Bis 2c unit 2
1/314
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ledford keen
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
315 Terms
plant cells one
nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplast, plasmodesmata (cell-cell jxn)
Plant cells 2
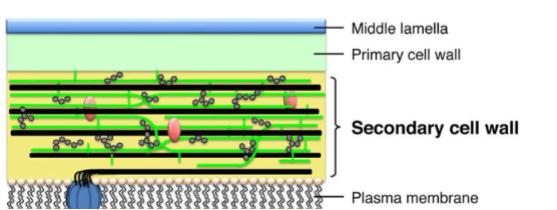
primary or secondary walls (secondary walls have ligin)
meristem
area where cells keep dividing
types of meristem
apical (sam or ram) and lateral
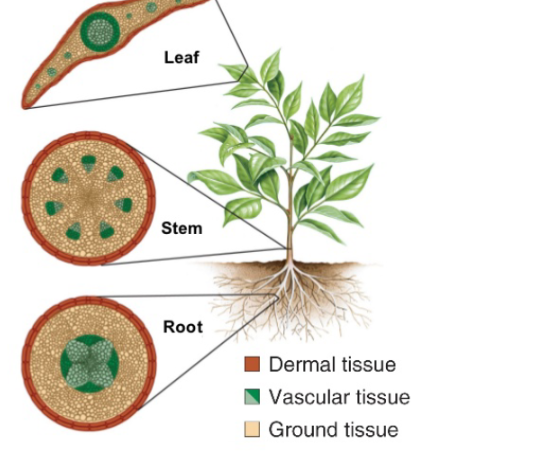
Dermal tissues
form the epidermis and secrete waxy compounds that protect the plant from desiccation
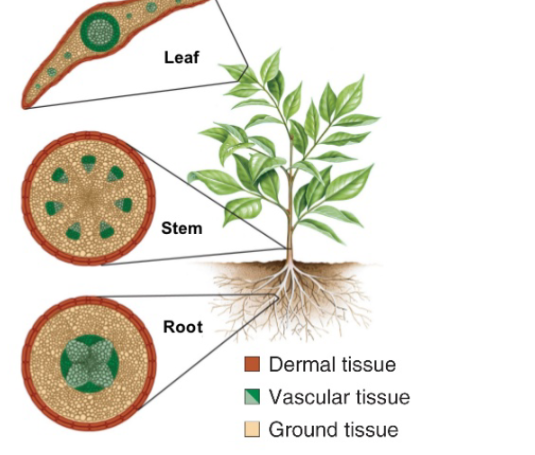
Vascular tissues
transport water, minerals and sugars, dominant sporophyte with complex, branched
growth
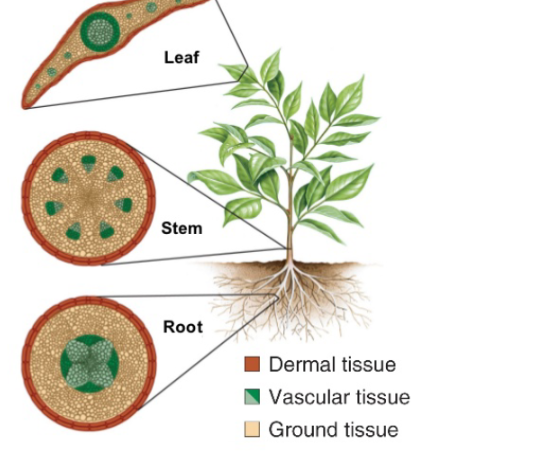
Ground tissues
fill in the inner space of the plant and perform metabolic, support and storage functions.
types of dermal tissue
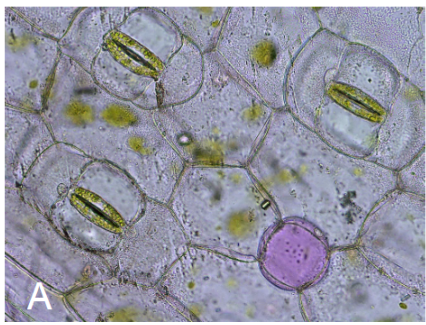
Guard
cells, trichomes, and root hairs
guard cells
stomata and regulate photosynthesis
trichomes
help capture prey

root hairs
location of water absorption

xylem
water, minerals and support made up of tracheids and vessel elements (lignified dead cells)
phloem
sugars (not lignified/alive)
types of vascular tissue
xylem and phloem
types of ground tissue
Parenchyma, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma
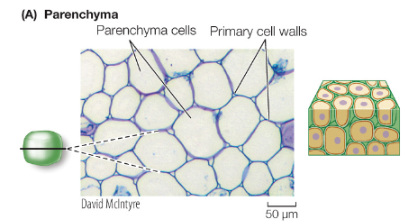
Parenchyma
living, storage & metabolism, thin cell primary cell wall, more inside the cell
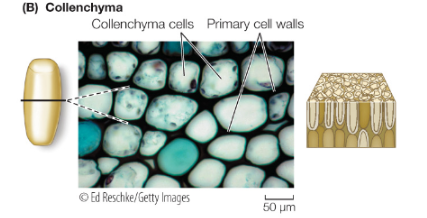
Collenchyma
living, flexible support, thick primary cell wall
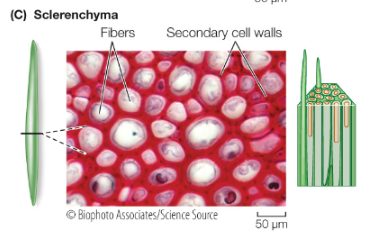
Sclerenchyma
dead, lignin, stiff support
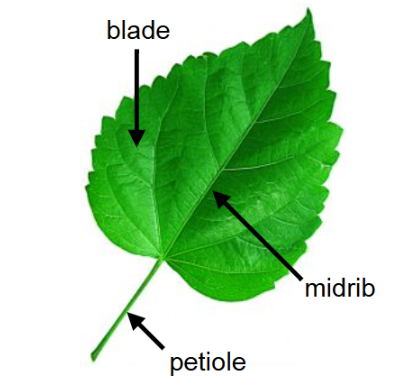
parts of leaf
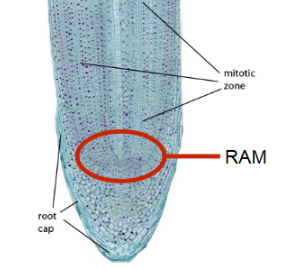
Roots have three main parts
1) root apical meristem, 2) root cap, and
3) root hair
root cap
protects the RAM as it grows through the soil
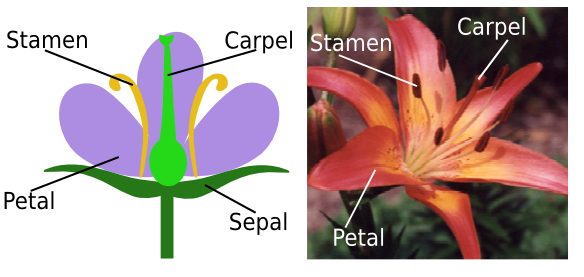
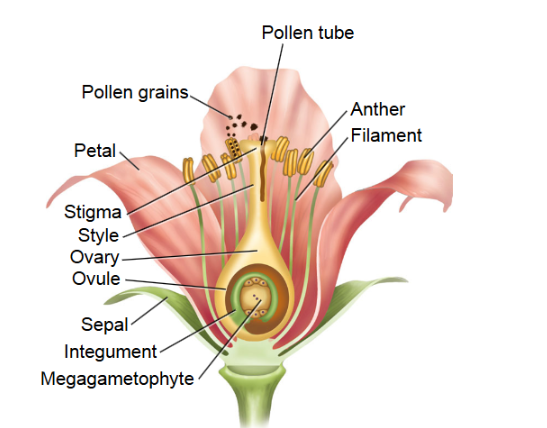
Flowers
combination of reproductive
and non-reproductive whorls
Algae
several early-diverging plant lineages, all of which are aquatic
Glaucophytes
freshwater, unicellular algae that have a layer of
peptidoglycan in their chloroplasts, use chlorophyll a, did primary endosymbiosis
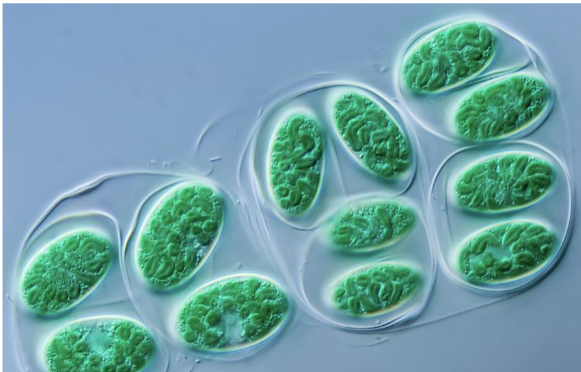
Red Algae
phycoerythrin give them unique color, diverse, marine, multicellular
Eukaryotes life cycle
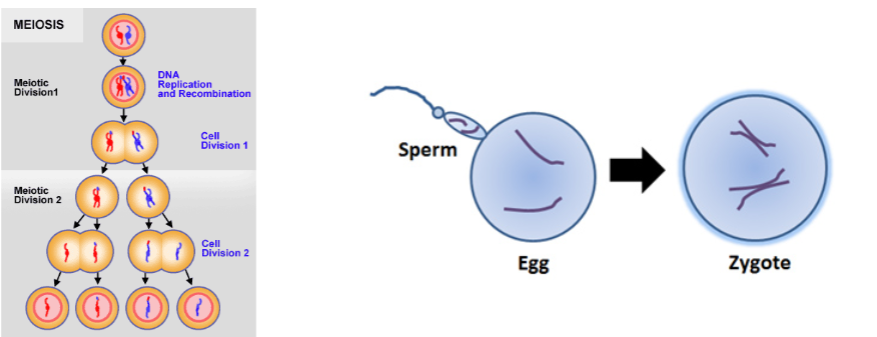
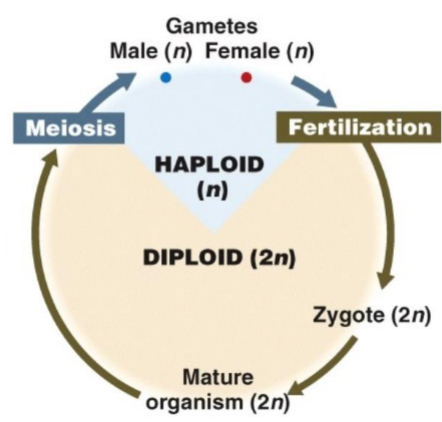
Diplontic life cycles
multicellular, diploid adult stage (animals)
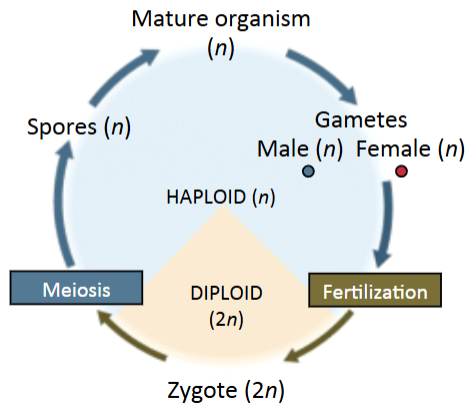
Haplontic life cycles
Lack a multicellular diploid (2n) stage (algae) and have no embryo. No sporophyte
Land plants
Bryophytes
small and usually live in moist environments. They
lack xylem and phloem, and do not have leaves or roots and have rhizoids (gametophyte dominant)
bryophytes types
liverworts, moss, and hornworts
rhizoids
multicellular extensions of the
gametophyte used for water absorption and anchoring (not roots)

Archegonia
structures that produce eggs

antheridia
structures that produce sperm
Sporopollenin
coats the outside of
spores to reduce water loss
Liverworts
have the smallest sporophytes among Land Plants

Mosses
taller with an elongate, stalked sporophyte (dominant gametophyte)
sporangium
cap of stalked sporophyte in moss
Hornworts
persistently green sporophyte with indeterminate
growth
synapomorphies of vascular plants
branching, independent sporophyte, roots, and tracheids
Roots
anchor the plant, absorb water and minerals, and store the products of photosynthesis
eudicots arrangement of vascular tissue
ordered vascular bundles

monocots arrangement of vascular tissue
scattered vascular bundles
Tracheids
first type of xylem tissue that evolved, they
transport water
Microphylls
leaves that have a single bundle of vascular tissue they evolved from sporangia and are a synapomorphy of lycophyes
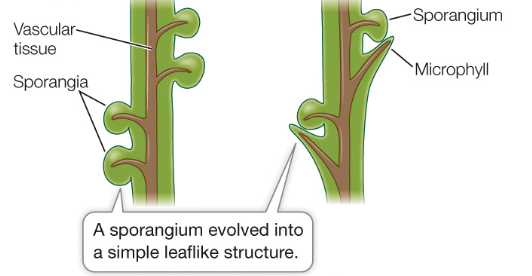
Sporangia
spore-producing structures which develop into gametophytes (n) via mitosis
strobilus (cone)
linear cluster of sporangia
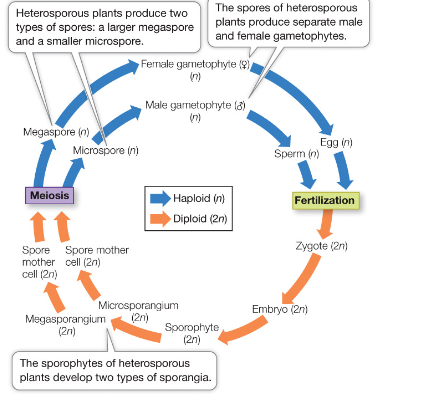
Heterospory
modification of the plant life cycle where there are
two sizes of spores. Each size of spore develops into a different
gametophyte
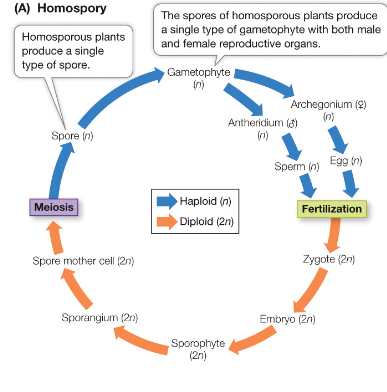
homospory
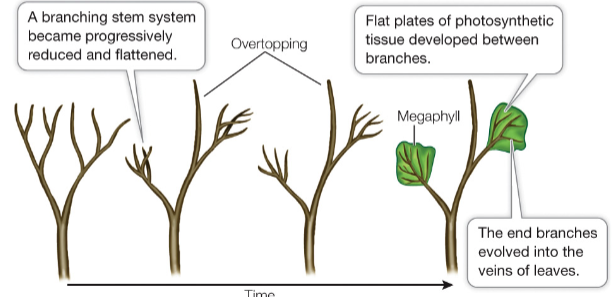
synaptomorphies of Euphyllophytes
Megaphylls, overtopping growth, and a DNA chloroplast inversion
Megaphylls
highly vascularized leaves and primary organ of photosynthesis
Overtopping
type of growth where there is uneven growth of the stem; it contrasts with the dichotomous branching of lycophytes
order of genes in the chloroplast DNA of Euphyllophytes
flipped
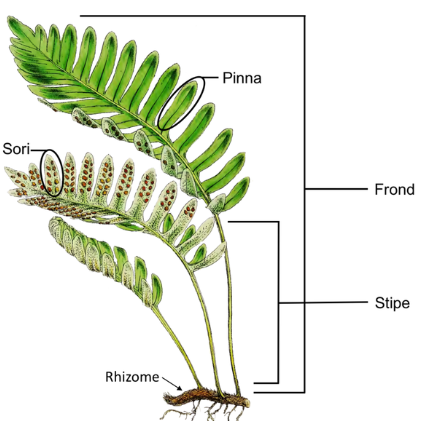
Ferns
largest groups of seedless vascular plants
(12,000 species) with a fossil record that spans 360 million years. Sporophyte dominant
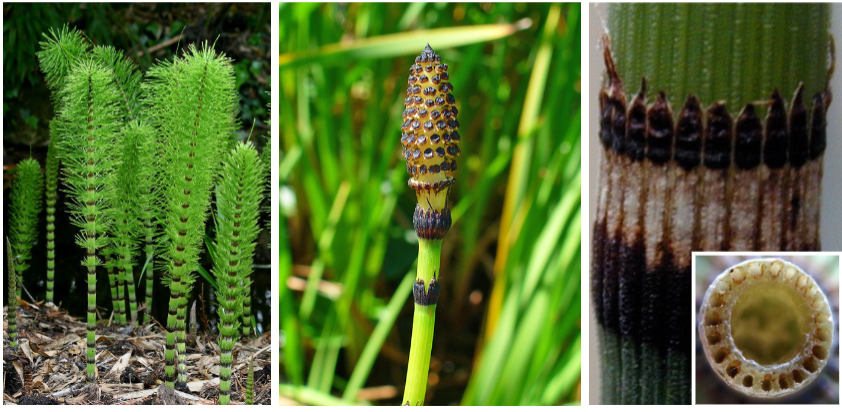
Equisetum (horsetails)
characterized by having a hollow stem with a whorl of reduced leaves. They have woody strobili at their tips

Whisk Ferns (Psilotum)
genus of monilophytes with reduced roots, dichotomous branching, sporangia at nodes, and “microphylls

Seed Plants
make seeds and pollen. Gametophyte is retained on and nourished by the sporophyte
Seed Plants synapomorphies
seeds, pollen, heterospory, 2ndary growth
angiosperms
are haploid and have a 3n nutritive tissue and 2n ovary wall to protect (fruits) and represent 90% of plant diversity and pollination via wind or animals
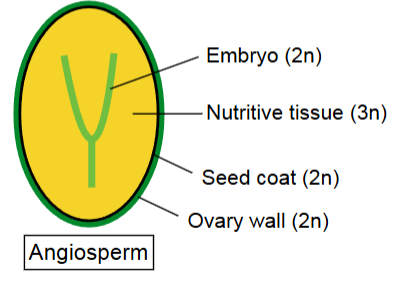
gymnosperm
contain embryos which germinate under favorable conditions n nutritive tissue and have no ovary wall for protection
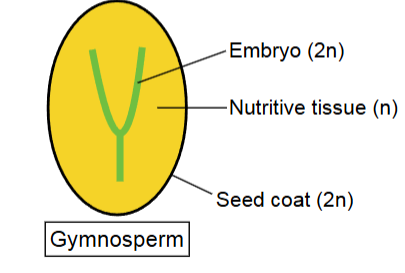
seed plants spores
still develop into gametophytes and dont leave parent plants; pollen is in dispersal stage
primary growth
length via meristems
secondary growth
width via lateral meristems
auxin
stimulates growth in Sam
Cytokinin
stimulates growth in Ram
auxin and cytokinin working together
growth in roots increase and so do cytokinin as they are both axillary meristems
Vascular cambian (BVC)
where secondary growth occurs

types of gymnosperms
cycads, ginkgo, gnetophytes, conifers
microsporangia
pollen cones (produce microspores)
microspores
develop into microgametophytes then disperse via wind
cycads
large, compound leaves and separate male and female plants

Gnetohytes groups
small group only including 3 genera (welwitschia, ephedra, gnetum)

Gnetophytes traits
paired, opposite leaves, vessel elements, double fertilization
Welwitschia
occur in fog deserts, use moisture from fog to stay alive. indeterminate leaves

land plant synapomorphy
waxy cuticle, sphytes, alter of generations, airborne species
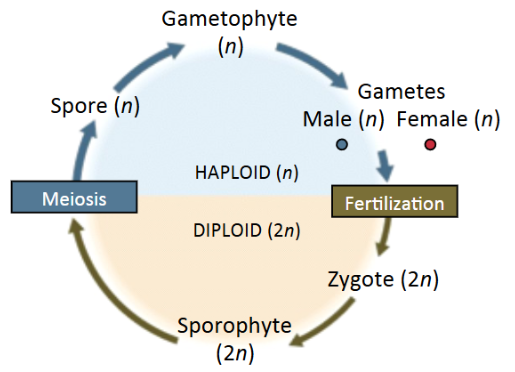
alterations of generation
haploid(gametophyte) to diploid (sporophyte) back to haploid (gametophyte)
synaptomorphy of plantae
chloroplast resulting from primary endosymbiosis
green plants
use chlorophyll b, carotenoids and store energy as starch inside chloroplast
Phloem parts
sieve tub elements and companion cells
sieve tubes
lack organelles so companion cells keep them alive
evolution of seed plants for males
male gametophyte (pollen) no longer form antheridium and non-motile nuclei that travel through the pollen tube to reach the egg

evolution of seed plants
gametophyte is retained on and nourished by the
sporophyte. The reduction of the gametophyte is a trend in plant evolution
is double fertilization homologous with angiogperms
No in gnetophytes, endosperm isn’t produced
ginko bilipa
last surviving member of a once more diverse widespread lineage (ginkgoales) and dioecious having motile sperm and produce seeds with a fleshy covering. Divided into 2 lobes

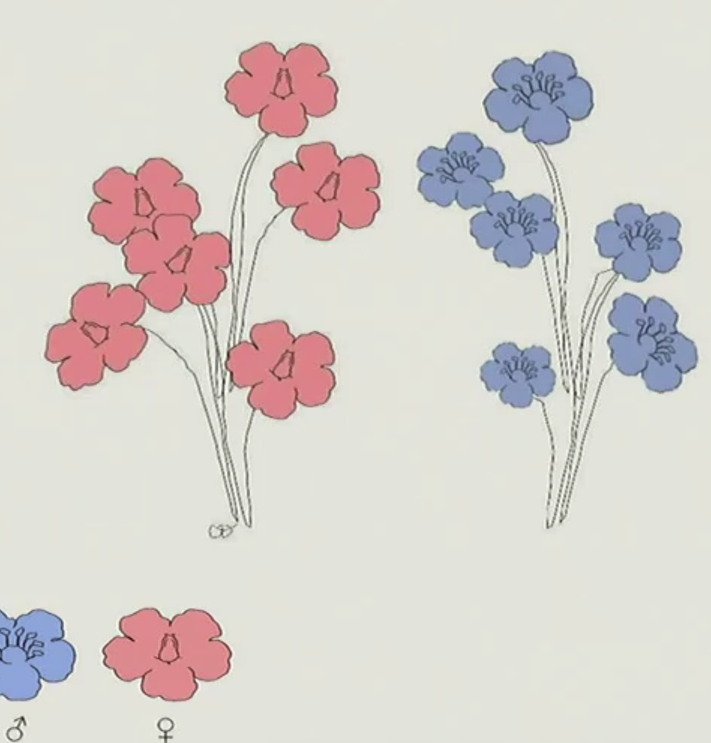
dioecious
separate male and female plants

female ginko biloba
popular in horticulture and fleshy part of seed smells bad

taiga
forms most of the biomass in the Northern Hemisphere. It is dominated by conifer
seronity
adaptation in plants where seeds only released when their is an environmental trigger (ex fire)
endemison
only live in one area in the world
relictual lineage
closest relative is really really far away
Bristlecone pines
re among the oldest living organisms, with some
individuals over 5,000 years old and their pine needles can live
45 years

synapomorphy of angiosperms
flowers, double fertilization,
and vessel elements
2 types of flowers
perfect or imperfect
perfect flowers
have both stamens and carpels
imperfect flowers
have either stamens or carpels
monecious
plant has both male and female
Double fertilization
one sperm cell (n) fertilizes the egg (n)
and a second sperm cell fertilizes the central cell (n+n) resulting in
endosperm (3n)
Fruit
means of seed dispersal. Botanical fruits are not always the same as culinary fruits
Pistil
one or more carpels
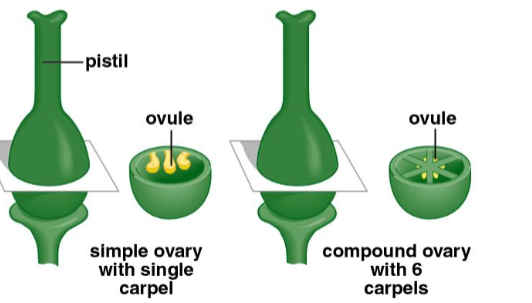
carpel
consists of the stigma, style, and ovary