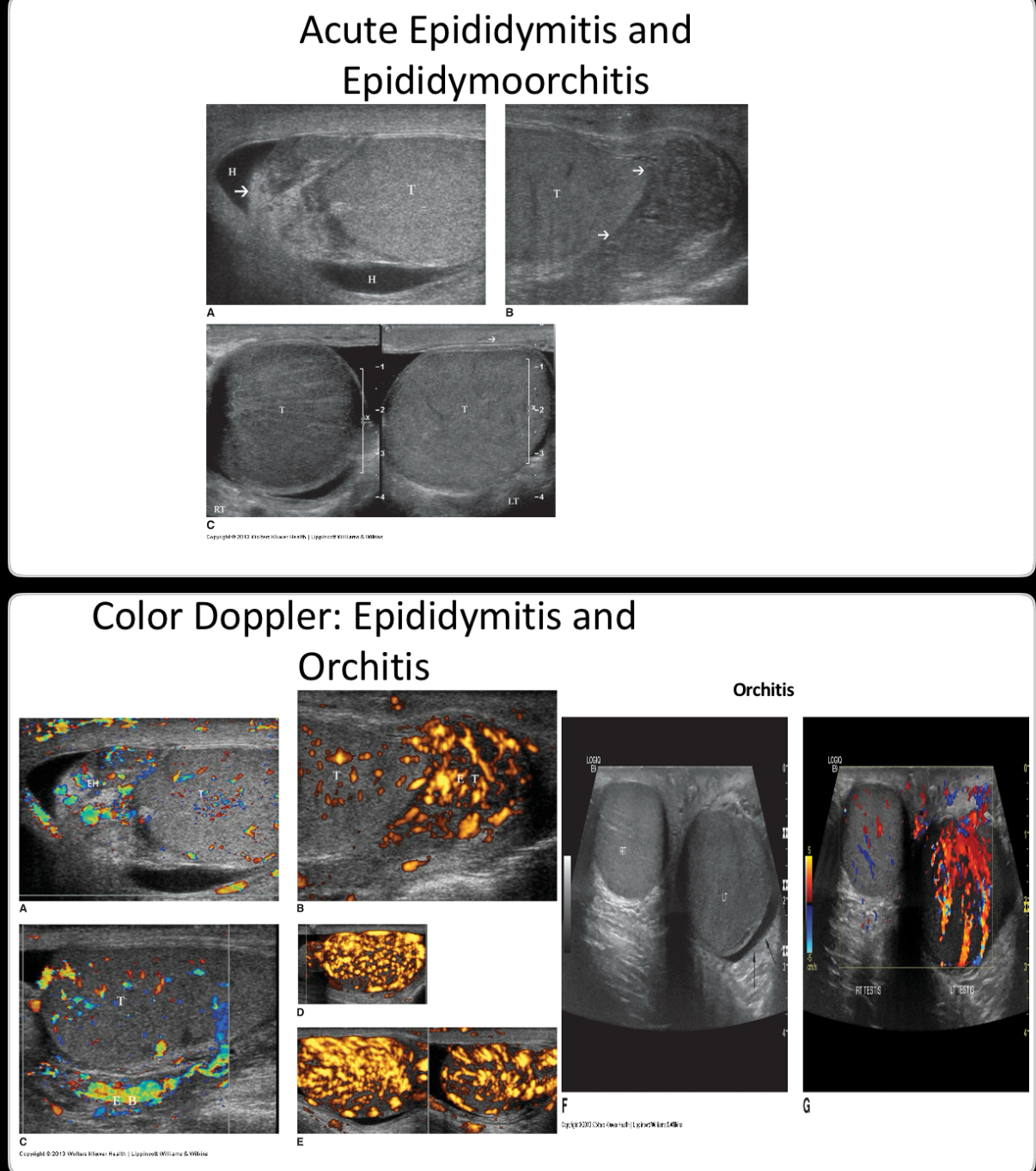
What does the following describe?
•inflammation of the epididymis
• often is secondary to sexually transmitted organisms such as Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhea.
•In pre-pubertal boys and men over 35 years of age, the disease is most frequently caused by Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis.
•The infection occurs from direct retrograde extension of pathogens, via the vas deferens, from a lower urinary tract source, such as urethritis, prostatitis, cystitis, and possibly following instrumentation such as catheterization
•Sonographically – enlarged hypoechoic epi, increased blood flow (hyperemia), reactive hydrocele, scrotal wall thickening.
Epididymitis
What does the following describe?
Abnormal accumulation of serous fluid between layers of tunica vaginalis.
Displaces the testicles posteriorly
Few ml is normal findings
Sometimes they cause scrotal wall thickening
Sonographically - anechoic with good sound transmission, low-level to medium-level echoes possible
hydrocele
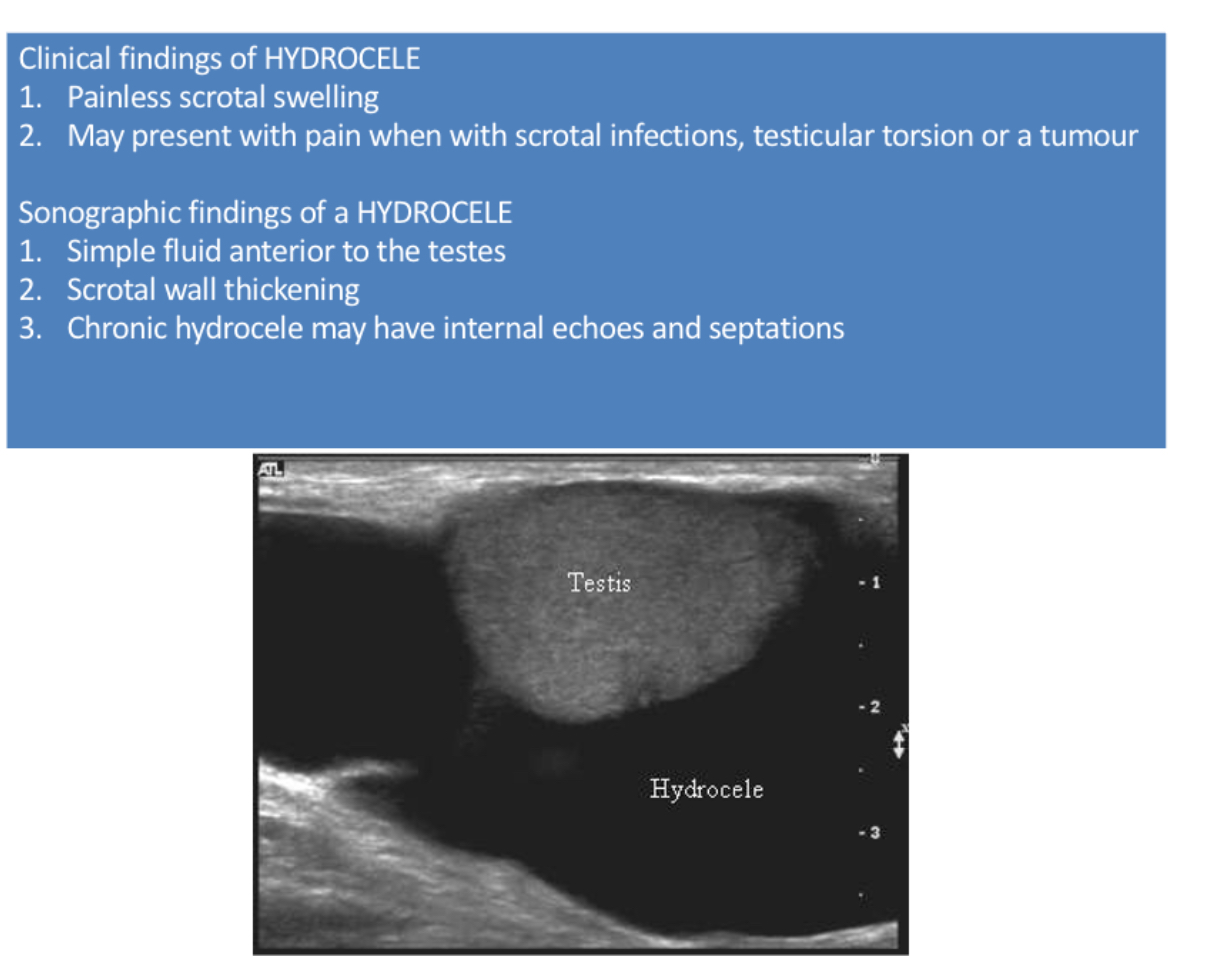
What is the most common cause of painless scrotal swelling?
hydrocele
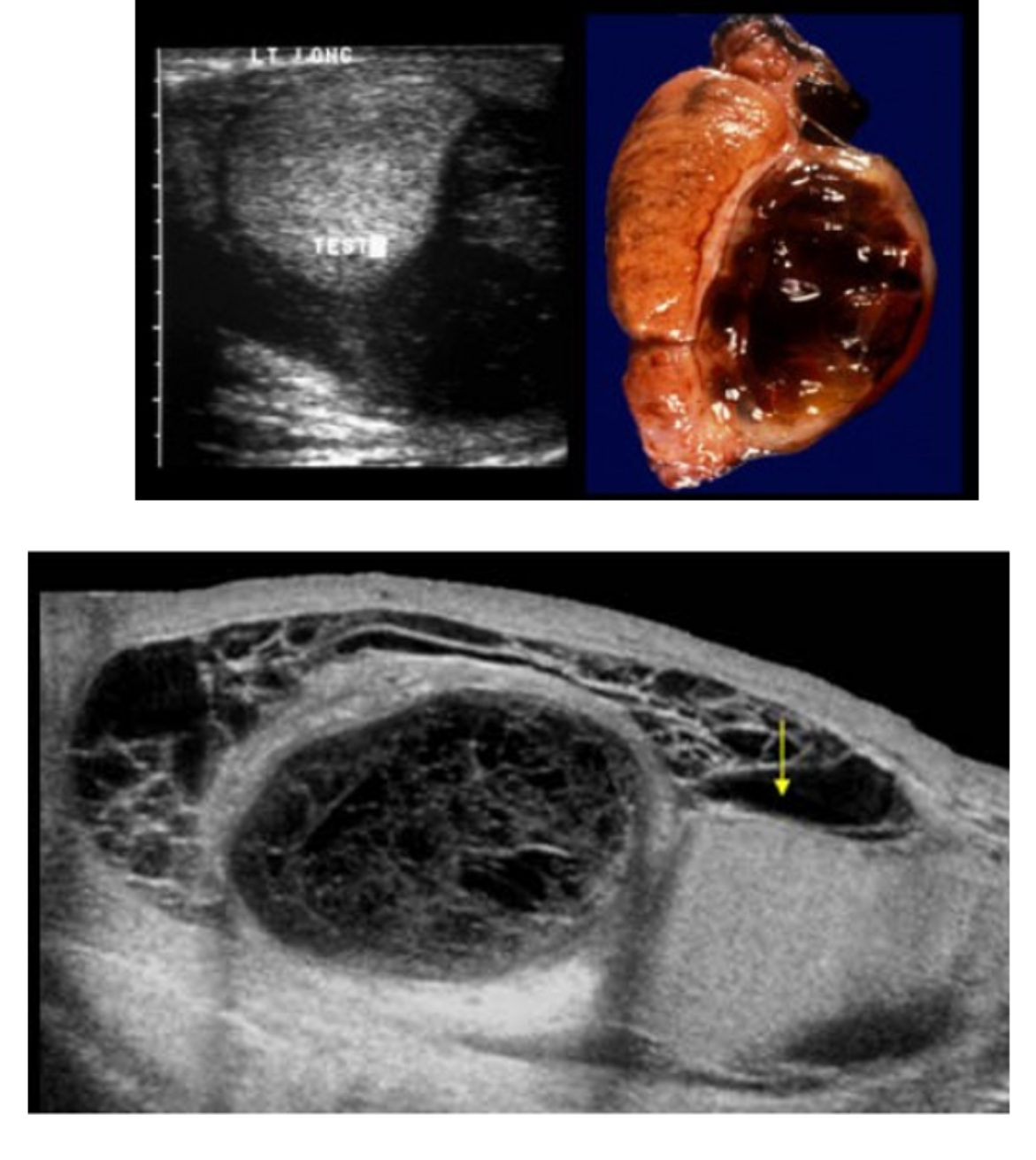
What does the following describe?
results from scrotal or intra-abdominal hemorrhage.
It represents bleeding between the layers of the tunica vaginalis and appears as complex fluid collection
With time, this collection can develop loculations, which appear as thick septations.
blood fills scrotal chamber; can be associated with trauma, surgery, torsion or neoplasms
hematoceles
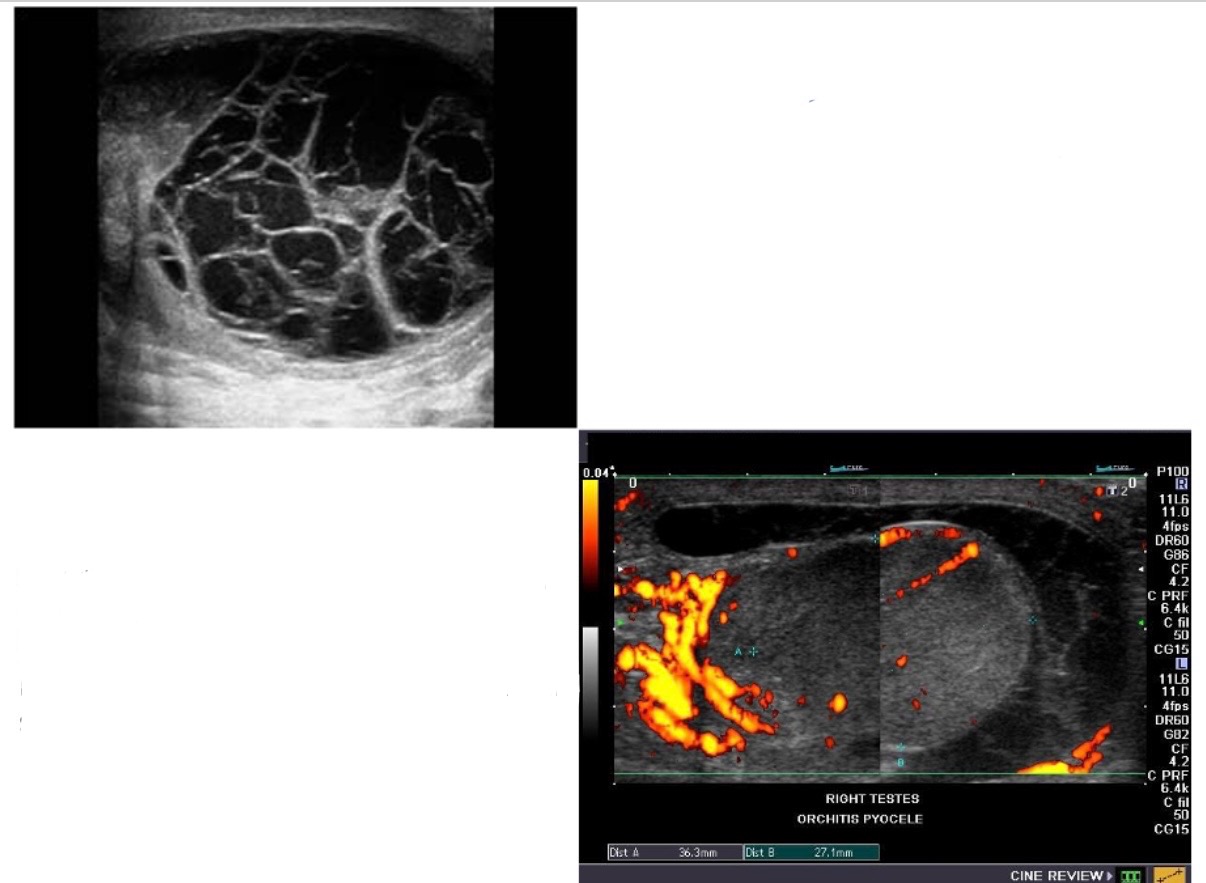
What is result from abscess rupture into existing hydrocele or directly into space between tunica vaginalis layers, both have septations & loculations;chronically skin thickening and calcifications?
pyoceles
Both spermatoceles and epididymal cysts are thought to occur as a result of dilatation of the _____________, whether secondary to vasectomy, scrotal surgery, trauma, or epididymitis
epididymal tubules
The most common location for spermatoceles is in the _____ of the epididymis, whereas epididymal cysts arise throughout the epididymis
head
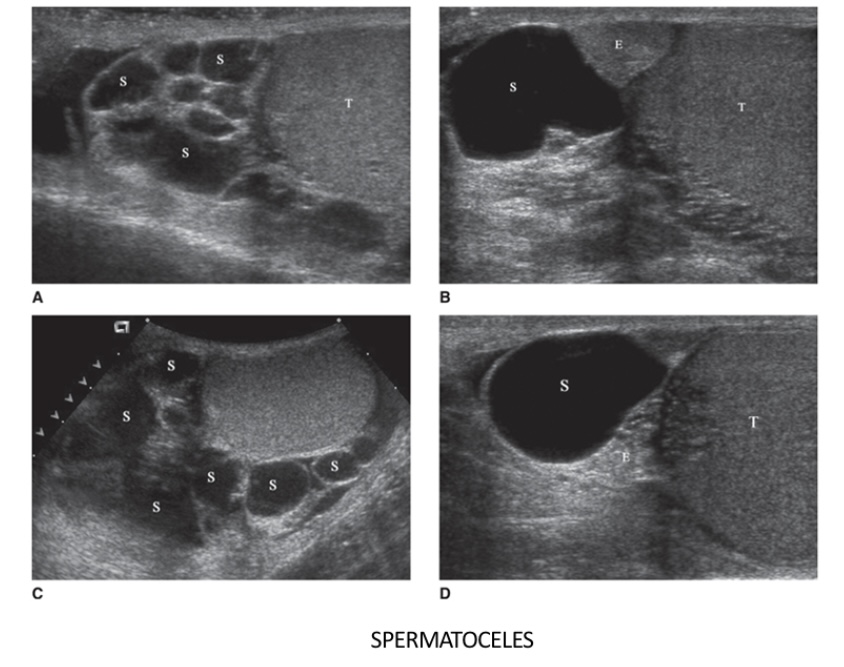
What does the following describe?
usually displace the testis anteriorly, distinguishing them from a hydrocele, the latter of which surrounds the testis
They are usually unilocular
Fluid is thick, milky, containing spermatozoa and has non viable sperms, fat lymphocytes
Spermatoceles
Epididymal cysts are composed of what?
clear fluid
What does the following describe?
Dilatation of the efferent ductules
manifests sonographically as multiple tiny cystic tubules located within or adjacent to the mediastinum testis
With color Doppler, dilated tubules are avascular and fluid filled
tubular ectasia of the rete testis
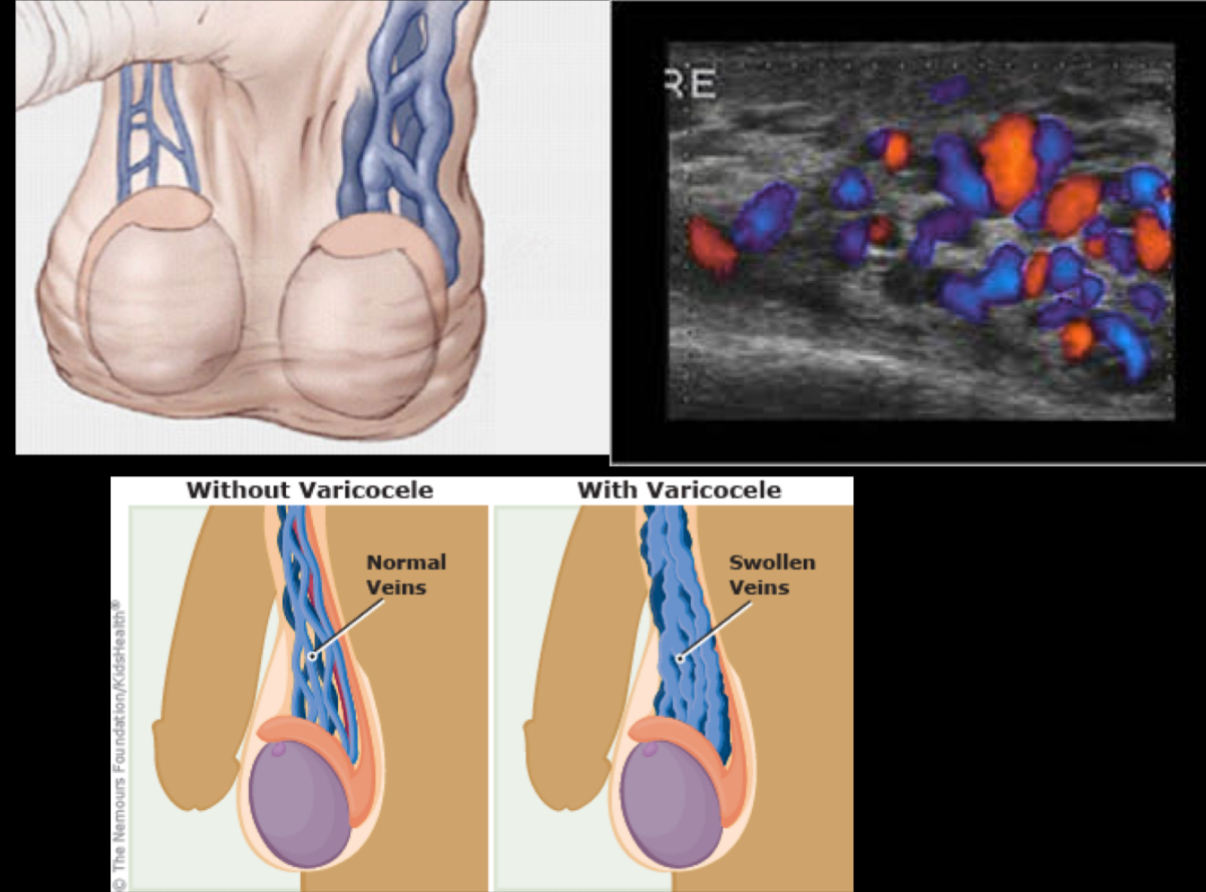
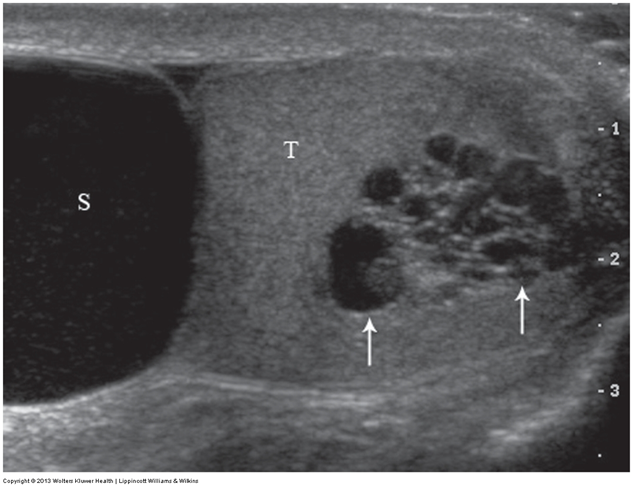
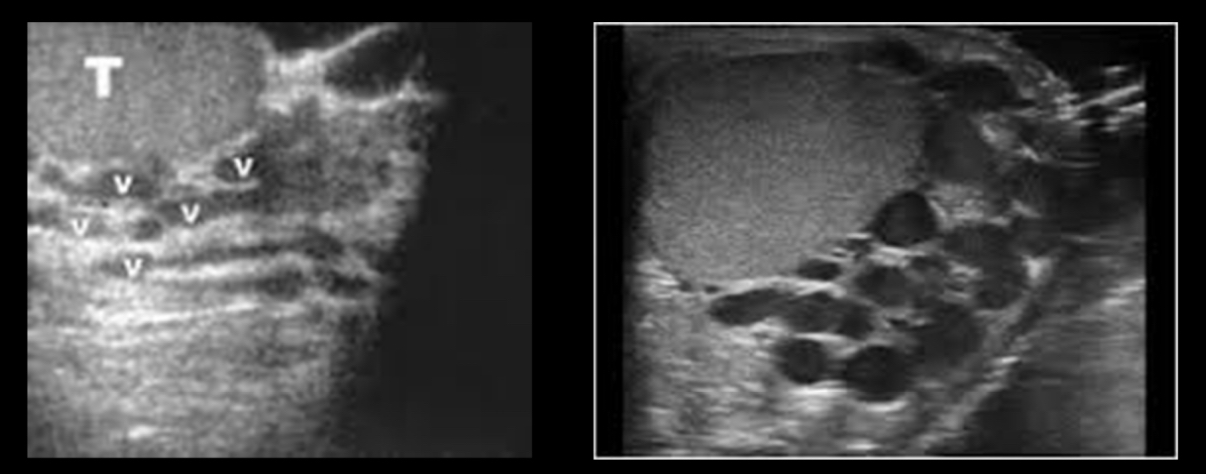
What does the following describe?
• distend with Valsalva maneuver, standing, or abdominal compression
–May produce aching pain when standing for periods of time or after heavy lifting
•Most common correctable cause of male infertility – associated with infertility
Varicoceles
True/False: Bilateral varicocoeles are not uncommon (≈15%), but isolated right varicocoeles are rare and should prompt evaluation for a secondary varicocele.
true
Most varicoceles are _____ and result from incompetent or congenitally absent valves in the testicular vein (internal spermatic vein). The side most commonly affected is the _____ side testicle.
primary, left
What does the following describe?
– are much less common and result from increased pressure in testicular vein due to
•compression (e.g. extrinsic mass),
•obstruction (e.g. renal vein thrombus),
•splenorenal shunting (portal hypertension).
Secondary varicocoeles
What is the diagnostic criteria for varicocoele?
–dilatation of pampiniform plexus veins >2-3 mm diameter
–The veins should be distended in Valsalva more than 2 mm.
–characteristically have a serpentine appearance
What is it called when bowel protrudes through inguinal canal into tunica vaginalis of scrotum (Peristalsis will be present and confirms diagnosis)?
scrotal hernia
A normal connection between the peritoneal cavity in the abdomen and the scrotal sac, known as the _______, exists in every male fetus. This connection may persist after birth, allowing abdominal contents such as gut or properitoneal or omental fat to descend into the scrotum.
processus vaginalis
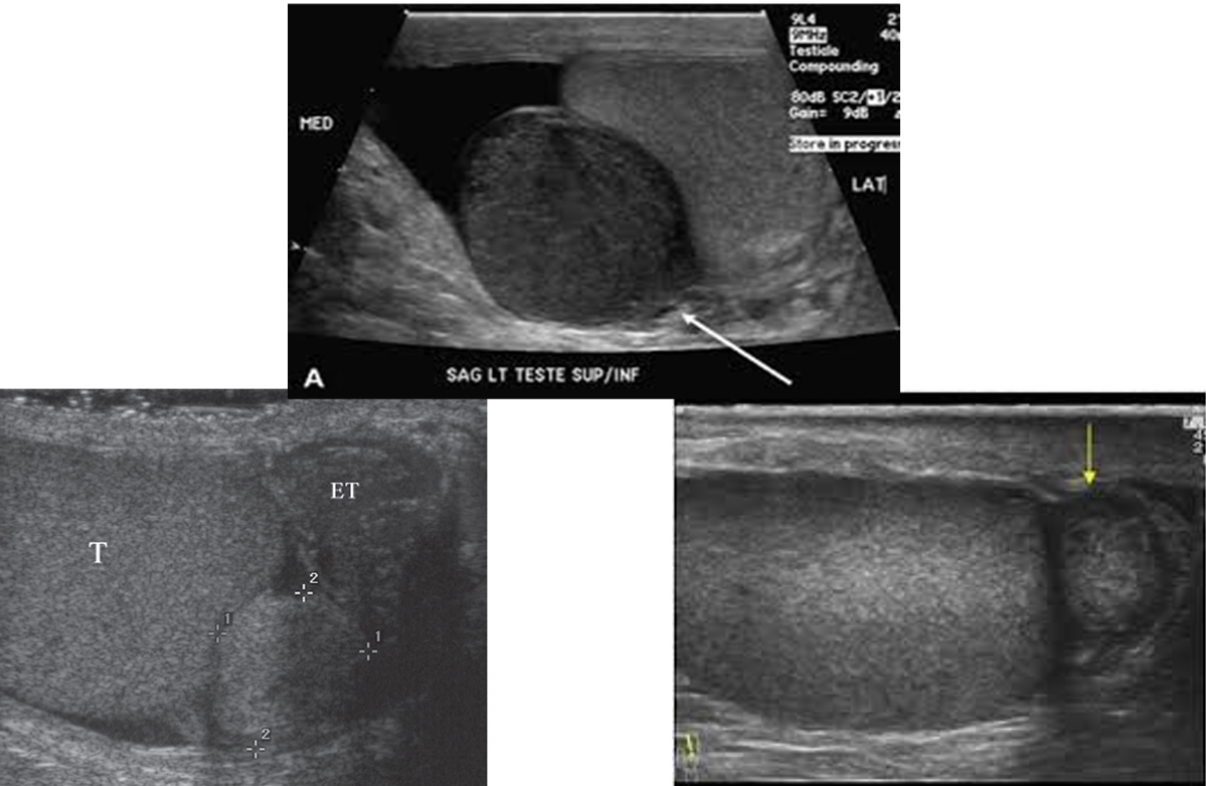
What is the most common (extratesticular) tumor?
adenomatoid tumor
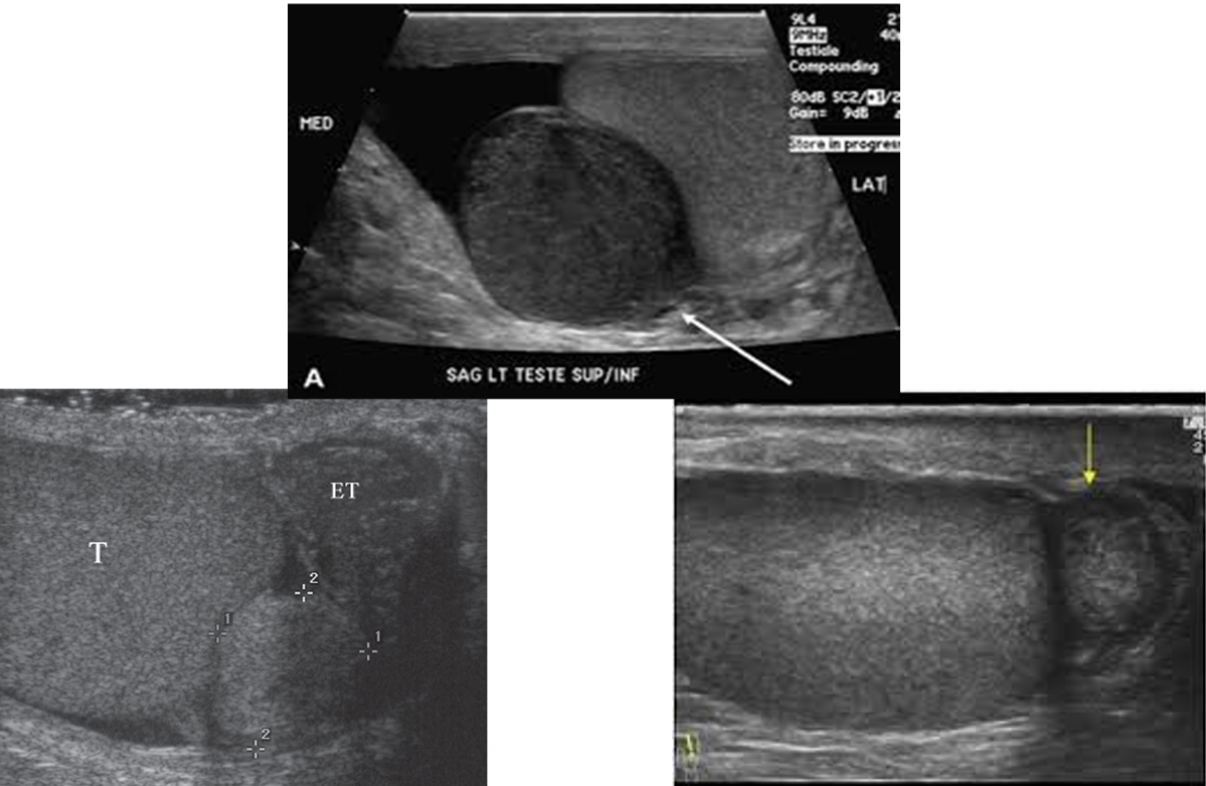
What does the following describe?
•Usually involve epididymis, most often tail
•In adults, usually benign, but in children more frequently malignant
•Sonographically – Unilateral, solitary, well defined, round or oval, measuring more than 5 cm diameter. May be hypoechoic
adenomatoid tumor
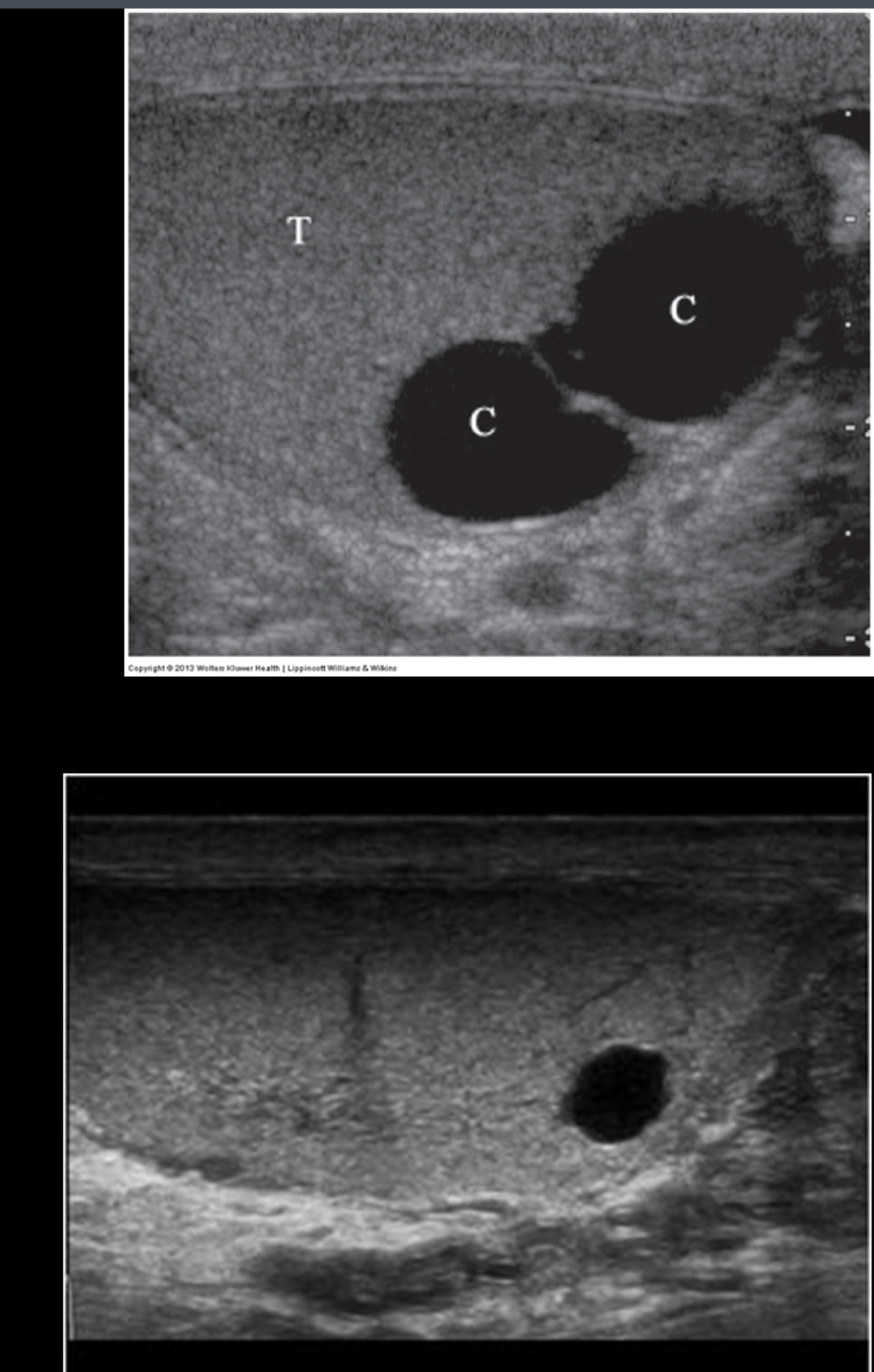
What does the following describe?
Discovered incidentally, occur in 8-10% of patients, two types
Cysts of tunica albuginea
Intratesticular cysts- Normally located near mediastinum testis & probably originate from rete testis
testicular cysts
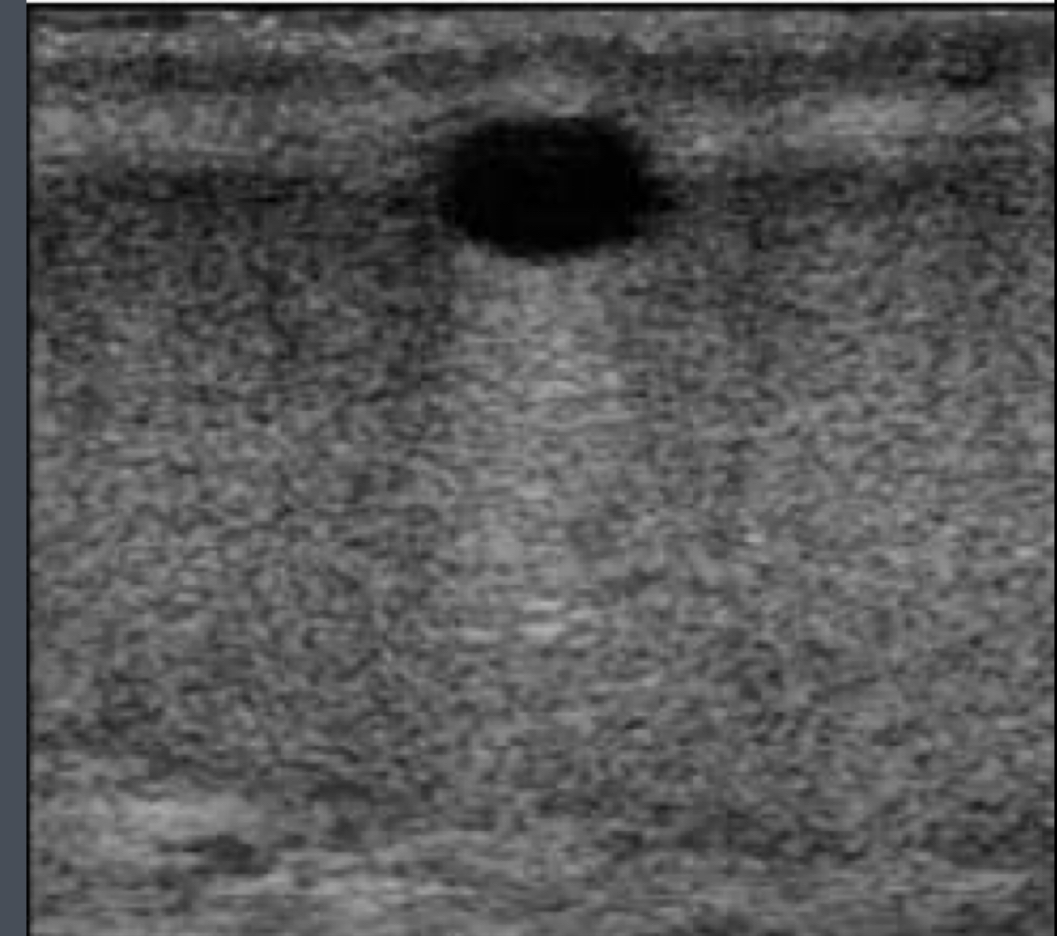
What does the following describe?
• are uncommon
• these cysts are believed to be mesothelial in origin
•Clinically, may present as a pain- less scrotal lump.
• are generally seen in men ages 50-60
tunica albuginea cysts
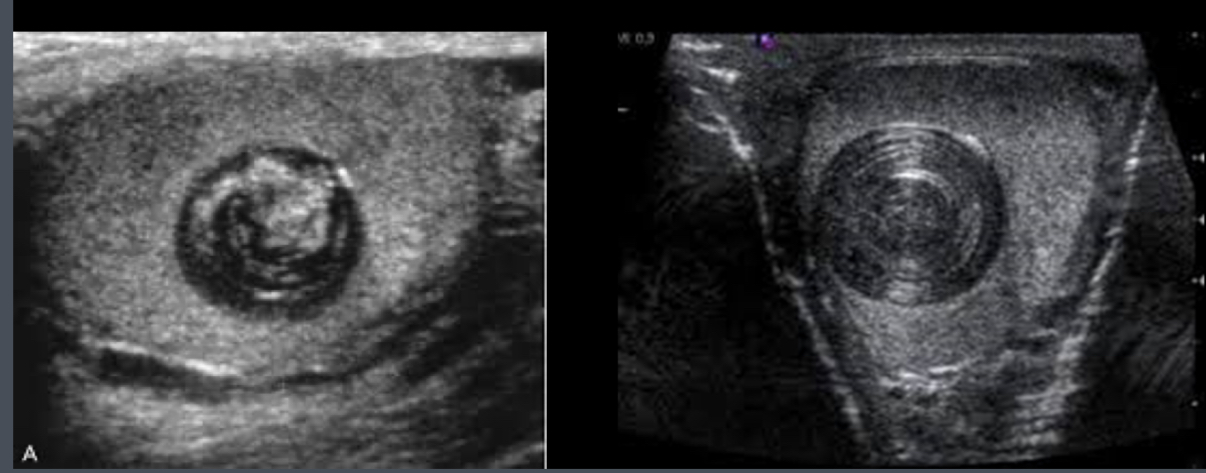
What does the following describe?
•Benign tumor of germ cell origin
•Well-circumscribed solid tumor beneath tunica albuginea
•Sonographically – well definied, solid, hypoechoic with echogenic capsule or onion ring pattern formed by layered keratin
•“Bow-tie”/ “onion ring” appearance: central echogenic pattern
Epidermoid Cyst