cardiovascular system notes
1/38
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Who proved that circulatory system is unidirectional and closed
william harvey
harvey’s circulation experiment
tied a tourniquet around someone’s arm and applied pressure to veins
4 chambers of the heart
2 atria and 2 ventricles
difference between atria and ventricles
atria collects blood, ventricles pump blood
systemic and pulmonary circulation
systemic = all around the body, pulmonary = to and from the lungs
left vs. right side
left supplies oxygenated blood to systemic circulation, right supplies deoxygenated blood to pulmonary circulation
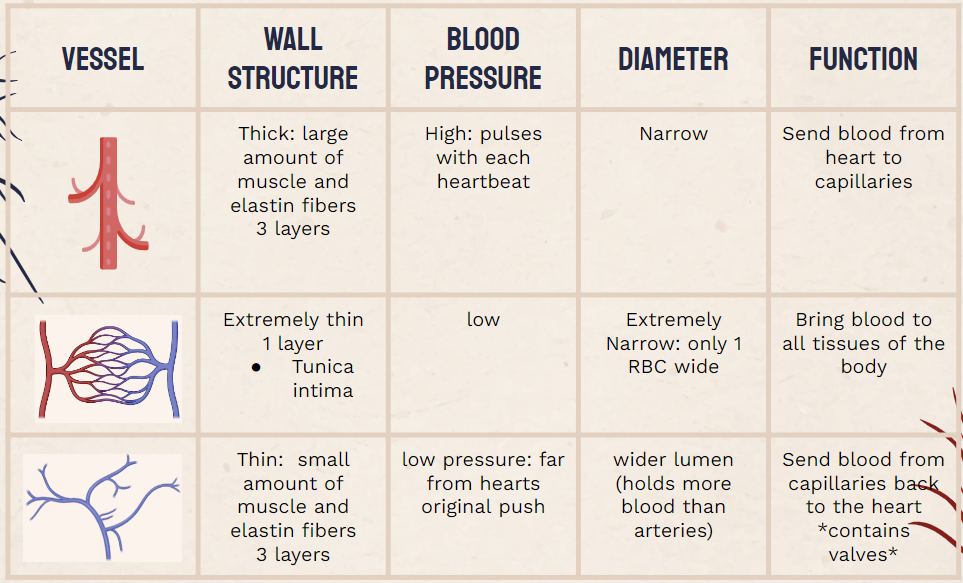
arteries
carry blood away from heart ventricles to tissues and lungs at high pressure
narrow lumen (tunica intima)
inner layer of artery, maintains blood pressure at 80-120 mmHg
Tunica media
layer of muscle and elastic fibres that contract and stretch with pulse
Tunica externa (adventita)
thick layer of collagen that prevents artery from rupturing
muscle fibres vs. elastic fibres
muscle fibres maintain rigidity and contract to increase pressure, elastic fibres stretch with blood flow
lumen
the hollow passage in an artery through which blood flows
elastic recoil
pressure exerted on artery is returned to blood when artery size goes back to normal
systolic blood pressure
higher blood pressure when the heart contracts
diastolic blood pressure
lower blood pressure when heart relaxes
vasocontriction
muscles around arteries constrict to resist blood pressure
vasodilation
muscles around arteries relax
flow of blood
heart—>arteries—>arterioles—>capillaries—>venules—>veins—>heart
types of capillary walls
continuous, fenestrated, sinusoid
continuous capillary walls
held together by tight junctions
continuous capillary walls
held together by tight junctions
fenestrated capillary walls
have pores in tissues specialized for absorption such as kidneys and intestines
sinusoidal capillary walls
open spaces between cells, permeable to large molecules (for example in the liver)
higher/lower hydrostatic pressure
higher pressure at arterioles—>from blood to tissue, lower pressure at venules—>from tissue to blood(waste, CO2)
veins
collect blood from tissues and convey it to heart’s atria at low pressure
veins contain ___ to prevent backflow
one way valves
skeletal muscle contraction
skeletal muscles surrounding veins contract to encourage blood flow in low pressure veins
veins run parallel to arteries
pulse from arteries stimulates blood flow in veins
vessel comparison graph
contraction of the heart is
myogenic = contraction comes from heart tissues
_____ directs contraction of heart tissue
SA Node (sinoatrial node)
primary pacemaker
SA Node —> secondary pacemaker (AV Node) —> Tertiary Pacemaker (Bundle of His)
fibrillation
irregular and uncoordinated heart contraction
electrical conduction
causes delay in heart contractions, allows for blood to fill up into ventricles following atrial contractions
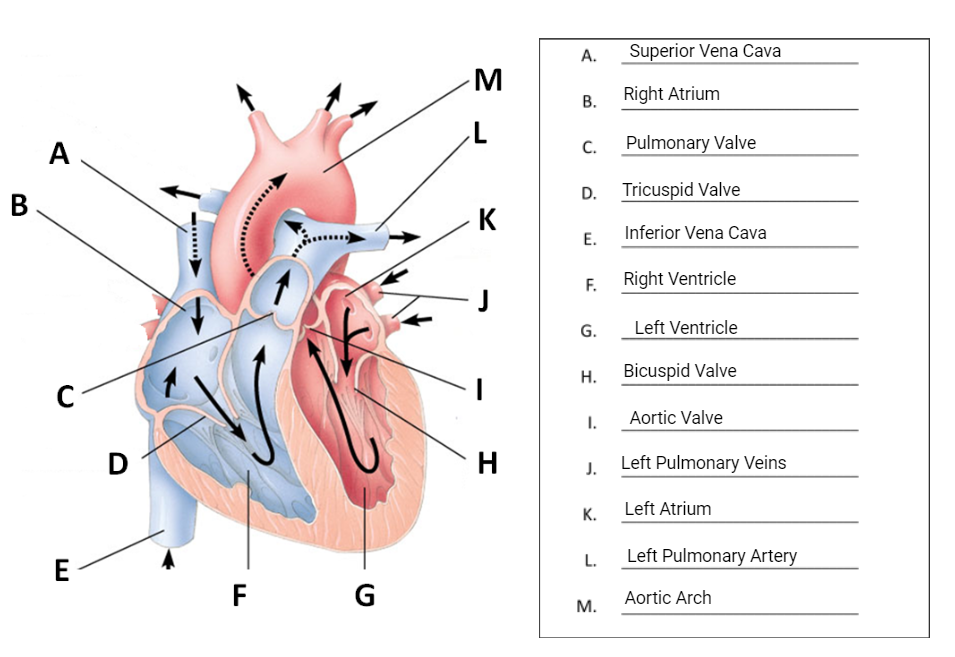
parts of the heart
labeled
which part of the brain involuntarily controls the heart contractions
medula oblangata
which nerve connected to medula oblangata increases heart rate
sympathetic nerve
which nerve connected to medula oblangata decreases heart rate
parasympathetic nerve (vagus nerve)`
where is the adrenal gland found
on kidneys