C3.1 Integration of body systems
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
C3.1.1 System integration

C3.1.2 Cells, tissues organs and body systems as hierarchy of subsystems integrated in multicellular living organism
Distinguish roles of nervous system and endocrine system in signalling
Using examples, emphasise role of blood system in transporting material b/w organs

C3.1.3 Integration of organs in animal bodies by hormonal and nervous signalling and by transport of materials and energy
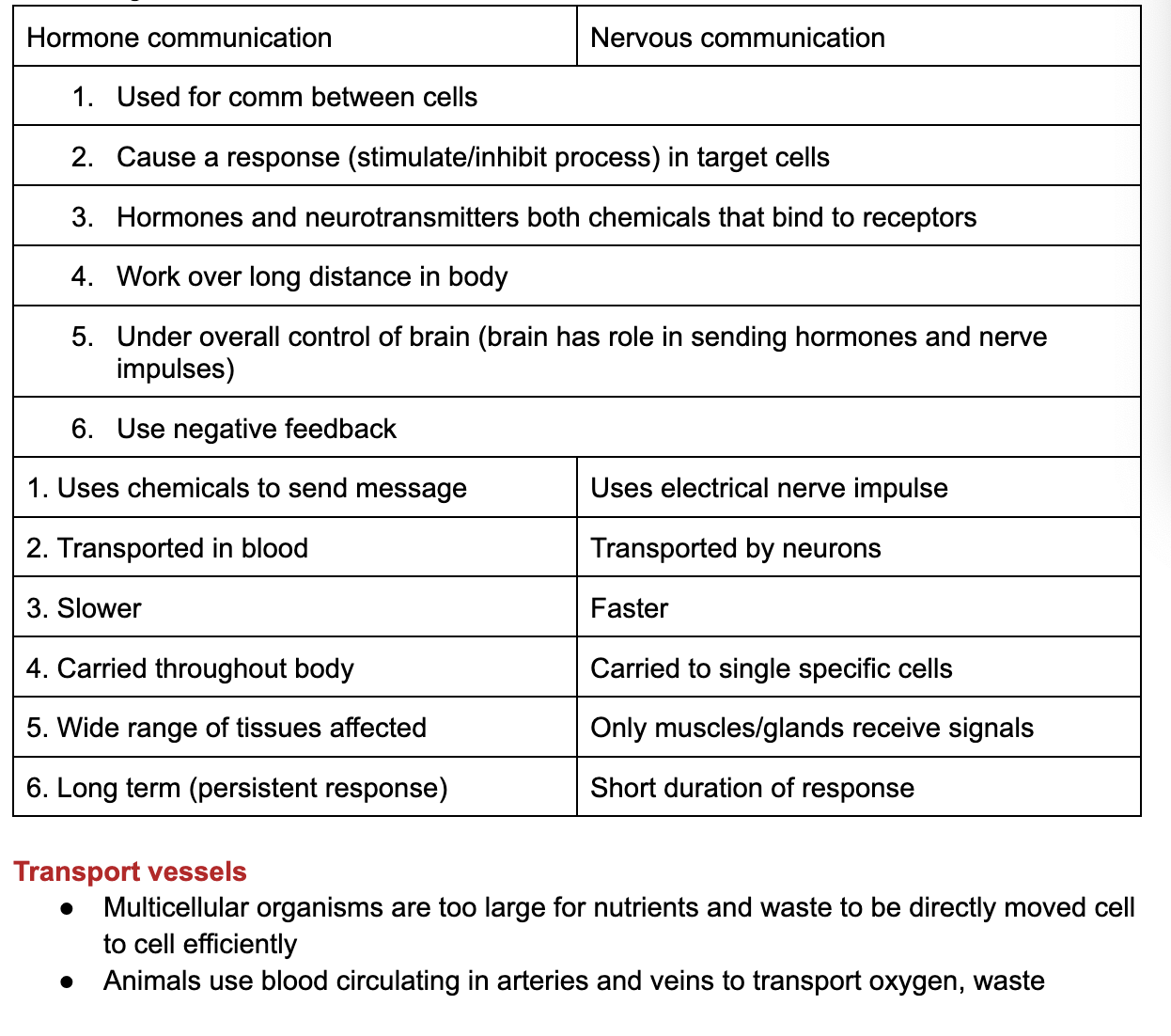
C3.1.4 Brain as central info integration organ
*Limit to role of brain in processing info combined from several inputs, in learning and memory

C3.1.5 Spinal cord: integrating centre for unconscious processes
Distinguish between conscious and unconscious processes
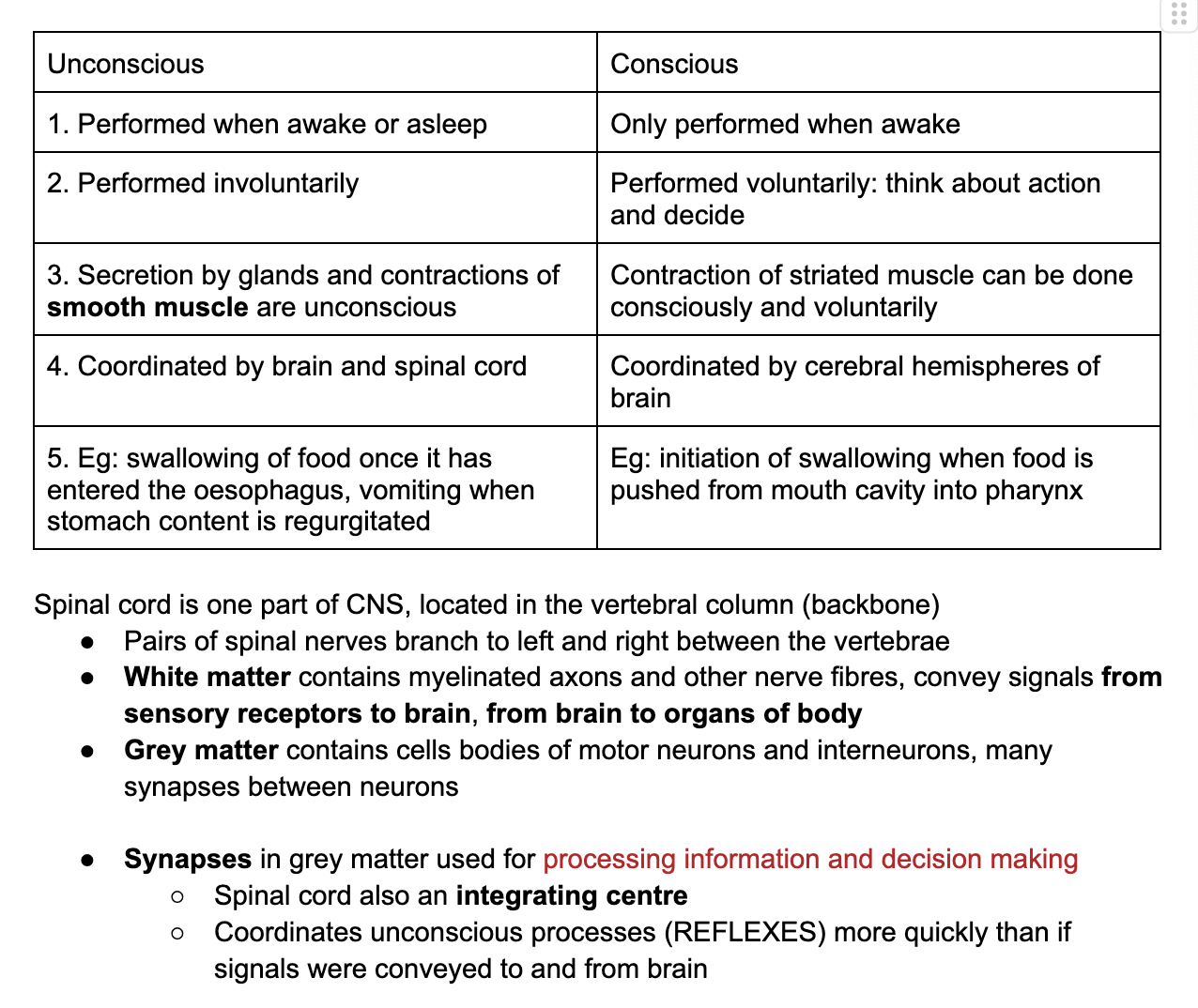
**C3.1.6 Input to spinal cord and cerebral hemispheres through sensory neurons

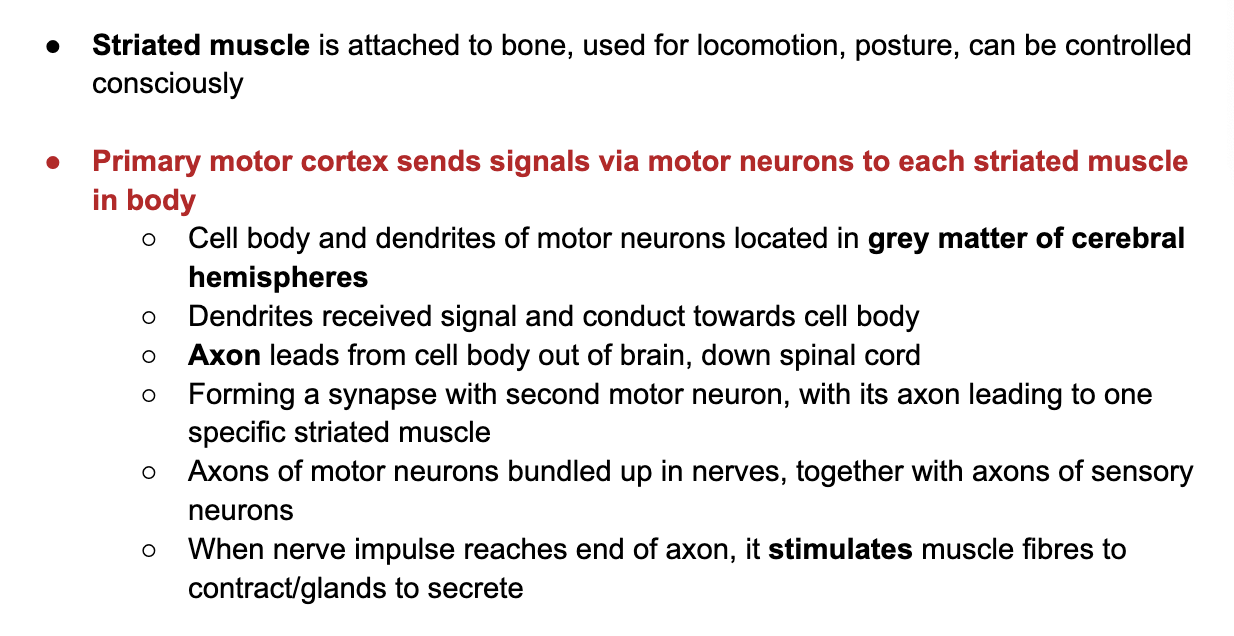
**C3.1.7 Output from cerebral hemispheres to muscles through motor neurons
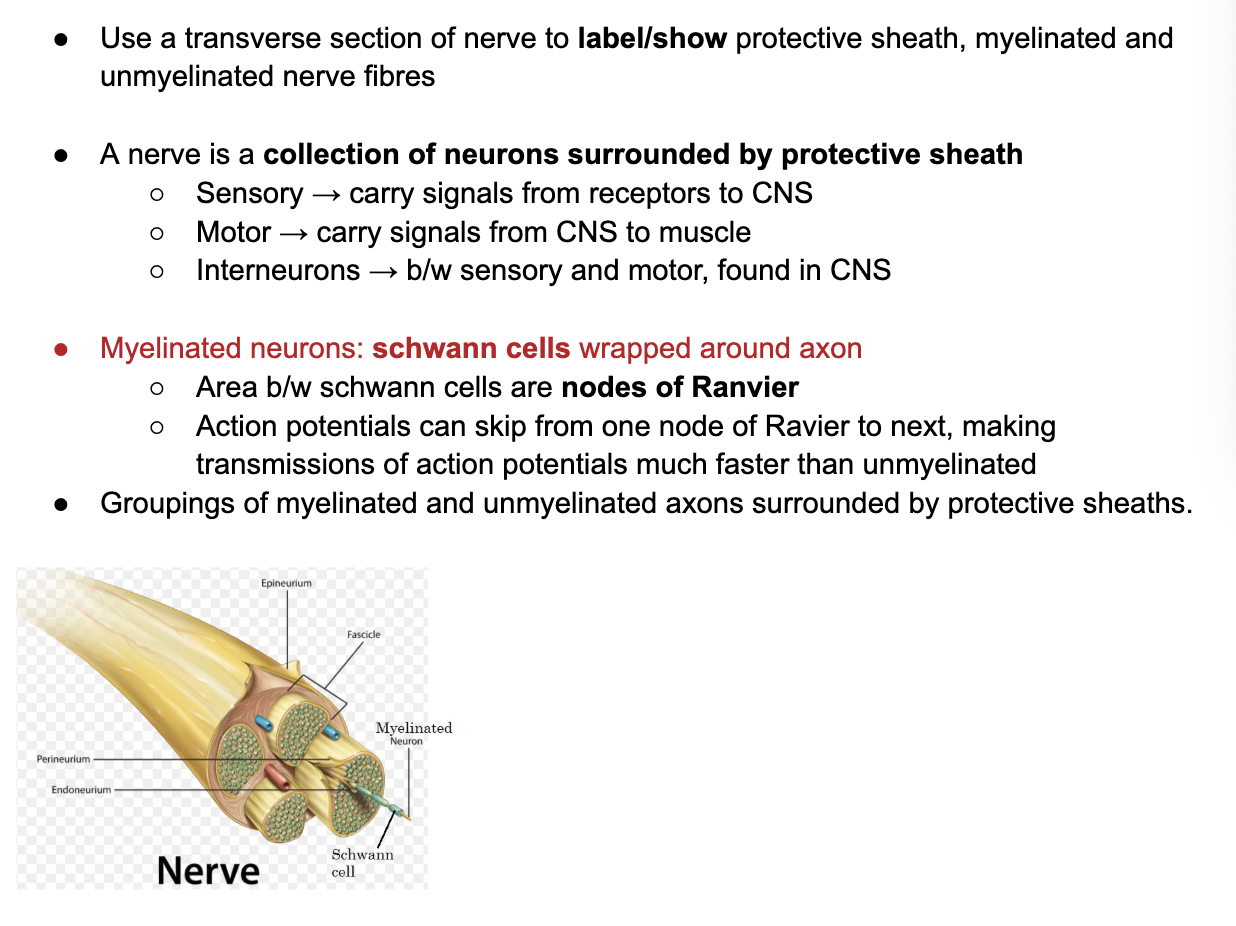
C3.1.8 Nerves: bundles of nerve fibres of both sensory and motor neurons
C3.1.9 Pain reflex arcs as an example of involuntary responses with skeletal muscle as effector
*essay qn: get the key words
* Example: pain reflex arc of hot object
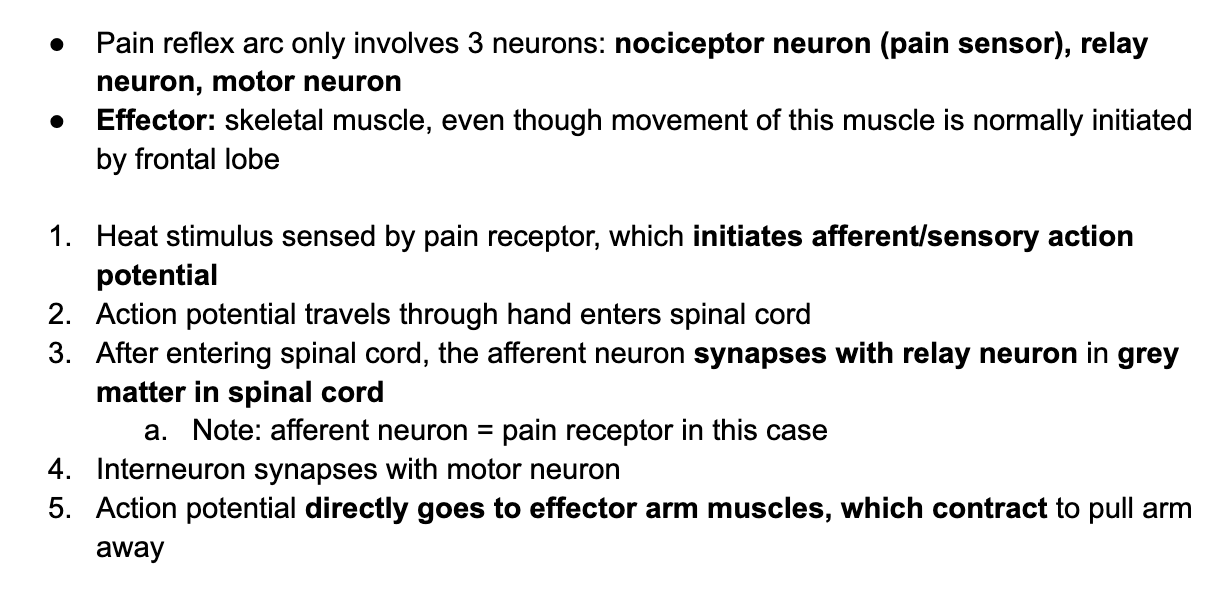
C3.1.10 Role of cerebellum in coordinating skeletal muscle contraction and balance

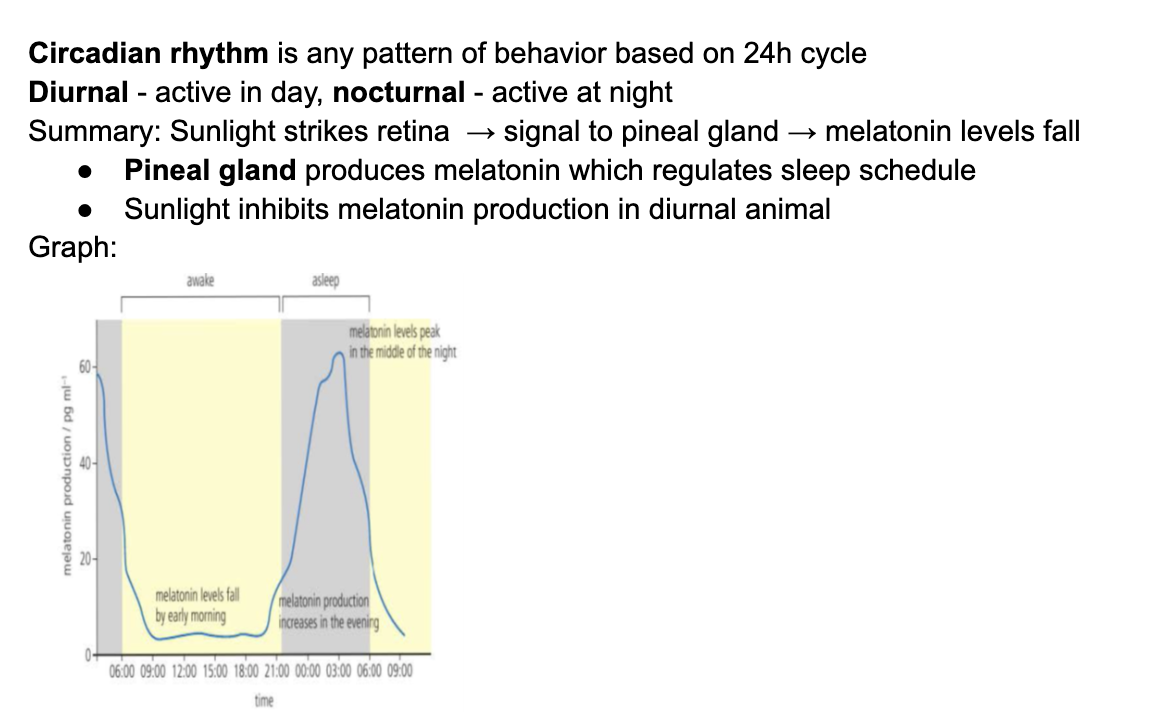
C3.1.11 Modulation of sleep patterns by melatonin secretion as part of circadian rhythms
Mcq graph
C3.1.12 Epinephrine secretion by adrenal gland to prepare body for vigorous activity
Memorise the various effects

C3.1.13 Control of endocrine system by hypothalamus and pituitary gland
*don’t have to know diff between posterior and anterior

**C3.1.14 Feedback control of heart rate following sensory input from baroreceptors and chemoreceptors

**C3.1.15 Feedback control of ventilation rate following sensory input from chemoreceptors
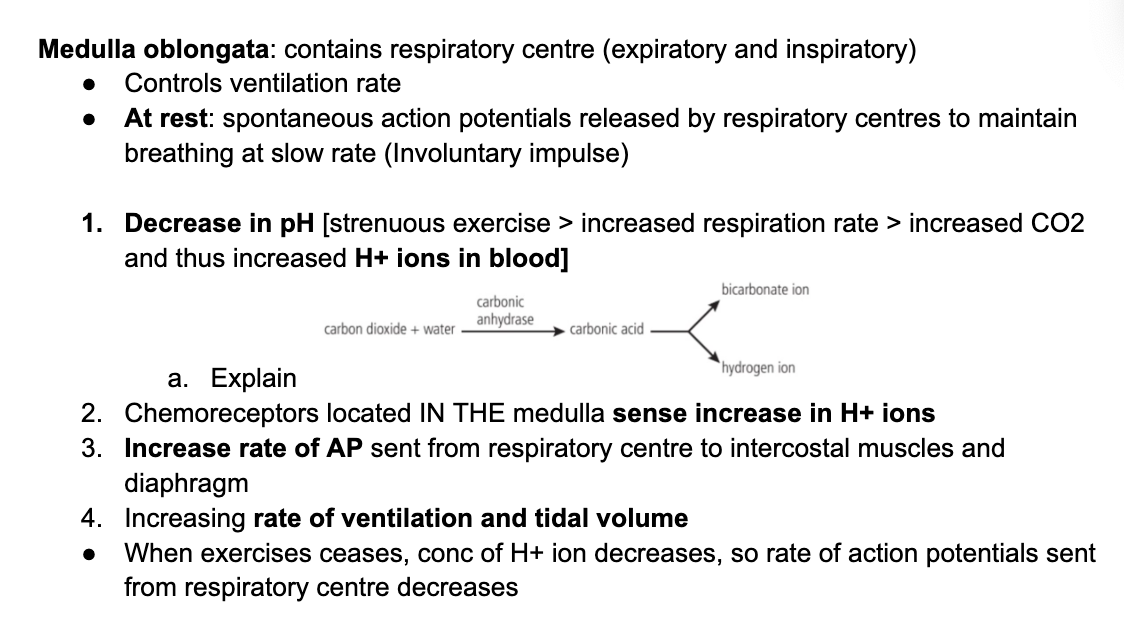
**C3.1.16 Control of peristalsis in digestive system by CNS and enteric nervous system (ENS)

C3.1.17 Observation of trophic responses in seedlings
C3.1.18 Positive phototropism as directional growth response to lateral light in plant shoots
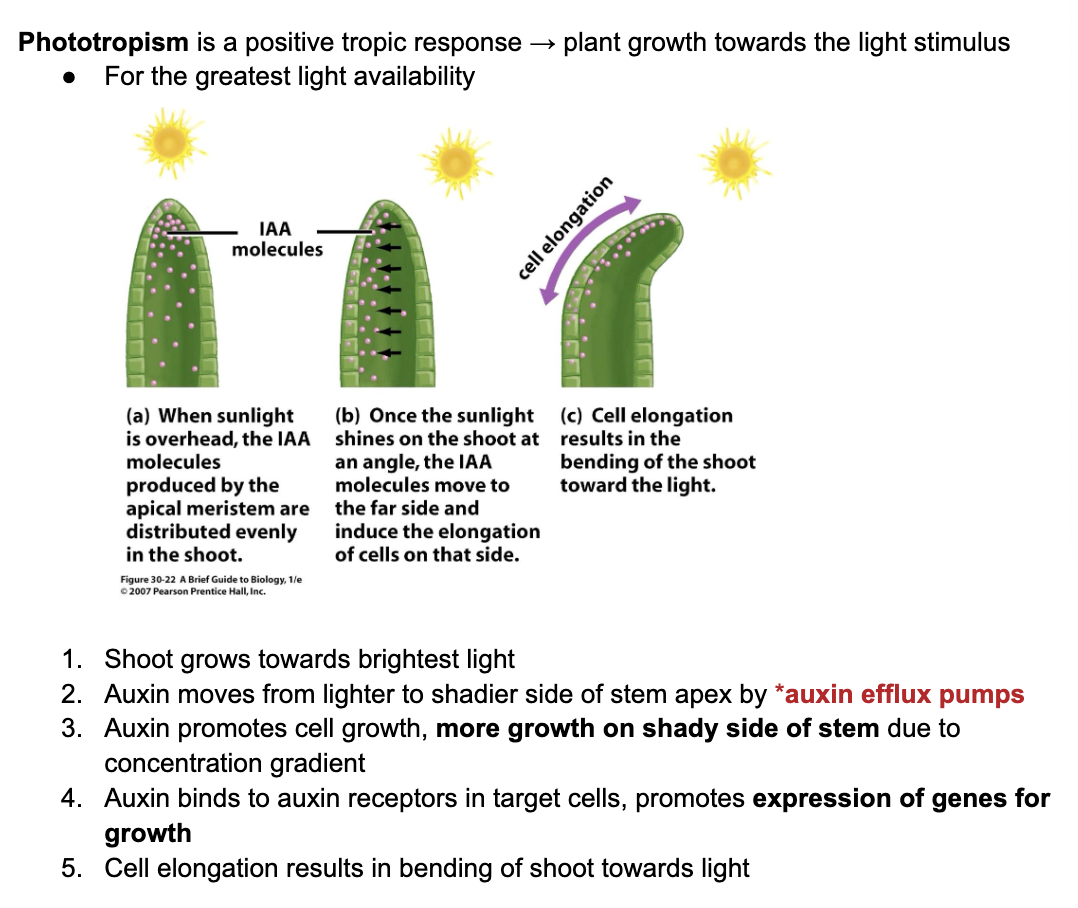
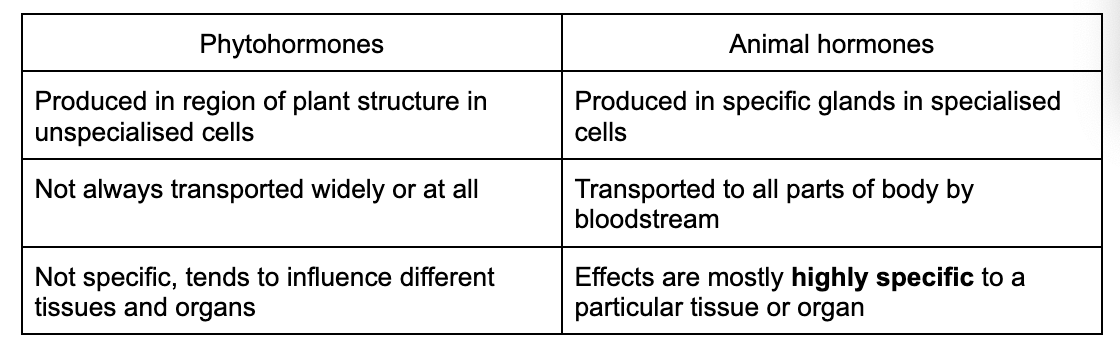
C3.1.19 Phytohormones as signalling chemicals controlling growth, development and response to stimuli in plants
Most impt: auxin in plant elongation
(Unlikely to come out)
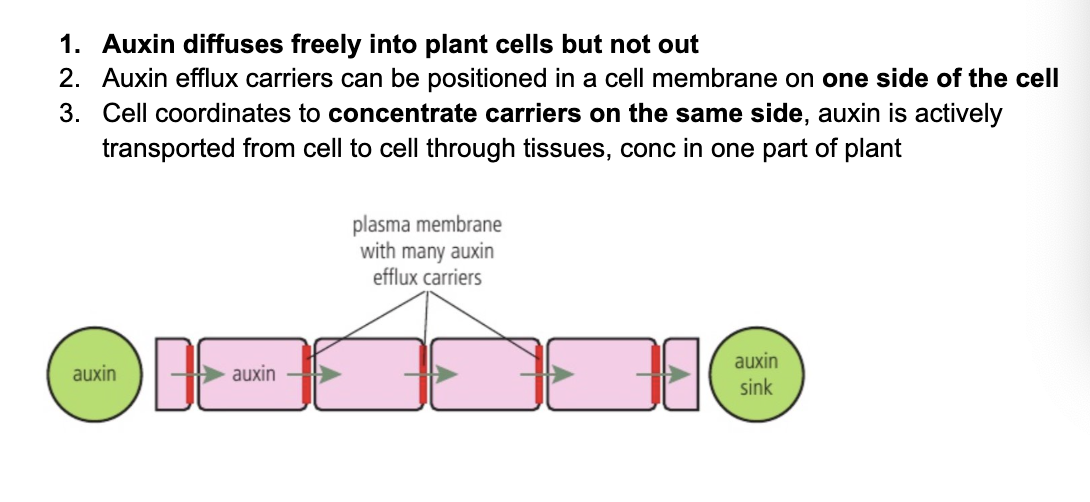
C3.1.20 Auxin efflux carriers as example of maintaining conc gradient of phytohormones
C3.1.21 Promotion of cell growth by auxin

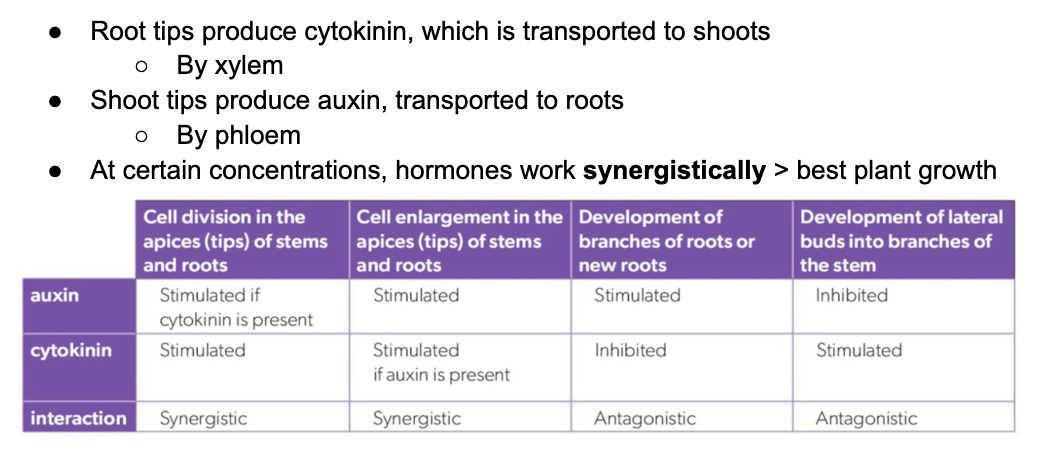
C3.1.22 Interactions between auxin and cytokinin as means of regulating root and shoot growth
C3.1.23 Positive feedback in food ripening and ethene production
