Psychology Exam Year 10
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study notes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Frontal lobe (where, what)
the frontal lobe is located at the front part of the brain and is responsible for higher cognitive functions such as reasoning, problem-solving, and controlling behavior.
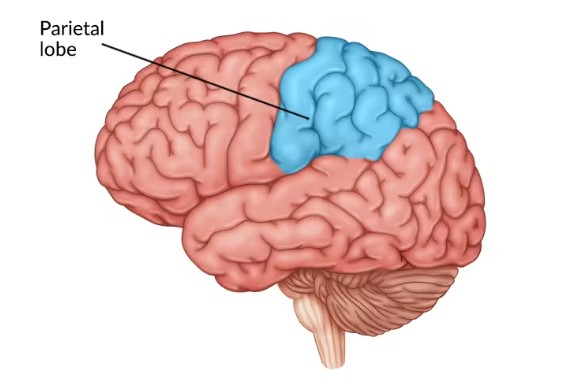
Parietal lobe (where, what)
The parietal lobe is located near the top of the head and is responsible for processing sensory information such as touch, temperature, and pain.
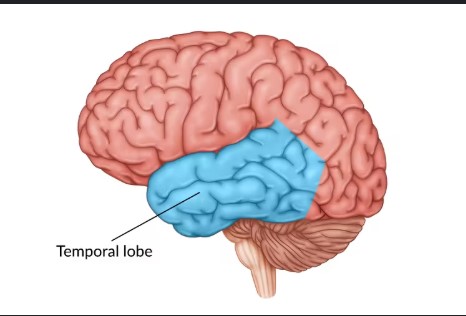
Temporal lobe (where, what)
The temporal lobe is located on the sides of the brain, playing a key role in processing auditory information and is involved in memory and emotion.
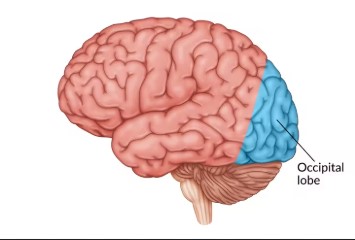
Occipital lobe (where, what)
The occipital lobe is located at the back of the brain and is primarily responsible for processing visual information.
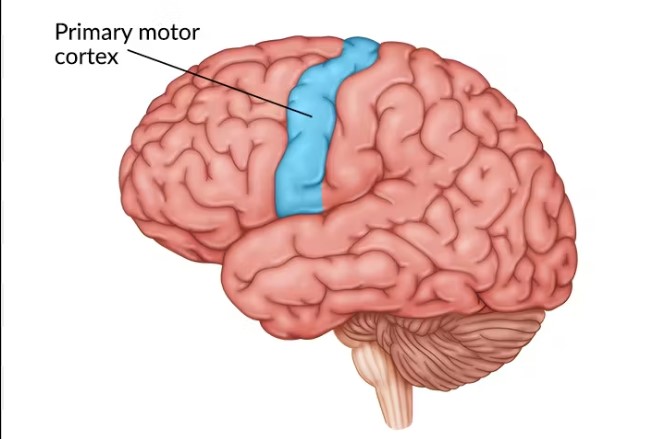
Motor cortex (function, location)
The motor cortex is located in the frontal lobe, responsible for planning and executing voluntary motor movements.
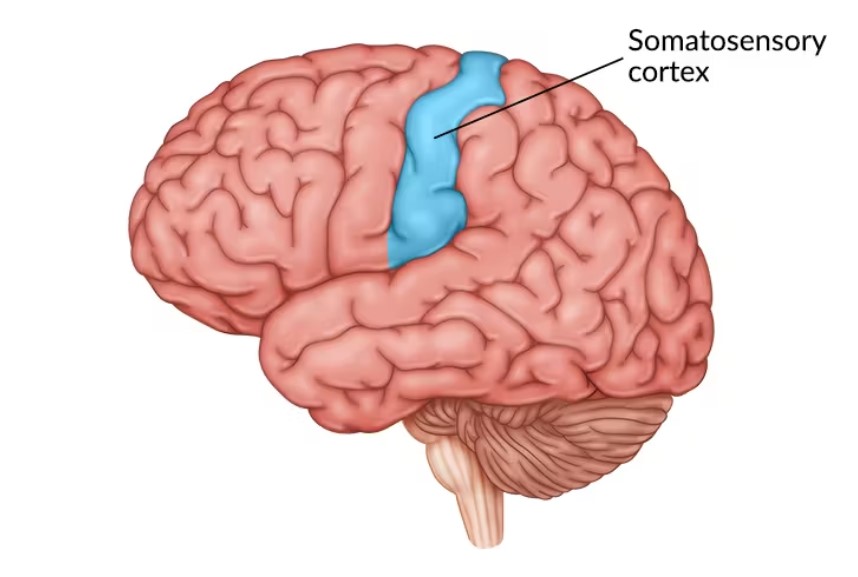
Somatosensory cortex (function, location)
The somatosensory cortex is located in the parietal lobe. It processes sensory information like touch, temperature, pain, and body position.
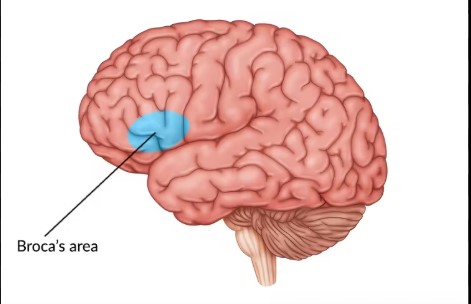
Broca’s Area (location, function, damage to this area causes..?)
Broca’s area is located in the frontal lobe. Damage to the area causes Broca’s aphasia, characterized by hesitant and fragmented speech with little grammatical structure. Broca's area is primarily responsible for speech production.
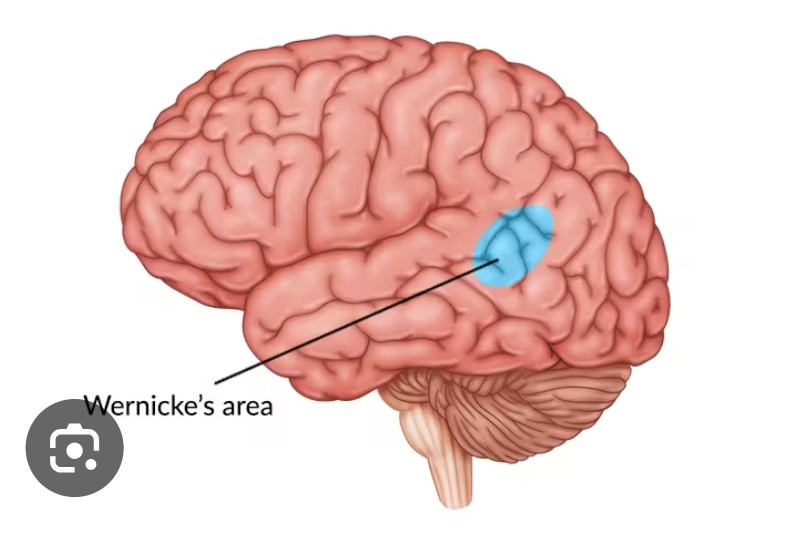
Wernicke’s Area (function, location, damage to this area causes…?)
Wernicke's area is a region of the brain in the temporal lobe, typically on the left side, that is crucial for the comprehension of language, both written and spoken. Damage to this area can result in a condition called Wernicke's aphasia, characterized by fluent but nonsensical speech, difficulty understanding what others are saying, and a lack of awareness that their own speech is meaningless
Auditory Cortex (function, location)
The auditory cortex is the part of the brain in the temporal lobe responsible for processing sounds, including speech and music. Located in the temporal lobe.
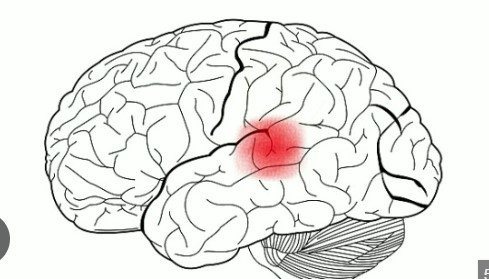
Visual Cortex (function, location)
The visual cortex is located in the occipital lobe, at the back of the brain. This area is the brain's primary visual processing center, receiving and processing visual information relayed from the eyes
Left hemisphere (functions)
This hemisphere is responsible for logic, language, maths, and analytical thinking.
Right Hemisphere (functions)
This hemisphere is responsible for creativity, spatial awareness, and emotion recognition.
Hemispheric specialisation:
Each hemisphere performs specific functions.
Role of working memory.
Working memory temporarily stores and manipulates information for cognitive tasks. It is crucial for reasoning, problem-solving, decision-making, and following multi-step instructions in daily life.
Types of long-term memory
Semantic, Episodic, Procedural, Classical conditioned memory
Classical conditioning Principles (acronyms)
UCS, UCR, CS, CR, NS
Classical conditioning definition
Classical conditioning is a learning process where a neutral stimulus becomes associated with a naturally occurring stimulus, causing it to eventually evoke the same automatic response
Five processes of observational learning
Attention, Retention, Reproduction, Motivation, Reinforcement
Fields of psychology
clinical, organisational, educational, forensic, criminal, neuropsychologist, criminal, counselling, evolutionary
Sampling methods
Convenience, random, stratified
Ethical principles
Informed consent, voluntary participation, withdrawal rights, confidentiality, debriefing, protection from harm, (minimal) deception
Convenience sampling method
Convenience sampling in psychology is a non-probability sampling method where researchers select participants who are readily accessible and easy to recruit, such as students in a psychology class or people in a mall
Random sampling method
In psychology, random sampling is a method of selecting participants from a larger population where every individual has an equal chance of being chosen, ensuring a less biased and more representative sample
Stratified sampling method
Stratified sampling in psychology is a method where the population is first divided into subgroups, or "strata," based on characteristics like age, gender, or education
Process of memories going from sensory to stm
attention (process)