CSUF MGMT 430 Final
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
lot size
the quantity that a stage of a supply chain either produces or purchases at a time
cycle inventory
the average inventory in a supply chain due to either production or purchases in lot sizes that are larger than those demanded by the customer
Q
quantity in a lot or batch size
D
demand per unit time
C or p
material cost
S
fixed ordering cost
H = hC
holding cost
fixed ordering cost
includes all costs that do not vary with the size of the order but are incurred each time an order is placed
holding cost
the cost of carrying one unit in inventory for a specified period of time
true
primary role of cycle inventory is to allow different stages to purchase products in lot sizes that minimize the total sum of material, ordering, and holding costs
price
average price paid per unit purchased is a key cost in the lot-sizing decision
CD
annual material cost
economic order quantity
lot sizing for a single product
annual demand of the product
D
fixed cost incurred per order
S
cost per unit
C
holding cost per year as a fraction of product cost
h
true
aggregating replenishment across products, retailers, or suppliers in a single order allows for a reduction in lot size for individual products
lot size based discount
discounts based on quantity ordered in a single lot
volume based discount
discount is based on total quantity purchased over a given period
forward buying
the purchase of any raw materials, supplies, components, or other items in advance of current requirements
safety inventory
carried to satisfy demand that exceeds the amount forecasted, as well as a contingency to potential disruptions in the supply line
true
raising the level of safety inventory increases product availability and inventory holding costs
true
safety inventory is determined by the uncertainty of both demand and supply and the desired level of product availability
continuous review
inventory is continuously tracked, order for a lot size Q is placed when the inventory declines to the reorder point (rop)
periodic review
inventory status is checked at regular periodic intervals, order is placed to raise the inventory level to a specified threshold
true
periodic review replenishment policies require more safety inventory than continuous review policies for the same lead time and level of product availability
postponement
delay product differentiation or customization until closer to the time the product is sold
reorder point
specifies the level to which the inventory balance of an item must fall before an order to replenish stock is initiated
commonality
different components are replaced by common components or same components are used for multiple products
modes of transportation
1. air
2. package carriers
3. truck (LTL or FTL)
4. rail
5. water
6. pipeline
7. intermodal
package carriers
small packages up to 150 lbs., door to door service, expensive
truck
significant fraction of goods moved, low fixed cost
rail
moves commodities over large distances, high fixed costs
water
very large loads at a low cost, slow
pipeline
primarily used for fuels, for large and stable flows, high fixed cost
intermodal
more than one mode of transportation for a shipment, has grown with increased use of containers
transportation infrastructure
governments take full responsibility or play a significant role in building and managing infrastructure
true
without a monopoly, deregulation and market forces help create an effective industry structure
direct shipment network to single destination
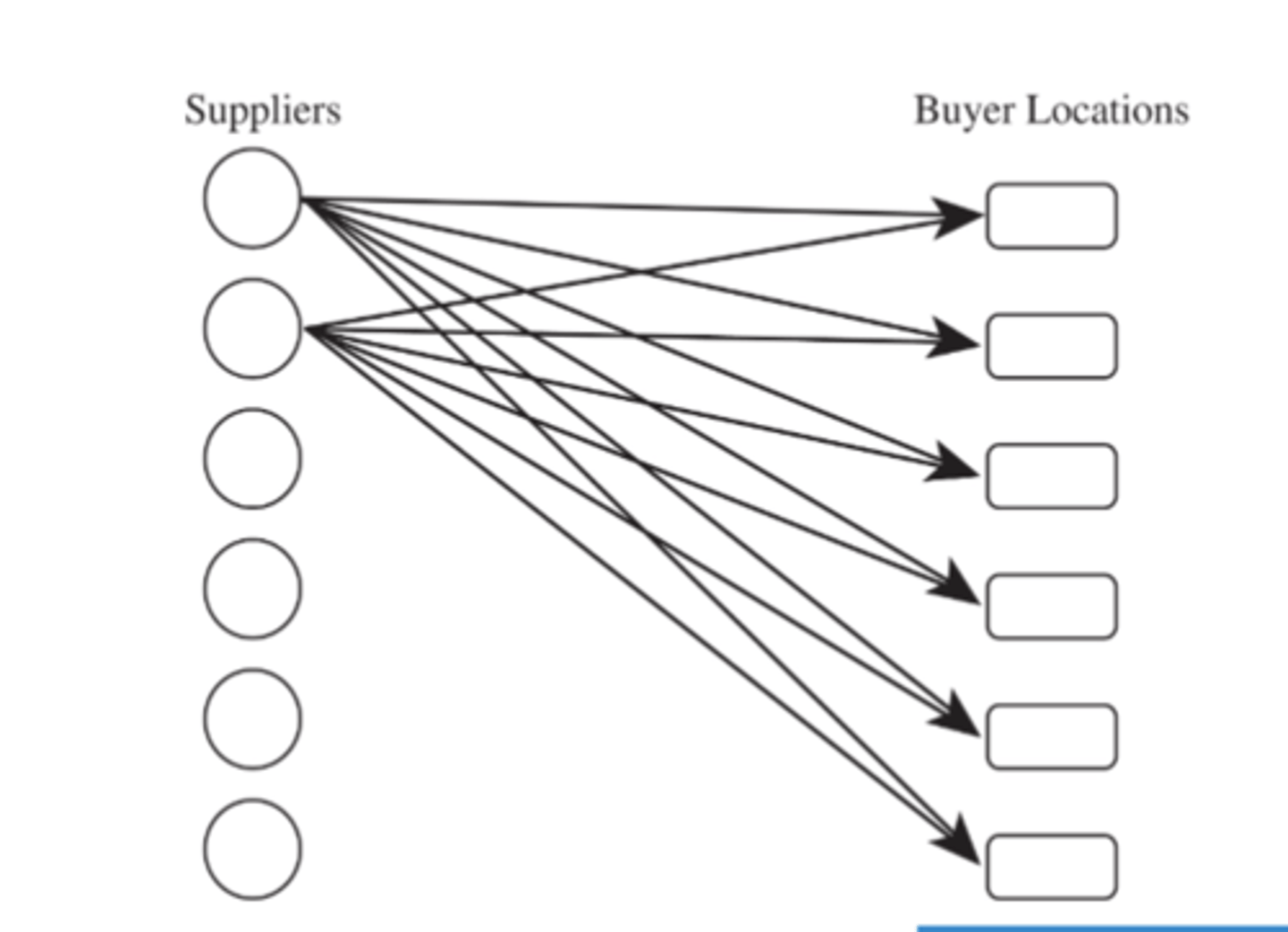
direct shipping with milk runs
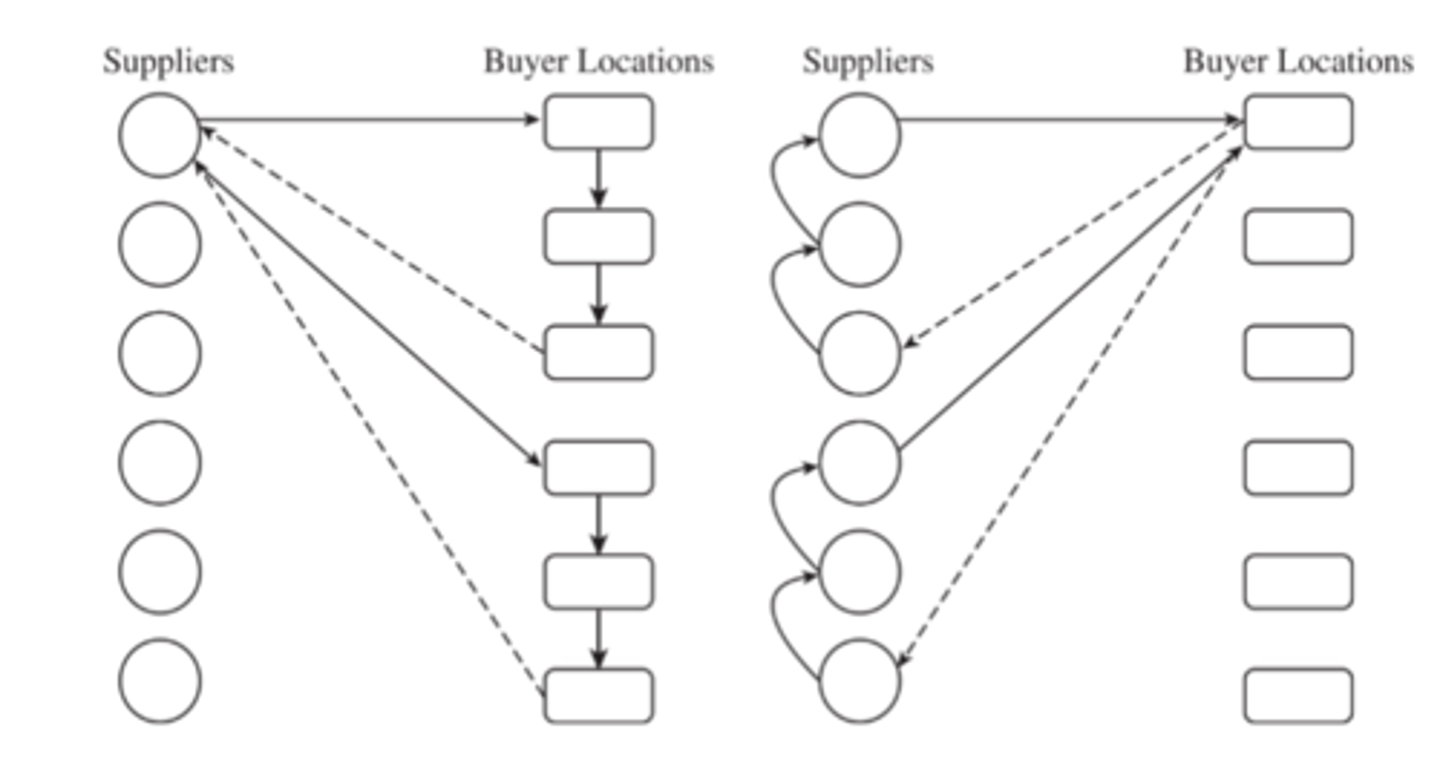
all shipments via intermediate distribution center with storage
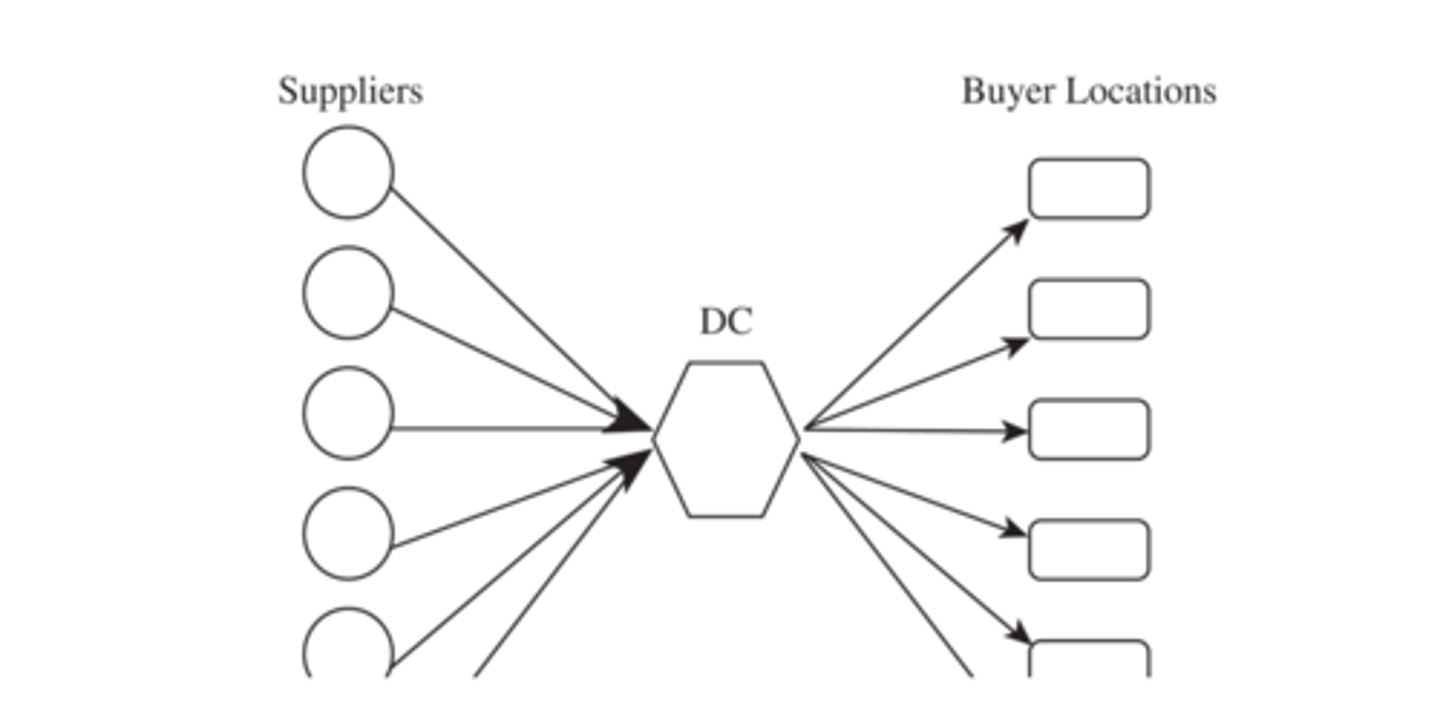
all shipments via intermediate transit point with storage
suppliers send their shipments to a central distribution center which are stored until needed by buyers and shipped to each buyer location
all shipments via intermediate transit point with cross docking
suppliers send their shipments to an intermediate transit point which are then cross docked and sent to buyer locations without storing them
shipping via dc using milk runs
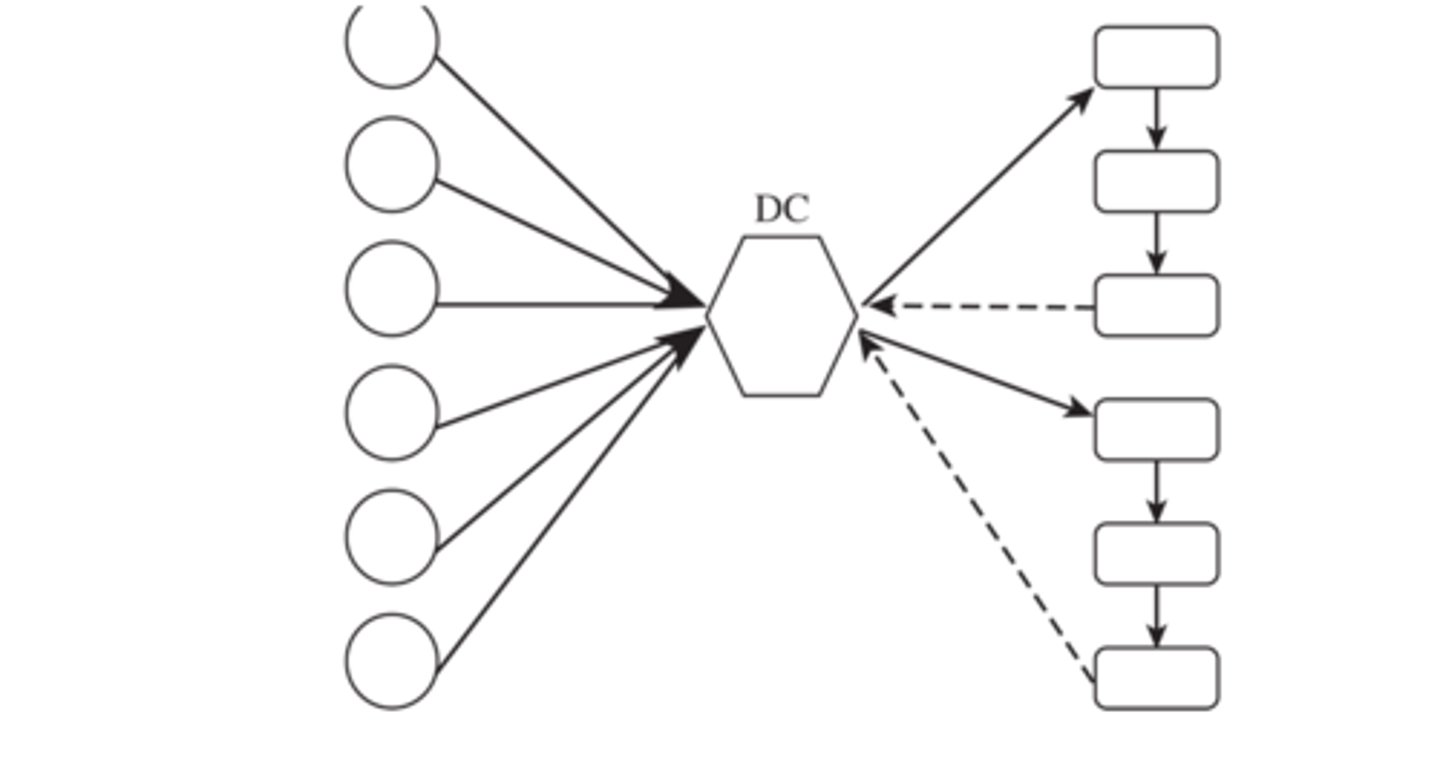
temporal aggregation
combining orders across time
procurement
companies acquire raw materials, components, products, services, or other resources from suppliers to execute their operations
sourcing
entire set of business processes required to purchase goods and services (who/where from)
outsourcing
supply chain function being performed by a third party (product or services)
free on board
indicates when the ownership of goods transfers from buyer to seller
offshoring
the relocation of business processes and services to a lower-cost foreign location
onshoring
relocation of business processes or production to a lower-cost location inside the same country as the business.
buyback
the buyer will purchase a certain quantity of goods, and the supplier will guarantee the repurchase of any unsold goods at an agreed-upon price
revenue sharing
a retailer pays a supplier a wholesale price for each unit purchased plus a percentage of the revenue the retailer generates
quantity flexibility
allows the buyer in a supply chain to postpone some of his purchases to a later date and at a favorable price after an improved forecast of the customer demand becomes available
quantity discount
economic incentive to encourage organizations to purchase goods in large quantities
erp
enterprise resource planning
enterprise resource planning
software that helps automate, streamline, and enhance essential business processes (collects financials, operations, and activities in one place)
tragedy of the commons
individuals with access to a shared resource act in their own interest and ultimately deplete the resource
facilities
offer the best opportunity to simultaneously improve the environmental and financial performances through innovation
cap and trade
a method for managing pollution in which a limit is placed on emissions and businesses or countries can buy and sell emissions allowances
carbon tax
a charge placed on greenhouse gas pollution mainly from burning fossil fuels
corporate social responsibility
a business model by which companies make a concerted effort to operate in ways that enhance rather than degrade society and the environment
true
reducing landfill waste use improves overall living conditions for animals, plants, and people alike by reducing the release of greenhouse gases