Marketing Chapter 11: Comprehensive Guide to Pricing Strategies, Tactics, and Legal Issues in Marketing
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Price
Price reflects money, time, or effort.
Revenue
Revenue equals Units sold times Price.
Profits
Profits equals Revenue minus Costs.
Profit maximization
Maximize profits on each unit sold.
Volume maximization
Maximize volume and revenue for a firm.
Survival pricing
Survival pricing to maximize cash flow.
Optimal price
Optimal price is the point at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
Price sensitivity
Marketers need to be aware of price sensitivity.
Price elasticity of demand
Price elasticity of demand should be considered.
Inelastic demand
Inelastic demand refers to a situation where demand does not change significantly with price changes.
Elastic demand
Elastic demand refers to a situation where demand changes significantly with price changes.
Size of Expenditure
Customers are less sensitive to the prices of small expenditures which, in the case of households, are defined relative to income.
Shared Costs
Customers are less price-sensitive when some or all of the purchase price is paid by others.
Switching Costs
Customers are less sensitive to the price of a product if there is added cost (both monetary and nonmonetary) associated with switching to a competitor.
Perceived Risk
Customers are less price-sensitive when it is difficult to compare competing products and the cost of not getting the expected benefits of a purchase is high.
The Price-Setting Process
The price-setting process includes defining pricing objectives, evaluating demand, determining costs, analyzing the competitive price environment, choosing a price, and monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of the price.

Define the Pricing Objectives
Step 1 of the price-setting process.
Evaluate Demand
Step 2 of the price-setting process.
Determine the Costs
Step 3 of the price-setting process.
Analyze the Competitive Price Environment
Step 4 of the price-setting process.
Choose a Price
Step 5 of the price-setting process.
Monitor and Evaluate the Effectiveness of the Price
Step 6 of the price-setting process.
Benefit
Customers are less price-sensitive when the product is a small part of the cost of a benefit with high economic or psychological importance.
Price-Quality Perceptions
Customers are less sensitive to a product's price to the extent that price is a proxy for the likely quality of the purchase.
Reference Prices
Customers are more price-sensitive the higher the product's price relative to the customers' price expectation.
Perceived Fairness
Customers are more sensitive to a product's price when it is outside the range that they perceive as 'fair' or 'reasonable.'
Price Framing
Customers are more price-sensitive when they perceive the price as a 'loss' rather than as a forgone 'gain.' They are more price-sensitive when the price is paid separately rather than as part of a bundle.
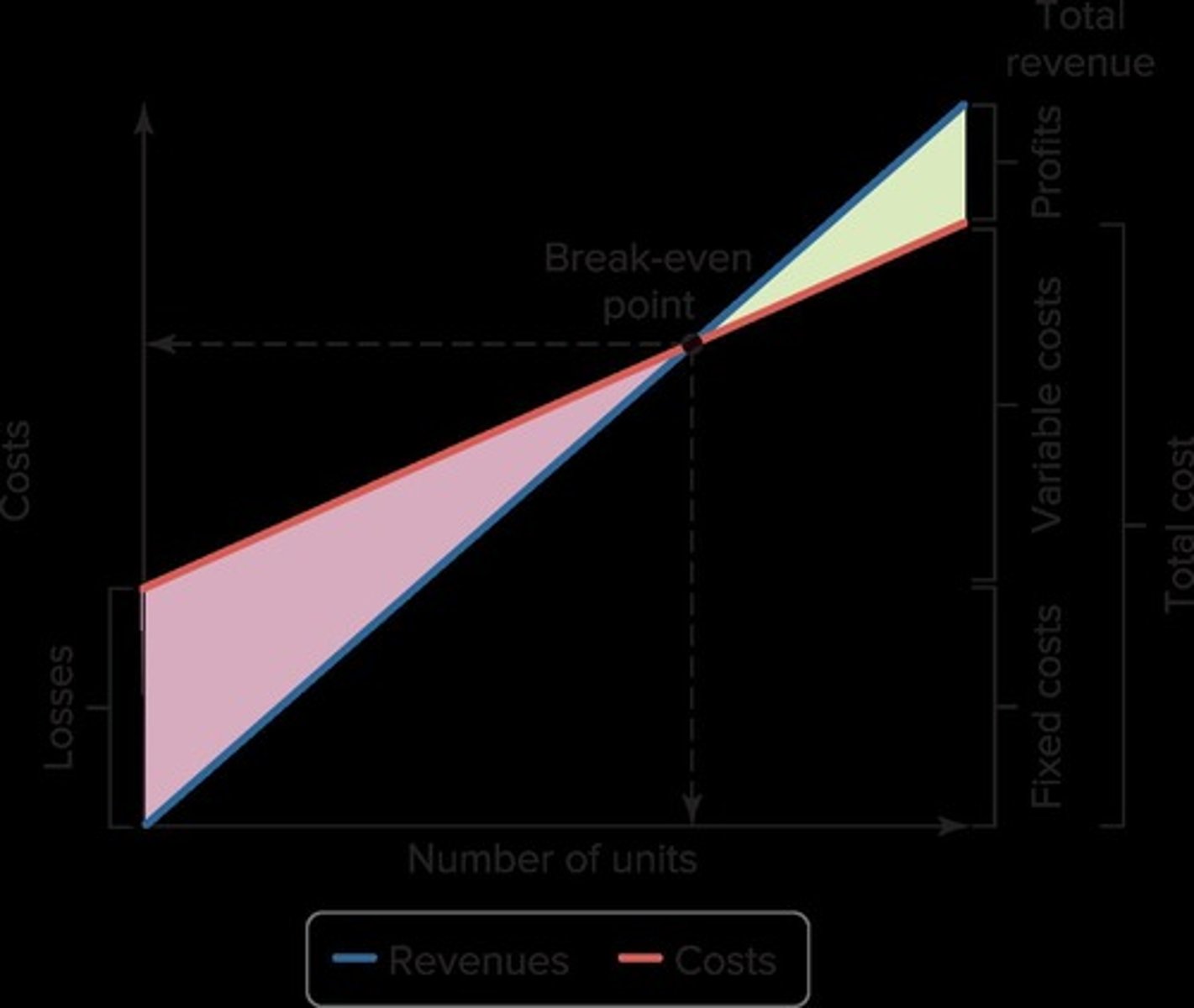
Fixed Costs
Costs that do not change with the level of output.
Variable Costs
Costs that vary with the level of output.
Break-even Analysis
A method to determine how much is needed to sell to earn a profit.
Break-even Point
The point at which total revenues equal total costs, resulting in no profit or loss.
Competitive Price Environment
The context in which a company sets prices based on the prices of competitors.
Underpricing
A common mistake where products are priced lower than their perceived value.
Markup Pricing
Also called cost-plus pricing; it involves adding a desired percent return to the unit cost of a product.
Profit Margin
The amount a product sells for above the total cost of the product itself.
Odd Pricing
Pricing strategy where prices end in odd numbers to give a feeling of receiving a deal, such as $19.95.
Escalator Clause
A clause in a contract that allows for adjustments in price based on certain conditions.
Shrinkflation
The practice of reducing the size or quantity of a product while maintaining the same price.
Unbundling
Separating components of a product or service to sell them individually.
Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Graph
A graphical representation of the relationship between costs, volume, and profits.
Pricing Strategies
Approaches to setting prices, including matching competitor prices, pricing lower for greater value, or pricing higher for superior products.
Reference Prices as Comparison
Using previously established prices to evaluate current pricing.
Price Increase Strategies
Methods to raise prices, including unbundling and using escalator clauses.
$19.95
Even pricing is easier to process.
$20.00
Prestige Pricing: Product priced higher than competitors to signal it is higher quality.
Luxury brands
Examples include Louis Vuitton or Mercedes-Benz.
Loss-Leader Pricing
Causes financial loss for firm but might attract more customers.
Seasonal Discounts
Prices lowered during off season to maintain customers and introduce new ones to the brand.
Price Bundling
Use to charge higher prices than for individual items. Examples include Amazon Prime, Disney+.
Mobile Applications
New era of pricing transparency.
Price comparison apps
An example is ShopSavvy.
Dynamic Pricing
Grown explosively; websites like StubHub constantly update prices to reflect changes in supply and demand.
Yield management
Helps marketers sell things like tickets.
Name-Your-Own-Price
Auction site searches to match price set by consumer.
Gray Market
Often occurs when price is significantly higher in one country than another; difficult to track.
Tariffs
Examples include fruits and vegetables; Chinese-made products.
Dumping
Many countries enact laws to curb this strategy.
Price Discrimination
Different prices for different customers, which is legal.
Price Fixing
Companies collude to set price, which is illegal.
Predatory Pricing
Aggressive strategy where prices start low and then are raised.
Deceptive Pricing
Intentionally misleading customers with price promotions, which is illegal.
Robinson-Patman Act
Lower prices allowed if discounted for quantity, price matching, or going-out-of-business sales.
Federal Trade Commission Act (FTCA)
Part of U.S. laws affecting pricing.
Wheeler-Lea Act
Part of U.S. laws affecting pricing.
Sherman Antitrust Act
Part of U.S. laws affecting pricing.
Price Matching
Lowe's price match guarantee provides an example of price discrimination allowed by the Robinson-Patman Act.
Even pricing
Pricing tactic that sets prices at even dollar amounts.
Marginal revenue
The change in total revenue that results from selling one additional unit of product.
Marginal cost
The change in total cost that results from producing one additional unit of product.