Intro and Organization of the Human Nervous System
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
NSUOCO 2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
The nervous system is the body’s command center, it regulates your body’s system. What is it responsible for controlling?
movements
thoughts (emotions)
automatic responses
digestion
breathing
sexual development
How can you damage your nervous system?
trauma, disease, toxins and aging
What is the nervous system composed of?
neurons - they send signals to and from cells all over the body
How does the nervous system interpret information and controls the body’s response?
moving limbs
feeling sensations
Motor neurons are also called
efferent
What does the term afferent correlate with?
sensory neurons
What does the central nervous system consists of?
The brain and spinal cord
What does the terms dorsal and ventral refer to?
dorsal - back 🐬
ventral - front
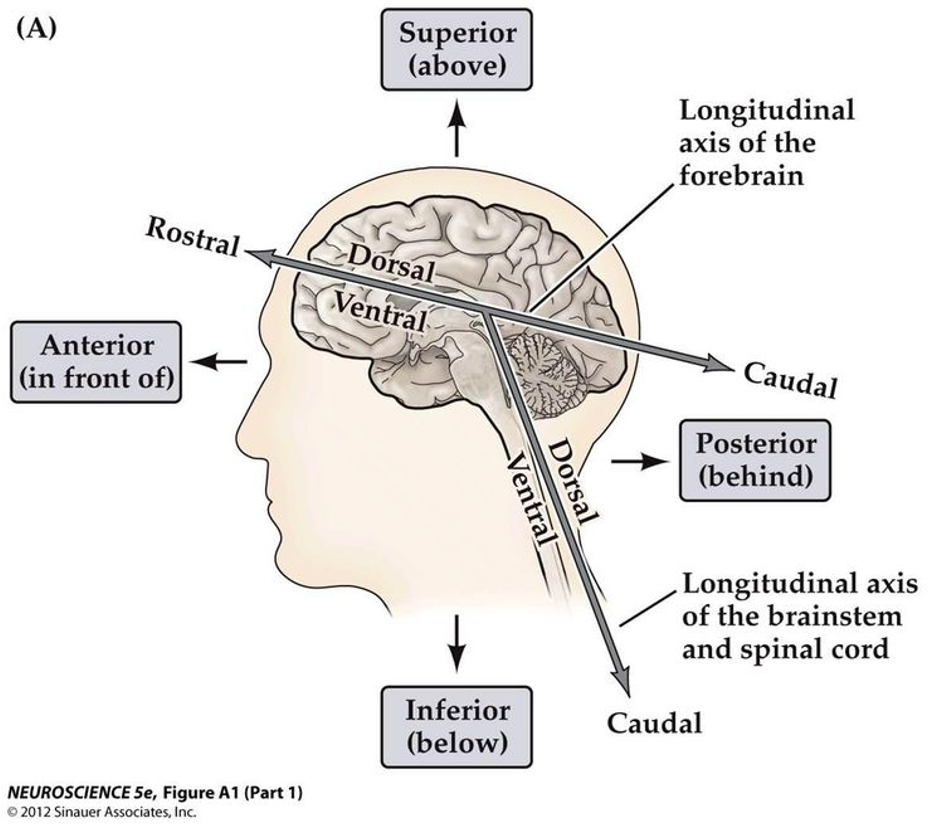
Where is the longitudinal axis of the forebrain?
Where is the longitudinal axis of the brainstem and spinal cord?
"Longitudinal" means relating to length, so this axis goes from the front to the back of an object.
its an imaginary line running through the middle of these structures
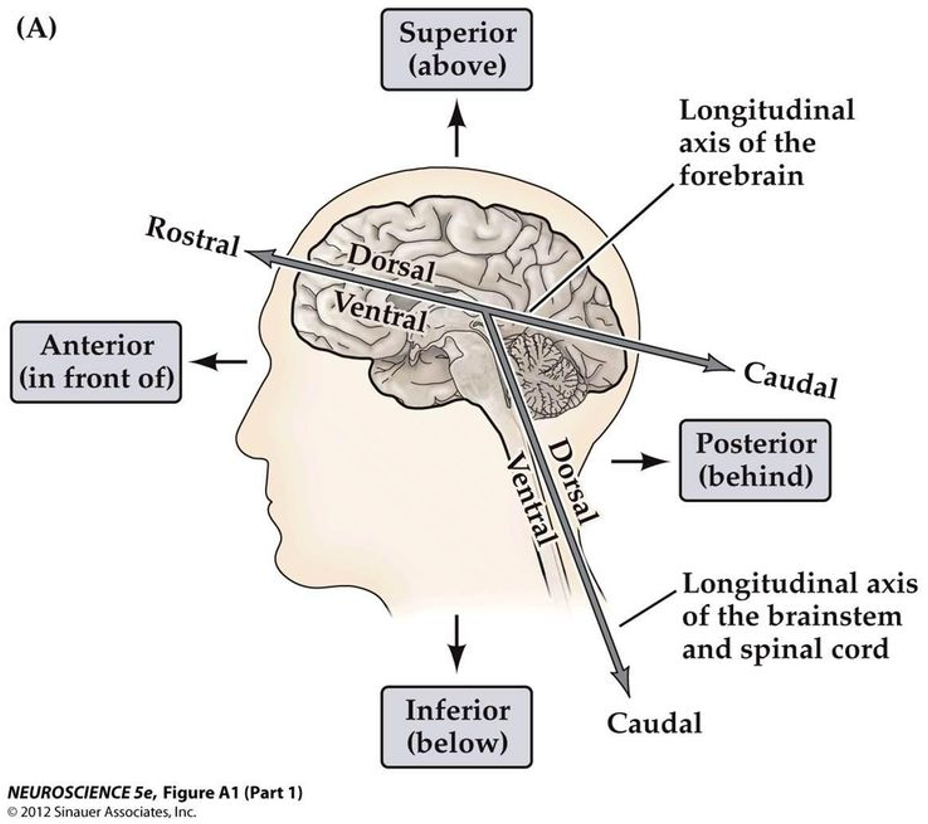
What are the anatomical sections we view the brain in?
Coronal (👑) aka frontal section
mid-sagittal aka medial section
horizontal section
The nerve lies outside the brain and spinal cord and what is it a compilation of?
hundred of thousands of axons with associated connective tissue and blood vessels
What is ganglia made of?
neuronal cell bodies located outside the brain and spinal cord
The enteric plexus is an extensive network of neurons that help regulate what? Where is it located?
the enteric plexus helps regulate the digestive system and it is located in the walls of the GI tract
What are dendrites and specialized cells that monitor changes in the internal or external environment?
sensory receptors
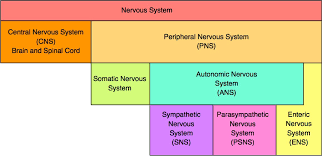
What is the CNS (central nervous system)?
the brain and spinal cord
What is the PNS (peripheral nervous system)?
consists of the somatic nervous system and autonomic nervous system which breaks down into the sympathetic, parasympathetic, and enteric nervous system
The entire CNS is encased in ______. The brain is within ______. The spinal cord is within a ________ in the ______.
The entire CNS is encased in bone.
The brain is within the cranium.
The spinal cord is within a canal in the vertebrae.
What surrounds the CNS?
CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) and the meninges.
How many cranial nerves do we have?
12 pairs of cranial nerves
How many spinal nerves?
31 pairs of spinal nerves
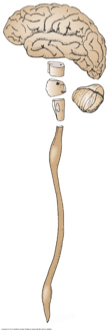
Label the picture with the following terms:
brainstem
spinal cord
cerebellum
medulla
cerebrum
midbrain
pons
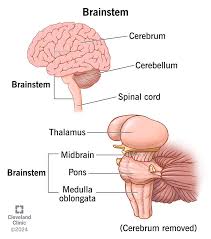
What are the 3 functions of the nervous system?
sensory
integrative
motor
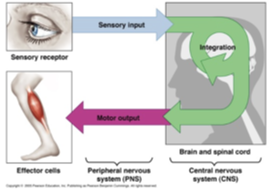
How does the sensory function perform?
receptors detect changes in internal and external body conditions
How does integrative functions work?
coordinates sensory information and makes decisions that are acted upon by using motor functions
How do motor functions perform?
effectors respond when they are stimulated by motor impulses coming from the CNS through the peripheral nerves
List the functions of the PNS (hint there’s 3).
–Carry sensory information from the periphery to the CNS
–Conveying motor commands from CNS to the muscles
–Regulate autonomic functions
more than _______ nerve cells run through the body.
100 billion
The PNS consists of cranial and spinal nerves that branch out from the brain and spinal cord to all parts of the body. How many pairs of cranial nerves are there and how many pairs of spinal nerves?
12; 31
What are the divisions of the PNS?
somatic nervous system
autonomic nervous system
enteric nervous system
What is the somatic nervous system?
sensory- sends info from bodily sensor receptors to the CNS and also sends special senses (vision, hearing, taste, smell) to the CNS
motor- controls impulses from the CNS to skeletal muscles
consciously controlled
VOLUNTARY
IMPORTANT:
The somatic nervous system is ________.
voluntary
Special sensations examples
vision
olfaction
tastes
hearing
equilibrium and position
General sensation include:
somatic sensations and visceral sensations. list some of each type.
somatic sensations
locomotor
touch
temperature
pain
proprioception
visceral sensations
dull pain
distention
The autonomic nervous system is __________.
involuntary - can be done without conscious effort
Along with the endocrine system, the autonomic nervous system is concerned with the regulation of
visceral activities that aid in maintaining homeostasis and it innervates structures like the heart, smooth muscle and glands
The ANS is made up of sensory neurons which
sends info FROM autonomic sensory receptors to the CNS.
Where are sensory receptors located?
in visceral organs, such as the stomach and lungs
in the ANS, motor controls nerve impulses from CNS to
SMOOTH MUSCLES, cardiac muscles and glands
What are the divisions of the ANS (autonomic nervous system)?
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
Sympathetic is ‘flight or fight’; what is also associated with it
•Emergency, Excitement, Embarrassment
•Increased heart rate
•Skeletal muscle blood vessels dilate
•Other blood vessels constrict
•Decreased GI activity
•“Fight or Flight”
•NE/epinephrine
Parasympathetic is ‘rest/digest’, associated with
SLUDD
Decreased heart rate
increased GI activity
acetylcholine
What is SLUDD?
Salivation
Lacrimation
Urination
Digestion
Diarrhea
What is the enteric nervous system?
“Brain of the Gut”
its involuntary and has sensory and motor functions
What are the sensory functions of the enteric system?
oversees chemical changes in the GI tract
What are the motor functions of the EntericNS?
contraction of smooth muscles to propel food through the GI tract
regulates secretions of tracts or organs
regulates activity of GI tract endocrine cells
What is gray matter composed of?
collection of neuronal cell bodies, dendrites, unmyelinated axons, axon terminal and neuroglia within the CNS
Why is gray matter gray?
the color of gray matter is due to NISSL bodies and lack of myelin
(UNMYELINATED AND NISSL BODIES)
What is myelin?
a mix of proteins and lipids, helps conduct nerve signals and protect the axons
What is white matter composed of?
collections of myelinated axons in the CNS
Why is white matter white?
white coloration comes from the lipid material in the myelin sheath
What matter has more motor output?
gray matter
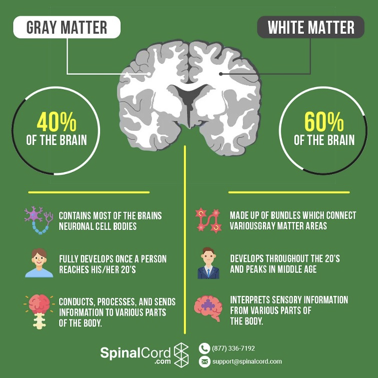
What is the function of white matter?
conducts, processes, communicates and sends nerve signals up and down the spinal cord through tracts
also sends nerve signals through commissural fibers and associated fibers
What are the functions of gray matter?
speech, hearing, feelings, seeing and memory
controls of the muscles
40%
The edges of the cerebrum (cortex) is ______ matter, while the center (nucleus) is ______
gray matter; white matter
What is the diencephalon and cerebrum apart of?
The forebrain
How can you view the diencephalon?
it is only visible upon cutting the brain
What is the midbrain composed of?
only the midbrain
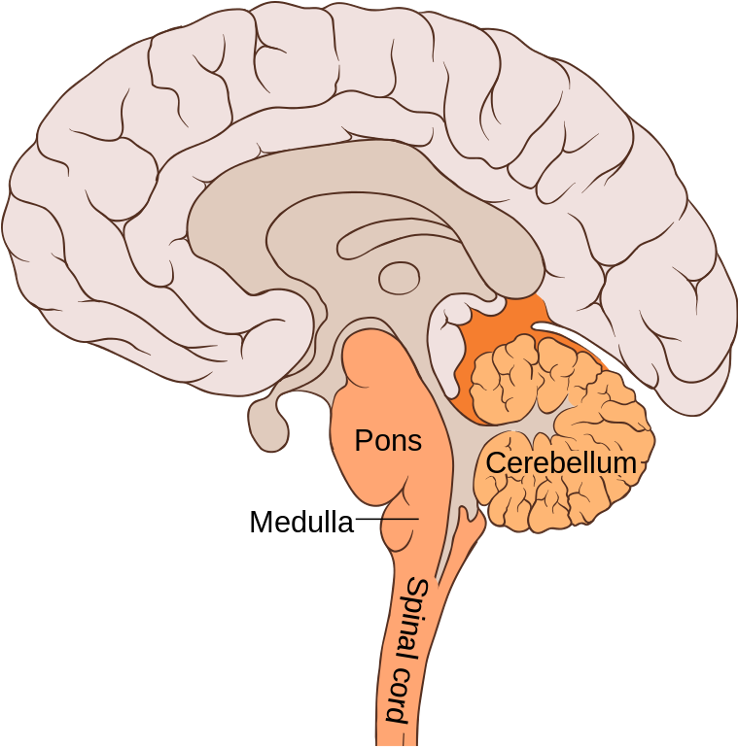
What is the hindbrain?
pons, medulla, and cerebellum
What encases the spinal cord?
the vertebral column
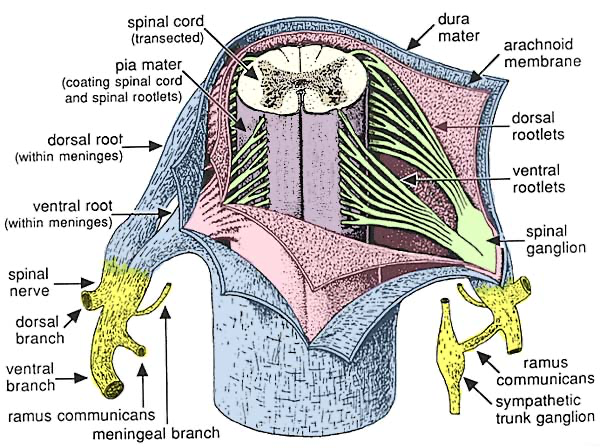
What are the meninges that surround the spinal cord?
dura, arachnoid, and pia mater (dap)
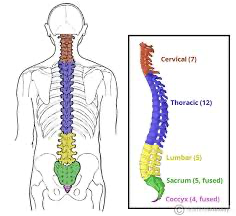
What are the 31 segments of the spinal cord divided into?
8 cervical,
12 thoracic,
5 lumbar,
5 sacral,
1 coccygeal
*it begins at the bottom of the brain stem and is continuous with medulla
What is the appropriate exits of the spinal cord?
cauda equina; it ends at the lower border of the first lumbar vetebrae
What are the vertebrae numerical categories?
hint: there’s a total of 33
7 cervical
12 thoracic
5 lumbar
5 sacral (fused)
4 coccygeal (fused)
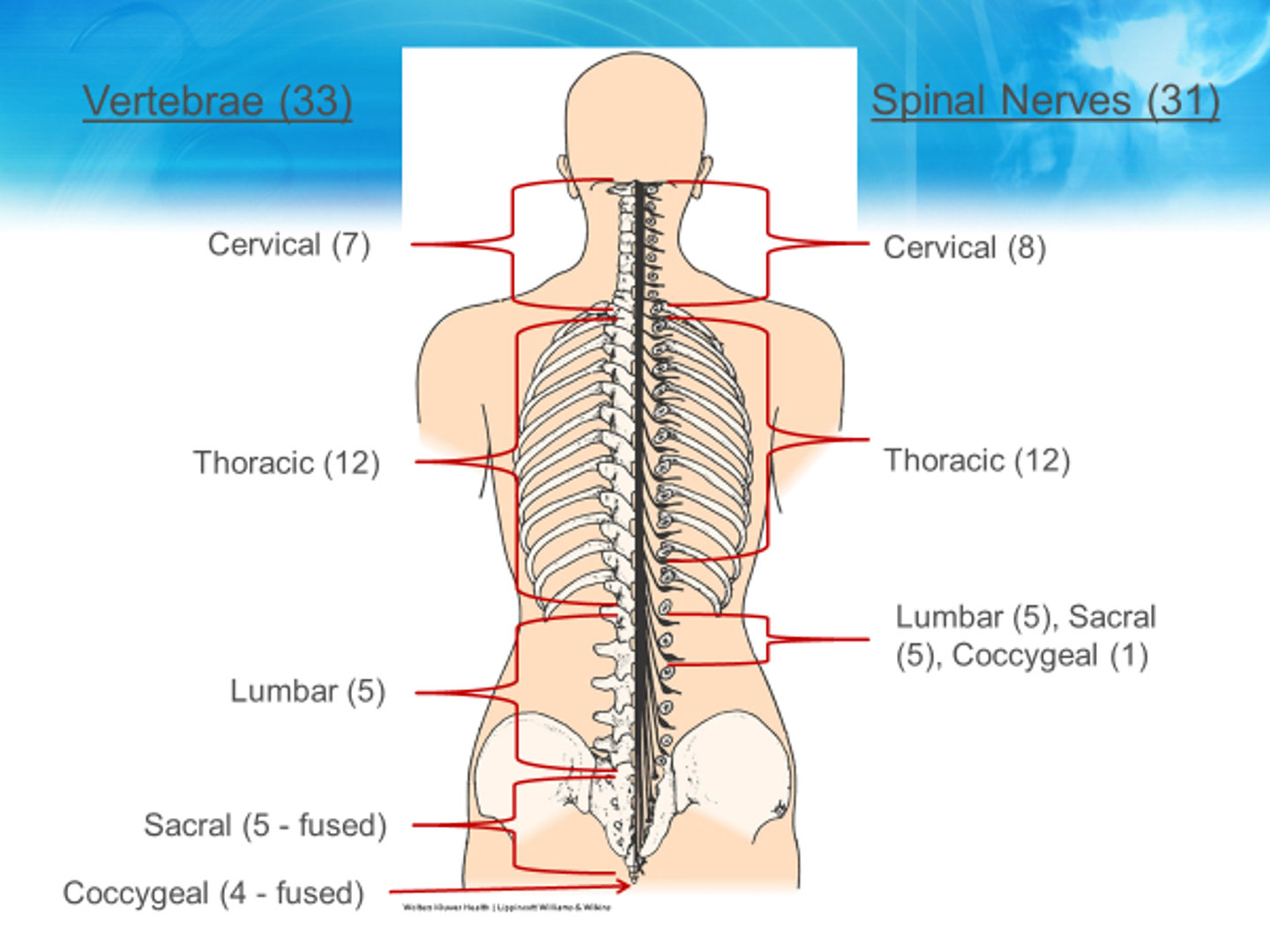
What is the difference between vertebrae (33) and spinal nerve (31) categories?
the cervical (7- vertebrae; 8 - spinal nerves)
and coccygeal (4 fused for vertebrae; and 1 for spinal nerves)
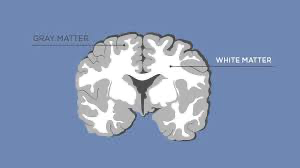
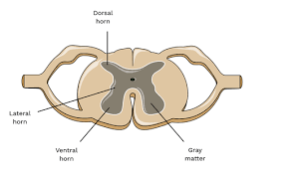
What is there to know about gray matter and white matter comparing cerebrum to spinal cord
in the cerebrum the gray matter surrounds white matter but in the spinal cord you have the exact opposite.
What does the spinal cord allow the body to do?
–Move
–Feel temperature, vibration, sharp and dull sensations
–Sense the position of your limbs
–Control blood pressure, heart rate, and body temperature
–Control bodily functions
–Receives messages from the brain when the body moves
–Sends messages to the brain so a person can feel sensations
What are the functions of the midbrain?
connects the forebrain and hindbrain
cerebral aqueduct
Where is the cerebral aqueduct and what does it do?
in the midbrain
allows for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to flow between the third ventricle and the fourth ventricle.
What is a spinal cord injury?
damage to any part of the spinal cord, including damage to the vertebrae, ligaments or disks of the spinal column
classified as complete of incomplete
What is a complete spinal injury?
all feeling and motor function are lost below the injury
What is an incomplete spinal injury?
retain some sensory or motor function below the injury
What are some traumatic vs nontraumatic spinal cord injuries?
traumatic
blunt trauma
gunshot/ knife wound
nontraumatic:
arthritis
cancer
inflammation
infections/ disk degeneration of the spine
What is quadriplegia?
paralysis of all four limbs
what is paraplegia?
paralysis of both lower limbs
signs and symptoms of spinal cord injuries?
–Loss of movement
–Loss or altered sensation, including the ability to feel heat, cold and touch
–Loss of bowel or bladder control
–Exaggerated reflex activities or spasms
–Changes in sexual function, sexual sensitivity and fertility
–Pain or an intense stinging sensation caused by damage to the nerve fibers in your spinal cord
–Difficulty breathing, coughing or clearing secretions from your lungs
Spinal cord injuries affect the nerve fibers passing through the injured area. What does an injury to the lumbar region affect?
it can affect your torso, legs, bowel and bladder control, and sexual function
What can a cervical injury affect?
it can affect your torso, legs, bowel and bladder control, and sexual function (same as lumbar) plus movements of your arms and ability to breathe
Spinal cord injury complications.
•Bladder control
•Bowel control
•Skin sensation
•Circulatory control
•Respiratory system
•Muscle tone
•Fitness and wellness
•Sexual health
•Pain
Depression
Who is at risk of spinal cord injuries?
men, between the ages of 16-30, also over 65
engage in risky behavior or already have a bone or joint disorder

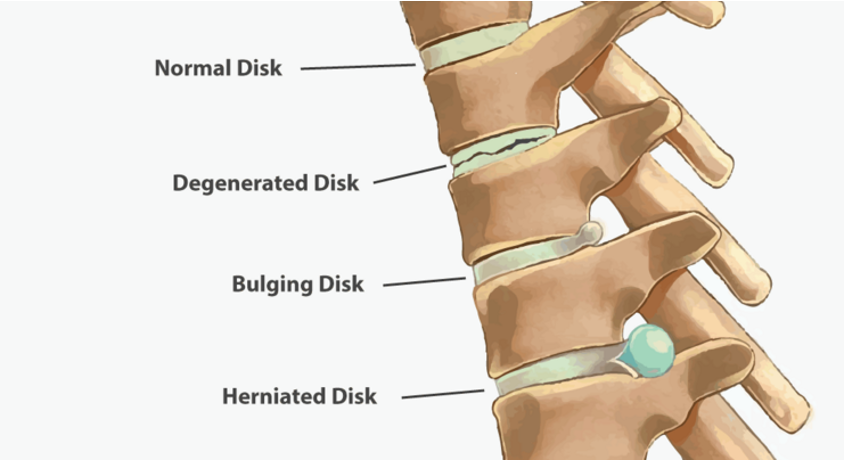
Spinal nerve injuries and disc categories, what is the main problem?
degenerative disc gets brittle
bulging in the soft tissue moves further out and eventually becomes herniated
THE problem is the disc starts to push on the nerve leading to a bunch of symptoms like neuropathy, burning senstion
What is special about the sciatic nerve?
it supplies nearly all of the skin of the leg, muscles of the back of the thigh, and those of the leg and foot.
What is the sciatic nerve derived from?
spinal nerves L4 through S3
The anterior root of the spinal cord is composed of
motor (efferent) nerve fiber
What composes the posterior root of the spinal cord?
The posterior root of the spinal cord is composed of sensory nerve fibers which carry sensory information from the body to the central nervous system (CNS)
What are treatment options of intervertebral disk degeneration?
–Physical Therapy/Exercises
–Disc Fusion
–Disc Replacement
What does the term “slipped disc” refer to?
a herniated disk, ruptured disk, or prolapsed disk
in which portions of an abnormal, injured, or degenerated disk have protruded against adjacent nerve tissues
frequently happening the low back, but any disk can rupture, including those in the neck
Spinal taps go into what?
go into the subarachnoid space, which is between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater.
Spinal block vs epidural
both types of anesthetics involving placement of needles in lower backs used for childbirth/ lower limb surgery
spinal block (thinner needle, in to the CSF, no catheter, last 1-2 hours)
epidural (catheter into epidural space)
What are some head injuries?
•Scalp bruising
•Scalp scrapes
•Skull fractures
What are some non-trauma brain injuries?
-Vascular- Stroke/ aneurysm
-Cancer
-Disease/infection
-Swelling/edema (benign increased intracranial pressure)