Exam 3: Electrical Potentials & Depolarization
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Electrophysiology
The branch of physiology that studies how cells produce electrical potentials and currents
______ is the basis for neural communication and muscle contraction
Electrophysiology
Electrical Potential
the difference in electrical charge across a membrane
Cells have more ____ particles on the inside of the membrane than the outside.
negative
What is the resting membrane potential for a neuron?
-70 mV
Electrical Current
a flow of charged particles from one point to another
What are currents in the body?
the movement of ions, such as Na+ or K+ through channels in the plasma membrane
Why does the resting membrane potential exist?
because of the unequal distribution of electrolytes between the extracellular fluid and the intracellular fluid
The resting membrane potential results from the combined effect of three factors. What are they?
ions diffuse down their concentration gradient through the membrane
the plasma membrane is selectively permeable and allows some ions to pass easier than others
the electrical attraction of cations and anions to each other
What ion has the greatest influence on the resting membrane potential?
potassium (K+)
Why does potassium have the greatest influence on RMP?
because the plasma membrane is more permeable to K+ than any other ion and K+ ions diffuse out of the cell, making the inside more negative.
K+ is about ____ times more concentrated in the ICF than in the ECF?
40 times
Why can’t cytoplasmic anions, such as phosphate, sulfates, ATP, proteins, etc, escape the plasma membrane?
because they are large and negatively charged
The cellular membrane is not very permeable to ____ and RMP is slightly influenced by it.
sodium (Na+)
Sodium is about ____ times more concentrated in the ECF than in the ICF?
12 times
How does sodium influence the resting membrane potential?
Some Na+ leak into the cell, diffusing down its concentration gradient
This Na+ leakage makes RMP slightly less negative than it would be if RMP were determined solely by K+
What does the sodium potassium pump do?
it moves 3 Na+ out of the cell for every 2 K+ it brings into the cell
Why does the sodium potassium pump work continuously?
to compensate for Na+ and K+ leakage
The sodium potassium pump requires a LOT of ____.
ATP
____ percent of energy required from the nervous system is used by the sodium potassium pump.
70%
Local potentials are (4)…
graded
decremental
reversable
excitatory or inhibitory
Graded
the size of the local potential varies, depending on the stimulus strength (the stronger the stimulus, the more Na+ gates open)
Decremental
the local potential gets weaker the further it gets from the point of stimulation (the shift in voltage caused by Na+ inflow diminishes with distance)
Reversible
if stimulation ceases, the cell quickly returns to its normal resting potential
Explain how local potentials can be either excitatory or inhibitory.
some neurotransmitters make the membrane potential more negative, so it becomes less likely to produce an action potential; while others make it more positive, increasing the likelihood of firing an action potential.
What are local potentials?
changes in membrane potential of a neuron occurring at and nearby the part of the cell that is stimulated
short range changes in voltage across a cell
Different neurons require different things in order to be stimulated. What are different ways that neurons can be stimulated?
by chemicals, light, heat, or mechanical disturbance (such as pressure or stretch)
How might a stimuli influence a local potential?
A chemical stimulant will bind to a receptor on the neuron
This opens Na+ gates and allows Na+ to enter the cell
This causes the ICF to become less negative and can lead to depolarization
Na+ entry results in a current that travels toward the cell’s trigger zone and can initiate an action potential if the threshold is reached.
Depolarization
a change in membrane potential toward zero mV
Current travels down an ____ , toward the…
axon; terminal branches
Action Potential
a dramatic change in the electrical potential of a cell membrane, that occurs when a stimulus triggers the opening of voltage-gated ion channels
Action potentials only occur when…
there is a high enough density of voltage-regulated gates
Soma
cell body
Trigger Zone
located at the axon hillock, this is where action potentials are generated
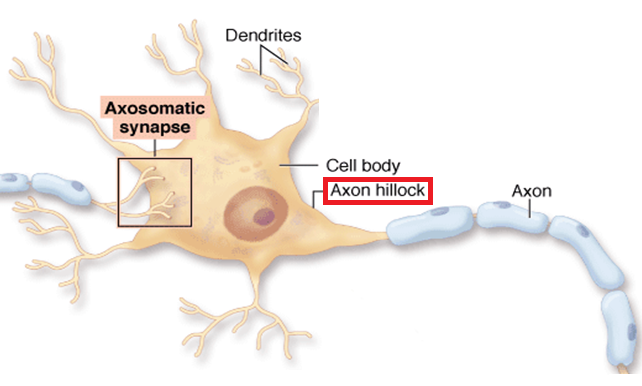
Describe the steps in which an Action Potential is produced (8).
A current arrives at the axon hillock and depolarizes the membrane
Depolarization must reach threshold (the critical voltage) to open voltage-regulated gates
Voltage gates Na+ channels open, Na+ enters and depolarizes the cell, which opes more channels
This results in a rapid positive feedback cycle as voltage rises
As membrane potential rises above 0 mV, Na+ channels are inactivated and close; voltage peaks at about +35 mV
Slow K+ channels open and outflow of K+ repolarizes the cell
K+ channels remain open for a time so that membrane birefly becomes hyperpolarized
RMP is restored as Na+ leaks in and extracellular K+ is removed by astrocytes
Hyperpolarized
becomes more negative than the RMP
What are the characteristics of action potentials (unlike local potentials)?
follows an all or none-law (if threshold is reached, neuron fires at its max voltage; if threshold is not reached, it does not fire)
Non-decremental: does not get weaker with distance
Irreversible: once started, goes to completion and cannot be stopped
What is the refractory period of an action potential?
the period of resistance to stimulation
What are the two phases of the refractory period?
absolute refractory period
relative refractory period
Absolute Refractory Period
no stimulation of any strength will trigger action potential
lasts as long as Na+ gates are open, then inactivated
Relative Refractory Period
only especially strong stimulus will trigger action potential
K+ gates are still open and any effect of incoming Na+ is opposed by the outgoing K+
Generally lasts until hyperpolarization ends