Business unit 2 chapter 4
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
handy’s model of organisational culture
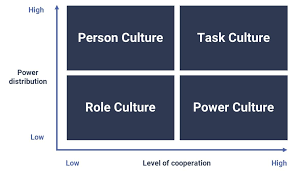
power culture pros and cons
Pros:
Quick decision making
Head management has the most business knowledge so decision making is made with expertise
Cons:
Demotivated workers (have little autonomy) → high labour turnover
Stressed head management → little delegation
Difficult to maintain control
Low morale
heavily reliant on the skills of the person in charge
role culture pros and cons
Pros:
Clear roles, everyone knows what they’re doing
Good promotion chances → motivates workers
Can acquire specialist expertise
Cons:
Tall structure, many layers of management → lots of supervision and bad communication
High labour costs → many layers and managers whose pay is higher
Slow decision making
difficult to adapt to change
inflexibility
person culture pros and cons
Pros:
Lots of autonomy → workers motivated
Good if workers can be trusted to get their work done
creativity
Cons:
Some workers can’t be trusted to get work done
low loyalty to the company
task culture pros and cons
(think matrix structure)
Pros:
Team work motivates
Workers can be allocated to teams based on their strengths
Cons:
Teams may develop own objectives
Groups might need time to become functional → by the time they become functional, project is over
Potential conflicts with who is working under who
strong culture definition & pros
- deeply fixed into the way a business does things
- however, if too rigid, a business won’t be able to respond to changes quickly
PROS:
Provides a sense of identity for employees
Better teamwork
Increased commitment of workers → lower labour turnover
Motivation → productivity
Better understanding and less misunderstandings
Reinforce company values
weak culture
difficult to identify the factors making up the culture or a lot of subcultures exist
views, rules, etc. not easily adopted by the workers. Poor work alignment
possible inconsistent behaviour resulting in poor performance
identified by poor customer service
inconsistent with business values
factors leading to strong or weak culture in a business
Surface manifestations (appearances)
Availability of training
Language “colleagues” “crew members”
Mottoes
Ceremonials
Norms (eg always being late to meetings can lead to weak culture)
Organizational plan
Core organizational values
Can reflect the actual culture of a business, but, they might not
Workers at the bottom of the hierarchy might have very different values from the ones that senior management want them to have
Basic assumptions
Unspoken beliefs & ways of working
Workers may share a general attitude, which affects quality of work
Hard to see and change
changing a culture → why and challenges
Why change?
A firm’s culture can provide it with an advantage over its competitors
Challenges in changing
Difficult to identify the factors that contribute towards a specific culture
Hard to manage people’s attitudes
Training can be successful in changing a culture if the benefits of the desired culture are emphasised
how corporate culture is formed
Based on the leaders attitudes
Based on the success of a company → more successful = higher expectations
Based on the type of product → determines level of skill needed by workers
ways to identify a corporate culture
how customers are treated
method & style of communication
how decisions are made
potential conflicts between shareholders and stakeholders
Shareholders vs employees
If the needs of employees are met (higher pay, better working conditions..) there’ll likely be a decrease in profit and dividends
Shareholders may insist that the rewards to employees shouldn’t come at the expense of dividends
Employees may threaten with industrial action
Shareholders vs customers
Likely to occur if business charges prices that are too high
Customers upset if R&D or customer service is neglected
less R&D spending = higher dividends
Shareholders vs directors and managers
Problems arise if directors and managers prioritize their own benefits eg remuneration
Common conflict is the balance between paying dividends and retaining profit for investment
Shareholders vs the environment
Environmentally responsible ways of production likely more expensive
Hofstede’s cultural dimensions → definition
underlying values that affect the cultural differences in businesses → useful in international business
Hofstede’s cultural dimensions → five variables?
Power distance
How much more power do managers have over subordinates
High distance suggests little communication
Individualism
How people see themselves within the organization
When it’s high, people tend to focus on their own success
Masculinity vs femininity
Masculine organisation might be described as competitive and assertive
Feminine, caring and co-operative
Uncertainty avoidance
Level at which an organisation will accept risk
Low uncertainty avoidance = will take risks
Long-term vs short-term orientation
A low score = organisation makes decision to get short-term rewards and immediate gratification in terms of shareholder value
Business audits and CSR
Some businesses respond to concerns about CSR by auditing relevant activities → eg use of child labour
Auditing involves checking evidence against established standards
Audits are then made public
Examples of social and environmental audits
Employment indicators
Human rights indicators
Ethics → eg animal testing
The communities in which the business operates
Product responsibility → eg safety
The environment: can form a separate audit
→ amount of energy/raw materials used eg water
→ amount of waste produced
→ amount of recycled material