Chemistry II Lesson 6: Carbohydrates and Lipids
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
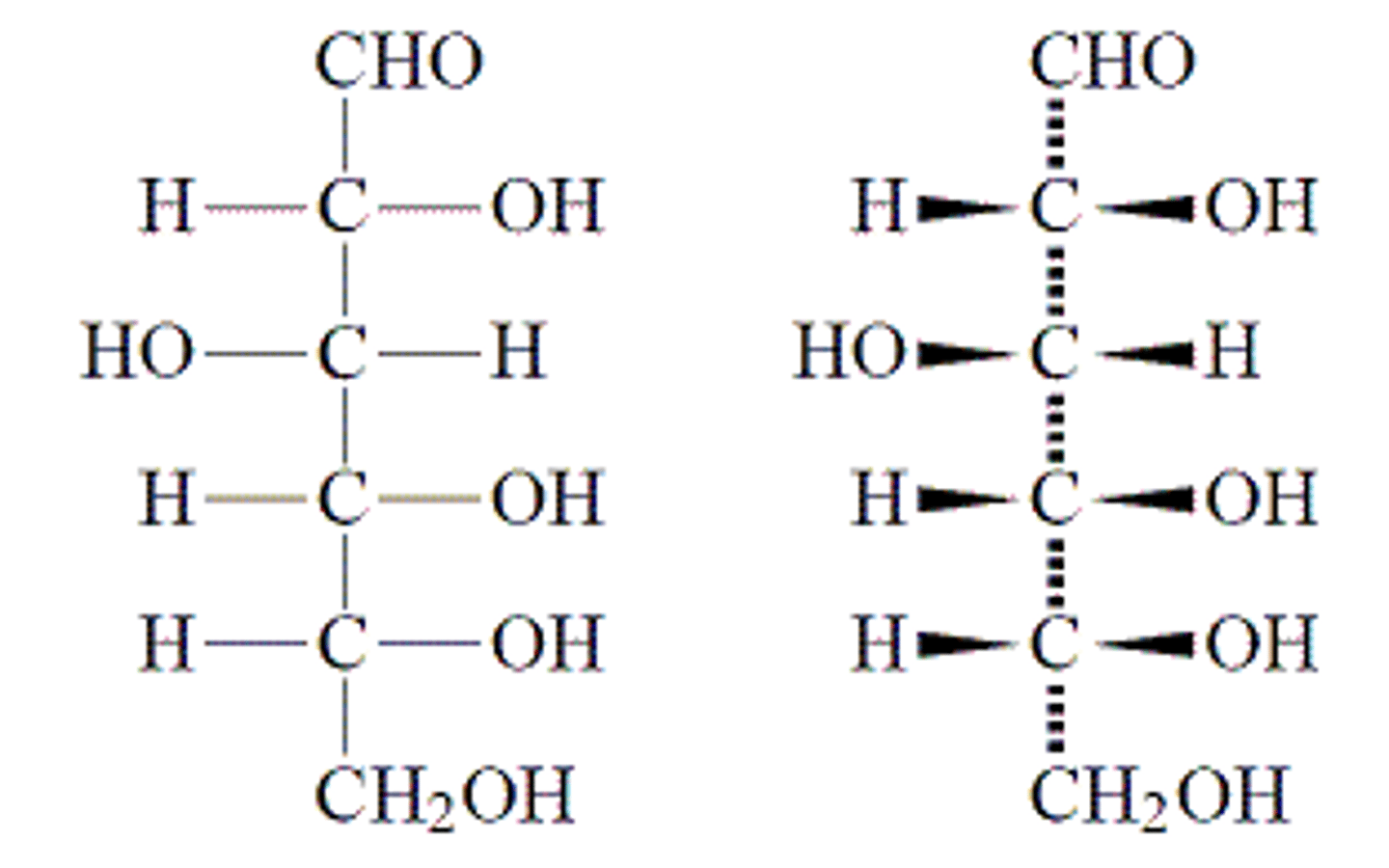
In a Fischer Projection, vertical bonds represent dashed or solid lines? Horizontal bonds represent dashed or solid lines?
Vertical bonds represent dashed lines (meaning the bond goes into the page).
Horizontal bonds represent solid lines (meaning the bond goes out of the page).
Which of the following is the general structure of a Carbohydrate?
(A) Cn(H2O)n
(B) Cn(H2O)m
(C) Cn(H2O)2n
(D) Cn(HO)m
(A) Cn(H2O)n
Cn(H2O)n is the general structure of a Carbohydrate.
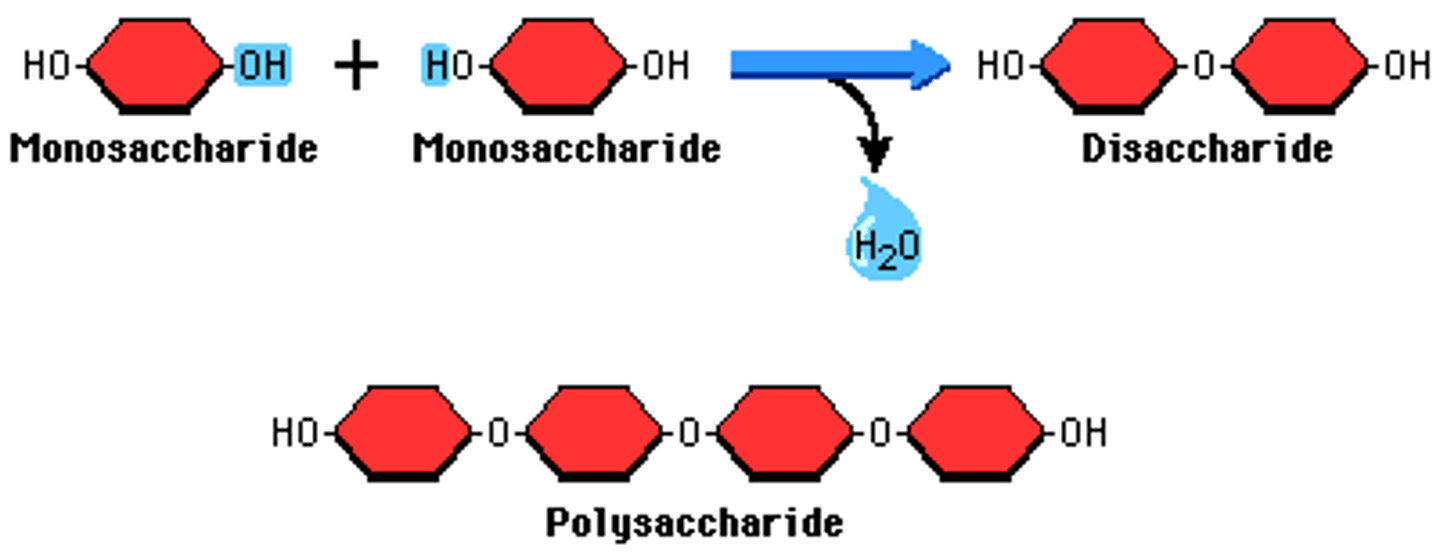
CRB Monosaccharide vs. Disaccharide vs. Polysaccharide?
Monosaccharide is composed of a single sugar monomer.
Disaccharide is composed of two sugar monomers.
Polysaccharide is composed of more than two sugar monomers.
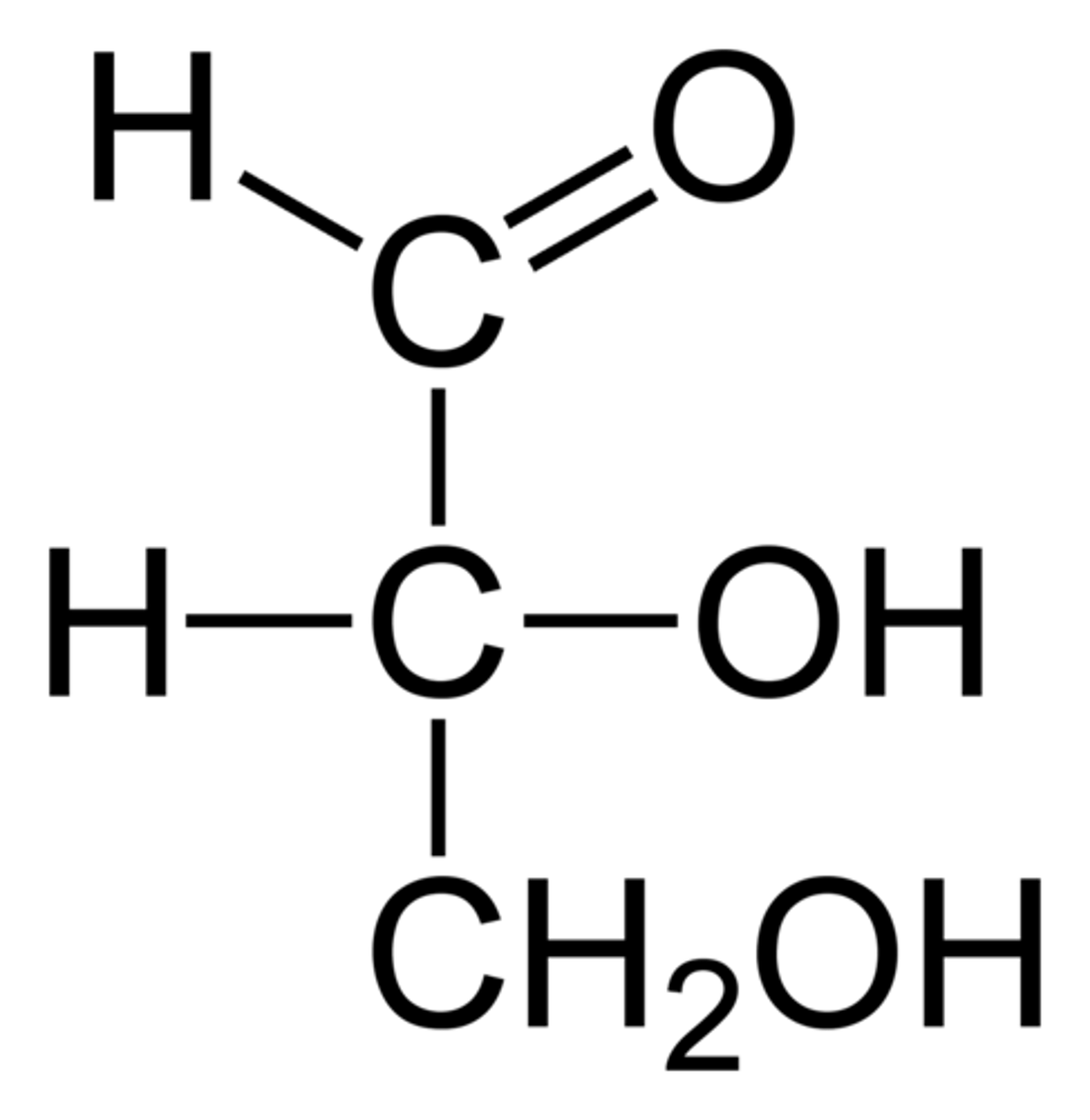
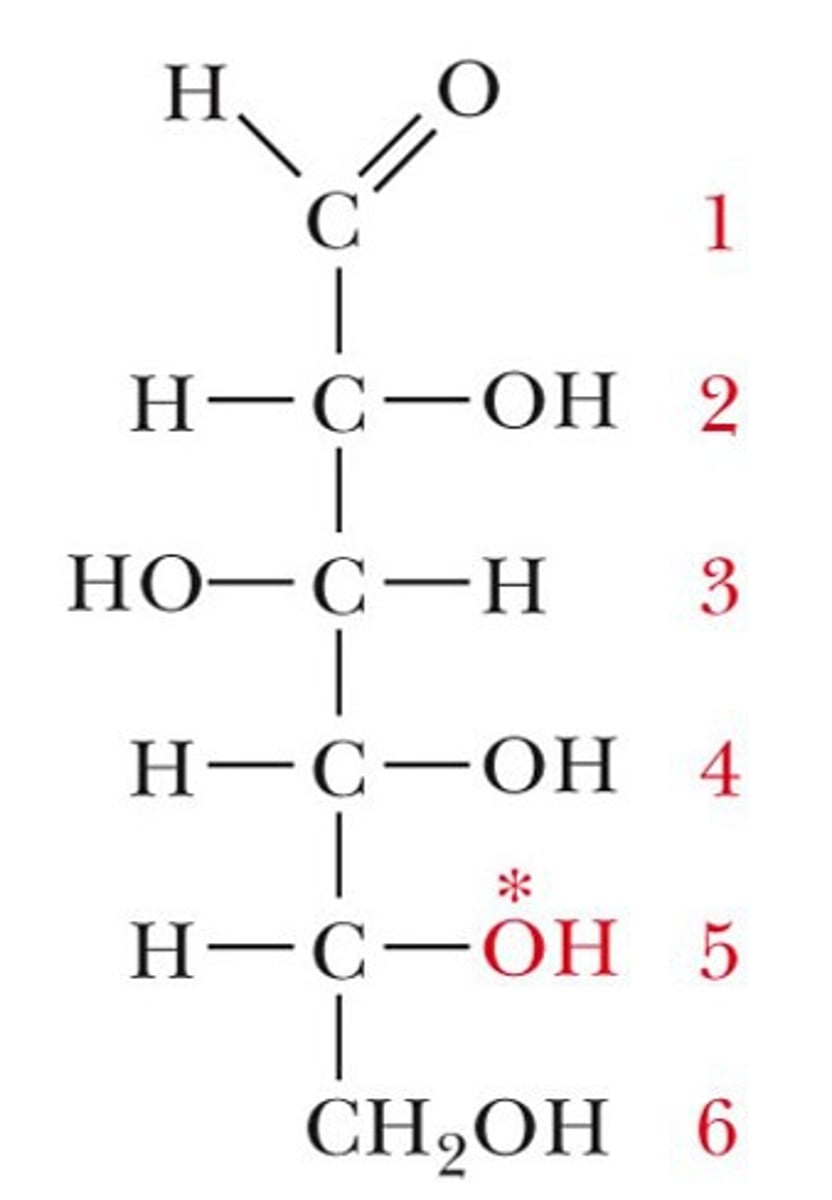
Draw the Fischer Projection for Glyceraldehyde.
Glyceraldehyde is considered the most simple carbohydrate.
Glyceraldehyde is considered an:
(A) Aldotriose
(B) Aldotetrose
(C) Aldopentose
(D) Aldohexose
(A) Aldotriose
Glyceraldehyde is considered an aldotriose because it has 3 carbons and contains an aldehyde functional group.
Draw the Fischer Projection for Glucose.
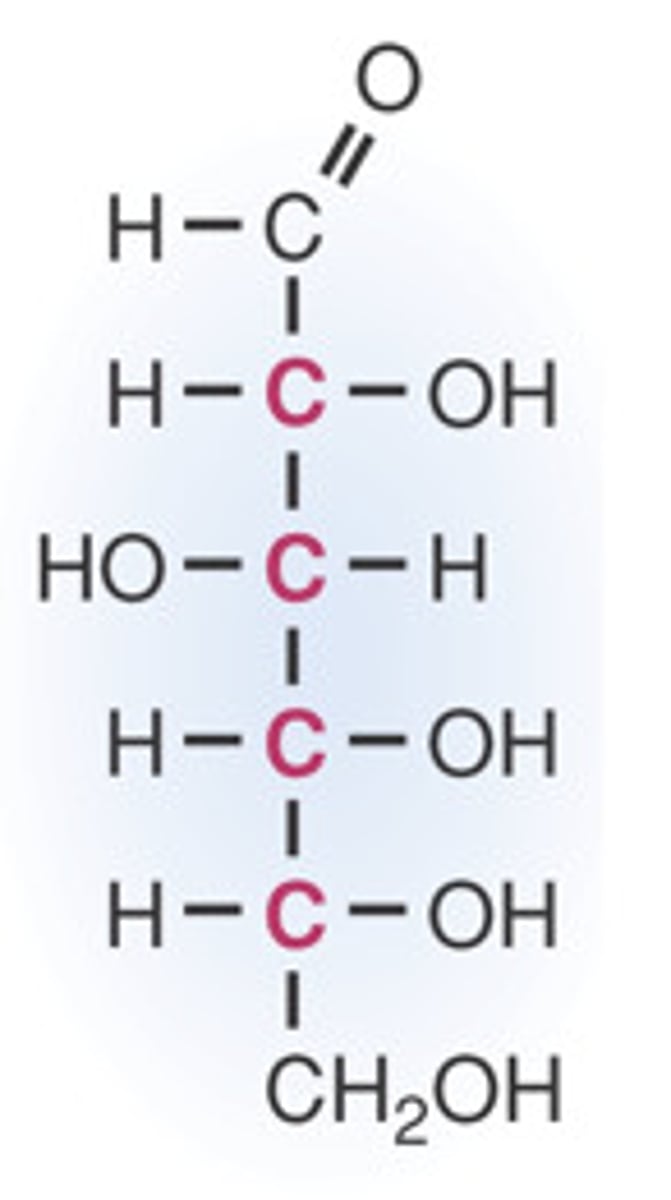
Draw the Fischer Projection for Fructose.
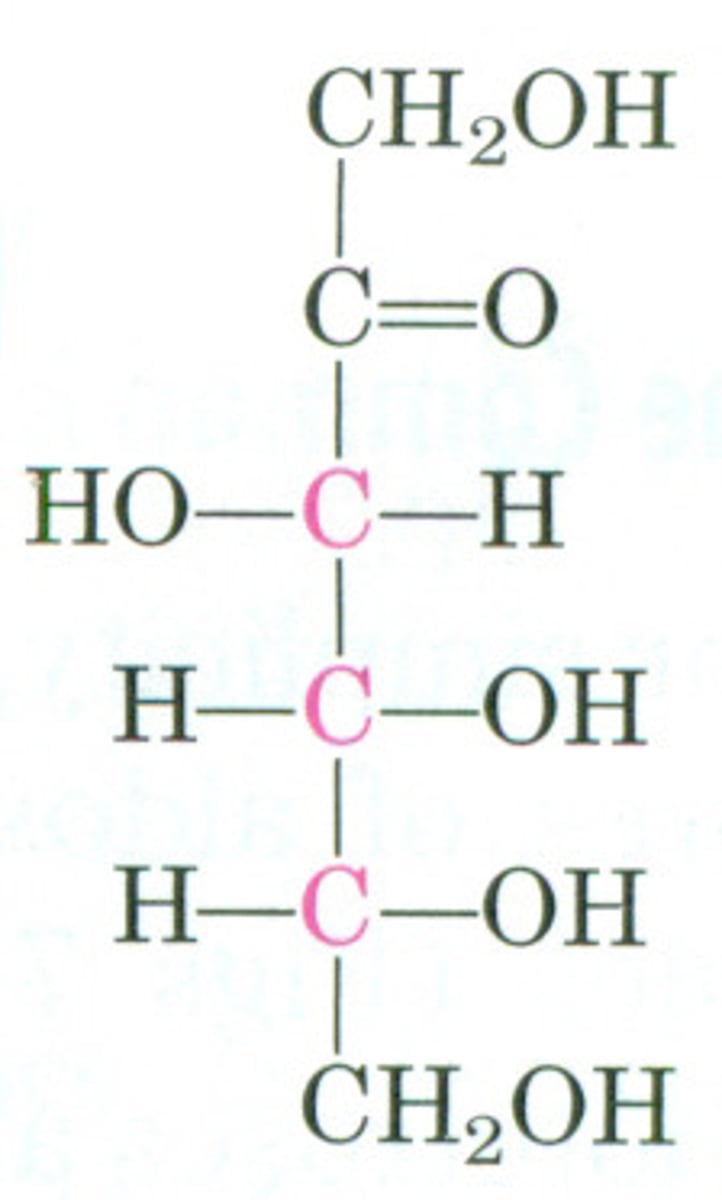
Glucose is considered a(n) ______________ and Fructose is considered a(n) _______________.
(A) Ketohexose, Aldohexose
(B) Aldohexose, Ketohexose
(C) Ketohexose, Ketohexose
(D) Aldohexose, Aldohexose
(B) Aldohexose, Ketohexose
Glucose is considered an aldohexose and Fructose is considered a ketohexose.
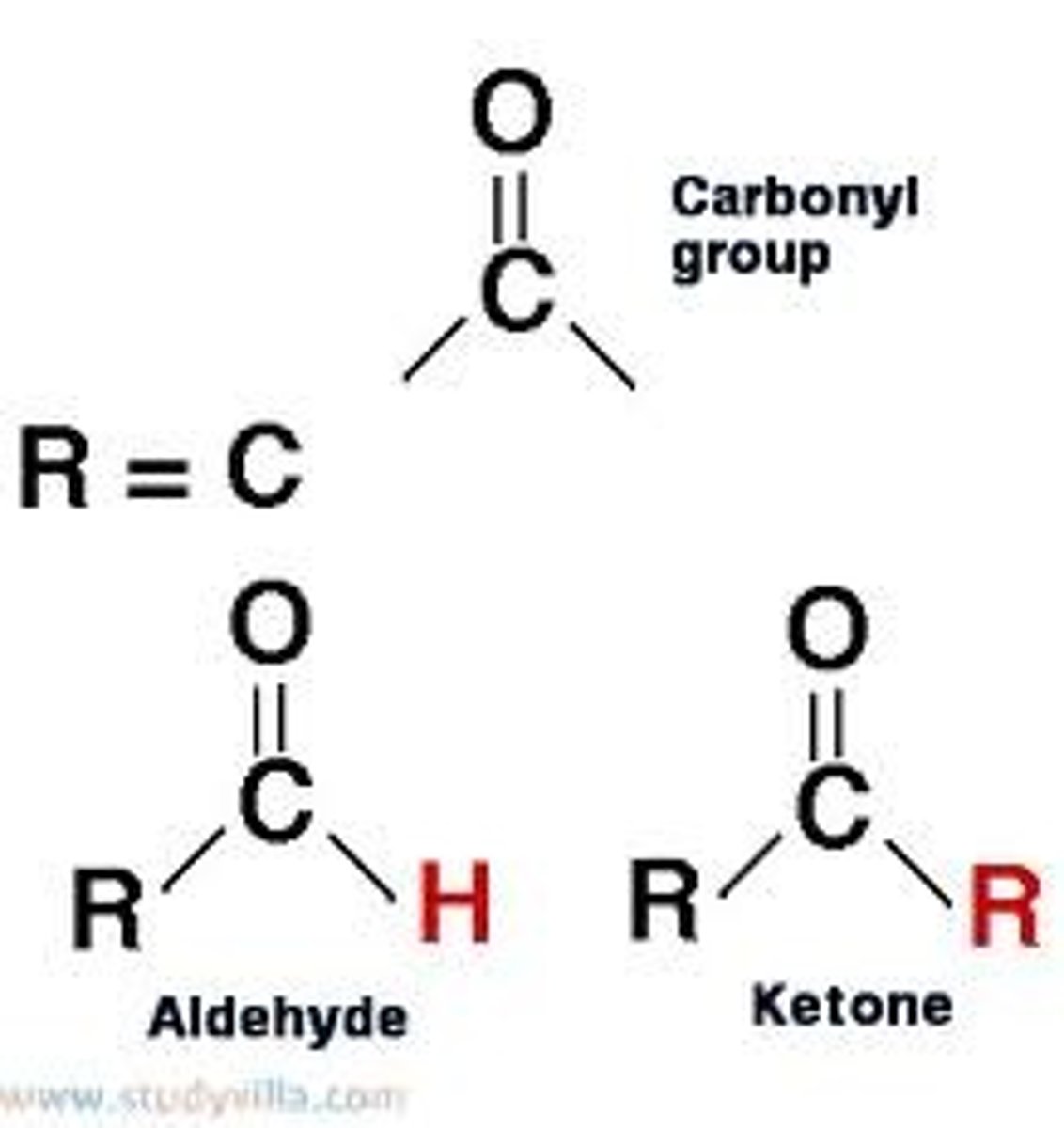
CRB The previous question relies upon knowing different types of carbonyls. Which of the following properly describes the difference between an aldehyde (aldo-) and ketone (keto-)?
(A) An aldehyde has two hydrogens bound to the carbonyl, whereas a ketone has one.
(B) The aldehyde has an oxygen double bond, whereas the ketone has a sulfur double bond.
(C) The aldehyde has one hydrogen bound to the carbonyl, whereas the ketone has two.
(D) The aldehyde has one carbon bound to the carbonyl, whereas the ketone has two.
(D) The aldehyde has one carbon bound to the carbonyl, whereas the ketone has two.
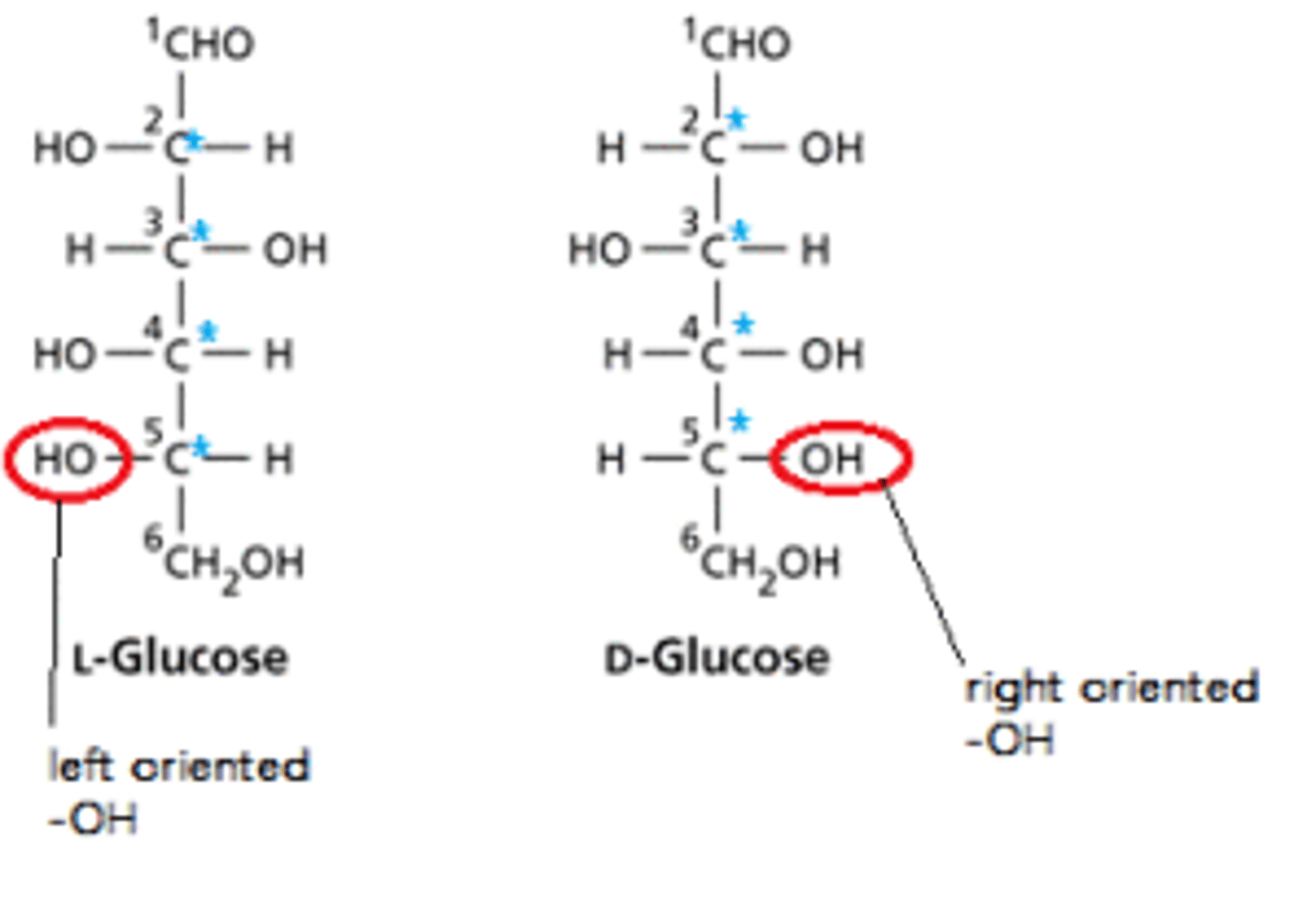
How is D- vs. L- designation determined for sugar molecules?
You look at the final chiral carbon and determine if it is R or S. R -> D. S -> L.
Draw D- vs L-glucose.
An easy way to distinguish the two is by what side the hydroxide on the final chiral carbon. With the aldehyde at the top of the Fischer projection, right side hydroxyls are D-glucose and left side hydroxyls are L-glucose.
What is the difference between a Hemiacetal vs. Acetal?
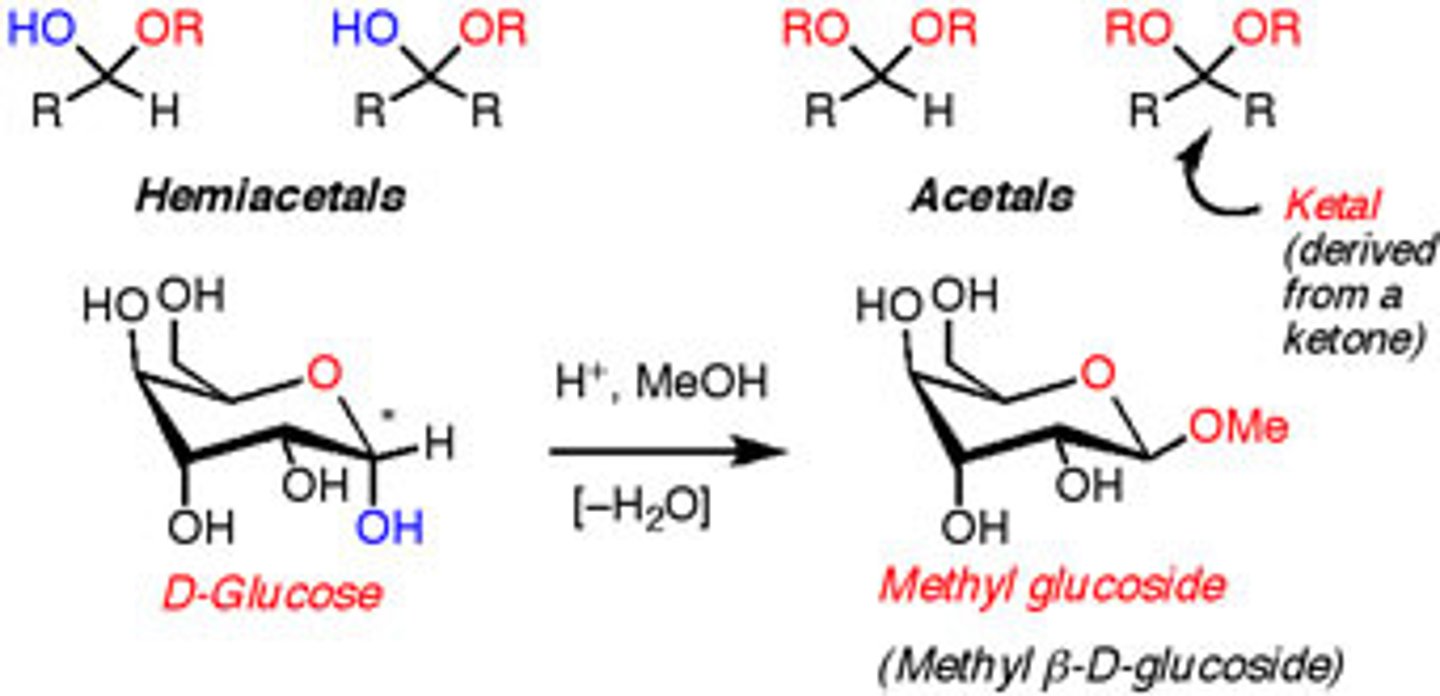
True or False? Sugars that are Hemiacetals are termed Glycosides.
False. Sugars that are ACETALS are termed Glycosides.
What type of reaction is used to form a Glycoside from a sugar monomer?
(A) Oxidation-reduction
(B) Ligase
(C) Condensation
(D) Hydrolysis
(C) Condensation
A condensation reaction is used to form a Glycoside from a sugar monomer
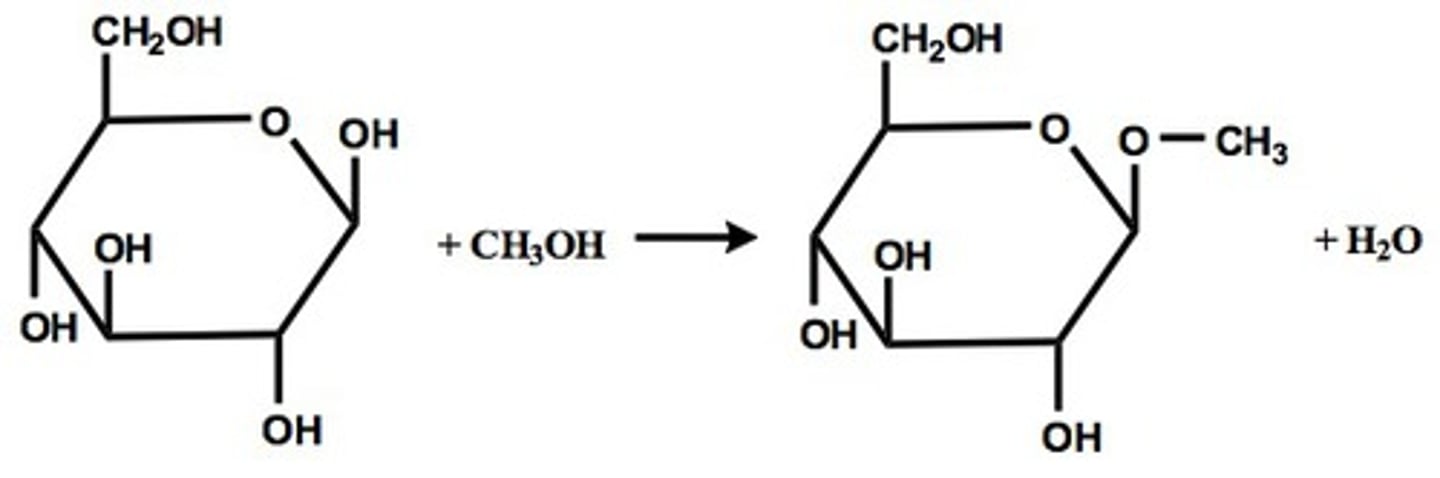
Draw the Glycoside Formation Reaction mechanism in the presence of acid.
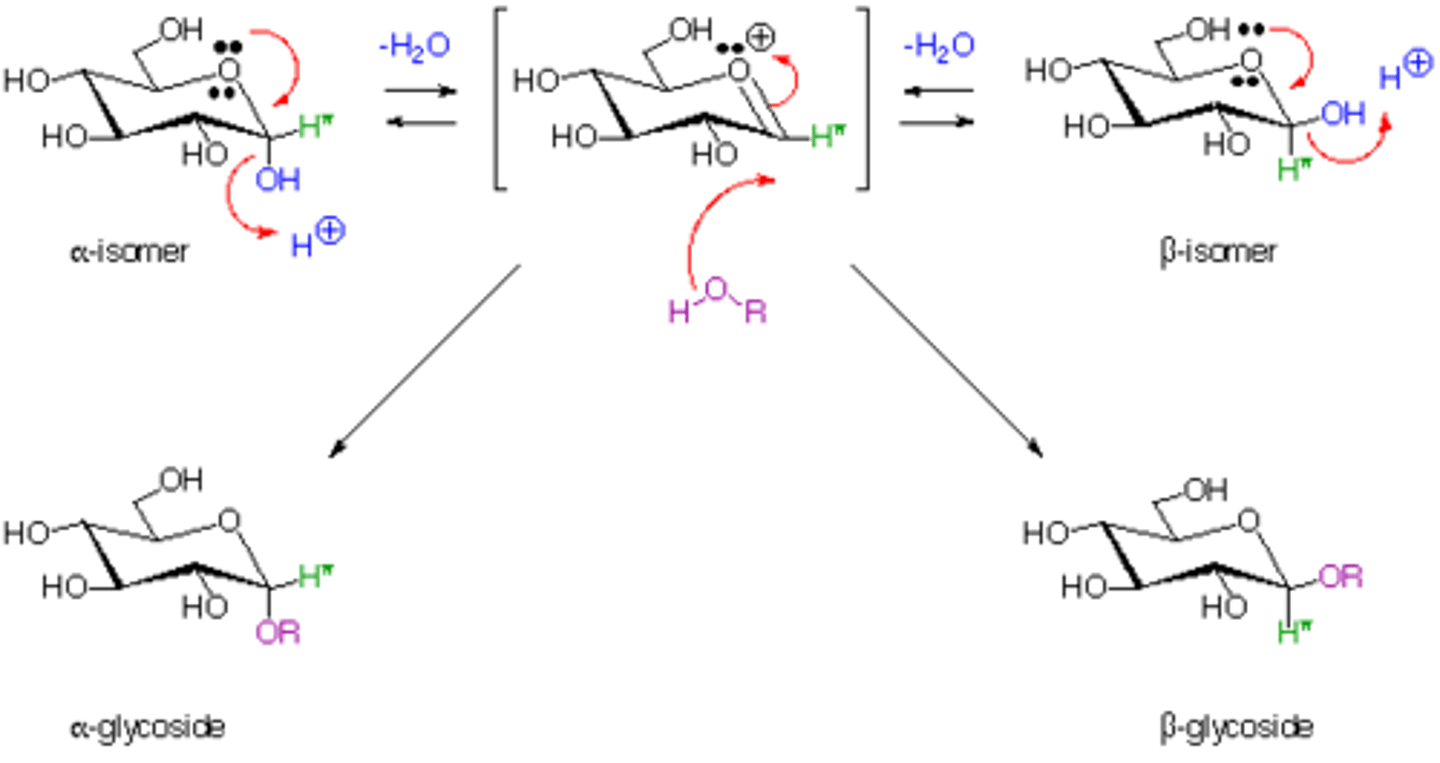
Why is it significant that you have a "Planar" Carbocation in the middle of the reaction mechanism in terms of the kind of products you would expect to get out of this reaction?
A "Planar" Carbocation can be attacked from above or below, resulting in two isomers of the Glycoside.
Draw α- vs. β-glucose. How do you determine whether a sugar is α- vs. β-?
α-sugars have the OH group in the trans conformation as compared with the final carbon.
β-sugars have the OH group in the cis conformation as compared with the final carbon.
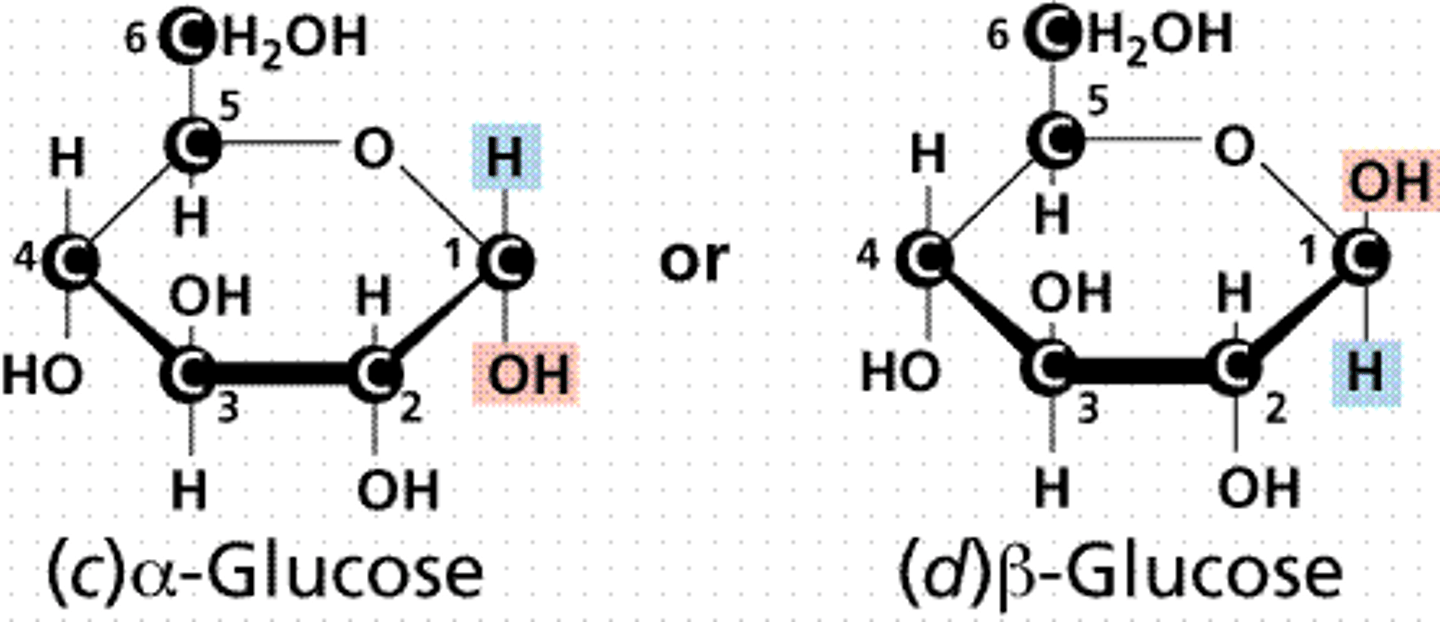
CRB Can an α-glucose be converted into a β-glucose in nature? If so, what is this process called?
(A) Yes, this process can occur and is called Transformation.
(B) Yes, this process can occur and is called Transduction.
(C) Yes, this process can occur and is called Mutarotation.
(D) No, these two forms of glucose do not interconvert in nature.
(C) Yes, this process can occur and is called Mutarotation.
CRB Draw out the mechanism for Mutarotation. What type of intermediate is involved?
An Open-chair (Open-Chain) form of D-glucose is involved, and the ring could close to form either the α-glucose or β-glucose.
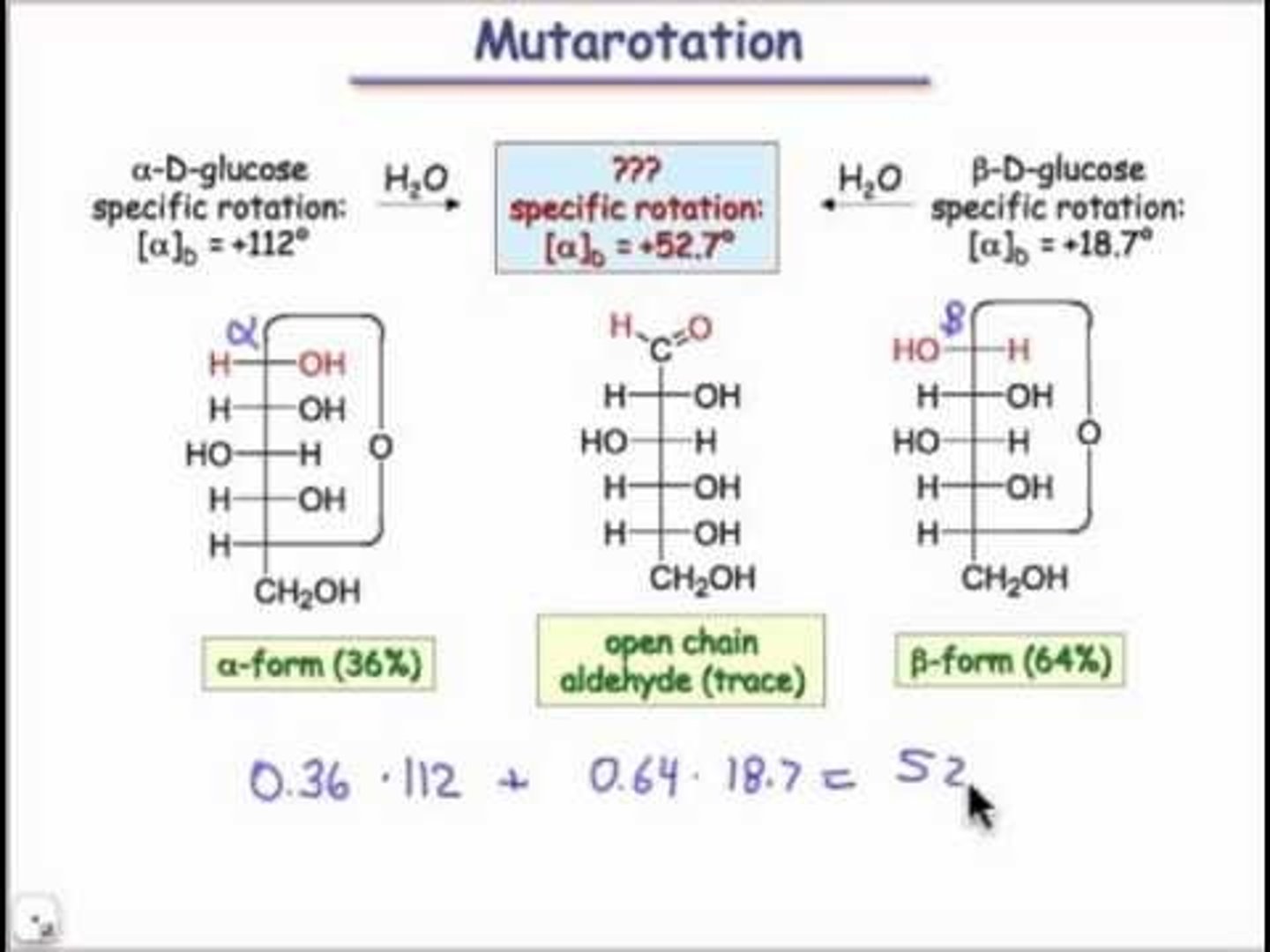
CRB Does the α-glucose naming have any relation to α-carbons and α-hydrogens?
(A) Yes, because they both use the α.
(B) Yes, because in the open-chain form, the carbon that determines if it is α- or β-glucose is the carbonyl carbon.
(C) Yes, because in a glucose ring, the carbon that determines α- or β-glucose is next to the carbonyl carbon.
(D) No, these are two separate naming conventions.
(D) No, these are two separate naming conventions.
The carbon that has the key hydroxyl group would be the carbonyl carbon, not the α-carbon anyways!
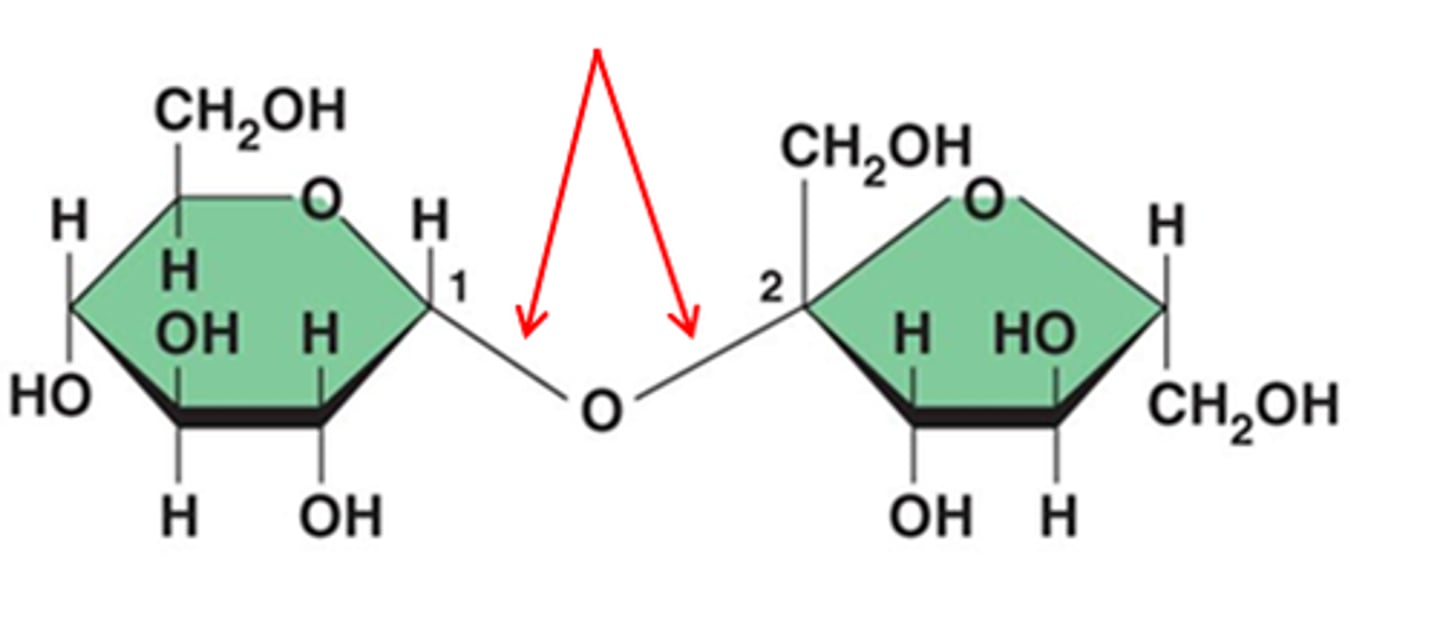
What is a Glycosidic Linkage?
A glycosidic linkage is the bond between two sugar monomers.
The breaking of a Glycosidic Linkage is what type of reaction?
(A) Oxidation-reduction
(B) Ligase
(C) Condensation
(D) Hydrolysis
(D) Hydrolysis
The breaking of a Glycosidic Linkage is a hydrolysis reaction (think HydroLYSIS).
CRB In a human liver cell, there are many types of glycosidic bonds. Which of the following are likely to be seen in glycogen?
I. Glucose-α-1,4-Glucose
II. Glucose-α-1,6-Glucose
III. Glucose-β-1,4-Glucose
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III
(B) I and II only
In glycogen, there are 2 main types of glycosidic bonds seen:
I. Glucose-α-1,4-Glucose within a glycogen chain
II. Glucose-α-1,6-Glucose at the branching points
CRB Glucose-β-1,4-Glucose bonds are often seen in the cell walls of plants and are not readily digested by humans. Why do we not break these bonds?
(A) Because these are β-glycosidic bonds and animals can only break down α-bonds.
(B) Because humans lack an enzyme for β-1,4 glycosidic bonds specifically.
(C) Because humans do not have the right intracellular conditions to spontaneously break these bonds.
(D) Not enough information is given.
(B) Because humans lack an enzyme for β-1,4 glycosidic bonds specifically.
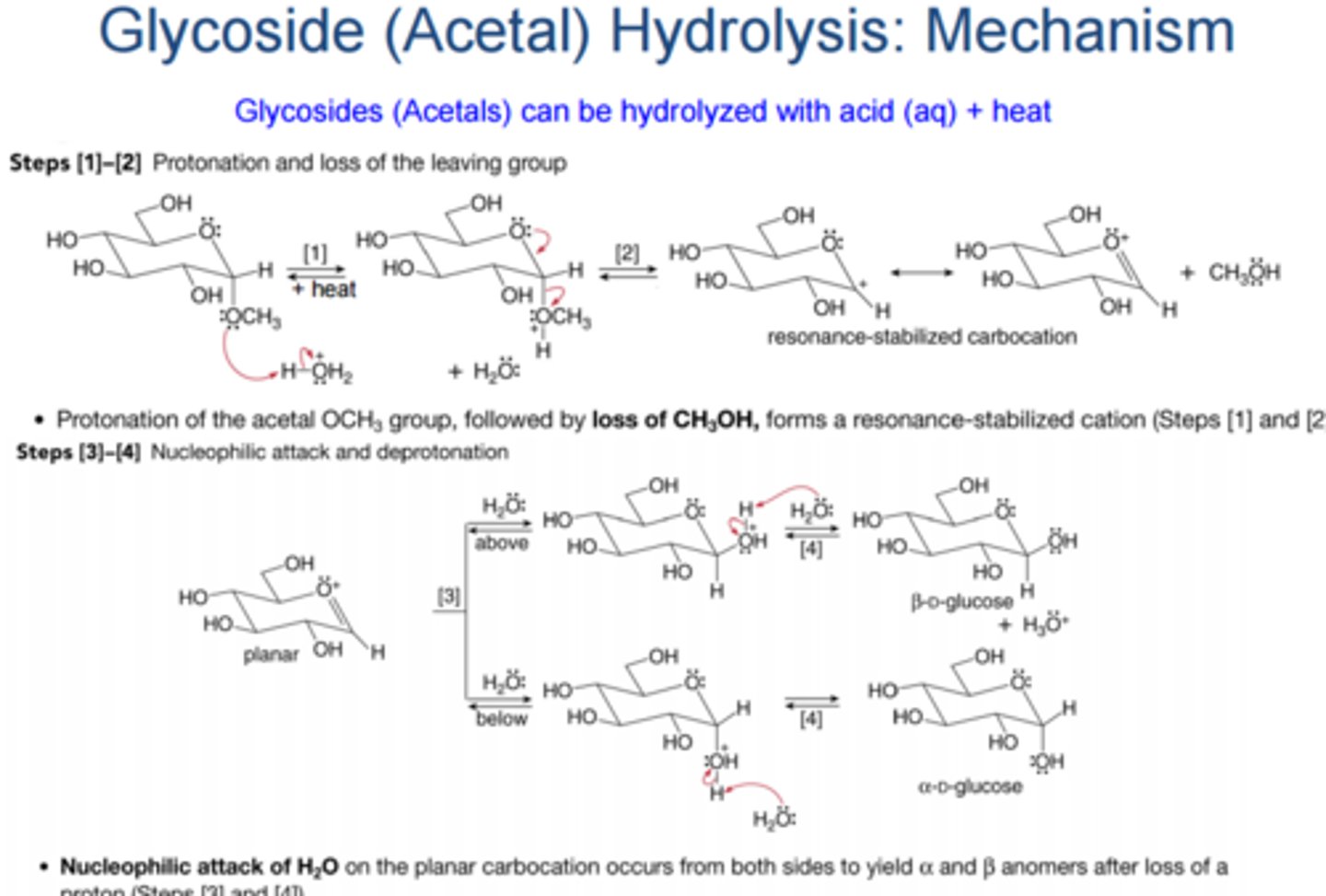
Draw the Glycoside Hydrolysis Mechanism.
It is the opposite of a Glycoside Formation Reaction.
CRB Fill in the blanks: A five-membered sugar ring is called a _________, whereas a six-membered sugar ring is called a ___________.
Fill in the blanks using:
- Furanose
- Aldose
- Ketose
- Pyranose
Furanose, Pyranose
A five-membered sugar ring is called a Furanose, whereas a six-membered sugar ring is called a Pyranose.
CRB Based on the previous question, how would you classify fructose and glucose, respectively, in their ringed structures?
(A) Furanose, Furanose
(B) Furanose, Pyranose
(C) Pyranose, Furanose
(D) Pyranose, Pyranose
(B) Furanose, Pyranose
Fructose forms a five membered ring, making it a furanose. Glucose forms a six-membered ring, making it a pyranose.
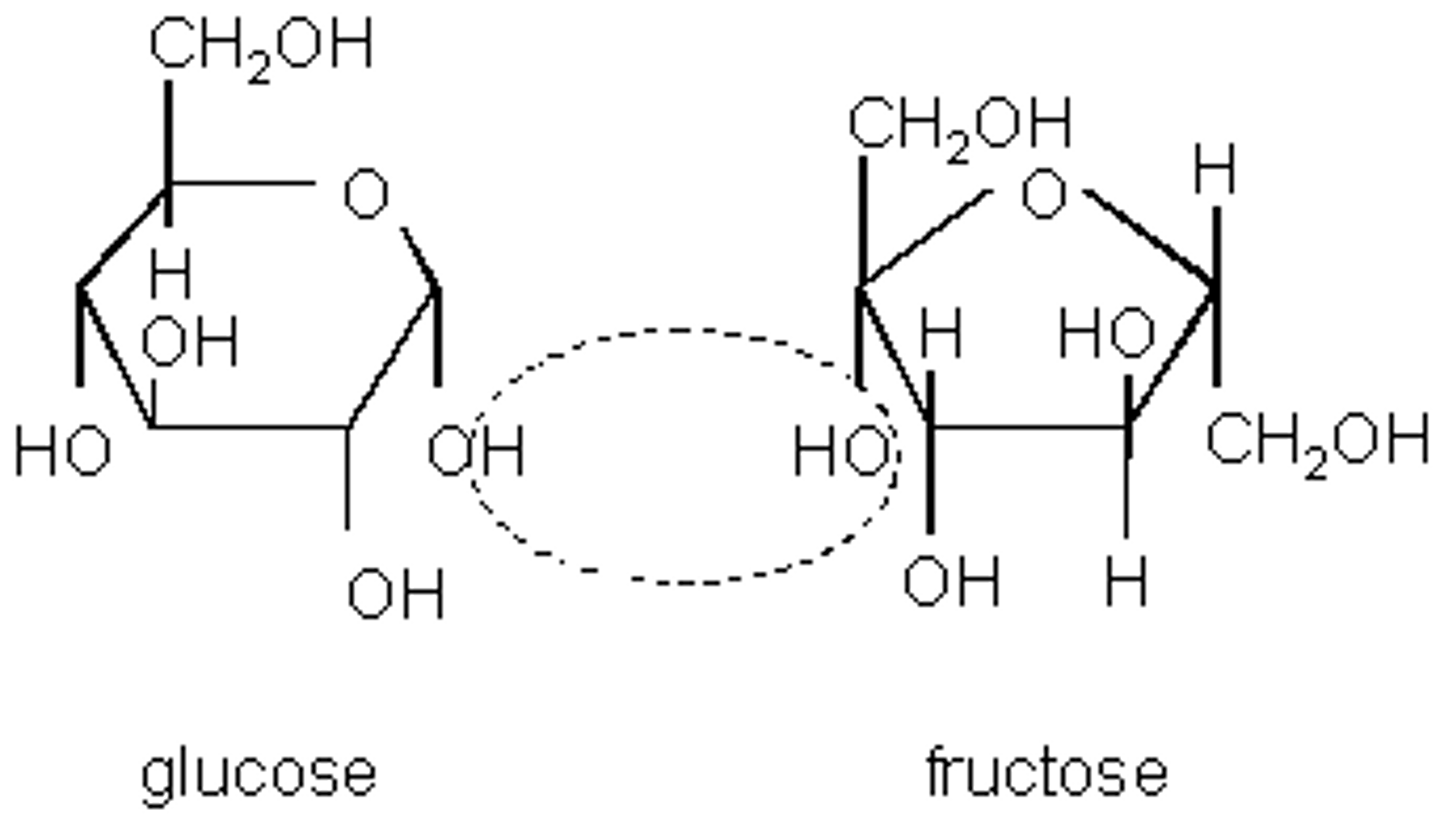
CRB There are also a class of sugars called "reducing sugars", which have an aldehyde-like structure at C1. Benedict's Test uses Cu2+ to test for these reducing sugars, and changes color when in the presence of those hemiacetals (aldehyde-like structures). Which of the following will react LEAST with Benedict's Test?
(A) Monosaccharides like glucose
(B) Disachharide Lactose
(C) Disachharide Maltose
(D) Polysaccharides like Glycogen
(D) Polysaccharides like Glycogen
Only sugars with a free C1 will be able to react in Benedict's Test, since glycosidic linkages often involve C1. Therefore, a polysaccharide would react least with this test.
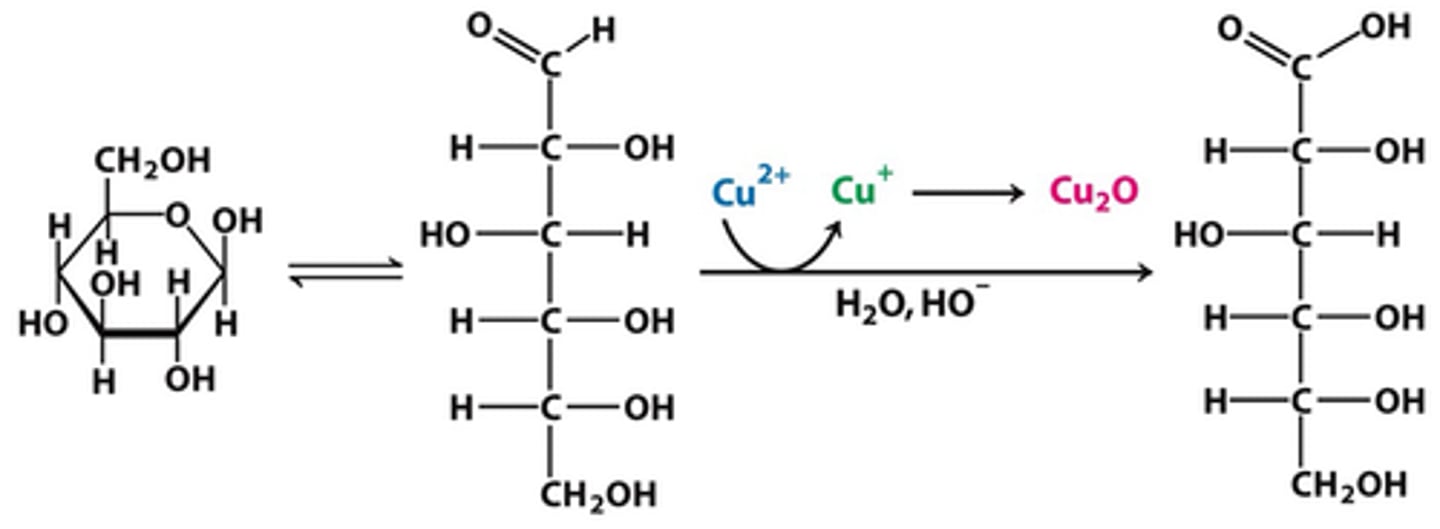
Saponification could also be known as an:
(A) Alcohol Hydrolysis
(B) Alcohol Condensation
(C) Ester Hydrolysis
(D) Ester Condensation
(C) Ester Hydrolysis
In a Saponification Reaction, the ester bonds of Triglycerol are hydrolyzed, forming individual fatty acids.
Draw the Base-catalyzed Saponification Reaction Mechanism.
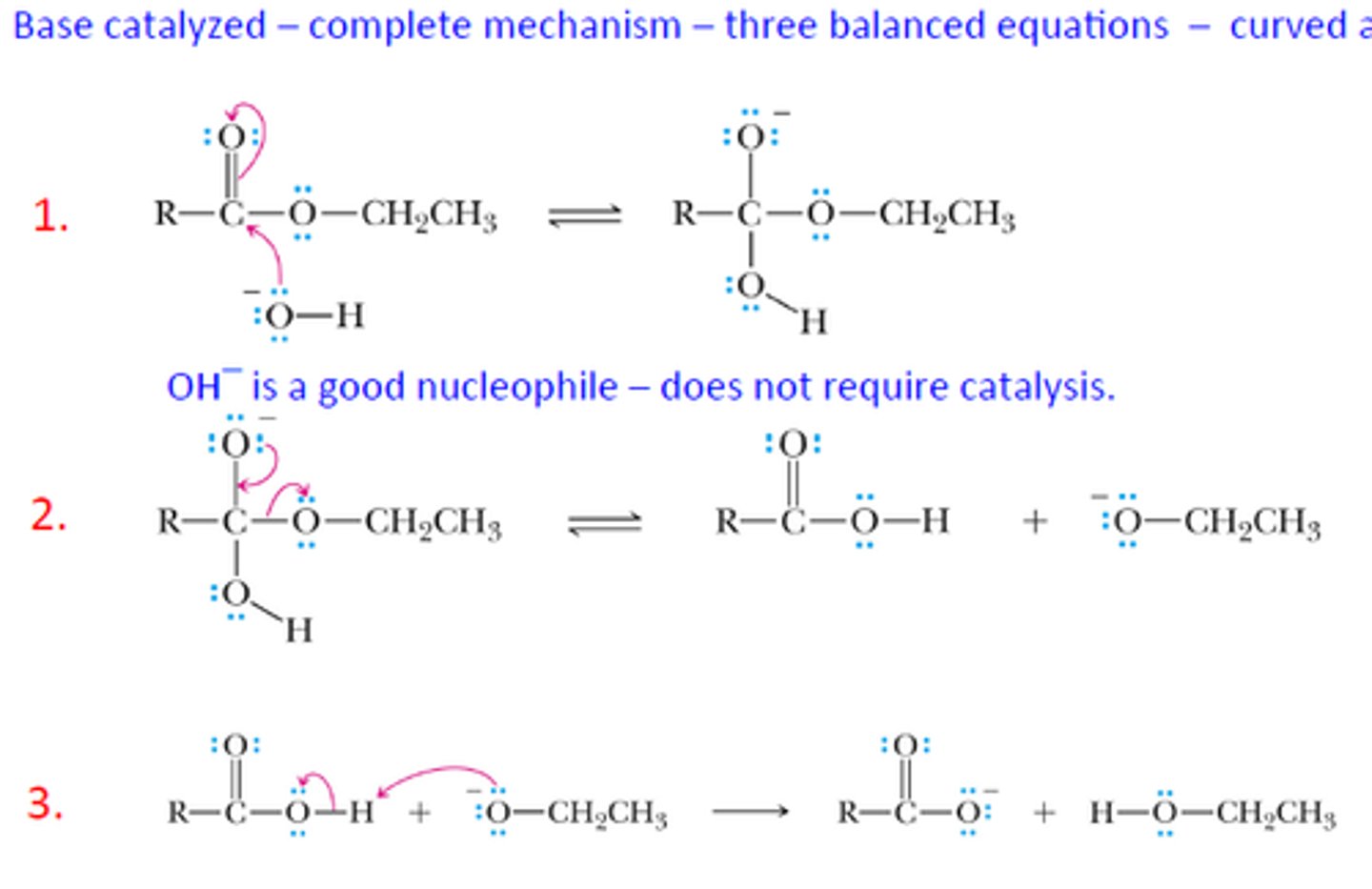
Why is this reaction called Saponification?
This reaction is called Saponification because it results in the formation of soap molecules.
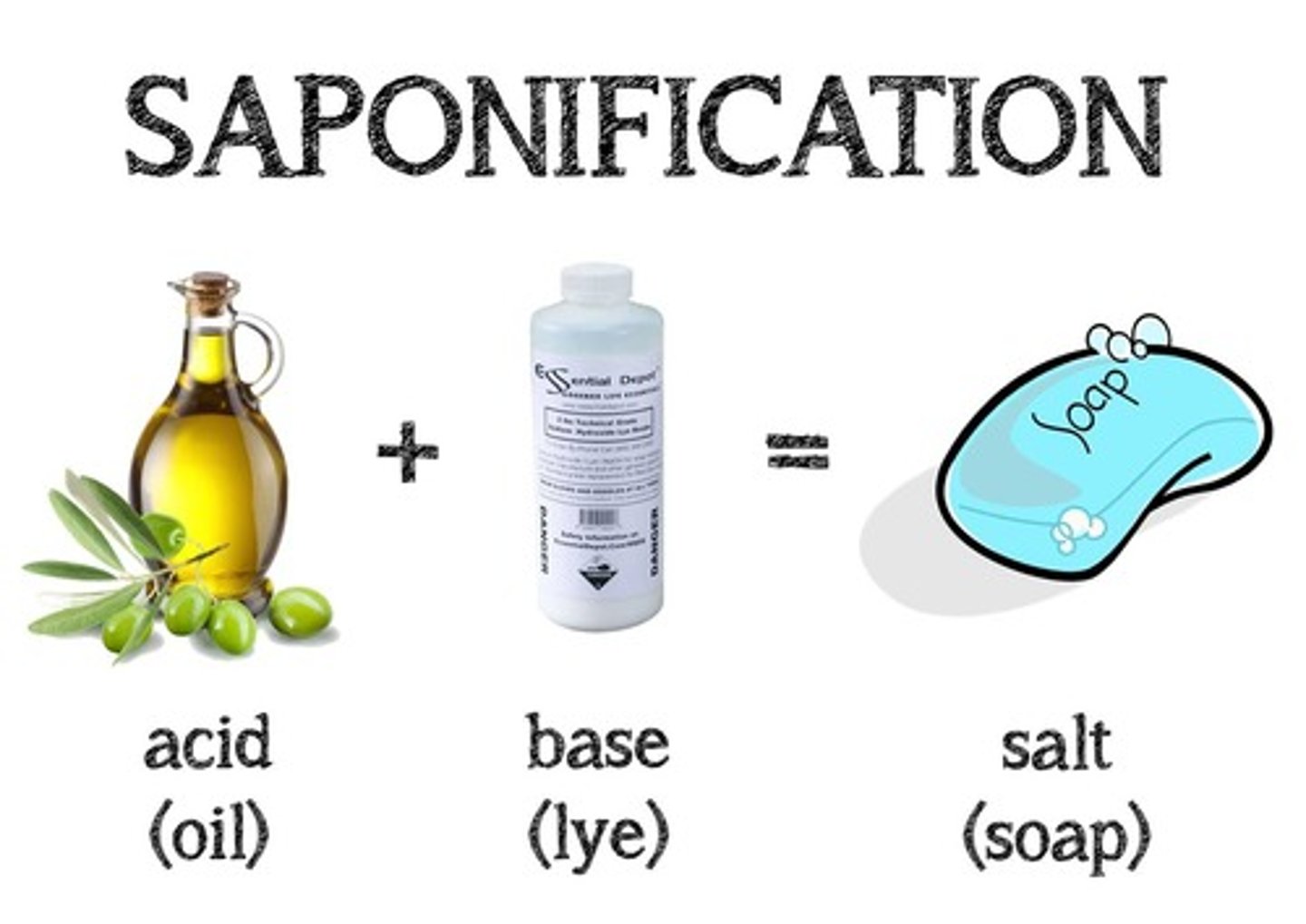
Why do Fatty Acids make for good soap molecules?
Fatty Acids make for good soap molecules because they have a non-polar tail that will trap non-polar greasy particles. Then the polar heads will be attracted to water, causing the grease to get dissolved in and washed away by the water.

CRB What is the term to describe molecules that have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties?
(A) Aliphatic
(B) Amphipathic
(C) Amphoteric
(D) Alimony
(B) Amphipathic
An amphipathic molecule has both hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties.
CRB Which of the following are important reasons why fatty acids are used for long-term storage of energy?
I. Fatty acids can pack tighter due to having greater waters-of-solvation than carbohydrates.
II. They are more reduced than carbohydrates.
III. They are more readily available for metabolism than carbohydrates.
(A) II only
(B) I and II only
(C) I and III only
(D) I, II and III
(A) II only
Fatty acids are used for long-term storage of energy for two important reasons:
I. They can pack tighter due to HAVING LESS waters-of-solvation than carbohydrates.
II. They are more reduced than carbohydrates.
Draw a generic Phospholipid.
Basically a Triglyceride with a Phosphate group.
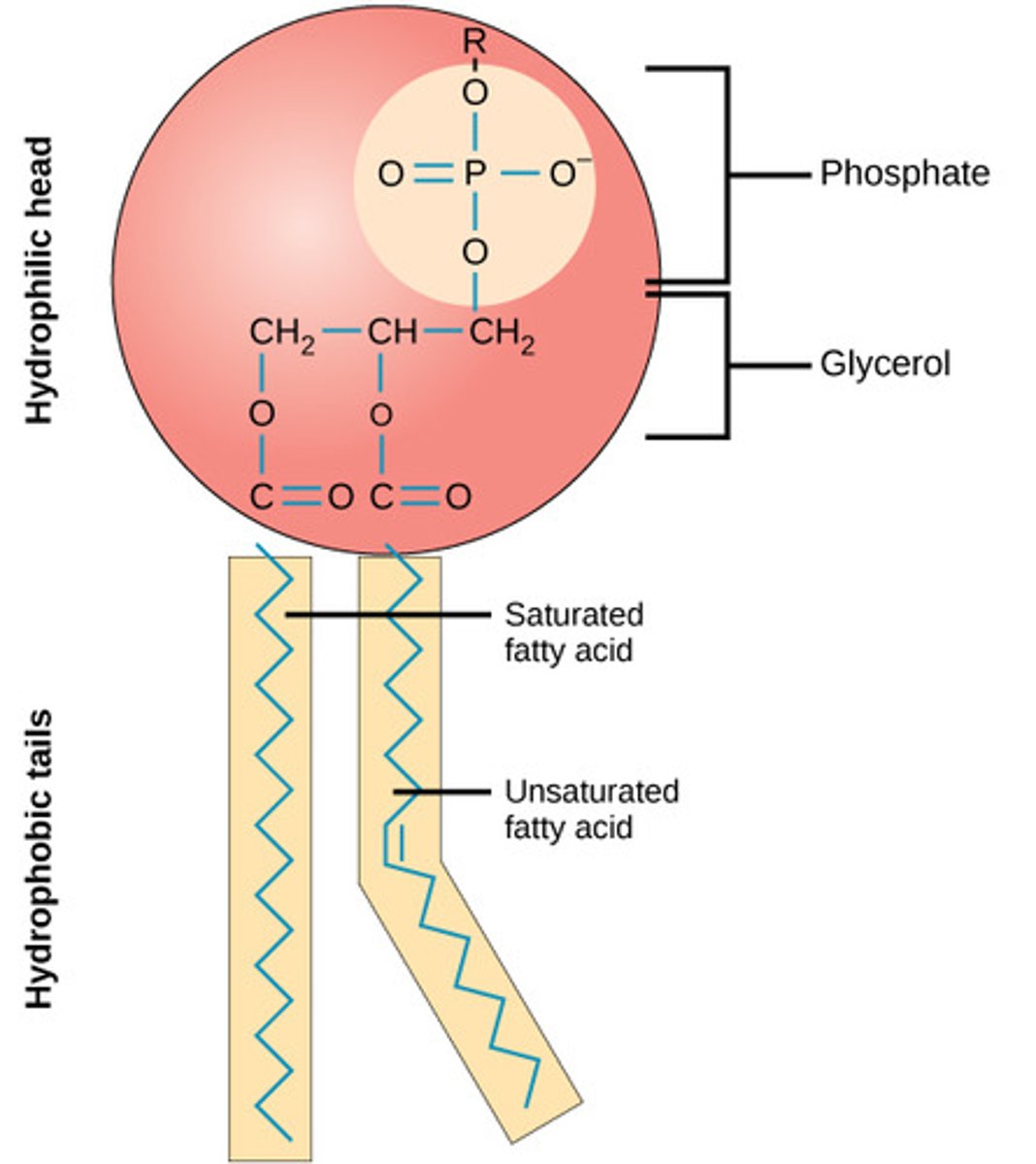
What about the structure of Phospholipids makes them work so well for Lipid Bilayers?
The Phosphate group is polar, which will face away from the bilayer and the Fatty Acid tails are non-polar and will thus face toward the center of bilayer towards each other.
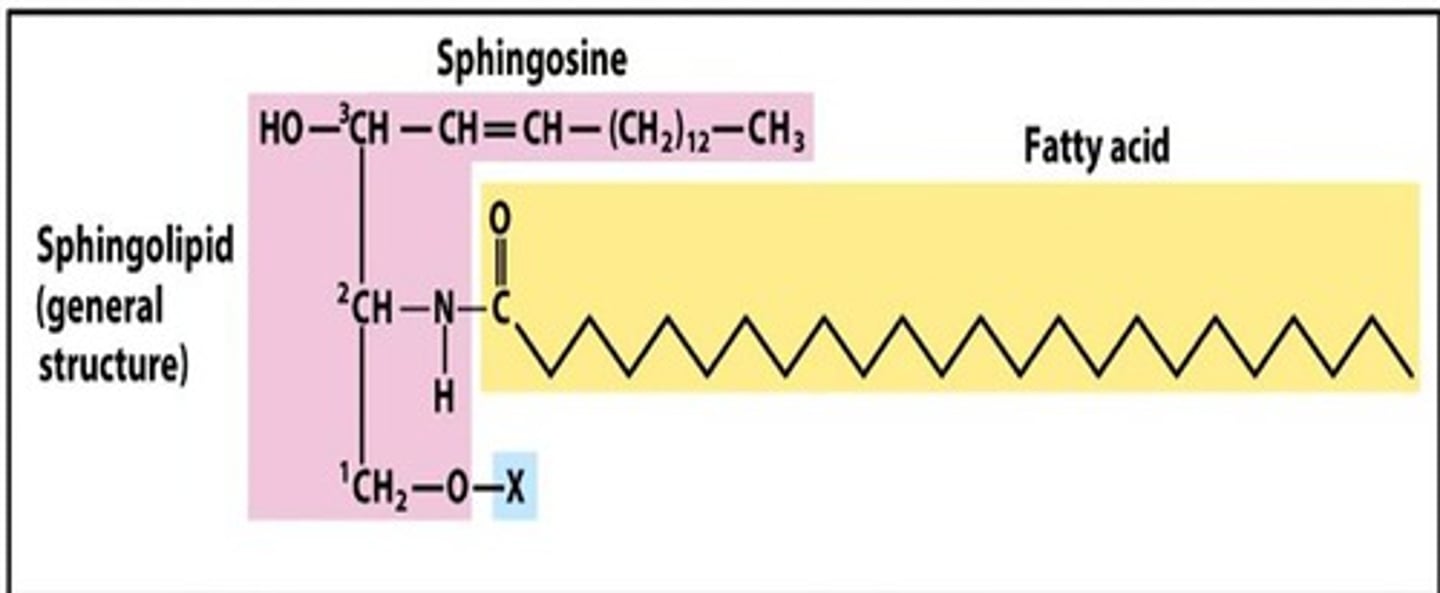
Draw the generic structure of a Sphingolipid.
Made of a high MW amino alcohol sphingosine, the X is where phosphate group would be
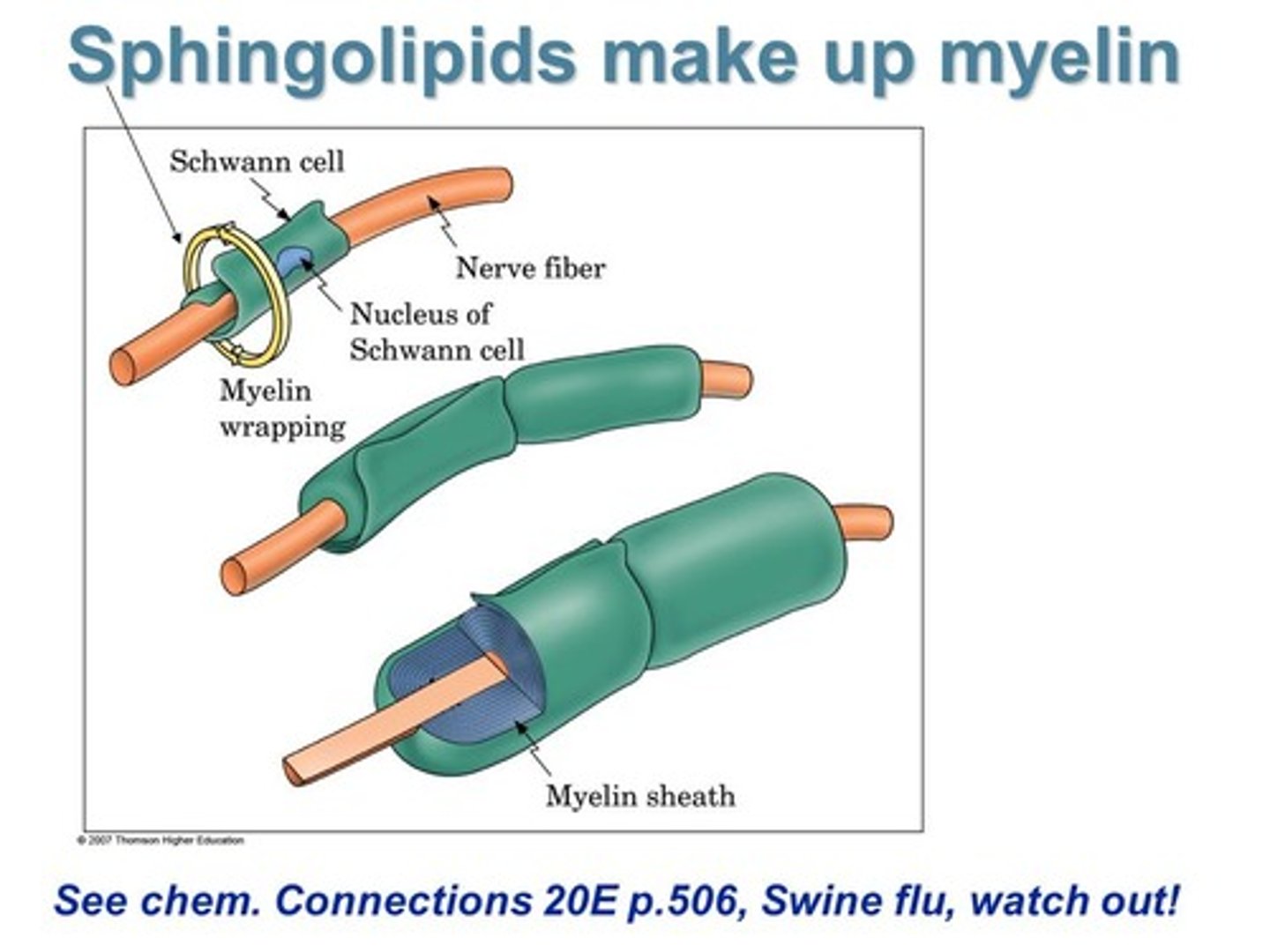
Describe the special role that Sphingolipids play within the Nervous System.
Sphingolipids are a key component of myelin which composes the Myelin Sheath.
Waxes are formed via the combination of two molecules with which two functional groups?
(A) Alcohol and an Ester
(B) Alcohol and a Carboxylic Acid
(C) Carboxylic Acid and an Ester
(D) Alcohol and an Alcohol
(B) Alcohol and a Carboxylic Acid
Waxes (esters) are formed via the combination of two molecules, one having an alcohol functional group and the other (typically a fatty acid) having a carboxylic acid functional group.
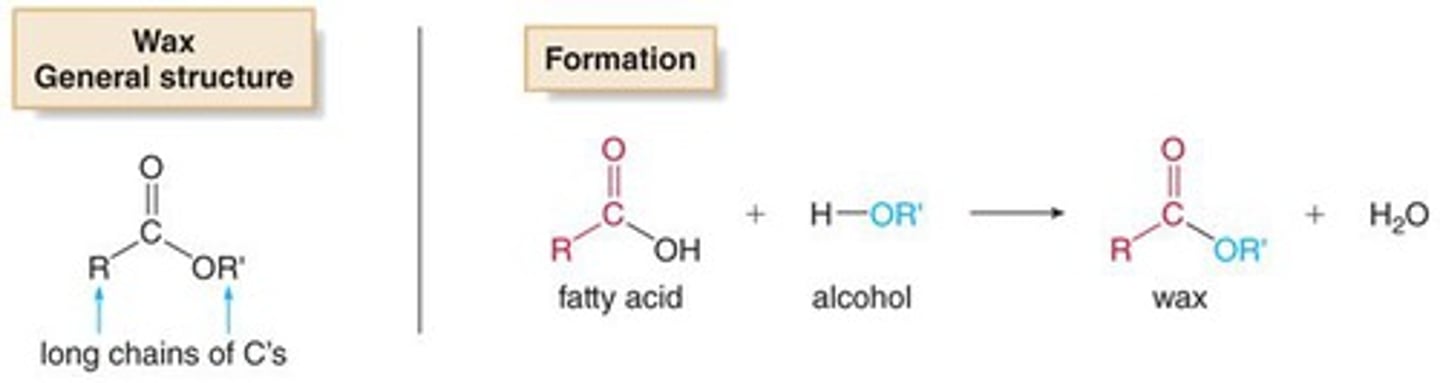
What about the structure of waxes makes them so good at repelling water?
Their two hydrophobic tails are what repel water.

Aspirin and Ibuprofen are Non-steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDS) work by inhibiting the production of what molecules?
(A) Triglycerides
(B) Prostaglandins
(C) Sphingolipids
(D) Steroids
(B) Prostaglandins
Aspirin and Ibuprofen are Non-steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDS) work by inhibiting the production of Prostaglandins.
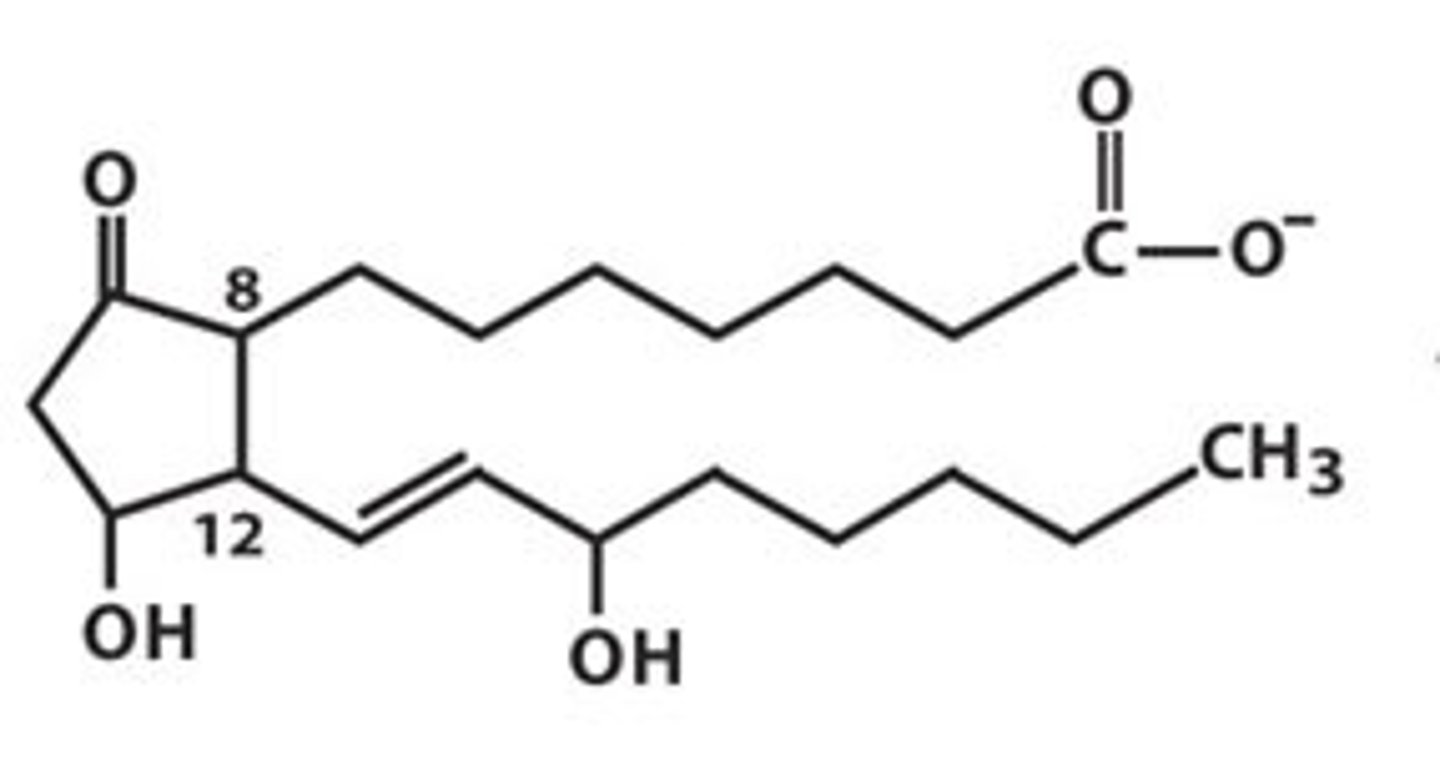
Which of the following is not a hydrolyzable lipid?
(A) Triglycerol
(B) Prostaglandins
(C) Phospholipids
(D) Wax
(B) Prostaglandins
Non-hydrolyzable lipids include prostaglandins, steroids, corticosteroids and fat-soluble vitamins.
Prostaglandins are considered to be Eicosanoids, which are typically signaling molecules. What makes something an Eicosanoid?
Eicosanoids are molecules with 20 carbons ("eico-" means 20).
Draw the generic ring structure of a Steroid.

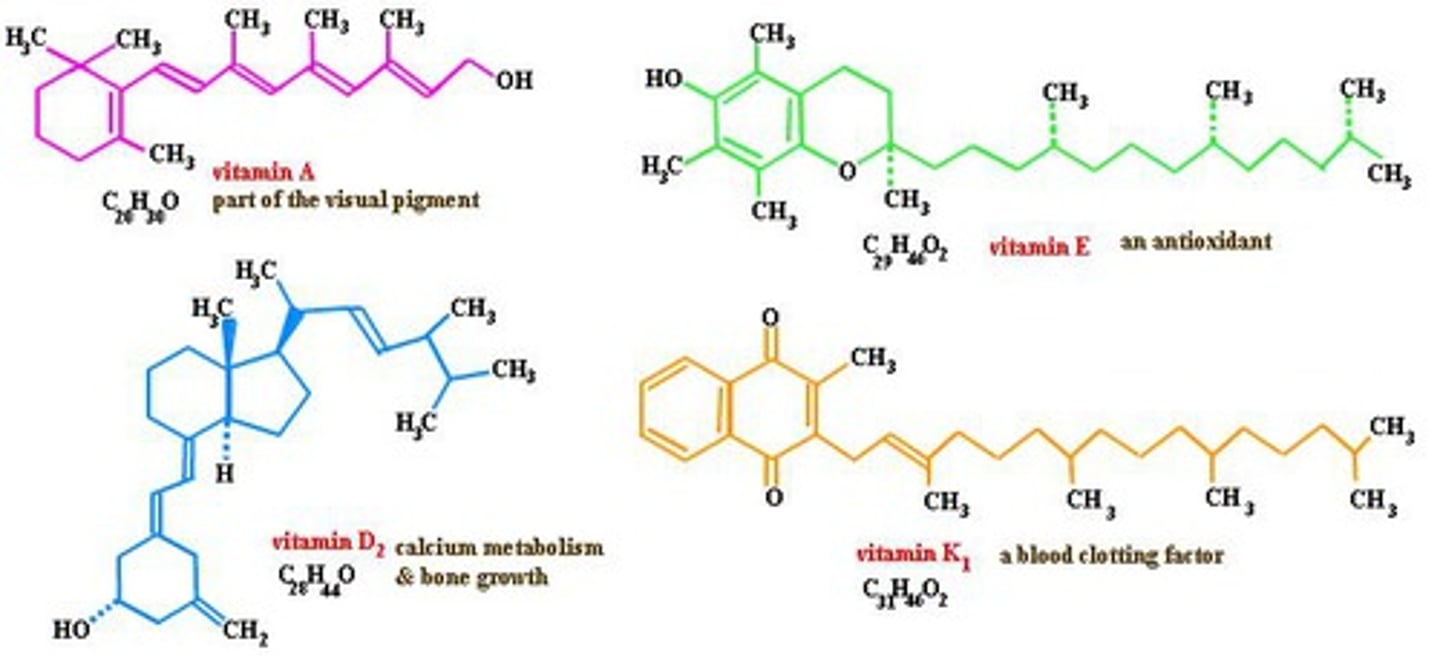
Name the four fat-soluble Vitamins and describe the basic function of each.
These fat-soluble vitamins generally serve as cofactors.