Photosynthesis Chap. 8
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Photosynthesis
conversion process that transforms sunlight → chemical energy stored in sugars
2 major modes of photosynthesis
autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition
Autotrophs
sustain self w/o eating other things, produce organic molecules fr
Autotrophs are the ____ of the biosphere
producers
Photosynthesis can also occur in
algae, certain protists and prokaryotes
Heterotrophs
live off other organisms, biosphere consumers
Decomposers
heterotrophs that consume feces/fallen leaves (fungi)
Photosynthesis most likely first occurred in
bacteria w/ infolded regions similar to chloroplast
Chloroplast
absorbs energy from sunlight and drives synthesis of organic compounds fr CO2 and H2O
Mesophyll
tissue in interior of leaf (where chloroplasts are found)
Stomata
microscopic pores that have CO2 entering and O2 exiting leaf
Stroma
dense fluid surrounded by 2 membranes
Thylakoids
sacs that make up a third of the membrane system and are suspended in the stroma, separates stroma from thylakoid space in sacs
Grana
thylakoid sacs stacked in columns
Chlorophyll
green pigment residing in thylakoid membranes of chloroplast, absorbs light energy to drive synthesis
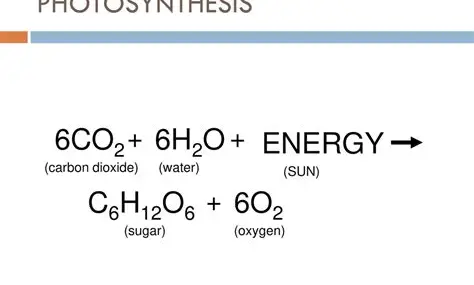
What is this
photosynthesis :D
C6H12O6
glucose
What is the direct product of photosynthesis
three carbon sugar that is used to make glucose

Simplest possible form of photosynthesis
O2 from plants comes from h2O or Co2
H2O
Co2 + 2H2S → [CH2O] + H2O +2S
Co2 + 2H2O → [CH2O] + H2O +O2
Co2 + 2H2X → [CH2O] + H2O +2X
which is sulfur bacteria
1)
Co2 + 2H2S → [CH2O] + H2O +2S
Co2 + 2H2O → [CH2O] + H2O +O2
Co2 + 2H2X → [CH2O] + H2O +2X
which is photosynthesis
2)
1) Energy released from sugar when e- w/ Hydrogens are transported by carriers to oxygen forming water as by product. e- lose potential energy, mitochondrion harnesses energy to synthesis ATP
1) Cellular Respiration
2 stages of photosynthesis
Light reactions and Calvin cycle
Light reaction process
convert solar energy → chemical energy, water split, O2 by product, transfer e- and H+ ions to NADP+ to be stored, NADp+ → NADPH by adding e-/H+, generate ATP by adding phosphate group to ADP
Photophosphorylation
how light reactions generate ATP using chemiosmosis that adds phosphate to ADP to make ATP
2 compounds of converted light energy → chemical
NADPH and ATP
NADPH
acts as reducing power over an acceptor
Light reaction does not produce
sugar
Calvin cycle
Co2 into organic molecules in the chloroplast, reduces (provided by NADPH) carbon → carbohydrate by adding e- and ATP, making sugar
Calvin cycle produces
SUGAR!
Carbon fixation
beginning of the Calvin cycle, the incorporation of carbon into organic compounds
Calvin cycle ____ fixed carbon to carbohydrate by adding electrons powered by _____, and the use of chemical energy in the form of ____
reduces, NADPH, ATP
light independent reaction and dark reactions
other names for Calvin cycle
Thylakoids of the chloroplasts are
sites of the light reactions
Calvin cycle occurs in the
stroma
Outside of thylakoids
NADP+ and ATP pick up electrons & phosphate which are released in the stroma
Electromagnetic energy
electromagnetic waves that are disturbances of electric/magnetic fields
Photons
discete particles of light
the shorter the wavelength
the greater the energy of each photon
Reflecting all light
white light
Absorbing all light
black
Wavelength of light that is reflected that we can see
visible light
Chlorophyll a
light capturing pigment that participates directly in the light reactions
Chlorophyll a suggests what kind of light works best for photosynthesis
violet blue and red
Chlorophyll b
accessory pigments
Carotenoids
separate group of accessory pigment, hydrocarbons that are yellow and orange, dissipates excessive damaging light energy
When molecule absorbs photon of light (excited state)
a molecule’s electron is elevated where it has more potential energy
Ground state
when electron is in its normal shell
When electrons drop back to ground state they release energy
in the form of heat
Reaction center complex
association of proteins holding onto special pair of chlorophyll a and a primary electron acceptor
How reaction center complex and light harvesting complex work together
energy transferred fr pigment-pigment molecule until it reaches chlorophyll a in reaction center complex
Chlorophyll a is special because
energy boosts electrons to higher level BUT can ALSO transfer to different molecule (primary electron acceptor)
When chlorophyll electron excited to higher energy level, primary electron acceptor captures it this is known
known as a redox reaction
Thylakoid membrane populated by 2 PS
PS II and PS I
P680
reaction center chlorophyll a PS II name, absorbs light at 680 nm
P700
reaction center chlorophyll a PS I name, absorbs light at 700 nm
Linear Electron flow
occurs in light reactions, the flow of electrons thru PS’s and molecular components
Step 1 of LEF
light makes a pigment molecule in PS II jump to higher energy level, falls back into ground state causing another to jump. electrons cont. jumping until reaching P680 where it excites the chlorophyll to higher energy
Step 2
the electron transferred from 680 is the primary electron acceptor making it 680+ (loss of e-)
Step 3
Enzyme catalyzes water into 2 e-, 2 H+ and O atom. Electrons transferred to 680+ replacing primary e- acceptor
Step 4
Photoexcited e- passes fr acceptor PSII to PS I via ETC, (e- carrier is Pq and cytochrome is Pc), redox reaction
Step 5
potential energy stored in proton gradient to mae ATP (chemisosmosis)
Step 6
Light energy transferred to PS I, exciting P700 chlorophyll a, electron transferred to PS primary acceptor, now it’s P700+ and can act as acceptor
Step 7
Photoexcited electrons passed in redox reactions from primary e- acceptor of PSI to 2nd ETC thru Fd
Step 8
NADP+ enzyme catalyzes transfer of electrons fr Fd to NADP+, 2 electrons required to make it NADPH which are available for Calvin cycle, cycle also removes H+ from stoma
Differences in chloroplast and mitochondria photophosphorylation
Chloro uses high energy electron dropped down ETC from water, does not need food → ATP (uses chemical energy)
Mito us extracted electrons from organic molecules, needs food → ATP
What diffuses protons down the gradients fr intermembrane space through ATP synthase → matrix
Mitochondrian chemiosmosis
ATP synthasized as H+ diffuse from thylakoid space to stroma thru ATP complexes
Chloroplasts chemiosmosis
Calvin cycle is considered to be
to be anabolic, building up out of simpler molcules
Calvin cycle simplified again
(again) C enters cycle in CO2, leaves as a sugar, ATP is spent and NADPH is consumed as reducing power for high energy electrons to make sugar
What is the carbohydrate produced from Calvin cycle
G3P
Fixing three CO2 makes
makes 6 G3P
Stages of Calvin cycle
Carbon fixation, Reduction and Regeneration of Co2
Carbon fixation
Co2 attaches to carbon-C sugar (RuBP) and is catalyzed by Rubisco, the product is a 6-carbon intermediate that splits into two 2-phosphoglycerate
Reduction
3 phosphoglycerate receives P from ATP abd becomes 1 Biphosp. NADPH donates e- to reduce it and makes it become G3P
Cycle begins w/ ____ carbons of carbohydrates in ___ molecules of__ carbon sugar RuBP and now there’s ___ carbons in the form of ___ molecules of G3P
15, 3, 5, 18, 6
Regeneration
5 molecules of G3P rearr to be 3 molecules of RuBP which spends 3 ATP
Net total of Calvin
9 ATP and 6 NADPH
C3 plants
intially fixated carbon via Rubisco, where calvin adds Co2 to ribulose biphosphate
As o2 is scarce, rubisco
adds o2 to calvin cycle which splits product forming 2-carbon compounds (photorespiration)
photorespiration is different because
produces no sugar and consumes ATP (does not generate)
C4 plants
carry out modified pathway for sugar synthesis that fixes CO2 into 4sugar compound
CAM Plants
fixation of carbon where Co2 is taken up in stomata when it opens at night. Store organic acid which releases co2 to become incorporated into sugar.