Unit 10 - The Vietnam War
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
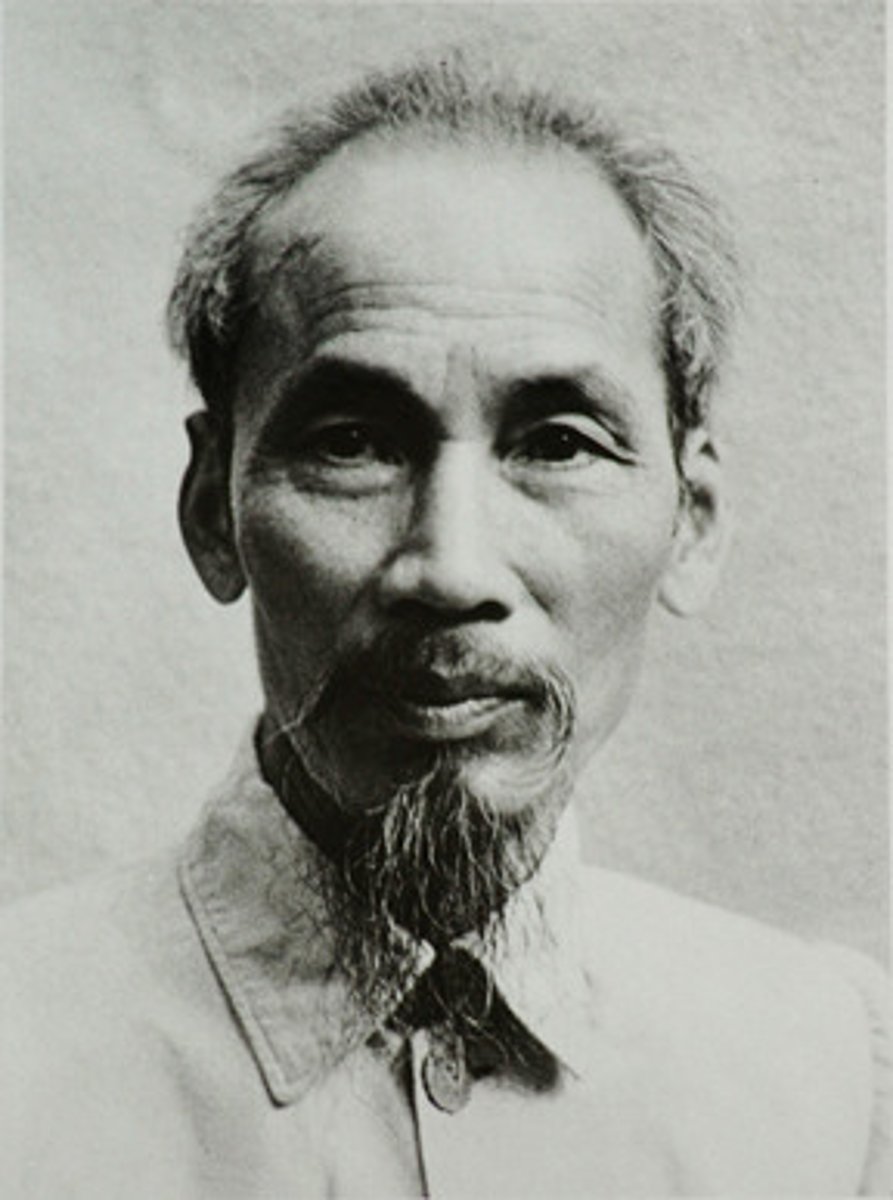
Ho Chi Minh
Communist leader of North Vietnam

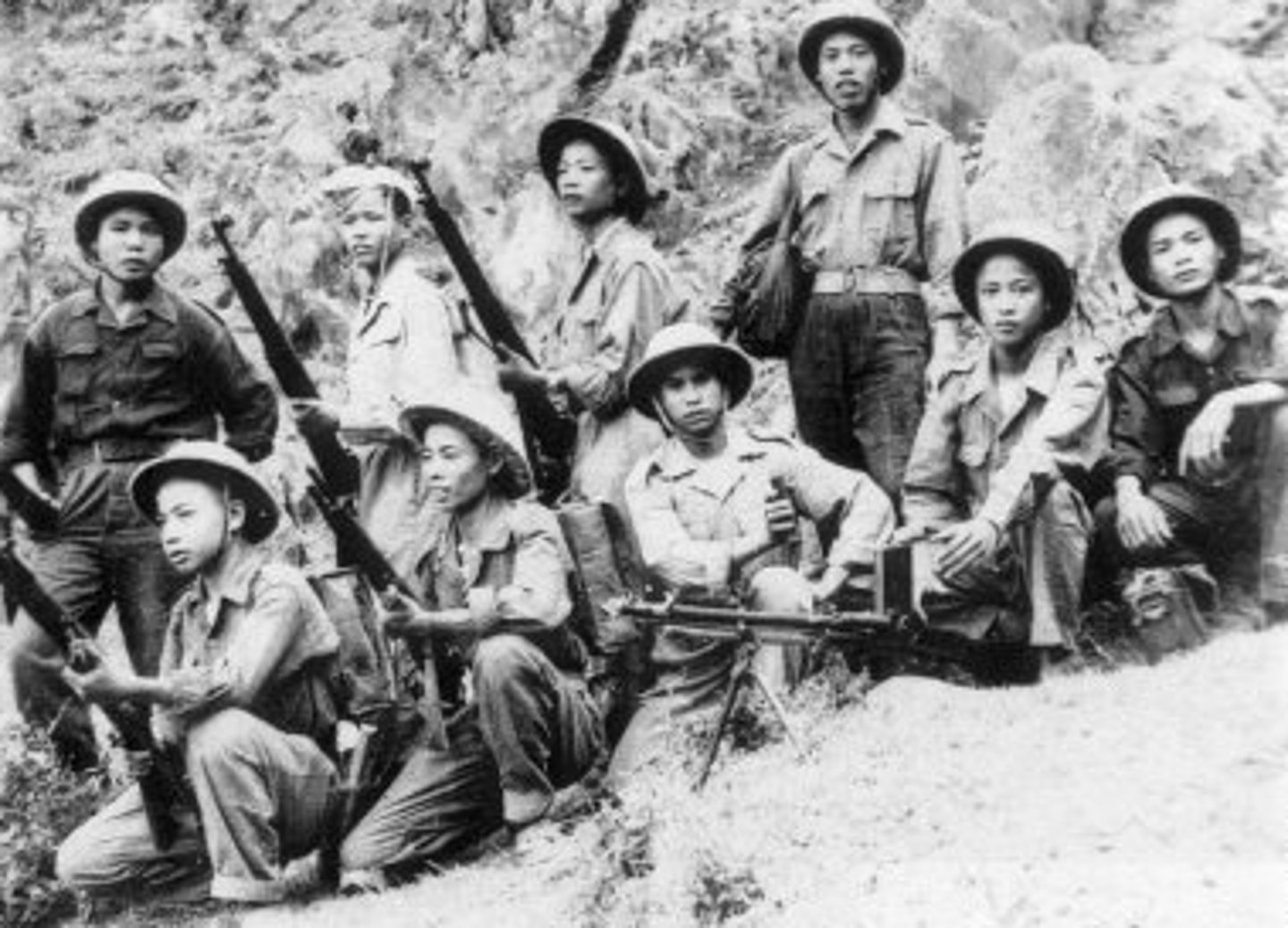
Vietminh
An organization of Vietnamese Communists and other nationalist groups that between 1946 and 1954 fought for Vietnamese independence from the French.

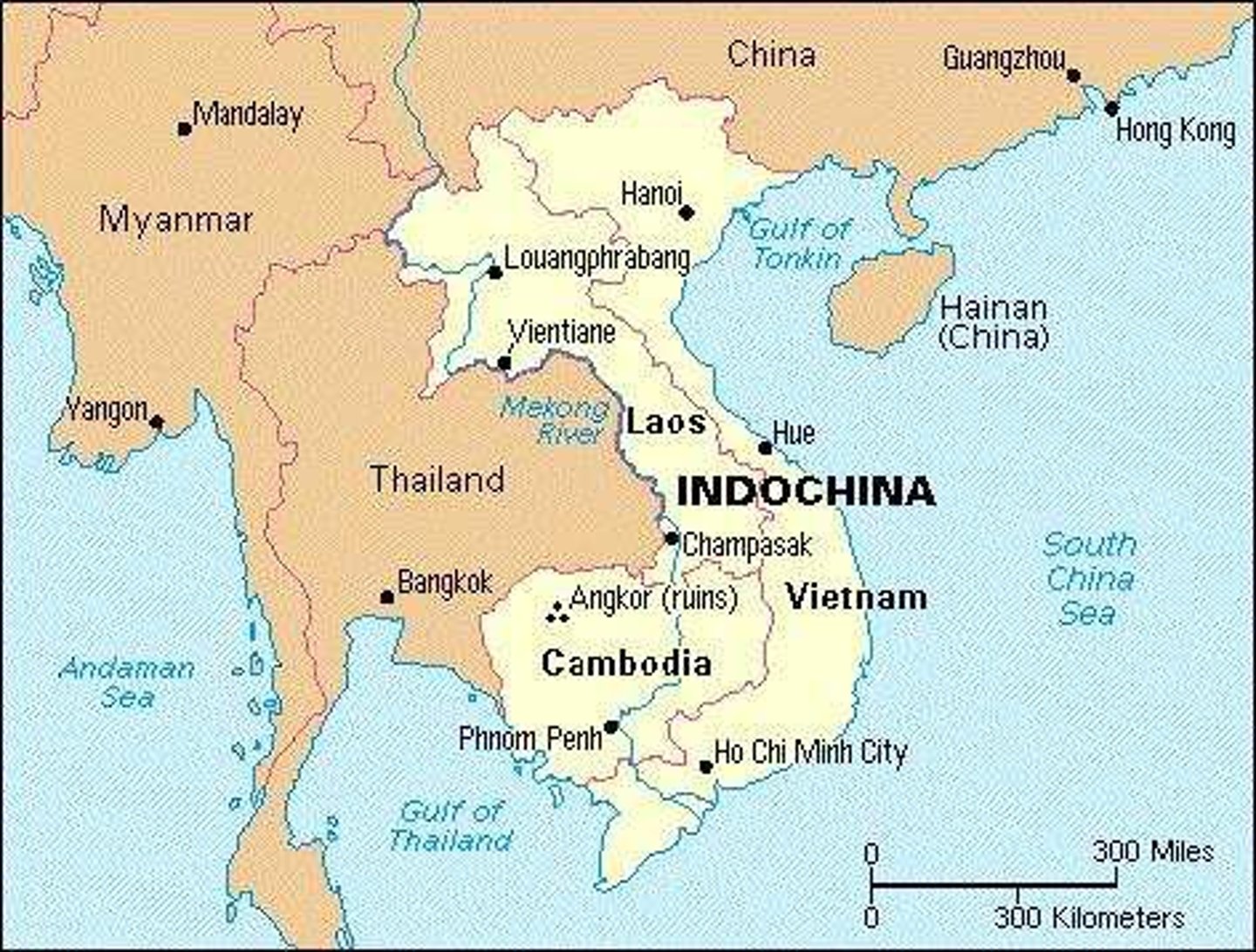
Indochina
a peninsula of southeastern Asia that includes Myanmar and Cambodia and Laos and Malaysia and Thailand and Vietnam
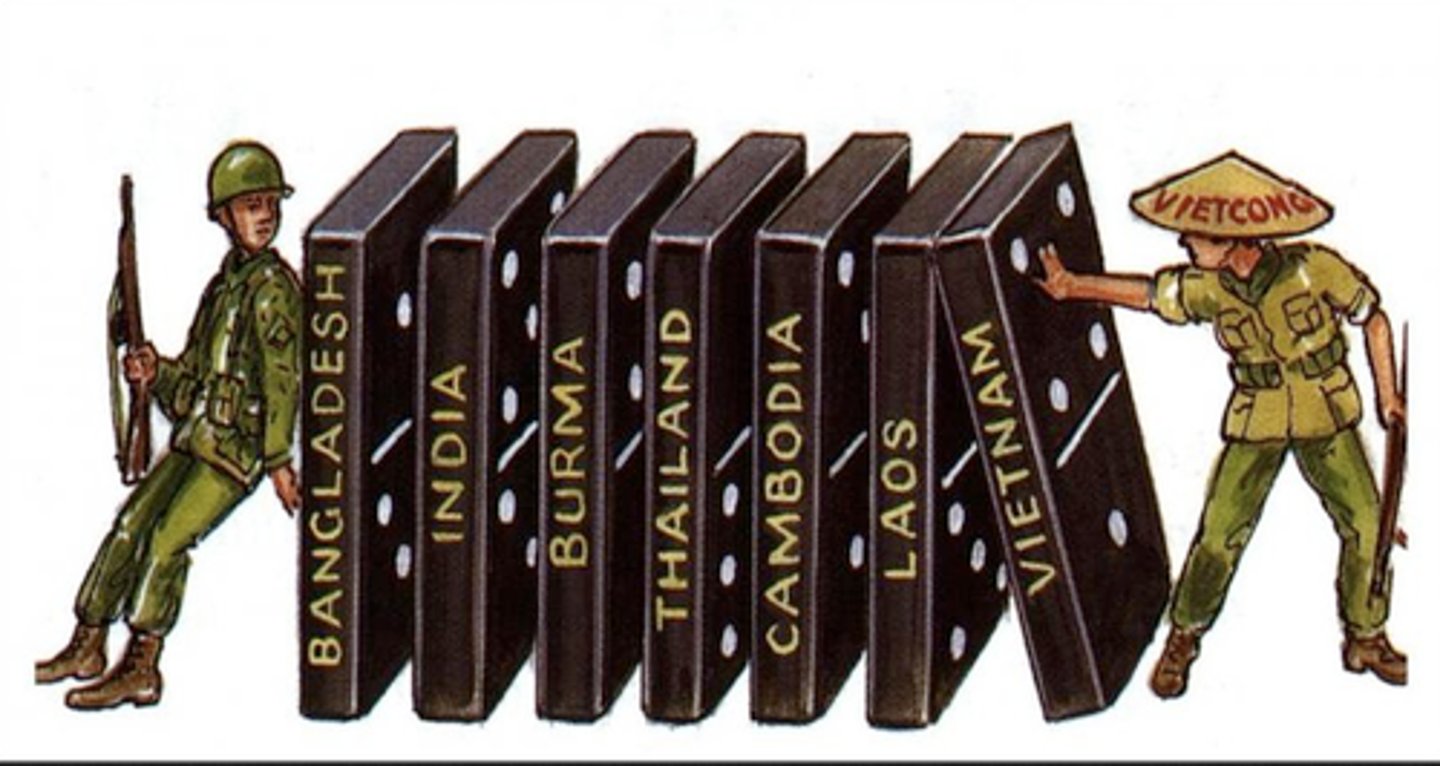
Domino Theory
A theory that if one nation comes under Communist control, then neighboring nations will also come under Communist control.

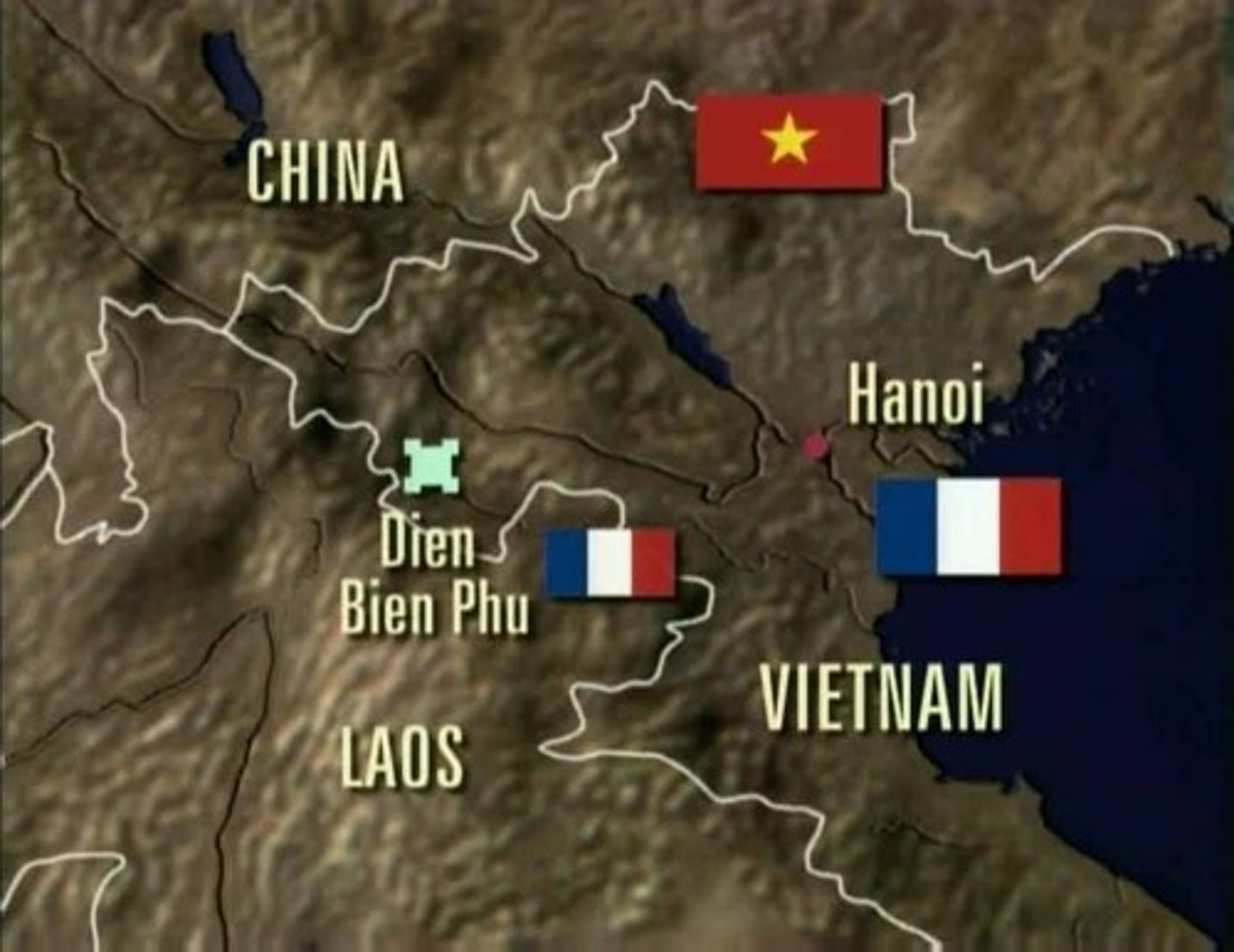
Dien Bien Phu (1954)
Disastrous defeat of a French army by Vietnamese Communists led by Ho Chi Minh. The U.S. was already involved in Indochina even before the defeat — giving U.S. military aid to the French.
- When the French then tried to convince the U.S. to send troops to Vietnam, Eisenhower refused.
- After the defeat, the French agreed to give up Indochina at the Geneva Conference of 1954.
Geneva Accords, 1954
1954 peace agreement between Ho Chi Minh's communists and the French gov't after the French loss at Dien Bien Phu; divided Vietnam into communist-controlled North and non-communist South until unification elections could be held in 1956. Diem cancelled the elections when he realized the communists would win, further escalating the violence.
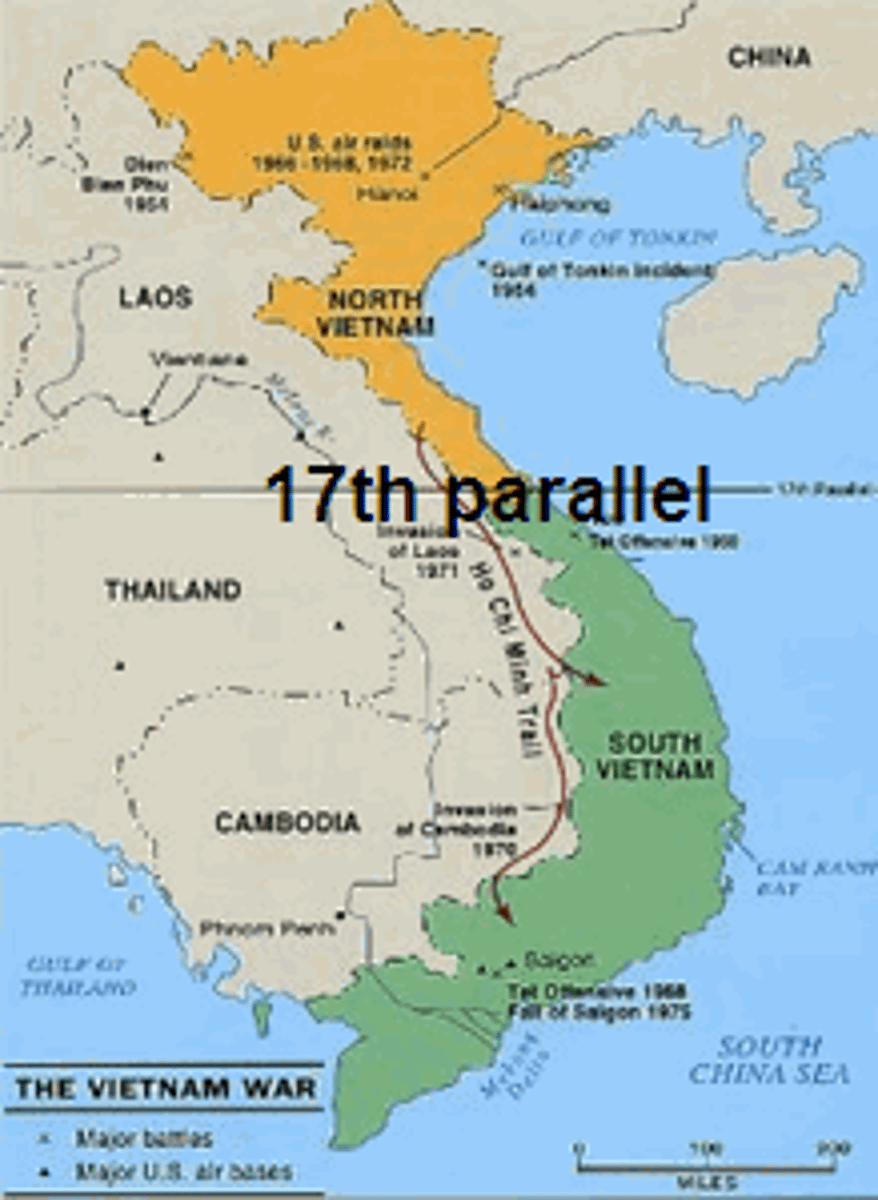
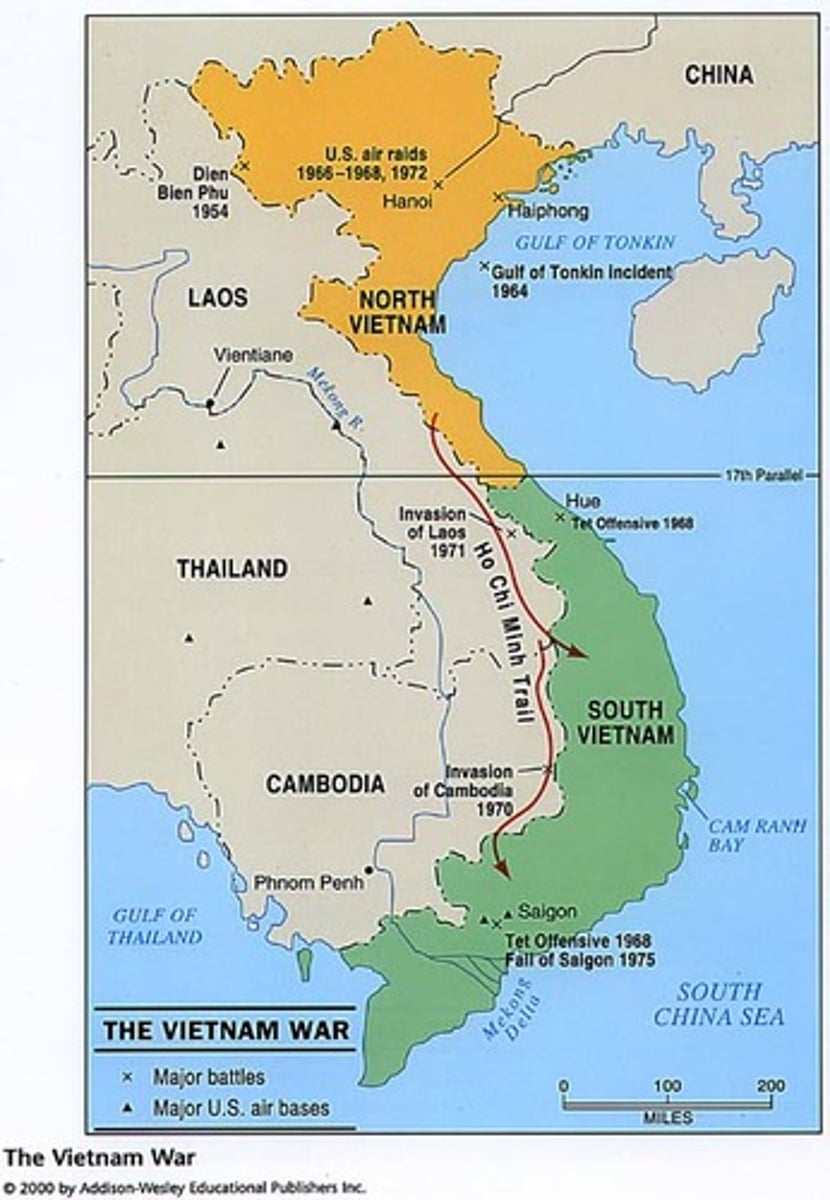
17th Parallel
Line of latitude that separated North and South Vietnam until 1975.
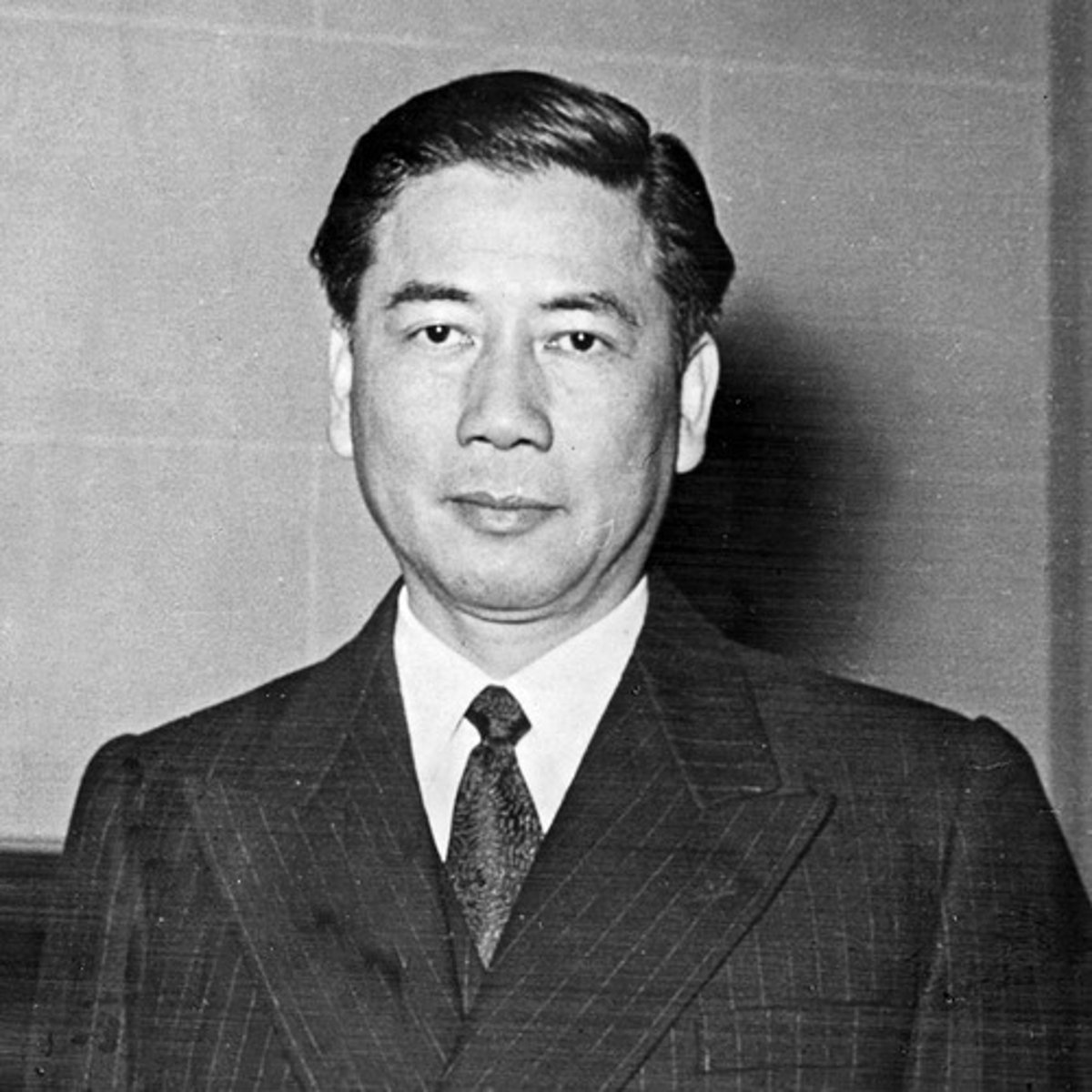
Ngo Dinh Diem (1901-1963)
First president of South Vietnam, where he took power following the Geneva Accords in 1954. Diem was propped up by the United States until he was overthrown and assassinated by a coup in 1963, which was signed-off on by JFK.

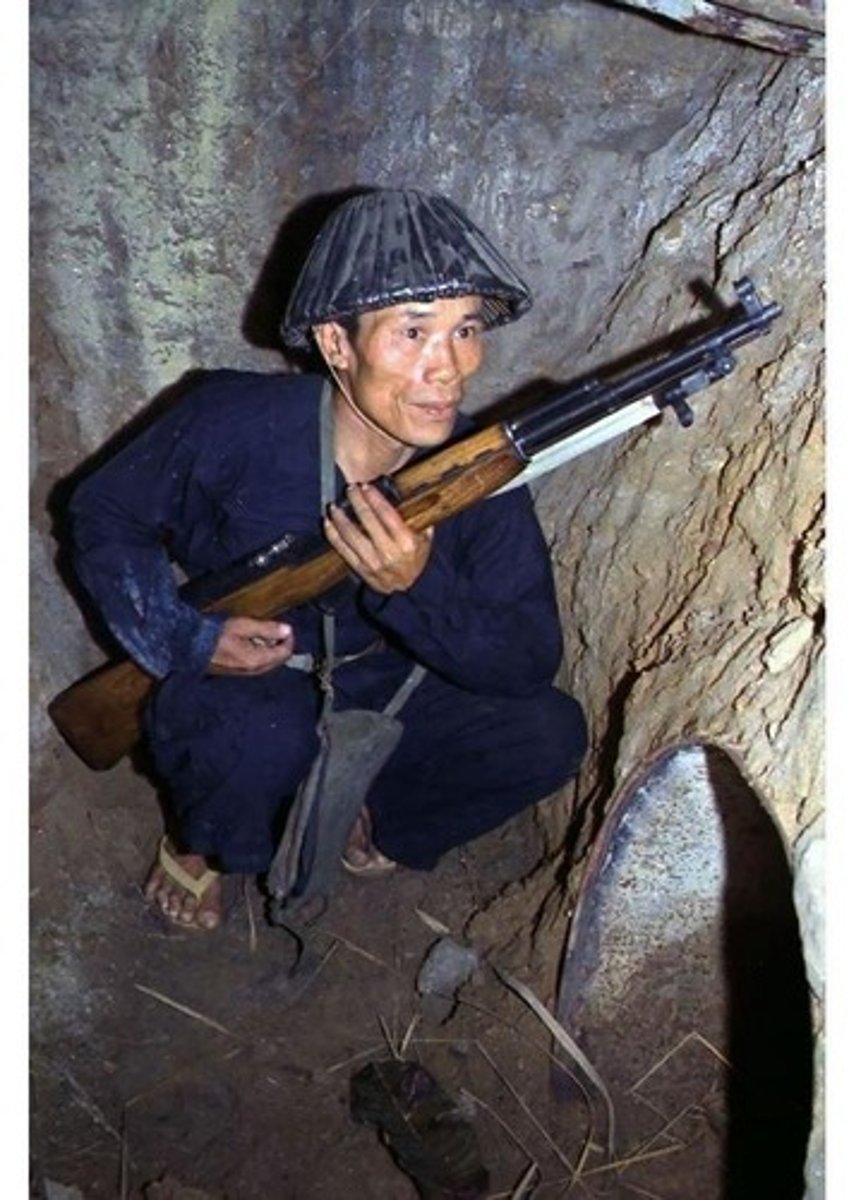
Vietcong (VC)
South Vietnamese communist rebels that waged a guerrilla war against the government of South Vietnam.

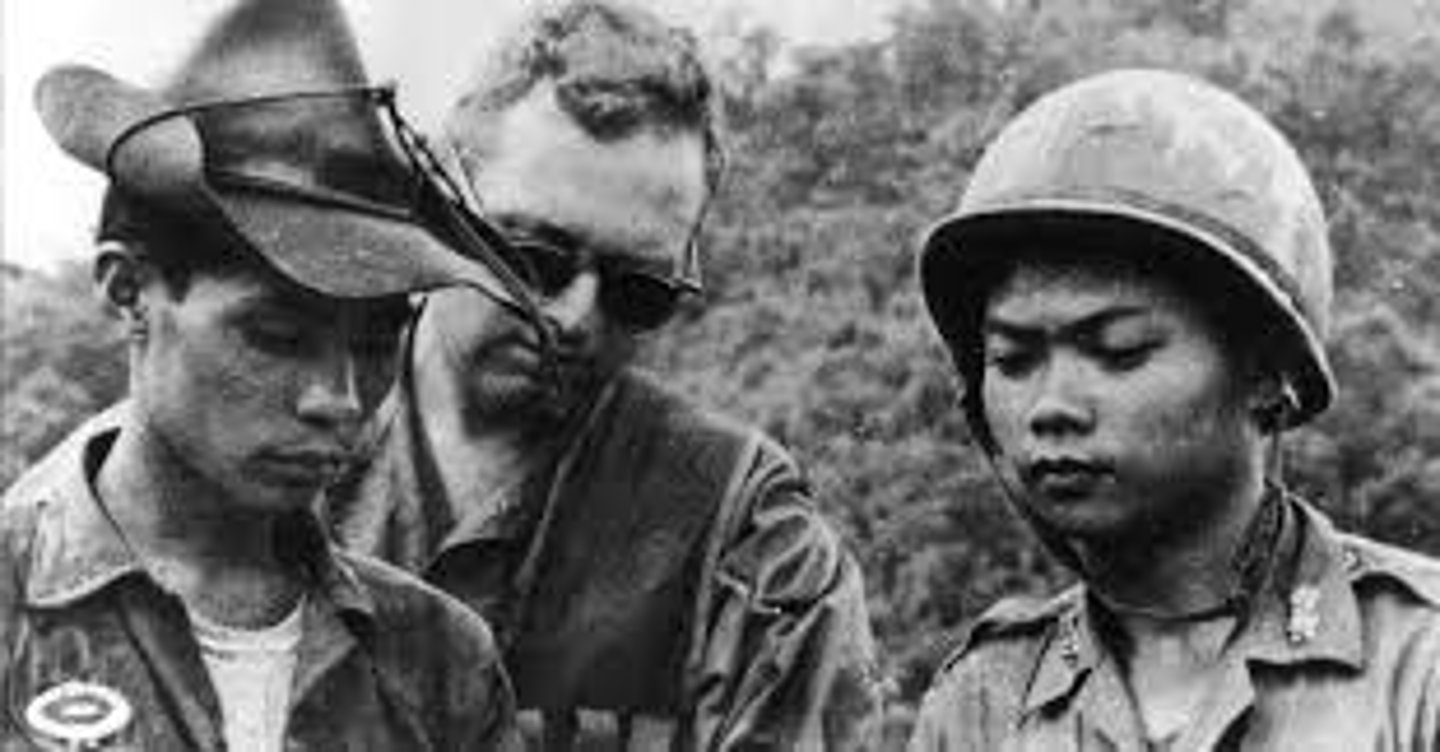
Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN)
South Vietnamese military forces that were supported by American forces.

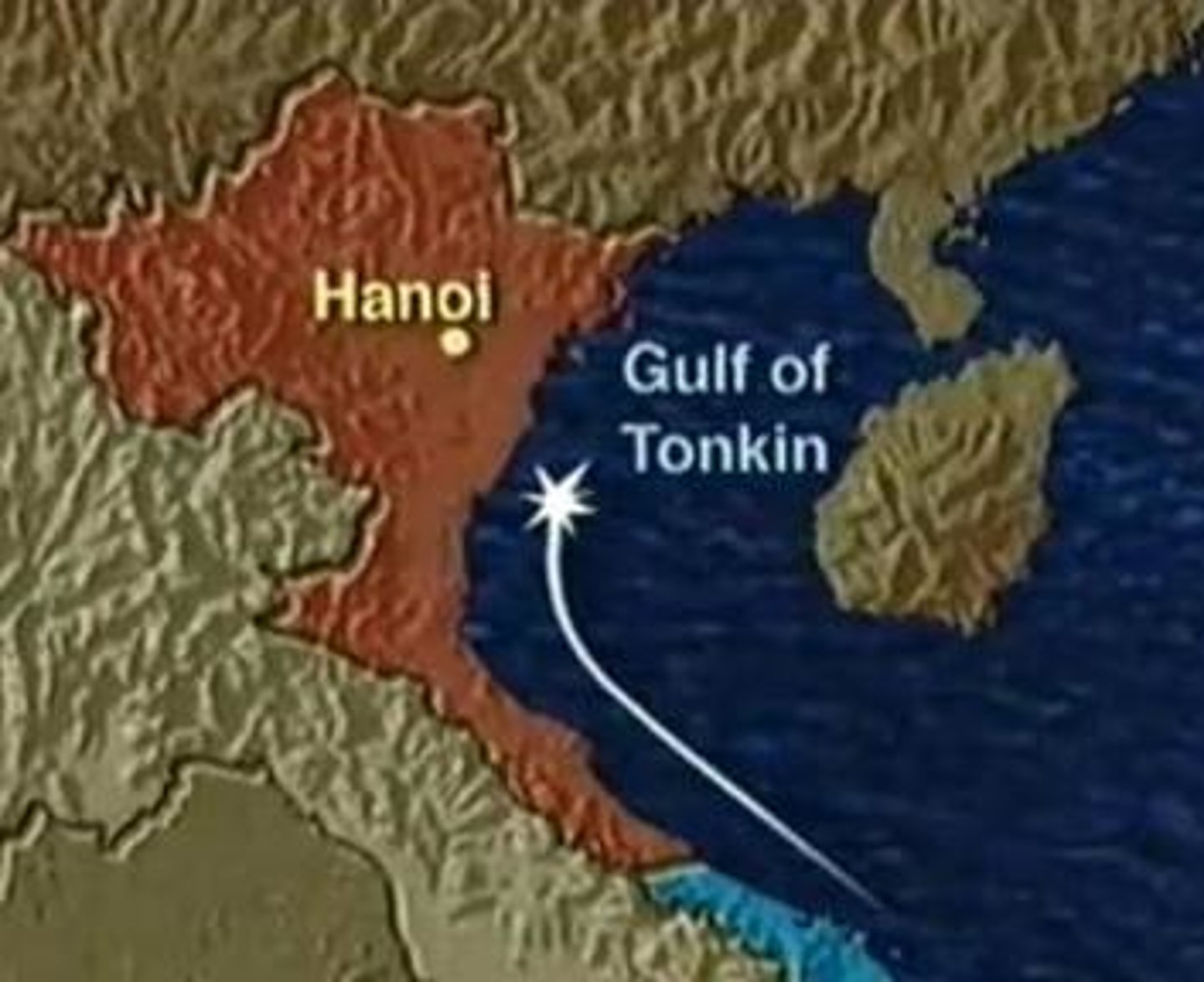
Tonkin Gulf Resolution (1964)
After President Johnson claimed North Vietnamese forces attacked U.S. boats in international
waters in the Gulf of Tonkin, U.S. Congress voted to give the president a "blank check" to do
whatever was necessary to stop communism from toppling the gov't of South Vietnam.
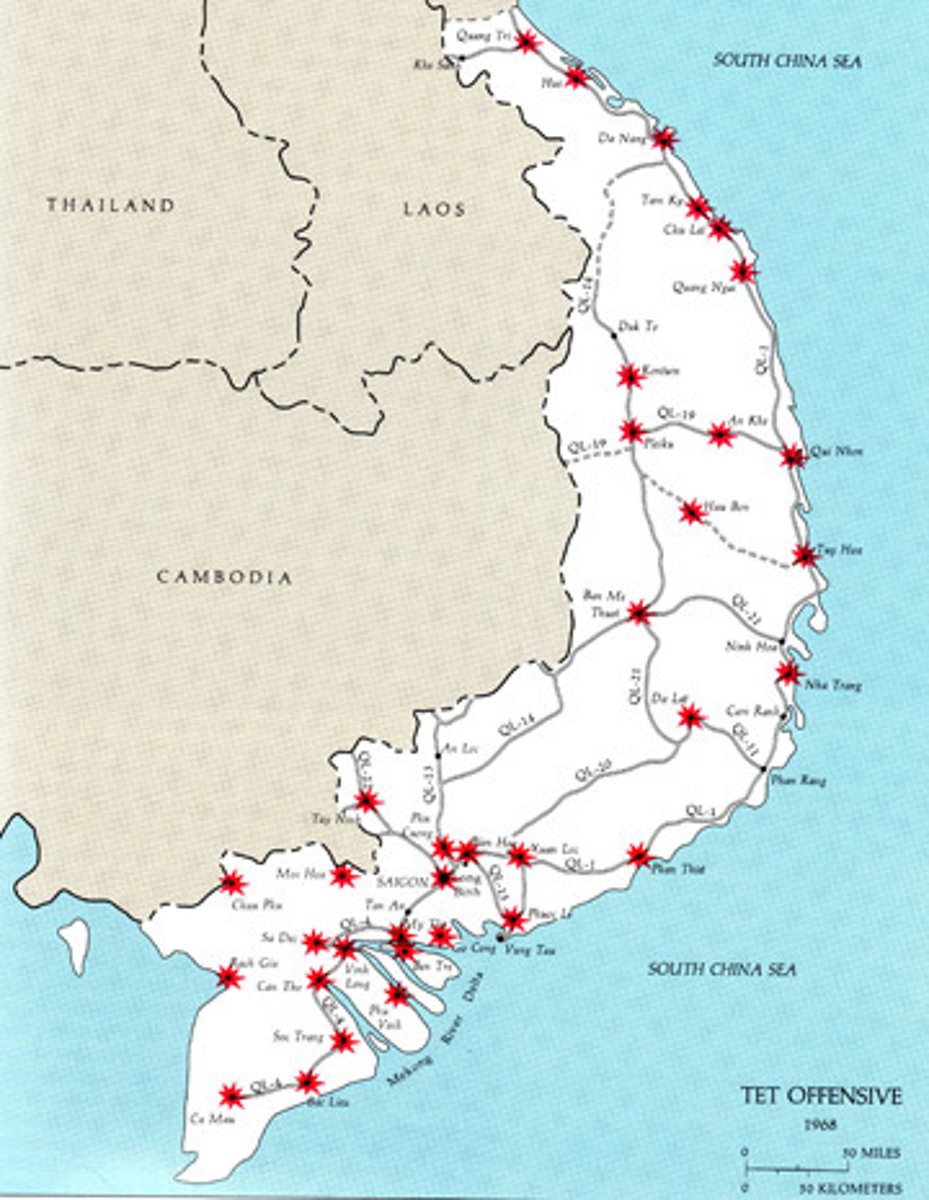
Tet Offensive (1968)
The Tet Offensive was one of the largest military campaigns of the Vietnam War, launched on January 30, 1968 by forces of the Viet Cong and North Vietnamese Army against the forces of South Vietnam, the United States, and their allies. It failed militarily, but had an enormous psychological impact on the US, showing that the war was far from over, and proving that the government was lying about the war.
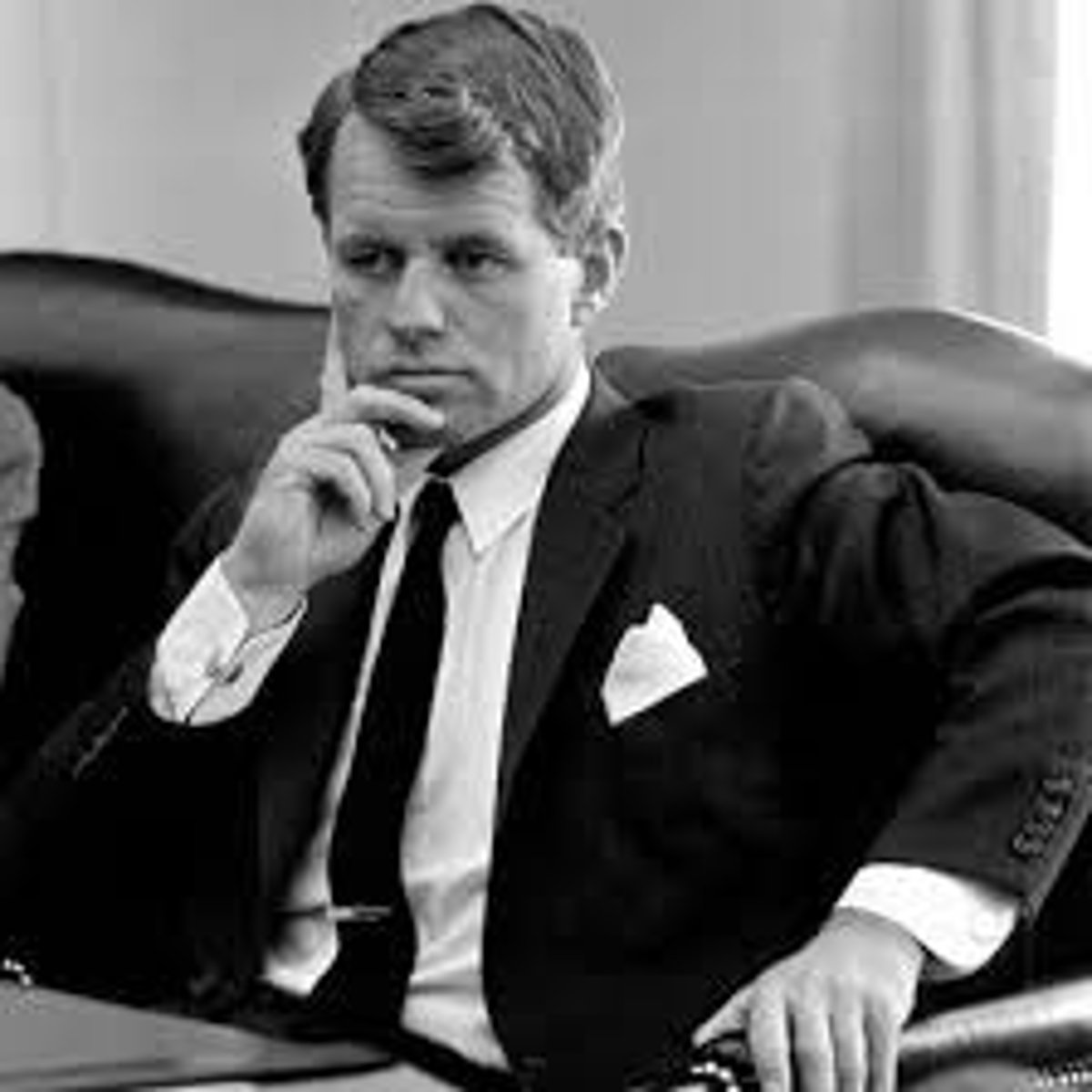
Robert "Bobby" Kennedy (RFK)
JFK's brother and attorney general. Assassinated 1968 during his campaign for POTUS.

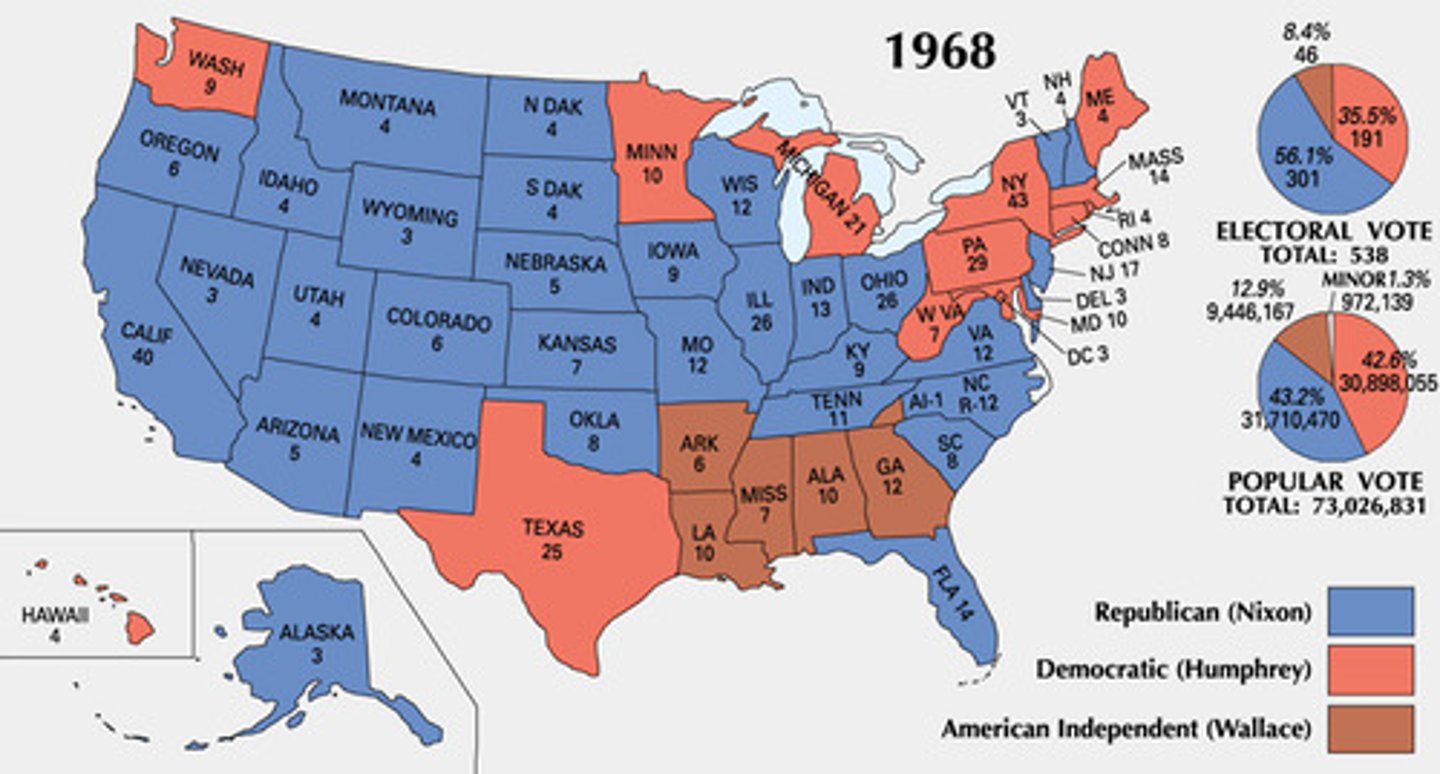
Election of 1968
Richard M. Nixon, a Republican, narrowly won by a 1% margin against Hubert Humphrey, a Democrat. The issues were the war in Vietnam and urban crisis of law and order.
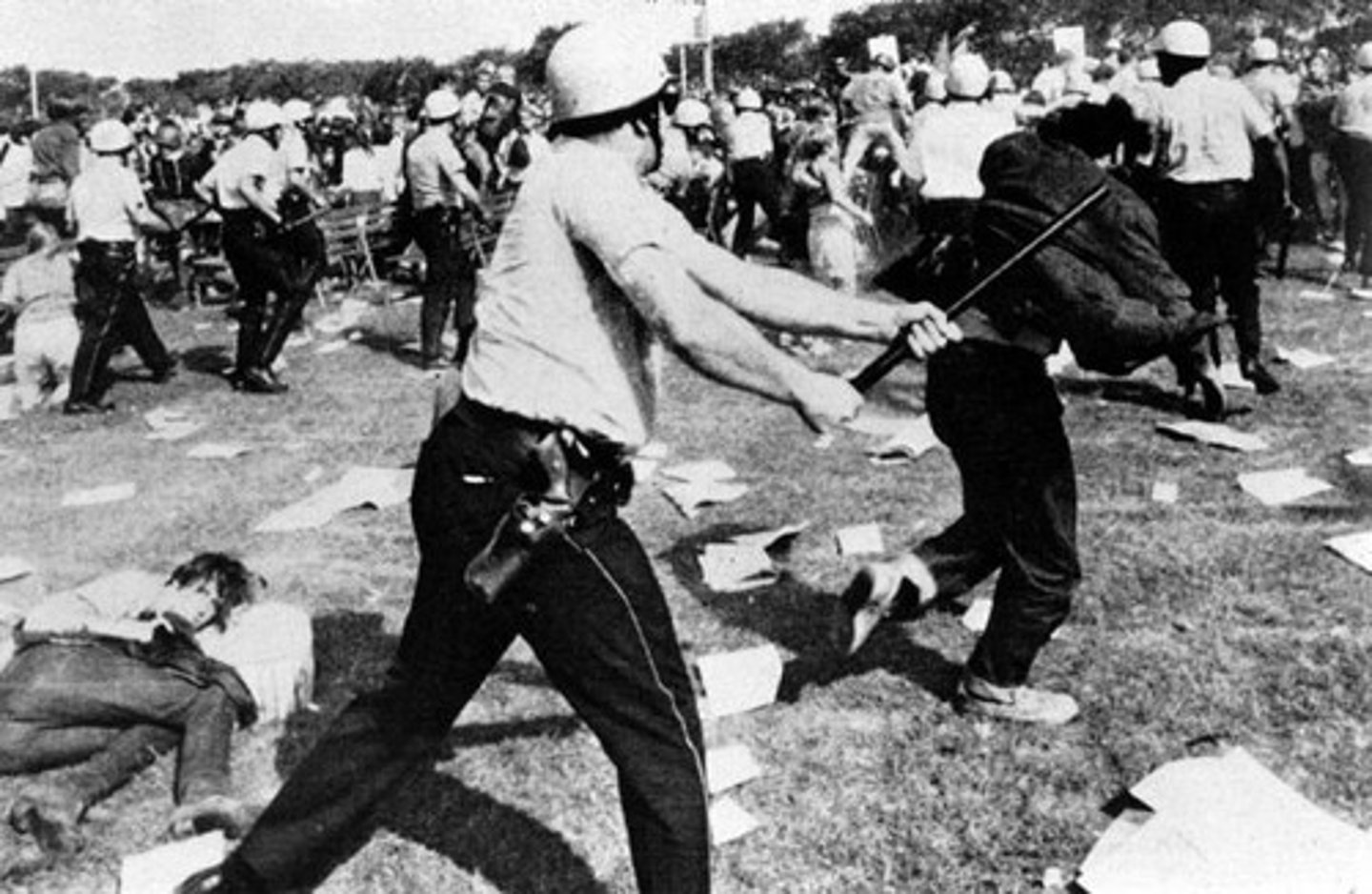
Democratic Convention of 1968
Chicago, 1968, where Democratic delegates gathered to nominate Vice-president Hubert Humphrey. The convention hall was protected with barbed wire and police to keep the protesters away. Massive anti-war protests outside of the convention resulted in scores of arrests and multiple instances of police brutality.

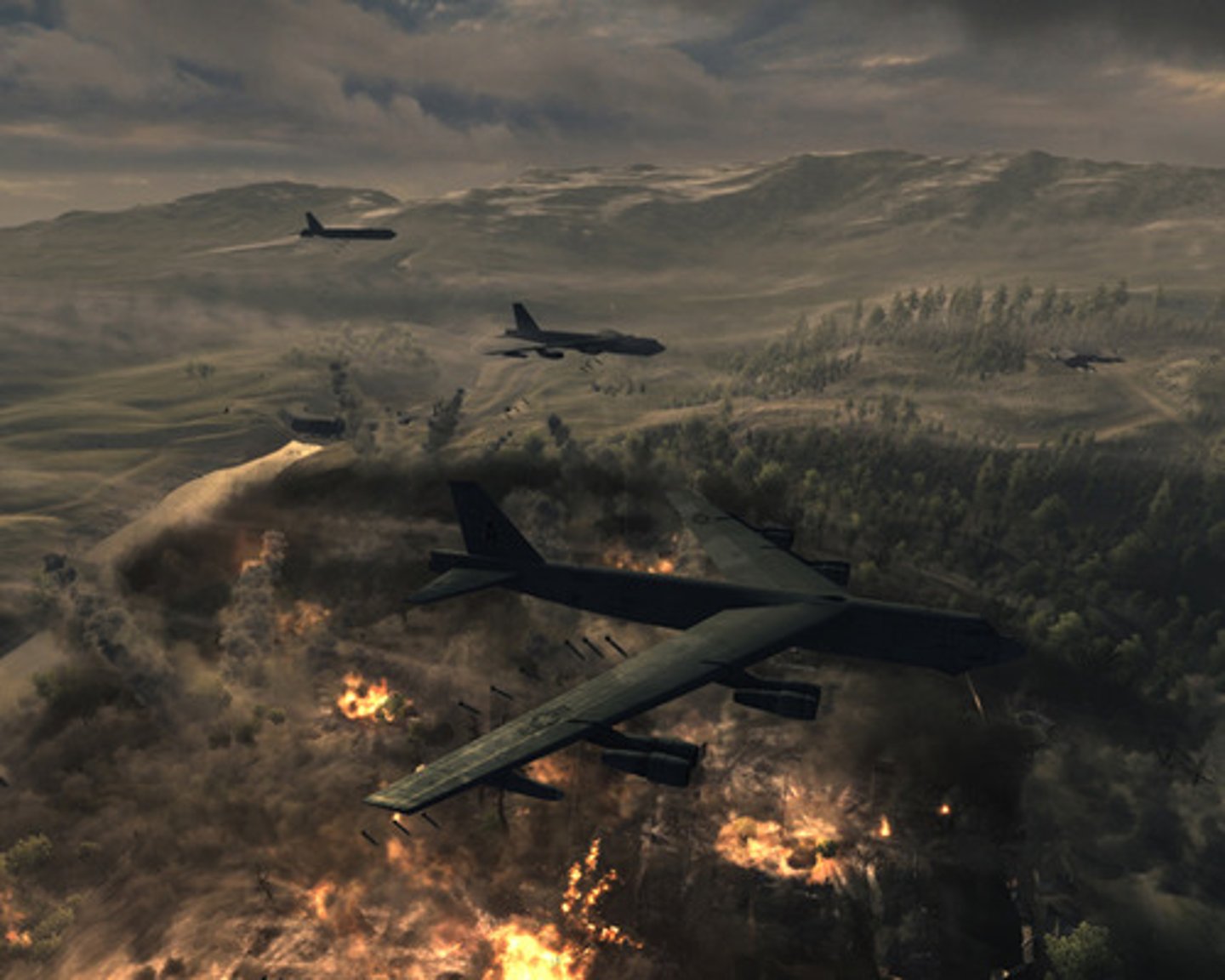
Operation Rolling Thunder (1965)
President Johnson's plan of entrance into the Vietnam War, which involved regular full-scale bombing runs against the North, as well as the entrance of some 184,000 American troops on the side of the South Vietnamese.

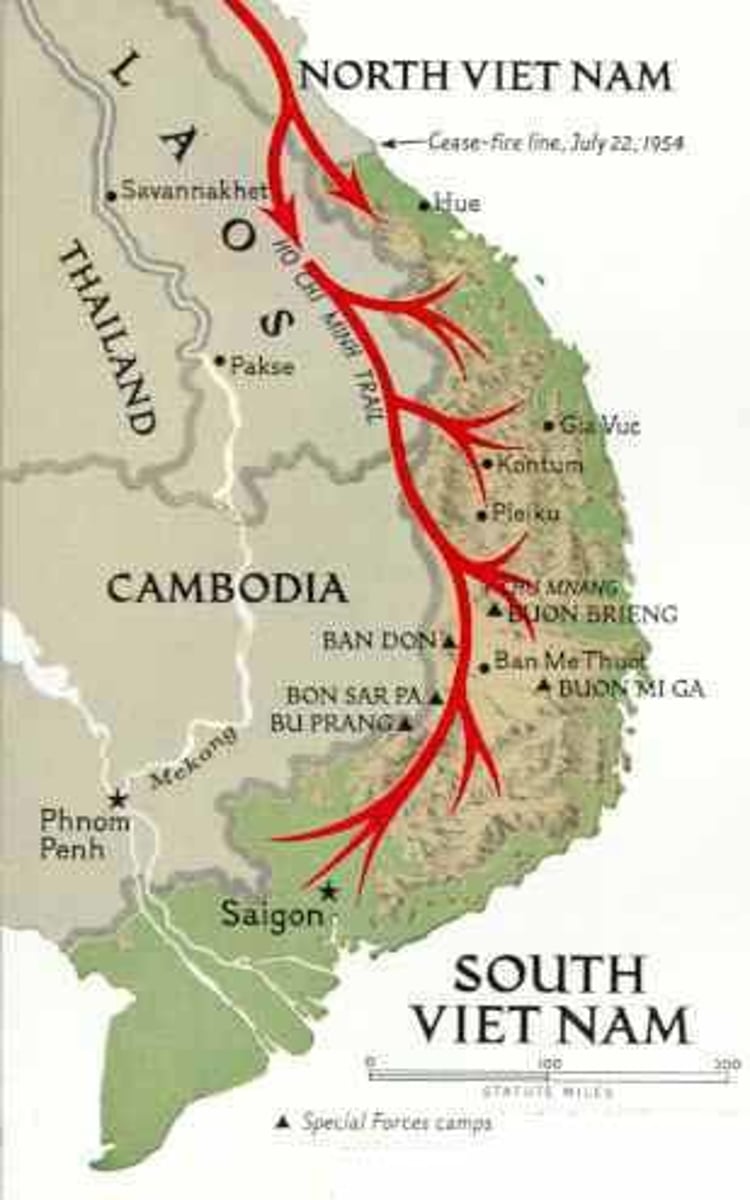
Ho Chi Minh Trail
A network of paths and trails used by the North Vietnamese Army to transport supplies to the Vietcong in South Vietnam.
General Westmoreland
The commander of all U.S. forces in Vietnam.

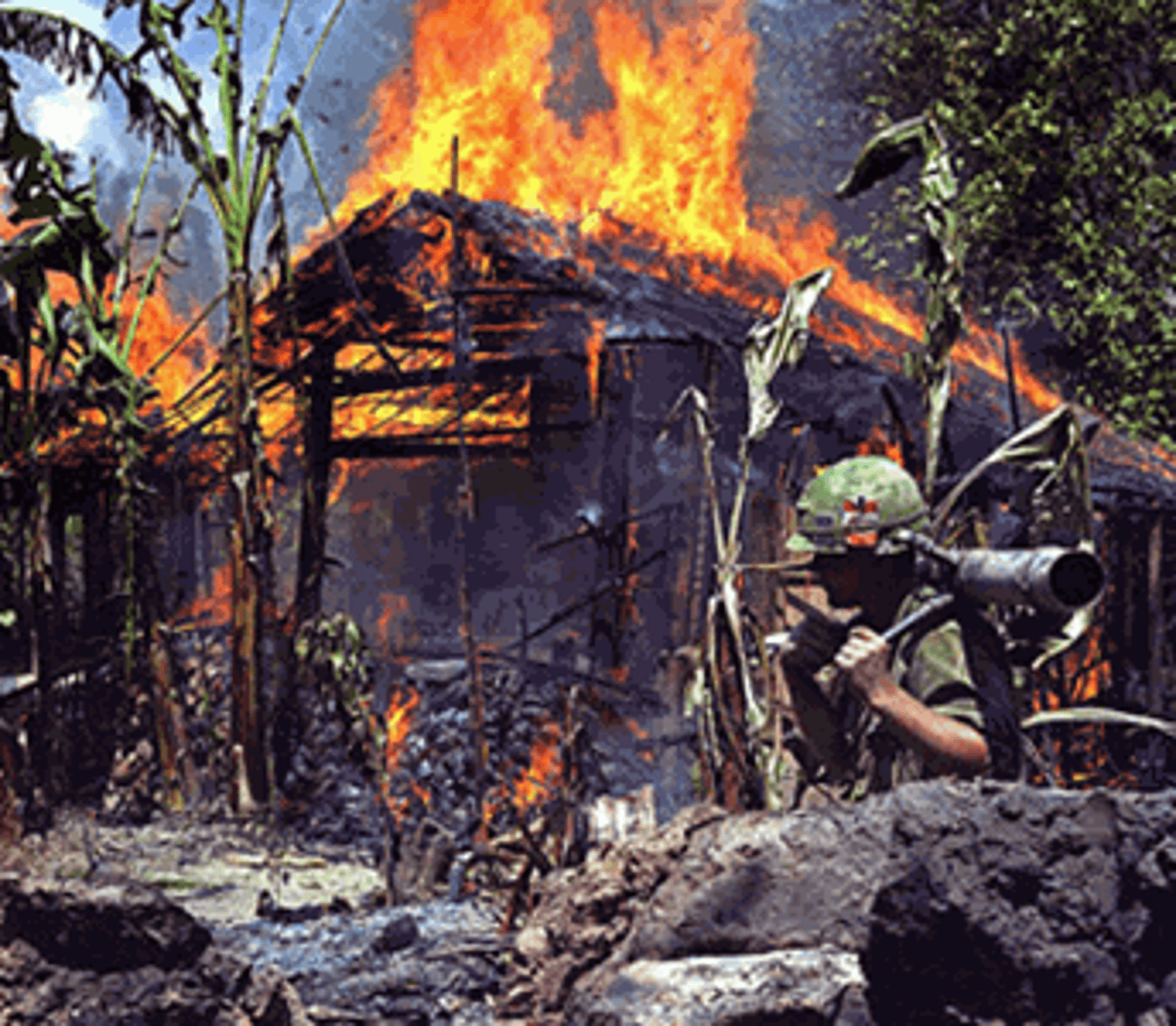
Pacification
Program to win the "hearts and minds" of South Vietnamese people, "pacifying" the opposition in countryside; involved construction projects, relocation of villagers, and burning of villages suspected of supporting the NVA and VC.

Draft
A law requiring people of a certain age (usually over 18) to serve in the military - halted after the Vietnam War.

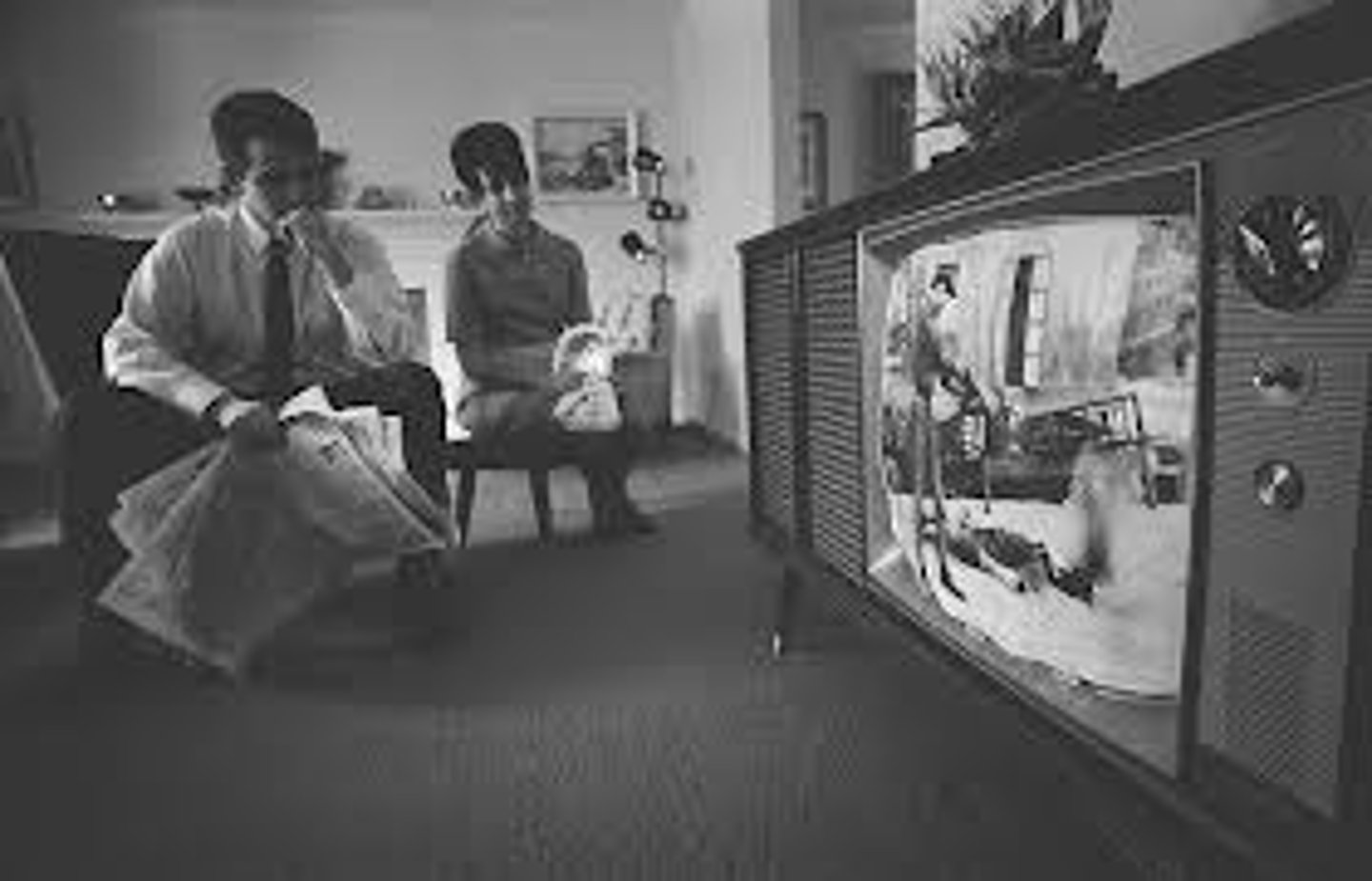
Living Room War
For the first time, Americans could sit in their living rooms and see the devastating effects of the war (including battles, body bags and caskets of U.S. soldiers) on their televisions.

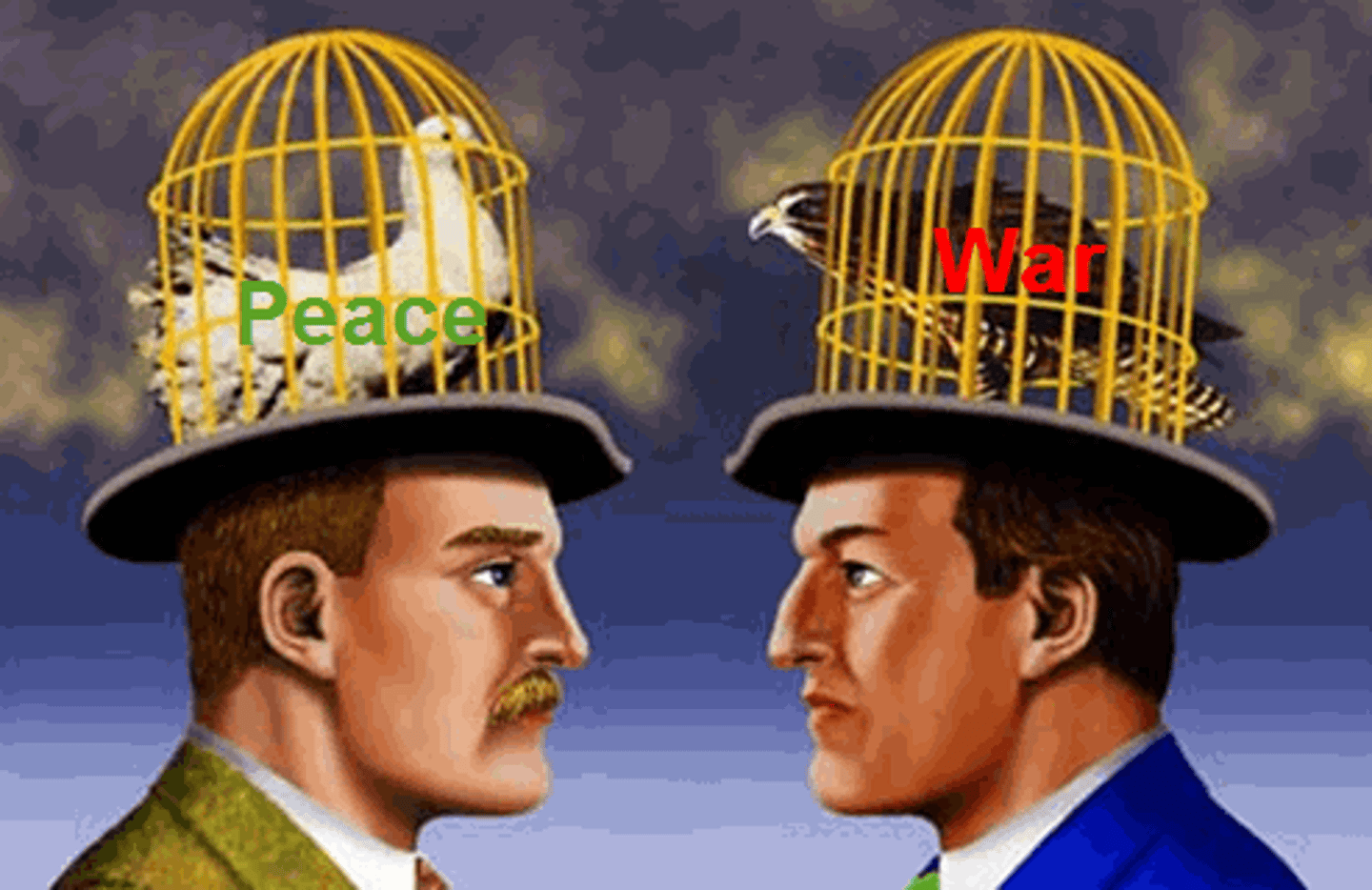
Hawks and Doves
Hawks are people who supported the war's goal. Doves were people who opposed the war.

Students for a Democratic Society (SDS)
Founded in 1962, the SDS was a popular college student organization that protested shortcomings in American life, notably racial injustice and the Vietnam War. It led thousands of campus protests before it disbanded at the end of the 1960's.

Silent Majority
A phrase used to describe people, whatever their economic status, who uphold traditional values - especially against the counterculture of the 1960's and support of the war in Vietnam.

Vietnamization, 1969
The US policy of withdrawing its troops and transferring the responsibility and direction of the war effort to the government of South Vietnam. It is important because it would bring the end of the Vietnam war in 1973 for the U.S. when it withdrew.

Kent State Massacre (1970)
Four college students killed and nine wounded by Ohio National Guard troops during an anti-ROTC protest and the U.S. invasion of Cambodia.
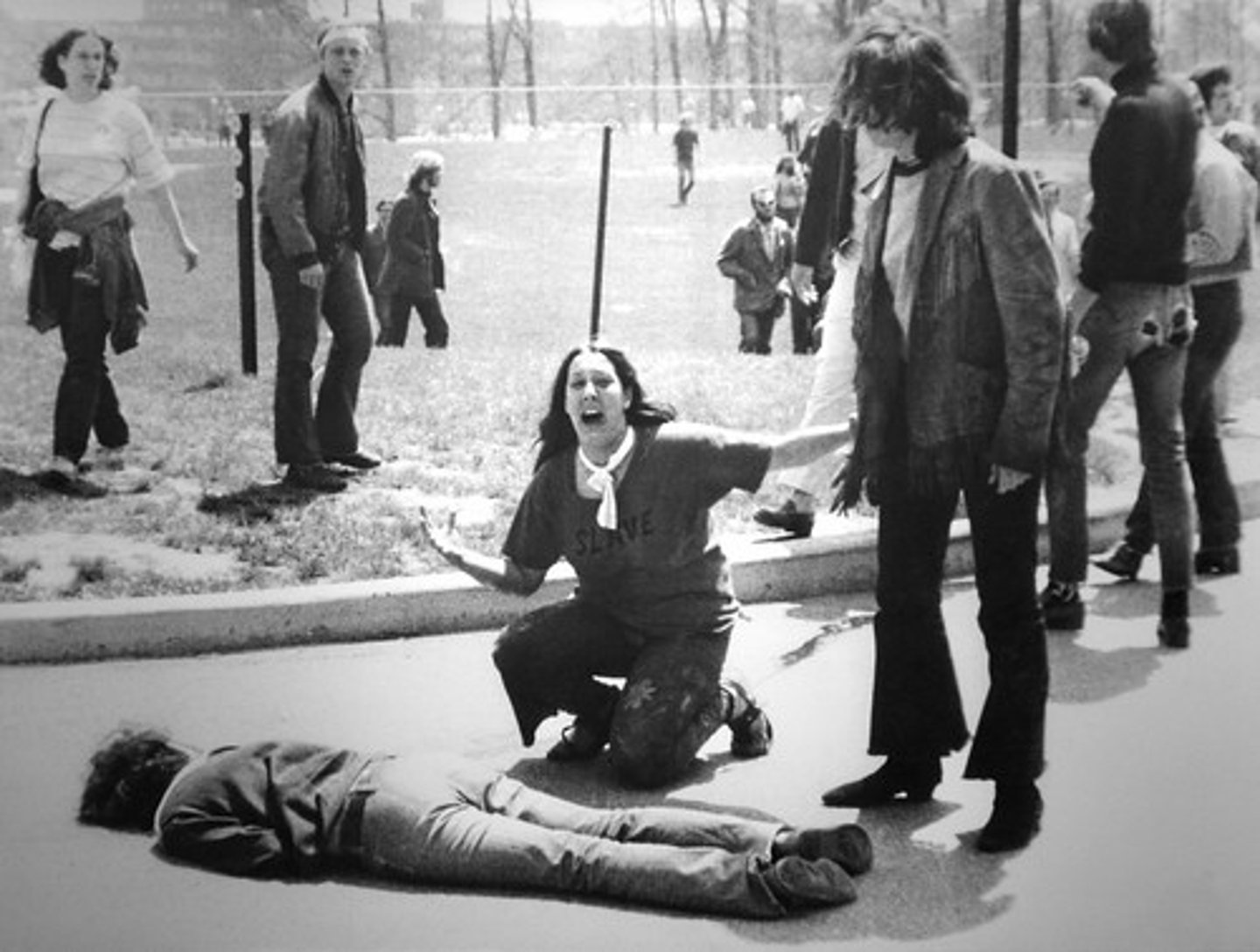

Antiwar movement (peace movement)
Social movement that protested the Vietnam War, seeking a peaceful resolution.

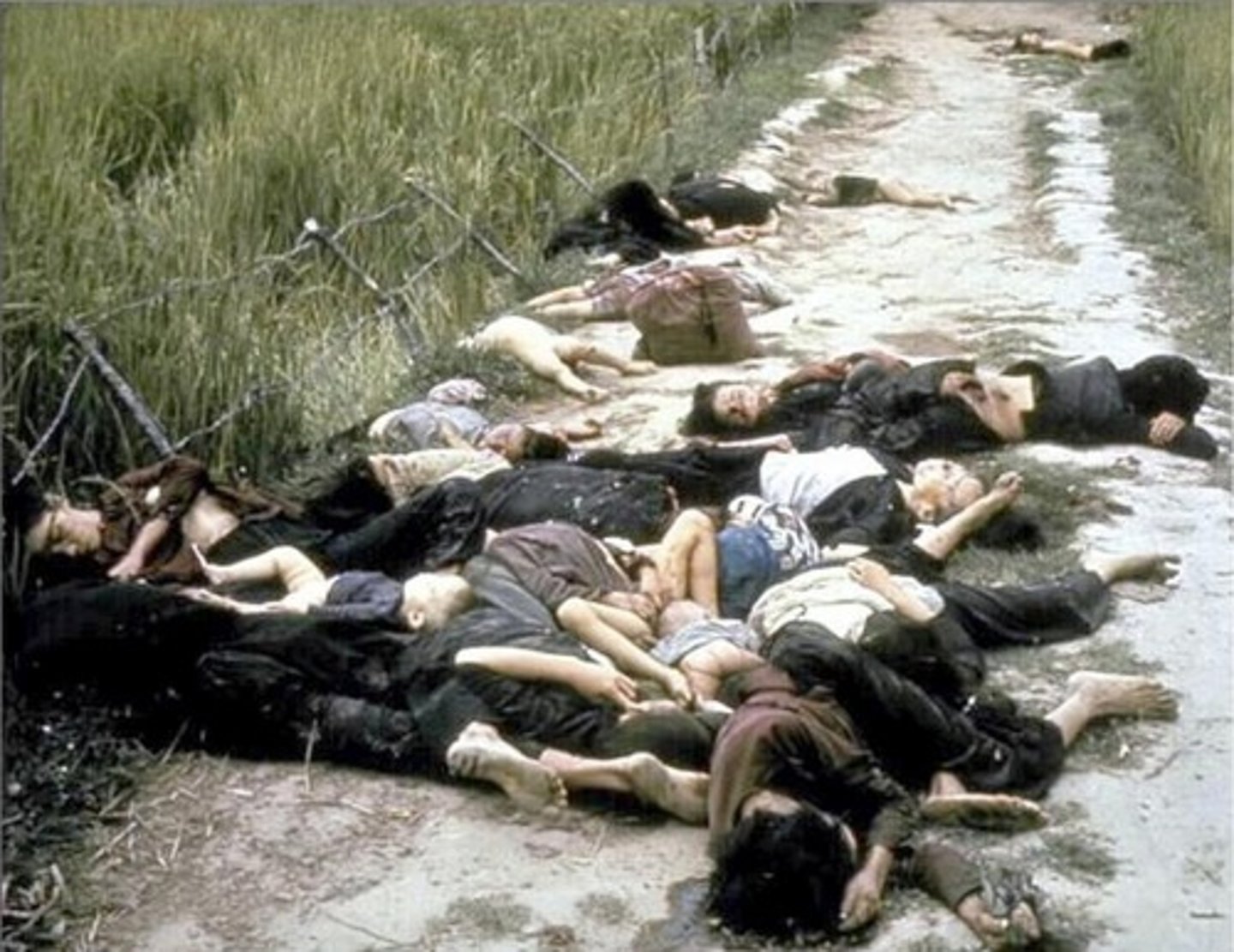
My Lai Massacre (1968)
A military "assault" in the small Vietnamese village of My Lai on March 16, 1968, in which American soldiers under the command of 2nd Lieutenant William Calley murdered hundreds of unarmed Vietnamese civilians, mostly women and children.
The atrocity produced public outrage and reduced support for the war in America and around the world when details of the massacre and an attempted cover-up were revealed in 1971.

Pentagon Papers, 1971
Secret document papers of the Pentagon (military wing of the U.S. gov't). An investigation led by Daniel Ellsberg, published by the New York Times in 1971, showed the blunders and deceptions that led the United States that led to the Vietnam War. Revealed the government misleading the public of its involvement in Vietnam, both about the intentions and the outcomes of the conflict.

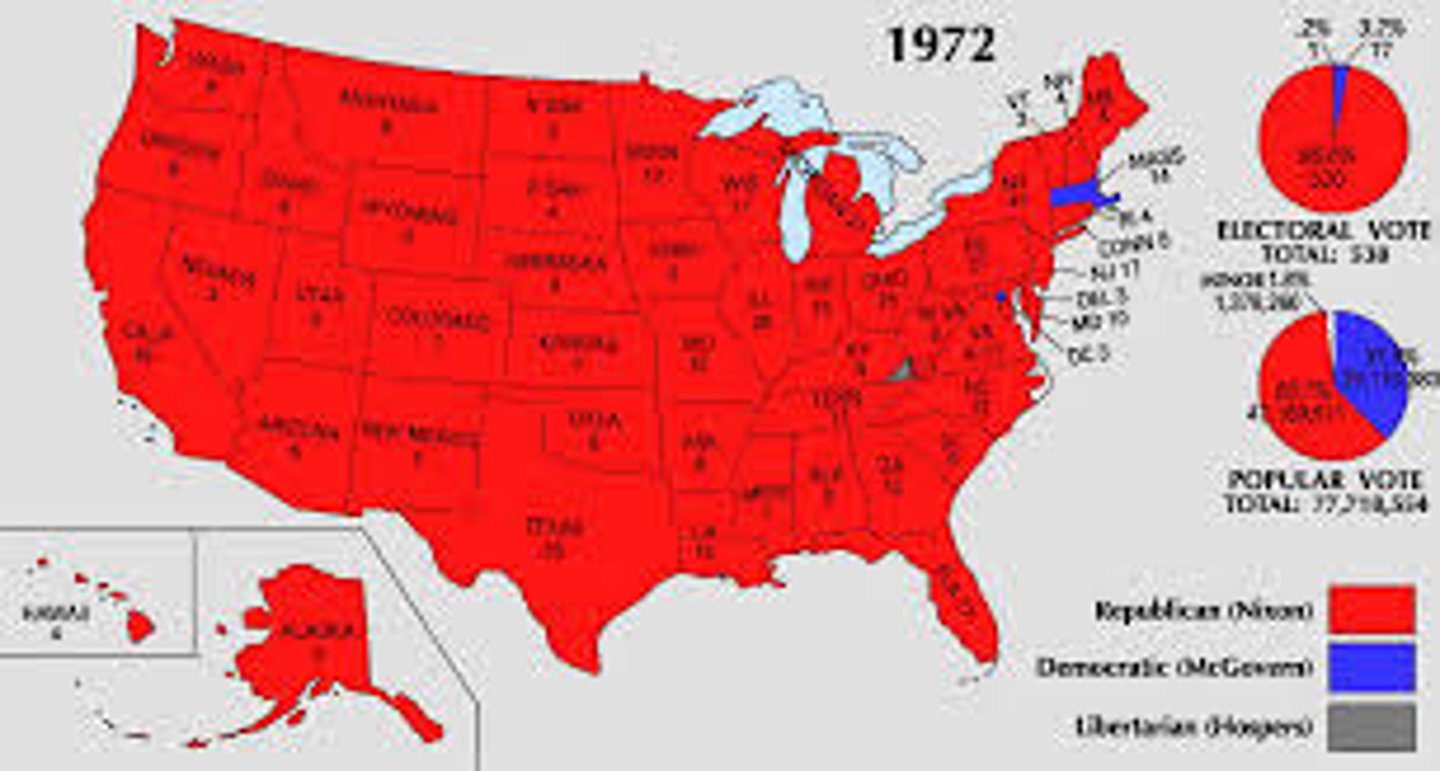
1972 Election
Republican Nixon wins re-election; defeated Democratic George McGovern in a landslide.
26th Amendment (1971)
Lowered the voting age from 21 to 18.

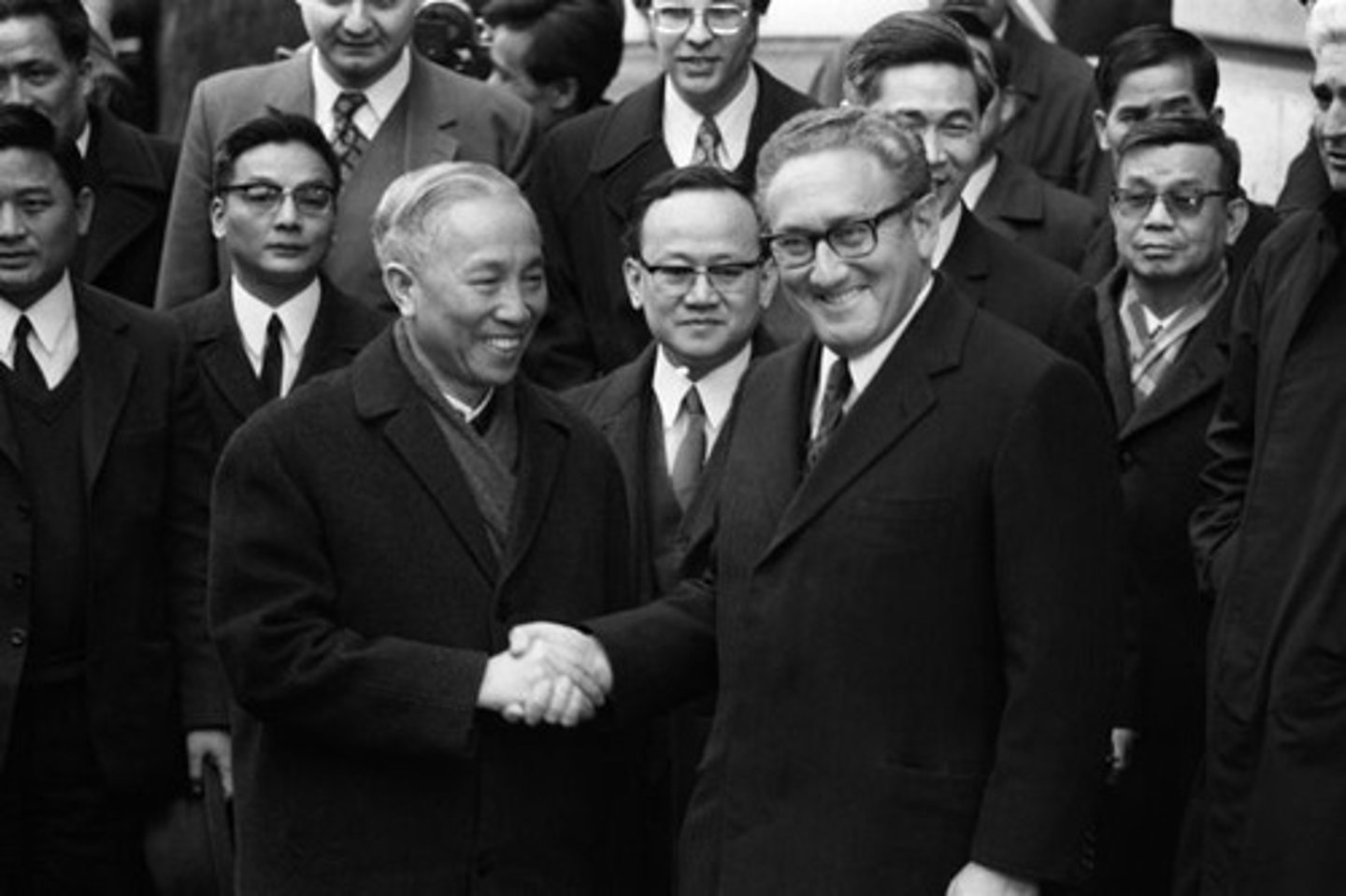
Paris Peace Accords (1973)
1973 peace agreements between the U.S., South Vietnam, North Vietnam, and the Vietcong that effectively ended the Vietnam War for the U.S.

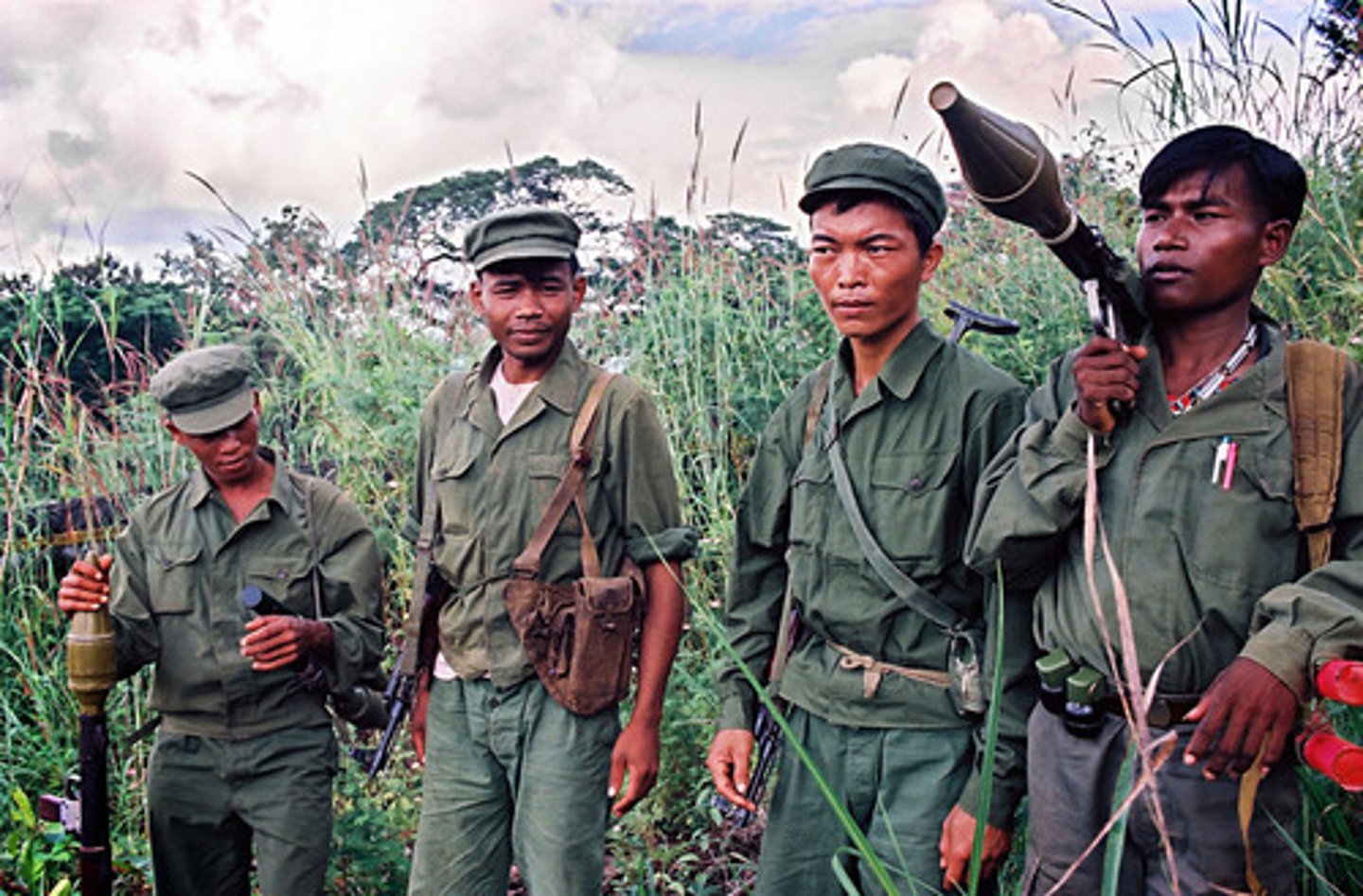
Khmer Rouge
A group of Communist rebels who seized power in Cambodia in 1975.

War Powers Act of 1973
Gave any POTUS the power to go to war under certain circumstances, but required that he/she could only do so for 90 days before being required to officially bring the matter before Congress.
