Pulmonary Embolism, Transient Ischemic Attack & Stroke
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 2 - sem 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Arteries
Thick muscular walls
High pressure
Carry oxygenated blood away from the left side of the heart
Veins
Thin walls
Low pressure
One-way valves
Carry deoxygenated blood to right side of the heart
Ventilation
Movement of air in and out of the alveoli
Inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide
Perfusion
Flow of blood through pulmonary capillaries around the alveoli
V/Q ratio
Ratio of ventilation to perfusion (V/Q)
Indicated how well air reaching the alveoli is matched with blood flow to alveoli
Low ventilation and good perfusion = low V/Q ratio
Good ventilation and bad perfusion = high V/Q ratio
Pulmonary embolism
Obstruction of one or more branches of the pulmonary artery by a particular that originates elsewhere in body
There is ventilation, but decreased perfusion
Pulmonary embolism classifications and clinical manifestations
PE comes from the vein and goes as far as it can before it gets stuck
Dyspnea (decrease gas exchange)
Pleuritic chest pain (chest pain from lung blockage)
Tachypnea
Hypotension (decrease blood flow → decrease CO → decrease BP)
Tachycardia (compensation due to hypotension)
Anxiety/confusion (lack of O2 to brain)
Cough
Hemoptysis (coughing up blood)
Pulmonary embolism causes
Deep vein thrombosis
Tumor
Air
Fat
Amniotic fluid
Venous thromboembolism risk factors
Venous stasis (blood flow stand still):
Prolonged bedrest
Post op/immobility
Pregnancy
Burns
Bacterial endocarditis (bacterial infection of the heart)
Hypercoagulability (more desiring to make clot):
Cancer
Oral contraceptives
Dehydration/hemoconcentration
Vessel wall damage:
Trauma or surgery
IV drug use
Atherosclerosis (where is the plaque?)

V/Q ratio mismatch
Decreased blood flow to alveoli leads to impaired gas exchange
Increased ventilation and decrease perfusion ratio
Results: hypoxemia and local vasoconstriction
Increased pulmonary vascular resistance
Blood cannot move past obstruction
If right ventricle cannot overcome resistance - left ventricle preload and cardiac output decreases
Results: hypoxia and hypotension
Pulmonary hypertension
Continued increase in pulmonary vascular resistance
Result: backflow blood into right ventricle and right-sided heart failure
Pulmonary embolism diagnostic testing
EKG (rule out MI)
Chest x-ray (excess fluid build up)
CT scan (see if there are any clots in the lung)
VQ scan
Pulmonary angiography (look for clots - slow and invasive)
Lower extremity ultrasound (scan for DVT)
D-dimer <0.4 mcg/mL (clotting fact level)
Arterial blood gas (show arterial blood flow)
Thrombolytics
Tissue Plasminogen activator (tPA): alteplase
dissolve clots that have formed
hemodynamically compromised (don’t give to someone who was just recently in trauma, active bleed, recent surgery)
*break down any clot
*symptomatic/high risk clot
Anticoagulants
Heparin continuous drip
prevent clot from increasing and decrease formation of new clots
warfarin PO (INR 2.0-3.0)
take 3-5 days to get therapeutic
this is what we want to discharge them on
*heparin this the bridge
*symptomatic/high risk clot
Anticoagulants PO
apixaban, rivaroxaban
inhibits conversion prothrombin to thrombin
no lab monitoring
*asymptomatic/low risk clot
Embolectomy
Minimally invasive
catheter directed thrombolysis- thrombolytic medication directly to clot
pressured saline or rotating tool used to remove the clot
Invasive
surgically removed
*symptomatic therapy is contraindicated
Inferior vena cave filter
Filter placed insider inferior vena cava between the DVT and the heart
Wire thing that sits in the inferior vena cava, it will grab it and stop it from getting into the lung
Can be removed once you can put back on the anticoagulants
The filter can move
*symptomatic therapy is contraindicated
Focused assessment, nursing diagnosis, interventions for PE
Focused assessment:
Respiratory (lungs, airway, ABC)
Vitals
NANDA labels
Ineffective airway clearance
Impaired gas exchange
Ineffective breathing pattern
Decrease cardiac output
Risk for bleeding
Interventions
High fowlers
Comfort them
Place O2 on them
Call rapid response
Bleeding/fall precautions
PE client education
Disease process & lifestyle modifications:
Diet - Low saturated fat & limit foods high in vitamin K
high fats → plaque → surgery → increase risk for clots
vitamin K = contradiction for Coumadin
Adequate fluid intake
Smoking cessation
Medications
Bleeding precautions
Signs & symptoms of recurrent PE/DVT (have them know and why)
Stroke
Disruption of blood flow to a localized area of the brain
Caused by:
a blockage of blood vessel
bleeding in the brain
Neurological deficits vary according to the location and extent of the brain involved
Types of stroke
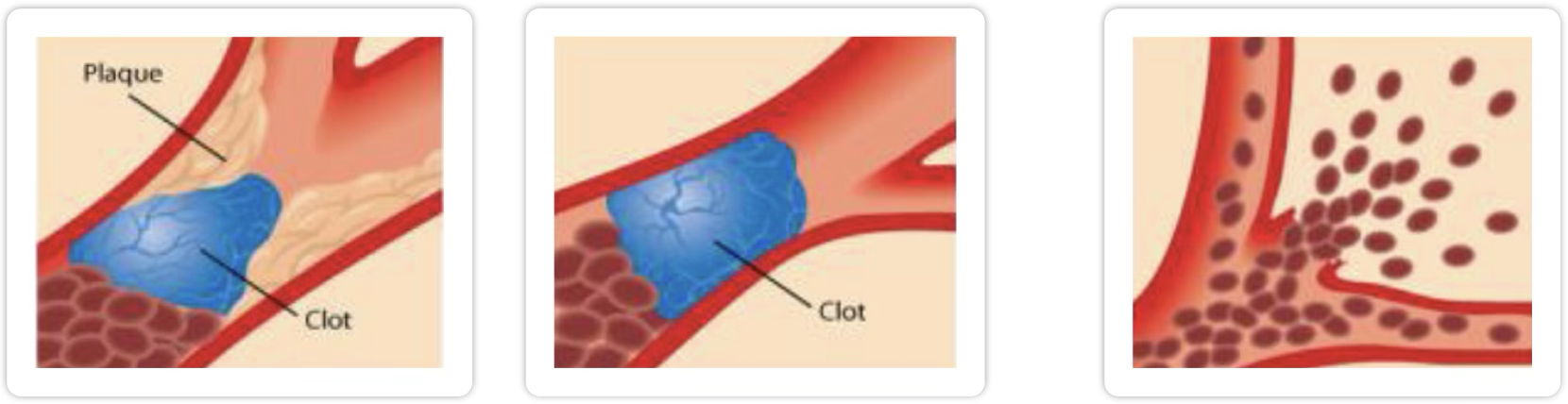
Ischemic (block) stroke - 87%
Thrombotic - plaque build up and then clot can’t get through leading to decrease blood flow
Embolic - clot from the heart that travels as far as it can before it becomes a problem
Hemorrhagic (bleed) stroke - 13%
Ischemic stroke
Thrombotic stroke
blood clot develops on plaque in a cerebral artery
blocks blood flow and lead to ischemia → infarct
symptoms may progress over hours to days
Embolic stroke
embolus circulates and lodges in cerebral artery
blocks blood flow immediately and leads to ischemia → infarct
neurologic defects or loss of consciousness to occur instantly
Treatment goal: restore blood flow to brain tissue ASAP
Hemorrhagic stroke
Occurs secondary to ruptured artery or aneurysm
sudden severe headache - “thunderclap” headache (worst headache ever)
neck stiffness and pain
Poor prognosis related to ischemia and increase intracranial pressure
Treatment goal: diagnose early and stop bleeding ASAP
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)
Brief interruption of cerebral blood flow causing transient neurologic dysfunction
Blood flow is restored before permanent damage occurs
Symptoms are present but completely resolve within minutes → 24 hours
Similar symptoms to an ischemic stroke - diagnostic testing is used to rule out stroke (don’t wait because it could be a stroke)
Seek immediate medical attention - TIA is a warning sign of an impending stroke
Stroke risk factors
Hypertension
Smoking
Hyperlipidemia
Diabetes
Atherosclerosis
Illicit drug use
Age
Atrial fibrillation
Hypercoagulability
Oral contraceptives
Cerebral aneurysm
What side if effected when a stroke happens?
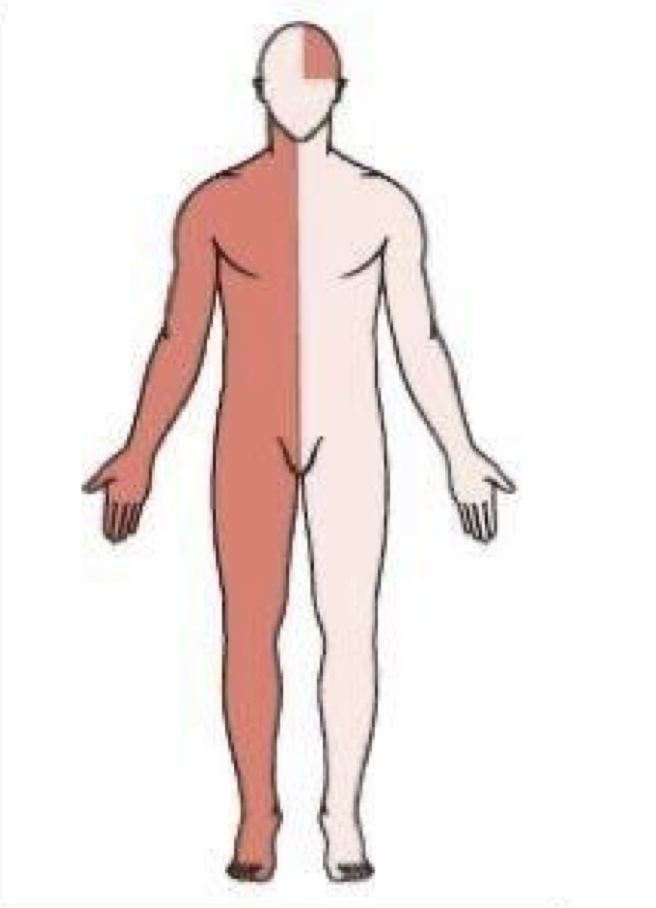
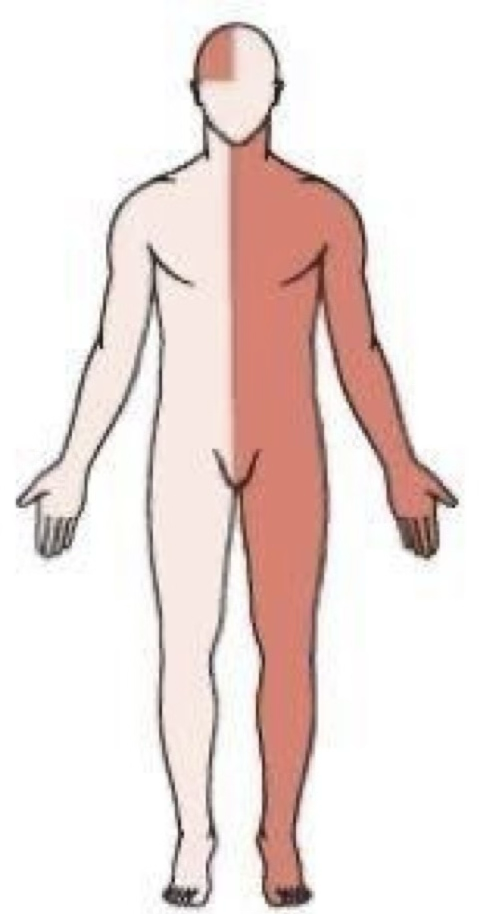
Right sided stroke effects the left sided motor function
Left sided stroke effects the right sided motor function
Left side stroke symptoms
Responsible for language, math, and reasoning
Right side hemiplegia or hemiparesis (paralysis/weakness)
Right hemianopsia (loss of vision half of the eye)
Language deficits
expressive aphasia
receptive aphasia
Agraphia (inability to write)
Depression
Right side stroke symptoms
Responsible for visual, spatial awareness & proprioception (body awareness)
Left hemiplegia or hemiparesis
Left hemianopsia
Altered perception of deficits
Loss of depth perception
Poor impulse control
Unilateral neglect syndrome
Stroke complications
Safety:
Weakness and paralysis
Skin integrity:
Frequent repositioning
Elevate paralyzed or weak limbs to minimize edema
Nutrition:
Dysphagia and aspiration
Enteral nutrition and medication administration
NG vs. PEG
NG = short term
PEG = long term
Stroke diagnostic testing
Computed tomography (CT) scan:
initial diagnostic test for stroke
rapidly determines type of stroke and treatment
performed on patients with contraindications to MRI
find out where it is, fast result, and type
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI):
identifies edema, ischemia and necrosis of blood vessels
Carotid doppler ultrasound: evaluate if carotid occlusion is a suspected cause of stroke
Echocardiogram: evaluate if stoke if due cardioembolic source
EKG: evaluate if cardiac condition caused clot formation
Laboratory tests: CBC, platelet, electrolytes, BUN, creatine, cholesterol
Acute stoke treatment
Ischemic stroke:
Thrombolyics - tPA
administer within 4.5 hours of symptom onset
monitor for intracranila bleeding
review inclusion and exclusion criteria
Invasive procedures - Thrombectomy
Hemorrhagic storke:
assess airway, breathing, and circulation
assess level of consciousness
monitor BP and increased intracranial pressure
Invasive procedures - titanium clip and coil
Assessment and nursing diagnosis for acute stroke
Neurological assessment and vital signs - BP (baseline assessment)
Glasgow Coma Scale - assess LOC
Administer O2 support
Continuous cardiac monitoring
HOB >30 degrees (decrease intracranial pressure)
NANDA labels
Ineffective tissue perfusion
Impaired swallowing → risk for aspiration
Sensory perceptual alterations → risk for injury
Impaired physical mobility → risk for fall
Impaired verbal communication
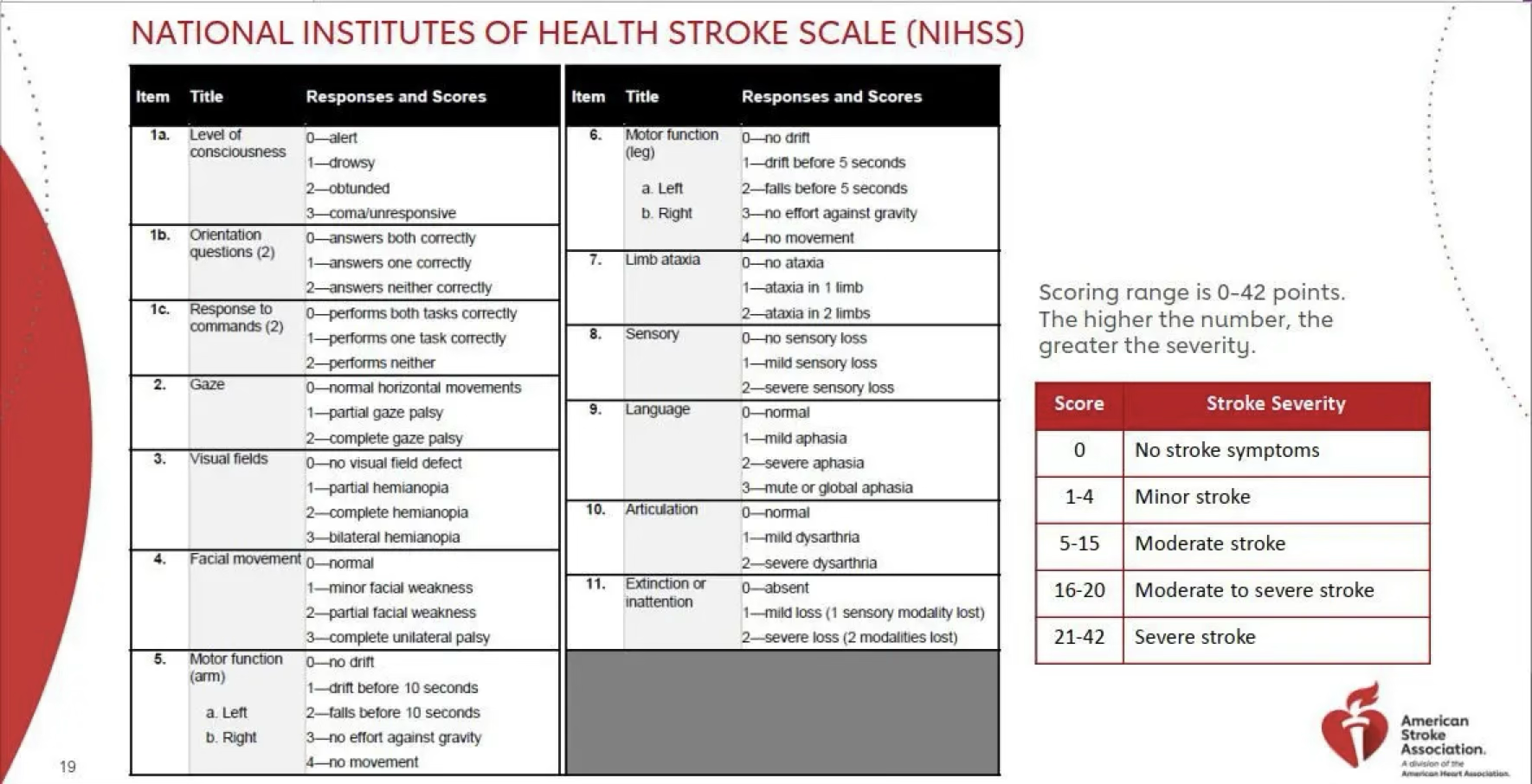
Anti-platelet
acetylsalicylic acid, clopidogrel
Indications:
prevention of ischemic stroke or TIA
primary prevention of acute myocardial infarction
Therapeutic actions: prevents platelets from clumping together by inhibiting factors that lead to clotting
Adverse effects:
bleeding/bruising
GI irritation
tinnitus
Contraindications:
bleeding disorders
peptic ulcer disease
thrombocytopenia
Nursing considerations: platelet level & bleeding risk
Client education:
value in prevention medications
monitor for bleeding
Anticoagulants - activated factor Xa inhibitor
apixaban, rivaroxaban
Indications:
stroke prevention for clients with a-fib
prevention and treatment of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
Therapeutic actions: inactivates factor Xa, decrease thrombin and thrombus development
Adverse effects:
bleeding/bruising
hemorrhage/GI bleed
Contraindications: active bleeding
Nursing considerations:
platelet level
no antidote available
Client education:
monitor for bruising and bleeding → bleeding precautions
avoid use of OTC NSAIDS and aspirin
no lab monitoring for therapautic level
Anticoagulants - Vitamin K inhibitors
warfarin
Indications:
prevention of ischemic stroke, DVT, PE
prevents cardioembolic events in a-fib
reduce risk for recurrent transient ischemic attacks or MI
Therapeutic actions: decreases blood clotting by reducing the action of Vitamin K
Adverse effects:
warfarin toxicity (INR goes too high, blood is too thin → give vitamin K)
bleeding/bruising
hemorrhage/GI bleed
Contraindications:
pregnancy- Category X
thrombocytopenia
active bleeding
liver disorders (liver clots)
Nursing Considerations:
protime & INR- (therapeutic level 2-3)
baseline CBC- PLT & HCT
antidote - Vitamin K
Client Education:
avoid foods high in Vitamin K
therapeutic effect takes 3-5 days
bleeding precautions
Anticoagulants - Heparin Sodium
Indications:
Conditions requiring prompt anticoagulation therapy (Intravenous route):
Evolving ischemic stroke, pulmonary embolism, massive deep vein thrombosis
Therapeutic Actions:
Activates antithrombin, deactivates thrombin (ending clotting) & factor Xa
Inhibits fibrin formation (never over clots that keep that clot there)
Adverse Effects:
Bleeding/Bruising
Hemorrhage/GI bleed
Contraindications:
active bleeding or recent surgeries
thrombocytopenia
Nursing Considerations:
monitor aPTT every 4-6 hours until therapeutic then daily
labs- aPTT normal 25-35 seconds (therapeutic level 60-80 seconds)
platelet & hematocrit
antidote - protamine sulfate
Client Education:
monitor for bruising & bleeding → bleeding precautions
avoid OTC NSAIDS & Aspirin
Thrombolytic Agents - Tissue Plasminogen activator (tPA)
alteplase
Indications:
acute ishcemic stroke
pulmonary embolism
acute myocardial infarction
restore patency to central IV catheters
Therapeutic Actions: dissolve clots that have already formed
Adverse Effects:
internal & superficial bleeding
cerebral hemorrhage
Contraindications:
history of hemotthagic stroke
recent surgery or trauma
active or recent internal bleeding
Nursing Considerations:
monitor labs- Protime, aPTT, Hgb, HCT
monitor client for bleeding & bruising-limit blood draws & injections. HOLD PRESSURE!
antidote - aminocaproic acid (Amicar)
Client Education:
observe for bleeding & bruising
bleeding precautions