Roles of Plant Hormones
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What do cytokinnins do?
Promotes cell division in roots and shoots
Key concepts of Cytokinnins
Cytokinnins = More Mitosis
More Mitosis = More Cells
More Cells = Plant Growth
Gibberellin Role
The seeds absorb water
The absorbed water causes gibberellins to be synthesised in the embryo
The gibberellins synthesised act as a transcription factor, turning on the sections of the DNA, allowing it to be transcribed into mRNA and then translated, producing the enzymes "amylase" and "protease".
These enzyme break down the food store.
Abscisic Acid (ABA) Role
When water becomes limiting, stomata need to close.
Therefore, root cells synthesise and release ABA. It is transported to the leaves.
ABA molecules then bind to receptors on the plasma membrane of guard cells. That triggers the ionic concentration of the guard cells to decrease.
If the ionic concentration decreases, then the water potential in the guard cells will also decrease, causing water to move out of those cells via osmosis.
When water is decreased, there is a reduction in the turgor pressure, causing stomata to close.
Where does meristematic tissue occur in plants?
Lateral bud meristems (that produce side shoots)
Apical bud meristems (that increase the length of a shoot from the top)
Intercalary meristems (that increase the length of a shoot by increasing the internodal length)
Cambium (that increases the width of stems)
What does auxin do?
Promotes bud growth by causing shoots to bend toward the light
Promotes root formation by causing roots to grow towards gravitational pull
Apical dominance
Inhibits ethene
What is apical dominance?
The shoot apex of a plant grows faster and prevents the growth of lateral buds present at the lower position along the shoot
What is geotropism and phototropism controlled by?
Auxins
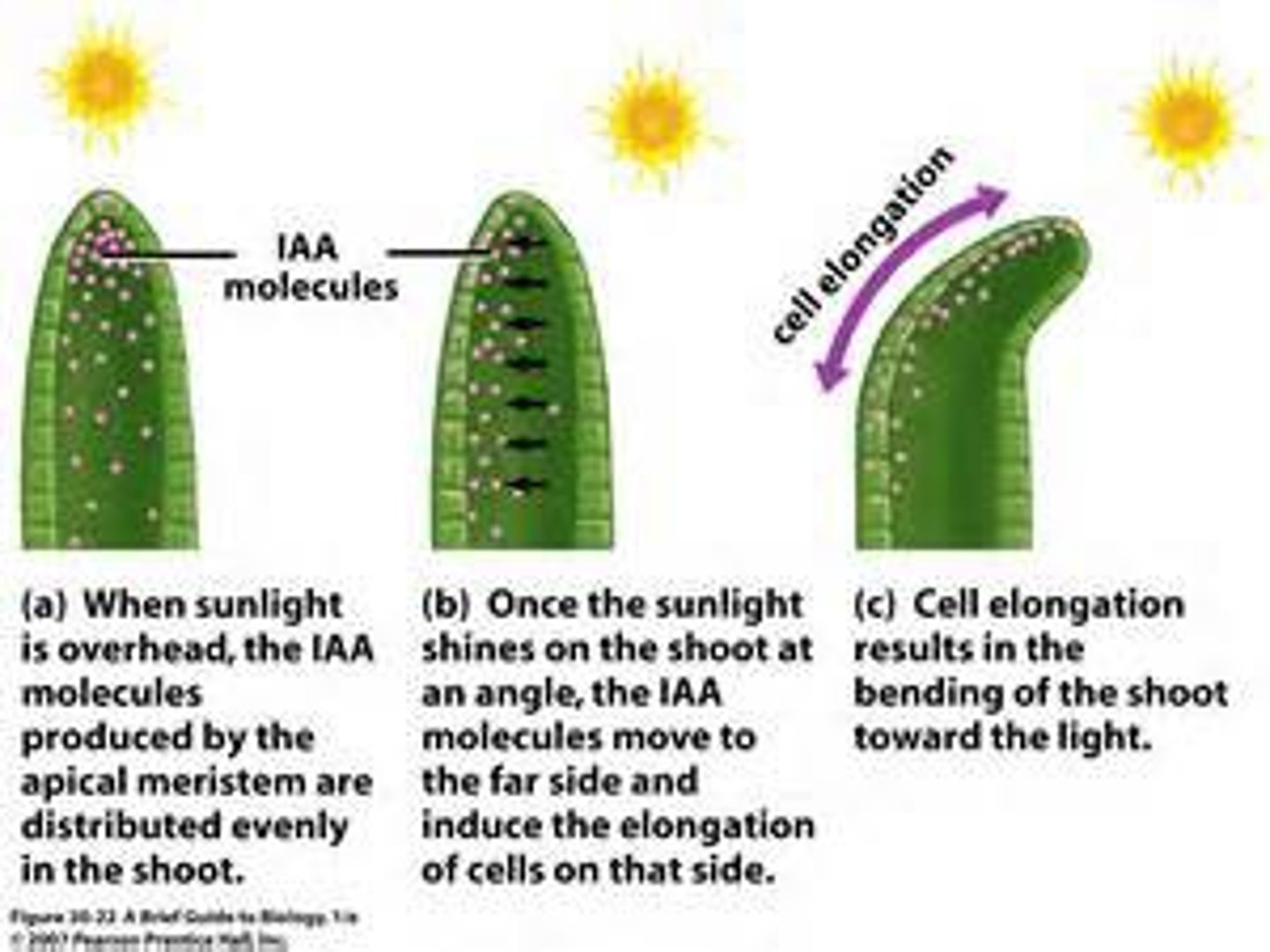
How do auxins enable phototropism?
Auxins are made in the shoot tip and diffuse down the shoot tip
Sunlight breaks down auxins
Shaded area has highest auxin concentration
This causes more cell division on the shaded side of the shoot, leading to the shoot bending towards the light
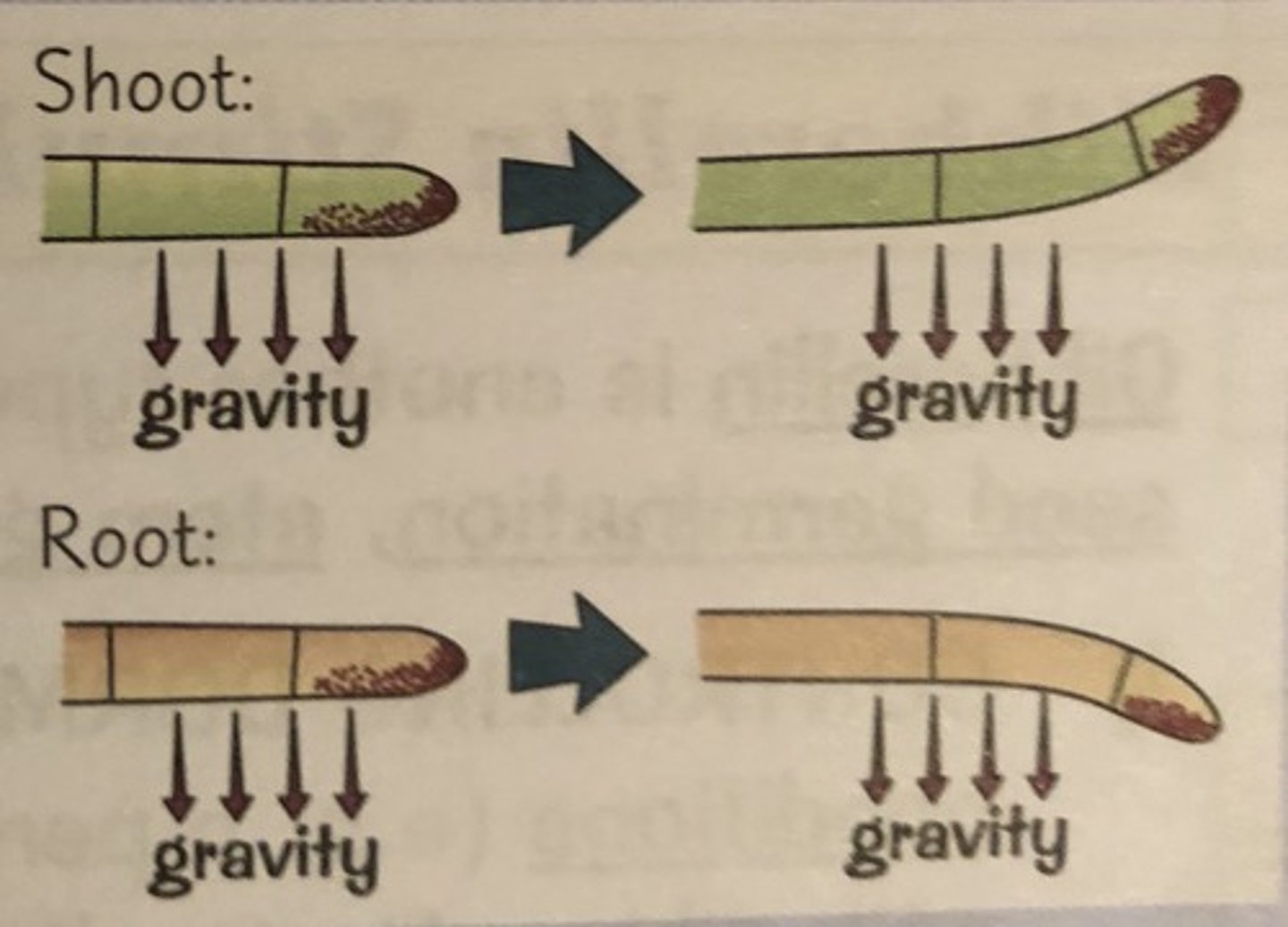
How do auxins enable root to grow downwards?
Auxins will gather on the side of the root where there is the most gravitational pull
In the roots, auxin inhibit cell division. This means that auxins will accumulate on the lower side of the root, and the upper side will experience more cell division and thus grow downwards.
Indoleacetic acid is an example of which type of plant hormone?
Auxin
What does ethene do in plants?
- Promote leaf fall (abscission)
- Promotes fruit ripening
Why are leaves lost during winter?
Energy/glucose needed to keep them in the winter, so trees will just get rid of the leaves.
Also, increase in darkness results in less auxin being made
What is the abscission zone?
Separation zone and protective layer is the abscission zone
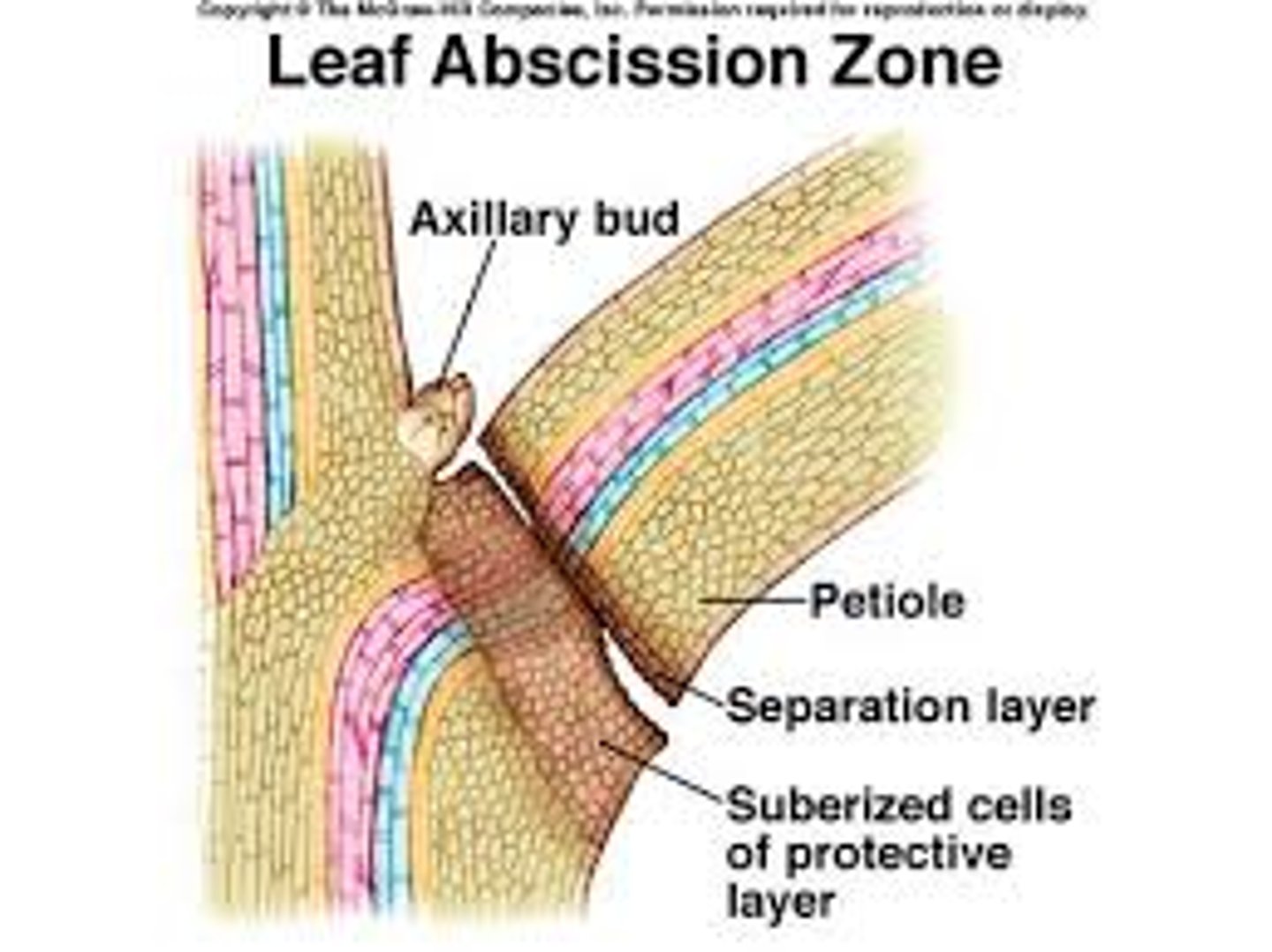
Ethene leads to leaf loss Process
Less auxin is being made due to increase in darkness
This allows ethene to be produced
Ethene stimulates the cells in the abscission zone to produce enzymes which digest and weaken the end of the leaf petiole
The leaf will eventually fall off and fatty deposits will be put there to prevent pathogens from entering